不同pH值硫酸铁溶液中碳酸盐岩型黄铜矿的浸出机理
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2021年第7期
论文作者:Kolela J NYEMBWE Elvis FOSSO-KANKEU Frans WAANDERS Martin MKANDAWIRE
文章页码:2139 - 2152
关键词:黄铜矿;碳酸岩;化学浸出;浸出机理;中间相;热力学行为
Key words:chalcopyrite; carbonatite; chemical leaching; leaching mechanism; intermediate phase; thermodynamic behavior
摘 要:在pH值0.5~2.5、温度25 °C和时间12 h的条件下,研究碳酸盐岩型黄铜矿在H2SO4-Fe2(SO4)3- FeSO4- H2O体系中的溶解行为。实验所用的颗粒粒度为53~75 μm。在所有pH条件下,Cu的回收率均低于15%。浸出渣的XRD、SEM-EDS和光学显微镜(OM)分析结果表明,溶解过程中形成了中间相。pH为0.5和1.0时的中间相分别是Cu3.39Fe0.61S4和Cu2S,而pH值为1.5和1.8时的主要矿物为Cu5FeS4。热力学模拟预测产物的生成顺序为CuFeS2→Cu5FeS4→Cu2S→CuS。Cu5FeS4 and Cu2S为可溶性中间相,而CuS和Cu3.39Fe0.61S4是难溶中间相,在整个溶解过程中不断积累。所得结果表明,CuFeS2浸出过程中CuS和Cu3.39Fe0.61S4的生成有助于形成钝化膜。
Abstract: The dissolution of a carbonatitic chalcopyrite (CuFeS2) was studied in H2SO4-Fe2(SO4)3-FeSO4-H2O at varying pH values (0.5-2.5) and 25 °C for 12 h. Experiments were conducted with a size fraction of 53-75 μm. Low Cu recoveries, below 15%, were observed in all pH regimes. The results from the XRD, SEM-EDS, and optical microscopic (OM) analyses of the residues indicated that the dissolution proceeded through the formation of transient phases. Cu3.39Fe0.61S4 and Cu2S were the intermediate phases at pH 0.5 and 1.0, respectively, whereas Cu5FeS4 was the major mineral at pH 1.5 and 1.8. The thermodynamic modelling predicted the sequential formation of CuFeS2→ Cu5FeS4→Cu2S→CuS. The soluble intermediates were Cu5FeS4 and Cu2S, whilst, CuS and Cu3.39Fe0.61S4 were the refractory phases, supporting their cumulating behaviour throughout the dissolution. The obtained results suggest that the formation of CuS and Cu3.39Fe0.61S4 could contribute to the passive film formed during CuFeS2 leaching.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 31(2021) 2139-2152
Kolela J NYEMBWE1,2, Elvis FOSSO-KANKEU1, Frans WAANDERS1, Martin MKANDAWIRE1,2
1. Water Pollution Monitoring and Remediation Initiatives Research Group, School of Chemical and Minerals Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, North-West University, South Africa;
2. Department of Chemistry, School of Science and Technology, Cape Breton University, Canada
Received 22 June 2020; accepted 4 March 2021
Abstract: The dissolution of a carbonatitic chalcopyrite (CuFeS2) was studied in H2SO4-Fe2(SO4)3-FeSO4-H2O at varying pH values (0.5-2.5) and 25 °C for 12 h. Experiments were conducted with a size fraction of 53-75 μm. Low Cu recoveries, below 15%, were observed in all pH regimes. The results from the XRD, SEM-EDS, and optical microscopic (OM) analyses of the residues indicated that the dissolution proceeded through the formation of transient phases. Cu3.39Fe0.61S4 and Cu2S were the intermediate phases at pH 0.5 and 1.0, respectively, whereas Cu5FeS4 was the major mineral at pH 1.5 and 1.8. The thermodynamic modelling predicted the sequential formation of CuFeS2→ Cu5FeS4→Cu2S→CuS. The soluble intermediates were Cu5FeS4 and Cu2S, whilst, CuS and Cu3.39Fe0.61S4 were the refractory phases, supporting their cumulating behaviour throughout the dissolution. The obtained results suggest that the formation of CuS and Cu3.39Fe0.61S4 could contribute to the passive film formed during CuFeS2 leaching.
Key words: chalcopyrite; carbonatite; chemical leaching; leaching mechanism; intermediate phase; thermodynamic behavior
1 Introduction
70%-80% of metallic copper (Cu) is obtained from the chalcopyrite (CuFeS2) mineral, the major natural copper sulphide mineral used for copper production [1-4] and the most refractory copper sulphide for hydrometallurgical recovery process. An estimated 85% of the copper production worldwide is produced via the pyrometallurgical route [5]. However, due to the environmental regulations and concerns of SO2 emissions from the pyrometallurgical process and the relative decrease in profit margins for mineral processing caused by a scarcity of high-grade ore bodies, the hydrometallurgical route appears to be the most attractive way for copper production [6]. Chalco- pyrite leaching is characterized by a slow and incomplete dissolution, mainly due to the formation of a diffusion barrier that builds up between the leaching solution and the chalcopyrite mineral [7]. Although numerous studies have been carried out to investigate the major factors influencing CuFeS2 leaching kinetics, researchers have not yet reached a consensus about the chemical compositions of the passivation layer [5-10], for example, ferric precipitates (jarosite, jarosite-like compounds and goethite [11], elemental sulfur (S0) [12,13] and polysulfide [14]) were reported to contribute to the dissolution barrier.
CuFeS2 dissolution appears to be a complex process, and it takes place according to Reaction (1) in ferric sulphate (H2SO4-Fe2(SO4)3-FeSO4-H2O). The dissolution involves chemical speciation transformation and evolution of three elements (S, Fe and Cu) on CuFeS2 surface, leading to the formation of mineral phase intermediates. For instance, CORDOBA et al [15] identified CuS as the intermediate product of CuFeS2 in the presence of ferric ion (Fe3+). While ELSHERIEF [16] observed Cu2S as the transition phase during the electrochemical dissolution. FU et al [17] recognized a Cu-rich, Fe-deficient polysulphide (Cu4Fe2S9) for CuFeS2 bioleaching. LU et al [18] thermodynamically revealed the presence of Cu5FeS4 and CuS for both oxidative and non-oxidative dissolution processes.
