DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2018.11.004
新型不锈钢复合管道生物膜形成特性与冲击消毒效能
耿攀1,李星1,王庭昆2,樊剑2,梁恒3
(1. 北京工业大学 建筑工程学院,北京,100124;
2. 云南昆钢新型复合材料发展有限公司,云南 昆明,605302;
3. 哈尔滨工业大学 环境学院,黑龙江 哈尔滨,150090)
摘要:通过生物膜环形反应器(BAR)研究在市政和建筑区域的供水系统中的新型不锈钢复合管管壁生物膜中微生物形成特点、微生物腐蚀特性以及冲击消毒控制措施,考察不锈钢复合管材管壁生物膜中微生物生长情况及微生物对管道的腐蚀速率,了解氯消毒剂对管壁生物膜中微生物的灭活效能。研究结果表明:在含有余氯的市政和建筑区域供水管网系统中,不锈钢复合管道在模拟实验开展80 d后仍会出现明显的生物增殖现象,在100~110 d期间生物量达到峰值,出现浊度和微生物超标的现象;管壁生物膜中微生物种类丰富,其中含有多种致病菌、耐氯病原菌以及易造成金属腐蚀的菌属,使供水的生物安全性和化学安全性受到潜在威胁;水中微生物造成不锈钢复合管材腐蚀电流密度增大,腐蚀电位降低,腐蚀速率明显增大;冲击消毒的氯质量浓度越高、消毒时间越长,生物膜微生物灭活效果越好;当氯质量浓度为5 mg/L,消毒60 min时,铁细菌、异养菌及其余细菌均可完全灭活;冲击氯消毒后管壁生物膜大量剥离和脱落,生物膜形态破坏明显,且消毒时间越长,生物膜破坏程度越大,可以有效控缓解生物对不锈钢复合管道的腐蚀,保障供水安全。
关键词:不锈钢复合管;管壁生物膜;微生物腐蚀;冲击氯消毒;生物安全性
中图分类号:X524 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2018)11-2663-07
Characteristics and shock disinfection efficiency of biofilm of a new stainless steel composite pipeline
GENG Pan1, LI Xing1, WANG Tingkun2, FAN Jian2, LIANG Heng3
(1. College of Architecture and Civil Engineering, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing 100124, China;
2. Yunnan Kungang New Composite Materials Development Co. Ltd., Yunnan 605302, China;
3. School of Environment, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150090, China)
Abstract: By using the biofilm annular reactor(BAR), the characteristics of microbial growth and microbial corrosion, and control measures of shock disinfection of a new stainless steel composite pipeline in the water supply system of municipal and construction area were studied. The microbial growth on the stainless steel composite pipeline wall, corrosion rate of the pipeline caused by microorganism, and inactivation efficiency of chlorine disinfection on biofilm were also investigated. The results show that in the water supply pipe network system of municipal and construction area with residual chlorine, biofilm proliferation of stainless steel composite pipeline is obvious after 80 d of operation. During 100—110 d, the biomass reaches the peak, and both the turbidity and microbial index exceed the standard values.The biofilm of the wall has a diversity of microorganisms in it, which contains a variety of pathogens, chlorine resistant pathogens and bacteria that can cause metal corrosion, posing a potential threat to the biosafety and chemical safety of drinking water. With microorganisms in water, the corrosion current density of the stainless steel composite pipeline increases, the corrosion potential decreases and the corrosion rate increases obviously. With high mass concentration of chlorine and long sterilization time, the inactivation effect of biofilm microbes is better. When the chlorine mass concentration is 5 mg/L, iron bacteria, heterotroph and other bacteria can be completely inactivated when sterilized for 60 min. After the shock of chlorine disinfection, the biofilm on the wall peels off, and biofilm morphology is damaged. The longer the disinfection time is, the greater the degree of biofilm damage is, which can effectively control the corrosion of stainless steel composite pipeline caused by biofilm and assure water safety.
