基于应变非线性软化的海底隧道围岩力学特性
章 敏,王星华,陈俊儒
(中南大学 土木建筑学院,湖南 长沙,410075)
摘 要:采用弹性、峰后具有拐点的应变非线性软化本构模型,且同时考虑中主应力效应,在海水渗流和不同排水工况下,对海底隧道围岩弹塑性区应力分布规律、围岩与支护之间作用关系以及最小支护阻力进行研究,分析海水压力、上覆岩层厚度、有效孔隙度对围岩力学特性的影响,提出渗流作用下隧道围岩稳定的海水压力临界值的概念,并绘制围岩(支护)特性曲线。研究结果表明:海底隧道排水越充分,围岩有效孔隙度越大,则塑性区开展范围越大,且递增幅度较大,围岩(支护)特性曲线也不同;当隧道埋深较浅时,在隧道周围只形成塑性区域,只有当埋深进一步加大时,才可能形成松弛区域。
关键词:海底隧道;应变;非线性软化;围岩;力学特性
中图分类号:U459.5 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2009)06-1744-07
Mechanical characteristics of surrounding rock in sub-sea tunnel based on strain nonlinear softening
ZHANG Min, WANG Xing-hua, CHEN Jun-ru
(School of Civil and Architectural Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410075, China)
Abstract: By using the constitutive model composed of elastic, strain nonlinear softening segment with inflexion, the effect of intermediate principle stress, the permeation of sea water and various work conditions of controlled drainage, the stress distribution laws in elastic and plastic zone of sub-sea tunnel, interaction principle between surrounding rock and reinforcement and the least supporting resistance were studied. The impacts of sea-water pressure, upper rock covers and effective porosity on the mechanical character of surrounding rock were discussed. The concept of critical sea-water pressure of rocks around tunnel was put forward by taking the water permeation effect into account, and corresponding ground (support) reaction curves were drawn. The results show that a fuller drainage and larger value of effective porosity make a bigger scope of plastic area and increasing-range and different ground (support) reaction curves, and when the burial depth of tunnel is shallow, the plastic region is merely formed. The slack region is possibly formed when the burial depth is further enlarged.
