J. Cent. South Univ. (2013) 20: 318–325
DOI: 10.1007/s11771-013-1490-2

Effect of cooling structure on thermal behavior of copper plates of slab continuous casting mold
MENG Xiang-ning(孟祥宁), ZHU Miao-yong(朱苗勇)
School of Materials and Metallurgy, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110819, China
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2013
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2013
Abstract: A three-dimensional finite-element model of slab continuous casting mold was conducted to clarify the effect of cooling structure on thermal behavior of copper plates. The results show that temperature distribution of hot surface is mainly governed by cooling structure and heat-transfer conditions. For hot surface centricity, maximum surface temperature promotions are 30 °C and 15 °C with thickness increments of copper plates of 5 mm and nickel layers of 1 mm, respectively. The surface temperature without nickel layers is depressed by 10 °C when the depth increment of water slots is 2 mm and that with nickel layers adjacent to and away from mold outlet is depressed by 7 °C and 5 °C, respectively. The specific trend of temperature distribution of transverse sections of copper plates is nearly free of cooling structure, but temperature is changed and its law is similar to the corresponding surface temperature.
Key words: slab continuous casting; mold; copper plate; cooling structure; thermal behavior; finite element analysis
1 Introduction
In conventional continuous casting of steel, a large amount of sensible and latent heat of molten steel dissipates in primary cooling zone to exert enormous heating load on continuous casting mold, and thermal stress, deformation resistance and high-temperature fatigue and creep are produced to make mold life-span shortened and casting unstable [1–2]. Therefore, an in-depth understanding of thermal behavior of mold and analysis of the effect of cooling structure on it are essential to promote production operation and improve metal quality, especially at a high casting speed.
Many studies have been carried out to shed light on thermal behavior of copper plates with high thermal load for continuous casting mold over the past years. O’Connor and Dantzig [3] developed a finite- element model to analyze the temperatures in the mold and cast slab and offer the temperature results to be used for computing the thermo-mechanical state in the mold of thin-slab continuous casters in order to assess the role of various process parameters impacting the mold life. Also, Park et al [4–5] calculated the heat-flux profiles in thin-slab continuous casting molds based on an inverse heat conduction model and mold wall temperature measured in-plant and then used them into a three-dimensional finite-element thermal-stress model to conduct elastic-visco-plastic analysis in order to predict the deformation of mold wall for the different mold shapes funnel-shaped and parallel. Deeply, Thomas [6] and Koric et al [7–8] focused on systematic study of predicting temperature, distortion and residual stress in a conventional continuous casting mold for steel slabs by three-dimensional finite-element thermal-stress models and in particular to clarify that mold life is significantly affected by temperature and its rigidity, but little affected by mechanical effect including clamping force, bolt prestress, friction and ferrostatic pressure. LIU and ZHU [9] established three-dimensional finite-element heat- transfer and thermal-stress models to predict the temperature, distortion and thermal stress in a slab continuous casting mold and analyzed the effect of copper plates thickness, water slots depth, nickel layers and casting speed on them in detail, and quantitatively proposed a series of suggestions for optimizing the cooling structure of mold. Recently, SANTILLANA et al [10] applied a validated CON1D model to quantify the combined effect of casting speed and mold plate thickness on heat transfer in a funnel-mold and gained further insight on the effect of mold wall thickness on hot surface temperature, slag layer velocity and heat flux. MENG and ZHU [11] added actual semicircular bottom of cooling water slots, designed to remove nuclear boiling and stress concentration, into meshed model of mold and simulated the temperature distribution of mold copper plates at high casting speed and the effect of casting speed on temperature difference between copper plates and solidifying shell adjacent to meniscus. In recent years, NAKADA et al [12], HANAO and KAWAMOTO [13] and SARASWAT et al [14] explored the effect of flux film and its properties on thermo-mechanical behavior in continuous casting mold systematically, and then conducted some studies on mold slag intensively. In this work, a finite-element entity model of slab continuous casting mold is established in strict accordance with its design diagram to predict temperature distribution of mold wall at a high casting speed and analyze the effect of cooling structure, including thickness of copper plates and nickel layers and depth of water slots.
2 Mathematical models
2.1 Finite-element entity model
The physical model following design diagram for temperature calculation of mold copper plates is established using a commercial finite-element analysis package ANSYSTM according to geometry shown in Figs. 1(a) and (b) and a representative three-dimensional quarter-mold shown in Fig. 1(c) is computational domain because of symmetry. Here, four cooling water slots closest to corner in narrow face of mold all lean 15° towards wide face of mold in order to enhance cooling, five water slots are arranged evenly between bolts in wide face and thirteen slots are arranged in narrow face including deep ones adjacent to bolts and other shallow ones and make up of primary cooling system together with cooling water apertures in steel backups. The copper plate surface is coated with a nickel layer in lower portion (above mold exit 500 mm) in order to reduce the greater wear due to solid–solid friction between mold wall and solidifying shell caused by ferrostatic pressure of molten steel. The whole hot surface of mold is flash welded with a very thin chrome layer (0.05 mm) in order to avoid copper element permeating into casting slab to produce stellated crack on slab surface. In addition, thermocouples are embedded 23 mm under hot surface and two rows of wide face 200 mm and 400 mm far from mold top and that of narrow face is 200 mm and 440 mm, respectively. The entity model in ANSYSTM system for finite-element analysis is meshed using three-dimensional 10-node tetrahedral thermal solid element as referred to SOLID87 in the ANSYSTM manual and meshed model is shown in Fig. 2. The local mesh scale of chrome and nickel layers and cooling water slots is conducted to ensure higher precision.

