ZrC颗粒增强低碳锰钢的显微组织与性能
唐明华1, 2,胡双开3,李建中3,邓彬2
(1. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083;
2. 湖南工学院 机械工程系,湖南 衡阳,421002;
3. 衡阳华菱钢管有限公司,湖南 衡阳,421001)
摘要:以粒径为0.2~1.0 μm的ZrC颗粒为增强相,采用压入铸造法制备含ZrC粒子的试验钢,通过热模拟实验、性能测试、透射电镜等方法,研究ZrC粒子对钢的组织细化和力学性能的影响。研究结果表明:ZrC粒子在基体20Mn2钢中分布均匀,能细化基体晶粒;在轧制过程中,ZrC粒子能加速形变诱导铁素体相变的进程,导致组织超细化;当ZrC粒子的平均粒径为0.4 μm、加入量(体积分数)为0.5%时,实验室轧后水冷可获得晶粒粒径为3.9 μm的9 mm中板,材料的屈服强度提高58%,综合性能显著提高,这主要归因于微米ZrC增强相良好的细晶强化及第二相强化作用。
关键词:ZrC粒子;低碳锰钢;形变诱导铁素体相变;性能
中图分类号:TG142.1 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2011)07-1947-06
Microstructure and properties of ZrC particles reinforced low carbon manganese steel
TANG Ming-hua1, 2, HU Shuang-kai3, LI Jian-zhong3, DENG Bin2
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Department of Mechanical Engineering, Hunan Institute Technology, Hengyang 421002, China;
3. Hengyang Hualing Steel Tube Co. Ltd., Hengyang 421001, China)
Abstract: Taking ZrC particles with the diameter of 0.2-1.0 μm as the enhancement, the tested steel containing ZrC particles were fabricated by presses casting method. The influence of addition of ZrC particles on microstructure and mechanical properties of the tested steel were investigated by the thermal simulation experiment, mechanical properties test and TEM so on. The results show that ZrC particles are distributed evenly in the substrate 20Mn2 steels and refine substrate crystal grain. In the rolling process, ZrC particles can accelerate the process of deformation induced ferrite transformation, thus increasing the nucleation rate of ferrite, resulting in ultrafine grain. The fine microstructure with a grain size of 3.9 μm is obtained for the plate with the thickness of 9 mm fabricated using the tested steel containing 0.5% (volume fraction) ZrC