DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2015.11.016
基于人体舒适度的室内温度优化设定方法
王玉山1, 2,彭辉1, 2, 3,王丹1, 2,刘明月1, 2,杨晗1, 2,武明源1, 2,覃业梅1, 2
(1. 中南大学 信息科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083;
2. 先进控制与智能自动化湖南省工程实验室,湖南 长沙,410083;
3. 两型社会与生态文明协同创新中心,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:建立一个简化的办公建筑热力学模型,模型中假设白天空调开放,夜间自然通风。通过对该模型的分析,建立空调冷负荷与室外温度、热物质温度、室内温度设定值等环境变量的定量关系。同时,为评估环境舒适度,采用描述人体舒适度的预测平均指标(predicted mean vote, IPMV),并确定IPMV与室内温度和平均辐射温度的定量关系。基于上述定量关系,以空调冷负荷最小化为优化目标,同时以-0.9≤IPMV≤0.9为限制条件,优化求解得到了最优的室内温度设定值。通过EnergyPlus等软件对优化结果进行仿真计算,与26 ℃固定温度设定值的情形相比,本文提出的室内温度优化设定方法既可保证室内人员的舒适度又可以降低空调能耗。
关键词:办公建筑;节能;动态优化;室内温度设定值;预测平均指标
中图分类号:TU111.19 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2015)11-4083-08
Optimization method for indoor air temperature based on thermal comfort
WANG Yushan1, 2, PENG Hui1, 2, 3, WANG Dan1, 2, LIU Mingyue1, 2, YANG Han1, 2,
WU Mingyuan1, 2, QIN Yemei1, 2
(1. School of Information Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Hunan Engineering Laboratory for Advanced Control and Intelligent Automation, Changsha 410083, China
3. Collaborative Innovation Center of Resource-conserving & Environment-friendly Society and
Ecological Civilization, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Assuming that the air-conditioner runs in the daytime and ceases at night, a simplified thermodynamic model for office buildings was established. The building model was analyzed to get a quantitative relationship between the cooling load and environment variables which include outdoor air temperature, thermal mass temperature and indoor air temperature. In order to guarantee thermal comfort, predicted mean vote (IPMV) which is used to describe the body comfort was applied. The relationship between IPMV, indoor air temperature and mean radiant temperature was also analyzed. Then the minimum cooling load of the air-condition was the optimization goal, and -0.9≤IPMV≤0.9 was constraint, and the optimal indoor air temperature was obtained through MATLAB Optimization Toolbox. Finally, based on the optimal indoor air temperature, the energy consumption of a simulated office building was computed through EnergyPlus. Compared with fixed 26 ℃ indoor air temperature, optimizing indoor air temperature is a very effective and feasible approach, and it can effectively reduce energy consumption of buildings, as well as guarantee the thermal comfort.
Key words: office building; energy conservation; dynamic optimization; indoor air temperature; predicted mean vote
在各类建筑中,办公建筑和大型公共建筑具有能耗总量大、能源效率低、节能潜力大的特点[1],是能耗大户。其建筑面积只占城镇建筑总面积的4%,但能耗却占城镇建筑总能耗的22%。做好大型公共建筑节能工作,对实现节能减排目标具有重大意义。在办公建筑和大型公共建筑中,空调能耗占建筑总能耗的40%~60%,因此,降低空调系统能耗是建筑节能的重要工作之一[2]。目前办公建筑多采用固定温度设定值的方法,这造成了空调系统能耗的浪费[3]。在降低空调能耗和有效评估人体舒适度方面,国内外学者已进行大量的研究。叶海等[4]提出了一种热环境客观评价的简易方法,解决了描述人体舒适度的预测平均指标(predicted mean vote,缩写PMV,记为IPMV)[5]不易于计算的问题,但未将其具体应用于建筑节能。高磊[6]从实际应用出发分析了降低空调能耗的一些实用措施,但是没有从建立建筑模型的角度研究节能方法。Mohamed等[7]应用多目标优化策略实现降低空调能耗,但是其仅讨论了以年为单位的分析应用,没有研究1 d中空调温度的动态优化。Yang等[8]建立了简化的办公建筑模型,并提出了一种用热物质和夜间通风降低空调负荷的方法。但是该方法未与舒适度指标相结合,因此不能优化各个时刻空调温度设定值。针对该问题,马庆[9]提出了一种动态优化室内温度设定值的方法,但是在其优化过程中没有考虑太阳辐射照度对室内温度的影响。本文作者提出的动态优化室内温度设定值的方法综合考虑了室外温度变化和太阳辐射照度的影响,结合夜间通风的方法,可以有效降低空调系统能耗,降低夏季高峰电力的用电负荷,同时又不会降低人的热舒适感觉,是一种很好的节能环保的方法。
1 办公建筑热力学模型
简化的办公建筑模型如图1所示[8]。图中,Ti为室内温度;Ts为室内温度设定值;T o为室外综合温度;Tm为外部热物质温度。假设在建筑模型中室内空气温度的分布是均衡的,白天空调开放,夜间自然通风、空调停止。热物质划分为内部热物质和外部热物质,与室外空气没有接触的热物质统一为内部热物质;与室外空气有直接接触的一面墙称为热物质墙,是外部热物质。除热物质墙外所有的围护结构视为理想隔热物质。房间隔墙表面之间的热辐射忽略不计。白天室内的所有热增益(包括透过门窗的太阳辐射增益)和产热都集合成一个热增益E,夜间不考虑室内热增益。假设热物质的温度分布是均衡的,其中内部热物质的温度与室内温度相同。这意味着热物质内部的热传递速度远远快于热物质表面的热传递速度。在白天室内温度与室内温度设定值相同,如图1(a)所示;在夜间通风率qv视为常数,如图1(b)所示。