CuFeS2+2Fe2(SO4)3→CuSO4+5FeSO4+2S0,
△G=-67.4 kJ/mol (1)
A comprehensive mechanism of CuFeS2 dissolution could be obtained by leached residues characterization by employing surface analytical methods (such as X-ray photoelectron spectro- scopy, X-ray absorption spectroscopy, X-ray diffractometry, scanning electron microscopy and Raman spectroscopy) and through control of solution chemical aspects among which the solution redox and pH are very important. Most recent studies on the Cu recoveries from CuFeS2 have only characterized solid residues at the resolved experimental end time. This has not allowed evaluating the entire mineral phase evolution taking place during dissolution. In this study, the dissolution mechanism of CuFeS2 in Fe2(SO4)3 solution was determined by direct observation (chemical, mineralogical and morphological) obtained periodically throughout the leaching experiments. The effect of acidity on the dissolution was evaluated at different pH values (0.5-2.5). The use of thermodynamic prediction data clarifies chemical reactions and establishes the phase conversion at a solid/liquid interface in the dissolution of carbonatite-concentrate leaching in an acidic ferric-sulfate system at room temperature.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials
Solutions of the desired pH were prepared using analytical-grade sulphuric acid (98% H2SO4, ACE), ferric sulphate (Fe2(SO4)3·H2O, ACE), and deionized water (<5.0 μS/cm). A pH meter and a temperature probe (Hanna pH HI 8424) were used to measure pH, which was regularly calibrated with standard buffer solutions at pH 4 and 7. The measured redox potential (Ag/AgCl) values were corrected to the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) as published by STRIGGOW [19].
2.2 Chalcopyrite
Concentrate CuFeS2 was obtained from a Phalaborwa Copper Mining Company (Limpopo Province, South Africa). The sample was dried in an oven at 50 °C for 7 d before sub-sampling. Homogenization was done in accordance with the soil sampling protocol by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency [20]. Approximately 0.5 kg of concentrate was sub-sampled and further dried at 105 °C for 2 h. The grains with sizes smaller than 200 μm were used as the dissolution feed. The powdered chalcopyrite sample was characterized in an earlier study by NYEMBWE et al [21] for its chemistry, mineral composition and morphology using the XRF, X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy–energy dispersive spectroscopy (SEM-EDS), respectively. The bulk compositions and mineral contents of the CuFeS2 sample used in this study are summarized in Fig. 1.
2.3 Leaching media
The CuFeS2 dissolution was conducted in acidified ferric sulphate solution (H2SO4-Fe2(SO4)3), obtained by mixing Fe2(SO4)3 with H2O and H2SO4. An initial Fe3+ concentration of 0.05 mol/L was used for all tests. The medium was agitated for 12 h prior to use. Dissolution tests were performed under atmospheric conditions at 21-24 °C. The medium pH was measured and maintained at 1.0, 1.5 and 1.8 with periodic addition of 98% H2SO4, respectively, while the solution oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) could evolve throughout the dissolution test. An additional test was conducted at free pH (not controlled) at an initial pH of 0.5. This intended to determine the effect of pH on the dissolution mechanism and mineral changes.
A pulp density of 10% was used in all tests, with 40 g of the dried chalcopyrite sample, mixed with 400 mL of the leaching liquor in a 600 mL Erlenmeyer flask. 10 mL sample was withdrawn every 20 min for chemical analysis, while the solution ORP was measured at intervals and converted to the SHE. Total Cu and Fe contents were analyzed using atomic absorption flame spectrometry (AAFS, Thermo Scientific ICE 3000 series).
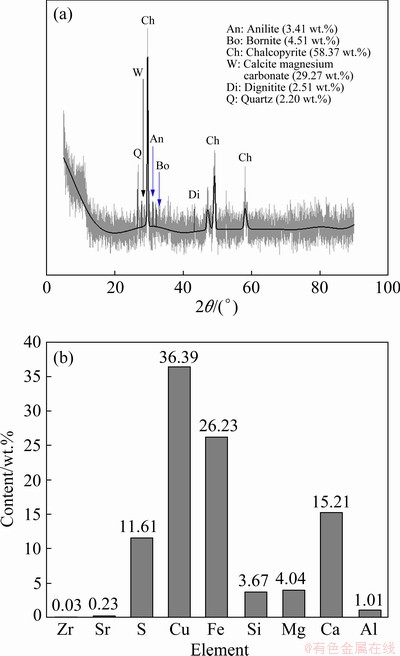
Fig. 1 XRD pattern showing bulk compositions (a) and mineral content (b) of CuFeS2 concentrate sample
2.4 Residue characterization
Solid samples were analyzed for mineral composition using XRD and optical phase identification and surface morphology using SEM–EDS and ore microscopy. The XRD analysis using a Rigaku Ultima IV was operated at 40 kV and 30 mA. PDXL analysis software was used, and the instrument’s detection limit was 2%. Data were recorded over the range 5° ≤ 2θ ≤ 95° at a scan rate of 0.5 (°)/min and a step width of 0.01°. Tescan SEM (operated at 20 kV) with EDS analysis was used for grain morphology and chemistry. Residues were carbon-coated prior to analysis. Lastly, the mineral identification was assessed using an optical microscope after mounting the samples on epoxy resin.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Effect of pH on Cu leaching recovery and rate curves
The leaching behaviour of CuFeS2 at different pH values (free, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5 and 1.8) is presented in Fig. 2. It also shows the recorded potential and the leaching behaviour of Fe considering its various states (Fe2+ and Fe3+). The mineral’s Fe dissolved was obtained after subtracting the initial Fe portion used as oxidant (leaching solution) from the total Fe reported under the AAFS (i.e., Fe mineral=Fe total (AAFS)-Fe used as oxidant (ferric sulfate)). More Cu dissolved at pH 1.8 than that at pH 1.5, 1.0, free pH and 0.5 (decreasing order of copper recovery). The obtained recoveries are similar to those reported by ANTONIJEVIC and BOGDANOVIC [22] and CORDOBA et al [15] who easily pointed out that chalcopyrite will be oxidized at higher pH values when oxygen is present in solutions.
All dissolution curves were asymptotic and characterized by different stages (Figs. 2(a1, b1, c1, d1, e1)): the first stage (0-60 min) was more rapid than the second stage (60-360 min), and the third stage was the plateau with no Cu dissolution (360-720 min). Our results supported those of KLAUBER et al [23] and SALINAS et al [24], but did not support those of JONES and PETERS [25] who observed a linear kinetic be havirour probably due to an extended dissolution time over 55 d. Our results also showed that the medium pH indicated the dissolution pattern. Highly acidic media characterized by low Cu recovery displayed a three-stage dissolution curve, while relatively high pH value showed only two-stage dissolution curves.
