
Microstructure evolution and grain growth behavior of Ti14 alloy during semi-solid isothermal process
CHEN Yong-nan1, WEI Jian-feng2, ZHAO Yong-qing3, ZHENG Jing3
1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Chang’an University, Xi’an 710064, China;
2. State Key Laboratory for Mechanical Behavior of Materials, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, China;
3. Northwest Institute for Nonferrous Metal Research, Xi’an 710016, China
Received 10 May 2010; accepted 29 November 2010
Abstract: Microstructure evolution of Ti14 (α+Ti2Cu) alloy during semi-solid isothermal process at different temperatures was investigated. The results reveal that both the temperature and holding time have effect on the grain growth behavior. The grains grow obviously and the degree of globularity increases with the increase of holding time. According to the statistic analysis of experimental data, the grain growth indices are 0.88 and 0.97 at 1 000 °C and 1 050 °C, respectively, which indicates that increasing isothermal temperature would accelerate microstructural evolution.
Key words: titanium alloy; Ti14 alloy; semi-solid; microstructure; grain growth index
1 Introduction
Semi-solid forming is an effective net-shape forming process, which combines the elements of both casting and forging. Compared with conventional forming methods, semi-solid forming can easily accomplish what conventional forming can, but requires lower deformation load due to its low deformation resistance, and consequently, it enables a decrease in energy and machining costs[1-2]. The semi-solid processing of Al[3-6], Mg[7] and steel[8-9] has been investigated by many scientists and engineers all over the world, and the results revealed that the existing of liquids causes various grain boundary behaviours including grain boundary rotation, diffusion as well as dislocation motion during the semi-solid processing, which lead to different grain growth characters and strongly affect the mechanical properties. However, the microstructure evolution of titanium alloys at semi-solid state has not been investigated yet. Most recently, some authors[10-13] reported that the semi-solid microstructure and deformation behaviors of Ti14 (Ti-0.5Al-13Cu-0.5Si,) alloys were quite different from the conventional one, but there was not further discussion on the grain growth behavior during semi-solid isothermal process which is very important for the semi-solid formability of titanium alloys. In order to obtain the knowledge of grain growth characteristics of titanium alloy at semi-solid state, the object of this work is to research the grain growth behaviors of Ti14 alloy at different semi-solid temperatures for different holding time.
2 Experimental
The as-cast Ti14 alloy used in this work was a new α+Ti2Cu type burn-resistant Ti alloy. The melting point of Ti2Cu is 990 °C. If the temperature rises above 990 °C, the alloy changes to semi-solid state[13]. The samples with a diameter of 8 mm and length of 12 mm were prepared and heated at 1 000 and 1 050 °C for 5, 10, 20 and 30 min, respectively, followed by water quenching to obtain the semi-solid microstructure of the alloy[10]. Microstructures were analyzed by optical microscopy (OM, OLYMPUS GX71) and the grain size was calculated using Olympics 3M software and mean transversal method. The shape factor of grain (ξ) is defined as[14]
 (1)
(1)
where p and A are interface length (μm) and sectional area (μm2) of grain, respectively. ξ changed from 0 to 1, where 0 represents an elongated cross-section and 1 represents a round.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructure evolution of Ti14 alloy at semi-solid state
The fraction of liquid at different temperatures could be estimated by Scheil equation[1]:
 (2)
(2)
where fl is liquid fraction; TM is the melt point of pure dissolvent; TL is the liquidus temperature of alloy; and k is the partition coefficient. According to formula(2), the estimated volume fraction of liquid increases with the increase of temperature.
Figure 1 represents the microstructure of the samples with different temperatures and holding time. Liquid segregates at grain boundaries and distributes discontinuously after holding for 5 min at 1 000 °C (Fig.1(a)). More liquid segregates at grain boundaries with the increase of holding time (Fig.1(b)). Finally, liquid continuously distributes along grain boundary and forms a network structure after isothermal treatment for more than 20 min (Figs.1(c) and (d)). The variety in microstructure of Ti14 alloy after isothermal treatment at 1 050 °C is similar to that at 1 000 °C (Figs.1(e)-(h)), but the continuously distributed liquid more easily form along gain boundaries for the higher activity energy of grain boundary.