图1 简化的办公房间模型
Fig. 1 A simple room model
1.1 室外综合温度
在分析外部热物质的传热问题时,考虑到其外表面同时受到太阳辐射和空气温度的综合热作用,这样建筑物单位外表面上得到的热量应取决于其表面换热量和吸收的太阳辐射之和[10]。为了计算方便,引入室外综合温度。室外综合温度等于室外空气温度加(太阳辐射对外部热物质的热作用产生的)当量温度[11],即:
 (1)
(1)
 (2)
(2)
式中:Tw为室外空气温度;Tq为当量温度;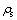 为外部热物质外表面对太阳辐射的吸收系数;I为太阳总辐射照度;
为外部热物质外表面对太阳辐射的吸收系数;I为太阳总辐射照度; 为外表面换热系数。
为外表面换热系数。
1) 室外空气温度。室外空气温度逐时曲线与正弦函数相近,室外空气温度可近似于正弦函数[12]:

 (3)
(3)
式中: 为室外空气温度平均值;
为室外空气温度平均值; 为室外空气温度最大值;t为计算时刻;
为室外空气温度最大值;t为计算时刻; 为角频率;t0为常数。
为角频率;t0为常数。
2) 当量温度。太阳辐射对外部热物质的热作用产生的当量温度在白天数值较大,在夜间几乎为零。为了便于计算用四次多项式拟合白天的当量温度[12]。拟合多项式为
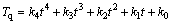 (4)
(4)
3) 室外综合温度。室外综合温度为室外空气温度与当量温度之和。综上所述,白天和夜间的室外综合温度To分别如式(5)和(6)所示:
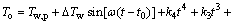
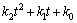 (5)
(5)
 (6)
(6)
1.2 白天热平衡方程
白天空调开启,对于外部热物质和室内空气的热平衡方程如式(7)和(8)所示[9]。
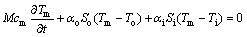 (7)
(7)
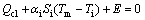 (8)
(8)
式中:M为外部热物质质量;cm为外部热物质的比热容; 为外部热物质外表面的换热系数;
为外部热物质外表面的换热系数; 为外部热物质外表面面积;
为外部热物质外表面面积; 为外部热物质内表面的换热系数;
为外部热物质内表面的换热系数;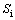 为外部热物质内表面面积;
为外部热物质内表面面积;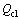 为空调冷负荷。
为空调冷负荷。
基于前面的假设,室内温度Ti与空调温度设定值Ts相等,后续公式中统一用Ts表示;外部热物质外表面面积So与外部热物质内表面面积Si相等,后续公式中统一用So表示。
将式(5)代入式(7),可得:
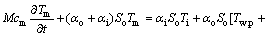
 (9)
(9)
令 ;
; ;
;
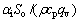 。
。
其中: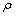 为空气密度;cp为空气比热容;
为空气密度;cp为空气比热容; 为基于夜间通风率qv的时间常数;
为基于夜间通风率qv的时间常数; 为量纲一的外部对流热传递数;
为量纲一的外部对流热传递数;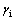 为量纲一的内部对流热传递数。将
为量纲一的内部对流热传递数。将 ,
, 和
和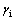 代入式(9),可得:
代入式(9),可得:

