氧化热对铝合金硬质氧化膜的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2012年第11期
论文作者:魏晓伟 陈朝英
文章页码:2707 - 2712
关键词:铝合金;2024铝合金;氧化热;硫酸电解液;硬质阳极氧化;氧化膜
Key words:aluminum alloy; 2024 aluminum alloy; oxidation heat; sulfuric acid electrolyte; hard anodic oxidation; anodic film
摘 要:采用自制的实验装置和硫酸电解液研究阳极氧化热对铝合金2024硬质氧化膜的影响。与氧化热由氧化膜传递到电解液中相比,氧化热由铝基体传递到冷却液中有利于氧化膜的生长,成膜速度、膜厚、致密度和硬度显著提高,并随着冷却液过冷度的增大而增大。氧化膜生长所需的冷却液过冷度与电解液过冷度、铝基体壁厚、氧化膜厚度、气泡覆盖特性参数以及电流密度有关。可通过控制冷却液温度来控制氧化膜的微观结构和性能。
Abstract: The special experimental device and sulfuric acid electrolyte were adopted to study the influence of anodic oxidation heat on hard anodic film for 2024 aluminum alloy. Compared with the oxidation heat transferred to the electrolyte through anodic film, the heat transferred to the coolant through aluminum substrate is more beneficial to the growth of anodic film. The film forming speed, film thickness, density and hardness are significantly increased as the degree of undercooling of the coolant increases. The degree of undercooling of the coolant, which is necessary for the growth of anodic film, is related to the degree of undercooling of the electrolyte, thickness of aluminum substrate, thickness of anodic film, natural parameters of bubble covering and current density. The microstructure and performance of the oxidation film could be controlled by the temperature of the coolant.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) 2707-2712
WEI Xiao-wei, CHEN Chao-yin
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Xihua University, Chengdu 610039, China
Received 6 September 2011; accepted 6 April 2012
Abstract: The special experimental device and sulfuric acid electrolyte were adopted to study the influence of anodic oxidation heat on hard anodic film for 2024 aluminum alloy. Compared with the oxidation heat transferred to the electrolyte through anodic film, the heat transferred to the coolant through aluminum substrate is more beneficial to the growth of anodic film. The film forming speed, film thickness, density and hardness are significantly increased as the degree of undercooling of the coolant increases. The degree of undercooling of the coolant, which is necessary for the growth of anodic film, is related to the degree of undercooling of the electrolyte, thickness of aluminum substrate, thickness of anodic film, natural parameters of bubble covering and current density. The microstructure and performance of the oxidation film could be controlled by the temperature of the coolant.
Key words: aluminum alloy; 2024 aluminum alloy; oxidation heat; sulfuric acid electrolyte; hard anodic oxidation; anodic film
1 Introduction
Conducting hard anodizing on the surface of aluminum parts will improve their ability of wear and corrosion resistance. Porosity of anodic film could also contribute to the preparation of functional film and template composite nanometer materials [1-5]. In general, the surface of aluminum parts only undertake partial anodic oxidation, such as aluminum piston head in the engine, the plate surface of sloping cam plate of scroll compressor, tooth surface of gear pump and internal surface of aluminum cylinder body. Traditional hard anodic oxidation uses the parts in the low temperature electrolyte as the positive pole, and after conducting the current, the anodic film of Al2O3 is obtained. If there is any surface which does not need oxidation, it will be sealed. The performance of anodic film depends on the microstructure of anodic film, which is usually composed of barrier layer and porosity layer. Film forming is a complex process involving physics, chemistry, electrochemistry, etc., and it is influenced by the type of electrolyte, voltage or current of anodic oxidation and reaction temperature. Therefore, there is no unified explanation to the mechanism of forming anodic film. Some typical explanations at present are critical current density model, internal swelling stress model and dissolution model supported by an electric field [6-8]. To obtain a high-quality anodic film and improve the production efficiency, many researchers studied the influence of electrolyte type, additive, current density and voltage waveform (e.g. DC superimposed pulse and positive and negative pulse) on anodic film [9-11], but the improvement of the performance of anodic film was limited and harmful to the environment protection and energy saving. These researches did not consider the oxidation heat (oxidation reaction heat and Joule heat when conducting current to anodic film) during the anodic oxidation of aluminum alloy, while oxidation heat is a major reason affecting the growth, structure and performance of anodic film. This indicates that both chemical dissolution and electric field dissolution are closely related to the heat or temperature of anodic film. If the heat in the anodic film is not eliminated in time, inevitably, the amount of corrosion of anodic film will be increased, anodic film forming efficiency will be lowered, thickness will decrease, porosity diameter will be enlarged, density will decrease, and even the product will be ablated and scrapped. At the same time, the Al3+ content in the electrolyte will be increased too fast, and the electrolyte will lose effect too early. In this work, special experimental device was used to transfer the heat generated in the anodic oxidation to the coolant through aluminum substrate effectively instead of to the electrolyte through anodic film, so as to understand the influence of oxidation heat on the growth, microstructure and performance of anodic film, and analysis results in terms of theory.