3.2 Grain growth and morphology during isothermal process
Figures 2(a) and (b) show effects of holding time on average grain size and grain shape of Ti14 alloy at 1 000 and 1 050 °C, respectively. The average grain size at semi-solid state increases with the increase of holding time which has little effect on titanium alloys in the solid state. The previous researches on the grain growth behaviors of titanium alloy show that grain grew through grain boundary migration controlled by atom diffusion[15-16], and grain exhibited a large growth rate at the first stage of the isothermal treatment; then the growth rate decreased with the increase of holding time; finally, the grain no longer grew with the variation of holding time. However, in this study, it is seen that grain exhibited a large growth rate during the semi-solid isothermal treatment. This may contribute to the change of gain growth mechanism. At the beginning of the isothermal treatment, liquid discontinuously distributed at grain boundaries, and the grain grew by coalescence growth mechanism. The liquid continuously distributed on grain boundaries to form thin film with increase of holding time, and the grain grew by breaking off the grain boundaries for Rayleigh instability[17], which was firstly observed in Ti alloy, and caused large growth rate at 1 050 °C, as shown in Fig.2(a). The above two grain growth mechanisms led to different morphologies of grains. It was interesting in finding that ξ decreased after holding for 20 min and then increased at 1 000 °C, but ξ at 1 050 °C increased with extending holding time. This is because that the as-cast Ti14 alloy consisted of equiaxial grains, and the grains had little change in the morphology at initial stage (Figs.1(a) and (b)). The grain grew via coalescence and broken off mechanism with the increase of holding time, which makes the grain shape more irregular (Fig.1(c)); as the holding time increases, more liquids distributed at grain boundaries to form thin film round the grains, resulting in a large degree of globularity (Fig.1(d)). While at 1 050 °C, more liquid phases were obtained compared with 1 000 °C, and a network structures form at the initial stage(Figs.1(e)-(h)), which is beneficial for grain to grow by broken-off mechanism, and results in a small ξ.
3.3 Grain growth index
The relationship between grain size and holding time can be described by Beck equation[18]:
 (3)
(3)
where Dt and D0 are current and initial (when t=5 min) values of the mean grain diameter; k is a constant related to temperature; and n is the grain growth index. If n is large, the grain grows quickly. The grain growth indices of Ti14 alloy with different temperatures and holding time were analyzed according to Eq.(3) and is presented in Fig.3. The slope of a linear fit was used to estimate the grain growth index of each temperature. These calculated grain growth indices were 0.88 at 1 000 °C, and 0.97 at 1 050 °C, respectively. These values are higher than the data for grain boundary self-diffusion, n=0.5-0.6, in titanium alloys and other metal. This may be related to the broken off mechanism which only occurs when grain boundaries consist of continued distributed liquid at semi-solid state. This confirms that existence of liquid accelerates grain growth behavior.
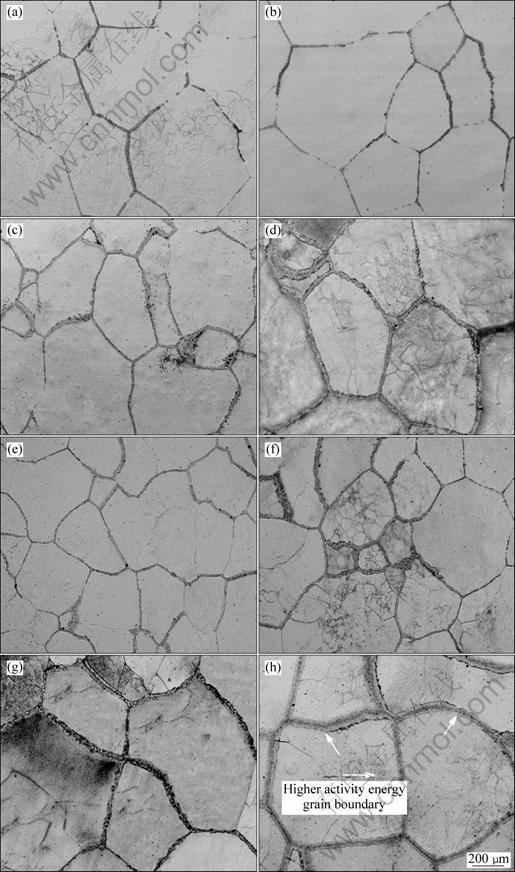

Fig.1 Grain boundary evolution of Ti14 alloy at 1 000 °C for 5 min (a), 10 min (b), 20 min (c), 30 min (d) and at 1 050 °C for 5 min (e), 10 min (f), 20 min (g) and 30 min (h)
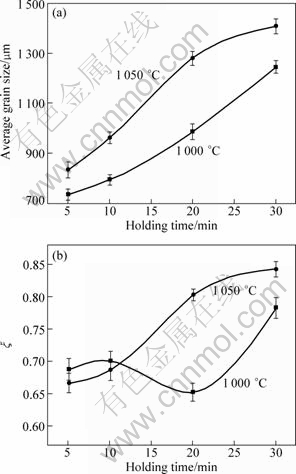
Fig.2 Effect of holding time on mean grain size (a) and grain shape (b) at different semi-solid temperatures
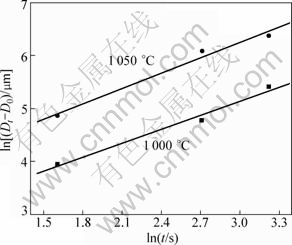
Fig.3 Curves of ln(Dt-D0) and ln t at different semi-solid temperatures for Ti14 alloy
4 Conclusions
1) Liquid distributes at grain boundary from discontinuum to continuum and finally network structure liquid grain boundary forms.