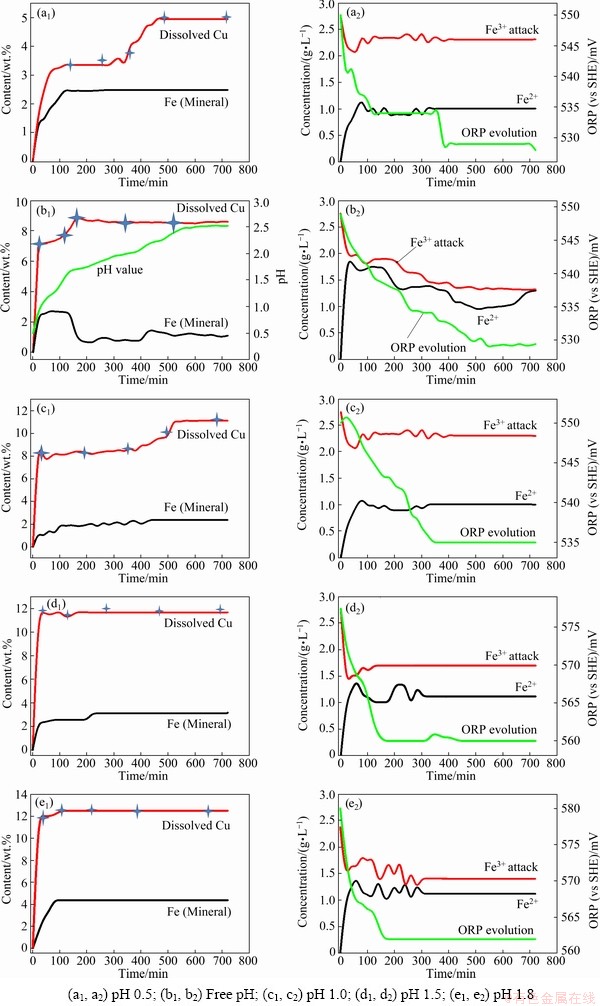
Fig. 2 Kinetic behaviour of Cu and Fe dissolution in chalcopyrite, with corresponding ORP values obtained at different pH values
Earlier investigations showed that the medium pH has a negligible effect on the leaching rate of CuFeS2 in ferric sulfate [26,27]. A low pH value should be maintained to avoid the formation of iron (Fe) precipitates [28]. Our results showed a slight increase in the dissolution rate associated with an increase in pH value. 3% of Cu was obtained within the first 40 min at pH 0.5 and only increased to 5% after 560 min. At pH 1.0, 8% Cu was recovered within the first 20 min and only increased to 11% after 600 min. While the dissolution conducted at pH values of 1.5 and 1.8 showed maximum Cu recoveries of 12% and 13% at the early stage of the dissolution respectively. Lastly, the free pH dissolution at a starting pH value of 0.5 revealed a higher Cu recovery (7.3% Cu after 20 min and increased to 8.7% after 260 min) than the static leaching test conducted at the same pH value. This could be due to the increase in pH value during the dissolution. However, the free pH recovery was lower than that of the other static dissolution tests (pH 1.0, 1.5 and 1.8) probably due to fast formation and precipitation of ferric-hydroxide (pH>1.82 was recorded after 240 min of dissolution). It could be said that high pH values promote fast dissolution rate as opposed to highly acidic media.
3.2 CuFeS2 dissolution breakdown
It is believed that CuFeS2 dissolution in the presence of Fe3+ takes place according to Reaction (1) and produces elemental sulphur and both CuSO4 and FeSO4 [3,26]. In this process, the results showed that the first step could be regarded as the ferric attack, that is, Fe3+ sharply decreased at the early stage of the dissolution (Fig. 2), which promotes the recovery of Fe and Cu. At this point, the solution owns two sources of Fe2+ (Fe2+ reduced from Fe3+ and the dissolved Fe from the mineral). KLAUBER [14] and BAI et al [29] reported that, in the presence of sufficient O2 and acidity level, Fe2+ is oxidized to Fe3+, as shown in Reaction (2):
4Fe2++O2+4H+→4Fe3++2H2O (2)
The obtained Fe results reveal that the oxidation of Fe2+ to Fe3+ did not occur or was relatively slow (Fig. 2), which could be attributed to the low experimental parameters [30]: low temperature (23 °C) and O2 pressure (2.1×104 Pa). An improved Cu recovery, associated with the oxidation of Fe2+ to Fe3+, was observed in a study conducted by LU et al [31], at 95 °C, with increasing oxygen partial pressure. Our results suggest that Fe2+ saturated the solution and further dissolution of Cu and Fe could not occur, causing the reaction to cease. Scheme 1 shows the mineral dissolution breakdown:
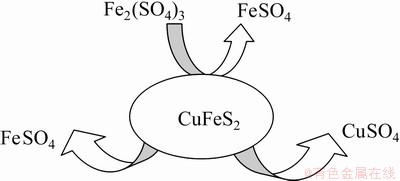
Scheme 1 Illustration of mineral dissolution breakdown process
It should be worth noting that the initial potential varied according to the solution pH and can also play a major role in the Cu recovery. It was observed that high pH (1.5 and 1.8) media possessed high initial ORP value. In all cases, the initial ORP values showed a similar trend, which decreased at the early dissolution stage and then remained steady till the end of the leaching. A decline from 550 to 529 mV, 549 to 527 mV, 555 to 534 mV, 577 to 562 mV and 580 to 561 mV was recorded for the free pH, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5 and 1.8 respectively. This decrease indicates the direct oxidation of that mineral by Fe3+ and suggests an increase of Fe2+ content in the solution. Earlier studies showed the existence of a potential range interval, referred to as critical range (400-450 mV (vs Ag/AgCl), corresponding to 600-660 mV (vs CEH) approximately, while using the conversion as published by STRIGGOW [19], in which optimum copper recoveries were obtained [32,33]. Except for the dissolution at pH 1.8, which was within the range and quickly dropped (after 40 min of leaching), all ORP values (pH 0.5-1.5) were well below the critical potential range and could explain the low recoveries observed under various pH regimes.