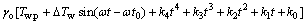 (10)
(10)
对式(10)解微分方程得到通解:

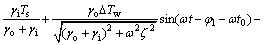
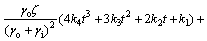
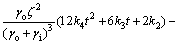
 (11)
(11)
式中:C1为常数;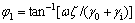 为外部热物质温度相对于室外空气温度的相移,
为外部热物质温度相对于室外空气温度的相移, 的取值为0~
的取值为0~ 。
。
将式(11)代入式(8),可得到空调冷负荷:

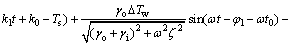

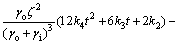
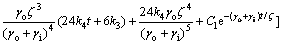 (12)
(12)
空调负荷为热负荷时,Qcl为正;空调负荷为冷负荷时,Qcl为负。
式(12)中的空调负荷可以分为4个部分:第1部分是稳态负荷,它一方面是室外空气温度平均值通过外部热物质传递热量到室内造成的空调负荷,另一方面是室内热增益造成的负荷;第2部分形式上为时间t的四次多项式,可以理解为当量温度造成的空调负荷;第3部分是周期波动的负荷,是受室外空气温度随时间变化影响造成的负荷;第4部分是受初始条件影响造成的负荷,它与夜间通风状况有关,而且它的影响随着t的增大而减小。
1.3 夜间热平衡方程
夜间空调关闭,内部热增益为0,此时的热平衡方程如式(13)和(14)所示[8]。
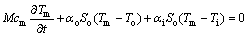 (13)
(13)
 (14)
(14)
令 ,得到
,得到

 (15)
(15)
方程(15)的通解是:

 (16)
(16)
其中:C2为常数; 。
。
室内温度设定值Ts的通解是:

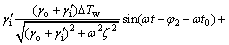
 (17)
(17)
1.4 边界条件
假设在1 d中,白天是从t1到t2时刻。由于热物质温度的变化是连续的,即在白天和夜间的临界时刻由式(11)和式(16)计算得到的Tm相同,所以,在t2和t1时刻有如下关系:
t=t2时刻,有:

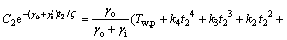
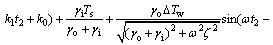

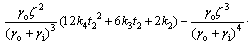
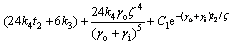 (18)
(18)
t=t1时刻,有:
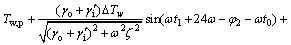




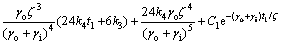 (19)
(19)
由方程(18)和(19)可以解出C1和C2。
2 舒适度指标模型
美国采暖制冷与空调工程师学会ASHRAE和国际化标准组织ISO规定了能够让多数人感到舒适的空气温度范围[13]。这些标准主要依据Fanger[14]提出的人体热舒适模型,即PMV模型。该模型综合了空气温度、平均辐射温度、空气的相对湿度、空气流速、新陈代谢率和服装热阻等6个影响人体热舒适的因素[15],是迄今为止最全面的评价热环境的模型。PMV模型将热感觉分为7个等级,其IPMV对应的热感觉标尺如表1所示[16]。
表1 IPMV对应的冷热感标尺
Table 1 Relations of thermal comfort feeling and IPMV