2 Experimental
2.1 Material and device
The commercial aluminium alloy 2024 used as test specimens was cut from the rolled sheet material, and the specimens with dimensions 120 mm×120 mm×1 mm were used to grow hard anodic layers. The special experimental device enabled one side of the specimen to contact the electrolyte for hard anodic oxidation while the other side contacted the coolant (40% C2H6O2 water solution) to get cooling off, which formed single-side hard oxidation. When both sides of the specimen were oxidized, the two sides of the specimen contacted the electrolyte, so the level of electrolyte was higher than the septum and the electrolyte was electrified. Figure 1 shows the structure of oxidation tank (PP) in the experimental device. The tank is composed of power supply for hard oxidation, cooling device and computer signal gathering and displaying device. The separator, anticorrosion composite cooler (connecting to the external refrigeration unit with automatic temperature control), negative plate, positive pole, mixing system, temperature sensor were set on the oxidation tank. The separator could separate the coolant from the electrolyte. The sample was clamped on the separator and sealed by O-type rubber seal ring. Both the contact areas between the specimen and the electrolyte and the coolant were 1 dm2. The part did not need oxidation which was filled and sealed by silicone rubber. The controllable temperature range of the coolant and the electrolyte was -8-10 °C (accuracy ±0.2 °C). Hard anodizing power supply provided constant direct current of 50 A (accuracy ±0.05 A) and voltage of 100 V.
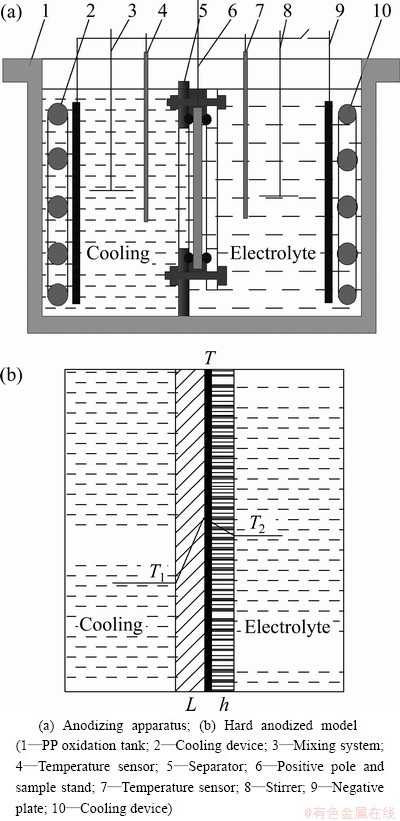
Fig. 1 Sketch map of hard anodic oxidation experimental device
2.2 Process
The specimen was eroded by alkali in NaOH solution and lighted in 40% HNO3 solution, and then cleaned in clear water. After drying, it was clamped on the separator. 98% H2SO4 and distilled water were used to make up H2SO4 electrolyte. The temperatures of electrolyte and coolant are given in Table 1. During two-side oxidation, the electrolyte not only electrochemically reacted with the surface of sample but also cooled it. The temperature of the coolant during single-side hard anodic oxidation was controlled at -2 °C and -5 °C, which enabled the oxidation heat to be transferred to the coolant through aluminum substrate. Both the oxidations used constant current with the density of 3 A/dm2, and the oxidation time was 60 min. The signals of dynamic current, voltage, temperature and time during the hard anodic oxidation were gathered by gathering system and transferred to the computer system to display the data and curve graph. The data were saved automatically.
