DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2018.10.033
微生物絮凝剂MBFA9对小球藻的沉降作用及其机理
张佳琪,曹琬,郑广泰,姜彬慧
(东北大学 资源与土木工程学院,辽宁 沈阳,110819)
摘要:以小球藻为研究对象,对絮凝菌类芽孢杆菌A9(Paebubacillus sp. A9)所产生的微生物絮凝剂MBFA9沉降水中微藻的性能进行研究。通过Zeta电位、结合键分析和扫描电镜表征探究MBFA9对小球藻的沉降机理。研究结果表明MBFA9对小球藻具有较好的沉降作用,其最佳沉降条件为:在小球藻对数生长期及平稳期添加Ca(OH)2调节pH至9.5,MBFA9添加量(体积分数)为0.2%(质量浓度为6 mg/L),在此最佳沉降条件下,沉降率为82.67%;随着pH升高,Zeta电位相应上升,在pH=9.5时达到最大;投加MBFA9后,分散状态的块状小球藻细胞迅速结合成网状结构,形成大的凝聚体而沉积,从而增大沉降速率。
关键词:小球藻;pH;微生物絮凝剂;沉降作用
中图分类号:X501 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2018)10-2636-07
Harvesting of microbial flocculant MBFA9 on Chlorella vulgaris and its mechanism
ZHANG Jiaqi, CAO Wan, ZHENG Guangtai, JIANG Binhui
(School of Resources and Civil Engineering, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110819, China)
Abstract: The characteristic and mechanism of harvesting Chlorella vulgaris by microbial flocculant MBFA9 which was produced by flocculation bacteria (Paebubacillus sp. A9) were studied. The sedimentation mechanism of Chlorella vulgaris by MBFA9 was investigated by Zeta potential, binding bond analysis and scanning electron microscopy. The results show that the sedimentation rate is 82.67% under the optimum settling conditions, i.e. adjusting pH=9.5 by adding Ca(OH)2 during exponential growth period and stationary period,and the additive volume fraction of MBFA9 is 0.1%. With the increase of pH, the Zeta potential increases accordingly and reaches the maximum when pH=9.5. After adding MBFA9, the dispersing state of Chlorella vulgaris cells combine rapidly into a network structure to form large agglomerates and deposite, leading to the increase of the sedimentation rate.
