金属注射成型生物医用Ti-22Nb合金的表面形貌和细胞相容性
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2018年第7期
论文作者:赵大鹏 陈钰凯 常可可 Thomas EBEL Bérengère J C LUTHRIGNER-FEYERABEND Regine WILLUMEIT-R?MER Florian PYCZAK
文章页码:1342 - 1350
关键词:金属注射成型;Ti-Nb合金;表面拓扑结构;细胞吸附;细胞增殖
Key words:metal injection molding; Ti-Nb alloy; surface topography; cell adhesion; cell proliferation
摘 要:采用金属注射成型(MIM)工艺制备Ti-22Nb(质量分数,%)和商业纯钛(CP-Ti)参比样,并选取电弧熔炼后抛光的Ti-22Nb作为另一种参比样。采用激光共聚焦显微镜、扫描电子显微镜和酶联免疫检测仪检测每组样品的表面拓扑结构和细胞相容性。结果显示,MIM工艺可以得到微米级粗糙度,而且采用混合元素粉而不是单一钛粉作为原料可以获得更高的表面粗糙度和比表面积。所有测试样品都不存在细胞毒性。人原代细胞在MIM Ti-22Nb样品表面(特别是在闭孔附近)的吸附效果更好。
Abstract: Metal injection molding (MIM) was applied to fabricating Ti-22Nb (mass fraction, %) and commercially-pure Ti (CP-Ti, selected as reference) discs. As references, arc-melted and polished Ti-22Nb discs were employed. The surface topography and cytocompatibility were comparatively assessed on each configuration by microscopic analysis using confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy and adhesion and viability tests. The results reveal that micron-scale roughness could be obtained via MIM process, and using blended Ti and Nb elemental powders instead of only Ti powder as raw materials leads to much higher surface roughness and surface area ratio. None of the three materials shows cytotoxicity, and the adhesion of human primary cells seems to be increased on the MIM Ti-22Nb specimens, especially around the closed-pores on the surface.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 28(2018) 1342-1350
Da-peng ZHAO1,2, Yu-kai CHEN1, Ke-ke CHANG3, Thomas EBEL2,  J C LUTHRIGNER-FEYERABEND2, Regine WILLUMEIT-
J C LUTHRIGNER-FEYERABEND2, Regine WILLUMEIT-  2, Florian PYCZAK2
2, Florian PYCZAK2
1. College of Biology, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China;
2. Institute of Materials Research, Helmholtz-Zentrum Geesthacht, 21502 Geesthacht, Germany;
3. Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo 315201, China
Received 12 November 2017; accepted 8 April 2018
Abstract: Metal injection molding (MIM) was applied to fabricating Ti-22Nb (mass fraction, %) and commercially-pure Ti (CP-Ti, selected as reference) discs. As references, arc-melted and polished Ti-22Nb discs were employed. The surface topography and cytocompatibility were comparatively assessed on each configuration by microscopic analysis using confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy and adhesion and viability tests. The results reveal that micron-scale roughness could be obtained via MIM process, and using blended Ti and Nb elemental powders instead of only Ti powder as raw materials leads to much higher surface roughness and surface area ratio. None of the three materials shows cytotoxicity, and the adhesion of human primary cells seems to be increased on the MIM Ti-22Nb specimens, especially around the closed-pores on the surface.
Key words: metal injection molding; Ti-Nb alloy; surface topography; cell adhesion; cell proliferation
1 Introduction
Owing to the excellent corrosion resistance, high specific strength and good biocompatibility, titanium (Ti) and its alloys have been extensively used for biomedical applications since 1970s [1-3]. Currently, the most widely used Ti-based surgical implant materials are commercially-pure Ti (CP-Ti) and Ti-6Al-4V alloy [4,5]. However, the stress-shielding effect, resulting from the mismatch of elastic modulus between them (100-120 GPa) and human bones (4-30 GPa), as well as the potential cytotoxicity of aluminum (Al) and vanadium (V) in Ti-6Al-4V, may lead to implant-loosening and long-term health problems [6,7]. In order to overcome the above-mentioned limitations, many β or near-β Ti alloys with non-toxic alloying elements, such as Ti-Nb and Ti-Ta alloys, have been developed [2,8,9].
The production of Ti-based implants is still hampered by the high cost of the conventional processing of complex shapes and the poor workability of Ti [10]. Owing to the high design flexibility and net-shape fabrication advantages, metal injection molding (MIM) is considered as a cost-effective powder metallurgy technique with the potential for Ti-based implants fabrication [11]. There have been many attempts in the fabrication of Ti and Ti-6Al-4V alloy by MIM, but much fewer investigations on MIM β or near-β Ti alloys have been performed [12]. The first successful fabrication of a MIM Ti-Nb alloy was reported in 2011 [13]. After that, ZHAO et al [8], KAFKAS and EBEL [14] and EBEL et al [15] focused on the microstructure control and mechanical properties of MIM Ti-Nb alloys. However, the cytocompatibility assessment of MIM Ti-Nb alloys, which is essential for clinical implants, has not been performed yet. Besides, although most MIM Ti and Ti alloys were fabricated by using pre-alloyed powders as raw materials, ZHAO et al [16] stated that using blended elemental instead of pre-alloyed powders in the MIM process shows many advantages, such as higher feasibility for composition design and lower cost. Nevertheless, the influence of using the powder mixture on the biocompatibility of MIM Ti alloys is still not clear. Consequently, it is necessary to evaluate the biocompatibility of MIM β or near-β Ti alloys, prepared by using blended elemental powders, before putting these alloys into clinical applications.