Key words: stainless steel composite pipeline; wall biofilm; microbial corrosion; chlorine shock disinfection; biosafety
输配水管道的材质和水质安全是保障市政和建筑区域内供水安全的重要因素,市政供水和建筑区域内的管道材质直接关系到水质安全。市政和建筑区域内的供水在输配过程中经常会出现水体污染现象,导致水质不达标,其中微生物的再生和管道的腐蚀与结垢是造成供水二次污染的主要原因。输配水管道中的微生物能利用氮、磷和有机碳等营养基质生长繁殖,逐渐在管壁形成生物膜,不仅使供水中微生物含量增加,而且会加速金属管道的腐蚀。微生物腐蚀较复杂,是电化学反应和化学反应共同作用的结果。微生物对管道的腐蚀约占管道损失的20%[1]。微生物主要通过改变电极电势和氧浓差电池腐蚀金属管道[2-3],其代谢过程中还会产生一些无机酸和有机酸,使 pH降低,加速金属的腐蚀,造成水体色度、浊度和总铁含量增加[4]。铁细菌是引起腐蚀的重要微生物,CHAMRITSKI等[5]的研究表明铁细菌会加速金属管材的腐蚀。采用不锈钢管材是提高输配水管道耐腐蚀性的有效措施,但存在成本较高等问题,限制了其使用范围。不锈钢复合管是由304不锈钢和碳钢2种材料同步复合成的新型管材,管内壁为304不锈钢,外壁为碳钢,兼具不锈钢管道的优良特性以及碳钢的成本优势。为了考察新型不锈钢复合管在市政和建筑区域供水输配过程中的生物安全性,有必要研究新型不锈钢复合管的微生物生长特性和消毒效能。为了控制管道的微生物再生问题,保障供水的生物安全性,通常在出厂水中投加一定量的消毒剂,以杀灭水中的微生物,抑制在输配过程中供水管道的微生物再生。周玲玲等[6]的研究结果表明,市政和建筑区域内供水中即使含有一定质量浓度的余氯,管壁生物膜中微生物仍会持续增加。管壁生物膜微生物对氯消毒剂的抵抗能力远强于悬浮态微生物的抵抗能力。陈笑居[7]的研究表明,当余氯质量浓度低于 0.5 mg/L时,管道中铁细菌生长无法得到有效控制。王洋等[8]的研究表明,0.3 mg/L的氯可以有效控制悬浮铁细菌的生长,但1.0 mg/L的氯仍无法杀灭管垢内的铁细菌。王若卿等[9]的研究表明高质量浓度氯能有效控制再生水管壁生物膜中微生物数量,消毒时间越长,微生物存活率越低。朱永娟等[10]的研究表明,短时间内加入高质量浓度的氯后,管壁生物膜中异养菌数量会迅速下降,对管道生物膜造成很大破坏。由此可见,高质量浓度的消毒剂对管壁微生物灭活和抑制产生有效的作用。本文作者考察新型不锈钢复合管在市政供水和建筑区域系统中微生物的生长情况、生物膜中的优势菌种及微生物腐蚀特性,研究氯冲击消毒技术对不锈钢复合管壁生物膜微生物的抑制和灭活效果,以便为新型不锈钢复合管输配水的生物安全性和适用性研究提供参考。
1 试验材料与方法
1.1 试验装置
1.1.1 管道模拟装置
试验采用生物膜环形反应器(BAR)模拟市政和建筑区域内供水管道系统。试验前,先使用NaClO溶液对BAR反应器、挂片和进出水管进行消毒灭菌,之后依次用自来水和超纯水将BAR反应器冲洗干净。BAR反应器由聚氯乙烯(PVC)材料制成的外层固定筒及内部转子组成,转子的凹槽中放置18个不锈钢复合挂片,每个挂片的面积约17 cm2;挂片可以通过BAR反应器顶部的端口取出。通过蠕动泵控制BAR反应器进水流量为6 mL/min,水力停留时间为4 h,水的相对流速为0.36 L/h,转子速度为50 r/min,有效容积为800 mL。
1.1.2 电化学工作电极
将不锈钢复合管材加工成直径为10 mm的圆柱形,在非试验表面焊接导线并用防水密封胶带封裹,之后用环氧树脂将非试验面封涂;试验表面分别经粒度为96.0,41.0,23.0,18.0,13.0和6.5 μm砂纸逐级打磨,采用丙酮除油后用无水乙醇进行灭菌处理,放置于干燥皿中备用。

图1 BAR反应器装置示意图
Fig. 1 Diagram of BAR experimental apparatus
1.2 试验用水