Table 1 Temperature of electrolyte and coolant

The thickness and the micro hardness of anodic film were tested with an eddy current thickness meter TT230 and an HXD-1000, respectively. The surface morphology of anodic film was observed by scanning electronic microscope SEM (JSM-6700F). The density of anodic film was measured according to the relevant testing methods of ASTM B 680-80. The oxidized sample was dipped into corrosive solution (35 mL/L, containing 85% H3PO4 and 20 g/L CrO3, and the temperature of 38 °C) to dissolve anodic film. The masses before (m1) and after (m2) the dissolution of the oxidized sample, were weighed by using electronic balance with the accuracy of 0.1mg, and the density ρ(g/cm3) of anodic film is
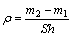

where S is the surface area of anodic film on the sample and h is the thickness of anodic film.
3 Results and analysis
3.1 Influence of temperature of coolant on thickness of anodic film
Figure 2 shows that, after 10 min oxidation, the thickness of anodic film increases approximately linearly with increasing the time till the end of the oxidation. It can be clearly seen that the thickness of anodic film during two-side oxidation increases as the temperature of electrolyte decreases. Like the common hard anodic oxidation, the thicknesses of films were low, which were 26 μm (0 °C) and 43 μm (-5 °C) respectively. During single-side oxidation in the electrolyte at 0 °C, the thicknesses of films were more and increased as the temperature of coolant decreased (-2 °C - -5 °C), which were 62 μm and 73 μm, respectively. Compared with two-side oxidation (the temperature of electrolyte was -5 °C), the thicknesses of single-side anodic films were increased by 45% and 70%. This indicates that the forming speed of anodic film during single-side oxidation is faster, while at the same cooling temperature, the forming speed is approximately two times that during two-side oxidation, as indicated in Fig. 2.
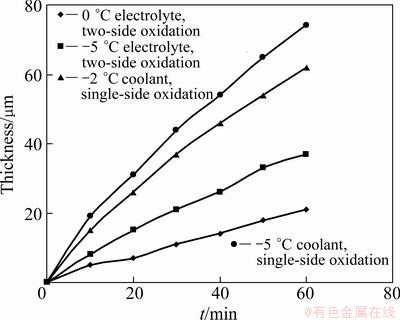
Fig. 2 Relationship among thickness and temperature of anodic film and time
3.2 Influence of coolant temperature to hardness of anodic film
Table 2 indicates the hardness and density of anodic film with different oxidation methods. During the two-side oxidation, though the hardness and density of the film were increased with the decrease of electrolyte temperature (0 °C - -5 °C), the hardness and density were low. The hardnesses were HV0.1 201 and HV0.1 284, respectively, and the densities were 2.21 g/cm3 and 2.42 g/cm3, respectively. But, the hardness and density of anodic film were higher during the single-side oxidation. Under the condition of high electrolyte temperature (0 °C), when the temperatures of coolant were -2 °C and -5°C, the hardnesses of anodic films were HV0.1454 and HV0.1516, and the densities were 2.87 g/cm3 and 3.13 g/cm3, respectively. Compared with the two-side oxidation at the electrolyte temperature of -5 °C, the hardnesses were raised by 60% and 82%, respectively, and the densities were raised by 19% and 30%, respectively. This indicates that, though the temperature of electrolyte is higher (0 °C), the corrosion amount of anodic film by the electrolyte is still lower and decreases as the coolant temperature is decreased, which is beneficial to the growth of anodic film.
