二元SnZn合金的电阻随温度变化的特性
余 瑾, 张 燕, 祖方遒, 席 赟, 李先芬, 徐 炜, 丁厚福
(合肥工业大学 材料科学与工程学院, 合肥 230009)
摘 要: 采用直流四电极法研究了常压下Sn-Zn合金系的电阻率随温度连续升温的变化规律。 结果表明: 合金Sn-Zn5、 Sn-Zn8.8、 Sn-Zn20、 Sn-Zn30、 Sn-Zn40、 Sn-Zn50和Sn-Zn70分别在970、 1008、 957、 950、 948、 926和873℃处发生了电阻率的突变现象。 对合金的进一步分析表明, Sn-Zn熔体电阻率在高温时的突变是由Zn在Sn-Zn熔体中大量汽化造成的, 即在此处发生了液-气结构转变; Sn-Zn合金在完全熔化至发生液-气结构转变的连续升温过程中, 合金中并不存在某种液-液结构的转变, 且液-液结构转变并非存在于在所有二元合金系中。
关键词: Sn-Zn合金; 液态结构; 电阻率; 汽化 中图分类号: 61.20.Gy;61.25.Mv;61.46.+w;66.30.Qa
文献标识码: A
Change character of electrical resistivity with temperature of Sn-Zn alloys
YU Jin, ZHANG Yan, ZU Fang-qiu, XI Yun, LI Xian-feng, XU Wei, DING Hou-fu
(College of Materials Science and Engineering,Hefei University of Technology, Hefei 230009, China)
Abstract: The change rule of electrical resistivity with the increase of temperatures of tin-zinc (Sn-Zn) alloys with different compositions were investigated using the direct current four-probe technique at constant pressure. The results show that some transitions occur at the temperatures of 970, 1008, 957, 950, 948, 926 and 873℃. According to the analysis of the resistivity—temperature (ρ—t) curves, the obtained significant abnormal variation of the electrical resistivity at high temperature of Sn-Zn alloys is considered to be caused by the abundant gasification of Zn component in Sn-Zn alloys, namely the liquid-gas structure transition takes place in melts. And no temperature-induced liquid-liquid structure transition exists in Sn-Zn melts.
Key words: Sn-Zn alloys; liquid structure; electrical resistivity; vaporization
