文章编号:1004-0609(2013)06-1560-07
Sn、Zr、Mo对Ti35Nb基合金组织与力学性能的影响
陈 锋,王 煜
(东南大学 材料科学与工程学院 江苏省先进金属材料高技术研究重点实验室,南京 211189)
摘 要:根据钛合金相关设计理论,采用无细胞毒性的合金元素Nb、Sn、Zr和Mo设计具有低弹性模量的近β型Ti35Nb-Sn-Zr-Mo五元钛合金,研究Sn、Zr和Mo合金元素对合金显微组织与力学性能的影响。结果表明:所设计合金在800 ℃固溶后的组织均为单一β等轴晶组织;平均晶粒尺寸随着Sn与Zr含量的增加而减小,而随着Mo含量的增加先减小后增大。随着Sn、Zr和Mo合金元素的增加,合金强度随之升高,而伸长率逐渐下降,弹性模量随着Sn和Mo含量的增加而升高,而随着Zr含量的增加先下降后升高。固溶处理后,具有最高容许应变的合金为Ti35Nb2Sn6Zr3Mo,其抗拉强度、屈服强度、弹性模量以及伸长率分别为664 MPa、641 MPa、59 GPa以及12.5%。
关键词:钛合金;Sn-Zr-Mo;钛合金设计理论;显微组织;力学性能
中图分类号:TG 156 文献标志码:A
Influence of Sn, Zr and Mo elements on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti35Nb based alloys
CHEN Feng, WANG Yu
(Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Metallic Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing 211189, China)
Abstract: Metastable β-type Ti35Nb-based alloys containing non-toxic elements Nb, Sn, Zr and Mo and with relative low elastic moduli, were designed based on the relative design theories of titanium alloys. The influence of Sn, Zr and Mo alloying elements on the microstructure and mechanical properties of the alloys was investigated. The results show that the designed alloys are all composed of single β phase after solid solution treatment at 800 ℃. The average grain sizes decrease with increasing Sn and Zr contents, while they decrease first and then increase with increasing Mo content. The strength of the alloys increases while the elongation decreases with increasing Sn, Zr and Mo contents. The elastic moduli of the alloys increase with increasing Sn and Mo contents, while they decrease first and then increase with increasing Zr content. The ultimate tensile strength, yield strength, elastic modulus and elongation of the Ti35Nb2Sn6Zr3Mo alloy with the highest allowable strain are 664 MPa, 641 MPa, 59 GPa and 12.5%, respectively.