3.3 Leached residue
3.3.1 Mineralogical characterization
Figures 3 and 4 show the solid residue(s) mineralogical characterization results obtained during the dissolution tests. The solids were characterized according to different Cu content curves (Figs. 2(a1, b1, c1, d1, e1)). The blue crosses in the figures show various solids assessed for their mineral contents. Figure 3 shows the qualitative mineral (XRD spectrum) contents of the leachate residue, while Fig. 4 displays the quantitative reference intensity ratio (RIR) results of various mineral phases observed. A decrease in CuFeS2 (2θ=29.45°) was observed in all five dissolution tests, suggesting a progressive Cu dissolution [33]. In addition, the solid residues exposed the presence of new Cu-rich (bornite (Bo), chalcocite (Cx), covellite (Co) and nukundamite (Nk)) mineral phases, which were relatively low or inexistent in the feed sample (Fig. 1(b)). The presence of these Cu-rich intermediates supports the earlier investigation by ACERO et al [34], which underlined the preferential dissolution of Fe over Cu, leading to the formation of an Fe-deficient CuFeS2 mineral (defect chalcopyrite structure (Cu1-xFe1-yS2-z) to which our identified species could be part of). Iron-related minerals (goethite, magnetite, hematite, wustite and jarosite) and sulphur (S) were also identified in the resulting solid residues.
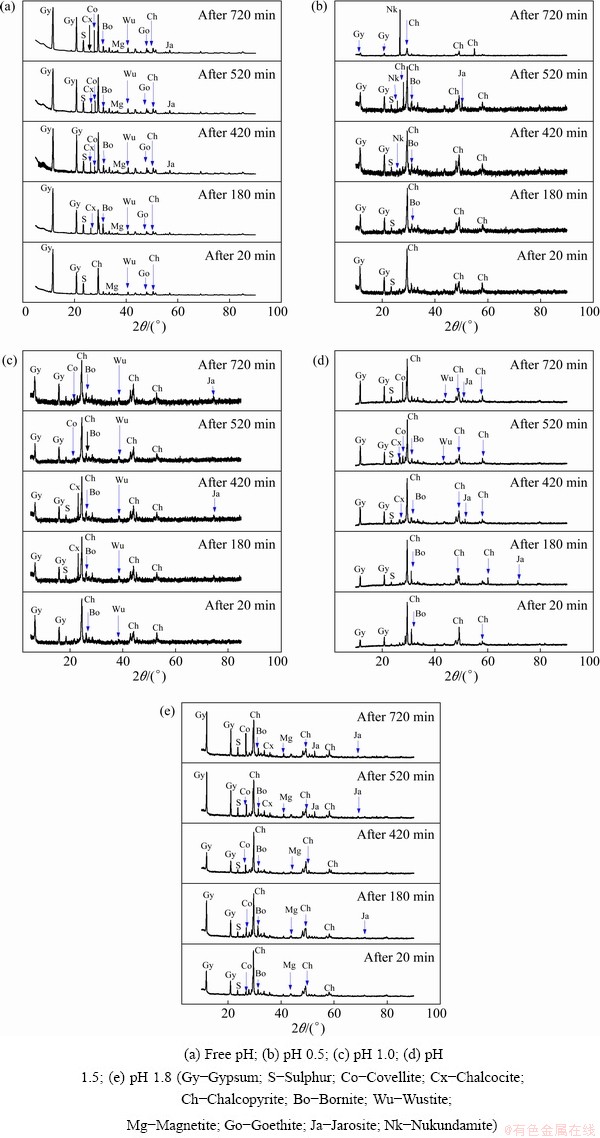
Fig. 3 Solid residue characterization results by XRD at different pH values
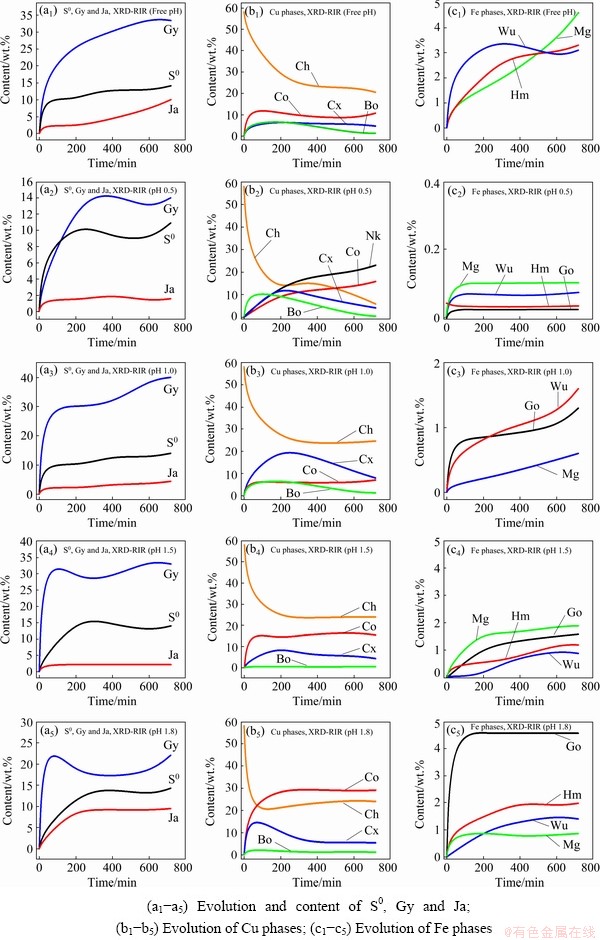
Fig. 4 XRD-RIR results showing phase evolution kinetics
The gypsum (Gy) phase was identified in all solid residues. Its content was found to increase with increasing pH value. More Gy was found in the solid residue at pH 1.8 than that at pH 1.5, 1.0 and 0.5. Slightly more Gy was obtained from the free pH experiment due to the increase of pH value. Similarly to Gy, varying proportions of iron compounds were recorded in solid residues and appeared to increase with increasing pH values which agreed with literatures [28,35], according to which, high acidity levels prevent the hydrolysis/precipitation of Fe. Sulphur (S0) was also observed in the solid residues as the reaction product (Reaction (1)), as also reported in the studies conducted by HAMMER et al [9] and SOKIC et al [36].