Key words: Chlorella vulgaris; pH; microbial flocculant; harvesting
藻类被认为是很有发展前景的新型生物燃料,美国能源部(DOE)认为污水处理和回用不可避免地会包含微藻生物燃料的生产。与其他生物燃料相比,藻类作为生物燃料具有以下优势:生长率和含油量高;可以产生多种脂类、烃类、复杂的油类物质;不需要利用耕地面积培养[1]。由于许多藻类个体较小(粒度为5~50 μm)、藻类在培养条件下被稀释(质量浓度为0.5~5.0 g/L)、藻类的密度与水的密度相近、净负表面电荷在水中会形成稳定的悬浮物,使藻类收集困难[2]。同样,在水处理系统中,藻类的去除对出水悬浮物的控制也很重要。藻类收集的费用占藻类生物燃料生产整体费用的20%~30%[3-5],因此,在保证收集效率的同时,降低成本是关键。目前,藻类收集方法有过滤、离心、溶气浮选法(DAF)、絮凝。其中,采用电絮凝、微生物絮凝、溶气浮选、正切流动过滤(TFF)的成本相差不大,但微生物絮凝藻类的效率要远比其他方法的高[6-16],随着新型高效微生物絮凝剂的研制,运行成本会大大降低,因此,在藻类收集方面,微生物絮凝法是较高效、经济的方法,且具有广阔的应用前景。微生物絮凝剂是一种天然高分子化合物,以其来源广、高效、无毒、可生物降解、无二次污染等特点近年来在污水处理、医药、食品加工业应用广泛。目前,国内外对微生物絮凝剂沉降藻类的研究还较少,亓华等[17]用微生物絮凝剂B-16和PAFC复配,藻类去除率为60.6%;LIU等[18]从芽孢杆菌C9提取出MBFC9,在质量浓度为8 mg/L时,小球藻的絮凝率为80.63%;LI等[19]从Shinella albus提取出MBFFLC-xn-1,在添加3.0 mmol/L FeCl3作为助凝剂后,小球藻的絮凝率为85.65%。由于无机和有机絮凝剂易对水体造成二次污染,因此,本文通过调节pH提高絮凝菌A9产生的微生物絮凝剂(microbial flocculants A9,即MBFA9)对小球藻的沉降作用。在微藻收集的过程中,pH、细胞表面性质、絮凝剂浓度、培养液中的离子强度都会影响收集效率[20-22]。本文作者研究MBFA9沉降收获小球藻过程中,不同pH、藻类生长期、MBFA9用量等因素对沉降小球藻效率的影响,并分析其影响机理。
1 材料与方法
1.1 小球藻的培养
将普通小球藻(Chlorella vulgaris)接种于16 L浮游生物培养箱中,培养基为水生5号;(NH4)2SO4 质量浓度为0.2 g/L,K2HPO4·3H2O为0.1 g/L,MgSO4·7H2O为0.08 g/L,Ca(NO3)2·4H2O为0.02 g/L、NaHCO3为0.3 g/L;柠檬酸体积分数为0.5 mL/L,柠檬酸铁为0.5 mL/L,土壤浸出液为1 mL/L。于20 ℃时光照24 h,通入空气。培养液初始pH=7.0。
1.2 微生物絮凝剂的制备
菌种来源:微生物絮凝剂产生菌A9由东北大学环境中心实验室保存,从果树根系土壤中分离筛选纯化获得,现保存于中国科学院微生物研究所菌种保藏中心,菌种编号为CGMCC2040。16SrRNA序列经分析确定A9为类芽孢杆菌属(Paebubacillus sp.)微生物。
普通培养基:牛肉膏质量浓度为5 g/L,蛋白胨为10 g/L,氯化钠为5 g/L;蒸馏水1 L,pH=7。
