DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2020-39720
采用溶剂热法制备的钠离子电池用石墨烯基锡铜负极材料
董 强1, 2,徐海嵩1, 2,潘 飞3,王沛然3,何雨石3,李林森3,马紫峰3
(1. 日立(中国)研究开发有限公司上海分公司,上海 200020;
2. 上海交通大学-日立材料创新联合实验室,上海 200240;
3. 上海交通大学 化学化工学院,上海电化学能源器件工程技术研究中心,上海 200240)
摘 要:将原位溶剂热法、冷冻干燥和高温煅烧相结合,制备了石墨烯基锡铜复合物(SnCu@GS)。对SnCu@GS的嵌钠特性和电化学性能进行了研究。结果表明:在溶剂热反应中,石墨烯构建了一个三维多孔导电网络且片层上均匀分布着直径约70 nm的锡铜纳米颗粒。通过相同方法制备的无石墨烯支撑的锡铜小球的粒径差异较大,分布范围为200~4 μm。这表明作为石墨烯导电网络来源的氧化石墨烯的引入可以有效防止纳米颗粒在反应过程中的二次团聚。SnCu@GS具有较好的循环稳定性和倍率性能,在200 mA/g电流密度下循环200次依然具有150 mA·h/g的可逆容量。
关键词:石墨烯;溶剂热法;锡铜;纳米颗粒;钠离子电池
文章编号:1004-0609(2021)-04-0931-07 中图分类号:TQ152 文献标志码:A
引文格式:董 强, 徐海嵩, 潘 飞, 等. 采用溶剂热法制备的钠离子电池用石墨烯基锡铜负极材料[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2021, 31(4): 931-937. DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2020-39720
DONG Qiang, XU Hai-song, PAN Fei, et al. Graphene-based SnCu anode synthesized via solverthermal method for sodium ion batteries[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2021, 31(4): 931-937. DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2020-39720
与锂离子电池相比,钠离子电池无论是成本还是安全性都占据一定的优势,非常适合应用在储能系统中[1-2]。但是钠离子半径(0.102 nm)比锂离子半径(0.069 nm)大 70%,这使得钠离子在电池材料中的嵌入与脱出相对缓慢,因此寻找具有良好脱嵌钠性能的材料已成为目前该领域的研究热点。
钠离子电池负极材料主要有三类,即嵌入类(碳材料和钛基氧化物等)、合金类(Sn,Sb,P 等)和转化类(MOx,MSx等)[3-4]。嵌入类材料一般循环寿命较好,但容量较低。合金类和转化类材料具有较高的理论容量,然而它们在充放电过程中会产生较大的体积膨胀,破坏电极结构的完整性,严重影响循环稳定性。因此,有效地设计材料结构(如微纳结构)与缓冲基质复合(如碳材料)来改善这类材料的电化学性能,成为重要的研究方向。
在一个较窄的电压区间内,具有较高嵌钠性能的材料必然具有较大的体积膨胀效应。单质锡完全嵌钠形成Na15Sn4合金时,其体积膨胀高达424%[5],因此引入导电性好、具有包覆抑制作用的缓冲材料是十分必要的[6]。石墨烯具有高电导率和良好的柔韧性等优点,是作为缓冲材料的一个合适的选择。本文通过溶剂热与高温还原相结合的方法制备了石墨烯基锡铜复合物,并对其结构、嵌钠特性和电化学性能进行研究。