实验用水为试验室的自来水:温度为18~20 ℃,pH为7.43~7.58,浊度为0.384~0.732 NTU,余氯质量浓度为0.06~0.18 mg/L,总有机碳(TOC)质量浓度为1.962~2.397 mg/L,高锰酸盐质量浓度为1.52~1.74 mg/L,溶解氧质量浓度为7.65~8.31 mg/L,总铁质量浓度为0.06~0.08 mg/L。
在微生物腐蚀试验中,有菌水为市政自来水,余氯质量浓度为0.06 mg/L,细菌总数为47 CFU/mL,异养菌平板计数(HPC)为156 CFU/mL。将市政自来水在紫外灯下照射2 h,使自来水中的细菌总数为0 CFU/mL,即制成无菌水。无菌水每天进行更换。
1.3 分析方法
1.3.1 消毒液的配置
采用市售NaClO溶液用超纯水配置成有效氯浓度分别为1,3和5 mg/L的氯消毒液备用。
1.3.2 水质检测
极化曲线采用电化学工作站(CHI604D,上海辰华,中国)测定,参比电极为饱和甘汞电极,对电极为铂电极;浊度采用浊度仪(2100N,HACH,美国)测定,总铁质量浓度采用铁离子测定仪(HI96745,HANNA,意大利)测定,TOC质量浓度采用总有机碳测定仪(Vario TOC,Elementar,德国)测定,氯质量浓度采用便携式余氯快速测定仪(S-CL501,清时捷,中国)测定。
1.3.3 微生物学指标检测
用2~3根经高温灭菌的棉签对挂片由上到下进行擦拭,直至将生物膜完全擦除。之后将棉签放入盛有10 mL已灭菌的超纯水试管中,并置于超声波清洗仪中作用20 min,使棉签上的生物膜充分溶于已灭菌的超纯水中。
总的细菌采用营养琼脂培养基在37 ℃的培养箱中培养24 h;铁细菌采用铁细菌培养基在30 ℃培养箱中培养7 d;异养菌采用R2A培养基在22 ℃的培养箱中培养7 d。
微生物灭活率计算公式为 (其中,S为微生物灭活率,N0为消毒前微生物的数量,N1为消毒后微生物数量)。
(其中,S为微生物灭活率,N0为消毒前微生物的数量,N1为消毒后微生物数量)。
1.3.4 生物膜形态检测
将消毒前后的生物膜挂片进行固定、喷金制样处理后,利用扫描电子显微镜(SEM) (FEI nova nano450,荷兰)对挂片的生物膜表面结构进行观察,选择合适的放大倍数拍摄并储存照片。
1.3.5 宏基因组分析
首先采集挂片上的生物膜(方法见1.3.3节),将采集的生物膜进行离心后提取DNA;然后,采用聚合酶链式反应引物341F(碱基序列为CCCTACACGACGCT- CTTCCGATCTG)和引物805R(碱基序列为GACTGGAGTTCCTTGGCACCCGAGAATTCA)进行扩增,之后,对扩增产物进行纯化;最后,将纯化产物按一定质量比混合后测序。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 生物膜微生物生长特性
图2和图3所示分别为BAR中不锈钢复合管壁上生物膜微生物生长情况以及进出水浊度的变化情况。由图2可知:细菌总数、铁细菌和异养菌的生长曲线大致相同;管道系统运行0~60 d期间,管壁生物膜上生物量水平较低,总的细菌、铁细菌和异养菌平均数量为1.7×102,1.1×102和2.4×102 CFU/cm2,出水浊度平均值为0.632 NTU;在管道运行60~80 d期间,管壁生物膜上微生物数量小幅度增加;运行80 d后,挂片生物量呈现对数增长趋势;在管道运行100~110 d时细菌总数、铁细菌数量及异养菌数量达到最大值,分别为1.0×105,1.8×104和1.7×105 CFU/cm2;在管道运行110~150 d期间,老化的生物膜开始脱落,管壁生物量呈现迅速下降并趋于稳定。管道材质对生物膜形成速率也有很大影响:PVC管材更易形成生物膜[11],在运行80 d左右时生物量就已达到最大值,且其中异养菌的数量远远大于不锈钢复合管道中异养菌数量。由图3可知:在运行0~100 d期间,管道系统的出水浊度呈现缓慢增加趋势;在120 d时出水浊度达到最高值,为1.367 NTU,出水的细菌总数、铁细菌数量和异养菌数量分别为120~300,50~110和700~1 300 CFU/mL,此时出水浊度和细菌总数指标均已超标,高于GB 5749—2006“生活饮用水卫生标准”中的限值。由此可见,长期运行的不锈钢复合管道也会形成明显的管壁生物膜,造成输配水管道的水体出现明显的污染现象。