在过去的几十年内, 对于合金的液态结构随温度或压强变化而变化的实验和理论研究已取得了很大进展。 一元系液体, 如Cs, Bi, Ga, Si, Se, C, H2O和SiO2[1-8]等, 甚至在一些多元液态系统如Al2O3-Y2O3[9]中, 都被发现存在液-液相转变。 随着对温度诱导或压强诱导的液态结构不连续转变理论不断深入的认识, 人们已经采用了多种方法来探索和研究合金中的液-液结构转变现象。 祖方遒等[10-13]已经用X射线衍射法证明了在In-Sn80中存在温度诱导的结构转变, 又对In-Sn, Pb-Sn和In-Bi等二元合金进行了内耗、 DSC和DTA实验, 同样证明了在这些合金中存在着液-液结构转变。
电阻率作为结构敏感物理量之一, 其测量方法已被广泛应用。 如通过对液态Pb-Sn, In-Sb和Bi-In[14-16]合金电阻率的测量, 观察到在液相线以上几百度的温度范围内, 电阻率发生了异常变化, 以此证明在熔体中发生液-液结构转变。 所有这些发现都表明了某些合金在高温区发生温度诱导的液-液结构转变[17-19]。
Sn-Zn合金是一种典型的二元共晶合金, 然而对其液态结构方面的研究报道极为少见。 本文作者通过直流四电极法对液态Sn-Zn合金的不同成分进行了电阻率的研究, 发现在Sn-Zn熔体中也发生类似的液-液结构转变。 从实验结果同样可以观察到在液相线以上几百度的温度范围内电阻率发生了与其他合金类似的突变现象。 但根据分析, 认为Sn-Zn熔体中的电阻率突变是由于Zn组元在SnZn合金中大量汽化造成的, 且在发生电阻率的突变之前, 熔体的电阻率随温度的增加呈线性增加。 因此, 本文作者认为在Sn-Zn熔体的连续升温过程中, 并没有发生某种液-液结构转变。 说明了液-液结构转变并非普遍存在于每种二元合金中, 这为从另一个角度去探索和认识液-液结构转变奠定了基础。 本文作者还通过实验结果在相图中绘出了Zn在Sn-Zn合金中的汽化线, 证明了用电阻率法来确定液态金属的汽化线是可行的。
1 实验
电阻测量采用直流四电极法将电流电极与电压电极分开, 使电流测量和电压测量分别构成回路。 这样能使引线电阻、 电极电阻及接触电阻的影响降低到最小程度, 即使在测量电阻很小的情况下也能具有很高的准确度。 测量时直流电流恒定为500mA, 由PF66M恒流源提供; 电压由KEITHLEY-2182纳伏表测量; 实验数据由计算机数据采集系统获得。 在实验过程中, 用于测量电阻的样杯材料为耐高温且具有低膨胀系数的石英玻璃; 电极材料采用直径为1mm的钨丝, 这样既保证良好的导电性, 也避免合金与电极发生反应。 整个实验在纯氩气气氛保护下进行, 以防止合金在测量过程中的氧化。 进行电流换向测量正反两个方向的电压降, 并换算成平均电压降, 这样就可消除测量系统误差和热电势的影响[20, 21]。 电阻测量原理遵循欧姆定律: R=U/I=ρL/S。
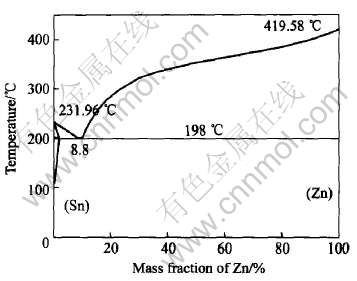
图1 Sn-Zn相图
Fig.1 Sn-Zn phase diagram
根据Sn-Zn相图(图1)研究了Sn-Zn5、 Sn-Zn8.8、 Sn-Zn20、 Sn-Zn30、 Sn-Zn40、 Sn-Zn50和Sn-Zn70的电阻率。 另外, 为了便于与Sn-Zn合金进行比较, 又研究了纯Zn和纯Sn的电阻率随温度的变化关系。 所有SnZn试样是由高纯Zn(99.99%)和高纯Sn(99.99%)制备而成。 将配制好的试样置于坩埚内, 为防止合金在熔化过程中被氧化, 在试样上浇入熔化的B2O3, 然后将其加热至500℃, 并在此温度保温30min。 在保温过程中, 适当振动坩埚以保证Zn、 Sn成分混合均匀, 然后将合金浇注到特制的电阻率测量样杯里, 冷却至室温, 以备进行电阻测量。 每一个试样都是以5℃/min的速率进行升温和降温实验。
2 结果与分析
图2和3所示为纯金属Sn和Zn的电阻率随温度的变化规律。 从图2和3中可以看出, 纯Sn、 Zn的固态电阻率都随温度呈线性增加, 其电阻率温度系数dρ/dt分别为0.0452和0.02495。 当试样熔化时, 其电阻率分别从18.7μΩ·cm和15.15μΩ·cm突然增加到42.3μΩ·cm和32.89μΩ·cm。 这是由于电子在无序液体中移动时, 电子平均自由程更短, 因此离子排列相对无序的液态金属比
