高温累积叠轧制备高性能多层铜/铝复合带材
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2019年第8期
论文作者:王琳 杜青林 李畅 崔晓辉 赵兴 喻海良
文章页码:1621 - 1630
关键词:扩散层;铜/铝复合带材;累积叠轧;轧制温度;金属间化合物;力学性能
Key words:diffusion layer; Cu/Al multilayers; accumulative roll bonding; rolling temperature; intermetallics; mechanical properties
摘 要:通过高温累积叠轧方法制备多层铜/铝复合带材。为获得高的界面结合强度,在叠轧前分别加热铜、铝带材至350、400、450和500 °C。采用拉伸试验评估其力学性能,通过光学显微镜和配备有能量色散光谱仪的扫描电子显微镜检测材料的显微组织。研究发现:随着轧制温度的升高,层状复合带材的极限拉应力、材料晶粒尺寸和扩散层厚度均增大。当轧制温度为400 °C时,复合带材具有最高的延展性,但屈服应力最低。随着轧制温度进一步升高,屈服应力和极限拉应力均增加,但延性略有下降。低温累积叠轧和高温累积叠轧制备的层状复合材料的力学性能分别由晶粒尺寸和扩散层厚度决定。
Abstract: Cu/Al multilayers were produced by high-temperature accumulative roll bonding (ARB) methods up to three passes. To achieve a high bonding strength, prior to ARB processing, the Cu and Al sheets were heated to 350, 400, 450 and 500 °C, respectively. The mechanical properties were evaluated by tensile tests. The microstructure was examined by optical microscopy and scanning electron microscopy equipped with energy dispersive spectrometry. The ultimate tensile stress, the grain size and the thickness of diffusion layer of lamellar composites increase with rolling temperature. When the rolling temperature is 400 °C, the laminates show the highest ductility, but the yield stress is the lowest. As the rolling temperature further increases, both the yield stress and the ultimate tensile stress increase and the ductility decreases slightly. The mechanical properties of lamellar composites processed by low and high temperature ARB are determined by grain size and the thickness of diffusion layer, respectively.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 29(2019) 1621-1630
Lin WANG1,2, Qing-lin DU1,2, Chang LI1,2, Xiao-hui CUI1,2,3, Xing ZHAO1,2,3, Hai-liang YU1,2,3
1. State Key Laboratory of High Performance Complex Manufacturing, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
3. Light Alloys Research Institute, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 24 December 2018; accepted 10 June 2019
Abstract: Cu/Al multilayers were produced by high-temperature accumulative roll bonding (ARB) methods up to three passes. To achieve a high bonding strength, prior to ARB processing, the Cu and Al sheets were heated to 350, 400, 450 and 500 °C, respectively. The mechanical properties were evaluated by tensile tests. The microstructure was examined by optical microscopy and scanning electron microscopy equipped with energy dispersive spectrometry. The ultimate tensile stress, the grain size and the thickness of diffusion layer of lamellar composites increase with rolling temperature. When the rolling temperature is 400 °C, the laminates show the highest ductility, but the yield stress is the lowest. As the rolling temperature further increases, both the yield stress and the ultimate tensile stress increase and the ductility decreases slightly. The mechanical properties of lamellar composites processed by low and high temperature ARB are determined by grain size and the thickness of diffusion layer, respectively.
Key words: diffusion layer; Cu/Al multilayers; accumulative roll bonding; rolling temperature; intermetallics; mechanical properties
1 Introduction
Ultrafine-grained materials processed by severe plastic deformation (SPD) have been the subjects of considerable researches due to their superior mechanical properties. Several SPD techniques including high- pressure torsion [1,2], equal channel angular pressing (ECAP) [3,4], accumulative roll bonding (ARB) [5,6] and asymmetric cryorolling [7-9] have been developed to fabricate ultrafine-grained materials. Among these techniques, ARB is widely used to produce metallic composites such as Al/Cu [10,11], Al/Ni [12], Al/Ti [13,14] and Al/Mg [15] laminated sheets.