CuFeS2 dissolution was accompanied by the formation of other copper sulphide phases (bornite, covellite, chalcocite and nukundamite). The proportion of these phases in the residues was found to be pH-dependent. Bornite (Cu5FeS4), chalcocite (Cu2S), covellite (CuS) and nukundamite (Cu3.39Fe0.61S4) were observed at pH 0.5, in which Cu3.39Fe0.61S4 was a major phase (Fig. 3(b)). At pH 1.0, Cu2S was the main copper-sulfide intermediate phase (Fig. 3(c)), while at pH 1.5 and 1.8, CuS and Cu5FeS4 were revealed as important transitory phases, Figs. 3(d, e).
Cu5FeS4 and Cu2S were the soluble intermediates phases, and their corresponding peak intensities decreased (Figs. 3(a-d)), suggesting eventual dissolution of these transitory phases during the dissolution test. On the other hand, CuS and Cu3.39Fe0.61S4 were found to cumulate by increasing their corresponding peak intensities throughout the whole dissolution process (pH 0.5, Fig. 3(b)). Their contents increase from 1.23% to 15.6% and 2.1% to 24% individually for CuS and Cu3.39Fe0.61S4 (Fig. 4). The cumulative properties could have advocated that both CuS and Cu3.39Fe0.61S4 are refractory intermediate phases. Our results showed that CuS is refractory in ferric sulfate media at room temperature. ANTONIJEVIC and BOGDANOVIC [22] observed that very acidic media favoured the formation of an Fe-deficient (Cu1-xFe1-yS2-z) phase due to the competition between Fe3+ and H+. The obtained results suggest that the Fe-deficient surface could correspond to Cu3.39Fe0.61S4 at pH 0.5.
The results also showed that different Cu dissolution stages observed on the Cu recovery curves (Fig. 2) could be related to the formation and dissolution of the intermediate phases. In all cases, the rapid Cu withdrawal (first stage) was related to the fast dissolution of the Cu and Fe on the surface of CuFeS2, while the second stage observed at pH 0.5 and 1.0 corresponded to the dissolution of the intermediates (CuS2 and Cu5FeS4). Lastly, the plateau stage referred to the encapsulation of the unreacted mineral by the refractory intermediate phases: covellite and nukundamite.
The free pH experiment at a starting pH value of 0.5 revealed the presence of CuS, Cu2S and Cu4FeS5 except for Cu3.39Fe0.61S4. It could be due to the fast increase of the pH value during the dissolution test. Further, the fast increase in pH value led to the rapid formation and accumulation of gypsum, and the Fe-related oxyhydroxide compounds as opposed to the static pH dissolution tests (Figs. 3(b-e)).
3.3.2 Surface chemistry and morphologies (SEM- EDS)
Figure 5 shows the morphology and the mass fractions of Cu, Fe and S of 12 H solid residue. In all cases, both S and Cu have increased relative to Fe. This confirms the preferential dissolution of Fe over Cu and supports the presence of the Cu-S intermediate phase and the build-up of S0 on the unreacted CuFeS2 surface, leading to the retarding effect due to an increased thickness. The residue morphologies also showed that the colour and surface morphology of the grains evolved during the dissolution; dark to light grey grains were observed and, in some instances, the crusty matter was identified on the granule surface. The chemical composition acquired using EDS supported the presence of various phases earlier identified under the XRD analysis.
More Fe precipitate products (crusty and earthy matter) were observed from the free pH residues than those at pH 1.8, 1.5, 1.0 and 0.5. The corresponding EDS analysis confirmed high proportions of Fe and S, which supported the high proportions of these related phases of two elements and identified during the XRD analysis. It could be attributed to the presence of Fe oxy/hydroxide precipitates.
The high contents of Cu and S retained on the leached residues could be related to the presence of Cu-S-rich intermediate phases as revealed earlier through the XRD patterns (Figs. 3(a-c)). This suggests that, during the release of Cu from CuFeS2, a CuS structure tends to envelop the mineral.
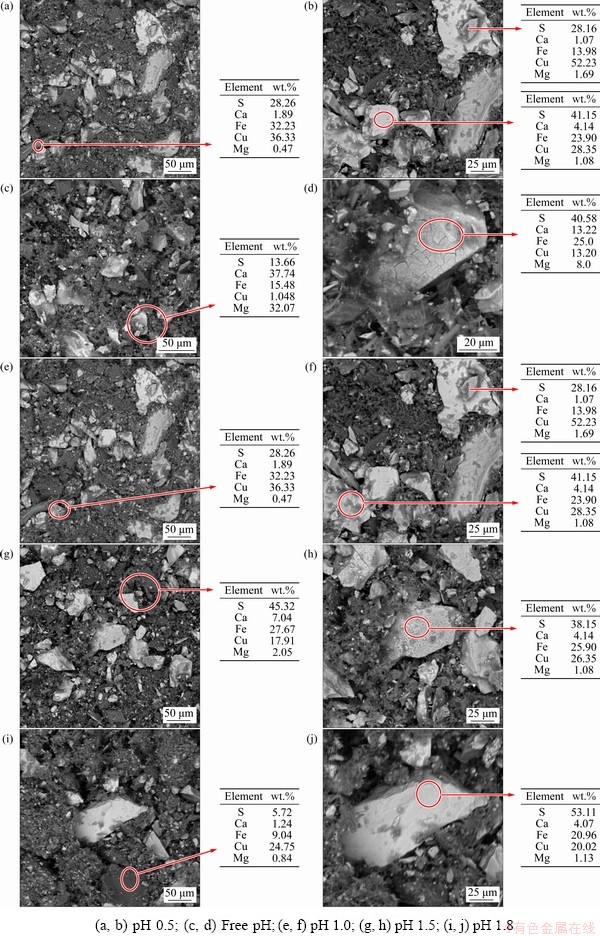
Fig. 5 Morphologies and chemical compositions of residues obtained from SEM-EDS
3.3.3 Mineral identification (ore microscopy)
Figure 6 shows the distinctive mineral features (colour) identified under the microscope. The presence of various intermediates observed under the XRD was confirmed under this technique. Yellow lamella is attributed to the CuFeS2 grain as its distinctive character, while the pinkish to brownish colour is ascribed to the existence of the Cu5FeS4 phase. The white or relatively greyish mineral is related to the Cu2S phase, and dark grey corresponds to the Cu3.39Fe0.61S4 [37-39]. This has provided evidence of the metamorphism or mineral alteration during the dissolution process, implying a partial and total replacement of CuFeS2 by the secondary copper sulphide phases. The results also revealed that the CuS characteristics (blue grains) appeared on the Cu5FeS4 structure, which suggests that the CuFeS2 does not directly transform into CuS. Rather, Cu5FeS4 is the intermediate phase between CuFeS2 and CuS.
