热轧对Ti-50.8Ni合金显微组织及摩擦学行为的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2021年第4期
论文作者:杨蕊 马巍 王超 王廷梅 王齐华
文章页码:967 - 979
关键词:Ti-Ni50.8合金;摩擦学性能;小角度晶界;重合位置点阵CSL晶界
Key words:Ti-50.8Ni alloy; tribological performance; small angle grain boundaries; coincidence site lattice (CSL) boundary
摘 要:研究室温下不同显微组织Ti-Ni50.8(摩尔分数,%)合金在往复运动模式下的摩擦学行为。与B19'相合金相比,热变形后奥氏体(B2)合金滑动过程中发生应力诱发马氏体相变,摩擦因数减小,耐磨性提高,但是多次热轧却降低合金的耐磨性。采用背散射电子衍射(EBSD)及透射电镜(TEM)对显微组织进行分析,结合相变能量损耗表明:强度较弱的热轧显微织构对其耐磨性的影响较小;奥氏体中{112}孪晶对B2-B19'相变的抑制作用明显强于高密度位错,与高KAM值的组织相比,合金中较高的重合位置点阵晶界可降低其马氏体相变开始温度。动态回复产生的大量小角度晶界和动态再结晶组织相当,可有效提高合金的耐磨性。
Abstract: We link different microstructures to tribological behaviors of Ti-50.8Ni (mole fraction, %) in reciprocating mode at room temperature (20 °C). Hot-rolled alloys with B2 phase exhibit lower coefficient of friction and wear rate compared to the ones with B19'. Stress-induced martensitic transformation occurs during sliding. However, multi-pass hot rolling weakens the wear resistance. In this study, microstructures were characterized through electron backscatter diffraction and transmission electron microscopy (EBSD/TEM). From the concept of energy conservation, the effects of weak intensity of hot-rolled textures on the wear resistance are minimal. Based on the result that the alloy with a higher portion of coincidence site lattice boundaries shows lower martensitic start transformation temperature in the DSC curves than that with higher KAM values, the delay on B2-B19' transformation from {112}B2 twins outweighs dislocations. Moreover, widely distributed small-angle grain boundaries owing to dynamic recovery improve the wear resistance effectively compared to those that are well-recrystallized.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 31(2021) 967-979
Rui YANG1,2, Wei MA1,2, Chao WANG1,2, Ting-mei WANG1,2, Qi-hua WANG1,2
1. State Key Laboratory of Solid Lubrication, Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Lanzhou 730000, China;
2. Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
Received 20 April 2020; accepted 15 January 2021
Abstract: We link different microstructures to tribological behaviors of Ti-50.8Ni (mole fraction, %) in reciprocating mode at room temperature (20 °C). Hot-rolled alloys with B2 phase exhibit lower coefficient of friction and wear rate compared to the ones with B19'. Stress-induced martensitic transformation occurs during sliding. However, multi-pass hot rolling weakens the wear resistance. In this study, microstructures were characterized through electron backscatter diffraction and transmission electron microscopy (EBSD/TEM). From the concept of energy conservation, the effects of weak intensity of hot-rolled textures on the wear resistance are minimal. Based on the result that the alloy with a higher portion of coincidence site lattice boundaries shows lower martensitic start transformation temperature in the DSC curves than that with higher KAM values, the delay on B2-B19' transformation from {112}B2 twins outweighs dislocations. Moreover, widely distributed small-angle grain boundaries owing to dynamic recovery improve the wear resistance effectively compared to those that are well-recrystallized.
Key words: Ti-50.8Ni alloy; tribological performance; small angle grain boundaries; coincidence site lattice (CSL) boundary
1 Introduction
TiNi shape memory alloys (TiNi SMAs) can be widely applied in industrial fields because of their irregular shape memory effect and pseudoelasticity attributed to stress introduced transformation (SIM) [1-3]. Researchers conducted extensive investigations on the deformation mechanisms and shape memory property of the alloy subjected to the hot rolling [4-7]. Generally, the dislocation slip and mechanical twinning are involved in the deformation [4-6]. A significant grain-size reduction, considerable amount of coherent precipitates, and defects introduced by ausforming will strengthen B2 matrix enormously. In addition to the dynamic recrystallization (DRx) and dynamic recovery (DRv) during the manufacturing at high temperatures, the microstructures of the alloys are crucial in determining their performance [8]. Moreover, the function, if any, of small angle grain boundaries (SAGBs, misorientation angle of θ<15°) existing extensively in the material in its tribology behaviors has never been explored in our view. Additionally, the twinning in the B2 phase is a crucial aspect of microstructure in the ausformed TiNi-based SMAs. The {112} and {114} twins in austenite phase directly correspond to the {113} and {201} twins in the B19' phase, respectively [9,10]. The Σ notation for various twins in the austenite phase is applied in the TiNi-based SMAs to explore their properties [11,12]. Furthermore, the correspondence between coincidence site lattice(CSL) boundaries and twin boundaries was explored in the TiNi alloy [13]. However, research exploring the phase transformation behaviors and performance of the complex microstructures under different service conditions is insufficient.