Single-phase nanostructured materials have extraordinary properties, but these materials are not stable under extreme conditions of temperature, strain and strain rate. Recent attention has been paid to metallic composites, comprised of different metals and alloys with varying properties, which are stable in harsh environments demanded by future energy systems. Cu/Al multilayers have been widely studied because of their high conductivity, low density and price competitiveness over copper and copper alloys [10,11,16,17]. Many researchers investigated interfacial bonding strength between Cu layer and Al layer. The thickness of diffusion zone exponentially increases with raising annealing temperature and annealing time [18]. YANG et al [19] fabricated Al/Cu laminates by diffusion bonding and rolling, and the shear tensile strength of Al/Cu interface reached a maximum value equivalent to 90% of the strength of the Al layer. ZHANG et al [20] reported that the electrical resistivity of Cu/Al composites increases with the thickness of intermetallic-layer. SHENG et al [21] found that low temperature annealing can enhance the bonding strength of cold-rolled Cu/Al bimetal composites. ABBASI et al [22] studied the growth rate of intermetallic compounds at the interface of cold-rolled Al/Cu bimetal sheets. HOSEINI-ATHAR et al [23] reported that the highest bonding strength is achieved for wavy interface, which results from the higher bonding area and small amounts of brittle intermetallic compounds. The ductility of Cu/Al/Cu composites increases as the ratio of gage width reduction of adjacent layers increases. LI et al [24] found that the thickness of the diffusion layer increases with the annealing temperature, which contributes to the enhanced interfacial bonding strength. GAO et al [25] found that the maximum peeling strength of Cu/Al/Cu strips is obtained when the laminates are annealed at 450 °C and further cold-rolled. In addition, the mechanical properties of Cu/Al laminates were also studied. Generally, the cooperative deformation capability of Cu/Al laminates increases with increasing strain rate and decreasing deformation temperature [26]. LI et al [27] fabricated Al/Cu/Al laminates by asymmetric rolling, and found that tensile strength and elongation increase as the strain rate increases from 1×10-3 s-1 to 1×10-1 s-1. LI et al [28] reported that the improvement in bonding strength and interfacial microstructure enhances the fracture performance of the laminated Cu/Al composites. Delaminating and microcracks near interface lead to the fracture of laminates during tensile test. The interface diffusion reaction of Cu/Al laminates during hot deformation is mainly determined by deformation temperature and strain, and temperature is the most important factor [29]. KIM and HONG [30] reported that the experimental fracture strains of Cu/Al/Cu laminates are larger than the values calculated using the rule of mixture for the as-rolled composites and those heat-treated up to 400 °C. Previous studies were focused not only on bi-layered or tri-layered Cu/Al laminates [18-30], but also on multilayered composites [31-37]. EIZADJOU et al [31] reported that the strength of Al/Cu laminates increases as the number of ARB passes increases and the enhancement of the strength is higher than that of Al/Al laminates. After the third ARB pass, the average Vickers hardness of both Cu and Al layers reaches the maximum value. HSIEH et al [32] studied the growth of intermetallic phases of ARB-processed Al/Cu laminates during annealing. TOROGHINEJAD et al [33,34] studied the evolution of texture and microstructure of Al/Cu laminates during ARB and folding process. RAHMATABADI et al [35-37] studied the fracture toughness, evolution of the microstructure and mechanical properties of the ultrafine-grained Al/Cu/Al multilayered composites subjected to room-temperature ARB process, and they found that the ultimate tensile strength increased with the increasing number of the ARB passes because of the change of the fracture mechanism to shear ductile fracture. Conventional ARB experiments were carried out at room temperature, to prevent the formation of intermetallic layers between Al layer and Cu layer. There are few reports on the mechanical response of Cu/Al composites fabricated by ARB with rolling temperatures higher than 300 °C.
The bonding strength between Cu and Al layer is lower than 60 MPa when the rolling reduction ratio is 50% at room temperature [38], but the strength increases [24] at higher rolling temperature. In addition, the diffusion layers in laminates rolled at various temperatures are different and may affect the tensile strength of Cu/Al laminates. In previous ARB processes, the rolling temperature is controlled as low as possible to restrict grain growth and to enhance grain refinement [32-34]. In this study, we investigated the influence of temperature on the mechanical behavior of Cu/Al multilayers.