3.4 Solid phase thermodynamics
Thermodynamics could assist in predicting the formation of various intermediate phases and could be used as the criterion to support their existence. It could also assist in determining the dissolution pathway model, based on the solid-state transformation phase changes. Based on the spontaneity value (Gibbs free energy change), Cu5FeS4 appears to be the most favourable intermediate phase to be formed (Reaction (5)), followed by chalcocite (Reaction (4)) and, lastly, covellite (Reaction (3)). These Cu-S phases could react further into new Cu-S-rich ones (Reactions (6)-(8)), or leach to promote Cu recovery (Reactions (9)-(11)). CuS is likely to form from Cu5FeS4 (Reaction (8)) than from Cu2S (Reaction (9)), this tends to support the distinctive feature of CuS next to Cu5FeS4 observed during mineral identification (Figs. 6(a, c, d, j)). It further suggests that Cu dissolution/withdrawal from the Cu5FeS4 phases is likely to occur via CuS formation as opposed to the direct dissolution of Cu5FeS4 according to Reaction (12). Similar to our results, ZHAO et al [40] also reported the presence of CuS due to a transient specie during the ferric leaching of Cu5FeS4, while the dissolution of Cu2S appeared to occur according to Reaction (11) without the formation of CuS as a transitional phase.
It should be noted that CuS appears to be refractory to dissolution since its free energy is positive, which supports its cumulative character earlier observed under the XRD analysis (Fig. 3) and CuS can contribute to the hindrance of Cu recovery. This further implies that the formation and dissolution of intermediate phases (Reactions (11) and (12)) hinder to some extent the rapid and direct Cu dissolution from the CuFeS2 phase (Reaction (1)). The reactions related to Cu3.39Fe0.61S4 decomposition were omitted due to lack of data from the HSC 5.11 software.
Formation of copper intermediate phases:
CuFeS2+Fe2(SO4)3 CuS+3FeSO4+S,
CuS+3FeSO4+S,
△G=-76.4 kJ/mol (3)
2CuFeS2+2Fe2(SO4)3 Cu2S+6FeSO4+3S,
Cu2S+6FeSO4+3S,
△G=-125.8 kJ/mol (4)
5CuFeS2+4Fe2(SO4)3 Cu5FeS4+12FeSO4+6S,
Cu5FeS4+12FeSO4+6S,
△G=-281.2 kJ/mol (5)
3.39CuFeS2+2.78Fe2(SO4)3=Cu3.39Fe0.61S4+
8.34FeSO4+2.78S (6)
Intermediate phase mutation/alterations:
Cu5FeS4+Fe2(SO4)3 2.5Cu2S+3FeSO4+1.5S,
2.5Cu2S+3FeSO4+1.5S,
△G=-139.2 kJ/mol (7)
Cu5FeS4+2Fe2(SO4)3 4CuS+5FeSO4+CuSO4,
4CuS+5FeSO4+CuSO4,
△G=-383.3 kJ/mol (8)
2Cu2S+Fe2(SO4)3 2CuS+2FeSO4+Cu2SO4,
2CuS+2FeSO4+Cu2SO4,
△G=80.7 kJ/mol (9)
The dissolution of intermediate phases for complete copper dissolution:
CuS+Fe2(SO4)3 2FeSO4+S+CuSO4,
2FeSO4+S+CuSO4,
△G=9.0 kJ/mol (10)
Cu2S+2Fe2(SO4)3 4FeSO4+S+2CuSO4,
4FeSO4+S+2CuSO4,
△G=-8.9 kJ/mol (11)
Cu5FeS4+6Fe2(SO4)3 13FeSO4+4S+5CuSO4,
13FeSO4+4S+5CuSO4,
△G=-55.7 kJ/mol (12)
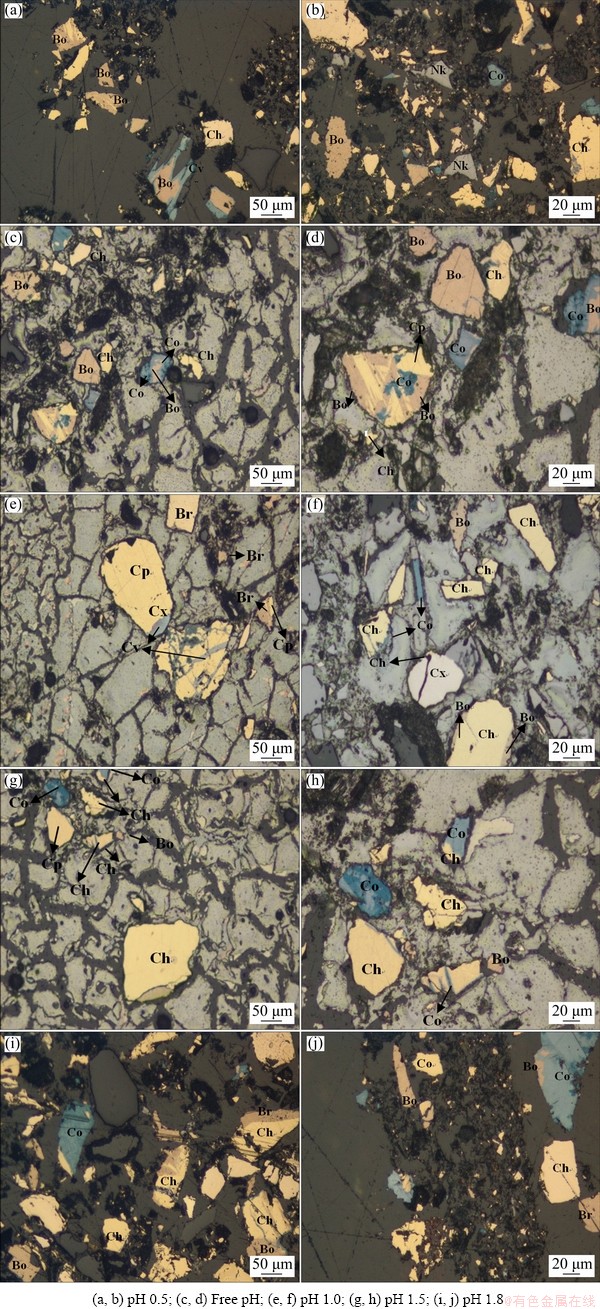
Fig. 6 Qualitative mineral identification (optical microscope) results showing chalcopyrite partial replacement by secondary sulphides during dissolution
Phase formation related to gangue mineral:
CaCO3+H2SO4 CaSO4+H2O+CO2↑,
CaSO4+H2O+CO2↑,
△G=-579.35 kJ/mol (13)
4 Conclusions
(1) The leaching of Cu from CuFeS2 concentrate in Fe2(SO4)3 was investigated at room temperature. Low Cu recoveries were obtained under all pH regimes. The maximum final copper extraction of 5%, 8.7%, 11%, 12% and 12% was attained at pH values of 0.5, free pH (0.5-2.5), 1.0, 1.5 and 1.8, respectively.