Key words: titanium alloy; Sn-Zr-Mo; titanium alloy design theory; microstructure; mechanical properties
钛及其合金具有良好的生物相容性和力学性能, 广泛用作生物植入体材料。纯钛与TC4(Ti6Al4V)是目前应用最广泛的生物体种植材料,但弹性模量均在110 GPa左右,远高于人骨的弹性模量(3~35 GPa)[1-2];而TC4中含有细胞毒性元素V和Al,生物相容性受到限制。目前,设计和开发具有低弹性模量的β钛合金成为医用钛合金材料开发的重点。大量实验表明,Nb、Sn、Zr和Mo等元素具有较好的生物相容性,对身体具有较小的毒性[3],因而由这些元素构成的低弹性模量β钛合金具有较大的应用潜力。作为植入体的医用钛合金应满足以下条件:1) 不含对人体有害的合金元素,具有良好的生物相容性;2) 具有与人体皮质骨更为匹配的许可应变和弹性模量,具有很好的生物力学相容性,力学性能如下[4]:σb≥600 MPa、δ≥10%、E≤90 GPa。
目前,在钛合金设计中d电子合金设计理论应用比较广泛,该理论引进两个参量:键级Bo和d电子轨道能级Md。Bo反映了两原子的共价键的强弱或结合 能的大小,Md就是电负性本身。一般来说,较低的Md值有利于相稳定,较高的Bo值有利于提高固溶强化效果。KURODA等[5]利用d电子合金设计理论设计了高强度低弹性模量Ti29Nb13Ta4.6Zr合金。ABDEL-HADY等[6]将Bo—Md图扩展到了Bo>2.84的部分(见图1),发现在β相区内,弹性模量随Bo和Md值的增加而降低,而β稳定性最弱的合金,即在β相区内靠近β/β+ω相分界的合金,其弹性模量最低。LAHEURTE等[7]指出当β钛合金为二元系合金时,弹性模量能够很好地符合d电子理论;当设计多元系合金时,弹性模量并不随着Bo与M d值的增大而降低,不能将Bo与M d值作为唯一的设计参数。所以在低弹性模量钛合金设计时还应该考虑其他参数,例如β稳定系数Kβ、Mo以及电子浓度e/a等[8]。研究表明,具有较低弹性模量的钛合金的Kβ值一般为1.0~1.5。部分学者对已有橡胶金属(属于β型钛合金)进行整理研究,发现合金的电子浓度e/a接近4.24时其弹性模量达到最小值[9]。
本文作者通过总结相关文献[5-6, 10-13]以及本文作者所在课题组前期所研究的43种Ti-Nb系医用钛合金,统计出具有高强低弹Ti-Nb系合金的Bo、Md、e/a以及Kβ的范围分别为2.85~2.88、2.43~2.47、4.20~4.27、1.0~1.6、8~13。在此,采用钛合金相关设计理论以及上述Ti-Nb系合金相关设计参数的经验值,设计高强低弹Ti35Nb-Sn-Zr-Mo五元系钛合金,并研究Sn、Zr和Mo合金元素含量对其组织和性能的影响。
1 实验
1.1 合金设计
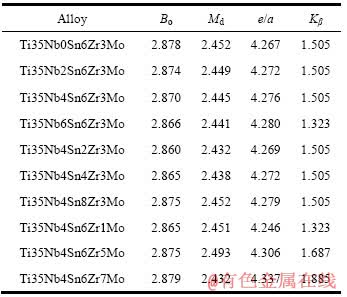
所设计合金以Ti35Nb为基础,同时加入不同含量的Sn、Mo和Zr 3种合金元素(质量分数,%),其成分、Bo、Md、e/a、Kβ值如表1所列。
10种不同成分钛合金的Bo、Md、e/a以及Kβ的取值范围分别为2.860~2.879、2.432~2.452、4.246~4.337、1.323~1.885,这与上述统计的具有高强低弹的Ti-Nb系合金的相关设计参数相吻合。合金的Bo与Md值绘在Bo—Md图上[6],可以预测所设计合金的弹性模量在60~70 GPa之间。另外,采用表1中所列合金成分的另一个重要目的是通过构成Ti35Nb(0,2,4,6)Sn6- Zr3Mo、Ti35Nb4Sn(2,4,6,8)Zr3Mo和Ti35Nb4Sn6Zr- (1,3,5,7)Mo 3组合金,可以分别研究Sn、Zr和Mo含量对合金组织与性能的影响。
表1 10种钛合金的Bo、Md、e/a、Kβ、Mo[eq]等相关设计参数
Table 1 Bo, Md, e/a and Kβ values of ten designed titanium alloys