2) Liquid phase increases with the increase of the temperature and holding time, grains grow and their shape tends to be round.
3) The grain growth indices of Ti14 alloy are 0.88
and 0.97 at 1 000 and 1050 °C, respectively, which means that the existence of liquid accelerates grain growth.
References
[1] FLEMING M C. Solidification processing [M]. McGraw Hill, 1974, 160.
[2] DONACHIE M J. Materials park [M]. OH: ASM International, 2000: 22.
[3] ESKIN D G, SUYITNO, KATGERMAN L. Mechanical properties in the semi-solid state and hot tearing of aluminium alloys[J]. Prog Mater Sci, 2004, 49(5): 629-711.
[4] MABUCHI M, IWASAKI H, HIGASHI K. An investigation of shear deformation in a semi-solid state of a high strain rate superplastic Si3N4p/Al-Mg-Si composite [J]. Acta Mater, 1998, 46(15): 5335-5343.
[5] CHINO Y, KOBATA M, IWASAKI H. An investigation of compressive deformation behaviour for AZ91 Mg alloy containing a small volume of liquid [J]. Acta Mater, 2003, 51(11): 3309-3318.
[6] SUYTINO D G, ESKIN, KATGERMAN L. Structure observations related to hot tearing of Al-Cu billets produced by direct-chill casting [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2006, 420(1): 1-7.
[7] HU K, PHILLION A B, MAIJER D M. Constitutive behavior of as-cast magnesium alloy Mg-Al3-Zn1 in the semi-solid state [J]. Script Mater, 2009, 60(6): 427-430.
[8] MOHAMED R, MITSUHARU T, HIROYUKI N. Effect of semi-solid processing on solidification microstructure and mechanical properties of gray cast iron [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2006, 417(1): 166-173.
[9] PU¨TTGEN W, HALLSTEDT B, BLECK W. On the microstructure and properties of 100Cr6 steel processed in the semi-solid state [J]. Acta Mater, 2007, 55(19): 6553-6560.
[10] CHEN Y N, WEI J F, ZHAO Y Q. Compressive deformation and forging behavior of Ti14 alloy in semi-solid state [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2009, 520(1): 16-22.
[11] CHEN Y N, WEI J F, ZHAO Y Q. Effect of semi-solid forging temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti14 alloy [J]. J Alloys Compounds, 2009, 487(1): 314-320.
[12] ZHAO Y Q, WU W L, CHANG H. Research on microstructure and mechanical properties of anew Ti2Cu alloy after semi-solid deformation [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2006, 416: 181-186.
[13] ZHAO Yong-qing, ZHU Kang-ying, ZHAO Xiang-miao. A polishing etchant for the Ti alloy: CN97103866[P]. 1997-12-17. (in Chinese)
[14] YANG Quan. Simulation to solidification and cast of metals [M]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University Press, 1996: 137. (in Chinese)
[15] SEETHARAMAN V, SEMIATIN S L. Plastic-flow and microstructure evolution during hot deformation of a gamma titanium aluminide alloy [J]. Mater Trans A, 1997, 28: 2309-2321.
[16] GIL F J, PLANELL J A. Behaviour of normal grain growth kinetics in single phase titanium and titanium alloys [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2000, 283(1): 17-24.
[17] LIU Zong-chang, REN Hui-ping, SONG Yi-quan. Testbook on solid-state phase transformation of metal [M]. Beijing: Metallurgy Industry Press, 2003: 28. (in Chinese)
[18] MAO Wei-min, ZHAO Xin-bing. The recrystallization and grain growth of metal [M]. Beijing: Metallurgy Industry Press, 1994: 236. (in Chinese)
Ti14合金半固态等温热处理过程中组织演化规律和
晶粒长大行为
陈永楠1,魏建锋2,赵永庆3,郑 晶3
1. 长安大学 材料科学与工程学院,西安 710064;
2. 西安交通大学 金属材料国家重点实验室,西安 710049;
3. 西北有色金属研究院,西安 710016
摘 要:研究在1 000 °C和1 050 °C半固态温度下Ti14合金保温不同时间时微观组织的演化过程,计算在不同半固态温度下晶粒的生长指数,并分析半固态温度和保温时间对晶界和晶粒尺寸以及形态的影响规律。结果表明:随着保温时间的延长,晶粒明显长大,晶粒形态趋于圆整,晶界处液相由不连续分布转变为连续分布,最终呈网格状;1 000 °C和1 050 °C对应的晶粒生长指数分别为0.88和0.97,表明升高温度加速了微观组织的演化。
关键词:钛合金;Ti14合金;半固态;微观组织;晶粒生长指数
(Edited by YANG Hua)
Foundation item: Projects (2005CCA06400, 2007CB613807) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China; Project (CHD2010JC115) supported by the Special Fund for Basic Scientific Research of Central Colleges, China
Corresponding author: CHEN Yong-nan; Tel: +86-29-82664764; E-mail: frank_cyn@163.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60815-7