化学涂层对玻璃表面与微颗粒耦合规律的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2012年第11期
论文作者:李 明 吴 超 刘一静 闫 晖
文章页码:2799 - 2805
关键词:微颗粒;粘附;玻璃表面;试剂涂层;粒径分布
Key words:micro-particles; adhesion; glass surface; reagent film; size distribution
摘 要:通过玻璃表面的试剂涂层与空气中微颗粒的耦合性实验发现,试剂涂层能明显改变表面与微颗粒的耦合能力,微颗粒平均粒径与采样的时间间隔、放置夹角和试剂浓度没有明显规律性联系,复合试剂耦合微颗粒的粒径比单一试剂的粒径小(2~3 μm),其中吐温60粘附微颗粒的粒径最大(4~5 μm),0.5%SDBS与0.5%氟碳复合试剂涂层表面粘附微颗粒数量的能力最强。每种试剂对微颗粒的粘附强度存在一个最佳范围。研究发现,复合试剂能获得单一试剂不具备的特殊物理化学性质,能有效改变固体表面与微颗粒的耦合性质。
Abstract: The experiments were conducted to investigate the behavior of airborne particles adhering to the glass slides which were coated by several reagent films. The results showed that the adhesion level could be significantly changed by the reagent films. There were no evident rules between the average size of particles and sampling time interval, the placing angle and reagent concentration. The average particle size on the surface coated by composite reagent (2-3 μm) was smaller than that on the single reagent coated surface, while the largest particle size (4-5 μm) was observed on the surface coated with the Tween 60. The experiment also demonstrated that the best adhesive performance was obtained on the surface which was coated with 0.5% SDBS and 0.5% fluorocarbon composite reagents. The experiment results indicated that each reagent had a certain optimum adhesive range to the particle. The composite reagents with different proportion of single reagents exhibited some particular physical and chemical properties, which could effectively change the adhesive performance between the solid surface and the particles.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) 2799-2805
LI Ming, WU Chao, LIU Yi-jing, YAN Hui
School of Resources and Safety Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 20 May 2012; accepted 30 October 2012
Abstract: The experiments were conducted to investigate the behavior of airborne particles adhering to the glass slides which were coated by several reagent films. The results showed that the adhesion level could be significantly changed by the reagent films. There were no evident rules between the average size of particles and sampling time interval, the placing angle and reagent concentration. The average particle size on the surface coated by composite reagent (2-3 μm) was smaller than that on the single reagent coated surface, while the largest particle size (4-5 μm) was observed on the surface coated with the Tween 60. The experiment also demonstrated that the best adhesive performance was obtained on the surface which was coated with 0.5% SDBS and 0.5% fluorocarbon composite reagents. The experiment results indicated that each reagent had a certain optimum adhesive range to the particle. The composite reagents with different proportion of single reagents exhibited some particular physical and chemical properties, which could effectively change the adhesive performance between the solid surface and the particles.
Key words: micro-particles; adhesion; glass surface; reagent film; size distribution
1 Introduction
It is well known that a large number of micro-particles in the atmosphere would deposit and attach on the solid surfaces in their surroundings, harming our environment, industrial production as well as human health. Up until now, a few experiments on particle deposition and characteristics have been conducted [1,2]. Some studies focused on the particle accumulating and depositing characteristics under different ventilating conditions [3]. Some research concentrated on sediment and adhesion behavior of dust particle on glass surface under various conditions [4], and some focused on effects of indoor and outdoor dust on indoor air quality [5]. Another experiment tested the effects of wall texture on particle deposition [6] and another concentrated on characteristics of particle deposition on smooth and rough vertical surfaces [7].
To prevent particles from adhering to surface and effectively removing the existing dust on the surface, some studies have been done on the adhesion force between particles and solid surfaces, the mechanisms and techniques on the removal of dust from the surface [8-11]. Specifically, the capability of dustproof and self-cleaning film surfaces, such as TiO2 which has a photo-catalytic capability [12-14] and super- hydrophobic function [15], was tested. Some researchers also studied the technique to prevent and remove the dust adhering on the surface of equipment for space exploration [16]. The current research mainly focus on decomposing the organic dust by photo-catalytic oxidation, physical cleaning technology and the technique of micro-nano pretreatment of the solid surface. Few research papers have reported the surface chemical modification technology for preventing and removing the dust on the solid surface, so this research is designed to investigate the processes and the effects of several new reagents treated glass surface on the adhesive ability to airborne particle.