液体发酵培养基:葡萄糖质量浓度为20 g/L,磷酸二氢钾为2 g/L,磷酸氢二钾为5 g/L,七水硫酸镁为0.2 g/L,氯化钠为0.1 g/L,脲为0.5 g/L,酵母膏为0.5 g/L;蒸馏水1 L,pH=7.0~7.5。
本文采用的MBFA9是A9在液体发酵培养基下培养48 h后的发酵液,经8 000 r/min离心去除菌体。通过控制相同的吸光度D,保证相同体积上清液所含发酵产物相同。
1.3 试验方法
采用分光光度法在最佳波长为685 nm条件下,检测小球藻絮凝前后吸光度,表征溶液中小球藻浓度的变化,并计算沉降率;采用pH计测量pH,用质量分数的10% NaOH,10% Ca(OH)2和11.4% HCl调节pH;采用Zeta电位仪测量藻液的Zeta电位,对每个样品平行检测3次;利用数码成像显微镜(Motic BA210LED Digital)和场发射扫描电镜(Zeiss ULTRA PLUS)观察小球藻絮凝前后的形态变化;通过加入尿素或EDTA的方法检测MBFA9与小球藻结合情况,进而分析其沉降机理。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 小球藻在不同生长时期对沉降率的影响
小球藻生长较缓慢,在接种1~3 d内没有明显生长,第4 天进入指数生长期,第7天进入平稳期。小球藻在指数增长阶段早期自沉降较好,最高自沉降率可达50%,加入絮凝剂后最高可达70%。小球藻在生长过程中pH变化范围为6.0~7.5。小球藻生长曲线及沉降率见图1。从图1可以看出:随着小球藻生物量升高,自沉降率逐渐升高。这是由于接种初期小球藻细胞处于停滞期,在溶液中为单细胞状态,不易聚集;而随着容器内生物量增加,容器内的大多数小球藻细胞都会处于指数增长期和平稳期,更容易聚集在一起形成团簇,形成团簇的小球藻细胞因质量更大更容易沉降。
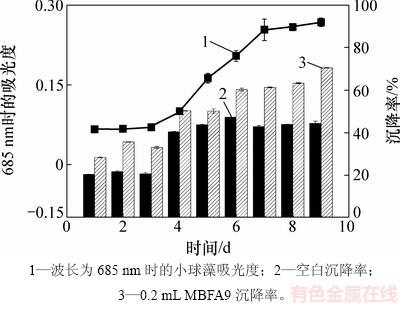
图1 小球藻生长曲线及沉降率
Fig. 1 Chlorella vulgaris growth curve and sedimentation rate
刘洁霞[23]对雪绿球藻(Chlorococcum nivale)、椭圆绿球藻(Chlorococcum ellipsoideum)、栅藻(Scenedesmus sp.)这3种绿藻早期生长阶段、指数生长阶段、平稳阶段的胞外多糖产量进行测定,发现这3种绿藻在指数生长阶段会产生更多的胞外多糖。小球藻在指数生长期添加MBFA9的效果不如在平稳期添加的效果好,这是由于指数生长期小球藻会分泌更多的胞外多糖,它们与培养液中金属离子络合,从而影响沉降效果[24-25]。
2.2 MBFA9添加量对小球藻沉降率的影响
小球藻在平稳期时加入MBFA9沉降效果较好,取平稳期小球藻100 mL,pH=7.5~8.0,分别加入不同体积的MBFA9。MBFA9添加量对沉降率的影响见图2。
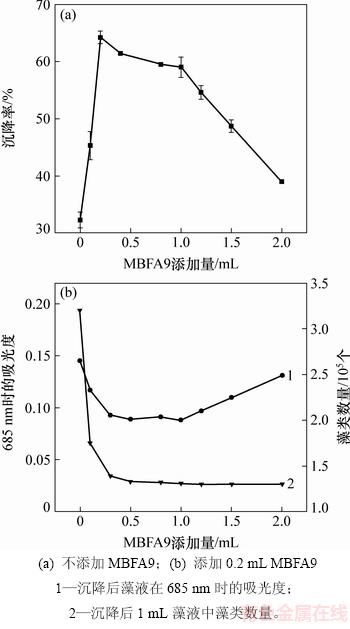
图2 MBFA9添加量对沉降率的影响
Fig. 2 Effect of MBFA9 addition on sedimentation rate of Chlorella vulgaris
从图2(a)可以看出:在不添加MBFA9时,小球藻自沉降率为30%左右,这是由于小球藻细胞较小,在自然条件下不易发生聚集;在添加0.2 mL MBFA9(多糖质量浓度为3 g/L)时,小球藻沉降率可以提高至65%左右;随着MBFA9添加量增加,小球藻的沉降率略提高;在絮凝剂添加量增加至1.0 mL时,沉降率开始下降,这是由于过多的絮凝剂会影响吸光度导致沉降率下降。为了消除絮凝剂对吸光度的影响,用藻类计数法检测沉降后上清液中小球藻的数量。从图2(b)可以看出:随着MBFA9添加量增加,沉降后1 mL藻液中小球藻的个数逐渐下降,直到MBFA9添加量达到1.0 mL后,藻液中小球藻的个数几乎没有变化,这表明絮凝剂添加量达到1.0 mL后,絮凝剂添加量增加并不能提高絮凝率,这是因为此时小球藻与絮凝剂的结合位点接近饱和。