Key words: sub-sea tunnel; strain; nonlinear softening; surrounding rock; mechanical characteristics
岩土(石)材料峰后力学行为的正确描述是解决岩土工程问题的关键。岩石在达到屈服强度后具有明显的软化现象,表现出弹性-塑性软化的特征,同时,海底隧道围岩长期处于饱水状态下,孔隙水对岩石的物理化学作用降低了岩石刚度和岩体中的有效应力,进一步恶化了围岩稳定条件[1]。郭富利等[2]对炭质页岩在不同围压和饱水状态下进行三轴试验发现,在围压较小(低于20 MPa)时,随着饱水时间的增大,岩石抗压强度呈指数型衰减;当围压较高时,才可不考虑饱水时间对岩体抗压强度带来的影响。目前,大部分研究者对富水条件下隧道围岩的弹塑性进行分析时,不考虑材料峰后强度衰减便进行理论分析和数值计算[3-4],得出的结果显然是偏不安全的。而已有的考虑岩(土)体实际强度软化的本构模型也大多采用线性软化模 型[5-6],且往往是在无地下水渗流的工况下对结构进行受力分析。由于世界上已建成的海底隧道埋深一般为40~50 m,初始地应力不高,为了在围岩分析中更加真实地反映岩体特别是软岩或破碎岩体材料的应力—应变关系,考虑材料的非线性软化特性很有必要。本文在文献[7]中建立的应变非线性软化模型的基础上,考虑海水渗流以及不同排水工况,对海底隧道围岩进行弹塑性分析,给出精度较高的弹塑性区应力、位移分布规律,同时,讨论各影响参数对围岩力学特性的影响。
1 理论分析模型
1.1 岩体材料本构关系
围岩岩体单轴压缩的应力—应变关系采用文献[7-8]中建议的本构模型:

在φ=30?时,取σc为5 MPa和8 MPa,绘出的σ—ε关系曲线如图1所示。从图1可以看出,软化段曲线性状能较好地反映岩石在到达峰值强度后,随着应变的增加,应
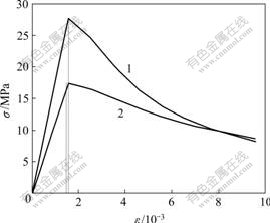
σc/MPa: 1—5; 2—8
图1 岩样单轴压缩时σ与ε的关系
Fig.1 Relationship between σ and ε under uni-axis compress
力下降,岩石发生应变软化的特性。在运用该本构方程时,为了更加真实地反映具体岩石的应力—应变特性,可在试验数据的基础上进行曲线拟合,得到符合实际情况的g和εc表达式。
1.2 力学模型
取隧道断面的形状为圆形,如图2所示。隧道半径为a,计算区域半径为b,可取隧道形心至海床面距离,上覆岩层厚为h=b-a,塑性区半径为R,隧道形心处的孔隙水压力和自重应力分别为pf和σb,支护阻力为pa,海水压力为p0。假设隧道围岩为均匀各向同性的多孔介质,且侧压力系数λ=1,有效孔隙度为φ,泊松比为μ。由于隧道受均匀压力,属轴对称问题,σ1=σθ,σ3=σr。若隧道无限长,则可当作平面应变问题处理,即平面外应变εz=ε2=0。
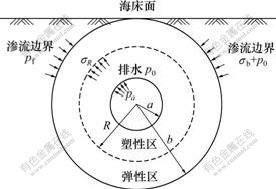
图2 力学分析模型
Fig.2 Mechanical analysis model
2 非线性软化下的围岩弹塑性分析
2.1 围岩中的孔隙水压力分布
海底隧道开挖后,由于隧道内外存在水压差,地下水将发生渗流。假设水流为稳定流,其运动服从Darcy定律,根据地下水水力学原理,可得出孔隙水压力在塑性区和弹性区的分布规律[9]。

2.2 弹性区应力和位移分析
根据力学平衡方程,弹性区岩体中的任意1点,其应力满足如下关系:

2.3 塑性区应力和位移分析
在塑性区内,假设体积不可压缩,则


2.4 塑性区半径的确定
在r=R处,隧道围岩弹性区一侧的应力同样满足式(16),得:

2.5 围岩与支护相互作用分析
为了研究水-围岩-衬砌三者相互作用问题以及不同支护刚度对支护受力变化的影响,可将衬砌视为受均匀外压pa的厚壁圆筒,内、外半径和材料弹性常数分别用r0,a,E′和u′表示,根据Lame公式可得[11]:

3 计算与讨论