2 Adhering mechanism of particle on solid surface
The adhering force is different significantly between various particles and solid surfaces, which is influenced by many factors [17]. The main adhering forces studied are ordered in decreasing magnitude as: capillary force > van der Waals force > gravity > buoyancy > electrostatic force. The features and structure of the surface could be changed when it is coated by a reagent, as shown in Fig. 1(a). Figure 1(b) shows the process of particles deposition and adhesion to the surface. The mechanism of adhesion is shown in Fig. 1(c).

Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of mechanism of particles adhering to solid surface coated with reagent
The adhering interaction between the particle and solid surface can be changed in the presence of reagent film. The mechanisms can be concluded as follows [17]: 1) The conductivity of electricity is improved when the solid surface is coated by the surfactant film, thereby reducing the amount of electric charge on the surface and decreasing the electrostatic force between the particles and solid surface. 2) The surface tension of the liquid is improved because of the surfactant film, resulting in the capillary force significantly decreasing along with the contact angle between the solid surface and liquid. 3) Because of the surfactant film forming a barrier around the solid surface, the distance between the particle and solid surface becomes large, resulting in the van der Waals force between them decreasing. 4) The chemical reaction between particles and solid surface becomes weak because of the separation of the reagent film, therefore, the chemical bond force between them decreases. 5) Because the surfactant is capable of cleaning the solid surface, the particles can be effectively separated and removed from the solid surface.
This research was conducted to investigate the characteristics of different particles adhering to various glass slides coated with reagent films. The effects of different contacting angle, contacting timing and various reagent on the adhesive performance between the surface and particles were taken into consideration.
3 Experimental
Five reagents were selected for the experiment as follows: 1) Anionic-surfactant: sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate (SDBS); 2) Nonionic-surfactant: Tween 60; 3) Special surfactant: fluorocarbon (DuPont 8710); 4) Diao brand liquid laundry detergent (produced by Nice Group Co.); 5) Kai-mi re-clean glass cleanser (produced by Xi'an Kai-mi Co., Ltd.).
This experiment was conducted in a laboratory at Central South University, China. The laboratory had four windows on one side of the wall (Fig. 2). The left-most and right-most windows were kept one-third open during the test. The testing slides were placed on top of an experimental table, with height of 1.1 m, in the middle of the room. Figure 2 displays the ichnography of the laboratory disposal. The tests were conducted under natural ventilating conditions.

Fig. 2 Ichnography of laboratory disposal
The experimental procedures were as follows: 1) Some of the glass slides were chosen for testing the cleanliness, which were selected at random from all the cleaning slides before experiment. 2) Different concentrations of SDBS were prepared, which were calculated as mass concentration (ab. concentration) of 0.5%, 1.0% and 5.0% respectively. 3) 18 slides were homogenously coated with the 0.5% SDBS solution, and they were placed in a drying oven at 85 °C. 4) After drying, 9 of the slides were placed on the horizontal clean tiles, while the other 9 slides were placed on the vertical tiles for the experiment. 5) The other concentrations of SDBS solutions were tested as the same steps 2 to 4. 6) For the control group, 18 clean slides without any pretreatment were placed on the tiles simultaneously. 7) The samples were taken on the 1st day, 5th day and 10th day. The amount and the average size of particles collected on the slides were observed by using an analytical micrograph system.
To make the description simple and clear in the figures, several symbols were used to substitute the reagents’ name and experimental cases, as follows: A—SDBS, B—Tween 60, C—Diao brand liquid laundry detergent, AF—0.5% SDBS and 0.5% fluorocarbon composite reagent, BF—0.5% Tween 60 and 0.5% fluorocarbon composite reagent, N—No reagent (clean slide); a—concentration is 0.5%, b—concentration is 1.0%, c—concentration is 5.0%; 0 and 90—the placement angles of 0° or 90°; 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9—sampling time interval, such as 1,2,3 means 1 d; 4,5,6 means 3 d; 7,8,9 means 10 d. The symbols and the numbers were used in the paper if there was no specific illustration.