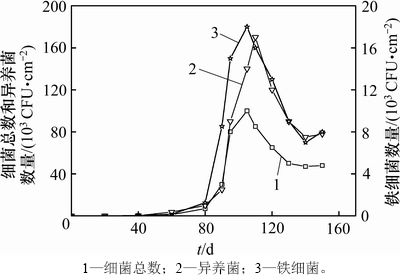
图2 BAR中挂片生物膜细菌数量变化
Fig. 2 Change of bacteria number of coupon biofilm in BAR

图3 BAR 进出水浊度变化
Fig. 3 Change of turbidity of water in and out of BAR
2.2 生物膜的细菌菌群特征
采用宏基因组16S测序方法分析模拟管道系统内成熟的生物膜中的菌群多样性,样本的覆盖率为0.96,Shannon指数为5.27,Simpson指数为0.02,表明生物膜中菌群具有多样性的特点。图4所示为生物膜中微生物在门水平上的分布情况。由图4可见:变形菌门(Proteobacteria)数量最多,其相对丰度为64.83%;其次为浮霉菌(Planctomycetes)、疣微菌门(Verrucomicrobia)、拟杆菌(Bacteroidetes)、广古菌门(Euryarchaeota)、厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)、酸杆菌门(Acidobacteria)和放线菌门(Actinobacteria),所占比例分别为12.68%,4.56%,3.97%,3.75%,3.45%,1.79%和1.71%,其余菌门所占比例均小于1.00%。与相同水质条件下PVC材质管壁生物膜中的微生物种群[11]相比,不锈钢复合管壁生物膜中变形菌门所占比例高43.23%,浮霉菌门、疣微菌门、广古菌门和酸杆菌门的数量也较多;而不锈钢复合管壁生物膜中厚壁菌门和拟杆菌门数量较少,二者所占比例比PVC管壁生物膜中的分别低41.46%和14.22%。

图4 生物膜中微生物在门水平上的分布
Fig. 4 Distribution of microbial community of the biolfilm at phylum level
变形菌门是供水管道生物膜中的优势菌群[12-13],不仅包含易造成金属腐蚀的铁细菌和硫酸盐还原菌,而且含有大肠杆菌、假单胞菌和沙门氏菌等致病菌。厚壁菌门中的枯草芽孢杆菌和拟杆菌门的黄杆菌都是腐生菌,其产生的黏性物质与铁细菌一同累积在管壁表面,可造成金属管道腐蚀[14]。变形菌门、厚壁菌门和放线菌门中都包含锰氧化细菌,能加速管道点蚀[15]。此外,上述菌门都包含一些耐氯菌,如军团菌和金黄葡萄球菌等致病菌,它们能够抵抗外界不良环境,在较低质量浓度的余氯条件下存活,从而对人体健康产生威胁。上述结果表明,市政和建筑区域供水管道生物膜中存在较多导致管壁腐蚀的菌种、致病菌和耐氯菌等,对饮用水的生物安全性和化学安全性造成一定威胁,因此,有必要控制管道生物膜的大量生成,确保市政和建筑区域供水管道的安全运行。
2.3 微生物腐蚀
图5所示为在自来水中有菌和无菌条件下,不锈钢复合管道腐蚀电位和电流密度变化。在有菌和无菌条件下不锈钢复合管道的初始腐蚀电位分别为-163 mV和-154 mV。由图5可看出:有菌水的腐蚀电位整体呈现明显降低趋势,无菌水腐蚀电位仅有轻微降低趋势。有菌水电位降低速率明显比无菌水的高,说明水中细菌的存在导致腐蚀加剧;在运行50~60 d期间,有菌水电位达到较稳定的状态,腐蚀加剧倾向变小,此时电位均值为-298 mV,比初始电位降低79%,而无菌水的电位基本维持在-145~-201 mV,均值为-169 mV,显著高于有菌水的电位。
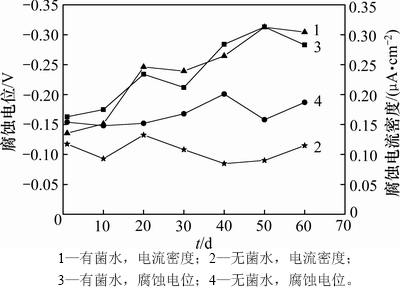
图5 有菌和无菌水中的腐蚀电位和电流密度变化
Fig. 5 Change of corrosion potential and current density in non-sterile and sterile water