In this work, MIM process was applied for the fabrication of a Ti-22Nb (mass fraction, %) alloy by using blended elemental powders. The aim is to evaluate the cytotoxicity of the MIM Ti-Nb alloy, and to understand the effects of using blended powders as raw materials on the cell response.
2 Experimental
2.1 Sample preparation
Gas atomized Ti powder (<45 μm, average particle size: 21 μm; supplied by TLS Technik GmbH, Bitterfeld, Germany) and hydride-dehydride (HDH) Nb powder (<124 μm, average particle size: 75 μm; supplied by MHC Industrial Corporation, Xianyang, China) were used in this work for the MIM fabrication. Figure 1 shows the powder morphology of the raw materials.
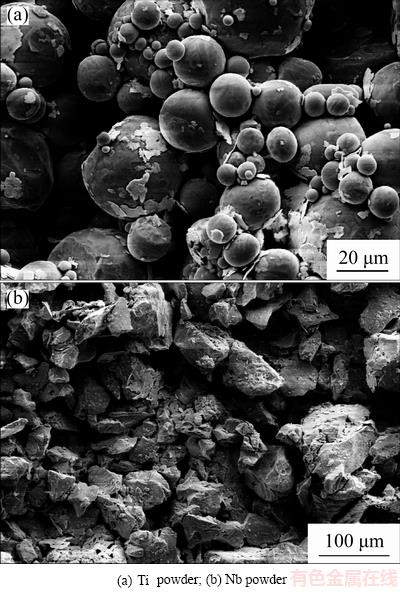

Fig. 1 Scanning electron micrographs of raw materials
Samples made from Ti-22Nb and CP-Ti were produced by a MIM process. The Ti powder and Nb powder were blended, and then mixed with the polymer binder consisting of a major fraction of paraffin wax, a minor fraction of polyethylene vinyl acetate and stearic acid at 120 °C for 2 h to form a feedstock. The same volume fraction of binder of 31% was applied for all MIM samples. After being injection-molded as discs shaped with a diameter of 10 mm and height of 2.5 mm, the green components were immersed into hexane at 40 °C for 20 h for solvent extraction. The thermal debinding and sintering were performed in one cycle in a XERION XVAC 1600 furnace. The maximum sintering temperature was 1500 °C and the holding time at that temperature was 2 h. The as-sintered Ti-22Nb and CP-Ti samples were referred to as Ti-22Nb (MIM) and CP-Ti (MIM), respectively. Argon arc-melting (AM) was applied to preparing reference Ti-22Nb samples by using Ti sponge (Timet Germany GmbH, Germany) and Nb pieces (Alfa Aesar, United States) as raw materials. Afterwards, the arc-melted Ti-22Nb samples were annealed at 1500 °C for 2 h, followed by cutting into the same dimensions as the Ti-22Nb (MIM) discs. The surfaces of the reference Ti-22Nb samples were polished by using SiO2 suspensions (50 nm) for 10 min, cleaned and then dried under normal atmosphere at room temperature. These as-polished Ti-22Nb specimens were referred to as Ti-22Nb (AM).
All samples were cleaned with Helmanex solution and then sterilized by autoclaving (20 min at 121 °C; Systec VE-150, Systec GmbH, Wettenberg, Germany) prior to biomedical tests.
2.2 Porosity and surface characterization
The immersion method outlined in ASTM B311 was applied for the density measurements. The porosity of the samples was calculated by using the following formula:
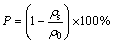 (1)
(1)
where ρs is the apparent density of the samples and ρ0 is the density of the fully-dense samples with the same composition (4.501 g/cm3 for CP-Ti, and 5.080 g/cm3 for Ti-22Nb [8]).
A non-contact measurement using confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM; VK-9700, Keyence, Japan) was employed to quantitatively evaluate the surface roughness and obtain a three dimensional (3-D) surface topography of the samples. At least three samples were evaluated for each configuration and three fields were acquired per group. The surface roughness parameters, i.e., Ra (arithmetical mean deviation of the profile, ISO 4287-1997), Rz (maximum height of the profile, ISO 4287-1997) and Rmr(c) (material ratio of the profile, Rmr=50%, ISO 4287-1997), were calculated by VK Analyzer software (Keyence, Japan) according to the standard – JIS B 0601:2001 (ISO 4287-1997).
2.3 Cell isolation and cell culture
All biological tests were performed with human umbilical cord perivascular (HUCPV) cells, a type of mesenchymal stem cell known to spontaneously form bone nodule in non-osteogenic culture condition [17]. HUCPV isolations were derived from Wharton’s jelly of the umbilical cord as previously described [18]. The cords were cut into pieces of around 5 cm. The vessels from the cord pieces were isolated and tied together at the ends with sutures, resulting in a vessel loop. They were placed in T-175 cell culture flasks (Greiner Bio-One GmbH, Frickenhausen, Germany) and cultured for ten days without changing medium, which consisted of α-MEM (Invitrogen Corporation, Karlsruhe, Germany) with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) for mesenchymal stem cells (Stem Cell Technologies, Vancouver, Canada). After observable outgrowth from the loops, the medium was changed every 2-3 days. At about 60% confluency, the cells were harvested with a cell scraper and subcultured at a density of 1000 cells/cm2. In the present experiments, cells of the third to fifth passage were used. The HUCPV cells were cultured under physiological conditions (5% CO2, 20% O2, 95% relative humidity, 37 °C).