particles with the diameter of 0.4 μm. The yield strength of the steel increases by 58% compared with that of commercial steel 20Mn2. All of these are mainly attributed to the effects of good fine crystal strengthening and second strengthens of micron ZrC particles.
Key words: ZrC particles; low carbon manganese steel; deformation induced ferrite transformation; properties
随着“新一代钢铁材料”研究和开发工作的不断深入,人们逐步认识到在奥氏体低温区变形通过形变诱导铁素体相变(Deformation-induced ferrite transformation, DIFT)获得超细晶钢的方法已成为开发传统钢铁材料潜在性能的重要手段。通过大量的实验和理论研究[1-2],人们对形变诱导相变的规律及其本质有了更深刻的了解[3-5]。超细铁素体主要是通过形变诱导铁素体相变终了温度Ar3的大应变并快冷以防止晶粒长大、终轧时采用尽可能高的应变速率和尽可能短的道次间隔等措施来获得的,但如此苛刻的变形条件在实际板材加工中是难以实现的,需要解决的问题是降低相变发生的大变形量;由于受变形装备轧制能力的限制,DIFT的工业应用目前还局限于薄规格、小直径产品,而采用现有DIFT工艺对于中厚板的组织细化仍有较大困难[6-7],所以,中厚板细晶钢的强化方式除了细化晶粒外,还应当引入其他的强化机制。为此,本文作者针对中厚板的组织细化特点,利用钢中的第二相粒子在凝固结晶及热加工过程中对钢组织的细化作用[8-9],以20Mn2钢为基体,并以平均颗粒粒径为0.2~1.0 μm的ZrC颗粒为增强相,采用铸造法制备含ZrC粒子的低碳钢锭坯;在此基础上,考察ZrC粒子在试验钢中的析出和固溶特点,并利用热模拟单向压缩试验,分析形变诱导相变过程中ZrC粒子对试验钢组织细化和力学性能的影响,通过对不同加工处理状态材料的力学性能测试以及显微组织观察,并利用透射电子显微镜对实验材料进行相分析,探索ZrC颗粒增强低碳低合金钢铁材料的强化机理,并与未加ZrC粒子时的进行比较。
1 实验
实验材料在中频感应熔炼炉中熔炼。在熔炼的同时加入纯度为99.9%的Nb,待熔炼脱氧后,用冲入法从外部压入粒径为0.2~1.0 μm和体积分数为0.2%~1.0%的ZrC粒子,制备低碳钢锭坯,所得实验材料的化学成分(质量分数,%)为:C,0.22;Si,0.36;Mn,1.60; Nb,0.05;P,0.014;S,0.016;余量为Fe。采用Gleeble-1500试验机进行热模拟试验,原材料经改锻、正火后由线切割加工成直径×长度为8 mm×15 mm圆棒试样,以10 ℃/s的速度将试样加热到1 000 ℃,保温3 min,然后以5 ℃/s的速度快速冷却到形变温度,以1 s-1的应变速率在Gleeble-1500试验机上进行不同变形条件的单道次热模拟单向压缩变形。因为在相同轧制条件下轧后水冷较轧后空冷的组织性能优越,所以,对变形后的试样立刻用流动水淬火冷却至室温,以固定其高温组织;实验室轧制坯料是取自试验钢锭坯改锻成长×宽×高为40 mm× 140 mm×70 mm的坯料。进行轧制实验,实验坯料奥氏体化温度为1 000~1 050 ℃,将板材温度急速冷却到形变诱导铁素体相变开始温度后进行轧制。终轧后水冷,钢板厚度为9 mm。从实验室轧制后的钢板取样,制备金相试样,试样经机械研磨及抛光后用4%硝酸酒精溶液腐蚀,基于XJG-05型金相显微镜分析中心处的组织,用截线法测定铁素体晶粒,用单位面积晶界上的铁素体晶粒数目比较测定铁素体转变量;将试样切出厚度为0.3 mm的薄片,用离子减薄仪进行双离子减薄,用TECNAI G2 20ST透射电镜观察试样的显微组织;按照国标GB/T 6394—2002对晶粒度评级,将试制钢板加工成直径×长度为10 mm×50 mm标准拉伸试样,在WJ-10万能材料试验机上进行纵向拉伸实验。采用梅氏试样进行冲击试验,在JB30A型冲击试验机上进行。