Table 2 Oxidation method, hardness (HV0.1) and density of anodic film

During the anodic oxidation of aluminum alloy, the anodic film grows while oxidation heat is produced, which will lead to the dissolution of anodic film by the electrolyte. The growth of anodic film is going on in the competition of growing speed and dissolution speed of anodic film. Anodic Al2O3 film is formed by transmission of Al3+ and O2- in the opposite direction through the interface of metal/anodic film/electrolyte, and oxidation heat is generated. Once the anodic film is formed, the transmission of electric charge will be barred [9,10]. The research indicates that the forming anodic film will be the barrier layer [12,13]. As the oxidation goes on, the barrier layer surface is eroded by electrolyte and becomes porous layer in the electric field. When the electrolyte is penetrated in the film pores, Al3+ and O2- ions are transferred between the surfaces of aluminum and the electrolyte through barrier layer. Anodic film gets thicker, and the oxidation heat is generated continually. Theoretically, generating 1 mol aluminum anodic film will release 1424 J/mol of heat, and the equation is
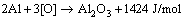
As illustrated in Fig. 1, it is assumed that the initial thickness of anodic film is h, the thickness of aluminum substrate is L, and that unit areas of both anodic oxidation surface and cooling surface are 1. Therefore, combining the condition of linear growth of anodic film in Fig. 2, the transmission of heat in oxidation could be expressed as one-dimension stable heat transfer model [14]. According to the above conditions, the equations of stable heat transfer for transmission of oxidation heat to the coolant and the electrolyte are
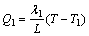 (1)
(1)
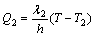 (2)
(2)
where T, T1 and T2 are the interface temperatures of aluminum substrate and oxidation film, the coolant and aluminum substrate, the electrolyte and oxidation film. T-T1=ΔT1 is the degree of undercooling of the coolant; T-T2=ΔT2 is the degree of undercooling of the electrolyte. In the condition of stirring, assuming that the temperature of aluminum substrate surface is same with that of the coolant T1 and the thermal conductivities of aluminum and porous anodic film are λ1=237 W/(m·K) and λ2≤6.7 W/(m·K) [14,15] respectively, the thickness change of aluminum substrate is negligible compared with the thickness of anodic film.
During the oxidation, a large number of bubbles are generated continuously on the surface of anodic film (resulting from oxidation heat and molecule forming of oxygen atoms), which can be regarded as air layer covering the anodic film and increase as the current density (J) increases. As the heat conductivity of gas (0.023 W/(m·K) is much lower than that of anodic film [14], the generation of air layer will further prevent the transmission of heat to the electrolyte. Assuming the bubble covering rate is θ(0≤θ≤1), the equation is
θ=γJ(0<γ<1) (3)
where γ is defined as the natural parameter of covering, which is related to the conditions of the anodic film surface, the electrolyte, the temperature, and fluid flow characteristics and can be obtained from the experiment. To transfer the heat to the coolant, the equation Q1≥Q2 will be satisfied. Equation (4) is given from Eqs. (1)-(3):
 (4)
(4)
In equation (4), K=L/h shows that oxidation heat transferred to the coolant is related to ΔT1, ΔT2, current density J, and the ratio K of current density J to thickness of anodic film h. When ΔT1, J and L are unchanged, the degree of undercooling of the coolant needed by the growth of anodic film ΔT2 is a function of the film thickness. It is thus clear that the value of K decreases as the thickness of anodic film increases during single-sided oxidation, which is beneficial for the transmission of more oxidation reaction heat to the coolant, and the dissolution of the electrolyte to anodic film is decreased and the thickness, density and hardness of anodic film are increased, as shown in Fig. 2 and Table 2. Though the temperature of the electrolyte is 0 °C, the thickness, density and hardness of anodic film are still higher than those obtained in two-side oxidation in the electrolyte at -5 °C. On the contrary, as for the two-side oxidation, oxidation heat can only transfer to the electrolyte through anodic film (see Eq. (2)), which leads to lower film forming speed and smaller thickness, density and hardness of anodic film. If oxidation film gets thick, the transmission of oxidation heat will be more difficult, and the amount of erosion of oxide film in the electrolyte should be increased. It is thus easy to explain why sharp corners and thin wall of aluminum alloy parts are difficult to obtain thick film and easily ablate in conventional oxidation process, particularly for the aluminum alloy containing a high content of copper [16]. Even a lower electrolyte temperature is more prone to erosion phenomena. Figure 3 shows the SEM images of anodic film during two-side and single-side oxidation, respectively. Figure 4 shows the cross-section micrograph of Fig. 3(a) and Fig. 3(c), respectively. It is clearly seen that the porosity diameter in single-side oxidation is smaller. And as the coolant temperature lowers, the density of anodic film increases, as shown in Fig. 3(b), Fig. 3(c) and Fig. 4(b), respectively.