小球藻自然沉降与添加MBFA9后的显微照片见图3。从图3可以看出:添加絮凝剂后,微藻聚集得更加紧密,且小球藻细胞完好。姜彬慧等[26]通过红外光谱分析进一步断定 A9 产生的絮凝剂 MBFA9 中含有乙酰氨基和羧基,由此可以推测MBFA9沉降小球藻的絮凝机理可能是吸附架桥,含量适宜、分布均匀的羧基可以使MBFA9分子充分伸展,产生架桥使小球藻细胞可以吸附到絮凝剂链上。
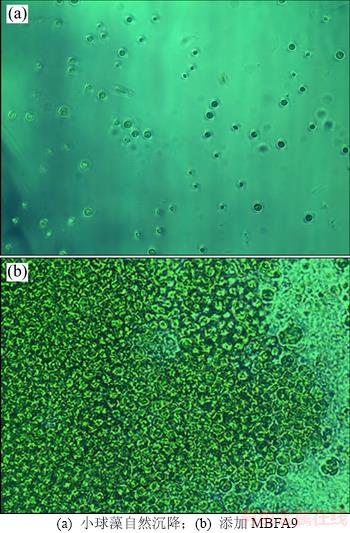
图3 小球藻自然沉降与添加MBFA9的显微照片
Fig. 3 Microscopic photos of natural sedimentation of Chlorella vulgaris and that when MBFA9 is added
2.3 pH对小球藻沉降率的影响
小球藻在指数生长早期时加入MBFA9后沉降率较低,故考虑pH对其沉降率的影响。取指数生长早期小球藻100 mL,调节pH分别至6.0,6.5,7.0,7.5,8.0,8.5,9.0和9.5,加入0.2 mL MBFA9。pH对小球藻沉降率的影响结果见图4。从图4可见:当pH降至6.0时,小球藻几乎不发生沉降;当藻液pH升至7.0及以上时,小球藻开始凝结;当pH=7.0~8.5时,小球藻发生团聚,但是这些团聚的小球藻仍然分散在培养液中,且其对应沉降率还较低;当pH升至9.5时,小球藻发生进一步团聚,形成更大的团块,在几分钟内快速沉降,自沉降率可达60%左右。由于小球藻表面带有羧酸(—COOH)与胺(—NH2),当溶液中 pH>4时,—COOH会解离成—COOH-,—NH2不带电荷,这导致小球藻细胞在pH>4时带负电荷[27-28]。由于营养液中含有MgSO4·7H2O,Ca(NO3)2·4H2O和柠檬酸铁会解离成Mg2+,Ca2+和Fe3+,在碱性条件下会发生水解形成不易溶的带正电荷的沉淀物,并通过网捕卷扫和静电中和作用凝聚带负电荷的小球藻细胞,这与YANG等[29]的研究结果相似。WU等[30]通过ICP-AES测定营养液中离子浓度的变化,Mg2+在沉降前后浓度明显下降,这表明Mg2+在高pH条件下形成Mg(OH)2,带正电荷的沉淀物中和了微藻表面的负电荷使其失去稳定性,同时,Mg(OH)2具有开链结构,即使很小的质量也能提供有效的体积分数高的结合微藻细胞。VANDAMME等[31]通过测定沉降前后离子浓度和添加EDTA确定升高pH对诱导小球藻沉降过程中Mg2+和Ca2+是否起到重要作用,发现Mg2+在升高pH诱导小球藻沉降过程中起重要作用。添加MBFA9后,沉降率可相应地增大10%~20%,这可能是MBFA9的主要成分为多糖,其相对分子质量较大,且具有多聚链结构,可以在适宜条件下使分散状态的块状小球藻细胞迅速结合成网状结构,形成大的凝聚体而沉积,从而加快沉降速率,提高沉降率。
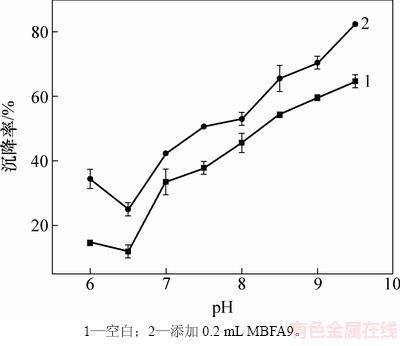
图4 pH对小球藻沉降率的影响
Fig. 4 Effect of pH on sedimentation rate of Chlorella vulgaris
2.4 Ca2+对小球藻沉降率的影响