(2) The dissolution process appeared to be driven by the medium pH value. It was observed that the pH value not only affected the formation of precipitates, but also dictated the dissolution rate, and curve stages. Highly acidic media (pH 0.5 and 1.0) showed a slow and three-stage dissolution rate curve contrary to the solution media at pH 1.5 and 1.8 which displayed a fast rate and two-stage curve.
(3) The solid characterisation under XRD, SEM-EDS and OM showed that the solution pH also determined the major transition phases. For instance, Cu3.39Fe0.61S4 and Cu2S were the main intermediate phases at pH 0.5 and 1.0, while Cu5FeS4 was the major mineral observed at pH 1.5 and 1.8. Furthermore, CuS and Cu3.39Fe0.61S4 covellite phases were found to cumulate.
(4) Thermodynamic predictions revealed that CuS and Cu3.39Fe0.61S4 are refractory transient phases as opposed to Cu2S and Cu5FeS4. This supported their cumulative properties identified during XRD. In addition, a mineral-formation sequence prioritizing bornite formation, followed by chalcocite as the major transformation of chalcopyrite dissolution in ferric sulfate was observed, with the covellite phase being the product of the alteration/dissolution of these phases (bornite and chalcocite).
(5) The obtained results suggest that, in addition to the sulfur (S) surrounding the unreacted mineral, the formation of CuS and Cu3.39Fe0.61S4 could contribute to the slow dissolution (passivation) of carbonatitic chalcopyrite at room temperature.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the sponsors from the North-West University, the local South African Mining Company by providing the samples, the Extraction Metallurgy Laboratory at the University of Johannesburg for equipment utilization, and the Department of Chemical Engineering at the North-West University for the support and promotion of this research.
Author Martin MKANDAWIRE is indebted to funding through NSERC-DG, CFI, Public Works and Government Service, Canada (formally Devco arm of ECBC), the Industrial Research Chair of Mine Water Management at CBU, ACOA and IRAP grants.
References
[1] MA Y L, LIU H C, XIA J L, NIE Z Y, ZHU H R, ZHAO D Y, MA C Y, ZHANG L, HONG C H, WEN W. Relatedness between catalytic effect of activated carbon and passivation phenomenon during chalcopyrite bioleaching by mixed thermophilic Archaea culture at 65°C [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27(6): 1374-1384.
[2] PETROVIC S J, BOGDANOVIC G D, ANTONIJEVIC M M. Leaching of chalcopyrite with hydrogen peroxide in hydrochloric acid solution [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28(7): 1444-1455.
[3] BAMPOLE D L, LUIS P, MULABA-BAFUBIANDI A F. Sustainable copper extraction from mixed chalcopyrite- chalcocite using biomass [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2019, 29(10): 2170-2182.
[4] ZHU P, LIU X D, CHEN A J, LIU H W, YIN H Q, QIU G Z, HAO X D, LIANG Y L. Comparative study on chalcopyrite bioleaching with assistance of different carbon materials by mixed moderate thermophiles [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2019, 29(6): 1294-1303.
[5] LI Y, KAWASHIMA N, LI J, CHANDRA A P, GERSON A R. A review of the structure, and fundamental mechanisms and kinetics of the leaching of chalcopyrite [J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2013, 197–198: 1–32.
[6] NIE Z T, ZHANG W W, LIU H C, ZHU H R, ZHAO C H, ZHANG D R, ZHU W, MA C Y, XIA J L. Bioleaching of chalcopyrite with different crystal phases by Acidianus manzaensis [J]. Transaction of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2019, 29(3): 617–624.
[7] NADERI H, ABDOLLAHY M, MOSTOUFI N, KOLEINI M J, SHOJAOSADATI S A, MANAFI Z. Kinetics of chemical leaching of chalcopyrite from low grade copper ore: Behavior of different size fractions [J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2011, 18(6): 638–645.
[8] TSHILOMBO A F. Mechanism and kinetics of chalcopyrite passivation and depassivation during ferric and microbial leaching [D]. British Columbia: University of British Columbia, 2004.
[9] HARMER S L, THOMAS J E, HARMER S L, FORNASIERO D, GERSON A R. The evolution of surface layers formed during chalcopyrite leaching: The evolution of surface layers formed during chalcopyrite leaching [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70: 4392-4402.
[10] OLVERA O G, REBOLLEDO M, ASSELIN E. Hydro- metallurgy atmospheric ferric sulfate leaching of chalcopyrite: Thermodynamics, kinetics and electro- chemistry [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2016, 165: 148–158.
[11] SANDSTROM A, SHCHUKAREV A, PAUL J. XPS characterization of chalcopyrite chemically and bio-leached at high and low redox potential [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2015, 18: 505–515.
[12] Mc MILLAN R S J, Mac KINNON D J, DUTRIZAC J E. Anodic dissolution of n-type and p-type chalcopyrite [J]. J Appl Electrochem, 1982, 12: 743–757.
[13] DUTRIZAC J E. Elemental sulphur formation during the ferric chloride leaching of chalcopyrite [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1990, 23(2–3): 153–176.
[14] KLAUBER C. A critical review of the surface chemistry of acidic ferric sulphate dissolution of chalcopyrite with regards to hindered dissolution [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2008, 86: 1–17.
[15] CORDOBA E M, MUNOZ J A, BLAZQUEZ M L, GONZALEZ F, BALLESTER A. Passivation of chalco- pyrite during its chemical leaching with ferric ion at 68 °C [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2009, 22: 229–235.
[16] ELSHERIEF A E. The influence of cathodic reduction, Fe2+ and Cu2+ ions on the electrochemical dissolution of chalcopyrite in acidic solution [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2002, 15: 215–223.
