DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2016.10.025
深埋隧道穿越富水破碎带围岩突水机理
李廷春1,吕连勋1, 2,段会玲1,陈伟1, 3
(1. 山东科技大学 山东省土木工程防灾减灾重点实验室,山东 青岛,266590;
2. 北京市勘察设计研究院有限公司,北京,100038;
3. 济南城建集团有限公司,山东 济南,250000)
摘要:基于隧道穿越处于复杂应力场与渗流场环境的富水破碎带时存在发生重大突水事故的安全隐患,通过对破碎岩体的渗流特点进行研究,建立孔隙颗粒介质流失的渗流模型;基于连续介质力学和变质量动力学理论,推导饱和破碎岩体变质量渗流-变形耦合理论模型;以福建漳州梁山隧道L7富水破碎带为工程背景,分析围岩的渗流场、应力场与位移场分布特性,并总结隧道断层破碎带的突水塌陷机理。研究结果表明:断层破碎带突水实质上是围岩的力学平衡和地下水的渗流平衡因施工扰动发生急剧变化,引起围岩应力重分布及地下水能量释放;隧道施工揭露断层后,岩体颗粒随孔隙空间的流体发生迁移形成新的渗流通道,导致地下水在水头压力作用下向工程临空面涌出,形成漏斗形的渗水区域;随着渗流作用时间的延长,地下水和岩土体逐渐流失,隧道上方的破碎岩体发生严重的滑移变形,形成椭圆形塌陷区域,与现场实际塌陷破坏规律基本吻合。本文提出的渗流-变形耦合模型对理解破碎岩体渗流力学机制和深埋隧道突水灾害的预防设计具有参考价值。
关键词:深埋隧道;岩体;断层破碎带;突水机理;流固耦合
中图分类号:U457+.5 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2016)10-3469-08
Water burst mechanism of deep buried tunnel passing through weak water-rich zone
LI Tingchun1, LYU Lianxun1, 2, DUAN Huiling1, CHEN Wei1, 3
(1. Disaster Prevention and Mitigation of Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Civil Engineering,
Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266590, China;
2. BGI Engineering Consultants Ltd., Beijing 100038, China;
3. Jinan Urban Construction Group Co. Ltd., Jinan 250000, China)
Abstract: Considering that there will be security risk of inrush accident when tunnel passes through the weak water-rich zone with complex underground stress field and seepage field environment, a seepage model of porous medium was established through the research of the seepage characteristics of broken rock mass. And theoretical model of fluid-solid coupling of saturated broken rocks was deduced based on the theory of dynamics of variable mass and continuum mechanics. Taking the L7 weak water-rich zone of the Liangshan Tunnel in Zhangzhou, Fujian Province, as engineering background, the distribution features of stress field, seepage field and displacement field of the surrounding rock were analyzed, and inrush collapse mechanism of the fault fracture zone was summarized. The results show that water inrush is actually caused by the stress distribution of surrounding rock and energy release of the groundwater, which results from the dramatic change of mechanical equilibrium of rock mass and seepage balance of the groundwater for construction disturbance. When the fault is exposed, rock particles loss in the pore space to form new seepage channel, leading to welling of groundwater under the pressure of water head to form funnel-shaped water seepage area. With the increase of the seepage time, groundwater and rock mass experience gradual loss and the fractured rock mass on the top of tunnel have serious slip deformation, forming oval subsidence area. This conclusion basically coincides with practical situation. The fluid-solid interaction model proposed has high practical significance to understand the seepage mechanics and prevention design of deep buried tunnel water inrush disaster.