对Ca2+对小球藻(指数生长早期)沉降率的影响见图5。pH升高有利于小球藻沉降。在实验室通常用NaOH调节pH,由于NaOH的价格较高,从降低成本的角度考虑,本文用NaOH和Ca(OH)2调节相同的pH,对微藻的沉降率进行比对,见图5。从图5可以看出:在相同pH并添加MBFA9的情况下,用Ca(OH)2调节pH(图5中Ca(OH)2)小球藻的沉降率高于用NaOH调节pH时小球藻的沉降率,沉降率提高10%~15%;在相同pH且不添加MBFA9的情况下,用Ca(OH)2调节pH时(图5中曲线3),小球藻的自沉降率同样大于NaOH调节pH(图5中空白1)时小球藻的自沉降率。这进一步说明Ca2+在升高pH沉降小球藻的过程中起到了重要的作用[32]。金属离子在小球藻的生理活动中可作为调节剂或酶的激活剂,对油脂积累也有重要作用。任宏宇[33]通过研究Ca2+质量浓度对微藻生长和油脂积累的影响发现:当Ca2+质量浓度由0 mg/L增加到98 mg/L时,油脂质量分数由10.6%增加到47.4%,最大油脂产率达到275.7 mg/(L·d)。CHEN等[34]发现Ca2+对环境刺激信号的传递起重要作用,可以通过传递Ca2+信号来调节小球藻C2(Chlorella sp. C2)的油脂合成。PRAKASH等[35]通过研究发现在自养培养普通小球藻(Chlorella vulgaris)时,增加Ca2+浓度可以提髙普通小球藻的油脂含量。
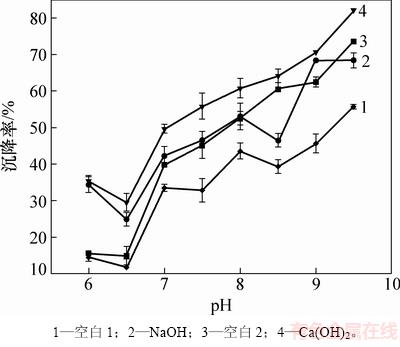
图5 不同pH下Ca2+对小球藻沉降率的影响
Fig. 5 Effect of Ca2+ on sedimentation rate of Chlorella vulgaris at different pH
2.5 MBFA9沉降小球藻的机理
通过分析Zeta电位在絮凝过程中的变化、MBFA9与小球藻细胞之间结合键分析与扫描电镜表征沉降结果的分析,探讨MBFA9沉降小球藻的机理。
2.5.1 Zeta电位检测
胶体颗粒在液体中是带电的。当固体与液体接触时,固-液两相界面上就会带有相反符号的电荷。Zeta电位是表征胶体分散体系稳定性的重要指标[32]。若颗粒带有许多负电荷或者正电荷,也就是说当Zeta电位的绝对值很高时,则它们就会相互排斥,整个体系具有较高的稳定性;反之,Zeta电位的绝对值很低,它们就会相互吸引,整个体系就会不稳定,容易生成沉淀物。胶体从稳定地悬浮在液体中到稳定性遭到破坏发生沉降的过程中,体系的Zeta电位是1个重要参数,它是决定1个悬浮胶体体系是否稳定的重要因素[32],因此,通过测定自然沉降后小球藻细胞和添加MBFA9小球藻细胞的Zeta电位来探讨MBFA9沉降小球藻的机理。当Zeta电位绝对值大于30 mV时,认为溶液体系稳定,不产生沉淀;当Zeta电位为0 mV时,溶液pH是该胶体颗粒的等电点,此时体系最不稳定,容易生成沉淀物。胶体从稳定地悬浮在液体中到稳定性遭到破坏发生沉降的过程中,体系的Zeta电位是决定悬浮胶体体系是否稳定的重要因素[32]。因此,本文通过测定自然沉降后小球藻细胞和添加MBFA9以后小球藻细胞的Zeta电位来探讨MBFA9沉降小球藻的机理。小球藻在不同pH下的Zeta电位及沉降率见图6。从图6可以看到:营养液中的pH会影响Zeta电位和沉降率;当pH从6.0升至7.5时,添加MBFA9后的小球藻Zeta电位逐渐升高到-9.87 mV,此时,小球藻自沉降率为37.8%,投加MBFA9后的沉降率为52.9%;当pH升高至9.5时,添加MBFA9后,小球藻Zeta电位升高至-5.33 mV,此时,絮凝率最高,为82.67%;当pH从6.0升至9.5时,小球藻的Zeta电位绝对值从14.15 mV降至6.32 mV,添加MBFA9后,小球藻Zeta电位从12.56 mV降至3.71 mV,这是因为溶液中的Ca2+和Mg2+易形成带正电荷的沉淀物,中和小球藻表明的负电荷,溶液的稳定性急剧下降,小球藻细胞间的相互作用增强,有利于小球藻细胞的聚集。最佳沉降率时小球藻的Zeta电位等电点量表明:在沉降过程中,除了金属阳离子形成的正电荷与小球藻表面细胞的负电荷发生吸附电中和作用外,还有MBFA9的架桥作用,因此,沉降效率有所提高。