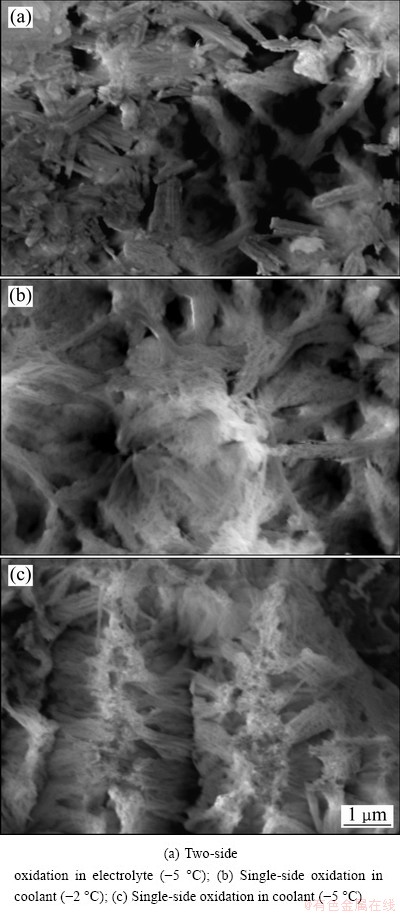
Fig. 3 Surface micrographs of anodic oxide film
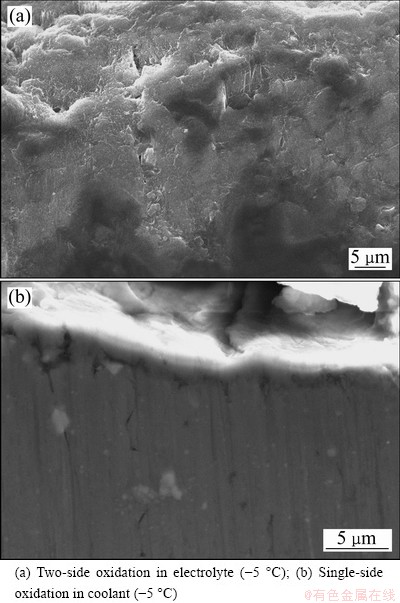
Fig. 4 Cross-section micrographs of anodic oxide film
4 Conclusions
1) Single-side hard anodizing is more helpful to the growth of anodic film than two-side hard anodizing. The degree of undercooling for the coolant satisfies the equation of 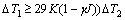 , which is related to the ratio K of thickness of aluminum substrate to thickness of anodic film, natural parameters of bubble covering γ and temperature of electrolyte and current density J. When the current density, the electrolyte and the temperature are constant, the microstructure and performance of the oxidation can be controlled.
, which is related to the ratio K of thickness of aluminum substrate to thickness of anodic film, natural parameters of bubble covering γ and temperature of electrolyte and current density J. When the current density, the electrolyte and the temperature are constant, the microstructure and performance of the oxidation can be controlled.
2) During the single-side oxidation, the transmission of oxidation heat to the coolant benefits the growth of anodic film with a higher film forming speed. And the film forming speed increases with the decrease of coolant temperature or the increase of undercooling degree. The thickness of anodic films is generated with small pore, high density and hardness.
References
[1] SANTOS A, VOJKUVKA L,  J, MARSAL L F, KEMMITT M E. In situ electrochemical dissolution of the oxide barrier layer of porous anodic alumina fabricated by hard anodization [J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2009, 632: 139-142.
J, MARSAL L F, KEMMITT M E. In situ electrochemical dissolution of the oxide barrier layer of porous anodic alumina fabricated by hard anodization [J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2009, 632: 139-142.
[2] GHAHREMANINEZHAD A, DOLATI A. A study on electrochemical growth behavior of the Co-Ni alloy nanowires in anodic aluminum oxide template [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 480: 275-278.
[3] HAN Ning, DENG Ping-ye, CHEN Jiang-chao, CHAI Lin-yu, GAO Hong-shuai, CHEN Yun-fa. Electrophoretic deposition of metal oxide films aimed for gas sensors application: The role of anodic aluminum oxide (AAO)/Al composite structure [J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2010, 144: 267-273.