1.2 试验方法
以高纯Ti、Nb、Sn、Zr和Mo为原料,根据所设计合金成分配比,经真空非自耗电弧炉熔炼得到纽扣状铸锭。将合金加热至800 ℃锻造成4 mm厚板材,经打磨及线切割后得到3 mm厚板材拉伸试样,如图1所示。将合金加热到β相区,在800 ℃固溶30 min,水淬。
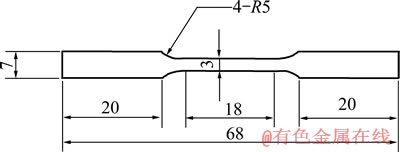
图1 板材拉伸试样示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of sheet tensile specimen (Unit: mm)
试样经打磨、机械抛光和浸蚀处理,用金相显微镜观察固溶处理后试样的显微组织,用XD-3A X线衍射仪分析合金的相结构,并由衍射图谱计算出晶胞体积。
用CMT 5105电子万能试验机进行拉伸性能测试,得到合金的抗拉强度σb、屈服强度σ0.2、伸长率δ、弹性模量E等力学性能。
2 结果与分析
2.1 固溶处理后的显微组织
图2和3所示分别为不同成分合金的固溶态金相组织及其XRD谱,可见合金经800 ℃固溶处理后均获得等轴的亚稳β相组织(为了便于比较Sn、Zr和Mo元素含量对晶粒大小的影响,图2(c)、(g)、(j)所示均为Ti35Nb4Sn6Zr3Mo同一合金的金相组织)。这是因为合金中添加元素的β稳定化能力较强(Kβ≥1.323),马氏体转变开始温度Ms低于室温,水淬时可避免形成马氏体而保留单一的亚稳β相。
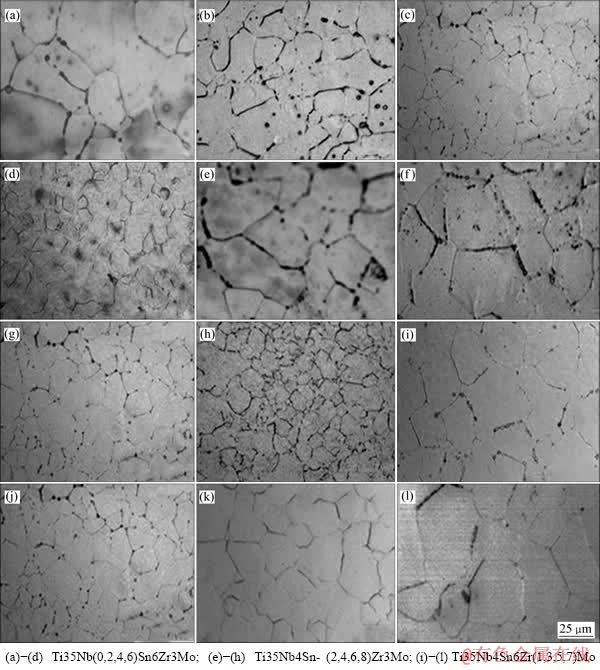
图2 不同成分合金固溶后的金相组织
Fig. 2 OM images of designed alloys after solution treatment
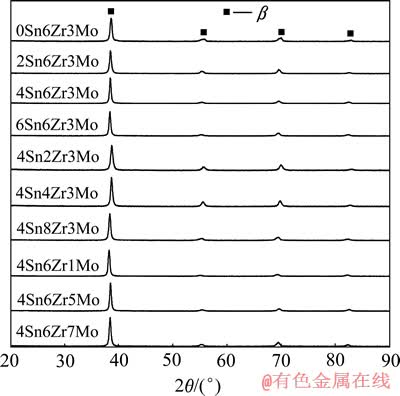
图3 所设计合金的XRD谱
Fig. 3 XRD patterns of designed alloys
Sn、Zr和Mo元素对晶粒尺寸的影响可能是两种机制竞争的结果[13]:一方面是随着合金元素的增加,合金的再结晶温度升高,使得合金在形变再结晶后β晶粒长大的驱动力降低,晶粒得到细化;另一方面所添加合金元素均具有β稳定化能力,能降低α+β/β转变点,使合金固溶处理时“过热度”增加(固溶处理温度一定),促使晶粒长大。
由图2(a)~(d)及图2(e)~(h)可知,随Sn与Zr元素的增加,Ti35Nb(0,2,4,6)Sn6Zr3Mo合金以及Ti35Nb4- Sn(2,4,6,8)Zr3Mo合金固溶后,β晶粒逐渐减小。添加Sn与Zr元素会使钛合金的再结晶温度升高,原因可能是在凝固过程中合金中低熔点的Sn倾向于在晶界处偏聚以及少量溶质Zr原子与晶界间存在交互作用[14],阻碍再结晶时晶界的迁移[15]。另一方面Sn与Zr元素的加入又会使钛合金的Ms以及(α+β)/β相变点降低[10, 16-17],从而使固溶处理时“过热度”增加。但莫畏[15]指出,当Sn含量小于18%时,1%Sn仅使(α+β)/β相变点降低1 ℃;当Zr元素含量较低时(<10%),1%Zr仅使(α+β)/β相变点降低2 ℃。在本试验条件下,Sn(≤6%)与Zr(≤8%)的含量较少,对“过热度”的影响很小,此时Sn和Zr元素主要起晶粒细化的作用。
由图2(i)~(l)可知,随着Mo含量的增加,Ti35Nb4Sn6Zr(1,3,5,7)Mo合金的晶粒尺寸先减小后增大。Mo熔点很高(2 883 K),因此,合金的再结晶温度会随Mo含量的增加而显著提高。另一方面,Mo是Ti的强β稳定化元素,通过淬火得到全β相组织Mo含量仅为11%[18]。Mo的加入可使合金的α+β/β转变点显著降低[15],使固溶处理时“过热度”增加。Mo含量对晶粒尺寸的影响是应该上述因素的共同作用结果:当Mo含量较低时,对“过热度”的影响较小,此时Mo对晶粒细化起主导作用;当Mo含量较高时(约5%),对“过热度”的影响显著增强,促使晶粒迅速长大。
2.2 固溶处理后的力学性能
图4所示为Sn、Zr和Mo元素含量对合金力学性能和晶胞体积的影响。