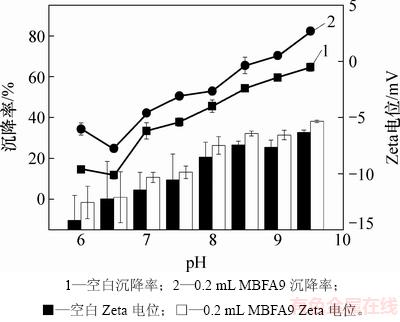
图6 小球藻在不同pH下Zeta电位及沉降率
Fig. 6 Sedimentation rate and Zeta potential of Chlorella vulgaris at different pH
2.5.2 MBFA9与小球藻结合键的检验结果
絮凝剂本身具有活性官能团,可与胶体或微粒发生吸附桥连作用形成絮体,因而可以通过化学方法初步判断絮凝剂与颗粒之间的结合键。将MBFA9沉降后的小球藻摇匀分别加入 EDTA 和尿素,结果表明:絮凝沉淀物对 EDTA 较敏感,小球藻溶液中絮体解絮;对尿素不敏感,絮体无明显解絮现象;尿素可以与小球藻颗粒间形成氢键,从而破坏MBFA9与小球藻颗粒间的氢键;而 EDTA 能够强烈破坏MBFA9与小球藻颗粒间的离子键。由此可初步推断MBFA9与颗粒之间的结合方式为离子键。
2.5.3 扫描电镜检测
将小球藻和最佳沉降条件下的小球藻预处理后,在扫描电镜下观察,结果见图7。
从图7(b)可以看出:小球细胞之间能够充分互相聚集在一起;当pH=9.5时,藻液中存在的阳离子水解产生带正电荷的沉淀物,中和了小球藻表面细胞,降低了细胞表面电荷密度;添加MBFA9后,由于其存在乙酰氨基、羧基等活性基团[26],可以凭借范德华力、氢键吸附小球藻细胞,由于絮凝剂主要成分为多糖,相对分子质量较大,且具有多链状结构,有利于架桥作用的发挥,形成一种网状结构,从而网捕和卷扫小块结合在一起的小球藻细胞,加快了沉降速度。SALIM等[36]用纤维藻和栅藻沉降小球藻,用扁藻沉降富油新绿藻,通过显微观察推测其机理为:纤维藻产生的EPS附着在纤维藻细胞表面,由于其带正电荷可以结合其他微藻细胞,从而形成巨大的网状结构,进而通过架桥作用使小球藻细胞沉降。
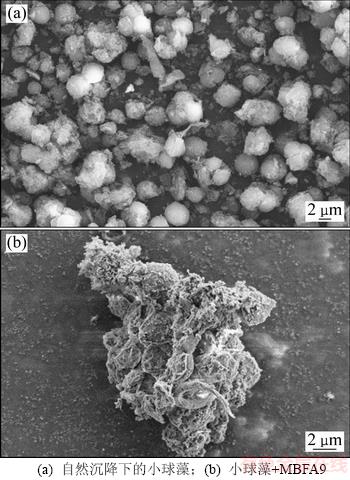
图7 小球藻在自然沉降与添加MBFA9条件下的FESEM
Fig. 7 FESEM of Chlorella vulgaris in natural sedimentation and when MBFA9 is added
3 结论
1) 微生物絮凝剂MBFA9对小球藻具有较好的沉降作用,在最佳条件下,小球藻的沉降率为82.67%,且沉降后小球藻细胞完好;沉降作用的主要影响因素是藻类的生长时期、溶液中的初始pH及絮凝剂的添加量,而对沉降率影响最大的因素是pH。
2) MBFA9沉降小球藻的机理主要为2个方面:① 多糖类的MBFA9的相对分子质量较大,具有多聚链状结构,在适宜条件下使分散状态的块状小球藻细胞迅速结合成网状结构,形成大的凝聚体而沉积,加快了沉降速率;② 当pH>7时,培养液中的金属阳离子会发生水解形成带正电荷的沉淀物与小球藻表面的负电荷发生中和反应,使其失去稳定性,进而通过卷扫网捕作用聚集小球藻细胞,对沉降有一定的促进作用。
3) 生物量会影响小球藻沉降,生物量越高,越易沉降。这是因为当生物量较高时,大多数小球藻细胞处于指数期和平台期,细胞容易团聚在一起形成团簇,由于细胞表面电荷已被中和,形成团簇的细胞因质量更大而更容易沉降。
参考文献:
[1] SHARMA K, GARG S, YAN L, et al. Critical analysis of current microalgae dewatering techniques[J]. Biofuels, 2013, 4(4): 397-407.