[4] KIM H S, KIM D H, LEE W, CHO S J, HAHN J H, AHN H S. Tribological properties of nanoporous anodic aluminum oxide film [J].Surface and Coatings Technology, 2010, 205(5): 1431-1437.
[5] DIMOGERONTAKIS T T A, GRAEVE I D, FRANSAER J, TERRYN H. Influence of the anodizing temperature on the porosity and the mechanical properties of the porous anodic oxide film [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2007, 201: 7310-7317.
[6] JIANG Xiao-xue, ZHAO Nai-qin. Review of fabrication and formation mechanisms for anodic aluminum oxide [J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2005, 4: 487-494. (in Chinese)
[7] GONG Yun-lan, WANG Wei, WANG Hui, GUO He-tong. The analysis of self-organizing process of anodic alumina films with nano-pore array structure [J]. Acta Phys Chim Sin, 2004, 20(2): l99-201. (in Chinese)
[8] MORKS M F, HAMDY A S, FAHIM N F, SHOEIB M A. Growth and characterization of anodic films on aluminum alloys in 5-sulfosalicylic acid solution [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2006, 200: 5071-5076.
[9] SALERNO M, PATRA N, LOSSO R, CINGOLANI R. Increased growth rate of anodic porous alumina by use of ionic liquid as electrolyte additive [J]. Materials Letters, 2009, 63: 1826-1829.
[10] FRATILA-APACHITEI L E, DUSZCZYK J, KATGERMAN L. A1-Si-(Cu) anodic oxide layers formed in H2SO4 at low temperature using different current waveforms [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2003, 165: 232-240.
[11] BENSALAH W, FEKI M, WERY M, AYEDI H F. Thick and dense anodic oxide layers formed on aluminum in sulphuric acid bath [J]. J Mater Sci Technol, 2010, 26(2): 113-118.
[12] PATERMARAKIS G, KARAYANNIS H S. The mechanism of growth of porous anodic A12O3 films on aluminium at high film thicknesses [J]. Elecrrochimica Acta, 1995, 40(16): 2641-2656.
[13] WEI Xiao-wei, DENG Li-hong. Preparation of PTFE composite anodic film on aluminium alloy 6061 using electrophoretic process [J]. Tribology-Materials, Surfaces & Interfaces, 2010(4): 74-77.
[14] ZHU Guang-jun. Transport phenomena [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2009: 1-305. (in Chinese)
[15] HONGLIANG, PICKENACKER O, TRIMIS D. Effects of porosity on effective heat conductivity of highly porous media of Al2O3 [J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2002(3): 479-485.
[16] MOON S, NAM Y, YANG C, JEONG Y. Growth of anodic oxide films on AC2A alloy in sulphuric acid solution [J]. Corrosion Science, 2011, 53: 1547-1553.
魏晓伟,陈朝英
西华大学 材料科学与工程学院,成都 610039
摘 要:采用自制的实验装置和硫酸电解液研究阳极氧化热对铝合金2024硬质氧化膜的影响。与氧化热由氧化膜传递到电解液中相比,氧化热由铝基体传递到冷却液中有利于氧化膜的生长,成膜速度、膜厚、致密度和硬度显著提高,并随着冷却液过冷度的增大而增大。氧化膜生长所需的冷却液过冷度与电解液过冷度、铝基体壁厚、氧化膜厚度、气泡覆盖特性参数以及电流密度有关。可通过控制冷却液温度来控制氧化膜的微观结构和性能。
关键词:铝合金;2024铝合金;氧化热;硫酸电解液;硬质阳极氧化;氧化膜
(Edited by LI Xiang-qun)
Foundation item: Project (SBZDPY-11-17) supported by the Fund on Key Laboratory Project for Hydrodynamic Force, Ministry of Education, China; Project (SZD0502-09-0) supported by Key Disciplines of Materials Processing Engineering of Sichuan Province, China
Corresponding author: WEI Xiao-wei; Tel: +86-28-87721298; E-mail: weixiaowei90@yeah.net
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61521-5