2.2.1 Sn含量对合金力学性能的影响
Ti35Nb(0,2,4,6)Sn6Zr3Mo合金的强度、伸长率以及弹性模量如图4(a1)和4(a2)所示。由图4可知,随着Sn含量的增加,合金的强度和弹性模量升高而塑性下降。Sn原子的半径为1.55 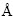 ,大于Ti的(1.47
,大于Ti的(1.47 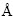 ),由图4(a3)可见,随着Sn元素的增加,β相的晶格畸变加剧,晶胞体积增大(这与HAO等[16]的研究结果是一致的),产生固溶强化效果。另外,Sn的晶粒细化作用亦使强度升高。
),由图4(a3)可见,随着Sn元素的增加,β相的晶格畸变加剧,晶胞体积增大(这与HAO等[16]的研究结果是一致的),产生固溶强化效果。另外,Sn的晶粒细化作用亦使强度升高。
β钛合金的弹性模量主要取决于结合键的本性和原子间距。原子间距越大或原子间结合力越弱,其弹性模量也就越低。由图4(a2)可见,随着Sn元素的增加,原子间距变大,但其弹性模量却随之升高,意味着添加Sn能增加合金的原子间结合力。郝传璞等[19]指出,合金元素Sn、Zr、Mo与Ti之间的混合焓分别为-21、0、-4 kJ/mol。混合焓越负,说明组元间的作用力越强,亦即Ti—Sn原子间结合力较强。徐东等[20]和彭森等[21]指出,Ti-Sn体系中合金的态密度显示了成键电子主要是由Ti元素的3p、3d轨道电子和Sn元素的5p轨道电子贡献,由于Ti—Sn键中p—p作用具有较强的方向性,且Ti—Sn键中的p—p成分比Ti—Ti键中的大,从而导致原子间交互作用增强。可能是由于Ti—Sn之间的原子结合力强于Ti—Ti的,抵消了添加Sn导致的晶胞体积增大对弹性模量的影响,使得合金的弹性模量随Sn含量的增加而升高。
2.2.2 Zr含量对合金力学性能的影响
Ti35Nb4Sn(2,4,6,8)Zr3Mo合金的强度、伸长率以及弹性模量如图4(b1)和4(b2)所示。由图4(b1)和(b2)可见,随着Zr含量的增加,合金的强度随之升高,而伸长率随之下降,弹性模量先下降后升高。Zr原子的半径为1.6 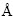 ,大于Ti的半径(1.47
,大于Ti的半径(1.47 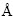 ),随着Zr元素的增加,β相的晶格畸变加剧,使晶胞体积逐渐变大(见图4(b3)),产生固溶强化。由于Zr的加入具有细化晶粒的作用,亦使合金强度升高。Zr与Ti同属于ⅣB族,能与Ti形成无限固溶体。Ti-Zr之间的混合焓为0,意味着添加Zr不会影响Ti—Zr原子间的作用力。但ABDEL- HADY等[22]采用第一性原理计算的Ti—Nb、Ti—Zr和Ti—Nb—Zr合金的原子结合能分别为4.80、4.80和4.97 eV,由此说明在Ti合金中同时添加Nb和Zr元素可以提高合金中原子间的结合能,从而增强原子间结合力。根据本实验结果可以推测,在Zr含量小于6%时,原子间距对弹性模量的影响占主导因素(图4(b3)亦显示Zr由2%增加到6%时晶胞体积增加幅度较大),所以Zr含量增加导致弹性模量下降。当Zr含量由6%增加至8%时,原子结合力增大占主导因素,使弹性模量上升。
),随着Zr元素的增加,β相的晶格畸变加剧,使晶胞体积逐渐变大(见图4(b3)),产生固溶强化。由于Zr的加入具有细化晶粒的作用,亦使合金强度升高。Zr与Ti同属于ⅣB族,能与Ti形成无限固溶体。Ti-Zr之间的混合焓为0,意味着添加Zr不会影响Ti—Zr原子间的作用力。但ABDEL- HADY等[22]采用第一性原理计算的Ti—Nb、Ti—Zr和Ti—Nb—Zr合金的原子结合能分别为4.80、4.80和4.97 eV,由此说明在Ti合金中同时添加Nb和Zr元素可以提高合金中原子间的结合能,从而增强原子间结合力。根据本实验结果可以推测,在Zr含量小于6%时,原子间距对弹性模量的影响占主导因素(图4(b3)亦显示Zr由2%增加到6%时晶胞体积增加幅度较大),所以Zr含量增加导致弹性模量下降。当Zr含量由6%增加至8%时,原子结合力增大占主导因素,使弹性模量上升。