Key words: deep buried tunnel; rock mass; fault fracture zone; water inrush mechanism; fluid-solid coupling
随着现代社会资源开发与基础设施建设的快速发展,越来越多的隧道工程不得不穿越或修建在软弱破碎地层中。破碎岩体长期处于复杂的应力场和渗流场环境中,岩土体的性质较差,受地表水和地下水的渗流作用以及开挖和支护过程的扰动影响,极易产生突水涌泥、岩土体塌陷等地质灾害问题[1-4]。据统计,在隧道工程施工过程中,由突涌水灾害造成的重大安全事故达到80%,其中断层型突水事故占30%[5]。隧道工程突涌水事故不仅会给隧道施工带来困难、造成严重的工期延误和经济损失,甚至会诱发水资源枯竭,引起地表塌陷等环境地质灾害,造成人员伤亡,威胁到社会稳定与经济发展。近年来,在大秦铁路军都山隧道、渝怀铁路武隆隧道、张集铁路旧堡隧道等工程建设过程中,因为揭露破碎带导致突水涌泥事故,造成了严重的经济损失和人员伤亡[4-7]。中国隧道建设的重心长期处于地形地质条件极端复杂的山区,一大批具有岩体破碎、高地应力、强渗透压等特点的深长隧道正在兴建[5-6]。目前,人们对有关岩溶隧道突水风险与治理措施进行了很多研究[7-10],但对于富水软弱破碎带隧道的突水机理研究较少。探究破碎岩体渗流与变形相耦合的特性,从水力耦合的角度揭示破碎岩体的渗流特性及其灾变规律,对深长隧道穿越富水破碎带的重大水害发生机理与预防设计具有重要的理论和实践意义。
1 饱和破碎岩体渗流模型
破碎岩体孔隙空间由天然孔隙(有机质孔和无机质孔)、天然裂隙、水力裂隙和人工裂隙等空间组成,属于孔隙-裂隙复合介质,但考虑到其充填物较松散,将其进行等效处理后视为孔隙介质。液体以流动状态赋存于孔隙空间中,将岩体内的软弱部分逐渐转化为流体中的悬浮颗粒,因此,破碎岩体可以看作由岩体骨架、孔隙液体以及流体中的悬浮颗粒3种介质构成。在断层破碎带、岩溶管道等不良地质揭露后,孔隙空间的悬浮颗粒逐渐从微观渗流通道流失,引起岩体渗透特性改变,最终诱发突水灾害。一方面,微小的固体颗粒在水力梯度作用下,随渗流作用不断产生并流失,造成岩体的孔隙率和渗透率不断增加,使岩体骨架的变形加大,岩体的破碎程度加剧;另一方面,岩体的损伤与变形加剧,导致孔隙空间的渗流速度加快,悬浮颗粒的流动更加通畅,流失速率加快。在岩体变形发展和颗粒渗流流失的共同作用下,破碎岩体的性质逐渐变差,这就是流固耦合效应。
为了研究悬浮颗粒迁移作用下破碎岩体的流固耦合问题,建立如图1所示的渗流模型,并进行以下基本假定:
1) 岩体处于完全饱和状态,孔隙空间充满流体介质。
2) 流体的渗流速度缓慢,且符合Darcy律。
3) 忽略流体对岩体骨架及悬浮颗粒的溶解作用,并忽略渗流过程中颗粒与骨架、颗粒与颗粒间的碰撞。
4) 渗流过程中仅考虑颗粒在水力梯度作用下的迁移效应,忽略颗粒因浓度梯度变化而发生的扩散效应。
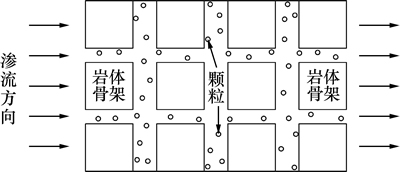
图1 破碎岩体渗流模型
Fig. 1 Seepage model of fractured rock mass
流体中悬浮颗粒的质量变化可以采用颗粒的质量浓度进行描述[11]。记岩体的总体积为V,孔隙率为n,孔隙液体与岩体骨架的密度分别为ρw和ρs,悬浮颗粒占流体介质的体积分数为φ,则颗粒的质量浓度ρsg为
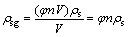 (1)
(1)
则流体介质中悬浮颗粒的质量浓度变化率ρ′sg为
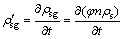 (2)
(2)
2 岩体变质量渗流-变形耦合模型
2.1 悬浮颗粒流失的质量守恒方程
将岩体孔隙空间内的渗流分解为三维坐标方向,取如图2所示的岩石微元体,则沿着x轴方向,单位时间内流入微元体的悬浮颗粒质量为
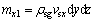 (3)
(3)
式中:vsx为悬浮颗粒的绝对速度在x轴方向的分量。