Recent studies concerning the applications of the alloy have reported that the alloys show outstanding wear resistance compared to the conventional metal materials [14]. Moreover, porous TiNi alloys display significant tribological performance owing to their self-adaptive behavior [15]. Therefore, studies demonstrating the tribological behaviors of the alloy have been conducted to explore their applications as wear-resistant materials [16-18]. WANG et al [16] revealed that the superior pseudoelasticity and transformation capacity of the TiNi SMAs endow them with excellent wear-resistance. Their unique stress–strain features have profound influence on the tribological behaviors under different experimental conditions [18]. Comprehensive experimental analyses of the effects of the grain size and phase state on their tribological behaviors were conducted [19-22]. MISOCHENKO et al [19] discovered that the worn surfaces of the alloy with small grain size could resist the adhesion more strongly than the coarse grain alloys. However, these experimental studies rarely focus on the tribological performance of the ausformed TiNi alloy.
As discussed above, hot rolling significantly influences the microstructure of the TiNi alloys, but the roles of the hot-rolled microstructures in wear performance of the alloys are ignored in current studies. Therefore, our study focuses on this topic. Through electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM), we identified the characteristics of the microstructures subjected to hot rolling. Additionally, reciprocating sliding wear tests were carried out to evaluate the corresponding tribological properties carefully. The findings elaborate the significant influence of the microstructure introduced from the thermo- mechanical processing on wear performance of the TiNi SMAs.
2 Experimental
The commercial 3.0 mm Ti-50.8Ni (at.%) sheets (TN-O) were subjected to hot rolling (Fig. 1(a)) at 850 °C to produce ausformed pieces with different microstructures. The samples were reduced to 2.0 mm in thickness via single pass hot rolling (TN-S). Multi-pass rolling (TN-M) was performed on the TN-S samples to reduce the thickness further. Before each pass rolling, the samples were annealed at 850 °C for 6 min. The hot rolling steps are summarized in Table 1. The transformation temperatures were analyzed by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC; Netzsch- STA449F3). X-ray diffraction (XRD) with Cu Kα radiation on EMPYRE was carried out to identify the major phases of the pieces. EBSD measure- ments of the hot-rolled samples were conducted. TEM samples were twin-jet polished in a solution of 6 vol.% HClO4 + 34 vol.% CH3(CH2)3OH + CH3OH after being mechanically worked to 40 μm. TEM images were obtained at an acceleration voltage of 300 kV using a Tenai F30.

Fig. 1 Schematic diagrams of hot rolling processing (a) and wear test (b)
Table 1 Description of rolling applied for TN-S and TN-M samples

All disks for wear tests were cut from hot-rolled sheets via electrical discharge machining. Before sliding wear, the alloys were mechanically polished and then electro-polished in an electrolyte of 20 vol.% H2SO4 + 80 vol.% CH3OH. Ball-on- plate wear tests were done at room temperature under linear reciprocating model (Fig. 1(b)) with constant normal loading of 3 N. GCr15 balls with diameter of 6 mm acted as counterfaces. The steel ball was slided against the rolled surface (ND) of the TiNi SMA at an average speed of 10 mm/s along the rolling direction (RD). The transverse direction (TD) is displayed in Fig. 1(b). The corresponding maximum contact stress (σmax) was estimated based on the Hertzian contact model, which was approximately 536 MPa. 3D profiles were used to calculate the wear rate carefully, and the worn surfaces were observed through scanning electron microscopy (SEM).
3 Results and discussion
3.1 DSC curves and XRD patterns
Figure 2 shows the DSC curves and XRD patterns of TN-O, TN-S, and TN-M samples. The transformation of all samples is a two-step process (B2-R, R-B19′) during cooling. Because the austenite initial temperature (As) for TN-O sample is slightly higher than the room temperature, the B19′ phase is retained if SIM occurs. The martensitic start transformation temperature (Ms) and As of the TN-S sample decrease significantly compared to the TN-M sample. Evidently, the martensitic transformation in the TN-S sample is retarded compared to that in the TN-M sample, though both sheets are in the B2 state, as shown in the XRD patterns. It is necessary to distinguish the effect of hot rolling on microstructures and reasonably elucidate the results.
3.2 Microstructure of hot-deformed alloys
Optical micrographs of the TN-O, TN-S, and TN-M samples in Figs. 3(a-c) show the presence of stripe-microstructure. It is the B19' in the TN-O sample but the B2 twins in the hot-rolled alloy. As shown in Figs. 3(d, e), inverse pole figure (IPF) maps of the TN-S and the TN-M samples clearly demonstrate the reduction in grain size. Moreover, the grains are homogenized after multiple hot rolling. DRx occurs during hot rolling, which is indicated from fine grains at triple boundaries (Fig. 3(d)). The abundant nucleation sites at the grain boundaries facilitate the recrystallized grains to nucleate significantly. Additionally, the grain orientation spread (GOS) map for the TN-S sample in Fig. 4 shows that the twins in the grains actively assist the formation of recrystallized grains, which is characterized by low misorientation angles. This can be attributed to the relatively large plastic strain in the twinned region. Regions with relatively high misorientation values are also observed.