Fig. 1 Schematic representation of physical model of slab continuous casting mold (Unit: mm):

Fig. 2 Meshed entity model for finite-element analysis
2.2 Heat-transfer model
In order to simulate thermal behavior of hot copper plates of mold during steady operation, the following assumptions were made: (1) heat transfer in mold is stable and symmetrical; (2) thermal properties of copper plates and steel backup are isotropic, and density and heat capacity are constant; (3) water in cooling channel is in plug flow and nuclear boiling of cooling water is neglected due to semicircular bottom of slots; (4) top and bottom of mold are considered to be adiabatic and heat absorption by mold powder on the free surface of molten steel is negligible. The thermal conductivity is dependent on temperature from solving the steady heat conduction equation using non-linear finite elements:
 (1)
(1)
where λ is thermal conductivity of copper and steel as a function of temperature T, axes of x, y and z in coordinate system are parallel to wide face, narrow face and casting direction, respectively, and their coordinate origin is at the mold exit. The boundary conditions for solution are as follows: (1) heat flux on hot surfaces of mold is a function of distance both across and down the mold and (2) convection heat transfer occurs in the interface between cooling water and copper plates. The former condition can be expressed in Eqs. (2) and (3) which are similar to the form proposed by SAVAGE and PRITCHSRD [15] and also been used in the recent report [16]. the slight difference is that the casting speed is eliminated because it is a constant in the present work. The latter condition is expressed in Eq. (4) and its heat transfer coefficient is expressed in Eq. (5). In addition, the heat flux beneath meniscus from 30 mm along off-corner to corner region of wide and narrow faces depress to 67 % of standard heat flux of wide and narrow faces to simulate large interfacial gaps near mold corner.
 (2)
(2)
 (3)
(3)
 (4)
(4)
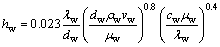 (5)
(5)
where q is heat flux (subscripts a, b and w represent above and below meniscus and cooling water, respectively), ai (i = 1, 2, 3) is equation coefficient, hw is heat transfer coefficient, λw is thermal conductivity, dw is hydraulic diameter of slot, ρw is density, vw is flow rate, μw is viscosity and cw is specific heat.
3 Results and discussion
The exactness of above-mentioned mathematical models had been confirmed by comparing predicted temperature on positions of thermocouples and in-plant measurements [11] using materials properties and operation conditions listed in Tables 1 and 2.
Table 1 Properties of copper, nickel, steel and cooling water

Table 2 Operation conditions of continuous casting mold

The temperature results on narrow face of mold are shown in Fig. 3. The temperature on off-corner bolt rises a certain degree and the temperature close to narrow face corner also goes up because there is not cooling water slot to reduce the influence from wide face. So, cooling water slot in the edge of narrow face is usually designed as slope to enhance cooling capacity. In this work, sloping off-corner water slot is an important concern as analyzing the effect of cooling structure on thermal behavior of copper plates of mold.