2 Experimental
The Cu/Al composites were fabricated using ARB process. The original materials were commercially pure Cu sheets (T2 copper) with thickness of 0.4 mm and commercially pure Al sheets (AA1100) with thickness of 1.0 mm, which were selected because of high strength, excellent ductility and broad industrial application. Both the Cu and the Al sheets before rolling were 60 mm wide. The rolling experiments were carried out on a four-high rolling mill of automated gauge control system with the working roll diameter of 170 mm under dry friction conditions. The composites were heated in a vacuum furnace and the two laminates were nailed tightly at four corners before rolling to reduce oxidation of the interface. Figure 1(a) schematically illustrates the ARB process to fabricate Cu/Al laminates. After surface cleaning treatment by wire brushing to foster bonding, the Cu and Al sheets were stacked as a sandwich-like structure Cu/Al/Cu for the first roll bonding. In order to achieve a good bonding quality between Cu and Al layers, prior to rolling process, the Cu and Al sheets were heated to 350, 400, 450 and 500 °C, respectively. The rolling step involved a 50% reduction in layer thickness. Then, the sample was halved, cleaned and restacked, and the ARB process continued by repeating the steps. The above processes were repeated three circles. For the first rolling pass, the laminates were heated for 20 min in a vacuum heating furnace. For the second and the third ARB passes, the laminates were heated for 5 min before rolling. Finally, there are five Cu layers and four Al layers in each specimen. Figure 1(b) illustrates the cross-sectional (rolling direction-normal direction) structure of the Cu/Al laminates. When the rolling temperature is low, the CuAl intermetallic layer between Cu layer and Al layer is neglectable in the fabricated Cu/Al laminates. But the intermetallic layer appears at high rolling temperature.
Dog-bone shaped tensile specimens were cut from the Cu/Al multilayered composites using an electrical discharge machine. The geometric dimensions of the tensile samples are shown in Fig. 2(a). The tensile tests were carried out on a DDL-100 testing machine at a strain rate of 0.03 s-1 at room temperature. An average of three tests was taken for each kind of multilayers. The optical microscopy (OLYMPUS BX51M) was used to observe the microstructure of Al layer after ARB processing. The morphology of the Al grains was obtained after anode coating. The scanning electron microscopy (SEM) equipped with energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS) on the platform of Phenom Prox Desktop was used to examine the microstructure of Cu layer and the element distribution near the Cu/Al interface. The aqua regia was used as the etchant for copper. In the EDS experiments, the accelerating voltage was 15 kV, and the distance between two measuring points was 0.35 mm.
3 Results

Fig. 1 Schematic illustration of accumulative roll bonding process (a) and fabricated Cu/Al multilayers at different rolling temperatures (b)
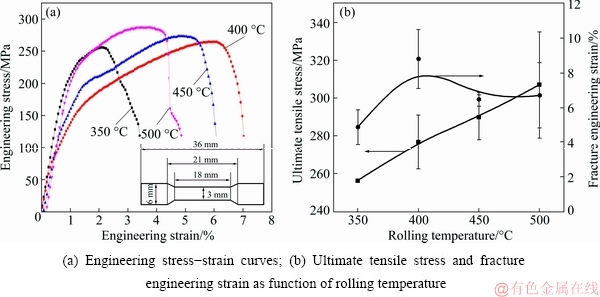
Fig. 2 Mechanical properties of Cu/Al laminates
Figure 2 shows the mechanical properties of ARB-processed Cu/Al laminates at different rolling temperatures. When the rolling temperature is 350 °C, the Cu/Al laminates show a high yield stress, but the fracture engineering strain is the lowest among the four rolling temperatures. When the rolling temperature is increased to 400 °C, the yield stress of the Cu/Al laminates decreases remarkably. However, with further increasing the rolling temperature to 450 and 500 °C, the yield stress of laminates changes to increase while their ductility is reduced slightly. Figure 2(b) shows that the ultimate tensile stress of laminates increases at higher rolling temperature, and also shows that the laminates subjected to rolling temperature of 400 °C have the best ductility. The mechanical properties of the ARB- processed Cu/Al laminates when the rolling temperature is higher than 400 °C are unexpected.
Figure 3 shows the macro-distribution of Cu layer and Al layer after three ARB passes. Deformations of Cu layers and Al layers during ARB are relatively uniform. In addition, the interface between Cu layer and Al layer are bonded well. Figures 4 and 5 show the optical microscopy images and SEM images of the microstructure of Al and Cu layers after ARB processing at different temperatures. The ARB-process at low temperature of 350 °C refines the grain size and the resulting composites show high yield stress and low ductility. With increasing the rolling temperature, the grain size increases obviously [39]. The mean size of grains increases from 9.4 to 13.5 mm when the rolling temperature increases from 350 to 500 °C (Fig. 4). After the ARB processing, the microstructure changes into a laminated structure (Fig. 5). In Fig. 5, when the rolling temperature is 350 °C, the mean thickness of laminated structures is 3.1 mm and increases to 7.5 mm when the rolling temperature is increased to 500 °C.