1 实验
1.1 材料制备
三维多孔石墨烯基锡铜复合物(SnCu@GS)的制备过程如下:首先,以天然石墨为原料,采用改良的Hummer法制取氧化石墨;接着,将30 mg氧化石墨超声分散于30 mL乙醇溶液中形成混合液。超声分散时,需向混合液中加入数滴去离子水以使氧化石墨表面充分浸润并在乙醇溶液中分散均匀,形成氧化石墨烯(GO)分散液。SnCl4·5H2O和Cu(CH3COO)2·H2O作为锡源和铜源,按摩尔比9:1分别向GO分散液中加入282.15 mg和17.85 mg,进一步进行超声分散。将以上分散均匀的混合溶液置于100 mL具有聚四氟乙烯内衬的水热釜中,在180 ℃下反应12 h,随后自然冷却至室温,制得黑色圆柱体凝胶。将凝胶浸入去离子水中10 h,以除去残留在凝胶中的杂质离子,然后通过冷冻干燥方法获得能保持三维结构的部分还原的SnO2·CuO@GO气凝胶。将干燥后的部分还原的SnO2·CuO@GO气凝胶样品在800 ℃的氢氩混合气氛(5%氢气,体积分数)下烧结1 h,即制备出SnCu@GS复合物。为了比较,通过以上类似过程制备了无石墨烯的锡铜粉末样品(SnCu powder)。
1.2 材料结构分析与表征
1.2.1 X射线衍射分析(XRD)
通过对实验制备的两种材料进行X射线衍射分析,并对比标准卡片,获得了材料的组成和结晶度等信息。本研究采用日本Rigaku公司生产的D/max-2200/PC型X射线衍射仪。以Cu(Kα)为辐射源,管电压为40 kV,管电流为30 mA,扫描速度为6 (°)/min,扫描范围为20°~80°。
1.2.2 X射线光电子能谱分析(XPS)
采用XPS分析SnCu@GS复合物表面的元素种类和金属价态,通过对碳谱的分峰拟合证明了氧化石墨烯被部分还原。氧谱中Sn—O键的拟合峰结合XRD数据进一步证明了石墨烯与锡铜颗粒间的电荷作用。本实验采用Kratos Axis Ultra DLD型X射线光电子能测试仪,且采用标准C 1s峰位置(结合能284.8 eV)进行标定。
1.2.3 场发射扫描电子显微镜(FESEM)
采用SEM的二次电子信号成像来观察SnCu@GS和锡铜粉末样品的表面形貌以及粒径大小。本研究采用美国FEI公司生产的Nova SEM 230型扫描电子显微镜。样品测试前先将导电胶粘贴在样品台上,再将少量的样品粉末粘在导电胶上,然后进行表面镀铂处理,最后放入仪器中进行观察。
1.2.4 透射电子显微镜(TEM)
透射电子显微镜主要用于观察SnCu@GS复合物纳米尺度下的局部形貌和颗粒分布状况,同时结合电子衍射图计算晶格间距,分析锡铜颗粒的晶面生长方向。本研究采用日本JEOL公司生产的JEM-2100F型号的透射电子显微镜。测试前将少量样品分散到乙醇中,超声处理5 min,然后滴到铜网上面,待干燥后测试。
1.3 电化学性能测试
以SnCu@GS复合物为活性组分、聚偏氟乙烯(PVDF)为黏结剂、碳黑(super P)为导电剂按质量比75:15:10搅浆涂布到铜箔上,经过切割压片后置于真空烘箱中80 ℃干燥4 h。测试用的扣式电池(CR2016)在有氩气保护的手套箱中进行;对电极为金属钠片,隔膜采用日本Advantec公司生产的GA 55型玻璃纤维膜;电解液选用1.0 mol/L NaClO4/PC体系。钠离子半电池在LAND CT2001A电池测试系统下进行恒流充放电,电压区间为0.01~0.75 V(vs Na/Na+)。充放电比容量以复合物在电极材料中所占的质量来计算。循环伏安测试在CHI 660型电化学工作站上进行,扫描速度为0.5 mV/s。所有电化学测试均在室温下进行。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 三维多孔SnCu@GS复合物表征