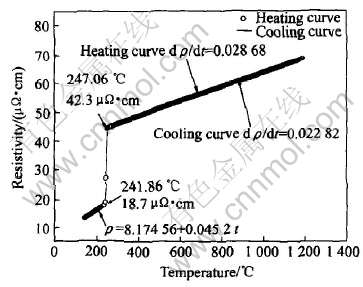
图2 纯Sn的电阻率随温度变化曲线
Fig.2 Change curve of resistivity with temperature for pure tin
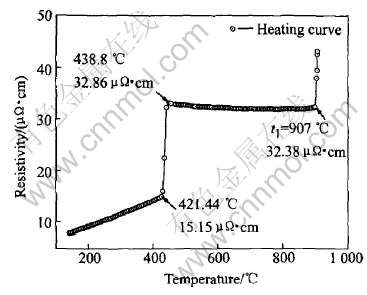
图3 纯Zn的电阻率随温度变化曲线
Fig.3 Change curve of resistivity with temperature of pure zinc
相应的带有更加有序原子排列的固态金属具有更高的电阻率[22, 23]。 随着温度的继续升高, 熔体Sn的电阻率在所测的温度范围内呈线性增加的, 其电阻率-温度方程为ρ=37.42846+0.022868t。 然而, 当熔体Zn完全熔化后, 其电阻率随温度的增加逐渐减小, 即液态Zn具有负的电阻率温度系数, 这与文献[24, 25]所报道的结果一致(图3)。 当温度到达907℃时, 电阻率出现突然增加, Zn完全汽化了。
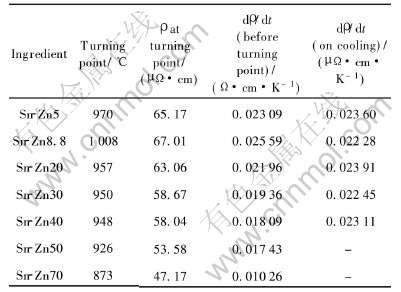
图4所示为合金Sn-Zn5, Sn-Zn8.8, Sn-Zn20, Sn-Zn30, Sn-Zn40, Sn-Zn50和Sn-Zn70的电阻率随温度的变化曲线。 由图4可看出, 7种Sn-Zn合金电阻率的变化规律明显与纯金属的不同。 在合金熔化温度范围内, 对于过共晶成分Sn-Zn20, Sn-Zn30, Sn-Zn40, Sn-Zn50和Sn-Zn70合金而言, 由于合金中先析共晶体的存在, 电阻率先是突然增加一定值, 然后以稍微平缓的速度随温度的上升而增加; 随着Zn含量在合金中的增大, 合金中的先析共晶体含量逐渐减少, 因此电阻率突然上升的幅度变小, 而随温度的平缓增加, 电阻率的增加幅度变大。 对亚共晶成分Sn-Zn5合金而言, 由于合金中的先析共晶体含量极少, 因此在熔化温度范围内, 电阻率温度曲线上几乎观察不到类似的现象。 随着温度的不断升高, 这7种合金的电阻率都在液相线以上几百度的温度范围内发生了突变, 但在电阻率突变之前, 电阻率都随温度线性增加而增加; 而在突变之后, 电阻率随温度的变化呈递增趋势。 并可以在电阻率-温度曲线上清楚地观察到每个成分电阻率突变的温度点, 如Sn-Zn5在970℃, Sn-Zn8.8在1008℃, Sn-Zn20在957℃, Sn-Zn30在950℃, Sn-Zn40在948℃, Sn-Zn50在926℃, Sn-Zn70在873℃。 表1列举了7种合金在升温过程中电阻率温度的特征值。
表1 SnZn合金电阻率温度曲线特征值的比较
Table 1 Comparison of ρ—t curves of Sn-Zn melts
从上述实验结果描述可知, Sn-Zn熔体也发生了类似于在Bi-In、 Pb-Sn、 Pb-Bi等合金中发现的在高温区的电阻率突变现象。 而对于Bi-In、 Pb-Sn、 Pb-Bi合金, 已经证明了是由于高温下发生的液-液结构转变而导致的。
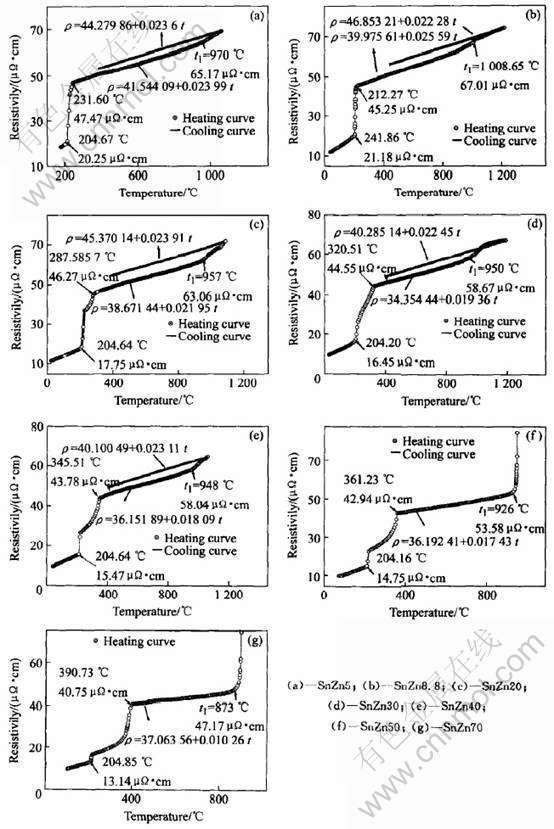
图4 SnZn合金的电阻率随温度变化曲线
Fig.4 Change curves of resistivity with temperature of Sn-Zn alloys
由图4(f)和(g)中可以看出, Sn-Zn50和Sn-Zn70合金分别在926℃和873℃发生电阻率的突变后, 电阻率在几十度的温度范围内迅速的增加, 直至趋于无穷。 这两种成分的电阻率突变现象与纯Zn的电阻率在沸点907℃处的突变现象十分相似, 且在实验完成后, 石英样杯内的试样明显减少, 又由于Zn的沸点是907℃, 因此, 可以认为这两种成分的电阻率突变的原因是由于当温度升高到某种程度时, Zn原子摆脱了原子间的相互束缚, 在Sn-Zn合金中发生了大量汽化。