4 Results and discussion
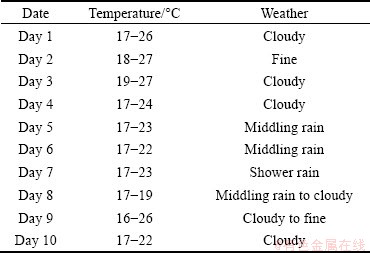
The weather conditions during the tests were recorded and analyzed as listed in Table 1.
Table 1 Outdoor weather conditions during experiment
4.1 Testing methods
The particles on the slides were observed and analyzed with the analytical micrograph system. Figure 3 shows a diagram of the three testing points along the middle line of each slide surface. Point P1 is at the distance of 55 mm from the label side, point P2 at the distance of 35 mm, and point P3 at the distance of 15 mm. Each testing area was 351864 μm2.
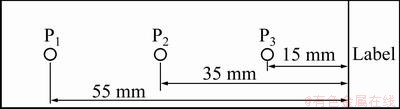
Fig. 3 Schematic diagram of testing points on slide
4.2 Results and analysis
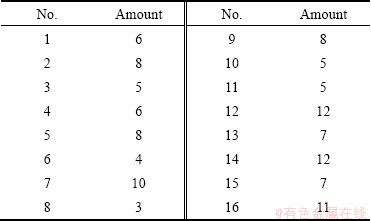
In order to understand the spread of particles on the slide surface, 16 slides were chosen at random before testing. And those slides were analyzed to obtain the number of the particles. The testing results are listed in Table 2.
Table 2 Number of particles on clean slides before testing
The number of the particles was obtained by sampling at three points, P1, P2, and P3, on each of the three slides. The sampling time intervals were 1 d, 5 d and 10 d. The average number of the particles was calculated, which is shown in Figs. 4-7.
By comparing the histograms in Figs. 4-7, the following findings were obtained.

Fig. 4 Particle number variation vs sampling frequency and SDBS concentration

Fig. 5 Particle number variation vs sampling frequency and Tween 60 concentration

Fig. 6 Particle number variation vs sampling frequency and liquid laundry detergent concentration
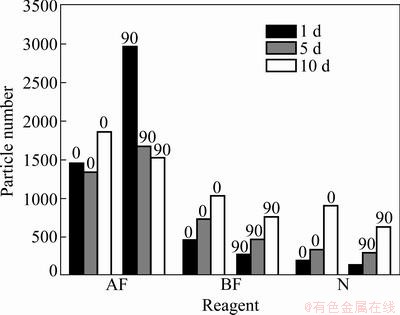
Fig. 7 Particle number variation vs sampling time interval and different reagents
1) The number of particles on cleaned slides ranges from 3 to 12, which could be negligible compared to the number of particles attached in the tests.
2) As expected, the number of particles on the horizontally placed slides was much more than that on the vertically placed slides for all the reagents used in the experiments. The number of particles attached to the slides coated with 0.5% SDBS and 0.5% fluorocarbon composite reagent was significantly more than that on the slides coated with the other reagents, while the number of particles attached to the slides treated with the liquid laundry detergent or no reagent was much less than the number of the particles on the slides treated with other reagents. These results indicated that 0.5% SDBS and 0.5% fluorocarbon composite reagents were more capable of exhibiting adhesive forces than the other reagents tested.
3) The reagent with the concentration of 1% Tween 60 was the most effective reagent for trapping particles on the slides compared to reagents at other concentrations.
4) On the clean slides, and the slides coated with the composite reagent, the number of particles adhered onto them was proportional to the sampling time interval. However, there was no relationship between the number of particles collected and the sampling time.
The functions of coating reagents with different mass concentrations (0.5% SDBS and 0.5% fluorocarbon, 0.5% Tween 60 and 0.5% fluorocarbon) were investigated and compared to the function of 1.0% concentration, according to the histogram of the same concentration with various reagents. Some conclusions can be obtained.