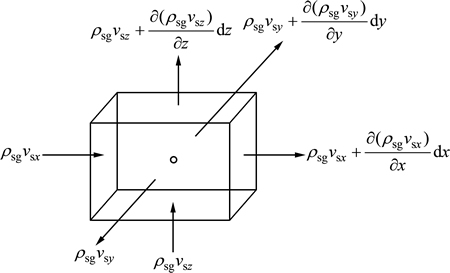
图2 微元体渗流示意图
Fig. 2 Schematic plot of micro-scale seepage
考虑流体渗流的连续性,单位时间内沿着x轴方向流出微元体的颗粒质量mx2为
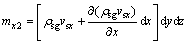 (4)
(4)
那么,在x方向净流入微元体的颗粒质量mx为
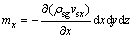 (5)
(5)
同理,可得y和z方向净流入的颗粒质量分别为
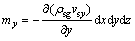
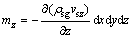
由颗粒质量浓度变化引起的微元体中颗粒的质量变化量为
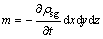 (6)
(6)
根据质量守恒定律,有
 (7)
(7)
此即饱和破碎岩体悬浮颗粒流失的质量守恒方程,将其写为矢量形式:
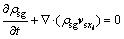 (8)
(8)
其中: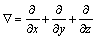 。
。
2.2 悬浮颗粒的运动方程
流体中悬浮颗粒的迁移可以看作是渗流作用的效果,此时液体介质与悬浮颗粒间会产生相对运动,并发生动量的传递。悬浮颗粒在流体中受复杂的作用力[12-15],忽略部分微小作用力对悬浮颗粒运动的影响,将力系简化后认为颗粒的运动主要受浮力、重力和曳力的作用,悬浮颗粒的运动方程为
 (9)
(9)
式中:ρs和ds分别为悬浮颗粒的密度与直径;CD为拽力系数;ρw为孔隙液体的密度;v为悬浮颗粒与液体间的相对速度。
2.3 液体介质的运动方程
将破碎岩体等效为连续多孔介质,孔隙空间的渗流满足Darcy定律,即
 (10)
(10)
式中:qi为液体的渗流速度;k为岩体的渗透系数(m2/(Pa·s));J为水力梯度。常密度流体在均质各向同性岩体中渗流的情况下,液体介质的运动方程具有如下形式:
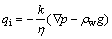 (11)
(11)
式中:p为孔隙水压力;η为含颗粒流体的动力黏度。流体的动力黏度η与纯液体的动力黏度η0有如下关 系[16]:
 (12)
(12)
2.4 岩体骨架的运动方程
记微元体受到应力为S,位移为us,体积力为SM,则固体介质的动量守恒方程为
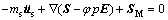 (13)
(13)
式中: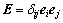 ,为单位张量;
,为单位张量; 为Kronecke符号;ei为单位矢量。将式(13)在三维状态下展开得
为Kronecke符号;ei为单位矢量。将式(13)在三维状态下展开得
 (14)
(14)
应力、应变与位移之间的关系为:
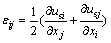 (15)
(15)
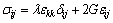 (16)
(16)
式中:λ和G分别为拉梅系数与剪切模量。将式(15)和(16)代入式(14),可得岩体骨架的运动方程:
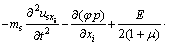
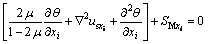 (17)
(17)
其中: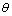 为体应变,
为体应变,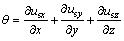 ;
; 为拉普拉斯算子,
为拉普拉斯算子,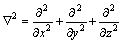 。
。
2.5 耦合作用方程