2.4 Cell biology assessments: Initial cell adhesion and viability assays
50000 HUCPV cells in 50 μL medium were seeded on the Ti-22Nb (MIM), CP-Ti (MIM) and Ti-22Nb (AM) samples (for each configuration, n=4; experiment was repeated three times) in twelve-well plates (pre-coated with 1% agarose to avoid adhesion on the well bottom) and left to adhere for 30 min. Thereafter, 3 mL cell culture medium was added to each samples and cells were further cultured for the remaining time (i.e., 10, 25 and 40 min). After each time point, the samples were rinsed with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and then transferred into new wells. The cells were detached from the samples using 0.05% trypsin (EDTA, Sigma-Aldrich Chemie GmbH, Munich, Germany), followed by counting cells using the cell counter system (CASY Model TT, Roche Diagnostic GmbH, Mannheim, Germany). Additionally, cell morphology after the same time points was assessed using SEM (AURIGA, Modular CrossBeam workstation, Carl Zeiss NTS GmbH, Germany). Therefore, the samples were fixed in 2.5% glutaraldehyde solution (Sigma-Aldrich Chemie GmbH, Munich, Germany), and stained with 1% osmium tetroxide (Sigma-Aldrich Chemie GmbH, Munich, Germany). Afterwards, the specimens were dehydrated through a two-propanol series and critical point dried using a critical point dryer (Leica EM CPD300, Leica Mikrosysteme GmbH, Vienna, Austria).
For cell proliferation assays, the methodology remained the same as the initial adhesion experiments, but the cultures were maintained for three or five days, followed by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT, Sigma-Aldrich Chemie GmbH, Munich, Germany) tests. 150 μL (1:10) MTT solution (5 mg/mL MTT in PBS) was added to the cell supernatant in each well. After an incubation of 4 h in the incubator, the cells were lysed and the purple formazan crystals formed by active cells were solubilized by adding 1.5 mL solubilization solution (10% sodium dodecyl sulphate in 0.01 mol/L HCl; Sigma-Aldrich Chemie GmbH, Munich, Germany) and overnight incubation at 37 °C under 5% CO2 and 95% humidity controlled atmosphere. In order to photometrically quantify the solubilized formazan product, a spectrophotometer (Tecan Sunrise, TECAN Deutschland GmbH, Crailsheim, Germany) was used and absorbance was measured at 570 nm with a reference wavelength of 655 nm.
2.5 Statistical evaluation
Statistics was performed using the SigmaStat package (Systat software GmbH, Erkrath, Germany). Standard analysis comparing more than two treatments was done by using the one-way ANOVA (analysis of variance). Depending on the data distribution, either a one-way ANOVA or an ANOVA on ranks was performed. Post-hoc tests were Holm-Sidak or Dunn’s versus the control group, respectively. Statistical values are indicated at the relevant experiments (P≤0.05).
3 Results
3.1 Porosity
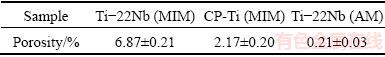
The porosities of Ti-22Nb (MIM), CP-Ti (MIM) and Ti-22Nb (AM) samples calculated according to Eq. (1) are presented in Table 1. Generally, the porosity of all samples is lower than 8%. The Ti-22Nb (MIM) samples show the highest porosity, while the Ti-22Nb (AM) specimens are almost fully dense.
Table 1 Porosity of Ti-22Nb (MIM), CP-Ti (MIM) and Ti-22Nb (AM) samples
3.2 Surface topography
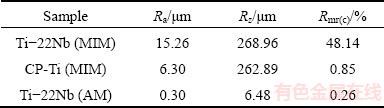
Before performing the cell biology assessments, CLSM was employed for the topographical surface examinations and roughness measurements. Figure 2 presents the three-dimensional topographic surface images of the Ti-22Nb (MIM), CP-Ti (MIM) and Ti-22Nb (AM) samples. The three configurations exhibit different surface structures. As shown in Fig. 2(a), the Ti-22Nb (MIM) alloy exhibits higher and more irregular peak dimensions than the other two; whereas, the Ti-22Nb (AM) alloy exhibits the smoothest surface (Fig. 2(c)). Such diversity between them is confirmed by the comparative Ra, Rz and Rmr(c) values, as given in Table 2. The Ti-22Nb (AM) alloy shows the lowest Ra, Rz and Rmr(c) compared with the other two. Although the profiles of the Ti-22Nb (MIM) and CP-Ti (MIM) samples present similar Rz, the Ra and Rmr(c) of the former are much higher than those of the latter.