图4 合金元素含量对合金力学性能和晶胞体积的影响
Fig. 4 Effects of alloying elements on mechanical properties and lattice volume of β phases
2.2.3 Mo含量对合金力学性能的影响
Ti35Nb4Sn6Zr(1,3,5,7)Mo合金的强度、伸长率以及弹性模量如图4(c1)和4(c2)所示。由图4(c1)和(c2)可知,随着Mo含量的增加,合金的强度和弹性模量升高而塑性下降,固溶强化是强度升高的关键因素。由于Mo的原子半径只有1.40 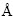 ,小于Ti的1.47
,小于Ti的1.47 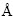 ,所以随着Mo含量的增加,β相的晶胞体积逐渐减小(见图4(c3))。原子间距的减小以及Ti—Mo原子之间强的相互作用(Mo与Ti之间的混合焓为-4 kJ/mol)导致弹性模量随Mo的增加而增大。YAO等[23]采用第一性原理赝势法计算了Ti1-xMox合金的晶胞常数和单个原子结合能,结果表明随着Mo含量的增加,晶胞常数减小,单个原子结合能的绝对值增大(原子结合力增强),从而进一步验证理论计算与实验值是相符合的。
,所以随着Mo含量的增加,β相的晶胞体积逐渐减小(见图4(c3))。原子间距的减小以及Ti—Mo原子之间强的相互作用(Mo与Ti之间的混合焓为-4 kJ/mol)导致弹性模量随Mo的增加而增大。YAO等[23]采用第一性原理赝势法计算了Ti1-xMox合金的晶胞常数和单个原子结合能,结果表明随着Mo含量的增加,晶胞常数减小,单个原子结合能的绝对值增大(原子结合力增强),从而进一步验证理论计算与实验值是相符合的。
本文作者所设计的10种合金的弹性模量在57~85 GPa之间,与利用Bo—Md相图所预测的弹性模量范围(60~70 GPa)基本吻合,其中Ti35Nb(0,2)-Sn6Zr3Mo两种合金的弹性模量仅分别为57和59 GPa。这两种合金除具有较高的Bo值与Md值外(见表1),其电子浓度也最接近4.24,且其Kβ为1.505。上述参数与低弹性模量钛合金的各项设计参数的经验值范围吻合较好。
在本实验中,以容许应变(屈服强度与弹性模量的比值)来衡量合金的综合力学性能(见图5),该值越高,说明合金的高强低弹性能越优异。从图5可知,在所设计的10种合金中具有最高容许应变的合金为Ti35Nb2Sn6Zr3Mo,其抗拉强度、屈服强度、弹性模量以及伸长率分别为664 MPa、641 MPa、59 GPa和12.5%,适合用作生物体植入材料。

图5 所设计合金的屈服强度与弹性模量的比值
Fig. 5 Ratio of yield strength to elastic modulus for designed alloys
3 结论
1) 根据相关钛合金设计理论所设计的Ti35Nb-Sn-Zr-Mo合金,800 ℃固溶处理后的组织均为单一β等轴晶;平均晶粒尺寸随着Sn与Zr含量的增加而减小,随着Mo含量的增加先减小后增大。
2) 随着Sn、Zr、Mo合金元素含量的增加,合金的强度随之升高,而伸长率随之下降;弹性模量随着Sn和Mo含量的增加而升高,随着Zr含量的增加先下降后升高。
3) 固溶处理后具有最高容许应变的合金为Ti35Nb2Sn6Zr3Mo,其抗拉强度、屈服强度、弹性模量以及伸长率分别为664 MPa、641 MPa、59 GPa和12.5%,适合用作生物体植入材料。
REFERENCES
[1] MITSUO N. Recent research and development in titanium alloys for biomedical applications and healthcare goods[J]. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials A, 2003, 243: 445-454.