2.1.1 XRD分析
铜修饰锡粉末样品和石墨烯负载锡复合物的XRD谱如图1所示。SnCu@GS以石墨烯为基底,其负载物由两相组成,分别为单质锡和Sn5Cu6合金相[7],谱图同标准卡片完全吻合,没有其他杂质相出现。锡的峰强度远大于Sn5Cu6的,说明单质锡是主相,这是由于实验中加入的铜盐摩尔量仅为锡盐的1/9。同时,尖锐的锡峰说明颗粒结晶性好,还原程度高[8]。
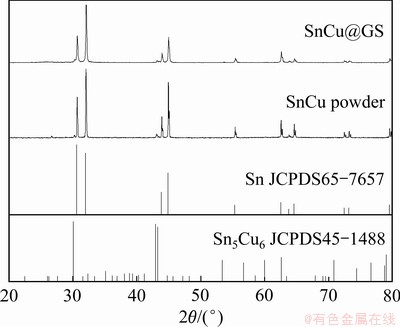
图1 SnCu粉末和SnCu@GS复合物的XRD谱
Fig. 1 XRD patterns for SnCu powder and SnCu@GS composite
2.1.2 XPS分析
对SnCu@GS复合物进行X射线光电子能谱分析(见图2),主要考察材料表面碳原子和氧原子的 化学键形式。由图2(a)可以看出,经过溶剂热和高温还原过程后,碳元素主要以C—C/C=C的形式存在[9],说明大部分羟基和羧基官能团已经被去除,石墨烯的还原程度较高[10]。图2(b)给出了结合能在530~536 eV处的O 1s谱,通过对谱图进行分峰和拟合可以发现,结合能在531 eV处存在Sn—O键,这说明依靠原位溶剂热方法和高温还原法制备的SnCu@GS材料中是存在化学键作用的。这种相互作用强于普通的物理吸附,是材料结构稳定的主要原因。
2.1.3 SEM、EDS和TEM分析
图3所示为SnCu@GS复合物和SnCu粉末的场发射扫描电镜像。从图3(a)~(c)可以看出,氧化石墨烯参与的溶剂热反应可以有效地制备出粒径小于90 nm的纳米锡铜颗粒,且颗粒在石墨烯片层上均匀双面负载,没有出现明显的堆积和团聚的现象。同时,石墨烯片的三维多孔结构也清晰可见,片层上还存在直径在50~80 nm的介孔,有利于电解液的浸润和钠离子的脱嵌。而图3(d)~(f)则与图3(a)~(c)形成鲜明对比,使用相同方法制备的锡铜合金在煅烧后团聚明显,颗粒直径相差超过1 μm,这直接导致其很难通过搅浆涂布的办法制备出均一的电极片。
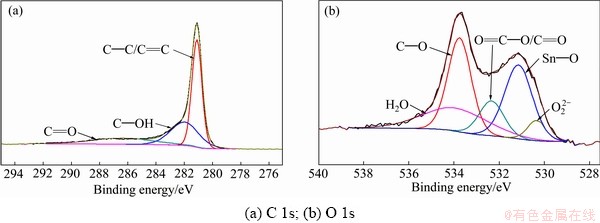
图2 SnCu@GS复合物的XPS谱
Fig. 2 XPS spectra of SnCu@GS composite
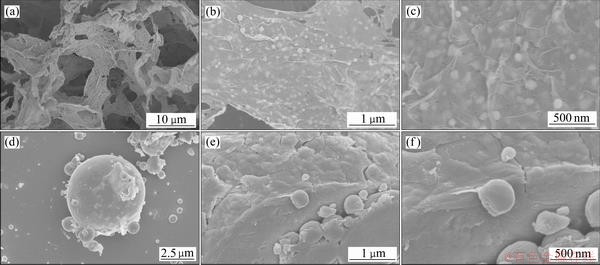
图3 SnCu@GS复合物和SnCu粉末的场发射扫描电镜像
Fig. 3 FESEM images of SnCu@GS composite((a), (b), (c)) and SnCu powder((d), (e), (f))
SnCu@GS复合物和锡铜粉末的EDS能谱分析结果如图4所示。由图4可知,分布在两种材料表面主要是单质锡,微量铜分布在锡球的表面,以Sn5Cu6合金相的形式存在。SnCu@GS复合物中氧元素主要来自石墨烯表面残留的羟基、羧基官能团以及连接石墨烯和单质锡两种物质的 C—O—Sn键(见图4(b))。锡元素的含量远高于氧元素的,说明二氧化锡经两步还原后基本没有残留。这一结果与XRD谱结论一致。