Fig. 3 Temperature at measuring points of thermocouples on narrow face of mold
3.1 Temperature distribution of hot copper surface
The temperature distribution of hot surface of mold copper plates is shown in Fig. 4. The thermal conductivity of plated nickel layers in lower portion of copper plates is significantly worse than that of copper, leading to a clear temperature interface between copper and nickel at the position of 500 mm above mold exit. The high-temperature isotherms in the region away from the mold corner form isothermal rings on both sides of boundary between copper and nickel. The isotherms from off-corner to corner depress gradually due to two-dimensional heat transfer enhancement and higher air-gap thermal resistance near the corner. The temperature distribution of wide face is uniform and the isotherms near corner are approximately parallel to casting direction. The isothermal rings away from off-corner have cyclical temperature fluctuations and their areas of high and low temperature are located at the positions of bolts and water slots, respectively. moreover, the terminals of cooling water slots cannot completely reach mold exit, and less cooling makes the temperature rise to a certain degree, thus forming a number of small closed isothermal rings. The impact of corner cooling on narrow face is significant and the isotherms near corner are sloping. However, air gap in narrow face is expanded by the larger shrinkage from wide face of slab and more fully filled by molten mold powder, although narrow face with mold taper of 1.1% per unit length, and isothermal rings remain flat due to uniformity of heat transfer. In addition, the extreme temperature of wide and narrow faces all occur near the meniscus and the maximum temperature of 307 °C occurs at the position 15 mm below meniscus in wide face.

Fig. 4 Temperature distribution of hot surface of copper plates:
The calculation results show that the temperature distributions of hot surface of mold with different cooling structures are all similar even if the specific temperature is determined under the exact heat-transfer conditions. moreover, it can be known that the trends of temperature distributions are all similar by comparing the results of transverse sections at different effective heights below meniscus, and the positions plating nickel layers are also like this. So, the temperature of hot surface centricities of copper plates and temperature distributions at representative heights were investigated to quantitatively analyze the effect of cooling structure of mold on thermal behavior of copper plates.
3.2 Effect of thickness of copper plates
The effect of thickness of mold copper plates on temperature of hot surface centricities is shown in Fig. 5. The peak heat flux produces a peak temperature in meniscus and another peak temperature is at the boundary of copper and nickel due to lower nickel thermal conductivity which induces higher temperature in lower mold portions. Two valley temperature, appear on hot surface, one corresponds to minimum heat flux in higher mold portions above nickel layer and another appears nearby mold bottom owing to absence of water slots. The thermal resistance is increased with thickness of copper plates, so the temperature difference between hot surface and steel backup is promoted and the temperature of hot surface is improved when heat flux is constant. The maximum promotion of surface temperature is about 30 °C near the meniscus and boundary between nickel and copper with thickness increment of 5 mm of copper plates. The hot surface temperature can be decreased by properly thinning copper plates and it is helpful to restrict thermal stress and deformation and extend life-span of mold. In the range of 50 mm above mold exit, the surface temperature is not prominently changed with thickness of copper plates, and the smaller change with thinner copper plates is due to insufficient cooling and significant impact from nickel layers.

Fig. 5 Effect of thickness of copper plates on temperature of hot surface centricities:
Figure 6 shows the temperature distribution of transverse sections of 45 mm copper plates in meniscus and the computational domain is selected as the range of 100 mm from centerline on wide face and the whole narrow face in this work. The plate thickness nearly has no effect on the trend of temperature distribution. The temperature is gradually depressed from hot surface to steel backup and the temperature gradient adjacent to surface is greater than that away from surface. The larger distance between water slots on both sides of binding bolts leads to the phenomenon that temperature at bolt positions is higher than that of other positions with same thickness. The temperature of wide face regards bolts as centre and distributes symmetrically. However, the temperature close to narrow face corner reduces obviously, and the local temperature rise is effectively weakened by sloping off-corner water slot, which helps to control thermal stress and deformation. Here, temperature of water slots is not changed significantly with thickness of copper plates, although the surface temperature is increased obviously. This is because the calculation is based on constant heat flux to investigate the effect of effective thickness of copper plates (from water slots roots to hot surface) on temperature distribution, but temperature of water slots mainly depends on the total heat carried by cooling water.