参考厦门海底隧道有关地质勘察报告,围岩和衬砌的计算参数采用表1所示数据,不考虑各参数在水下环境中所引起的变化,在计算过程中假设各参数为不变量。
表1 围岩和衬砌计算参数
Table 1 Calculation parameters of surrounding rock and lining
在海底隧道防排水设计中,完全避免渗水是不可能的,也是不必要的[12]。为了比较不同排水情况下围岩特性曲线,本文与文献[9]一样,考虑6种排水工况,即p1=0(全排),p1=0.2pf(限排),p1=0.4pf(限排),p1=0.6pf(限排),p1=0.8pf(限排),p1=1.0pf(不排)。其中:p1为洞壁处水压,pf为全水压。
3.1 不同因素对塑性区半径的影响分析
a. 在上覆岩层厚度为50 m、不考虑支护阻力的情况下,在不同排水条件下p0—R的关系曲线如图3所示。由图3可见,随着海水压力和排水量的增加,塑性区域呈现出非线性增长的趋势,围岩承载能力逐渐丧失,之后曲线变化逐渐平缓。这表明在海底隧道开挖过程中,特别是深海隧道的开挖过程中,存在一个临界海水深度问题。即当海水深度达到临界深度时,水深变化对塑性区半径影响显著,隧道围岩处于非稳定状态,在此情况下,围岩即使受到轻微的扰动,也将发生突水事故。
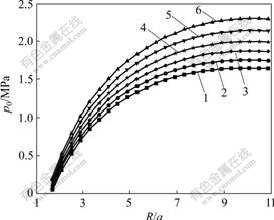
p1: 1—0; 2—0.2pf; 3—0.4pf; 4—0.6pf; 5—0.8pf; 6—1.0pf
图3 海水压力p1与塑性区R/a的关系曲线
Fig.3 Relationships between sea water pressure p0 and R/a of plastic zone
b. 在海水深度为30 m,pa=0即在无支护条件下,不同埋深和有效孔隙度对塑性区半径的影响见图4。由图4可见,在一定埋深下,排水量和有效孔隙度越大,塑性区半径越大,且在排水较充分即p1较小时,有效孔隙度对结果影响显著。引入这个系数,考虑了岩石孔隙特性不同于松散体介质,水流主要以裂隙流为主,太沙基的有效孔隙应力需修正[13]。同时,在实际地下水渗流过程中,存在水头损失,需对总水头进行折减。对于该参数的选取,目前尚无成熟的方法,建议结合隧址岩性和现场试验综合考虑确定。
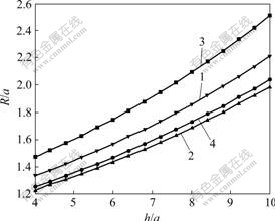
1—p1=0, φ=0.3; 2—p1=0.8pf, φ=0.3; 3—p1=0, φ=0.6; 4—p1=0.8pf, φ=0.6
图4 p1和φ不同时塑性区R/a与h/a的关系曲线
Fig.4 Relationships between R/a of plastic zone and h/a for different p1 and φ
3.2 围岩与支护相互作用分析
当海水深度为30 m,上覆岩层厚度为50 m,隧道半径为5 m时,不同排水量下围岩特性曲线如图5所示。同时考虑3种不同支护情况:C30模筑混凝土衬砌,厚度为0.2 m;C30模筑混凝土衬砌,厚度为0.3 m;C30模筑混凝土衬砌,厚度为0.6 m。在Δu= 1 cm,即支护前洞壁释放位移为1 cm时,支护特性曲线如图6所示。
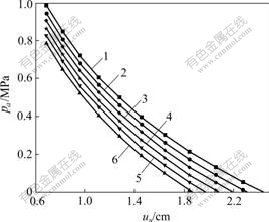
p1: 1—0; 2—0.2pf; 3—0.4pf; 4—0.6pf; 5—0.8pf; 6—1.0pf
图5 不同排水工况下围岩特性曲线
Fig.5 Ground reaction curves with controlled drainage
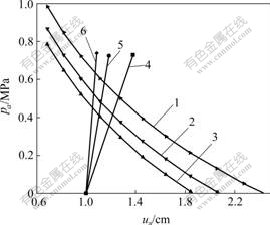
1—p1=0; 2—p1=0.6pf; 3—p1=1.0pf; 4—支护1(衬砌厚度为0.2 m); 5—支护2(衬砌厚度为0.3 m); 6—支护3(衬砌厚度为0.6 m)
图6 不同排水工况下围岩及支护特性曲线
Fig.6 Ground and support reaction curves with controlled drainage