从图5(a)~(c)可以看出,纳米复合物颗粒的直径为50~90 nm,颗粒分布均匀,有效利用了石墨烯大比表面积的优势。图5(d)所示为纳米锡铜和石墨烯界面的高分辨TEM像,插图所示为晶格条纹作快速傅里叶变换(FFT)后获得的电子衍射图。通过软件计算得到颗粒上的晶间距为0.20 nm,这与XRD中单质锡标准卡片65-7657的(211)面的晶间距相一致[11]。
2.2 电化学性能
图6所示为SnCu@GS复合物在0.5 mV/s扫描速度下测得的循环伏安曲线。由图6可以发现,材料的两个主要氧化峰电位分别为0.63 V和0.75 V处,还原峰电位低于0.5 V,因此充放电电压区间应选择在0.01~0.75 V之间。
图7(a)所示为SnCu@GS复合物的倍率性能。在不同的电流密度下半电池均表现出良好的循环稳定性:材料首次可逆容量为388 mA·h/g,首次库伦效率为52%;循环50次后,当电流密度恢复到100 mA/g时,该材料的可逆容量依然保持在310 mA·h/g。这表明石墨烯在充放电过程中有效地抑制了锡嵌钠过程的体积膨胀效应,防止了容量的快速衰减。图7(b)所示为SnCu@GS复合物在不同电流密度下的充放电曲线。可以发现充电曲线中有两个较明显的电压平台,平均电压值在大约0.2 V和0.63 V处,说明这两个电压下存在大量的脱钠反应[12]。
在电流密度200 mA/g下进一步测试了材料的循环稳定性能(见图8)。循环200次后SnCu@GS的可逆比容量依然保持在150 mA·h/g左右,这表明材料结构相对稳定,石墨烯构建的三维网络有效抑制了锡在嵌钠过程中的团聚现象以及在脱钠过程中的粉体破碎现象[13-15],适合对具有脱嵌钠性能的活性材料进行改性并应用于钠离子电池体系。
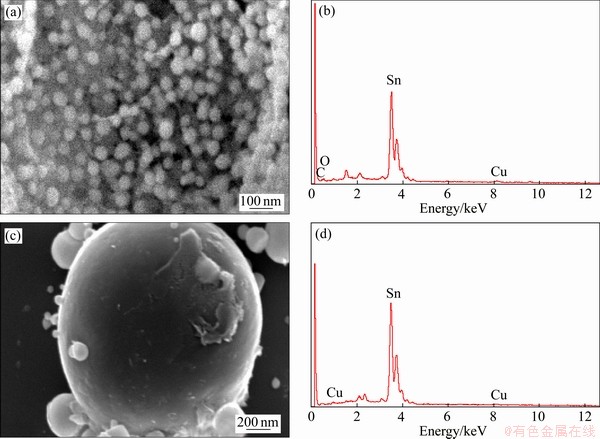
图4 SnCu@GS复合物和SnCu粉末的SEM像和EDS能谱分析结果
Fig. 4 SEM images((a), (c)) and EDS spectra((c), (d)) for SnCu@GS composite((a), (b)) and SnCu powder((c), (d))
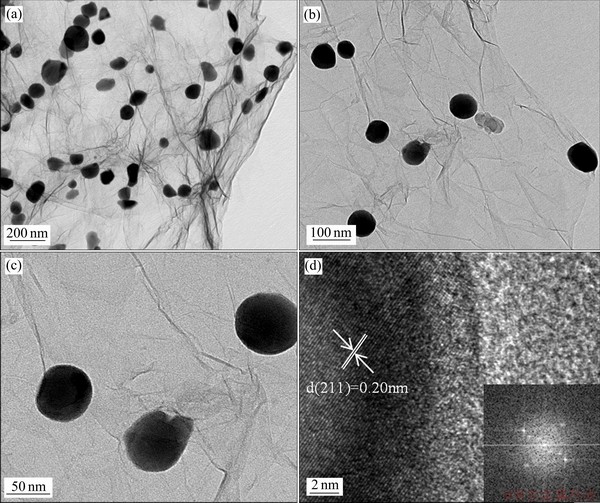
图5 SnCu@GS复合物的TEM像和高分辨TEM像
Fig. 5 TEM images((a), (b), (c)) and HRTEM image(d) of SnCu@GS composite
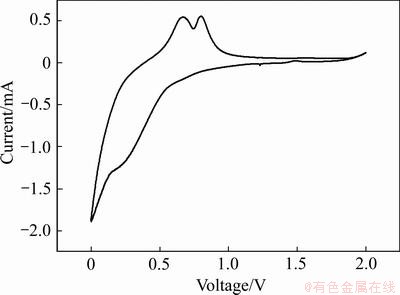
图6 以扫描速度0.5 mV/s在0.01~2.0 V电压区间内测定的SnCu@GS复合物的循环伏安曲线
Fig. 6 CV curves of SnCu@GS composite in potential range from 0.01 V to 2.0 V at scanning rate of 0.5 mV/s
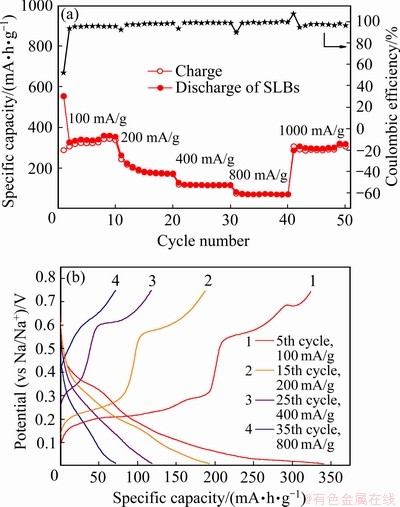
图7 SnCu@GS复合物的倍率性能和不同电流密度下的充放电曲线
Fig. 7 Rate capability of SnCu@GS(a) and voltage profiles of SnCu@GS composite at different current densities(b)
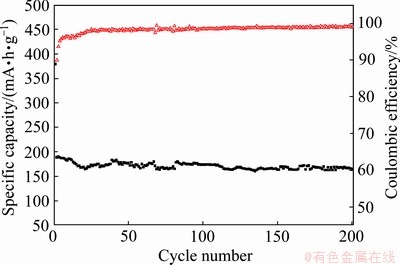
图8 SnCu@GS复合物在200 mA/g电流密度下的循环性能和相应的库仑效率
Fig. 8 Cycle performance(a) and coulombic efficiency(b) of SnCu@GS composite at current density of 200 mA/g