[17] FU Kai-bin, LIN Hai, MO Xiao-lan, WANG Han, WEN Hong-wei, WEN Zi-long. Comparative study on the passivation layers of copper sulphide minerals during bioleaching [J]. Int J Miner Metall Mater, 2012, 19(10): 886–892.
[18] LU D, WANG W, CHANG Y, XIE F, JIANG K. Thermodynamic analysis of possible chalcopyrite dissolution mechanism in sulfuric acidic aqueous solution [J]. Metals, 2016, 6(12): 1–15.
[19] STRIGGOW B. Field measurement of oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) [M]. Georgia: US Environmental Protective Agency (US-EPA), 2013.
[20] SIMONS K. Soil Sampling [M]. Geogia: US Environmental Protective Agency (US-EPA), 2014.
[21] NYEMBWE K J, FOSSO-KANKEU E, WAANDERS F, NYEMBWE K D. Structural, compositional and mineralogical characterization of carbonatitic copper sulfide: Run of mine, concentrate and tailings [J]. International Journal Minerals Metallurgy Materials, 2019, 26(2): 143–151.
[22] ANTONIJEVIC G D, BOGDANOVIC M M. Investigation of the leaching of chalcopyritic ore in acidic solutions [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2004, 73: 245–256.
[23] KLAUBER C, PARKER A, van BRONSWIJK W, WATLING H. Sulphur speciation of leached chalcopyrite surfaces as determined by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2001, 62(1–4): 65–94.
[24] SALINAS K E, HERREROS O, TORRES C M. Leaching of primary copper sulfide ore [J]. Minerals, 2018, 8: 1–12.
[25] JONES D L, PETERS E. Extractive metallurgy of copper [M]. New York: AIME, 1976.
[26] MUNOZ P B, MILLER J D, WADSWORTH M E. Reaction mechanism for the acid ferric sulfate leaching of chalcopyrite [J]. Metallurgical Transaction B, 1979, 10(2): 149–158.
[27] GOMEZ C, FIGUEROA M, MUNOZ J, BLAZQUEZ M L, BALLESTER A. Electrochemistry of chalcopyrite [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1996, 43(1-3): 331–344.
[28] DUTRIZAC J E. The dissolution of chalcopyrite in ferric sulfate and ferric chloride media [J]. Metallurgical Transaction B, 1981, 12(2): 371–378.
[29] BAI Jing, WEN Jian-kang, HUANG Song-tao, WU Biao. Chemical leaching mechanism of chalcopyrite with difference mineralization [J]. Rare Metals, 2013, 32(1): 63–66.
[30] RUIZ M C, MONTES K S, PADILLA R. Chalcopyrite leaching in sulfate-chloride media at ambient pressure [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2011, 109(1–2): 37–42.
[31] LU Z Y, JEFFREY M I, LAWSON F. The effect of chloride ions on the dissolution of chalcopyrite in acidic solutions [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2000, 56: 189–202.
[32] TSHILOMBO O M, OJUMU T V. Investigation of the effect of pH operating conditions on bioleaching of low-grade chalcopyrite in column reactors [J]. Adv Mater Res, 2013, 825: 401–405.
[33] SANTOS A L A, ARENA F A, BENEDETTI A V, BEVILAQUA D. Effect of redox potential on chalcopyrite dissolution imposed by addition of ferrous ions [J]. Eclética Química Journal, 2017, 42(1): 40–50.
[34] ACERO P, CAMA J, AYORA C, ASTA M P. Chalcopyrite dissolution rate law from pH 1 to 3 [J]. Geologica Acta, 2009, 7(3): 389–397.
[35] VILCAEZ J, SUTO K, INOUE C. Bioleaching of chalcopyrite with thermophiles: Temperature-pH-ORP dependence [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2008, 88: 37-44.
[36] SOKIC M D, MARKOVIC B, ZIVKOVIC D. Kinetics of chalcopyrite leaching by sodium nitrate in sulphuric acid [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2009, 95(3-4): 273-279.
[37] HATERT F R. Transformation sequences of copper sulfides at Vielsalm [J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 2005, 43: 623–635.
[38] PAQUOT F X, NGULUBE C. Development and optimization of mixed sulphide/oxide copper ore treatment at Kansanshi [J]. The Journal of Southern African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 2015, 115: 1253–1258.
[39] HJELTSTR A. Copper minerals under the microscope [D]. Uppsala: Uppsala University, 2015.
[40] ZHAO H B, HU M H, LI Y N, ZHU S, QIN W Q, QIU G Z, WANG J. Comparison of electrochemical dissolution of chalcopyrite and bornite in acid culture medium [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(1): 303–313.
Kolela J NYEMBWE1,2, Elvis FOSSO-KANKEU1, Frans WAANDERS1, Martin MKANDAWIRE1,2
1. Water Pollution Monitoring and Remediation Initiatives Research Group, School of Chemical and Minerals Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, North-West University, South Africa;
2. Department of Chemistry, School of Science and Technology, Cape Breton University, Canada
摘 要:在pH值0.5~2.5、温度25 °C和时间12 h的条件下,研究碳酸盐岩型黄铜矿在H2SO4-Fe2(SO4)3- FeSO4- H2O体系中的溶解行为。实验所用的颗粒粒度为53~75 μm。在所有pH条件下,Cu的回收率均低于15%。浸出渣的XRD、SEM-EDS和光学显微镜(OM)分析结果表明,溶解过程中形成了中间相。pH为0.5和1.0时的中间相分别是Cu3.39Fe0.61S4和Cu2S,而pH值为1.5和1.8时的主要矿物为Cu5FeS4。热力学模拟预测产物的生成顺序为CuFeS2→Cu5FeS4→Cu2S→CuS。Cu5FeS4 and Cu2S为可溶性中间相,而CuS和Cu3.39Fe0.61S4是难溶中间相,在整个溶解过程中不断积累。所得结果表明,CuFeS2浸出过程中CuS和Cu3.39Fe0.61S4的生成有助于形成钝化膜。
关键词:黄铜矿;碳酸岩;化学浸出;浸出机理;中间相;热力学行为
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Corresponding author: Elvis FOSSO-KANKEU, E-mail: elvis.fossokankeu@nwu.ac.za, elvisfosso.ef@gmail.com, djosnyembwe@gmail.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(21)65644-3
1003-6326/ 2021 The Nonferrous Metals Society of China. Published by Elsevier Ltd & Science Press
2021 The Nonferrous Metals Society of China. Published by Elsevier Ltd & Science Press