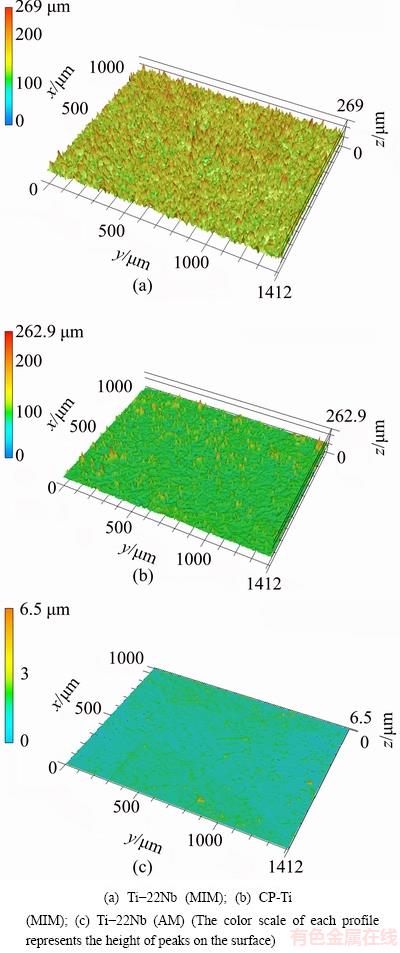
Fig. 2 Topographic three-dimensional views of surfaces (1.412 mm × 1.000 mm)
Table 2 Roughness parameters on studied surfaces
3.3 Initial cell adhesion
The initial cell adhesion of HUCPV cells on the Ti-22Nb (MIM), CP-Ti (MIM) and Ti-22Nb (AM) samples was determined by using a cell counter system. Figure 3 shows the cell numbers on different samples after initial cell adhesion for 10, 25 and 40 min. In general, a significantly enhanced adhesion of HUCPV cells, i.e., a larger cell number, is observed in all the samples with longer incubation time. The cell numbers on the three configurations do not show significant difference after cell adhesion for 10 or 25 min, as shown in Fig. 3. However, after incubation for 40 min, a significantly larger cell number on the Ti-22Nb (MIM) is observed compared with the one on the Ti-22Nb (AM) samples.
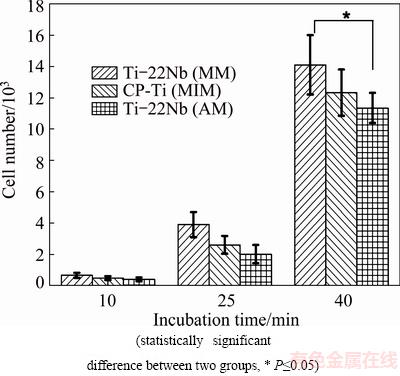
Fig. 3 HUCPV cell numbers after adhesion on different materials for 10, 25 and 40 min
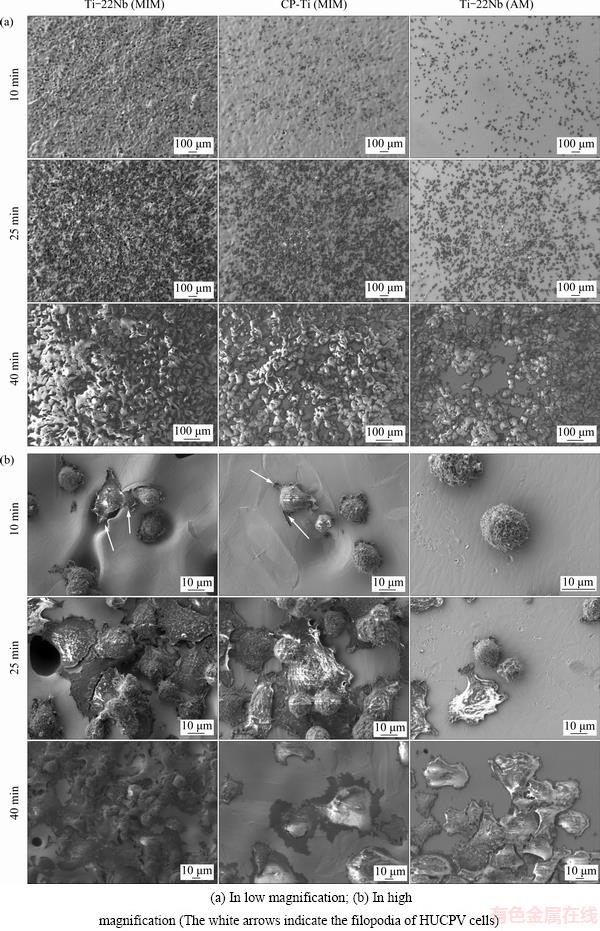
Fig. 4 SEM images of HUCPV cells after adhesion on different materials for 10, 25 and 40 min
In order to evaluate the interaction between materials and HUCPV cells during initial cell adhesion, SEM images of the adhered cells on different samples were taken and selected ones are presented in Fig. 4. At low magnification (Fig. 4(a)), cells present homogeneous distribution on all material surfaces, and with increasing incubation time, more HUCPV cells adhere on the surface of various samples. A slight preference of the cells to adhere on the materials with higher surface roughness is observed. The differences in cell morphology on the Ti-22Nb (MIM), CP-Ti (MIM) and Ti-22Nb (AM) samples are shown at higher magnification in Fig. 4(b). After incubation for 10 min, the HUCPV cells on the Ti-22Nb (MIM) and CP-Ti (MIM) specimens start to spread. The filopodia are observed on them (see the white arrows in Fig. 4(b)), and the membrane protrusions at the cell margins are preferentially adhered around the pores on the surface. However, the cells on the Ti-22Nb (AM) specimens are still spherical. After incubation for 25 min, the cell spreading starts on the Ti-22Nb (AM) samples, while most cells on the other two configurations appear flat. After incubation for 40 min, the HUCPV cells are stably attached on all samples, and tend to grow multilayered and cover the whole surface.
3.4 Viability assays
The proliferation of HUCPV cells was studied after three and five days (MTT assays). Figure 5 shows the results as well as the statistical analyses of the proliferation assays. The MTT absorbance of cells grown on the samples after five days is significantly higher than that obtained after three days for each configuration. It is important to note that no real great disparities are observed among the different samples in the same proliferation time group.