国际标准化组织将温热环境舒适范围规定为-0.5≤IPMV≤0.5。在我国,为了减少建筑空调能耗,一般将舒适度范围规定为-1≤IPMV≤1。为了获得较满意的舒适度,本文中限定-0.9≤IPMV≤0.9。
在确定影响热舒适的6个主要因素后,便可以计算出预测平均热反应指标IPMV,从而对一个环境进行热感觉评价。但IPMV的计算较为复杂,须在计算机上迭代求解,这对工程应用极为不利,文中采用一个评价热环境的无因次指标,即热平衡数(NHB)。热平衡数NHB是叶海等[4]提出的一种简易的热环境客观评价方法。它计算较为简单,在-1≤IPMV≤1的范围内能准确地估算IPMV[4]。其简化后的方程如式(20)和(21)所示。
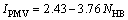 (20)
(20)
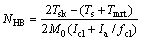 (21)
(21)
其中:Tsk为皮肤平均温度;Icl为服装的基本热阻;M0为新陈代谢率;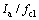 为空气层热阻与服装面积系数的比值;Tmrt为平均辐射温度。
为空气层热阻与服装面积系数的比值;Tmrt为平均辐射温度。
Tmrt由下式得到[9]。
 (22)
(22)
其中:Sj为房间j表面的表面积。
令 ,
, ,D1和D2代入式(21)和(22)得到:
,D1和D2代入式(21)和(22)得到:
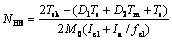 (23)
(23)
将式(23)代入式(20),得:
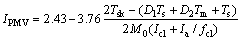 (24)
(24)
3 室内温度设定值的动态优化
在前面建立的建筑物简化热力学模型与舒适度模型的基础上,以能耗最小即空调的冷负荷最小为优化目标,实现对室内温度设定值的动态优化,因为计算冷负荷时Qcl为负值,所以,取-Qcl,其目标函数为
 (25)
(25)
Qcl由式(12)计算得到。
为了满足室内舒适度的要求,优化过程中限定IPMV为
-0.9≤IPMV≤0.9 (26)
IPMV由式(24)计算得到。
以式(25)作为目标函数,式(26)作为不等式约束,式(11)作为等式约束,即得到了所需的优化模型。将有关的建筑物参数等代入优化模型并求解该模型,即可得到满足人体舒适度要求的最优室内温度设定曲线。
4 案例分析
以某办公建筑内的一间房间为例,假设房间长×宽×高为12 m×6 m×4.5 m;夜间通风率为648 m3/h;空气密度为1.16 kg/m3,比热容为1.012 kJ/(kg·K);墙厚0.2 m,密度为2 500 kg/m3,比热容为0.75 kJ/(kg·K);墙外表面换热系数为19 W/(m2·K);墙内表面换热系数为7 W/(m2·K);室外空气温度最大值为311 K;室外空气温度平均值为304 K;内部热增益为700 W;制冷时间段开始时刻t1为06:00,结束时刻t2为18:00;常数t0=8;皮肤平均温度为306.65 K;新陈代谢率为70.6 W/m2;服装的基本热阻为0.113 (m2·K)/W;空气层热阻与服装面积系数的比值为0.1 (m2·K)/W;查询 GB 50736—2012[17]得到各时刻太阳总辐射照度,代入式(2)得到当量温度,结合式(4),用MATLAB拟合得到常数k0=124.987 951,k1=-52.656 424,k2=7.818 063,k3=-0.468 670,k4=0.009 764;根据以上参数可以计算得到D1,D2, ,
,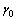 ,
,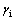 ,
, 和
和  等参数;解方程组(18)和(19)得到C1和C2。
等参数;解方程组(18)和(19)得到C1和C2。
将上述各参数代入目标函数公式(25),不等式约束公式(26)和等式约束公式(11),利用MATLAB对模型进行优化求解,其优化后的室内温度设定值和热物质内表面温度分别见表2和表3,其优化后的轨迹如图2和图3所示。
表2 室内温度设定值
Table 2 Indoor air temperature setting