由图6可见,随着隧道排水量的增加,即p1减小,围岩特性曲线向右移动,说明围岩发生同等的位移所需的支护阻力增大。且在同一排水量条件下,支护刚度越大,即衬砌越厚,所需的支护阻力越大,洞壁位移越小。但随着衬砌厚度的进一步增加,支护结构对减少洞壁位移、提高围岩承载力的效果逐渐不明显。所以,在隧道设计过程中,应根据排水情况,经济合理地确定衬砌结构厚度。
3.3 围岩内应力分布规律分析
图7所示是在海水深度为40 m,p1=0,pa=0时,隧道开挖后洞壁围岩径向应力和切向应力分布规律。由图7可知,随着埋深的加大,在同一处径向应力与原岩应力的比值逐渐减小,同时,围岩内的切向应力升高区域逐渐由洞壁向外扩展,这说明塑性区域不断扩大,而应力峰值逐渐降低。
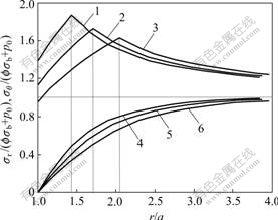
h/a: 1—6,  ;2—8,
;2—8,  ;3—10,
;3—10,  ;4—6,
;4—6,  ;5—8,
;5—8,  ;6—10,
;6—10, 
图7 隧道开挖后应力重分布曲线
Fig.7 Stresses redistribution curves after tunnel excavation
3.4 最小支护阻力的确定
当塑性区剪切滑移发展到一定程度后,隧道周围岩体松动塌落而出现松弛区,在这一区域内围岩切向正应力低于初始地应力。围岩特性曲线中,形变压力曲线与松动压力曲线相交的点,就是可能出现最小围岩压力pmin的点。pmin的确定对支护设计极其重要。对于pmin的确定,目前尚无统一的方法。王秀英等[9]将松弛区内滑移体重力平衡所需的抗力等于松弛区半径处的切向应力作为确定pmin的条件,即
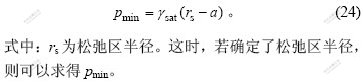
由连续性条件r=rs处,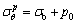 ,同时,结合r=R处径向应力连续性条件
,同时,结合r=R处径向应力连续性条件 ,将各式中pa用pmin(见式(24))代入。通过MATLAB软件对R和rs进行求解。在海水深度为40 m时,不同上覆岩层厚度下的R,rs和pmin如图8和图9所示。
,将各式中pa用pmin(见式(24))代入。通过MATLAB软件对R和rs进行求解。在海水深度为40 m时,不同上覆岩层厚度下的R,rs和pmin如图8和图9所示。
由图8和图9可知,围岩出现松张区后,最小支护阻力明显减少。实践表明,当支护阻力降低到pmin时,围岩将达到极限变形量,这时,支护承受松动压力,这对围岩和支护结构体系是不利的,应尽量避 免。同时由图7可知,当隧道上覆岩层较薄时,孔边切向应力高于原岩应力,离隧道较远时才接近原岩应力水平,这说明当埋深较浅时,在隧道周围只形成塑性区域,只有当埋深进一步加大时,才可能形成松弛区域。
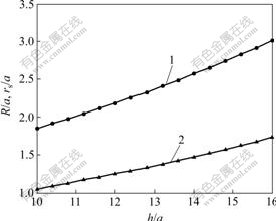
1—R/a; 2—rs/a
图8 塑性区、松弛区R/a和rs/a与h/a的关系曲线
Fig.8 Relationships among R/a, rs/a and h/a
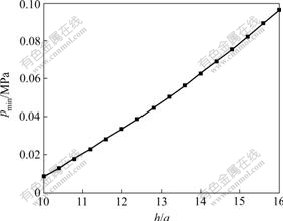
图9 最小围岩压力与h/a的关系曲线
Fig.9 Relationship between pmin and h/a
4 结 论
a. 基于应变非线性软化模型, 考虑海水渗流以及不同排水工况,导出了精度较高的海底隧道围岩应力、位移分布的解析解。
b. 在渗流作用下,当海水压力接近临界压力时,隧道围岩处于非稳定平衡态,此时,如受到轻微的扰动,围岩将因失稳而坍塌,从而发生突水事故。
c. 不同排水条件和有效孔隙度的选取对围岩力学性能有明显影响。排水越充分,有效孔隙度越大,则塑性区开展范围越大,且递增幅度较大,围岩(支护)特性曲线也不同。故在隧道防排水设计中,应在合理选取有效孔隙度的基础上,充分比较不同排水量对围岩稳定和支护结构的影响效果,经济合理地拟定渗 流量。
参考文献:
[1] 冯启言, 韩宝平, 隋旺华. 鲁西南地区红层软岩水岩作用特征与工程应用[J]. 工程地质学报, 1999, 7(3): 266-271.