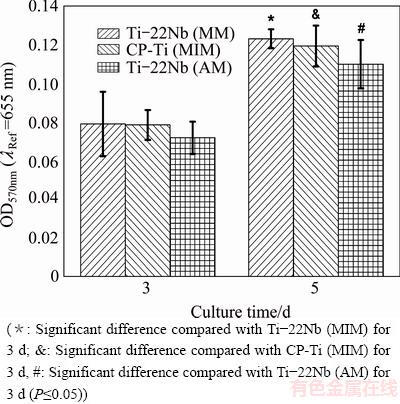
Fig. 5 MTT measurement results of HUCPV cell proliferation assays after adhesion on various materials for 3 and 5 d
4 Discussion
4.1 Surface properties
Ti-Nb alloys are considered as more promising candidates for biomedical applications compared with CP-Ti and Ti-6Al-4V alloy [19]. The Ti-Nb alloys fabricated by traditional processes, e.g., arc-melting technique, have been extensively investigated via both in vitro [20,21] and in vivo [22,23] assessments, and no cytotoxic or allergenic effects have ever been found concerning these alloys. Nevertheless, the biocompatibility of the MIM Ti-Nb alloys has not been examined yet. Although the MIM process may slightly increase the oxygen and carbon content compared with the raw materials [8], it usually does not significantly change the chemical composition of the products, and thus should not influence the cytocompatibility [11]. But some physical features of MIM products, especially the porosity and surface topography, could also have an impact on the biological response. As presented in Table 1, all samples show a porosity lower than 8%, which is usually considered as the threshold between open and closed porosity [24]. Open porosity of implants can lead to bone ingrowth and vascularization, but closed porosity does not exhibit interconnection dimensions. Thus, the influence of closed porosity on cell fate should be only determined by the pores on the outside surface [25,26]. Consequently, when discussing its effects on cells, the closed porosity in all samples in this work can be categorized as one part of surface topography.
MIM products usually exhibit surface topography with micron-scale roughness [27], so the Ti-22Nb (MIM) and CP-Ti (MIM) show much rougher surfaces than the polished Ti-22Nb (AM) samples, as shown in Fig. 2 and Table 2. Since the same paraffin wax-based binder system and volume fraction (31%) were applied for fabricating the Ti-22Nb (MIM) and CP-Ti (MIM) samples, the different surface topographical parameters of these two MIM configurations are probably not due to the binder system. LUTHRINGER et al [18] and  et al [28] reported that the surface roughness of MIM Ti-based implants highly depends on the powder size of raw materials and the solidification behavior during sintering. In the present work, compared with the CP-Ti (MIM) samples, the Ti-22Nb (MIM) samples show higher Ra but comparable Rz, indicating that the addition of the irregular-shaped Nb powders leads to considerable change in surface topography. Rmr(c) (Rmr=50%) is a parameter describing the full area the material occupied at half maximum amplitude. For different surfaces with peaks or valleys similar in size, Rmr(c) can reflect the surface area ratio (the ratio of the real surface area to its geometrical projection), i.e., a higher value of Rmr(c) suggests a higher surface area ratio. The significant difference between Rmr(c) of the Ti-22Nb (MIM) and CP-Ti (MIM) samples indicates that the former has significantly more peaks and valleys than the latter, which can be confirmed by the 3D-topographical images, as shown in Fig. 3. The differences between the surface topography and roughness of the Ti-22Nb (MIM) and CP-Ti (MIM) samples should be attributed to two factors. On one hand, both particle size and morphology are different for the two raw powders. As presented in Fig. 1, the Nb powders exhibit irregular shape, while most Ti powders are spherical. The irregular particles usually have a lower packing density but higher binder removal efficiency, which would inevitably influence the surface topography [29]. Besides, the particle size of the former is significantly larger than that of the latter. The larger diameter of initial powder particles usually contributes to higher roughness of the sintered specimens [28]. On the other hand, the diffusion coefficient of Nb in β-Ti is significantly lower than that of Ti in β-Ti, at temperatures ranging from 900 to 1500 °C [16], so during sintering, the shrinkage rate of the Ti-22Nb (MIM) samples is probably constrained compared with that of the CP-Ti (MIM) samples, resulting in much more irregular structures on the surface of the former, as shown in Fig. 2(a).
et al [28] reported that the surface roughness of MIM Ti-based implants highly depends on the powder size of raw materials and the solidification behavior during sintering. In the present work, compared with the CP-Ti (MIM) samples, the Ti-22Nb (MIM) samples show higher Ra but comparable Rz, indicating that the addition of the irregular-shaped Nb powders leads to considerable change in surface topography. Rmr(c) (Rmr=50%) is a parameter describing the full area the material occupied at half maximum amplitude. For different surfaces with peaks or valleys similar in size, Rmr(c) can reflect the surface area ratio (the ratio of the real surface area to its geometrical projection), i.e., a higher value of Rmr(c) suggests a higher surface area ratio. The significant difference between Rmr(c) of the Ti-22Nb (MIM) and CP-Ti (MIM) samples indicates that the former has significantly more peaks and valleys than the latter, which can be confirmed by the 3D-topographical images, as shown in Fig. 3. The differences between the surface topography and roughness of the Ti-22Nb (MIM) and CP-Ti (MIM) samples should be attributed to two factors. On one hand, both particle size and morphology are different for the two raw powders. As presented in Fig. 1, the Nb powders exhibit irregular shape, while most Ti powders are spherical. The irregular particles usually have a lower packing density but higher binder removal efficiency, which would inevitably influence the surface topography [29]. Besides, the particle size of the former is significantly larger than that of the latter. The larger diameter of initial powder particles usually contributes to higher roughness of the sintered specimens [28]. On the other hand, the diffusion coefficient of Nb in β-Ti is significantly lower than that of Ti in β-Ti, at temperatures ranging from 900 to 1500 °C [16], so during sintering, the shrinkage rate of the Ti-22Nb (MIM) samples is probably constrained compared with that of the CP-Ti (MIM) samples, resulting in much more irregular structures on the surface of the former, as shown in Fig. 2(a).