Fig. 2 DSC curves for TN-O (a), TN-S (b) and TN-M (c) samples, and XRD patterns (d)

Fig. 3 Optical micrographs of TN-O (a), TN-S (b) and TN-M (c) samples, and IPF maps for TN-S (d) and TN-M (e) samples
Generally, a significant texture exists in the hot-rolled sample, specifically for non-ferrous metals. As shown by the IPF maps along the RD and TD for the TN-S and the TN-M samples in Fig. 5, the γ-fiber, <111> parallel to TD, is the main texture fiber in the hot-rolled sheets. However, the texture intensity is weak. Therefore, the effect of the texture on the tribology behaviors in the transverse direction can be negligible. The major differences are in the RD. The <101> fiber texture is prominent along the RD in the TN-S sample but it is the <111> fiber in the TN-M sample.

Fig. 4 Grain orientation spread map for TN-S sample

Fig. 5 Inverse pole figures (IPF) for TN-S (a) and TN-M (b) samples along RD and TD, respectively
To evaluate the local plastic strain and geometrically necessary dislocation (GND) activity properly, Kernel Average Misorientation (KAM) criterion presenting the average orientation difference between a point inside the grain and its adjacent neighbors in the same grain is applied. A high relative frequency of the high KAM (more than 1°) implies high density of dislocations [13]. Moreover, a more pronounced intergranular local misorientation in the TN-M sample implies that the dislocation density is high, which will be ascribed to the minor thickness reduction at the final pass. The KAM value of the microstructure subjected to hot deformation and DRv is lower than that of the DRx grains. That is, DRx narrows the KAM distribution [8], as shown in Figs. 6(a) and (c).
DRv and DRx will consume SAGBs and high angle grain boundaries (HAGBs, misorientation angle of θ>15° because of recrystallization. Black and green lines in Figs. 7(a) and (b) are the HAGBs and SAGBs, respectively. The significant accumulation of the SAGBs inside the grains in TN-S sample indicates the widespread occurrence of DRv. The annealing in-between the rolling passes increases the portion of the recrystallized grains in the TN-M sample. Nevertheless, the storage energy available from final step with small thickness reduction is insufficient for the occurrence of DRv. Therefore, a high KAM value is shown in Fig. 6(d).

Fig. 6 Histograms (a, c) and KAM maps (b, d) for TN-S (a, b) and TN-M (c, d) samples

Fig. 7 Grain boundary maps of TN-S (a) and TN-M (b) samples
Most studies on TiNi alloys focus on the martensitic transformation and corresponding performances. Nonetheless, the significant defect of the microstructure of SMA is the twinning in the austenite structure [6,9,12,13]. CSL boundaries correspond to the twin boundaries in the TiNi alloy. The Σ values of {112}, {114}, {113}, and {115} boundaries are Σ3, Σ9, Σ11 and Σ27, respectively [13]. The B2 phase is significantly refined during the thermal cycling and heterogeneous Σ3 and Σ9 boundaries are established [23]. Figure 8 shows the CSL features in the hot-rolled samples. The fraction of the CSL boundaries reduces from 8.24% in the TN-S sample to 4.7% in the TN-M sample. The proportion of the Σ3 boundary decreases significantly with multi- rolling processes.
To investigate the microstructure characters at a more microscopic scale, TEM images of the hot-rolled materials are shown in Figs. 9 and 10. The dominant planar defects are {112} compound twins in Fig. 9 whereas it is the {114} twins in Fig. 10. Furthermore, dislocations with various structures are established. As shown in Figs. 9(e, f), the dislocation annihilation associated to DRv could introduce dislocation cells in the TN-S sample, which is directly related to the SAGBs in Fig. 7(a). Fine grains characterized by low misorientation angles in Fig. 4 confirm the appearance of DRx. This explains the lower KAM value in the TN-S sample. The large portion of HAGBs in the TN-M sample is caused by DRx when it is subjected to multiple intermediate annealing and rolling. However, low storage energy created because of the small thickness reduction in the last pass cannot provide sufficient power to DRv. Consequently, as shown in Fig. 6(d), high dislocation regions (Fig. 10(b)) with high KAM values are observed. Moreover, dislocation couples showing the opposite Burgers vector are shown in Fig. 10(c). Notably, twinning in bcc solid solution is disfavored. This is because the nearest neighbor relations must be changed for the twinning in the B2-structure to indicate the formation of a new crystal structure. Consequently, the dislocation slip becomes an easier process. However, this study shows that it is not true for the deformation of the alloy at elevated temperatures, which is also confirmed by AHADI et al [5]. For the typical twin-lamellated micro- structure to originate in a wide range of ausforming conditions, the twinning process competes successfully with the dislocation slipping (Figs. 5 and 6). The main twins are the {112} and the {114} planes [11-13]. The deformation mechanism map of the B2 phase constructed by BENAFAN et al [6] shows similar results from 320 to 440 °C, which has been also confirmed in the local canning compression of Ti49.1Ni50.9 at 300 °C [24]. Twinning of the B2 austenitic phase is significant to accommodate the arbitrary deformation of the TiNi alloy. The combination of shear and shuffle in the B2 phase contributes to the occurrence of the {211} twin mirror symmetry, whereas an interface shift also occurs for the {114} twin [25,26]. The energy barriers for slip, {211}, and {114} twinning systems are 142, 79, and 148 mJ/m2, respectively [27]; thus, the {211} twining is preferred as a deformation mode. Therefore, the various planar defects and slip significantly influence the deformation of the alloy at high temperatures. The non-homogeneous distribution of internal stresses resulted from the specific arrangement of defects such as dislocations, twins, and point defects, which are the cause of the multistage transformation [28-31]. Dislocations and twins in the austenite phase hinder martensitic transformation [29,30]. Therefore, the obstruction to SIM from dislocations is slight compared to the {112} and {114} twins although they may hinder it.