为了实现模型中液体渗流与岩体骨架变形的动态平衡,还需要建立颗粒流失过程中材料性质变化的相关方程。
易知某时刻t岩体骨架微元dV的质量为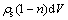 。假定在时间[t,t+dt]内,岩体颗粒的流失质量为
。假定在时间[t,t+dt]内,岩体颗粒的流失质量为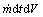 ,则有
,则有
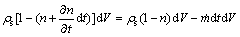 (18)
(18)
化简后,得
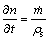 (19)
(19)
已知破碎岩体孔隙率与渗透率之间满足[12]
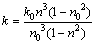 (20)
(20)
其中:k0为初始渗透率;n为孔隙率;n0为初始孔隙率。孔隙空间中液体质点的速度v与渗流速度vs之间满足 Dupuit-Forchheimer关系式[17]:
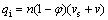 (21)
(21)
式(8),(9),(11),(17),(19),(20)和(21)构成了饱和破碎岩体中悬浮颗粒流失的变质量渗流-变形耦合模型基本方程。
3 数值模拟分析实例
3.1 工程概况
梁山隧道位于福建省漳州市,设计为客货两用单洞双线隧道,是厦深铁路全线的控制工程。隧道全长9.89 km,进口里程为DK94+000 km,出口里程为DK103+888 km。隧址区主要地层为燕山早期侵入花岗岩,隧道最大埋深约为680.0 m,开挖高度约15.1 m,跨度约16.1 m。
梁山隧道施工至洞身DK96+505~DK96+533 km段揭露1条L7富水破碎带,经探测发现[18]:断层破碎带宽为21~25 m,倾角为75°~85°,与隧道平面夹角约61°;L7断层破碎带夹层物质主要为全风化花岗岩以及辉绿岩和闪长玢岩,软弱夹层主要呈砂土状,含水量极高。施工记录显示[18-19]:该隧道施工至破碎带处1月内,先后发生了4次严重突水涌泥事故,总涌泥量达20 000 m3,导致地表塌陷成1个25 m深的椭圆形陷坑。针对破碎带突水灾害情况,施工方采用“水平旋喷超前加固圈+拱墙大管棚超前支护+掌子面水平旋喷改良预加固”的方案进行处理。
3.2 耦合模型的程序设计
在Visual Studio 2012环境中,借助C++语言开发平台,将上述理论模型编译为DLL(动态链接库),嵌入有限差分软件FLAC3D中进行二次开发。由于应力场的变化影响了渗流场,渗透系数的改变又会引起液体、颗粒与骨架的形变,可见水力作用是相互耦合的。对每加载时步,其计算流程如下。
1) 由初始条件求解单元的初始应力状态及水压力p。
2) 设置初始渗透率k0与初始孔隙率n0,计算孔隙液体、颗粒与骨架的速度等参量。
3) 在计算过程中对渗透系数参数进行修正,并根据其修正值kn+1,计算孔隙率的变化值nn+1。
4) 计算颗粒质量浓度变化率 ,求解颗粒的质量变化mn+1。
,求解颗粒的质量变化mn+1。
5) 进行迭代计算,比较颗粒质量变化的差值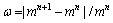 ,直至误差ω满足精度要求为止。
,直至误差ω满足精度要求为止。
3.3 计算模型和模拟方案
根据工程地质勘察资料,隧道掌子面整体位于断层破碎带内部,因此,选取隧道与破碎带相交部位作为计算区域建立数值计算模型。为了防止软弱破碎围岩开挖引起过大变形,导致计算过程不能收敛,建模时采用变更后的支护方案,仅从围岩的渗流场、应力场与位移场分布规律分析突水机理。考虑到破碎带对围岩开挖的扰动影响较大,模型宽度方向两侧各取隧道跨度的5倍,高度方向向下取隧道高度的5倍。为了简化计算,模型的上边界取为初始地下水位(地表以下90 m),并将水位线以上的岩层作为地面超载施加于上部边界。
计算模型的上部边界固定孔隙水压力为0,左、右两边界和底部边界均设为不透水边界;模型的力学边界采用位移边界条件,底部边界约束竖向位移,上部边界为自由边界,左、右两端采用水平位移约束。具体计算模型如图3所示。