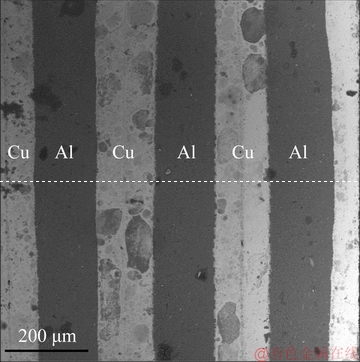
Fig. 3 SEM image of ARB processed Cu/Al laminate
Figure 6 shows the SEM images of the micro- structure near the interface between Cu layer and Al layer. When the rolling temperature is 350 °C, it is difficult to detect the Al/Cu intermetallic layer in the laminate after three ARB passes. However, when the rolling temperature is increased to 400 °C, intermetallic layer appears near the interface. As the rolling temperature increases, the thickness of intermetallic layer between Cu layer and Al layer increases. Figure 6(d) shows that the intermetallic layer becomes serrated after ARB processing at 500 °C, which is a common feature of bimetallic composites after high-temperature rolling [40].
Figures 7(a-d) show the EDS mapping of Al and Cu element distribution near the interface between Cu layer and Al layer. With increasing the rolling temperature, the thickness of diffusion zone between Cu layer and Al layer increases significantly and four tests were taken at random places for each sample. The average thickness of diffusion layer is only 1.79 mm at rolling temperature of 350 °C and increases to 27.87 mm at 500 °C. Here, we assume that the thickness of diffusion layer is zero for the Cu/Al laminate processed by ARB at room temperature. The relationship between the mean thickness of diffusion layer (tdiffusion_layer) and the rolling temperature (T) is shown in Fig. 7(e), which can be fitted by
 (1)
(1)
Equation (1) is fitted by the allometry model, and the thickness of diffusion layer and rolling temperature is exponentially related [18], with the scaling exponent of the equation being 6.11688. It is obvious that the mean thickness of diffusion layer between Cu layer and Al layer increases quickly with raising rolling temperature.
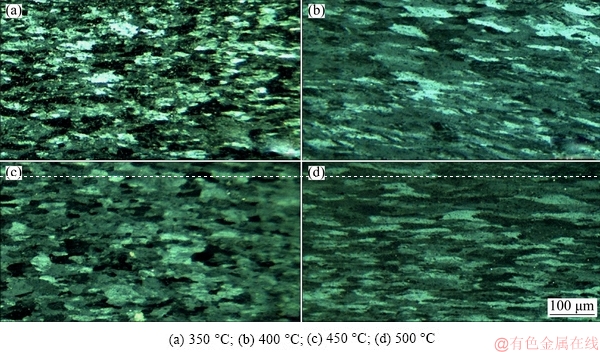
Fig. 4 Optical microscopy images of microstructure in Al layer after ARB processing at different rolling temperatures

Fig. 5 SEM images of microstructure in copper layer after ARB processing at different rolling temperatures

Fig. 6 SEM images of microstructure near interface between Cu layer and Al layer after three ARB passes

Fig. 7 Cu and Al element distributions near Cu/Al interface after three ARB passes for rolling temperature at 350 °C (a), 400 °C (b), 450 °C (c) and 500 °C (d), mean thickness of diffusion layer between Al layer and Cu layer (e) and volume fraction of diffusion layer (f) vs rolling temperature
We further assume that the thicknesses of diffusion layer are the same in the laminates, and since there are six Cu/Al interfaces in the laminates, the volume fraction of diffusion layer in the laminates can be obtained, as shown in Fig. 7(f). When the rolling temperature is 400 °C, the volume fraction of diffusion layer is 3.9%. When the rolling temperature increases to 450 °C, the volume fraction of diffusion layer is 12.7%. The change in the thickness of the diffusion layer is related with the mechanical properties well. It is obvious that the effect of diffusion layer on the mechanical behavior of the laminates cannot be neglected when the rolling temperature is higher than 450 °C.
Figure 8 shows the SEM images of fracture surface of laminates after tensile tests. In Fig. 8(b), the dimples are deeper and the number of dimples is more compared with other samples, which implies the higher ductility of samples when the rolling temperature is 400 °C. In addition, the debonding between layers is very clearly seen when the rolling temperature is 350 °C (Fig. 8(a)), and the debonding between layers is slight when the rolling temperature is 500 °C (Fig. 8(d)). These results mean that the bonding strength increases with rolling temperature.