腐蚀电流密度反映金属腐蚀速率,电流密度越大,腐蚀速率越大。在初始条件下,有菌和无菌水腐蚀电流密度分别为0.135 6和0.117 4 μA/cm2。从图5可看出:有菌水的腐蚀电流密度整体呈现急剧增加的趋势,而无菌水电流密度却有略微降低趋势。有菌水的腐蚀电流密度明显比无菌水的高,说明水中细菌导致腐蚀速率增加;在运行10~40 d期间,有菌水的腐蚀电流密度显著增加,均值为0.225 2 μA/cm2;运行50~60 d期间,有菌水的腐蚀速率达到最大值,电流密度均值为0.308 5 μA/cm2;而无菌水的腐蚀速率在运行期间缓慢降低,电流密度均值为0.103 9 μA/cm2,明显低于有菌水的腐蚀电流密度。腐蚀电位和腐蚀电流密度结果均表明微生物的存在会加快不锈钢复合管材的腐蚀。
微生物对于管道的腐蚀是一个较缓慢的过程。随着运行时间延长,有菌水的微生物代谢产物破坏管材钝化膜[16],造成管材的抗蚀性降低,加速阴极去极化过程,腐蚀向管材内部深入,形成点蚀[17]。为了控制微生物对管道的腐蚀,抑制和阻止管壁微生物的生长至关重要。
2.4 冲击消毒的管壁微生物灭活效能
采用高质量浓度的氯对管壁生物膜进行冲击消毒,总的细菌、铁细菌和异养菌灭活率如图6所示。由图6可见:随着氯质量浓度的增加,管壁微生物灭活效果不断提高;在氯质量浓度为1 mg/L时,随着消毒时间的增加,消毒效果明显改善;消毒180 min时,管壁生物膜中细菌总数、铁细菌和异养菌灭活率分别为1.17,1.26和1.32,消毒效果不佳。在氯质量浓度为3 mg/L时,随着消毒时间增加,总的细菌、铁细菌和异养菌灭活率明显大于氯质量浓度为1 mg/L时的灭活率;在消毒120 min时,总的细菌、铁细菌和异养菌均已趋于完全灭活,灭活率分别为2.88,3.02和3.34;随后,细菌灭活率呈现平稳趋势。在氯质量浓度为5 mg/L时,消毒0~60min时,细菌灭活率显著增加,消毒60 min时总的细菌、铁细菌和异养菌均已趋于完全灭活,灭活率分别为2.64,2.84和3.44,随后,细菌灭活率仅略微增加,可见质量浓度为5 mg/L的氯只需60 min的冲击消毒时间即可达到极佳的消毒效果。
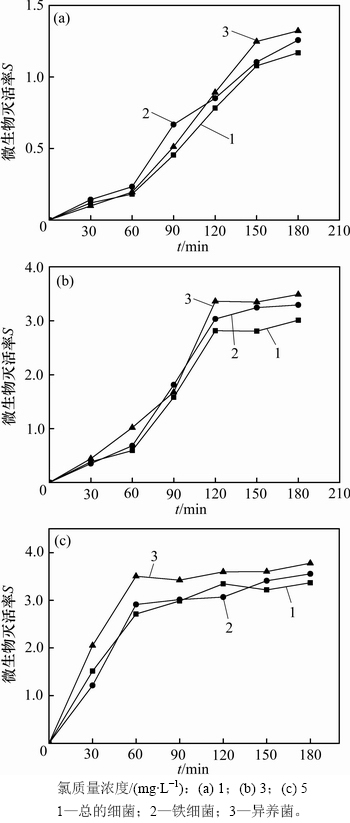
图6 氯质量浓度对生物膜微生物灭活率影响
Fig. 6 Effect of chlorine mass concentration on bacteria inactivation
从上述结果可看出:氯质量浓度对管壁生物膜的灭活有很大影响,较低质量浓度的氯需要更长的消毒时间才能达到相同的消毒效果,高质量浓度氯则在很短的消毒时间内就可完全灭活管壁生物膜的微生物。考虑到在水中投加更高质量浓度的氯会造成感官不适,且生物膜中的微生物具有较强的抗氯性[18],采用适宜质量浓度氯同时适当延长消毒时间更有利于各种微生物的杀灭,本文采用质量浓度为5 mg/L左右的氯进行60 min的冲击消毒在实际应用中有更好的适用性。
2.5 生物膜表面形态变化特征
为了进一步研究冲击氯消毒的效果,对消毒前后的生物膜形态进行检测。图7所示为用5 mg/L氯消毒前后的生物膜表面形态变化。由图7可以看出:成熟的生物膜具有一定厚度,表面凹凸不平,结构密实且呈块状;进行氯冲击消毒后,生物膜的厚度和块状大小均出现了较明显的变化;当消毒30 min时,生物膜出现萎缩现象,并发生部分脱落,此时,消毒对生物膜的破坏程度较小,生物膜表面结构仍比较密实;当消毒60 min时,有更多的生物膜脱落,造成管壁大部分裸露,生物膜表面变得松散凌乱。由此可见,冲击氯消毒可使管壁生物膜形态破坏,生物膜出现了大幅度剥离和脱落,从而有效减缓微生物对不锈钢复合管壁的腐蚀作用。

图7 消毒前后生物膜表面形态变化
Fig. 7 Change of surface morphology of biofilm before and after disinfection
3 结论