Fig. 8 Histogram of CSL boundaries of TN-S and TN-M samples

Fig. 9 TEM micrographs for TN-S bright field (BF) image (a), selected area electron diffraction (SAED) patterns (b) of region A in (a) and corresponding schematic diagram (c), dark field (DF) image corresponding to  (d) and dislocation structures (e, f)
(d) and dislocation structures (e, f)
3.3 Wear results
The tribological behaviors of the samples are shown in Figs. 11 and 12. Furrows and plastic tearing in Fig. 11 suggest that abrasion occurs in all the samples. However, adhesive traces for the TN-M sample become significantly apparent in Figs. 11(c1–c3). This is because delaminating is the main wear mechanism for the TN-O and the TN-S samples. Wear rate (R) is based on a volumetric material loss using the following expression:
 (1)
(1)
where A is the average cross-sectional area of the wear track, L is the wear track length, N is the total sliding passes and Fn is the normal load [32]. The typical 3D profiles and cross-sectional area of scars are shown in Figs. 12(a-c). It is noteworthy that the wear rate of TN-S sample is (0.67±0.05)× 10-3 mm3/(N·m), which is lower than that of the TN-M sample ((1.07±0.08)×10-3 mm3/(N·m)) while the COF at stable stage for them is closely comparable (Fig. 12(d)). The COF of the TN-O sample is the highest in all the samples studied here, which is due to the weaker strength of B19' in TN-O sample [20]. The XRD results of the wear scars identify the understandable appearance of martensitic phase in all the scars (Fig. 12(e)). This demonstrates that the materials of the scars experience the SIM transformation during the sliding wear.

Fig. 10 TEM micrographs for TN-M BF image showing grain boundary and SAED pattern of area A inserted in (a), BF image showing high density of dislocation (b), BF image showing dislocation structure (c), BF image showing twins (d), corresponding SAED pattern (e), and DF image (f) of  diffraction spot in (e)
diffraction spot in (e)
The appearance of the B19' in the wear tracks is understandable. Calculations of elastic stress distributions indicate that the compression and shear stress are dominant during the reciprocating sliding [32]. HAMILTON and GOODMAN [33] established an elastic model and calculated the subsurface stress field in the sliding contact. They found that the position where the maximum shear stress (τmax) of the sample will shift to the contact surface or near surface as the friction pair being in dynamic contact. A significant relationship (τmax=0.56σmax) exists as the COF is 0.5. The investigation of the SIM transformation in TiNi alloy under compression-shear with different strain rates (10-4 to 103 s-1) indicates the occurrence of the localized transformation [34,35]. Moreover, the corresponding strain rate obtained during the sliding of copper at a speed of 10 mm/s is 10 s-1 [36]. Thus, the occurrence of SIM is critical to the tribological behaviors of the alloy in this study. The loading under the current condition is mild, and the contact stress is too small to initiate amorphization. Additionally, TN-S sample absorbs more friction energy and shows better wear- resistance. The martensitic transformation in the TiNi alloy is significantly influenced by the grain size as it changes in a wide range. The B19′ transformation occurs in the grains coarser than 60 nm, but it is absent in the smaller grains [37]. The coarse-grained (average grain size 35 μm) and ultrafine-grained (110 nm) Ti49.3Ni50.7 alloys are deformed by SIM [38]. According to the Clausius-Clapeyron equation for the thermoelastic martensitic transformation, 400 MPa is a representative critical stress corresponding to the SIM transformation at a temperature of 50 K above Ms [39]. This can verify the temperature dependence of the critical stress for transformation. From DSC curves for the TN-S samples, the Ms is approximately -25 °C. The critical stress of the SIM transformation at room temperature (20 °C) is is about 400 MPa. Furthermore, the appearance of the B19' in the worn microstructure at 20 °C (higher than Af for the TN-S, sample) indicates the occurrences of heavy plastic deformation of the martensite and the retained austenite.