4.2 Cell response
LUTHRINGER et al [18] claimed that the HUCPV cell is an excellent model for initial cell adhesion and proliferation assessments, so it was used in the present work. As shown in Fig. 3, Fig. 4(a) and Fig. 5, the Ti-22Nb (MIM) samples show better or at least comparable cytocompatibility when being compared with the CP-Ti (MIM) and Ti-22Nb (AM) specimens. Since both CP-Ti and Ti-Nb alloys have been confirmed to be highly biocompatible and do not show significant difference in biocompatibility [11,20], the surface topographical properties probably play a dominant role in determining the cell behavior on the various samples.
HOTCHKISS et al [30] stated that the parameters describing surface roughness are generally privileged in the characterization of the surface topography that directly affects the osseointegration, and RUPP et al [31] indicated that Ra is the most commonly used parameter to describe implant surface roughness. Ti-based implants with higher Ra usually exhibit preferable cell attachment and increased pullout strength, which is supported by both in vitro and in vivo studies [32,33]. Usually difference in topography carries wettability changes and, due to this, difference in protein adsorption happens. Cell adhesion is directly influenced by this change [34]. In the present work, the low Ra of the Ti-22Nb (AM) samples indicates that there are almost no micron-scale structures on them, and therefore, the HUCPV cells adhered on them still show spherical morphology after incubation for 10 min; whereas, the cell spreading on the Ti-22Nb (MIM) and CP-Ti (MIM) specimens, both of which show much higher Ra, seems to be improved, as shown in Fig. 4(b). Besides, it has been observed that the initial cell adhesion is preferable around pores on the Ti-22Nb (MIM) and CP-Ti (MIM) samples rather than the smooth regions of the surfaces, indicating that the surface structure with higher curvature might be favorable for cell adhesion. Previous investigations stated that only Ra is not enough to explain the cell response on Ti-based implants [30,33]. The interaction between cells and implants highly depends on the surface area ratio [35], so it is reasonable that the Ti-22Nb (MIM) samples with the highest Rmr(c) exhibit better cell spreading behavior than the other two configurations. After incubation for 40 min, the HUCPV cells on all samples appear flat and multilayered (Fig. 4(b)), which is a sign of direct surface adhesion. After the adhered cells spreading on the whole surface, further proliferation after three or five days might be less influenced by the surface topography, so no great disparities are observed among the samples for the same proliferation time.
5 Conclusions
1) MIM process was successfully applied to fabricating the Ti-22Nb (MIM) and CP-Ti (MIM) samples with a porosity of less than 8%. Both of them show micron-scale surface roughness, but using blended Ti and Nb elemental powders instead of only gas-atomized Ti powder leads to much higher Ra and Rmr(c), which should be attributed to the irregular shape and relatively large particle size of the Nb powder as well as the significantly lower diffusion coefficient of Nb in β-Ti compared with that of Ti in β-Ti.
2) From the biological point of view, the Ti-22Nb (MIM) samples exhibit improved or at least comparable cytocompatibility with the CP-Ti (MIM) and Ti-22Nb (AM) samples, which have been known to be highly biocompatible. The Ti-22Nb (MIM) samples, which exhibit higher roughness and surface area ratio, are preferable for cell adhesion and filopodia spreading. Therefore, it is concluded that the surface topography seems to be the decisive factor for the cytocompatibility of MIM Ti alloys, and using blended elemental powder as raw materials in the MIM process appears to be ideally suited to bone cell adhesion and proliferation when being used in an as-MIMed surface condition.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Dr. Frank FEYERABEND, Dr. Uwe LORENZ, Andreas DOBERNOWSKY, Wolfgang LIMBERG, Petra FISCHER, Dr. Michael OEHRING and Dr. Jonathan PAUL from Helmholtz-Zentrum Geesthacht, Germany.
References
[1] KHORASANI A M, GOLDBERG M, DOEVEN E H, LITTLEFAIR G. Titanium in biomedical applications—Properties and fabrication: A review [J]. Journal of Biomaterials and Tissue Engineering, 2015, 5: 593-619.
[2] SHARKEEV Y, KOMAROVA E, SEDELNIKOVA M, SUN Ze-min, ZHU Qi-fang, ZHANG Jing, TOLKACHEVA T, UVARKIN P. Structure and properties of micro-arc calcium phosphate coatings on pure titanium and Ti-40Nb alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27: 125-133.
[3] ZHANG Rui, WAN Yi, AI Xing, WANG Teng, MEN Bo. Preparation of micro-nanostructure on titanium implants and its bioactivity [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26: 1019-1024.
[4] GUO Yong-yuan, CHENG Meng-qi, CHEN De-sheng, XUE Xiao-bing, ZHANG Xian-long. In vitro corrosion resistance and cytotoxicity of novel TiNbTaZr alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22: s175-s180.