2 结果与分析
2.1 奥氏体中ZrC粒子的析出与固溶
图1所示为不同再加热温度下奥氏体中的ZrC粒子典型TEM形貌与分布。
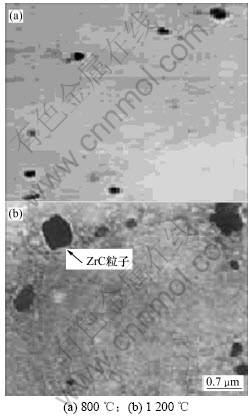
图1 不同再加热温度下奥氏体中ZrC粒子的形貌和分布
Fig.1 Morphology and distribution of ZrC particles in austenite at different reheating temperatures
由图1可见:在经历了高温凝固结晶后,ZrC粒子仍然能够存在于钢中而不溶解消失,而且能够进入铸态晶粒内部而不完全偏聚于晶界,这说明从外部添加的ZrC颗粒容易在钢中均匀分布;奥氏体中析出的ZrC粒子其形态随再加热温度的变化而变化,在较低的温度下以分布较均匀的小粒子为主,形状不规则,在较高温度下呈方状形貌,粒子数量减少,尺寸较大。
根据析出相质点对晶界的钉扎理论,弥散均匀分布于基体中的ZrC粒子将影响奥氏体晶粒长大。因为奥氏体晶粒长大是受扩散控制的晶界迁移而使晶界减少的自发过程,当运动的晶界遇到析出相质点时,由于受到质点的钉扎作用,将有效阻止奥氏体晶粒长大。ZrC粒子对奥氏体晶粒的钉扎力F由下式确定[10]:
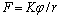 (1)
(1)
式中:K为常数; 为粒子的体积分数;r为粒子的半径。可见,粒子体积分数越大,质点的平均尺寸越小,则晶界的钉扎力就越大,由此引起晶界运动的阻力增大,即奥氏体晶粒越细小。因此,在同样的热加工条件下,添加了ZrC粒子的试验钢,其奥氏体晶粒尺寸应明显小于未添加ZrC粒子的尺寸。由于奥氏体晶界是形变诱导铁素体的优先形核地点,待奥氏体晶界作为形核位置被消耗完毕后,铁素体主要以长大为主,即出现形核位置饱和,因此,铁素体晶粒与奥氏体晶粒有对应关系。王立军等[11]的研究指出:当原始组织中奥氏体晶粒较细时,变形相对均匀,畸变区分布也均匀。因此 细晶奥氏体变形后可得到更多的、更均匀的铁素体。
为粒子的体积分数;r为粒子的半径。可见,粒子体积分数越大,质点的平均尺寸越小,则晶界的钉扎力就越大,由此引起晶界运动的阻力增大,即奥氏体晶粒越细小。因此,在同样的热加工条件下,添加了ZrC粒子的试验钢,其奥氏体晶粒尺寸应明显小于未添加ZrC粒子的尺寸。由于奥氏体晶界是形变诱导铁素体的优先形核地点,待奥氏体晶界作为形核位置被消耗完毕后,铁素体主要以长大为主,即出现形核位置饱和,因此,铁素体晶粒与奥氏体晶粒有对应关系。王立军等[11]的研究指出:当原始组织中奥氏体晶粒较细时,变形相对均匀,畸变区分布也均匀。因此 细晶奥氏体变形后可得到更多的、更均匀的铁素体。
2.2 ZrC粒子对DIFT的促进作用
图2所示为试验钢在930 ℃的试样进行60%热模拟变形后直接水淬的显微组织演变。经对比分析发现外加ZrC颗粒对DIFT的影响非常明显:未添加ZrC粒子时,由于合金仍处于奥氏体相区,所以,淬水组织全部转变为板条马氏体,组织中未见铁素体晶粒,如图2(a)所示,这说明未添加ZrC粒子的试验钢在此变形条件下不能发生DIFT;图2(b)所示为添加了ZrC粒子后与图2(a)中相同变形条件下的淬水组织,其组织为马氏体和少量等轴铁素体(3.8 μm),显然,等轴铁素体是在变形中形成的DIFT 铁素体。邓小铁等[12]的研究认为:形变诱导铁素体提前发生的原因是因为ZrC粒子作为形变和再结晶核心,促进了集中形变区的形成,因而加速了DIFT进程,以致部分奥氏体在随后的形变过程中发生DIFT相变,形成完全的等轴超细铁素体晶粒,而剩余奥氏体则在随后的快速冷却中转变为马氏体组织。
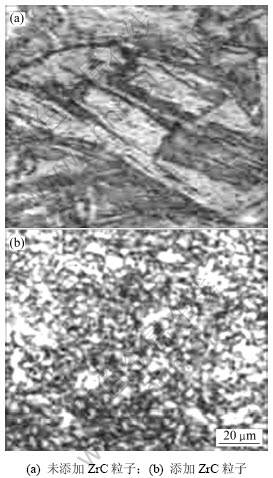
图2 试验钢经930 ℃和60%变形后的淬水组织演变