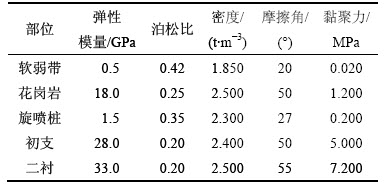
围岩的物理力学参数由工程勘察报告提供,并根据参数折减的要求进行相应修正。梁山隧道围岩及衬砌的力学参数如表1所示。数值计算中围岩与衬砌的力学模型均采用Mohr-Coulomb模型。
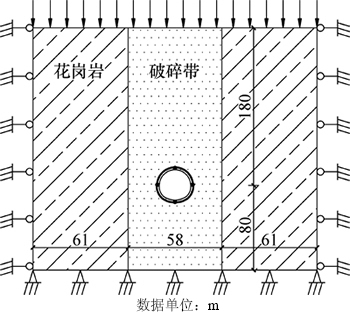
图3 计算模型
Fig. 3 Calculation model
表1 梁山隧道围岩及衬砌物理力学参数
Table 1 Parameters of surrounding rock and lining
3.4 渗流场分布特性
为了解隧道开挖前后围岩渗流场的变化情况,提取隧道拱顶、拱底和边墙节点的孔隙水压力变化时程曲线,如图4所示。从图4可以看出:在隧道开挖过程中,由于地下水体能量的瞬间释放,各监测点的孔隙水压力均大幅度降低;此外,围岩孔隙水压力的变化幅度具有一定的规律,从拱底节点至拱顶节点其变化程度逐渐增大。
图5所示为隧道开挖后围岩的孔隙水压力云图。从图5可以看出:由于开挖部分孔压消散,隧道周边围岩的孔隙水压力严重下降,造成渗流场发生改变;地下水在水头压力作用下,形成1个漏斗形状的渗水区域。这与富水破碎带岩层隧道开挖的实际情况相符。
根据模型各单元的流速矢量计算开挖断面的涌水量,结果如图6所示。从图6可见:隧道开挖断面的涌水速度急剧增加,并在短时间内趋于稳定,计算过程中最大涌水量为16.72 m3/h。这说明地下水的渗流通道在施工扰动影响下迅速变大,在隧道揭露位置形成较大的水排泄通道,导致地下水在隧道内快速排泄。
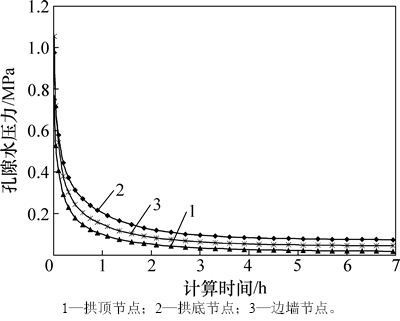
图4 隧道关键点孔隙水压力变化时程曲线
Fig. 4 Time-history curves of pore pressure of key points
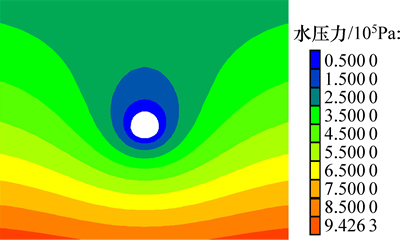
图5 隧道开挖后孔隙水压力云图
Fig. 5 Pore pressure nephogram after tunnel excavation
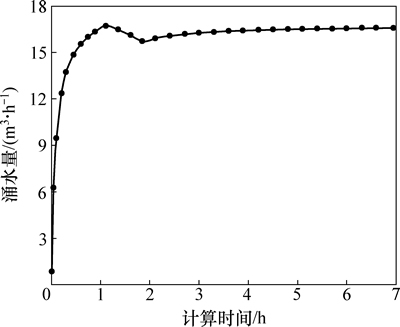
图6 隧道断面涌水量变化曲线
Fig. 6 Curve of tunnel seepage volume
3.5 应力场分布特性
由于计算模型的上边界取为地下水位线,在计算过程中,各岩层始终处于完全饱和状态(地下水饱和度为1),因此,在分析应力场计算结果时,既可以采用有效应力分析,也可以采用总应力分析。图7所示为隧道开挖后围岩的竖向总应力分布云图。
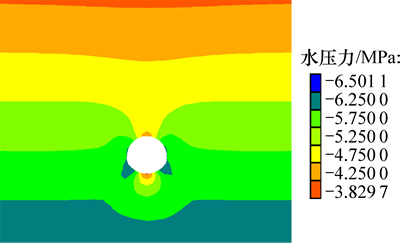
图7 隧道开挖后竖向总应力云图
Fig. 7 Vertical total stress nephogram after tunnel excavation
从图7可以看出:由于隧道开挖,岩体内部的力学平衡状态发生急剧变化,导致围岩应力场重新分布;隧道局部围岩甚至出现了应力集中现象,这在两侧边墙的底角部位尤为明显;隧道开挖对应力场的扰动影响随距离的增加逐渐减弱,远离隧道的围岩,应力状态基本上仍处于随深度变化递增的趋势。
3.6 位移场分布特性
图8所示为隧道开挖后拱顶、拱底和边墙节点的竖向位移变化时程曲线。从图8可以看出:由于开挖使隧道附近围岩受到的支撑作用急剧变化,隧道拱顶发生瞬时沉降、拱底发生瞬时底臌现象,而隧道边墙节点的瞬时变形不明显;随着渗流时间增长,各监测点相继发生沉降,且沉降量越来越大;不同部位监测点的时程曲线规律基本一致,但当计算最终趋于平衡后,各监测点的最大沉降量有所差异,其中拱顶部位的沉降量最大。
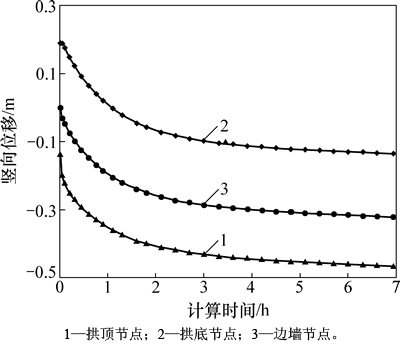
图8 隧道关键点竖向位移变化时程曲线
Fig. 8 Time-history curves of vertical displacement of key point