Fig. 8 SEM images of fracture surface of Cu/Al laminates fabricated at different rolling temperatures
4 Discussion
In Fig. 2, the Cu/Al multilayers processed by ARB at 500 °C show the highest yield strength and tensile strength among all samples. In this study, the ARB processing parameters are the same except for the rolling temperature. It is obvious that the rolling temperature affects the grain sizes of Cu layer and Al layer in laminates. Generally, with finer grain size, the yield stress of the composites increases [1-5]. Under plastic deformation, the grain size in metals is related to dislocation cell thickness and dislocation density, which can be described in Eqs. (2)-(5) [41,42]:
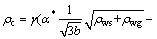
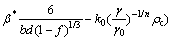 (2)
(2)
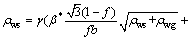
 (3)
(3)
 (4)
(4)
where ρc is dislocation cell thickness; ρws is statistical dislocation density; ρwg is geometrically necessary dislocation density; γ is shear strain rate; α* and β* are dislocation evolution rate control parameters for the materials; n is temperature sensitivity parameter (n=B/T, B is a materials parameter, and T is temperature); f is the volume fraction of dislocation cell wall; b is the magnitude of the Burgers vector of the material; d is dislocation cell size; ξ is fraction of the dislocations incoming into cell walls from the cell interiors; k0 is the dislocation annihilation rate parameter,
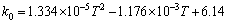 (5)
(5)
From Eqs. (2)-(5), when the temperature is higher than the room temperature, the dislocation density will reduce with increasing the temperature. Especially, grain growth occurs in sheets at higher temperature during deformation, which will result in coarse grain in the rolled sheets. As shown in Figs. 4 and 5, after three ARB passes, the grain size in pure Al and pure copper increases dramatically as the rolling temperature increases from 350 to 500 °C. According to the Hall-Petch equation, the yield stress reduces with increasing grain size in crystalline materials [1,3]. This can explain the decrease of yield stress of the Cu/Al laminates subjected to ARB at the rolling temperature of 350 and 400 °C. But, the yield stress of laminates increases as the rolling temperature increases from 400 to 500 °C although the grain size of laminates increases.
Increasing the rolling temperature might lead to higher bonding strength [18,21-25]. In Fig. 8, the bonding quality between Cu layer and Al layer is the best when the Cu/Al multilayers are fabricated by ARB at 500 °C. PENG et al [43] studied the effect of rolling temperature on the bonding strength of Cu/Al laminates from 350 to 500 °C and found that the bonding strength reaches the largest value when the rolling temperature is 430 °C. However, the relationship between bonding strength and mechanical properties of laminates is still under debate [38]. HEYDARI VINI and SEDIGHI [44] reported that the tensile strength of AA1050/AA5083 laminates processed by warm ARB increases with increasing rolling pass, but the bonding strength and elongation first decrease if the number of laminated layers is less than 8 and then increase by further increasing the number of laminated layers. Thus, the bonding strength between layers also cannot explain the change of mechanical properties of laminates subjected to ARB when the temperature is higher than 400 °C.
In Fig. 6 and Fig. 7(e), the thickness of diffusion layer in laminates changes as rolling temperature varies, which affects the mechanical properties of laminates [13]. LI et al [45] reported that Al/Cu laminates have the highest tensile strength after annealing at 300 °C for 1 h compared with cold-rolled sheets. In Cu/Al laminates, the intermetallic diffusion layer contains Al2Cu, AlCu, Al3Cu4 and Al4Cu9 [46]. The microhardness of AlCu intermetallic is larger than that of the Al layer and the Cu layer, which may reach nine times of the microhardness of pure Cu when the copper content in the as-solidified Al-Cu alloys is 80-90 at.% [47]. Thus, increasing the thickness of diffusion layer will increase the tensile strength. The interface diffusion happens during both the heating and rolling process. The diffusion is determined by the rolling processes which play an important role in bonding the two layers together and lead to the formation of bonded interface. In Fig. 7(f), the volume fractions of diffusion layer in the laminates are 1.2%, 3.9%, 12.7% and 19.7% for the rolling temperature at 350, 400, 450 and 500 °C, respectively. When the rolling temperature is 350 and 400 °C, the strength contribution from diffusion layer on the mechanical properties is much less than the effect of grain size in Cu layer and Al layer. However, when the rolling temperature is 450 and 500 °C, the diffusion layer plays a key role in the mechanical properties of laminates compared to the coarser grains at higher rolling temperature. Thus, the yield strength of Cu/Al composites increases due to the larger fractions of diffusion layer, although the coarser grains reduce yield strength slightly. In addition, the ultimate tensile strength is also affected by the diffusion layer in composites. As the diffusion layer thickness increases, the ultimate tensile strength increases.