Fig. 11 SEM micrographs of wear scars

Fig. 12 3D profiles and cross-sectional area of wear tracks for TN-O (a), TN-S (b) and TN-M (c) samples, COF (d), and XRD patterns of wear scars (e)
However, there is a great gap among the wear resistances, which may be attributed to the difference of the texture and microstructure. Considering the different textures along the RD and the orientation dependence of SIM transformation, we analyzed the influence by applying the contact theory. The tangential force on the contact surface affects the stress distribution and the size and shape of the contact surfaces. Nevertheless, the tangential and load force will affect each other when the elastic modulus and Poisson ratio of the two sliding bodies are different. As the COF is less than 1.0, the load and deformation caused by tangential force can be independent of each other, and the two can overlap to become equivalent stress [33]. SIM transformation and martensite reorientation both are important to the performance of the TiNi alloy. First, the energy per unit volume required to reorient martensite is independent of texture [40]. Hence, the main factor may be the dependence of the critical stress to the SIM. A Taylor-type model for textured alloys is used to explain the effect of the texture. The orientation dependence of the Taylor factor has been reported for the SIM transformation [41]. From concept of the energy conservation, BUCHHEIT et al [42] described the work of transformation as
 (2)
(2)
where 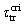 and
and  are the critical stresses for martensitic transformation in shear and tension, respectively, and
are the critical stresses for martensitic transformation in shear and tension, respectively, and  and
and  are the strains associated with the transformation in shear and tension in the [hkl] crystal orientation, respectively. The investigation on stress–strain response of single crystal established that the [110] orientation has a
are the strains associated with the transformation in shear and tension in the [hkl] crystal orientation, respectively. The investigation on stress–strain response of single crystal established that the [110] orientation has a  of 198 MPa whereas that of the [111] orientation is 235 MPa. Both orientations have similar experimental εtension values (5.3% and 5.1% for the [110] and [111] orientations, respectively) [43]. Therefore, the work of transformation in shear in the [110] orientation is slightly less than that in the [111] orientation. That is, the <111> fibers along the RD in the TN-M sample will improve any wear resistance when sliding along RD. However, the wear resistance of the TN-S sample is better than that of the TN-M sample. The low intensity of textures weakens its influence further.
of 198 MPa whereas that of the [111] orientation is 235 MPa. Both orientations have similar experimental εtension values (5.3% and 5.1% for the [110] and [111] orientations, respectively) [43]. Therefore, the work of transformation in shear in the [110] orientation is slightly less than that in the [111] orientation. That is, the <111> fibers along the RD in the TN-M sample will improve any wear resistance when sliding along RD. However, the wear resistance of the TN-S sample is better than that of the TN-M sample. The low intensity of textures weakens its influence further.
According to the Hall-Petch relationship in crystal bulk, grain size has a crucial influence on the strength of metal materials. As the grain size decreases, the strength and hardness of the metal material increase. Therefore, the wear resistance is strong. However, the TN-S samples show better wear resistance than the TN-M samples (Fig. 11), although the grain size decreases and they are more homogeneous (Fig. 3). Moreover, the adhesive component of the wear surface for the TN-M samples is more distinctive than that for the TN-S samples (Figs. 11(b) and (c)), which is different from the experimental results investigating the influence of grain size (30, 100 and 250 nm) of TiNi SMA on its corresponding tribological performance [19]. Meanwhile, the TN-O and TN-S samples show similar worn surfaces although they are in different phase states. Therefore, the substructures of the alloy significantly influence the wear mechanism. In particular, the wear rate for the TN-S sample is lower, albeit TN-S sample shows coarser grains compared with TN-M sample. This indicates that the grain size is not the critical aspect in current experiments. According to the microstructure results, sub-grains with SAGBs and low Σ are attributed to twinning, which may be mainly responsible for the results. The significant increase in the fraction of low Σ CSL boundaries improves properties of the materials. The introduction of special boundaries is critical to the grain boundary engineering. The Σ3 boundaries can act as barriers to plastic flow [44]. As shown in Fig. 8, the fraction of CSL boundaries in the TN-S sample is larger than that in the TN-M sample. Dislocations suppress the SIM transformation and lower the value of Ms [29]. However, the interruption from the high density of dislocations may be minor compared to that of the twins. This is because the microstructure with higher KAM values displays higher Ms than that with larger portion of CSL boundaries. The {112} twin in austenite phase is similar to the {113} twin in the B19′ [9]. The Σ3 {112} boundaries can transform to martensitic grain and twin boundaries during martensitic transformation and delay the transformation [45,46]. The {112} twin stabilizes the B2 austenite and predominantly enhances the stress level of the TiNi SMA [30]. Additionally, SAGB is an important factor. Some parts of grains are in austenitic state while a substantial volume of grains transforms. The retained austenite is subjected to deformation exceeding the martensite elasticity during sliding. SAGBs act as strong barrier for the dislocation motion [47]. SAGBs and the high density of dislocations strengthen the retained austenitic grains and improve the wear resistance; nevertheless, the function of SAGBs is not limited to that because of the high plasticity owing to their easy migration [48]. Consequently, the wear resistance is improved. Therefore, it is necessary to induce the CSL boundaries and SAGBs to acquire excellent tribological performance of the Ti-50.8Ni alloy.