提取隧道开挖后围岩的竖向变形云图,如图9所示。由图9可见:计算区域内所有位移均为负值,表明隧道附近围岩的位移方向竖直向下;隧道两侧花岗岩的位移变化较平缓,且大致处于随深度增加变形递减的趋势;断层破碎带区域岩体破碎且受开挖扰动影响较大,导致发生严重的岩土体位移变形;断层破碎带处岩体发生整体滑移变形,在隧道正上方形成椭圆形的塌陷区域,这恰与梁山隧道断层上部地表塌陷的实际破坏规律相符。
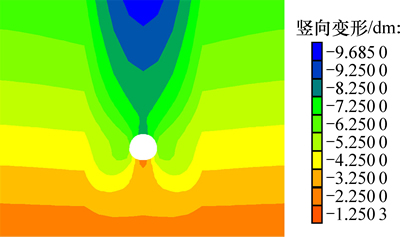
图9 隧道开挖后竖向变形云图
Fig. 9 Vertical deformation nephogram after tunnel excavation
4 深埋隧道富水断层突水机理分析
4.1 深埋隧道富水断层突水因素
深埋隧道穿越富水破碎带时在施工过程中易发生突水灾害,其影响因素可以归结为2个方面:断层破碎带特殊的水文地质条件和隧道开挖与支护过程的施工扰动。
4.1.1 水文地质条件
断层破碎带特殊的水文地质条件是近断层隧道施工中发生重大水害的根本原因。受多期构造运动的作用,断层地质构造非常复杂,岩体节理裂隙异常发育,自稳能力极弱。此外,断层破碎带的含水构造与导水构造,形成了隧道周围潜在的突水通道,具有很强的致灾能力,在很大程度上决定了突水风险。
4.1.2 工程扰动
开挖和支护过程的施工扰动是隧道突水事故发生的直接原因。以往的工程实践证明[5]:在没有受到施工扰动的情况下,原始地质条件的渗流场和地应力场都处于一定的平衡状态。也就是说,导致隧道突水事故的直接原因不是构造交汇区的控水优势,而是工程扰动改变了地下水的渗流状态,引起构造带地层变形活化。
4.2 深埋隧道富水断层突水塌陷机理
结合工程实际与数值计算结果分析,认为断层突水实质上是破碎围岩的力学平衡和地下水的渗流平衡因隧道的施工扰动而发生急剧变化,引起应力重新分布以及地下水能量的瞬间释放,并以流体状态快速涌向工程临空面的一种动力破坏现象。其突水塌陷机理可以图10进行概括。
隧道施工揭露断层后,附近围岩的渗流场、应力场及位移场均不断发生变化。在地下水渗透力的拖曳下,突水口附近的岩体颗粒受到的动水压力超过颗粒间的内聚力,岩体颗粒的极限平衡状态被打破,随孔隙空间的流体发生迁移,形成新的渗流通道。随着渗流作用时间延长,渗流通道迅速变大,使得揭露位置成为地下水的排泄通道。对于深埋隧道,上部岩土体可以有效阻止地表水对地下水的补给,因此,地下水的快速排泄将导致地下水位急剧下降,引起水力梯度显著增加。此时,基岩面附近的岩土体产生瞬时负压,岩体受到的渗透力也迅速增大,局部软弱岩体会随水流一起涌出,最终引起质变,发生隧道内的突水和涌泥事故。随着突水涌泥的发展,越来越多的地下水和岩土体流失,上部破碎岩体受到周围完整岩体的支撑力越来越小,在真空吸蚀力的作用下,软弱破碎带的岩土体就会发生塌陷。
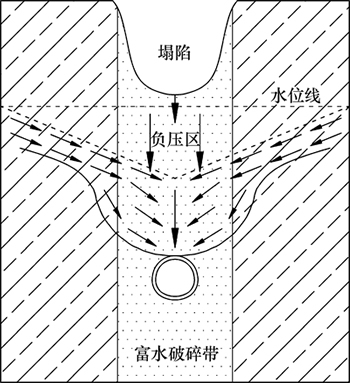
图10 隧道断层突水塌陷机理
Fig. 10 Mechanism of water inrush through fault
5 结论
1) 进行深埋隧道富水软弱带地段的开挖分析时,应该考虑裂隙岩体渗流场与应力场之间的耦合效应,不能把二者分开单独考虑。在构建饱和破碎岩体的流固耦合效应模型时,对破碎围岩的渗流过程进行合理假设是关键。建立在不同假设条件下的理论推导,所得到的岩体骨架、液体介质与悬浮颗粒的运动方式以及颗粒流失过程中液体渗流与岩体骨架变形的耦合方程是不同的。
2) 基于连续介质力学和变质量动力学理论,建立的岩体变质量渗流-变形耦合模型符合工程实际情况,推导出颗粒流失的质量守恒方程、介质运动方程和考虑材料性质变化的耦合效应方程,能够从理论上解决模型中液体渗流与岩体骨架变形之间的动态平衡关系。
3) 计算得到了开挖过程中围岩的渗流场、应力场与位移场分布特性。隧道开挖后围岩应力场与渗流场的改变使地下水在水头压力作用下向工程临空面渗透,形成1个漏斗形状的渗水区域;同时,隧道上方的破碎岩体发生严重的滑移变形,形成1个椭圆形的塌陷区域。对比分析数值计算结果和实际观测结果基本相符,进一步说明了渗流-变形耦合模型的合理性和正确性。