5 Conclusions
(1) Multilayered Cu/Al composites were fabricated by accumulative roll bonding at 350, 400, 450 and 500 °C. The thickness of diffusion layer between Cu layer and Al layer increases with raising rolling temperature. When the rolling temperature increases to 500 °C, the volume fraction of diffusion layer in laminates reaches up to 19.7%, while it is only 1.2% for the rolling temperature of 300 °C.
(2) When the rolling temperature is 450 or 500 °C, both the ultimate tensile strength and the ductility of ARB-processed Cu/Al laminates are higher than those of laminates at the rolling temperature of 350 °C.
(3) When the rolling temperature is lower than 400 °C, the grain size determines the mechanical properties of Cu/Al laminates subjected to accumulative roll bonding. When the rolling temperature is higher than 450 °C, the diffusion layer plays the key role compared to the effect of grain size. These results offer us a new way to optimize the mechanical properties of multilayered composites through controlling the thickness of diffusion layer during ARB.
References
[1] ZHILYAEV A P, LANGDON T G. Using high-pressure torsion for metal processing: Fundamentals and applications [J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2008, 53: 893-979.
[2] SUN Y, AINDOW M, HEBERT R J, LANGDON T G, LAVERNIA E J. High-pressure torsion-induced phase transformations and grain refinement in Al/Ti composites [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2017, 52: 12170-12184.
[3] VALIEV R Z, LANGDON T G. Principles of equal-channel angular pressing as a processing tool for grain refinement [J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2006, 51: 881-981.
[4] LIU F, YUAN H, GOEL S, LIU Y, WANG J T. Bulk nanolaminated nickel: Preparation, microstructure, mechanical property, and thermal stability [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2018, 49: 576-594.
[5] TSUJI N, SAITO Y, LEE S H, MINAMINO Y. ARB (accumulative roll-bonding) and other new techniques to produce bulk ultrafine grained materials [J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2003, 5: 338-344.
[6] YU H L, LU C, TIEU K, KONG C. Fabrication of nanostructured aluminum sheets using four-layer accumulative roll bonding [J]. Materials and Manufacturing Processes, 2014, 29(4): 448-453.
[7] YU H L, DU Q L, GODBOLE A, LU C, KONG C. Improvement in strength and ductility of asymmetric-cryorolled copper sheets under low-temperature annealing [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2018, 49: 4398-4403.
[8] YU H L, YAN M, LI J T, GODBOLE A, LU C, TIEU K, LI H J, KONG C. Mechanical properties and microstructure of a Ti-6Al-4V alloy subjected to cold rolling, asymmetric rolling and asymmetric cryorolling [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2018, 710: 10-16.
[9] YU H L, LU C, TIEU K, LI H J, GODBOLE A, KONG C, ZHAO X. Simultaneous grain growth and grain refinement in bulk ultrafine-grained copper under tensile deformation at room temperature [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A. 2016, 47: 3785-3789.
[10] KIM I K, HONG S I. Effect of heat treatment on the bending behavior of tri-layered Cu/Al/Cu composite plates [J]. Materials and Design, 2013, 47: 590-598.
[11] YU H L, LU C, TIEU K, LI H J, GODBOLE A, KONG C. Nanoporous Al sandwich foils by using size effect of Al layer thickness during Cu/Al/Cu laminate rolling [J]. Philosophical Magazine, 2018, 98: 1537-1549.
[12] AZIMI M, TOROGHINEJAD M R. SHAMANIAN M, KESTENS L A I. Grain and texture evolution in nano/ultrafine-grained bimetallic Al/Ni composite during accumulative roll bonding [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2018, 53: 12553-12569.
[13] YU H L, LU C, TIEU K, LI H J, GODBOLE A, LIU X, KONG C. Interface bonding mechanism of Al/Ti/Al laminate sheets subjected to room-temperature rolling and cryorolling [J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2017, 32: 3761-3768.
[14] YU H L, LU C, TIEU K, LI H J, GODBOLE A, KONG C. Annealing effect on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al/Ti/Al laminate sheets [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A. 2016, 660: 195-204.
[15] NIE J F, LIU M X, WANG F, ZHAO Y H, LI Y S, CAO Y, ZHU Y T. Fabrication of Al/Mg/Al composites via accumulative roll bonding and their mechanical properties [J]. Materials, 2016, 9: 951.