4 Conclusions
(1) The TN-S and TN-D samples show the <111> fiber along the TD. TN-S sample displays the <101> fiber along the RD, whereas the TN-M sample displays the <111> fiber along the RD. Based on the concept of energy conservation, Taylor-type model for textured alloys, and the intensity of textures, the influences of hot-rolled textures on the wear resistance are small.
(2) SAGBs associated to the DRv, small DRx grains with low in-grain misorientation existed in both coarse grains and triple boundaries were observed in single pass hot-rolled sheets. The reduced and homogenized grain size with high KAM values is the prominent microstructures subjected to multiple pass hot rolling in addition to the low SAGBs.
(3) During hot rolling, the deformation of the Ti-50.8Ni sample is governed by the {112}B2 and the {114}B2 mechanical twins and dislocations. In particular, the {112}B2 is relatively dominant in the TN-S sample, but the {114}B2 is primary in the TN-M sample. Moreover, dislocation cells are widely distributed in the TN-S sample whereas high densities of dislocation regions and dislocation couples are obtained in the TN-M sample.
(4) The tribology behaviors of the coarse grain Ti-50.8Ni are not only related to the phase composition, but also greatly influenced by the substructures of the B2 matrix. The {112}B2 twins hinder the B2-B19' transformation significantly compared with a high density of dislocation, but it cannot suppress the martensitic trasfomation completely. SAGBs accommodate plastic deformation further. Therefore, the introduction of a large proportion of SAGBs and low-Σ CSL boundaries in the austenite Ti-50.8Ni alloy via hot rolling, specifically the Σ3, improves the wear resistance of the coarse grain alloy.
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China-Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation of China Aerospace Advanced Manufacturing Technology Research Joint Fund (U1737204), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51673205) and the Key Research Program of Frontier Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences (QYZDJ-SSW-SLH056).
References
[1] OTSUKA K, REN Xiao-bin. Physical metallurgy of Ti-Ni-based shape memory alloys [J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2005, 50: 511-678.
[2] BAHADOR A, HAMAZAH E, KONDOH K, ASMA ABUBAKAR T, YUSOF F, UMEDA J, SAUD S N, IBRAHIM M K. Microstructure and superelastic properties of free forged Ti-Ni shape-memory alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28(3): 502-514.
[3] JIANG Shu-yong, YU Jun-bo, ZHANG Yan-qiu, XING Xiao-dong. Mechanically-induced martensite transformation of NiTiFe shape memory alloy subjected to plane strain compression [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2020, 30(5): 1325-1334.
[4] SURESH K S, KIM D I, BHAUMIK S K, SUWAS S. Evolution of microstructure and texture in Ni49.4Ti38.6Hf12 shape memory alloy during hot rolling [J]. Intermetallics, 2013, 42: 1-8.
[5] AHADI A, REZAEI E, TAHERI A K. Effect of hot rolling on microstructure and transformation cycling behaviour of equiatomic NiTi shape memory alloy [J]. Material Science and Technology, 2012, 28: 727-732.
[6] BENAFAN O, NOEBE R D, PADULA S A, GARG A, CLAUSEN B, VOGEL S, VAIDYANATHAN R. Temperature dependent deformation of the B2 austenite phase of a NiTi shape memory alloy [J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2013, 51: 103-121.
[7] ATAEI M, ZAREI-HANZAKI A, SHAMSOLHODAEI A. Shape memory response and mechanical properties of warm deformed NiTi intermetallic alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2017, 680: 291-296.
[8] BASU R, JAIN L, MAJI B, KRISHNAN M. Dynamic recrystallization in a Ni-Ti-Fe shape memory alloy: Effects on austenite-martensite phase transformation [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 639: 94-101.
[9] COWDHURY P, SEHITOGLU H. Deformation physics of shape memory alloys: Fundamentals at atomistic frontier [J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2017, 88: 49-88.
[10] KARAMAN I, KULKARNI A V, LUO Z P. Transformation behaviour and unusual twinning in a NiTi shape memory alloy ausformed using equal channel angular extrusion [J]. Philosophical Magazine, 2005, 85: 1729-1745.
[11] II S, MATSUDA M, MATSUI T, FUJIMOTO T, KAKISAKA A, KIKUTAKE T, TSUREKAWA S, IKEDA K I, NISHIDA M. Controlling grain boundary character distribution of high-temperature B2 phase in Ti-Ni-Fe alloy [J]. Intermetallics, 2012, 31: 65-71.