1) 在含有余氯的市政和建筑区域供水管网系统中,不锈钢复合管道在连续运行80 d后仍会出现管壁微生物明显增殖现象,在100~110 d时生物量达到峰值,细菌总数、铁细菌数及异养菌数量分别为1.0×105,1.8×104和1.7×105 CFU/cm2,管道出水浊度和微生物指标均超标。
2) 管壁生物膜细菌具有多样性,其中变形菌门为优势菌,占细菌总数的64.83%,并含有大肠杆菌、军团菌和金黄葡萄球菌等多种致病菌、耐氯病原菌以及造成金属腐蚀的菌属,对供水的生物安全性和化学安全性造成潜在威胁。
3) 有菌水的腐蚀电位出现显著降低趋势,腐蚀电流密度总体呈现明显增大趋势,而无菌水的腐蚀电位和腐蚀电流密度则均呈稳定趋势,表明有菌水对金属管道的腐蚀速率明显比灭菌水的大,微生物会明显加速金属管道的腐蚀。
4) 冲击氯消毒对管壁生物膜的微生物有显著灭活效果。氯质量浓度越高,微生物的灭活率越高;当氯质量浓度为5 mg/L、消毒时间为60 min时,总的细菌、铁细菌和异养菌均可达到完全灭活;氯冲击消毒管壁可显著破坏管壁生物膜的形态,造成生物膜大幅度剥离和脱落,能有效地控制管壁生物膜的形成,保障供水安全。
参考文献:
[1] XU Congmin, ZHANG Yaoheng, CHENG Guangxu, et al. Localized corrosion behavior of 316L stainless steel in the presence of sulfate-reducing and iron-oxidizing bacteria[J]. Materials Science and Engineering. 2007, 443(1/2): 235-241.
[2] WANG Yang, ZHANG Xiaojian, FENG Shuo, et al. Study on inactivation of iron bacteria isolated from real drinking water distribution systems by free chlorine and chloramine[J]. Annals of Microbiology, 2009, 59(2): 353-358.
[3] 卢玉琢. 铁锰氧化菌及硫酸盐还原菌在典型水环境中对金属腐蚀的影响研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学材料科学与工程学院, 2011: 6.
LU Yuzhuo. Study on corrosion of steel induced by iron bacteria and SRB in certain aquatic environment[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University. School of Materials Science and Engineering, 2011: 6.
[4] 林生, 程晓如. 供水系统二次污染的原因与控制方法[J]. 净水技术, 2008, 27(6): 24-29.
LIN Sheng, CHENG Xiaoru. Study on the reasons and the control methods of secondary pollution in water supply system[J].Water Purification Technology, 2008, 27(6): 24-29.
[5] CHAMRITSKI I G, BURNS G R, WEBSTER B J, et al. Effect of iron-oxidizing bacteria on pitting of stainless steel[J]. Corrosion, 2004, 60(7): 658-669.
[6] 周玲玲, 张永吉, 黄飞, 等. 给水管壁生物膜特性与控制方法[J]. 净水技术, 2008, 27(4): 5-8.