Fig.2 Change of microstructure of tested steel at 930 ℃ and deformation of 60%
必须指出的是:采用淬水法来证明DIFT的可靠性时应当谨慎。这是因为这类钢的淬透性较低,而变形又进一步降低了奥氏体的稳定性,铁素体有可能在淬水过程中形成[13],从而给形变诱导铁素体的鉴别带来严重干扰。图3所示为形变诱导铁素体的TEM形貌,电镜分析结果表明:奥氏体晶界有大量等轴状的铁素体形核,在奥氏体晶内和变形带上的某些部位,也有大片的条状铁素体析出,这些晶内铁素体的形成可在一定程度上增加铁素体的形核率,从而进一步细化铁素体晶粒并使铁素体晶粒的分布有利,而变形带作为具有较高能量的畸变区,与晶界一样也是铁素体析出的有利形核地点。结合显微组织观察可以发现在铁素体晶粒边界有渗碳体析出。这是因为在较快变形速度(1 s-1)变形时将使扩散不可能充分进行,导致碳在铁素体中过饱和,这样,在铁素体边界以渗碳体的形式析出。这说明形变诱导铁素体是由碳原子长程扩散和铁原子短程扩散耦合相变的结果。
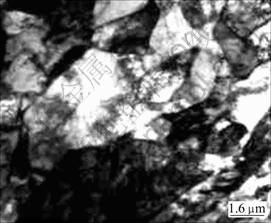
图3 形变诱导铁素体的TEM形貌
Fig.3 TEM micrograph showing morphology of DIFT in steel deformed at 930 ℃ and deformation of 60%
2.3 ZrC粒子对铁素体晶粒细化的影响
在DIFT过程中,形变基体产生的形变储存能是基体再结晶的驱动能,当ZrC粒子在形变过程中以应变诱导析出的方式沉淀析出后,将有效钉扎位错使之不容易发生回复和再结晶,从而显著推迟再结晶的发生;应变诱导析出的ZrC粒子还使基体的形变储存能随形变继续进行不断累积,这就明显增大了奥氏体相的自由能;因此,在随后的冷却过程中发生铁素体相变时,形变储存能将有效促进铁素体相的形成,使铁素体相形成的上限温度Ad3比平衡温度Ae3明显升高或使确定温度下的铁素体形成量明显大于平衡形成量;此外,由于形变基体中晶格畸变和扭折晶界的存在,可明显增大铁素体的非均匀形核率,使得形变诱导铁素体的晶粒尺寸明显细化且分布均匀。
图4所示为形变诱导铁素体晶粒粒径随外加ZrC粒子体积分数的变化关系。刘微等[14]指出,在第二相粒子对材料性能影响的诸多因素中,粒子粒径是决定其是否有利的最重要因素,因此,本工作不考虑粒子平均粒径大于1 μm的情况。由图4可见:随着ZrC粒子体积分数的增加,形变诱导铁素体的晶粒粒径不断减少,即铁素体形核率增大,晶粒细化程度增加。这说明添加ZrC后,由于形变的作用,在ZrC/奥氏体相界面及晶内产生了大量变形带、位错等聚集形变能的缺陷,这些都为相变提供了有利的形核位置及能量,γ→α转变的形核率将随形核位置的增加而提高,所以,组织不断细化;但是,当添加的ZrC粒子体积分数达到一定程度(0.6%)以后,铁素体的晶粒粒径随ZrC粒子体积分数的增加反而增大,这表明ZrC粒子对铁素体形核率的促进作用存在一个临界值,超过此临界值时,过量的ZrC粒子将不利于试验钢的组织细化。其可能的原因是铁素体形核在此刻达到了饱和状态,ZrC粒子的形核促进作用相对于体积分数较小时,明显减弱,同时,较高数量的非金属夹杂物由于以网状形式析出于奥氏体晶界,对铁素体形核产生了抑制作用。

图4 铁素体晶粒粒径随ZrC粒子体积分数的变化关系
Fig.4 Change of ferrite grain size with volume fraction of ZrC particles for steel after deformation
2.4 ZrC粒子对试验钢力学性能的影响
表1所示为试验钢的硬度(正火态)随ZrC颗粒参数的变化关系。从表1可见:即使添加少量的ZrC粒子,材料的硬度也有较大的提升,说明ZrC粒子对钢的凝固结晶组织起到了很好的细化作用;而晶粒的细化可以提高奥氏体淬火获得马氏体的临界冷却速度,使得奥氏体淬火后向贝氏体转变,所以,DIFT后钢的强硬性将因细晶强化、形变强化及第二相强化的综合效应达到更高的状态。从表1所示的硬度测试结果来看,只有当粒子细小(d<1 μm)时,才表现出Orowaw强化的本质,即颗粒粒度较大时(d>1 μm),Orowan强化机制的表现并不突出。从表1还可见:ZrC粒子最佳的添加量为0.60%,此时的硬度(HBS)为233,为不加入ZrC时的1.34倍,这说明具有适当粒径和体积分数的ZrC颗粒能使增强体颗粒和基体结合充分,从而更好地改善材料的性能。