[16] KHODIR S A, AHMED M M Z, AHMED E, MOHAMED S M R, ABDEL-ALEEM H. Effect of intermetallic compound phases on the mechanical properties of the dissimilar Al/Cu friction stir welded joints [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2016, 25: 4367-4378.
[17] HUANG Hua-gui, DONG Yi-kang, YAN Meng, DU Feng-shan. Evolution of bonding interface in solid-liquid cast-rolling bonding of Cu/Al clad strip [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27: 1019-1025.
[18] USCINOWICZ R. Impact of temperature on shear strength of single lap Al-Cu bimetallic joint [J]. Composites: Part B, 2013, 44: 344-356.
[19] YANG Y H, LIN G Y, CHEN D D, ZHANG R, WANG D Z, QI F. Fabrication of Al-Cu laminated composites by diffusion rolling procedure [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2014, 30: 973-976.
[20] ZHANG Jian, WANG Bin-hao, CHEN Guo-hong, WANG Ruo-min, MIAO Chun-hui, ZHENG Zhi-xiang, TANG Wen-ming. Formation and growth of Cu-Al IMCs and their effect on electrical property of electroplated Cu/Al laminar composites [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26: 3283-3291.
[21] SHENG L Y, YANG F, XI T F, LAI C, YE H Q. Influence of heat treatment on interface of Cu/Al bimetal composite fabricated by cold rolling [J]. Composites: Part B, 2011, 42: 1468-1473.
[22] ABBASI M, KARIMI TAHERI A, SALEHI M T. Growth rate of intermetallic compounds in Al/Cu bimetal produced by cold roll welding process [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2001, 319: 233-241.
[23] HOSEINI-ATHAR M M, TOLAMINEJAD B. Interface morphology and mechanical properties of Al-Cu-Al laminated composites fabricated by explosive welding and subsequent rolling process [J]. Metal and Materials International, 2016, 22: 670-680.
[24] LI H, CHEN W, DONG L, SHI Y, LIU J, FU Y. Interface bonding mechanism and annealing effect on Cu-Al joint produced by solid-liquid compound casting [J]. Journal of Material Processing Technology, 2018, 252: 795-803.
[25] GAO H T, LIU X H, QI J L, AI Z R, LIU L Z. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Cu/Al/Cu clad strip processed by the powder-in-tube method [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2018, 251: 1-11.
[26] LIU S, WANG A, LIANG T, XIE J. Hot deformation behavior of Cu/Al laminated composites under interface constraint effect [J]. Materials Research Express, 2018, 5: 066531.
[27] LI X, ZU G, WANG P. Effect of strain rate on tensile performance of Al/Cu/Al laminated composites produced by asymmetrical roll bonding [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2013, 575: 61-64.
[28] LI X B, YANG Y, XU Y S, ZU G Y. Deformation behaviour and crack propagation on interface of Al/Cu laminated composites in uniaxial tensile test [J]. Rare Metals, 2018, https:// doi.org/10.1007/s12598-018-0998-x.
[29] ZHANG Y, QIN J, ZHAO H. Interface diffusion reaction of Cu/Al laminates under hot pressing [J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2013, 38: 42-42.
[30] KIM W N, HONG S I. Interactive deformation and enhanced ductility of tri-layered Cu/Al/Cu clad composite [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2016, 651: 976-986.
[31] EIZADJOU M, KAZEMI TALACHI A, DANESH MANESH H, SHAKUR SHAHABI H, JANGHORBAN K. Investigation of structure and mechanical properties of multi-layered Al/Cu composite produced by accumulative roll bonding (ARB) process [J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2008, 68: 2003-2009.
[32] HSIEH C C, SHI M S, WU W. Growth of intermetallic phases in Al/Cu composites at various annealing temperatures during the ARB process [J]. Metals and Materials International, 2012, 18: 1-6.
[33] TOROGHINEJAD M R, JAMAATI R, HOSEINI M, SZPUNAR J A, DUTKIEWICZ J. Texture evolution of nanostructured aluminum- copper composite produced by the accumulative roll bonding and folding process [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2012, 44: 1587-1598.
[34] TOROGHINEJAD M R, JAMAATI R, SZPUNAR J A, DUTKIEWICZ J. Investigation of nanostructured aluminum/copper composite produced by accumulative roll bonding and folding process [J]. Materials and Design, 2013, 51: 274-279.