4) 断层突水实质上是破碎围岩的力学平衡和地下水的渗流平衡因隧道的施工扰动而发生急剧变化,导致围岩应力重分布以及地下水能量瞬间释放。隧道施工揭露断层后,打破了岩土体的极限平衡状态,岩体颗粒随渗流作用迅速流失,形成新的地下水排泄通道,局部软弱岩体在真空吸蚀力和渗透力的作用下随水流一起涌出,引发隧道内的突水和涌泥事故。
参考文献:
[1] JEON S, KIM J, SEO Y, et al. Effect of a fault and weak plane on the stability of a tunnel in rock:a scaled model test and numerical analysis[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2004, 41(Suppl 1): 658-663.
[2] KUN M, ONARGAN T. Influence of the fault zone in shallow tunneling: A case study of Izmir Metro Tunnel[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2013, 33(1): 34-45.
[3] 李术才, 周宗青, 李利平, 等. 岩溶隧道突水风险评价理论与方法及工程应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2013, 32(9): 1858-1867.
LI Shucai, ZHOU Zongqing, LI Liping, et al. Risk evaluation theory and method of water inrush in karst tunnels and its applications[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2013, 32(9): 1858-1867.
[4] LI Shucai, ZHOU Zongqing, LI Liping, et al. Risk assessment of water inrush in karst tunnels based on attribute synthetic evaluation system[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2013, 38(3): 50-58.
[5] 石少帅. 深长隧道充填型致灾构造渗透失稳突涌水机理与风险控制及工程应用[D]. 济南: 山东大学土建与水利学院, 2014: 1-30.
SHI Shaoshuai. Study on seepage failure mechanism and risk control of water inrush induced by filled disaster structure in deep-long tunnel and engineering applications[D]. Jinan: Shandong University. School of Civil Engineering, 2014: 1-30.
[6] 陈国顺. 富水软弱带地段深埋隧道受力特征及施工技术分析[D]. 长沙: 中南大学土木工程学院, 2013: 7-35.
CHEN Guoshun. Research on mechanics characteristic and construction technology for deep tunnel in watery and weak stratum[D]. Changsha: Central South University. School of Civil Engineering, 2013: 7-35.