3 结论
1) 通过原位溶剂热反应、冷冻干燥和高温还原相结合的方法,成功制备出适用于钠离子电池的SnCu@GS复合负极材料。在溶剂热反应中,直径约70 nm的锡铜纳米颗粒均匀分布在石墨烯构建的三维多孔导电网络且片层上。而通过相同方法制备的无石墨烯支撑的锡铜小球的粒径差异较大,分布范围为200 nm~4 μm。其中,作为石墨烯导电网络来源的氧化石墨烯用作表面活性剂,有效地抑制了反应过程中纳米颗粒的二次团聚。
2) SnCu@GS复合材料具有较好的倍率和循环性能,在0.01~0.75 V的充放电区间, 200 mA/g电流密度下循环200次依然具有150 mA·h/g的可逆容量,这与石墨烯和铜元素的引入是密切相关的。更重要的是,通过本方法可以制备其他石墨烯金属负载材料,并有望应用于催化及其他能源领域。
REFERENCES
[1] NAYAK P, YANG Liang-tao, BREHM W, et al. From lithium-ion to sodium-ion batteries: Advantages, challenges, and surprises[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Edition), 2018, 57(1): 102-120.
[2] HWANG Jang-yeon, MYUNG Seung-taek, SUN Yang-kook. Sodium-ion batteries: Present and future[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(12): 3529-3614.
[3] ALCANTARA R, JIMENEZ-MATEOS J, LAVELA P, et al. Carbon black: A promising electrode material for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2001, 3(11): 639-642.
[4] JIAN Ze-lang, ZHAO Bin, LIU Pan, et al. Fe2O3 nanocrystals anchored onto graphene nanosheets as the anode material for low-cost sodium-ion batteries[J]. Chemical Communications, 2014, 50(10): 1215-1217.
[5] LI M Y, DU Z J, KHALEEL M A, et al. Materials and engineering endeavors towards practical sodium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2020, 25: 520-536.
[6] LI Zhi, DING Jia, MITLIN D. Tin and tin compounds for sodium ion battery anodes: Phase transformations and performance[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2015, 48(6): 1657-1665.