表3 热物质表面温度
Table 3 Thermal mass temperature

F

图2 各个时刻的温度轨迹
Fig. 2 Curves of temperature in each moment
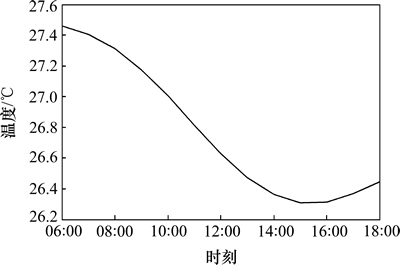
图3 室内温度最优设定值的变化轨迹
Fig. 3 Curve of optimal indoor air temperature
由图2可以看出:室外空气温度在14:00左右达到最大值,随后开始降低。中午太阳辐射强烈,受太阳辐射影响室外综合温度远高于室外空气温度,而早上和傍晚太阳辐射微弱,室外综合温度的值接近于室外空气温度值。热物质表面温度受夜间通风的影响,早晨温度值较低,随着室外综合温度的升高,热物质表面温度也随之升高。室内温度设定值的走势与热物质表面温度的走势刚好相反。
由图3可以看出:早晨室外温度和热物质表面温度都较低,不需要很低的室温就可以维持较为舒适的水平。随后热物质表面温度升高,室内温度设定值下降,在15:00左右达到最小值。热物质温度的惯性使得室内温度设定值的峰值较室外温度的峰值有一定的延迟。
将优化得到的室内温度设定值Ts和热物质表面温度Tm代入式(24)计算得到房间的舒适度指标IPMV,其变化曲线如图4所示。
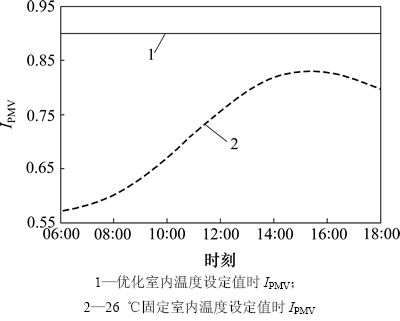
图4 舒适度指标IPMV曲线
Fig. 4 Curves of thermal comfort IPMV
由图4可以看出:采用优化室内温度设定值时IPMV一直维持在上限0.9处,这是因为室内温度设定值越高,其与室外的温差就越小,节能效果越好,而为了使能耗最小,必须在保证IPMV不超越上限的条件下,尽可能调高室内温度设定值。当室内温度高时,热感觉较明显,IPMV也高。
由图4还可以看出:当室内温度设定值为26 ℃时,IPMV的波动较大。而采用优化室内温度设定值时IPMV始终维持在0.9,此情况下人体热舒适度维持在一个稳定的水平上,室内的人感觉较为舒适。
EnergyPlus是一款能耗分析计算软件[18]。用户输入描述建筑物理特征和相关设备的参数之后,该软件就能计算得到设定条件下的冷热负荷量。为了进一步验证本文优化方法的节能效果,采用建筑全能耗分析软件EnergyPlus对房间能耗进行仿真计算,将图3中给出的室内温度优化设定值与26 ℃固定室内温度设定值2种情况下对应的能耗进行比较,以观察节能效果。将上述办公房间模型的各参数以及房间温度设定值等数据输入EnergyPlus得到图5所示的仿真结果。
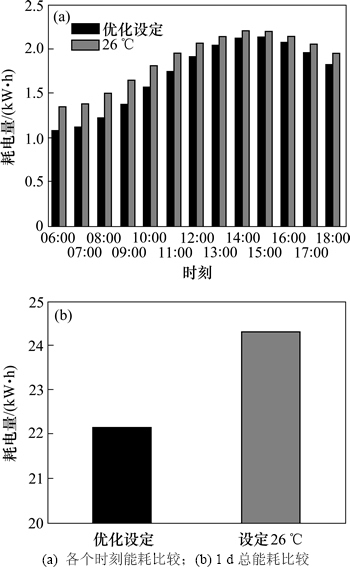
图5 2种室内温度设定情形下的空调能耗比较
Fig. 5 Energy comparison in cases of two indoor air temperature settings
由图5可以看出:在建筑参数、内部负荷都相同时,采用动态优化得到室内温度设定值的方法具有明显的节能效果。针对上述72 m2的房间,优化温度设定值相比于26 ℃固定设定值,每天空调可以节约用电2.2 kW·h,节能效果达到9%。假设一栋楼有100间类似的房间,采用动态优化设定值的方法,一栋楼1月(按20个工作日算)可以节约空调能耗可达4 400 kW·h。若进一步将舒适度水平降低为国家标准限定的-1≤IPMV≤1,则节能效果会更加明显。
5 结论
1) 建立简化的办公建筑模型及其热平衡方程,以空调负荷最小为优化目标,舒适度指标为限制条件,优化求解得到动态的优化室内温度设定值。
2) 经验证,得到的优化温度设定值可以满足室内人员的舒适度要求,相比于目前固定室内温度设定值的方法,动态优化温度设定值可以有效降低能耗。因此动态优化温度设定值方法是一种节能环保的方法。
3) 将动态优化室内温度设定值方法推广应用到办公建筑对于节能减排具有重要意义。
参考文献:
[1] 吕萌萌, 梁传志, 武海滨, 等. 基于情景分析法的政府办公建筑和大型公共建筑节能政策研究[C]// 第九届国际绿色建筑与建筑节能大会论文集. 北京: 2013: 1-9.
L Mengmeng, LIANG Chuanzhi, WU Haibin, et al. Research on energy saving policy of office buildings based on scenario analysis[C]// The Ninth International Conference on Green and Energy Efficient Building. Beijing: 2013: 1-9.
Mengmeng, LIANG Chuanzhi, WU Haibin, et al. Research on energy saving policy of office buildings based on scenario analysis[C]// The Ninth International Conference on Green and Energy Efficient Building. Beijing: 2013: 1-9.
[2] 刘珠雄. 办公建筑空调系统运行管理节能的探讨[J]. 福建建设科技, 2013(1): 55-56.
LIU Zhuxiong. Discussion about operation management and energy saving of air conditioning system in office building[J]. Fujian Construction Science & Technology, 2013(1): 55-56.
[3] 马庆, 李歧强, 聂清珍. 公共建筑空调温度设定值的动态优化控制研究[J]. 系统工程学报, 2011, 26(4): 435-441.
MA Qing, LI Qiqiang, NIE Qingzhen. Research on dynamic optimization of air-conditioner temperature setting control on public buildings[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering, 2011, 26(4): 435-441.
[4] 叶海, 魏润柏. 热环境客观评价的一种简易方法[J]. 人类工效学, 2004, 10(3): 16-19.
YE Hai, WEI Runbai. A simple method for objective evaluation of thermal environment[J]. Chinese Journal of Ergonomics, 2004, 10(3): 16-19.
[5] Mohamed Sahari K S, Abdul Jalal M F, Homod R Z, et al. Dynamic indoor thermal comfort model identification based on neural computing PMV index[C]// Earth and Environmental Science. Putrajaya: 2013: 1-4.