[12] SURESH K S, KIM D I, BHAUMIK S K, SUWAS S. Interrelation of grain boundary microstructure and texture in a hot rolled Ni-rich NiTi alloy [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2012, 66: 602-605.
[13] NISHIDA M, MATSUDA M, FUJIMOTO T, TANKA K, KAKISAKA A, NAKASHIMA H. Crystallography of deformation twin boundaries in a B2 type Ti-Ni alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2006, 438: 495-499.
[14] ZHANG C, FARHAT Z N. Sliding wear of superelastic TiNi alloy [J]. Wear, 2009, 267: 394-400.
[15] LI Xiao-lei, CHEN Xin-chun, ZHANG Chen-hui, LUO Jian-bin. Preparation of self-lubricating NiTi alloy and its self-adaptive behavior [J]. Tribology International, 2019, 130: 43-51.
[16] WANG Yun-xue, XU Ren-bo, HU Sheng-mou, TU Fu-quan, JIN Wei-wei. Research combining experiment and FEM analysis on sliding wear behaviors and mechanisms of TiNi alloy [J]. Wear, 2017, 386-387: 218-222.
[17] ARCNIEGAS A, CASALS J, MANERO J M, PENA J, GIL F J. Study of hardness and wear behaviour of NiTi shape memory alloys [J]. Journal of Alloy and Compounds, 2008, 460: 213-219.
[18] LEVINTANT-ZAYONTS N, STARZYNSKI G, KUCHARSKI S, KOPEC M. Characterization of NiTi SMA in its unusual behaviour in wear tests [J]. Tribology International, 2019, 137: 313-323.
[19] MISOCHENKO A A, CHERTOVSKIKH S V, SHUSTER L S, STOLYAROV V V. Influence of grain size and contact temperature on the tribological behaviour of shape memory Ti49.3Ni50.7 alloy [J]. Tribology Letter, 2017, 65: 1-7.
[20] GIALANELLA S, ISCHIA G, STRAFFELINI G. Phase composition and wear behavior of NiTi alloys [J]. Journal of Material Science, 2008, 43: 1701-1710.
[21] YAN L, LIU Y. Effect of temperature on the wear behavior of NiTi shape memory alloy [J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2015, 30: 186-196.
[22] NEUPANE R, FARHAT Z. Wear and dent resistance of superelastic TiNi alloy [J]. Wear, 2013, 301: 682-687.
[23] BUCSEK A N, CASALENA L, PAGAN D C, PAUL P P, CHUMLYAKOV Y, MILLS M J, STEBNER A P. Three- dimensional in situ characterization of phase transformation induced austenite grain refinement in nickel-titanium [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2019, 162: 361-366.
[24] HU Li, JIANG Shu-yong, LIU Si-wei, ZHANG Yan-qiu, ZHAO Ya-nan, ZHAO Cheng-zhi. Transformation twinning and deformation twinning of NiTi shape memory alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2016, 660: 1-10.
[25] EZAZ T, SEHITOGLU H. Coupled shear and shuffle modes during twin growth in B2-NiTi [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2011, 98(24): 241906.
[26] EZAZ T, SEHITOGLU H, MAIER H. Energetics of (114) twinning in B2 NiTi under coupled shear and shuffle [J]. Acta Materialia, 2012, 60: 339-348.
[27] EZAZ T, WANG J, SEHITOGLU H, MAIER H. Plastic deformation of NiTi shape memory alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 2013, 61: 67-78.
[28] CHROBAK D, STROZ D, MORAWIEC H. Effect of early stages of precipitation and recovery on the multi-step transformation in deformed and annealed near-equiatomic NiTi alloy [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2015, 48: 571-576.
[29] ZHANG Jian, SOMSEN C, SIMON T, DING Xiang-dong, HOU Sen, REN Shuai, REN Xiao-bing, EGGELER G, OTSUKA K, SUN Jun. Leaf-like dislocation substructures and the decrease of martensitic start temperatures: A new explanation for functional fatigue during thermally induced martensitic transformations in coarse-grained Ni-rich Ti-Ni shape memory alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 2012, 60: 1999-2006.
[30] ZHANG Yan-qiu, JIANG Shu-yong, WANG Man, Atomistic investigation on superelasticity of NiTi shape memory alloy with complex microstructures based on molecular dynamics simulation [J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2020, 125: 27-51.
[31] SEHITOGLU H, JUN J, ZHANG X, KARAMAN I, CHUMLYKOV Y, MAIER H J, GALL K. Shape memory and pseudoelastic behavior of 51.5%Ni-Ti single crystals in solutionized and overaged state [J]. Acta Materialia, 2001, 49: 3609-3620.
[32] OLVER A V, SPIKES H A, BOWER A F, JOHNSON K L. The residual-stress distribution in a plastically deformed model asperity [J]. Wear, 1986, 107: 151-174.