1) At the low concentration of various reagents, the adhesive ability between the particles and solid surface coated by SDBS was stronger than that by other reagent because the presence of SDBS changed the hydrophobic property of solid surface, which could greatly reduce the surface tension, increase the adhesion intension between the solid surface and particles. But the number of particles on the slides coated by SDBS was randomly varied with sampling time interval.
2) For different composite reagents, the adhesive ability of composite reagent with the SDBS and fluorocarbon was stronger than that of the other tested reagents, while the composite reagent coupled Tween 60 and fluorocarbon exhibited the weakest adhesive ability. It could be illuminated that the interaction between two kinds of reagents was positive correlation for some reagents, but the other was negative correlation. The specific index was the adhesive ability between the glass surface and particle in the test. It became enhanced for positive correlation, and it weakened for negative correlation.
3) The number of particles increased strictly with sampling time interval for single 0.5% Tween 60 and the composited Tween 60 and fluorocarbon reagent, while this rules could not be obtained for other reagents. This result shows that the stability of adhesive behavior is better when the reagent films include Tween 60.
4) The number of particles on the slides coated by 1.0% reagent was more than those coated with other concentrations, indicating that within a range of reagent concentration, the ability of adhesion or capturing the particles could be promoted. This suggested that there was evident correlation between the reagent concentration and its adhesive intensity. When it deviated from a given range of mass concentration, the adhesive ability would become weak, indicating that there was a best concentration interval for the certain reagent to achieve the best adhesion intensity.
The particle size was obtained by testing three areas (P1, P2, P3) on the surface of three homogeneous slides, with sampling time intervals of 1 d, 5 d and 10 d, respectively. Figures 8-11 show the average size values which were calculated from the test data.

Fig. 8 Average size of particles vs sampling time interval for SDBS

Fig. 9 Average size of particle vs sampling time interval for Tween 60
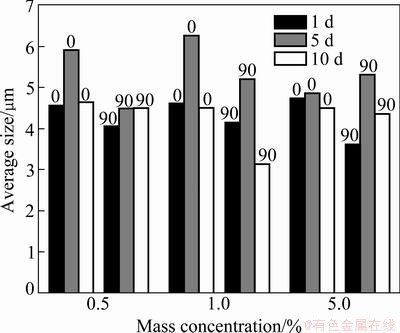
Fig. 10 Average size of particle vs sampling time interval for liquid laundry detergent
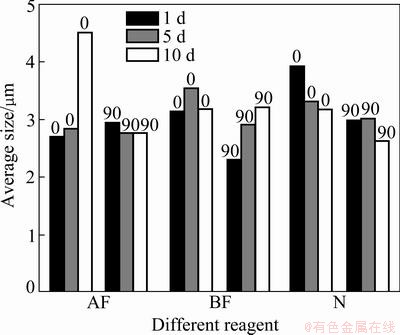
Fig. 11 Average size of particle vs sampling time intervals for none, AF and BF
Comparing the histograms in Figs. 8-11, some conclusions can be obtained.
1) On the whole, the average size of particles was correlated neither with the mass concentrations, nor with the angles of placement, and it did not increase with sampling time interval, illuminating that the particle size was not obviously affected by the reagent film. It
increased with sampling time interval for 5.0% Tween 60 and 5.0% SDBS, illuminating that the adhesive power increased at high concentration of the reagent, and high concentration could promote the abilities of the slides surface to capture the larger particles.
2) By comparing the particle size distribution, it was found that the effects of two composite reagents were smaller in terms of particle size, which was consistent with the results obtained from the slides without reagent treatment. While the adhesive action of the single reagents is stronger, and the largest particle size captured by the Tween varied from 4 to 5 μm. This could highlight this research on the selection of reagent type, optimization proportion of composite reagent which could affect the size distribution of the particles adhered on the surface.
The two composite reagents were investigated and compared to the function of 1.0% concentration. The average number of particles was calculated from the test data, and some conclusions can be achieved.
1) With the concentration of 0.5%, the average size of particles on the surface treated with the single reagents was larger than that on the surface treated with the composited reagents, demonstrating that the fluorocarbon surfactant had a special feature to change the adhesive action of surface, thereby improving the adhesion ability of the surface.