图5比较了Sn-Zn30和纯Sn在完成升温实验后的降温过程中的电阻率随温度的变化。 可以发现, 它们的电阻率温度系数是相当接近的。 电阻率是结构敏感物理量之一, 其电阻率温度系数是每种合金所特有的, 因此可以认为, Sn-Zn30在降温过程中, 其成分已经接近纯Sn。 由于Zn的沸点为907℃, 本文作者推断Sn-Zn30的电阻率突变原因与Sn-Zn50和Sn-Zn70的一致, 都是Zn组元高温下在合金中的大量汽化所致。 此外, 实验完成后, 样杯中试样质量的减少进一步证明了以上的推断。 根据表1所列的其他成分降温时的电阻率温度系数, 发现其与纯Sn的相比较, 都比较接近, 且都出现了在完成实验后试样质量明显减少的现象, 这证明了其他成分在升温过程中都发生了Zn的大量汽化。 测量样杯时的误差, 造成实验结果图上的电阻率的绝对值存在微小偏差[26]。
综上所述, 将这7种Sn-Zn合金的电阻率在高温区发生的异常变化的原因理解为: 当熔体的温度达到足够高时, Zn原子摆脱了原子间的相互束缚, 且由于Zn较低的沸点(907℃), 因而导致Zn组元在Sn-Zn合金中的大量汽化, 也即熔体在某个温度发生了液-气结构转变。 然而在熔体在完全熔化后至发生液-气结构转变的温度范围内, 其电阻率随温度是连续变化的, 因而认为在这段温度区间内, 并没有发现有某种液-液结构转变的发生。 这个实验结果与早期采用内耗法研究Sn-Zn合金同样没有发现有液-液结构转变的现象是一致的[27]。 对于Sn-Zn合金的电阻率随温度变化特性的研究, 说明了液-液结构转变并非普遍存在于每种二元合金中, 可以说Sn-Zn合金符合传统观念所认为的合金在液相线至气相线之间的温度范围内, 结构是连续变化的。
由表1可知, Zn在不同成分中的汽化温度是不同的, 在共晶成分Sn-Zn8.8合金中, 汽化温度最高, 这与不同成分的固态结构有着密切关系。 从侧面说明了共晶成分Sn-Zn熔体中的原子间的作用力或是作用方式最为特殊。 图6所示为根据Zn在各个成分中的不同汽化温度, 在Sn-Zn相图上绘出了Zn在合金中汽化温度曲线。
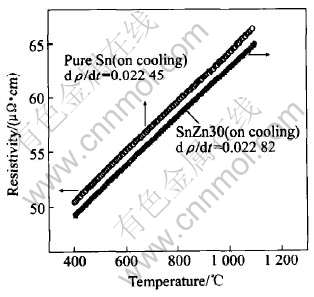
图5 Sn和Sn-Zn30合金降温电阻率随温度的变化曲线
Fig.5 Change curves of resistivity with temperature of Sn and SnZn30 alloys during cooling
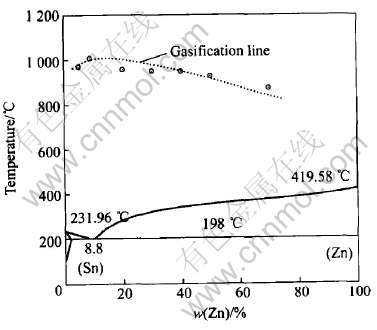
图6 不同成分Zn的汽化温度变化曲线
Fig.6 Change curves of vaporizing temperature of Zn with different contents
3 结论
1) 利用电阻率法对Sn-Zn合金的电阻率随温度变化规律进行了研究, 和纯Sn、 纯Zn的电阻率比较发现, Sn-Zn合金电阻率随温度的连续升高出现了突变。
2) 7种不同成分Sn-Zn5, Sn-Zn8.8, Sn-Zn20, Sn-Zn30, Sn-Zn40, Sn-Zn50和Sn-Zn70合金的电阻率的突变现象是由于高温下Zn组元在Sn-Zn合金中的大量汽化, 即发生了液-气结构转变所致。 且Sn-Zn熔体的连续升温过程中没有发生某种液-液结构转变。
3) Zn组元在Sn-Zn合金中气化温度随成分的变化而改变, Zn组元在共晶成分Sn-Zn8.8合金中的汽化温度最高, 随Zn含量的增加或减少, Zn组元的汽化温度逐渐降低。 也说明了共晶成分的Sn-Zn熔体中的原子间相互作用力要强于比其他成分中的。
4) 在相图中绘出了Zn在Sn-Zn合金中的汽化线, 证明采用电阻率法来确定液态金属的汽化线也是行之有效的。