表1 试验钢正火态的硬度随ZrC颗粒的变化关系
Table 1 Change of hardness of tested steel with ZrC particles under normalizing condition
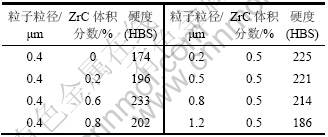
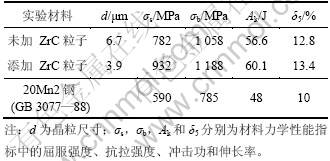
杨平等[15]报道,在铁素体钢中,细小弥散析出的第二相析出物因不足以达到裂纹临界尺寸而不易激发裂纹,并且裂纹遇之发生转折, 这样就对裂纹的扩展有一定的阻滞作用,使其对钢材韧性和疲劳性能的损害显著降低甚至消除。因此,可以预测:变形后,合理地控制保温时间可在提高材料强度的同时有效地改善材料的韧性。表2所示为试验钢经900 ℃和80%应变后力学性能测试结果(ZrC的平均粒径为0.4 μm,体积分数为0.5%)。从表2可见:相对于未添加ZrC粒子的情形,添加了ZrC粒子的试验钢组织进一步细化,强度大幅度提高,同时,塑性和韧性也略有增加。应当指出的是:随着轧制变形量的增加,铁素体晶粒尺寸也会有所减小,但与加入ZrC粒子的细化效果相比,尺寸减小幅度要小得多,因此,表2中的结果不但证明了添加ZrC粒子后比较单纯的DIFT或奥氏体高温形变再结晶,钢铁材料具有更好的晶粒细化效果,同时也证明了细晶强化的特点是在提高强度的同时,还能保持塑性和韧性不下降。
表2 试验钢经900 ℃和80%应变后的力学性能
Table 2 Properties of tested steel after straining at 900 ℃ and deformation of 80%
在以上试验研究的基础上制定实验室轧制工艺并进行实验。实验室坯料是添加了ZrC粒子(平均粒径为0.4 μm,体积分数为0.5%)的试验钢锭坯改锻成长× 宽×高为40 mm×140 mm×70 mm的坯料,终轧后水冷,钢板厚度为9 mm。结果表明:铁素体晶粒均匀细小,晶粒粒径被细化至3.9 μm;力学性能测试结果为:σb= 1 188 MPa,σs=932 MPa,与试样钢成分接近的20Mn2淬回火态相比,分别提高51%和58%以上,而塑性比20Mn2的强。
2.5 ZrC颗粒增强试验钢的强韧化机理
微米ZrC颗粒增强试验钢强韧性应归因于细晶强化、形变强化和第二相强化耦合作用的结果。首先,由于均匀分布于基体相中的ZrC颗粒钉扎奥氏体晶界,有效细化了初始奥氏体晶粒,在轧制变形中,ZrC颗粒又阻碍位错的运动,造成位错增殖,从而增加了相变时的形核位置,加快了γ→α形核速率,加速了DIFT进程,因而,铁素体的转变量高且晶粒得到细化;同时,因为材料的变形属于两相不均匀变形(ZrC/奥氏体),变形时首先在较软的基体上进行,较硬的颗粒不变形或变形很少,在界面上形成较高的形变不匹配,从而产生较高的形变应力。当该应力集中在ZrC粒子的某个部位时,在晶体某个柱面的分切应力作用下,在交界的柱面上萌生位错环并沿柱面移动,该应力的释放靠放出位错环实现,从而增加了基体位错的密度,大量的位错之间产生摩擦、缠绕,在应力的作用下形成细小的胞状组织即亚晶,因此,ZrC粒子因阻碍晶界的迁移,使基体的晶粒细小化,按照Hall-Petch关系,材料的强度大幅度提高;同时,晶粒细化后,裂纹沿晶界扩展的阻力越大,使得材料的塑性和韧性也随之提高。可见:ZrC粒子对晶粒细化的贡献提高了高强度钢的使用安全性。
图5所示为ZrC粒子绕过位错的第二相强化Orowan机理。在轧制变形中位错越过第二相颗粒的机制有切过机制和绕过机制(Orowan机制)[16],当第二相相对较软或尺寸很小时主要为切过机制,而当第二相较硬或尺寸较大时主要为Orowan机制。可见:对每一种特定的第二相而言,粒子的强化机制存在一个临界尺寸,小于临界尺寸时切过机制起作用,而大于临界尺寸时Orowan机制起作用。由于本实验所添加的ZrC粒子其粒径远大于从钢液中内生析出的合金元素Nb的碳化物粒子粒径(30~200 nm),因此,ZrC粒子相对于Nb在钢的凝固结晶及变形过程中对材料的强韧化起了更为重要的作用。