[33] HAMILTON G M, GOODMAN L E. The stress field created by a circular sliding contact [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1966, 33: 371-376.
[34] ELIBOL C, WAGNER M F X. Investigation of the stress- induced martensitic transformation in pseudoelastic NiTi under uniaxial tension, compression and compression-shear [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2015, 621: 76-81.
[35] ELIBOL C, WAGNER M F X. Strain rate effects on the localization of the stress-induced martensitic transformation in pseudoelastic NiTi under uniaxial tension, compression and compression-shear [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2015, 643: 194-202.
[36] CHEN X, SCHNEIDER R, GUMBSCH P, GREINER C. Microstructure evolution and deformation mechanisms during high rate and cryogenic sliding of copper [J]. Acta Materialia, 2018, 161: 138-149.
[37] BIAN X, SALEH A A, PERELOMA E V, DAVIES C H J, GAZDER A A. A digital image correlation study of a NiTi alloy subjected to monotonic uniaxial and cyclic loading-unloading in tension [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2018, 726: 102-112.
[38] KUMAR J V T, JAYAPRAKASAM S, PADMANABHAN K A, MISOCHENKO A A, STOLYATOV V V. On the tensile behaviour of coarse and ultrafine grained NiTi [J]. Materials Characterization, 2019, 149: 41-51.
[39] LIU Y O, YANG H. The concern of elasticity in stress- induced martensitic transformation in NiTi [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1999, 260: 240-245.
[40] LAPLANCHE G, BIRK T, SCHNEIDER S, FRENZEL J, EGGELER G. Effect of temperature and texture on the reorientation of martensite variants in NiTi shape memory alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 2017, 127: 143-152.
[41] NOBORU O, ATSUSHI A, HIROYUKI O. A discussion on the mechanical properties of shape memory alloys based on a polycrystal model [J]. Materials Transactions, JIM, 1989, 30(10): 756-764.
[42] BUCHHEIT T E, KUMPF S L, WERT J A. Stress-induced martensitic transformation of a NiTi alloy in isothermal shear, tension and compression [J]. Acta Materialia, 1998, 46(15): 5579-5591.
[43] GALL K, SEHITOGLU H, CHUMLYAKOV Y I, KIREEVA I V. Tension-compression asymmetry of the stress–strain response in aged single crystal and polycrystalline NiTi [J]. Acta Materialia, 1999, 47(4): 1203-1217.
[44] RANDLE V. Twinning-related grain boundary engineering [J]. Acta Materialia, 2004, 52: 4067-4081.
[45] QIN Sheng-jian, SHANG Jia-xiang, WANG Fu-he, CHEN Yue. Symmetrical tilt grain boundary engineering of NiTi shape memory alloy: An atomistic insight [J]. Materials and Design, 2018, 137: 361-370.
[46] ZHEN Zhi-bin, SHANG Jia-xiang, CHEN Yue. Shear deformation behavior of the austenitic Σ3{112} twin boundary in NiTi shape memory alloy: An atomistic study [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 509: 145318.
[47] CHEN Si-jing, YU Qian. The role of low angle grain boundary in deformation of titanium and its size effect [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2019, 163: 148-151.
[48] BOBYLEV S V, OVID’KO I A. Stress-driven migration of deformation-distorted grain boundaries in nanomaterials [J]. Acta Materialia, 2015, 88: 260-270.
杨 蕊1,2,马 巍1,2,王 超1,2,王廷梅1,2,王齐华1,2
1. 中国科学院 兰州化学物理研究所 固体润滑国家重点实验室,兰州 730000;
2. 中国科学院 材料科学与光电工程中心,北京 100049
摘 要:研究室温下不同显微组织Ti-Ni50.8(摩尔分数,%)合金在往复运动模式下的摩擦学行为。与B19'相合金相比,热变形后奥氏体(B2)合金滑动过程中发生应力诱发马氏体相变,摩擦因数减小,耐磨性提高,但是多次热轧却降低合金的耐磨性。采用背散射电子衍射(EBSD)及透射电镜(TEM)对显微组织进行分析,结合相变能量损耗表明:强度较弱的热轧显微织构对其耐磨性的影响较小;奥氏体中{112}孪晶对B2-B19'相变的抑制作用明显强于高密度位错,与高KAM值的组织相比,合金中较高的重合位置点阵晶界可降低其马氏体相变开始温度。动态回复产生的大量小角度晶界和动态再结晶组织相当,可有效提高合金的耐磨性。
关键词:Ti-Ni50.8合金;摩擦学性能;小角度晶界;重合位置点阵CSL晶界
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Corresponding author: Qi-hua WANG; Tel: +86-931-4968180; E-mail: wangqh@licp.cas.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(21)65553-X
1003-6326/ 2021 The Nonferrous Metals Society of China. Published by Elsevier Ltd & Science Press
2021 The Nonferrous Metals Society of China. Published by Elsevier Ltd & Science Press