[2] VERGINI S, ARAVANTINOU A F, MANARIOTIS I D. Harvesting of freshwater and marine microalgae by common flocculants and magnetic microparticles[J]. Journal of Applied Phycology, 2016, 28(2): 1041-1049.
[3] GRIMA E M, BELARB E H, FERNANDEZ F G A, et al. Recovery of microalgal biomass and metabolites: process options and economics[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2003, 20(7/8): 491-515.
[4] STEPHENS E, ROSS I, KING Z, et al. An economic and technical evaluation of microalgal biofuels[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2010, 28(2): 126-128.
[5] WILLIAMS P J L B, LAURENS L M L. Microalgae as biodiesel & biomass feedstocks: review & analysis of the biochemistry, energetics & economics[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2010, 3(5): 554-590.
[6] CUI Y, YUAN W, CHENG J. Understanding pH and ionic strength effects on aluminum sulfate-induced microalgae flocculation[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2014, 173(7): 1692-1702.
[7] BARRUT B, BLANCHETON J P, MULLER A, et al. Separation efciency of a vacuum gas lift for microalgae harvesting[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2013, 128(1): 235–240.
[8] LEE A K, LEWIS D M, ASHNAN P J. Harvesting of marine microalgae by electroflocculation: the energetics, plant design, and economics[J]. Applied Energy, 2013, 108(8): 45-53.
[9] GRIMA E M, BELARBI E H, FERNANDEZ F A, et al. Recovery ofmicroalgal biomass and metabolites:process options and economics[J]. Biotechnol Adv, 2003, 20(7): 491–515.
[10] DANQUAH M K, ANG L, UDUMAN N, et al. Dewatering of microalgal culture for biodiesel production: exploring polymer flocculation and tangential flow filtration[J]. Chem Technol Biot, 2009, 84(7): 1078–1083.
[11] HEASMAN M, DIEMAR J, O'CONNOR W, et al. Development of extended shelf-life microalgae concentrate diets harvested by centrifugation for bivalve mollusks: a summary[J]. Aquaculture Research, 2000, 31(8/9): 637–659.
[12] HENDERSON R, PARSONS S A, JEFFERSON B. The impact of algal properties and pre-oxidation on solid-liquid separation of algae[J]. Water Research, 2008, 42(8/9): 1827-1845.
[13] HUNTLEY M E, JOHNSON Z I, BROWN S L, et al. Demonstrated largescale production of marine microalgae for fuels and feed[J]. Algal Res, 2015, 10(51): 249-265.
[14] DANQUAH M K, GLADMAN B, MOHEIMANI N, et al. Microalgal growth characteristics and subsequent influence on dewatering efficiency[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2009, 151(1/2/3): 47-57.
[15] HUNG M T, LIU J C. Microfiltration for separation of green algae from water[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B:Biointerfaces, 2006, 51(2): 157-164.
[16] GONG Qingli, CUI Jianzhou, PAN Kehou, et al. Ultra-filtration application in condensing chlorella cultured solution[J]. Marine Sciences, 2004, 28(1): 5-7.
[17] 亓华, 田顺, 谢恩亮. 微生物絮凝剂B-16用于给水处理的研究[J]. 供水技术, 2008, 6(2): 10-12.
QI Hua, TIAN Shun, XIE Enliang. Application of microbiological flocculant B-16 in drinking water treatment[J]. Water Technology, 2008, 6(2): 10-12.
[18] LIU Chong, WANG Ke, JIANG Jinhong, et al. A novel bioflocculant produced by a salt-tolerant, alkaliphilic and biofilm-forming strain Bacillus agaradhaerens C9 and its application in harvesting Chlorella minutissima UTEX2341[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 93(15): 166-172.
[19] LI Yi, XU Yanting, LIU Lei, et al. First evidence of bioflocculant from Shinella albus with flocculation activity on harvesting of Chlorella vulgaris biomass[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 218(10): 807-815.
[20] MANHEIM D, NELSON Y. Settling and bioflocculation of two species of algae used in wastewater treatment and Algae biomass production[J]. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy, 2013, 32(4): 946-954.
[21] UDUMAN N, QI Y, DANQUAH M K, et al. Dewatering of microalgal cultures: a major bottleneck to algae-based fuels[J]. Journal of Renewable & Sustainable Energy, 2010, 2(1): 23-571.