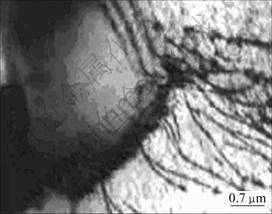
图5 位错绕过ZrC粒子的Orowan机制
Fig.5 TEM image showing Orowan mechanism of dislocations moving around ZrC particles
3 结论
(1) 当ZrC粒子的粒径小于1 μm时,粒子对位错产生较大的阻力,形成集中形变区,因而提高铁素体形核率,导致晶粒(组织)超细化。
(2) ZrC/奥氏体相界面的不均匀变形在界面产生形变位错源,使基体中的位错增值,形成位错胞,提高了试验钢的强度。由于ZrC粒子的阻碍,裂纹沿晶界扩展的阻力越大,使得材料的塑性和韧性提高。
(3) 添加了平均粒径为0.4 μm、体积分数为0.5%的ZrC粒子的试验钢,实验室轧制9 mm中板可获得超细组织,晶粒粒度达到3.9 μm;相比于20Mn2钢淬回火态的标准参考值,屈服强度提高58%,塑性和韧性不下降。
参考文献:
[1] 翁宇庆. 超细晶钢——钢的组织细化与控制技术[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2003: 72-133.
WENG Yu-qing. Ultrafine grain steel—Steel microstructure refinement and control technology [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2003: 72-133.
[2] 董瀚. 先进钢铁材料——高性能结构材料技术丛书[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008: 12-36.
DONG Han. Advanced steel—Series high performance structural materials technology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2008: 12-36.
[3] Wang G D, Liu X H, Du L X, et al. Research and development of C-Mn super-steel[C]//Shanghai: ICASS, 2004: 60-67.
[4] Yang Z M. The obtain of rebar products of low carbon steel with ultra-fine grain structure[C]//Shanghai: ICASS, 2004: 74-79.
[5] Liu Q Y, Deng S H, Yang X J, et al. Effects of dissolution and precipitation of Nb in microalloyed steel on deformation induced ferrite transformation[C]//Proceedings of the Joint International Conference of HSLA Steels 2005 and ISUGS 2005. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2005: 175-184.
[6] Liu Y C, Sun Z Q, Ren P D, et al. 460 MPa grade ultra-low alloy high strength steel plate for mining machinery[C]//Shanghai: ICASS, 2004: 263-266.