REFERENCES
[1]Grimsditch M, Rahman A, Polian A. Elastic moduli of H//2O: liquid, ice Ⅵ and ice Ⅶ[J]. Materials Research Society Symposia Proceedings, 1984, 22: 143-146.
[2]Winter R, Hua D W, Song X, et al. Structural and dynamical properties of the sol-gen transition[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1990, 94(6): 2706-2719.
[3]Harrington S, Zhang R, Poole P H, et al. Liquid-liquid phase transition: evidence from simulations[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1997, 78: 2409
[4]Brazhkin V V, Popova S V, Voloshin R N. High-pressure transformation in simple melts[J]. High Pressure Research, 1997,15(5): 267-305
[5]Katayama Y, Mizutani T, Utsumi W, et al. A first-order liquid-liquid phase transition in phosphorus[J]. Nature, 2000, 403(6766): 170-173.
[6]Franzese G, Malescio G, Skibinsky A, et al. Meastable liquid-liquid phase transition in a single-component system with only one crystal phase and no density anomaly[J]. Physical Review E, 2002, 66: 051206.
[7]Glosili N J, Ree F H, Viecelli J A. Modeling the kinetics of carbon coagulation in explosives detonation[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Materials Design, 1998, 5: 265-278.
[8]Stanleyl H E. Cooperative molecular motions in water: The liquid-liquid critical point hypothesis[J]. Physica A, 1997, 236(1-2): 19-37.
[9]Aasland S, McMillan P F. Density -driven liquid-liquid phase separation in the system Al2O3-Y2O3[J]. Nature, 1994, 369: 633-636.
[10]Zu F Q, Zhu Z G, Guo L J, et al. Observation of anomalous discontinuous liquid-structure change with temperature[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2002, 89: 125505.