[22] GONZALEZFERNANDEZ C, BALLESTEROS M. Microalgae autoflocculation: an alternative to high-energy consuming harvesting methods[J]. Journal of Applied Phycology, 2013, 25(4): 991-999.
[23] 刘洁霞. pH值诱导能源微藻原位絮凝方法的建立及机理研究[D]. 广州: 暨南大学化学与材料学院, 2014: 22-25.
LIU Jiexia. Establishment of pH-induced in-situ flocculation of energy microalgae and investigation of the mechanism[D]. Guangzhou: Jinan University. School of Chemistry and Materials, 2014: 22-25.
[24] CHEN Li, LI Pengfu, LIU Zhili, et al. The released polysaccharide of the cyanobacterium Aphanothecehalo- phyticainhibits flocculation of the alga with ferric chloride[J]. J Apply Phycol, 2008, 21(3): 327-331.
[25] MORINEAUTHOMAS O, JAOUEN P, LEGENTILHOMME P. The role of exopolysaccharides in fouling phenomenon during ultrafiltration of microalgae (Chlorellasp. and Porphyridium purpureum): advantage of a swirling decaying flow[J]. Bioprocess & Biosystems Engineering, 2002, 25(1): 35-42.
[26] 姜彬慧, 李若男, 李凤达, 等. 类芽孢杆菌产絮凝多糖发酵条件优化及成分分析[J]. 环境科学研究, 2014, 27(5): 547-553.
JIANG Binhui, LI Ruonan, LI Fengda, et al. Optimization of fermentation conditions and composition analysis of polysaccharide-based bioflocculant produced by Paenibacillus sp. A9[J]. Research of Environment Science, 2014, 27(5): 547-553.
[27] LIU Jiexia, ZHU Yi, TAO Yujun, et al. Freshwater microalgae harvested via flocculation induced by pH decrease[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2013, 6(1): 98-109.
[28] VANDAMME D, FOUBERT I, MUYLAERT K. Flocculation as a low-cost method for harvesting microalgae for bulk biomass production[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2013, 31(4): 233-239.
[29] YANG Fangfang, XIANG Wenzhou, FAN Jiewei, et al. High pH-induced flocculation of marine Chlorella, sp. for biofuel production[J]. Journal of Applied Phycology, 2015, 28(2): 1-10.
[30] WU Zechen, ZHU Yi, HUANG Weiya, et al. Evaluation of flocculation induced by pH increase for harvesting microalgae and reuse of flocculated medium[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 110(4): 496-502.
[31] VANDAMME D, FOUBERT I, FRAEYE I, et al. Flocculation of Chlorella vulgaris induced by high pH:role of magnesium and calcium and practical implications[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 105(2): 114-119.
[32] LAM G P, GIRALDO J B, VERMUE M H, et al. Understanding the salinity effect on cationic polymers in inducing flocculation of the microalga Neochloris oleoabundans[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2016, 225(10): 10-17.
[33] 任宏宇. 微藻油脂合成策略及暗发酵细菌-微藻耦合产能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学市政环境工程学院, 2016: 9-11.
REN Hongyu. Strategies for microalgal lipid synthesis and energy production by combination of dark fermentative bacteria and microalgae[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology. School of Municipal and Environmental Engineering, 2016: 9-11.
[34] CHEN Hui, ZHANG Yunming, HE Chenliu, et al. Ca2+ signal transduction related to neutral lipid synthesis in an oil-producing green alga Chlorella sp. C2[J]. Plant & Cell Physiology, 2014, 55(3): 634-644.
[35] PRAKASH C, GORAIN S, KUMAR B, et al. Effects of calcium, magnesium and sodium chloride in enhancing lipid accumulation in two green microalgae[J]. Environmental Technology, 2013, 34(13/14/15/16): 1887-1894.
[36] SALIM S, BOSMA R, VERMUE M H, et al. Harvesting of microalgae by bio-flocculation[J]. Journal of Applied Phycology, 2011, 23(5): 849-855.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期:2017-11-29;修回日期:2018-01-08
基金项目(Foundation item):国家科技重大专项(2013ZX07202-010-05);国家自然科学基金资助项目(51278090)(Project(2013ZX07202-010-05) supported by the Major Project of National Science and Technology; Project(51278090) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China)
通信作者:姜彬慧,博士,教授,从事水污染控制研究;E-mail:jiangbinhui@mail.neu.edu.cn