[5] LAN Chun-bo, LI Guo, WU Yu, GUO Li-li, CHEN Feng. Effects of cold deformation on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-35Nb-2Zr-0.3O alloy for biomedical applications [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27: 1537-1542.
[6] GEETHA M, SINGH A K, ASOKAMANI R, GOGIA A K. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants—A review [J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2009, 54: 397-425.
[7] ZHAO Da-peng, CHANG Ke-ke, EBEL T, QIAN Ma, WILLUMEIT R, YAN Ming, PYCZAK F. Titanium carbide precipitation in Ti-22Nb alloy fabricated by metal injection moulding [J]. Powder Metallurgy, 2014, 57: 2-4.
[8] ZHAO Da-peng, CHANG Ke-ke, EBEL T, QIAN Ma, WILLUMEIT R, YAN Ming, PYCZAK F. Microstructure and mechanical behavior of metal injection molded Ti-Nb binary alloys as biomedical material [J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2013, 28: 171-182.
[9] ZHAO Da-peng, EBEL T, YAN Ming, QIAN Ma. Trace carbon in biomedical beta-titanium alloys: Recent progress [J]. JOM, 2015, 67: 2236-2243.
[10] BOLZONI L, RUIZ-NAVAS E M, NEUBAUER E, GORDO E. Mechanical properties and microstructural evolution of vacuum hot-pressed titanium and Ti-6Al-7Nb alloy [J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2012, 9: 91-99.
[11] DEMANGEL C,  D, VAYSSADE M, DUVAL J L, VIGNERON P, NAGEL M D, PUIPPE J C. Cytocompatibility of titanium metal injection molding with various anodic oxidation post-treatments [J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2012, 32: 1919-1925.
D, VAYSSADE M, DUVAL J L, VIGNERON P, NAGEL M D, PUIPPE J C. Cytocompatibility of titanium metal injection molding with various anodic oxidation post-treatments [J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2012, 32: 1919-1925.
[12] DEHGHAN-MANSHADI A, BERMINGHAM M J, DARGUSCH M S, STJOHN D H, QIAN M. Metal injection moulding of titanium and titanium alloys: Challenges and recent development [J]. Powder Technology, 2017, 319: 289-301.
[13] BIDAUX J E, CLOSUIT C, RODRIGUEZ-ARBAIZAR M, CARRENO-MORELLI E. Metal injection moulding of Ti-Nb alloys for implant application [J]. European Cells and Materials, 2011, 22: 32.
[14] KAFKAS F, EBEL T. Metallurgical and mechanical properties of Ti-24Nb-4Zr-8Sn alloy fabricated by metal injection molding [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014, 617: 359-366.
[15] EBEL T, BEI IG T, EBNER S, LUO X, NAGARAM A B, ZHAO D. Reduction of the embrittlement effect of binder contamination in MIM processing of Ti alloys [J]. Powder Metallurgy, 2017, 60: 157-166.
[16] ZHAO Da-peng, CHANG Ke-ke, EBEL T, NIE He-min, WILLUMEIT R, PYCZAK F. Sintering behavior and mechanical properties of a metal injection molded Ti-Nb binary alloy as biomaterial [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 640: 393-400.
[17] SARUGASER R, LICKORISH D, BAKSH D, HOSSEINI M M, DAVIES J E. Human umbilical cord perivascular (HUCPV) cells: A source of mesenchymal progenitors [J]. Stem Cells, 2005, 23: 220-229.
[18] LUTHRINGER B J C, ALI F, AKAICHI H, FEYERABEND F, EBEL T, WILLUMEIT R. Production, characterisation, and cytocompatibility of porous titanium-based particulate scaffolds [J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine, 2013, 24: 2337-2358.
[19] BIESIEKIERSKI A, LIN Ji-xing, LI Yun-cang, PING De-hai, YAMABE-MITARAI Y, WEN Cui-e. Impact of ruthenium on mechanical properties, biological response and thermal processing of beta-type Ti-Nb-Ru alloys [J]. Acta Biomater, 2017, 48: 461-467.
[20] DONATO T A G, de ALMEIDA L H, NOGUEIRA R A, NIEMEYER T C, GRANDINI C R, CARAM R, SCHNEIDER S G, SANTOS A R Jr. Cytotoxicity study of some Ti alloys used as biomaterial [J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2009, 29: 1365-1369.
[21] WANG Xiao-peng, CHEN Yu-yong, XU Li-juan, LIU Zhi-guang, WOO K D. Effects of Sn content on the microstructure, mechanical properties and biocompatibility of Ti-Nb-Sn/hydroxyapatite biocomposites synthesized by powder metallurgy [J]. Materials & Design, 2013, 49: 511-519.
[22] MIURA K, YAMADA N, HANADA S, JUNG T K, ITOI E. The bone tissue compatibility of a new Ti-Nb-Sn alloy with a low Young’s modulus [J]. Acta Biomater, 2011, 7: 2320-2326.
[23] YU Sen, YU Zhen-tao, WANG Gui, HAN Jian-ye, MA Xi-qun, DARGUSCH M S. Biocompatibility and osteoconduction of active porous calcium-phosphate films on a novel Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-25Nb biomedical alloy [J]. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2011, 85: 103-115.
[24] GERMAN R M. Powder injection molding [M]. New York: Metal Powder Industries Federation, 1990.