[2] WANG K. The use of titanium for medical applications in the USA[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1996, 213: 134-137.
[3] VAN N R. Titanium: the implant of today[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1987, 22(11): 3801-3811.
[4] 浦素云. 金属植入材料及腐蚀 [M]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学出版社, 1990: 1-20.
PU Su-yun. Metal implant materials and corrosion[M]. Beijing: Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics Press, 1990: 1-20.
[5] KURDOA D, NIINOMI M, MORINAGA M, KATO Y, YASHIRO T. Design and mechanical properties of new type titanium alloys for implant materials[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1998, 243: 244-249.
[6] MOHAMED A H, HINOSHITA K, MORINAGA M. General approach to phase stability and elastic properties of β-type Ti-alloys using electronic parameters[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2006, 55: 477-480.
[7] LAHERUTE P, PRIMA F, EBERHARDT A. Mechanical properties of low modulus β titanium alloys designed from the electronic approach[J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2010(3): 565-573.
[8] 于振涛, 周 廉, 王克光. 生物医用β型钛合金的设计与开发[J]. 稀有金属快报, 2004, 23: 5-10.
YU Zhen-tao, ZHOU Lian, WANG Ke-guang. Design and development of biomedical β-Ti alloys[J]. Rare Metals Research, 2004, 23: 5-10.
[9] 张小明, 田 锋, 殷为宏. 橡胶金属的塑性变形行为[J]. 钛工业进展, 2005, 22(3): 5-7.
ZHANG Xiao-ming, TIAN Feng, YIN Wei-hong. Plastic deformation mechanism of multi-functional Ti alloy “gum metal”[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2005, 22(3): 5-7.
[10] BANERGEE R, NAG S, TECHSCHULTE J. Strengthening mechanisms in Ti-Nb-Zr-Ta and Ti-Mo-Zr-Fe orthopaedic alloys[J]. Biomaterials, 2004(25): 3413-3419.