Fig. 6 Temperature distribution of transverse sections of 45 mm copper plates in meniscus (unit:°C):
3.3 Effect of thickness of nickel layers
The effect of thickness of nickel layers on temperature of hot surface centricities is shown in Fig. 7 and the situation of plating nickel layer for the whole surface is not considered because it is unnecessary for the upper portion of mold with lubrication from liquid flux film. The thermal resistance is increased with thickness of nickel layers and hot surface temperature is promoted. The maximum promotion of surface temperature is 10–15 °C at the boundary between nickel and copper with thickness increment of 1 mm of nickel layers, and the promotion of surface temperature narrow face is slightly higher than that of wide face, caused by larger heat flux on narrow face. There are no water slots near the mold exit, and almost no effective thickness of copper plates, so that surface temperature change in that area is less with nickel layers.

Fig. 7 Effect of thickness of nickel layers on temperature of hot surface centricities:
Figure 8 shows the temperature distribution of transverse sections of copper plates with 3 mm nickel layers 600 mm below meniscus. The trend of temperature distribution is not changed with thickness of nickel layers. The surface temperature is increased significantly with layer thickness and temperature gradient of nickel-plated is distinctly higher than that without nickel layers due to lower thermal conductivity. Also, the local temperature rise is weakened by sloping water slot, which is suitable for casting process.
3.4 Effect of depth of cooling water slots
The effect of depth of cooling water slots on temperature of hot surface centricities is shown in Fig. 9 and the effect of slots width is not included because deformation resistance of copper plates would be dropped rapidly by the wider slots. The surface temperature is reduced with slots depth because the effective thickness of copper plates is decreased and the cooling area is increased, especially for constant water flow in this work. The surface temperature without nickel layers is depressed about 10 °C with depth increments of 2 mm of deep and shallow slots and those with nickel layers adjacent to and away from mold exit are depressed approximately 7 °C and 5 °C, respectively. The impact of slots depth on surface temperature with nickel layers is smaller than that without nickel layers also due to lower thermal conductivity of nickel.

Fig. 8 Temperature distribution of transverse sections of copper plates with 3 mm nickel layers:
Figure 10 shows the temperature distribution of transverse sections of copper plates in meniscus with 20 mm shallow water slots and 23 mm deep ones. Also, the trend of temperature distribution is almost not affected by slots depth. The temperatures at roots of shallow and deep slots represent upward trend and are all higher than 100 °C, although temperature of hot surface and steel backup is decreased by the deeper slots, thus possibility of nuclear boiling is promoted and cooling capacity may be weakened, so the water slots depth as designed in Fig. 1 is reasonable.

Fig. 9 Effect of depth of cooling water slots on temperature of hot surface centricities:

Fig. 10 Temperature distribution of transverse sections of copper plates with 2 mm slots depth increments:
4 Conclusions
1) The temperature distribution of hot surface of mold copper plates is determined by cooling structure and heat transfer conditions. There is a clear temperature interface between copper and nickel and isothermal rings formed in the region away from the mold corner. The extreme temperature of wide and narrow faces occurs in meniscus and the maximum temperature of 307 °C in the position 15 mm below meniscus in wide face.
2) The temperature distribution of wide face is uniform and the isotherms near corner are approximately parallel to casting direction. The terminals of cooling water slots cannot completely reach mold exit, thus forming a number of small closed isothermal rings. The impact of corner cooling on narrow face is significant and the isotherms near corner are sloping. However, air gap in narrow face is expanded by the larger shrinkage from wide face of slab and more fully filled by molten mold powder, and isothermal rings remain flat due to uniformity of heat transfer.
3) The maximum promotion of surface temperature is about 30 °C and 15 °C with thickness increments of 5 mm for copper plates and 1 mm for nickel layers. The surface temperature without nickel layers is depressed by about 10 °C with depth increments of 2 mm deep and shallow slots and those with nickel layers adjacent to and away from mold exit are depressed by approximately 7 °C and 5 °C, respectively. Properly thinning copper plates is helpful to restrict thermal stress and deformation, and the impact of slots depth on surface temperature with nickel layers is smaller than that without nickel layers.
4) The temperature distributions of transverse sections of copper plates are similar with different cooling structures and binding bolts are regarded as centre and distribute symmetrically, and temperature at bolt positions is higher than that of other positions with same thickness. The local temperature rise is effectively weakened by sloping off-corner water slot, but too deep ones make possibility of nuclear boiling promoted, and the current design is reasonable.
References
[1] YU Hai-liang, LIU Xiang-hua. Longitudinal crack on slab surface at straightening stage during continuous casting using finite element method [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2010, 17(2): 235–238.
[2] ZHOU Shu-cai, BAI Chen-guang, LEI Ya, REN Zheng-de, CAO Peng-jun, YANG Zhi-li. Effect of low-frequency rotary electromagnetic-field on solidification structure of continuous casting austenitic stainless steel [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2009, 16(3): 360–364.
[3] O’CONNOR T G, DANTZIG J A. Modeling the thin-slab continuous-casting mold [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 1994, 25(3): 443-457.
[4] PARK J K, THOMAS B G, SAMARASEKERA I V, YOON U S. Thermal and mechanical behavior of copper molds during thin-slab casting (I): plant trial and mathematical modeling [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2002, 33(3): 425–436.
[5] PARK J K, THOMAS B G, SAMARASEKERA I V, YOON U S. Thermal and mechanical behavior of copper molds during thin-slab casting (II): mold crack formation [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2002, 33(3): 437–449.
[6] THOMAS B G. Modeling of the continuous casting of steel: past, present, and future [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2002, 33(6): 795–812.
[7] KORIC S, HIBBELER L C, THOMAS B G. Explicit coupled thermo-mechanical finite element model of steel solidification [J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2009, 78(1): 1–31.
[8] KORIC S, THOMAS B G. Thermo-mechanical models of steel solidification based on two elastic visco-plastic constitutive laws [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2008, 197(1/2/3): 408–418.
[9] LIU X D, ZHU M Y. Finite element analysis of thermal and mechanical behavior in a slab continuous casting mold [J]. ISIJ International, 2006, 46(11): 1652–1659.
[10] SANTILLANA B, HIBBELER L C, THOMAS B G, HAMOEN A, KAMPERMAN A, KNOOP W V D. Heat transfer in funnel-mould casting: effect of plate thickness [J]. ISIJ International, 2008, 48(10): 1380–1388.
[11] MENG X N, ZHU M Y. Thermal behavior of hot copper plates for slab continuous casting mold with high casting speed [J]. ISIJ International, 2009, 49(9): 1356–1361.
[12] NAKADA H, SUSA M, SEKO Y, HAYASHI M, NAGATA K. Mechanism of heat transfer reduction by crystallization of mold flux for continuous casting [J]. ISIJ International, 2008, 48(4): 446–453.
[13] HANAO M, KAWAMOTO M. Flux film in the mold of high speed continuous casting [J]. ISIJ International, 2008, 48(2): 180–185.
[14] SARASWAT R, MAIJER D M, LEE P D, MILLS K C. The effect of mould flux properties on thermo-mechanical behaviour during billet continuous casting [J]. ISIJ International, 2007, 47(1): 95–104.
[15] SAVAGE J, PRITCHARD W H. The problem of rupture of the billet in the continuous casting of steel [J]. Journal of the Iron and Steel Institute, 1954, 178(11): 269–277.
[16] SHAMSI M R R I, AJMANI S K. Three dimensional turbulent fluid flow and heat transfer mathematical model for the analysis of a continuous slab caster [J]. ISIJ International, 2007, 47(3): 433–442.
(Edited by HE Yun-bin)
Foundation item: Project(51004031) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(50925415) supported by the National Outstanding Young Scientist Foundation of China; Project(20100042120012) supported by the Special Research Fund for Doctoral Programs of Ministry of Education of China; Project(N090402022) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China
Received date: 2011–12–09; Accepted date: 2012–04–10
Corresponding author: MENG Xiang-ning, Associate Professor, PhD; Tel: +86–24–83671706; E-mail: xn_meng@126.com