[7] 刘招伟, 何满潮, 王树仁. 圆梁山隧道岩溶突水机理及防治对策研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2006, 27(2): 228-232.
LIU Zhaowei, HE Manchao, WANG Shuren. Study on karst water burst mechanism and prevention countermeasures in Yuanliangshan tunnel[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2006, 27(2): 228-232.
[8] 赵延林, 曹平, 万文, 等. 巷道前伏承压溶洞突水灾变流固耦合分析[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 45(5): 1598-1604.
ZHAO Yanlin, CAO Ping, WAN Wen, et al. Fluid-solid coupling analysis of water bursting catastrophe from concealed confined karst cave before roadway[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2014, 45(5): 1598-1604.
[9] 范威, 王川, 金晓文, 等. 吉莲高速公路钟家山隧道涌突水条件分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2015(2): 38-43.
FAN Wei, WANG Chuan, JIN Xiaowen, et al. Water inrush condition analysis of the Znongjiashan tunnel in the Jilian Highway[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2015(2): 38-43.
[10] ALIJA S, TORRIJO F J, QUINTA-FERREIRA M. Geological engineering problems associated with tunnel construction in karst rock masses: the case of Gavarres tunnel (Spain)[J]. Engineering Geology, 2013, 157(4): 103-111.
[11] 姚邦华, 茅献彪, 魏建平, 等. 考虑颗粒迁移的陷落柱流固耦合动力学模型研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2014, 43(1): 30-35.
YAO Banghua, MAO Xianbiao, WEI Jianping, et al. Study on coupled fluid-solid model for collapse columns considering the effect of particle transport[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2014, 43(1): 30-35.
[12] 姚邦华. 破碎岩体变质量流固耦合动力学理论及应用研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学深部岩土力学与地下工程国家重点实验室, 2012: 62-75.
YAO Banghua. Research on variable mass fluid-solid coupling dynamic theory of broken rock mass and application[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining & Technology. State Key Laboratory for Geomechanics and Deep Underground Engineering, 2012: 62-75.
[13] MARK W D. Recent results of experiments with Saffman-Taylor flow[J]. Nonlinear Evolution and Chaotic Phenomena, 1988, 176: 313-317.
[14] MCCLOUD K V, MAHER J V. Experimental perturbations to Saffman-Taylor flow[J]. Physics Reports, 1995, 260(3): 139-185.
[15] 倪晋仁, 王光谦, 熊育武, 等. 泥石流的结构两相流模型: Ⅱ.应用[J]. 地理学报, 1998, 53(1): 77-85.
NI Jinren, WANG Guangqian, XIONG Yuwu, et al. Conceptual two-phase flow model of debris flow : Ⅱ. Application[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1998, 53(1): 77-85.
[16] 费祥俊. 高浓度浑水的黏滞系数(刚度系数)[J]. 水利学报, 1982(3): 57-63.
FEI Xiangjun. Coefficient of velocity for muddy water with high concentration[J]. Journal of Hydraulic, 1982(3): 57-63.
[17] YOUNGS E G, SMART P, HERBERTSON J G. Drainage design: soil physical principles[M]. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1992: 25-60.
[18] 周鑫. 厦深铁路梁山隧道L7深埋富水软弱带超前预加固体系支护机理分析[J]. 现代隧道技术, 2013, 50(4): 138-145.
ZOU Xin. On the support mechanism of the pre-reinforcement system for the L7 deep, weak water-rich zone passed through by the Liangshan tunnel[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 2013, 50(4): 138-145.
[19] 林福地. 水平旋喷加固在厦深铁路梁山隧道断层突水涌泥段处理中的应用[J]. 现代隧道技术, 2012, 49(Suppl): 322-329.
LIN Fudi. On the application of horizontal jet grouting for water inrush through fault by the Liangshan Tunnel[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 2012, 49(Suppl): 322-329.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期:2015-10-10;修回日期:2015-12-21
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(51279096, 51409154);山东省自然科学基金资助项目(ZR2012EEM030)(Projects(51279096, 51409154) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(ZR2012EEM030) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province)
通信作者:李廷春,博士,教授,博士生导师,从事裂隙岩石力学特征研究;E-mail:tchli_sd@163.com