[35] RAHMATABADI D, TAYYEBI M, HASHEMI R, FARAJI G. Evaluation on of microstructure and mechanical properties of multilayer Al 5052-Cu composite produced by accumulative roll bonding [J]. Powder Metallurgy and Metal Ceramics, 2018, 57: 144-153.
[36] RAHMATABADI D, MOHAMMADI B, HASHEMI R, SHOJAEE T. An experimental study of fracture toughness for nano/ultrafine grained Al5052/Cu multilayered composite processed by accumulative roll bonding [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, 2018, 140: 101001.
[37] RAHMATABADI D, TAYYEBI M, HASHEMI R, FARAJI G. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al/Cu/Mg laminated composite sheets produced by the ARB process [J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2018, 25: 564-572.
[38] LI H, NAGAI K, YIN F X. Progress in cold roll bonding of metals [J]. Sciences and Technology of Advanced Materials 2008, 9: 023001.
[39] YU H L, LU C, TIEU K, LI H J, GODBOLE A, ZHANG S H. Special rolling techniques for improvement of mechanical properties of ultrafine-grained metal sheets: A review [J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2016, 18: 754-769.
[40] KIM J S, LEE D H, JUNG S P, LEE K S, KIM K J, KIM H S, LEE B J, CHANG Y W, YUH J, LEE S. Novel strip-cast Mg/Al sheets with excellent tensile and interfacial bonding properties [J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 26333.
[41] DING H, SHEN N, SHIN Y. Prediction modeling of grain refinement during multi-pass cold rolling [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2012, 212: 1003-1013.
[42] BAIK S C, ESTRIN Y, KIM H S, HELLMING R J. Dislocation density-based modeling of deformation behavior of aluminum under equal channel angular processing [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 351: 86-97.
[43] PENG X K, HENESS G, YEUNG W Y. Effect of rolling temperature on interface and bond strength development of roll bonded copper/aluminium metal laminates [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1999, 34: 277-281.
[44] HEYDARI VINI M, SEDIGHI M. Mechanical properties and bond strength of bimetallic AA1050/AA5083 laminates fabricated by warm-accumulative roll bonding [J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 2018, 57: 160-167.
[45] LI Xiao-bing, ZU Guo-xin, WANG Ping. Microstructural development and its effects on mechanical properties of Al/Cu laminated composite [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25: 36-45.
[46] CHEN C Y, HWANG W S. Effect of annealing on the interfacial structure of aluminum-copper joints [J]. Materials Transactions, 2007, 48: 1938-1947.
[47] BOUKHRIS N, LALLOUCHE S, DEBILI M Y, DRAISSIA M. Microhardness variation and related microstructure in Al-Cu alloys prepared by HF induction melting and RF sputtering [J]. European Physical Journal Applied Physics, 2009, 45: 30501.
王 琳1,2,杜青林1,2,李 畅1,2,崔晓辉1,2,3,赵 兴1,2,3,喻海良1,2,3
1. 中南大学 高性能复杂制造国家重点实验室,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 机电工程学院,长沙 410083;
3. 中南大学 轻合金研究院,长沙 410083
摘 要:通过高温累积叠轧方法制备多层铜/铝复合带材。为获得高的界面结合强度,在叠轧前分别加热铜、铝带材至350、400、450和500 °C。采用拉伸试验评估其力学性能,通过光学显微镜和配备有能量色散光谱仪的扫描电子显微镜检测材料的显微组织。研究发现:随着轧制温度的升高,层状复合带材的极限拉应力、材料晶粒尺寸和扩散层厚度均增大。当轧制温度为400 °C时,复合带材具有最高的延展性,但屈服应力最低。随着轧制温度进一步升高,屈服应力和极限拉应力均增加,但延性略有下降。低温累积叠轧和高温累积叠轧制备的层状复合材料的力学性能分别由晶粒尺寸和扩散层厚度决定。
关键词:扩散层;铜/铝复合带材;累积叠轧;轧制温度;金属间化合物;力学性能
(Edited by Bing YANG)
Foundation item: Project (51674303) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project supported by National Youth Thousand Plan of China; Project (2018RS3015) supported by Huxiang High-Level Talent Gathering Program of Hunan Province, China; Project (2019CX006) supported by Innovation Driven Program of Central South University, China; Project supported by the Research Fund of the Key Laboratory of High Performance Complex Manufacturing at Central South University, China
Corresponding author: Hai-liang YU; Tel:+86-18511635397; E-mail: yuhailiang@csu.edu.cn, yuhailiang1980@tom.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(19)65069-7