2) At the same concentration (1.0%), the difference in the adhesive action of composite reagent was larger than that of single reagent. For example, the average size of particles was smaller for 0.5% SDBS and 0.5% fluorocarbon composite reagent than in other cases, and the particle size was the largest for 0.5% Tween 60 and 0.5% fluorocarbon composite reagent.
3) By comparing the performance of the reagents at the concentration of 5.0%, it was found that the average size of particles increased strictly with sampling time interval for SDBS, showing that the stability and continuity of adhesive action of SDBS was better than that of the other reagent films.
5 Level of confidence and error of obtained results
Since some uncontrollable factors influenced the testing results of this experiment, the following section discusses the reliability and error of the results.
It is well known that the changes in atmospheric environment could affect the particle size, the quantity and the kinematics of dust, which has been investigated by HOEK et al [18]. KOPONEN et al [5] also found that the ventilation condition had a strong influence on indoor particles. However, in this research, all slides were placed in the same area (S<1 m2), so it is assumed that the test slides were all in the same atmospheric environment during the experiment.
There are two methods to study the relationship between airborne particles and adhered particles. The first one is to use artificial environment technology to control the experimental conditions. For example, HANDANI et al [19] measured the deposition of fine particles on building internal surface coverings. The study evaluated the loss-rate coefficients of 0.35, 0.53, 0.7, 1 and 2 μm particles on eight coverings were commonly found in buildings (two vinyl sheets, two wallpapers, two wood surfaces, one custom-made plaster surface, and one custom-made concrete surface) under three airflow intensity levels. The results showed that, if particle deposition clearly increases with near-wall airflow velocity, the role of the three-dimensional surface roughness is less evident because of the complex topographies of these real coverings. The other method is to conduct detailed surveys to determine the exact change of airborne particles in the experimental space. The survey data will then be used to study the relationship between airborne particles and adhered particles.
Characteristic of airborne particles changes with the region, season, surrounding environment and other factors, which is always fluctuating, resulting in the change of the adhering results. There was evident difference observed at the same location. For example, the average size of particles varied from 15 to 25 μm in Ref. [4], while the average size found in this study ranged from 4 to 5 μm. The amount of adhering particles only reflected the airborne particle at some regions under given conditions, which would limit the experiment conducting, while this could be improved by overcoming the shortcoming, such as increasing the number of measure, reasonably selecting testing time and optimizing the space position.
6 Conclusions
1) The adhesion ability of the surface coated by reagent is stronger than that without treatment, showing that the reagent film can significantly change the adhesive ability of solid surface. The SDBS solution exhibits the most strong adhesion force in this experiment. There is a best range of reagent concentration to achieve the strongest power of adhesive action for each certain reagent.
2) For the two different composite reagents, the influence on the adhesive property significantly disaccord between the number and size of particles. It agrees in the size of particles, while it disagrees in the number of particles.
3) The average size of particles is correlated with neither mass concentrations, nor the angles of placement, or the sampling time interval. The average size of particles on the surface coated by composite reagent was smaller than that on the single reagent coated surface, which varied from 2 to 3 μm. The largest particle size was observed with Tween 60 coated surface, which varied from 4 to 5 μm. It could be concluded that it is significant to conduct the research on the composite reagents to obtain some specific physical and chemical features, for improving the coupling performance between the solid surface and particles.
References
[1] NOLL K E, ALUKO O. Changes in large particle size distribution due to dry deposition processes [J]. Aerosol Science, 2006, 37: 1797-1808.
[2] LI Ming, WU Chao, PAN Wei. Sedimentation behavior of indoor airborne microparticles [J]. J China Univ Mining & Technol, 2008, 18: 588-593.
[3] ZHAO Bin, ZHANG Ying, LI Xian-ting, YANG Xu-dong, HUANG Dong-tao. Comparison of indoor aerosol particle concentration and deposition in different ventilated rooms by numerical method [J]. Building and Environment, 2004, 39: 1-8.
[4] LI Ming, WU Chao, LI Zi-jun. Test of sediment and adhesion behavior of dust particle on glass surface in room at various conditions [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2008, 21: 136-139. (in Chinese)
[5] KOPONEN I K, ASMI A, KERONEN P, KATRI P, MARKKU K. Indoor air measurement campaign in Helsinki, Finland 1999—The effect of outdoor air pollution on indoor air [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2001, 35: 1465-1477.