[25] MASTROGIACOMO M, SCAGLIONE S, MARTINETTI R, DOLCINI L, BELTRAME F, CANCEDDA R, QUARTO R. Role of scaffold internal structure on in vivo bone formation in macroporous calcium phosphate bioceramics [J]. Biomaterials, 2006, 27: 3230-3237.
[26] BANDYOPADHYAY A, ESPANA F, BALLA V K, BOSE S, OHGAMI Y, DAVIES N M. Influence of porosity on mechanical properties and in vivo response of Ti6Al4V implants [J]. Acta Biomaterilia, 2010, 6: 1640-1648.
[27] FERRI O M, EBEL T, BORMANN R. Influence of surface quality and porosity on fatigue behaviour of Ti-6Al-4V components processed by MIM [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 527: 1800-1805.
[28] AUZENE D, MALLEJAC C, DEMANGEL C, LEBEL F, DUVAL J, VIGNERON P, PUIPPE J. Influence of surface aspects and properties of MIM titanium alloys for medical applications [J]. Powder Injection Moulding International, 2012, 6: 57-61.
[29] WHITTAKER D. Titanium powder injection moulding (Ti-PIM): Australian conference reviews developments [J]. Powder Injection Moulding International, 2012, 6: 53-60.
[30] HOTCHKISS K M, REDDY G B, HYZY S L, SCHWARTZ Z, BOYAN B D, OLIVARES-NAVARRETE R. Titanium surface characteristics, including topography and wettability, alter macrophage activation [J]. Acta Biomaterilia, 2016, 31: 425-434.
[31] RUPP F, SCHEIDELER L, REHBEIN D, AXMANN D, GEIS-GERSTORFER J. Roughness induced dynamic changes of wettability of acid etched titanium implant modifications [J]. Biomaterials, 2004, 25: 1429-1438.
[32]  S, SCHWARTZ Z, WANG L, LOHMANN C H, TURNER J D, WIELAND M, COCHRAN D L, BOYAN B D. Microrough implant surface topographies increase osteogenesis by reducing osteoclast formation and activity [J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research: Part A, 2004, 70: 361-369.
S, SCHWARTZ Z, WANG L, LOHMANN C H, TURNER J D, WIELAND M, COCHRAN D L, BOYAN B D. Microrough implant surface topographies increase osteogenesis by reducing osteoclast formation and activity [J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research: Part A, 2004, 70: 361-369.
[33] BAGNO A, DI BELLO C. Surface treatments and roughness properties of Ti-based biomaterials [J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine, 2004, 15: 935-949.
[34] ROSALES-LEAL J I,  M A, MAZZAGLIA G,
M A, MAZZAGLIA G,  P J, D
P J, D AZ- RODR
AZ- RODR GUEZ L, GARC
GUEZ L, GARC A-MART
A-MART NEZ O, VALLECILLO- CAPILLA M, RUIZ C, CABRERIZO-V
NEZ O, VALLECILLO- CAPILLA M, RUIZ C, CABRERIZO-V LCHEZ M A. Effect of roughness, wettability and morphology of engineered titanium surfaces on osteoblast-like cell adhesion [J]. Colloids & Surfaces A: Physicochemical & Engineering Aspects, 2010, 365: 222-229.
LCHEZ M A. Effect of roughness, wettability and morphology of engineered titanium surfaces on osteoblast-like cell adhesion [J]. Colloids & Surfaces A: Physicochemical & Engineering Aspects, 2010, 365: 222-229.
[35] KLOKKEVOLD P R, JOHNSON P, DADGOSTARI S, DAVIES J E, CAPUTO A, NISHIMURA R D. Early endosseous integration enhanced by dual acid etching of titanium: a torque removal study in the rabbit [J]. Clinical Oral Implants Research, 2001, 12: 350-357.
赵大鹏1,2,陈钰凯1,常可可3,Thomas EBEL2,  J C LUTHRIGNER-FEYERABEND2, Regine WILLUMEIT-
J C LUTHRIGNER-FEYERABEND2, Regine WILLUMEIT-  2, Florian PYCZAK2
2, Florian PYCZAK2
1. 湖南大学 生物学院,长沙 410082;
2. Institute of Materials Research, Helmholtz-Zentrum Geesthacht, 21502 Geesthacht, Germany;
3. 中国科学院 宁波材料技术与工程研究所,宁波 315201
摘 要:采用金属注射成型(MIM)工艺制备Ti-22Nb(质量分数,%)和商业纯钛(CP-Ti)参比样,并选取电弧熔炼后抛光的Ti-22Nb作为另一种参比样。采用激光共聚焦显微镜、扫描电子显微镜和酶联免疫检测仪检测每组样品的表面拓扑结构和细胞相容性。结果显示,MIM工艺可以得到微米级粗糙度,而且采用混合元素粉而不是单一钛粉作为原料可以获得更高的表面粗糙度和比表面积。所有测试样品都不存在细胞毒性。人原代细胞在MIM Ti-22Nb样品表面(特别是在闭孔附近)的吸附效果更好。
关键词:金属注射成型;Ti-Nb合金;表面拓扑结构;细胞吸附;细胞增殖
(Edited by Bing YANG)
Foundation item: Projects (51604104, 51701232) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2010637006) supported by Helmholtz-CSC Fellowship Program, Germany
Corresponding author: Da-peng ZHAO, Tel: +86-731-88822606, E-mail: dpzhao@hnu.edu.cn;
Ke-ke CHANG, Tel: +86-574-86686593, E-mail: changkeke@nimte.ac.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64772-7