[7] LIN Yong-mao, ABEL P, GUPTA A, et al. Sn-Cu nanocomposite anodes for rechargeable sodium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2013, 5(17): 8273-8277.
[8] DERRIEN G, HASSOUN J, PANERO S, et al. Nanostructured Sn-C composite as an advanced anode material in high-performance lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2007, 19(17): 2336-2340.
[9] ZHANG Hong-wei, ZHOU Liang, YU Cheng-zhong. Highly crystallized Fe2O3 nanocrystals on graphene: A lithium ion battery anode material with enhanced cycling[J]. RSC Advances, 2014, 4(1): 495-499.
[10] MA Jing-jing, WANG Jiu-lin, HE Yu-Shi, et al. A solvothermal strategy: One-step in situ synthesis of self- assembled 3D graphene-based composites with enhanced lithium storage capacity[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(24): 9200-9207.
[11] JEONG N, HWANG K, YANG S, et al. Controlled growth, characterization and thermodynamic behavior of bismuth-tin nanostructures sheathed in carbon nanotubes[J]. Materials Characterization, 2014, 89: 69-80.
[12] BAGGETTO L, GANESH P, MEISNER R, et al. Characterization of sodium ion electrochemical reaction with tin anodes: Experiment and theory[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 234: 48-59.
[13] ZHU Jun-sheng, WANG Dian-long, CAO Li-bo, et al. Ultrafast preparation of three-dimensional porous tin- graphene composites with superior lithium ion storage[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(32): 12918-12923.
[14] YANG Sheng, YUE Wen-bo, ZHU Jia, et al. Graphene-based mesoporous SnO2 with enhanced electrochemical performance for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2013, 23(28): 3570-3576.
[15] XU Chun-mei, WU Yi-shan, ZHAO Xu-yang, et al. Sulfur/three-dimensional graphene composite for high performance lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 275: 22-25.
Graphene-based SnCu anode synthesized via solverthermal method for sodium ion batteries
DONG Qiang1, 2, XU Hai-song1, 2, PAN Fei3, WANG Pei-ran3, HE Yu-shi3, LI Lin-seng3, MA Zi-feng3
( 1. Hitachi (China) Research & Development Corporation, Shanghai 200020, China;
2. Shanghai Jiao Tong University-Hitachi Materials Technology Innovation Joint Laboratory, Shanghai 200240, China;
3. Shanghai Electrochemical Energy Devices Research Center, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China)
Abstract: The SnCu@GS (SnCu nanoparticles anchored on graphene sheets) composite was successfully synthesized by a strategy integrating an in-situ solvothermal method and a freeze-drying process with a subsequent annealing procedure. The electrochemical performance of nano-sized SnCu granules anchored on graphene matrix as an anode for sodium-ion batteries was also investigated. The results reveal that graphene constructs a three-dimensional porous conductive framework in solvothermal reaction and leads to a well dispersion of SnCu nanoparticles with an average diameter of about 70 nm on graphene sheets. In contrast, SnCu spheres without graphene network obtained through the same route exhibit various diameters from 200 nm to 4 μm. The introduction of graphene oxide (GO) which is the original source of conductive GS network, can effectively inhibit the secondary aggregation of nanoparticles. The SnCu@GS composite shows superior cycling stability and rate capability. The specific reversible capacity of the SnCu@GS electrode can still maintain about 150 mA·h/g at a current density of 200 mA/g after 200 cycles.
Key words: graphene; solvothermal synthesis; tin-copper; nanoparticle; sodium-ion battery
Foundation item: Projects(21938005, 21676165) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Projects(19ZR1424600, 19ZR1475100) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai, China; Project(19DZ1205500) supported by the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality, China
Received date: 2020-05-27; Accepted date: 2020-09-25
Corresponding author: HE Yu-shi; Tel: +86-21-54747717; E-mail: ys-he@sjtu.edu.cn
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(21938005,21676165);上海市自然科学基金资助项目(19ZR1424600,19ZR1475100);上海市科技创新行动计划资助项目(19DZ1205500)
收稿日期:2020-05-27;修订日期:2020-09-25
通信作者:何雨石,副研究员,博士;电话:021-54747717;E-mail:ys-he@sjtu.edu.cn