ZHOU Lingling, ZHANG Yongji, HUANG Fei, et al. The characteristics and control methods of biofilm in drinking water distribution system[J].Water Purification Technology, 2008, 27(4): 5-8.
[7] 陈笑居. 给水管道的微生物腐蚀[D]. 哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学市政环境工程学院, 2011: 49.
CHEN Xiaoju. Microbiologically influenced corrosion in water distribution systems[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology. School of Municipal and Environmental Engineering, 2011: 49.
[8] 王洋, 张晓健, 陈雨乔, 等. 给水管网管壁铁细菌生长特性模拟及控制对策研究[J]. 环境科学, 2009, 30(11): 3293-3299.
WANG Yang, ZHANG Xiaojian, CHEN Yuqiao, et al. Growth characteristics and control of iron bacteria on cast iron in drinking water distribution systems[J]. Environmental Science, 2009, 30(11): 3293-3299.
[9] 王若卿, 王怡, 袁洛薇. 高浓度消毒剂对再生水管道生物膜中微生物的影响[J]. 中国给水排水, 2016, 32(5): 14-17.
WANG Ruoqing, WANG Yi, YUAN Luowei. Influence of high-concentration disinfectant on microorganisms in biofilm formed in reclaimed water pipeline[J]. China Water and Waste Water, 2016, 32(5): 14-17.
[10] 朱永娟, 杨艳玲, 李星, 等. 预氯化对管道生物膜净水效能影响及性能恢复[J]. 中国环境科学, 2013, 33(5): 843-847.
ZHU Yongjuan, YANG Yanling, LI Xing, et al. Influence of pre-chlorination on pipeline biofilm water purification efficiency and recovery process[J]. China Environmental Science, 2013, 33(5): 843-847.
[11] 王帅, 杨艳玲, 李星, 等. 氯和氯胺冲击消毒对二次供水管道生物膜的控制作用[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2017, 49(8): 1-7.
WANG Shuai, YANG Yanling, LI Xing, et al. Effect of shock chlorine and chloramine disinfection on biofilm disinfection in pipe system of secondary water supply[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017, 49(8): 1-7.
[12] LAUTENSCHLAGER K, HWANG C, LIU Wentao, et al. A microbiology-based multi-parametric approach towards assessing biological stability in drinking water distribution networks[J]. Water Research, 2013, 47(9): 3015-3025.
[13] LUO Jianghan, LIANG Heng, YAN Lijun, et al. Microbial community structures in a closed raw water distribution system biofilm as revealed by 454-pyrosequencing analysis and the effect of microbial biofilm communities on raw water quality[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 148(11): 189-195.
[14] 李勇, 杨肖曦, 赵磊, 等. 现河注水井井筒腐蚀及其机理研究[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护技术, 2007, 27(1): 66-68.
LI Yong, YANG Xiaoxi, ZHAO Lei, et al. Corrosion cause of Xianhe water injection wellbores[J].Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 2007, 27(1): 66-68.
[15] DICKINSON W H, LEWANDOWSKI Z. Manganese biofouling and the corrosion behavior of stainless steel[J]. Biofouling, 1996, 10(1/2/3): 79.
[16] 张文华. 不锈钢及其热处理[M]. 沈阳:辽宁科学技术出版社2010: 348.
ZHNNG Wenhua. Stainless steel and its heat treatment[M]. Shenyang: Liaoning Science and Technology Press, 2010: 348.
[17] 齐北萌. 供水系统铸铁管材的腐蚀行为及影响因素研究[D]. 哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学环境学院, 2014: 41.
QI Beimeng. Corrosion behavior and influencing factors of cast iron pipes in water supply system[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology. School of Environment, 2014: 41.
[18] BEHNKE S, CAMPER A K. Chlorine dioxide disinfection of single and dual species biofilms, detached biofilm and planktonic cells[J]. Biofouling, 2012, 28(6): 635-647.
(编辑 伍锦花)
收稿日期:2017-11-09;修回日期:2018-01-07
基金项目(Foundation item):国家水体污染控制与治理科技重大专项(2014ZX07406-002);云南省科技计划项目(2015IB022) (Project(2014ZX07406- 002) supported by the National Water Pollution Control and Control Science and Technology Major Program; Project(2015IB022) supported by the Science and Technology Program of Yunnan Province)
通信作者:李星,博士(后),研究员,博士生导师,从事给水处理研究;E-mail: lixing@bjut.edu.cn