[11]Zu F Q, Guo L J, Zhu Z G, et al. Relative energy dissipation: sensitive to structural changes of liquids[J]. Chin Phys Lett, 2002, 19: 94-97.
[12]Zu F Q, Zhu Z G, Guo L J, et al. Liquid-liquid phase transition in Pb-Sn melts[J]. Phys Rev B, 2001, 64: 1802031-4.
[13]Zu F Q, Zhu Z G, Zhang B, et al. Post-melting anomaly of Pb-Bi alloys observed by internal friction technique[J]. J Phys Condens Matter, 2001, 13: 11435-42.
[14]XI Yun, ZU Fang-qiu, LI Xian-fen, et al. High-temperature abnormal behavior of resistivities for Bi-In melts[J]. Phys Lett A, 2004, 329(3):221-225.
[15]Li X F, Zu F Q, Ding H F, et al. Unusual change of electrical resistivity with temperature in liquid Pb-Sn alloys[J], Physica B, 2005, 358 :126-131.
[16]LU Kun-quan, WANG Qiang, LI Chen-xi, et al. The structures, electronic states and properties in liquid Ga-Sb and In-Sb systems[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2002, 312-314: 34-40.
[17]王翠萍, 刘兴军, 马云庆, 等. Cu-Ni-Sn三元系相平衡的热力学计算[J]. 中国有色金属学报,2005, 15(11): 1848-1853.
WANG Cui-ping, LIU Xing-jun, MA Yun-qing, et al. Thermo dynamic calculation of phase equilibria in Cu-Ni-Sn ternary system[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 15(11): 1848-1853.
[18]李友芬,孙根生, 武世民, 等. La2O3基导电陶瓷高温电阻率的测试和研究[J]. 中国有色金属学报,1997, 7(1):159-161.
[CM(22*2]LI You-fen, SUN Gen-sheng, WU Shi-min, et al.[CM)]Measurement and study of resistivity of conductive ceramics based on La2O3 at high temperature[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 1997, 7(1): 159-161.
[19]姜国圣, 王志法, 张迎九, 等. DG合金电阻性能的影响因素[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 1998, 8(5): 395-398.
JIANG Guo-sheng, WANG Zhi-fa, ZHANG Ying-jiu, et al. Factors affecting DG alloys electrical resistivity[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 1998, 8(3): 395-398.
[20]Zhang J X, Fung P C W, Zeng W G. Dissipation function of the first-order phase transformation in solids via internal-friction measurements[J]. Physical Review B,1995, 52(1): 268-270.
[21]余瑾, 祖方遒, 丁厚福, 等. 连续变温金属固-液电阻率测试装置及应用[J]. 稀有金属, 2004, 28(5): 880-884.
YU Jin, ZU Fang-qiu, DING Hou-fu, et al. Design and application of instrument of electrical resistivity testing for solid-liquid metal during temperature continuous change[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2004,28(5): 880-884.
[22]Zhu Z G, Zu F Q, Guo L J, et al. Internal friction method: suitable also for structural changes of liquids[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2004, A370: 427-430.
[23]Faber T E. An Introduction to the Theory of Liquid Metals[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1972.
[24]Ziman J M. A Theory of the Electrical Properties of Liquid Metals[M]. London: Oxford University Press ,1961.
[25]Shimoji M. Liquid Metals[M]. Beijing: Academic Press,1977.
[26]Zu F Q, Chen Z H, Tao J J, et al. Corrosion resistance of Zr-Al-Ni-Cu(Nb) bulk amorphous alloys[J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2004, 14(5): 961-965.
[27]祖方遒. 液态合金结构变化的研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学院固体物理研究所, 2002.
ZU Fang-qiu. Study on Structural Transitions of Liquid Alloys[D]. Heifei: Institute of Solid State Physics Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2002.
(编辑李艳红)
基金项目: 国家自然科学基金资助项目(50371024); 国家教育部重点资助项目(104106)
收稿日期: 2005-11-11; 修订日期: 2006-04-03
通讯作者: 祖方遒; 电话: 0551-2905057; E-mail: fangqiuzu@hotmail.com