FENG Qi-yan, HAN Bao-ping, SUI Wang-hua. Characteristics of water-rock interaction of red-beds and its application to engineering in southwestern Shandong[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 1999, 7(3): 266-271.
[2] 郭富利, 张顶立, 苏 洁, 等. 地下水和围压对软岩力学性质影响的试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, 26(11): 2325-2332.
GUO Fu-li, ZHANG Ding-li, SU Jie, et al. Experimental study on influences of groundwater and confining pressure on mechanical behaviors of soft rock effect[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(11): 2325-2332.
[3] Lee S W, Jung J W, Nam S W, et al. The influence of seepage forces on ground reaction curve of circular opening[J]. Tunneling and Underground Space Technology, 2006, 22: 28-38.
[4] Lee I M, Nam S W. The study of seepage forces acting on the tunnel lining and tunnel face in shallow tunnels[J]. Tunneling and Underground Space Technology, 2001, 16: 31-40.
[5] LIU Jie, ZHANG Ke-neng. Analysis of pile load-transfer under pile-side softening[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2003, 9(3): 231-236.
[6] HAO Dong-xue, LUAN Mao-tian, CHEN Rong. Analysis of cylindrical cavity expansion with linear softening and large strain behavior based on extended SMP[J]. Electronic Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2008, 13(A): 1-12.
[7] 潘 岳, 王志强. 基于应变非线性软化的圆形硐室围岩弹塑性分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2005, 24(6): 915-920.
PAN Yue, WANG Zhi-qiang. Elasto-plastic analysis on surrounding rock of circular chamber based on strain nonlinear softening[J].Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(6): 915-920.
[8] 潘 岳, 王志强, 吴敏应. 非线性硬化与非线性软化的巷、隧道围岩塑性分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2006, 27(7): 1038-1042.
PAN Yue, WANG Zhi-qiang, WU Min-ying. Plastic analysis of surrounding rock of tunnel based on strain nonlinear hardening and nonlinear softening[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2006, 27(7): 1038-1042.
[9] 王秀英, 谭忠盛, 王梦恕, 等. 山岭隧道堵水限排围岩力学特性分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2008, 29(1): 75-80.
WANG Xiu-ying, TAN Zhong-sheng, WANG Meng-shu, et al. Analysis of mechanical character of surrounding rock with controlled drainage in mountain tunnels[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2008, 29(1): 75-80.
[10] 郑雨天. 岩石力学的弹塑黏性理论基础[M]. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社, 1988.
ZHENG Yu-tian. Fundamentals of elastic-plastic-sticky theory of rock mechanics[M]. Beijing: China Coal Industry Press, 1988.
[11] 蔡美峰. 岩石力学与工程[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004.
CAI Mei-feng. Rock mechanics and engineering[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2004.
[12] 吕 明, Grov E, Nilsen B, 等. 挪威海底隧道经验[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2005, 24(23): 4219-4225.
L? Ming, Grov E, Nilsen B, et al. Norwegian experience in subsea tunnelling[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(23): 4219-4225.
[13] 李宗利, 任青文, 王亚红. 考虑渗流场影响深埋圆形隧洞的弹塑性解[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2004, 23(8): 1291-1295.
LI Zong-li, REN Qing-wen, WANG Ya-hong. Elasto-plastic analytical solution of deep-circle tunnel considering fluid flow field[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 23(8): 1291-1295.
收稿日期:2008-11-08;修回日期:2009-03-09
基金项目:国家高技术研究发展计划(863计划)项目(2007AA11Z134)
通信作者:章 敏(1984-),男,江西新余人,博士研究生,从事隧道工程的研究;电话:0731-82656715;E-mail: zhangmin021410@126.com