[6] ANADIE M, LIMAM K, ALLARD F. Indoor particle pollution: effect of wall textures on particle deposition [J]. Building and Environment, 2001, 36: 821-827.
[7] LAI A C K. Modeling indoor coarse particle deposition onto smooth and rough vertical surfaces [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2005, 39: 3823-3830.
[8] FUKUNISHI A, MORI Y. Adhesion force between particles and substrate in a humid atmosphere studied by atomic force microscopy [J]. Advanced Powder Technol, 2006, 17: 567-580.
[9] KATAINEN J, PAAJANEN M, AHTOLA E, PORE V, LAHTINEN J. Adhesion as an interplay between particle size and surface roughness [J]. Jounal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2006, 304: 524-529.
[10] MORI Y. Effect of surface hydrophobicity on interaction between particle and flat plate at final stage of wet coating process [J]. Colloid and Surface A: Physicochem Eng, 2007, 311: 61-66.
[11] LIM K S, LEE S H, PARK H S. Prediction for particle removal efficiency of a reverse jet scrubber [J]. Aerosol Science, 2006, 37: 1826-1839.
[12] TUNG W S, DAOUD W A. Photocatalytic self-cleaning kerations: A fesibility study [J]. Acta Biomateralia, 2009, 5: 50-56.
[13] GUAN Kai-shu. Relationship between photocatalytic activity, hydrophilicity and self-cleaning effect of TiO2/SiO2 films [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2005, 191: 155-160.
[14] WANG Ru, XU Yue-hua, CHEN Ming-jie, JIA Jin-liang. Effect of erbium doping on photo catalytic properties of TiO2 films on glass surface [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 19(10): 1866-1871. (in Chinese)
[15] NIMITTRAOOLCHAI O U, SUPOTHINA S. Deposition of organic- based superhydrophobic films for anti-adhesion and self-cleaning applications [J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2008, 28: 947-952.
[16] KAWAMOTO H, MIWA T. Mitigation of lunar dust adhered to mechanical parts of equipment used for lunar exploration [J]. Journal of Electrostatics, 2011, 69: 365-369.
[17] LI Ming. Research on mechanism of solid particle adhesion and remove from surface and dustproof technology of surface [D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2009. (in Chinese)
[18] HOEK G, KOS G, HARRISON R, de HARTOG J, MELIESTE K, ten BRINK H, KATSOUYANNI K, KARAKSTSANI A, LIANOU M, KOTRONAROU A, KAVOURAS L, PEKKANEN J, VALLIOUS M, KULMALA M, PUUSTINEN A, THOMAS S, MEDDINGS C, AYRES J, van WIJNEN J, HAMERI K. Indoor-outdoor relationships of particle number and mass in four European cities [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2008, 42: 156-169.
[19] HANDANI S EI, LIMAN K L, ABADIE M O, BENDOU A. Deposition of fine particles on building internal surfaces [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2008, 42: 8893-8901.
李 明,吴 超,刘一静,闫 晖
中南大学 资源与安全工程学院,长沙 410083
摘 要:通过玻璃表面的试剂涂层与空气中微颗粒的耦合性实验发现,试剂涂层能明显改变表面与微颗粒的耦合能力,微颗粒平均粒径与采样的时间间隔、放置夹角和试剂浓度没有明显规律性联系,复合试剂耦合微颗粒的粒径比单一试剂的粒径小(2~3 μm),其中吐温60粘附微颗粒的粒径最大(4~5 μm),0.5%SDBS与0.5%氟碳复合试剂涂层表面粘附微颗粒数量的能力最强。每种试剂对微颗粒的粘附强度存在一个最佳范围。研究发现,复合试剂能获得单一试剂不具备的特殊物理化学性质,能有效改变固体表面与微颗粒的耦合性质。
关键词:微颗粒;粘附;玻璃表面;试剂涂层;粒径分布
(Edited by YUAN Sai-qian)
Foundation item: Project (50974132) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2011QNZT094) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China
Corresponding author: LI Ming; Tel:+86-731-88879612; E-mail: liming_csu@csu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61535-5