[7] Zhang X Z, Zhang L N, Ma Y. Nano-precipitation of new plain low carbon steel by CSP process[C]//Shanghai: ICASS, 2004: 84-88.
[8] 唐明华, 刘志义, 胡双开, 等. ZrC/奥氏体相界面形变诱导相变动力学[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2010, 41(1): 120-124.
TANG Ming-hua, LIU Zhi-yi, HU Shuang-kai, et al. Transitional dynamics of deformation induced phase transformation at ZrC/austenitic interface[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2010, 41(1): 120-124.
[9] 刘海峰, 刘耀辉, 于思荣. 原位合成VC颗粒增强钢基复合材料组织及其形成机理[J]. 复合材料学报, 2001, 18(4): 58-63.
LIU Hai-feng, LIU Yao-hui, YU Si-rong. Microstructure of in situ VC particulates reinforced steel matrix composite and its forming mechanism[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2001, 18(4): 58-63.
[10] 杨颖, 侯华兴, 马玉璞, 等. 再加热温度对含Nb,Ti钢第二相粒子固溶及晶粒长大的影响[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2008, 20(7): 38-42.
YANG Ying, HOU Hua-xin, MA Yu-pu, et al. Effect of reheating temperature on solid solution of second phase particle and grain growth in steel containing niobium and titanium[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2008, 20(7): 38-42.
[11] 王立军, 姚连登, 任海鹏, 等. 微合金化对超细晶中厚板显微组织的影响[J]. 东北大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 28(4): 510-513.
WANG Li-jun, YAO Lian-deng, REN Hai-peng, et al. Effect of microalloying on ultrafine-grained microstructure of plates[J]. Journal of Northeastern University: Natural Science, 2007, 28(4): 510-513.
[12] 邓小铁, 刘志义, 郑青春. 变形方式对含ZrC粒子的20Mn2钢晶粒细化的影响[J]. 材料导报, 2005, 19(8): 128-131.
DENG Xiao-tie, LIU Zhi-yi, ZHENG Qing-chun. Effect of deforming method on grain-refining in 20Mn2 steel containing ZrC particles[J]. Material Herald, 2005, 19(8): 128-131.
[13] 杨景红, 刘清友, 孙冬柏, 等. 冷速及变形对X70级管线钢相变及组织的影响[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2008, 29(5): 59-63.
YANG Jing-hong, LIU Qing-you, SUN Dong-bai, et al. Effect of cooling rate and deformation on transformation and microstructure of a X70 grade pipeline steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2008, 29(5): 59-63.
[14] 刘微, 王立群, 陈新旺. 含铌钢第二相粒子固溶析出规律研究[J]. 山东冶金, 2004(S1): 171-173.
LIU Wei, WANG Li-qun, CHEN Xing-wang. Study of dissolution-precipitation of second-phase particles containing Nb steel[J]. Shandong Metallurgy, 2004(S1): 171-173.
[15] 杨平, 傅云义, 崔凤娥, 等. Q235碳素钢应变强化相变的基本特点及影响因素[J]. 金属学报, 2001, 37(6): 592-600.
YANG Ping, FU Yun-yi, CUI Feng-e, et al. Characteristics of strain enhanced transformation and Its influencing factors in Q235 plain carbon steel[J]. Acta Metallurica Sinica, 2001, 37(6): 592-600.
[16] 胡赓祥, 蔡珣, 戎咏华, 等. 材料科学基础[M]. 上海: 上海交通大学出版社, 2006: 186-187.
HU Gen-xiang, CAI Xun, RONG Yong-hua, et al. Scientific foundation of materials[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Traffic University Press, 2006: 186-187.
(编辑 杨幼平)
收稿日期:2010-08-15;修回日期:2010-11-02
基金项目:湖南省自然科学衡阳联合基金资助项目(10JJ9022)
通信作者:唐明华(1965-),男,湖南衡阳人,副教授,博士研究生,从事金属材料强韧化理论与技术研究;电话:0734-2568802;E-mail: hyhuaxtmh@163.com