[11] 赵 杰, 段洪涛, 李海涛. 低弹性模量Ti-27Nb-8Zr医用钛合金组织与力学性能[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2010(39): 1707-1710.
ZHAO Jie, DUAN Hong-tao, LI Hai-tao. Microstructure and mechanical properties of biomedical Ti-27Nb-8Zr alloy with low elastic modulus[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2010(39): 1707-1710.
[12] 顾桂月, 陈 锋, 余新泉. 热处理对Ti30Nb5Ta6Zr合金组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2010(4): 678-681.
GU Gui-yue, CHEN Feng, YU Xin-quan. Influence of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti30Nb5Ta6Zr alloy[J]. Rare Metals Materials and Engineering, 2010(4): 678-681.
[13] 楚 扬. 高强低弹近β型钛植入材料的组织和性能研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2011: 8.
CHU Yang. Research on the microstructure and properties of near β titanium alloy with low elastic modulus and high strength for human implant[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2011: 8.
[14] OKAZAKI Y. Effect of alloying elements on mechanical properties of titanium alloys for medical implants[J]. Materials Transcations, 1993, 12: 1217-1222.
[15] 莫 畏. 钛的金属学和热处理[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2009: 234.
MO Wei. Metallurgy and heat treatment of titanium[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2009: 234.
[16] HAO Y L, LI S J, SUN S Y. Effect of Zr and Sn on Young’s modulus and superelasticity of Ti-Nb based alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2006, 411: 112-118.
[17] TAKAHASHI E, SAKURAI T, WATANABE S. Effect of heat treatment and Sn content on superelasticity in biocompatible TiNbSn alloys[J]. Material Transcations, 2002, 43: 2978-2983.
[18] 章四琪, 黄劲松. 有色金属熔炼与铸锭[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2005: 129-147.
ZHANG Si-qi, HUANG Jin-song. Non-ferrous metal smelting and ingot[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2005: 129-147.
[19] 郝传璞, 王 清, 马仁涛, 王英敏, 羌建兵, 董 闯. 体心立方固溶体合金中的“团簇+连接原子”结构模型[J].物理学报, 2011, 60: 1161101.
HAO Chuang-pu, WANG Qing, MA Ren-tao, WANG Yin-min, QIANG Jian-bing, DONG Chuang. Cluster-plus-glue-atom model in bcc solid solution alloys[J]. Acta Phys Sin, 2011, 60: 1161101.
[20] 徐东生, 李 东, 胡壮麟. Ti3Sn和Ti3Sn-Nb的电子结构与力学行为[J]. 材料科学进展, 1993(7): 497-501.
XU Dong-sheng, LI Dong, HU Zhuang-lin. Electronic structure and mechanical behavior of Ti3Sn and Ti3Sn-Nb[J]. Material Science Progress, 1993(7): 497-501.
[21] 彭 森, 吴孟强, 王秀锋, 张树人. Ti-Sn体系合金稳定性及其电子结构的研究[J]. 材料导报, 2011, 24: 73-76.
PENG Sen, WU Meng-qiang, WANG Xiu-feng, ZHANG Shu-ren. Study of structure stabilities and electronic characteristics of Ti-Sn intermetallic compounds[J]. Material Science, 2011, 24: 73-76.
[22] MOHAMED A H, FUWA H, HINOSHITA K. Phase stability change with Zr content in β-type Ti-Nb alloys[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2007, 57: 1000-1003.
[23] YAO Qiang, SUN Jian, XING Hui. Influence of Nb and Mo contents on phase stability and elastic property of β-type Ti-X alloys[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2007, 17: 1417-1421.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:江苏省科技支撑计划资助项目(BE2011778);常州市科技支撑计划资助项目(CE20115036)
收稿日期:2012-09-14;修订日期:2013-03-20
通信作者:陈 锋,教授,博士;电话:13813811205;E-mail: fengchen@seu.edu.cn