[6] 高磊. 办公楼中央空调系统的节能分析[J]. 建筑节能, 2012, 40(8): 14-16.
GAO Lei. Energy-efficiency analysis on central air-conditioning system in office building[J]. Building Energy Efficiency, 2012, 40(8): 14-16.
[7] Mohamed H, Ala H, Kai S. Impact of adaptive thermal comfort criteria on building energy use and cooling equipment size using a multi-objective optimization scheme[J]. Energy and Buildings, 2011, 43(9): 2055-2067.
[8] YANG Lina, LI Yuguo. Cooling load reduction by using thermal mass and night ventilation[J]. Energy and Buildings, 2008, 40(11): 2052-2058.
[9] 马庆. 办公建筑空调系统用能优化研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学控制科学与工程学院, 2012: 24-36.
MA Qing. Research on using energy optimization of air conditioning system in office buildings[D]. Jinan: Shandong University. School of Control Science and Engineering, 2012: 24-36.
[10] 何天祺. 供暖通风与空气调节[M]. 重庆: 重庆大学出版社, 2008: 14-15.
HE Tianqi. Heating ventilation and air conditioning[M]. Chongqing: Chongqing University Press, 2008: 14-15.
[11] 刘念雄, 秦佑国. 建筑热环境[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2005: 146-147.
LIU Nianxiong, QIN Youguo. Building thermal environment [M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2005: 146-147.
[12] 谢冬明. 湖南北部地区村镇住宅热环境及节能技术研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学土木工程学院, 2008: 47-49.
XIE Dongming. The research of thermal environment and energy efficiency technology in rural buildings in northern Hunan[D]. Changsha: Hunan University. School of Civil Engineering, 2008: 47-49.
[13] 王海英, 胡松涛. 对PMV热舒适模型适用性的分析[J]. 建筑科学, 2009, 25(6): 108-114.
WANG Haiying, HU Songtao. Analysis on the applicability of PMV thermal comfort model[J]. Building Science, 2009, 25(6): 108-114.
[14] Fanger P O. Thermal comfort[M]. Copenhagen: Danish Technical Press, 1970: 110-114.
[15] Romana D A F, BorisIgor P, Giuseppe R. The role of measurement accuracy on the thermal environment assessment by means of PMV index[J]. Building and Environment, 2011, 46(7): 1361-1369.
[16] DUAN Chenxu, DING Xudong, SHI Fenggang, et al. PMV- based fuzzy algorithms for controlling indoor temperature[C]// 2011 6th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications. Piscataway: IEEE, 2011: 1492-1496.
[17] GB 50736—2012, 民用建筑供暖通风与空气调节设计规范[S].
GB 50736—2012, Design code for heating ventilation and air conditioning of civil buildings[S].
[18] Vishal G, Akshey J, Jyotirmay M, et al. Development and analysis of a tool for speed up of EnergyPlus through parallelization[J]. Journal of Building Performance Simulation, 2013, 6(1): 1-13.
(编辑 杨幼平)
收稿日期:2015-01-07;修回日期:2015-03-31
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(71271215,71221061);国家国际科技合作计划项目(2011DFA10440);国家创新群体科学基金资助项目(71221061) (Projects(71271215, 71221061) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2011DFA10440) supported by the International Science & Technology Cooperation Program of China)
通信作者:彭辉,教授,博士生导师,从事复杂系统建模控制与优化、先进控制理论与智能自动化系统、工业过程控制系统开发研究;E-mail: huipeng@csu.edu.cn