DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2018.12.10
激光喷丸对镍铝青铜组织演变及腐蚀性能的影响
程光坤,胡树兵,曾思琪
(华中科技大学 材料成形与模具技术国家重点实验室,武汉 430074)
摘 要:采用激光喷丸强化技术在镍铝青铜合金(NAB)表面形成细晶层,采用 XRD、SEM、EBSD、TEM 等方法对其组织结构进行表征,并通过浸泡腐蚀试验研究激光喷丸处理对于NAB合金耐腐蚀性能的影响。结果表明:激光喷丸处理能够使得合金表层晶粒细化、小角度晶界比例增多以及位错增值。当激光光斑能量分别为3 J和6 J时,试样表面硬度相对于基体硬度分别提升31.5%和41.8%,合金表层硬度提升是由于晶粒细化、位错增值和残余压应力场的共同作用。除此之外,浸泡腐蚀结果表明激光喷丸处理能够改善合金的耐腐蚀性能,这是由晶粒细化导致的。
关键词:镍铝青铜;激光喷丸;组织;硬度;耐腐蚀性能
文章编号:1004-0609(2018)-12-2476-10 中图分类号:TG178 文献标志码:A
镍铝青铜具有良好的综合力学性能、耐磨性能以及耐腐蚀性能,所以被广泛用于船舶动力装置以及海水处理装置中[1-4]。在通常的铸造条件下,镍铝青铜组织包含富铜的α相、β相马氏体和多种不同形态的κ相;且不同的热处理工艺对其性能影响很大[5-8]。WU等[7]研究了不同热处理方式对镍铝青铜力学性能影响,结果表明,900°正火使得合金的抗拉强度和屈服强度提高,但其塑性降低。李振亚等[8]研究了时效温度对镍铝青铜合金硬质相演变的影响,结果表明,在420~450 ℃时效温度区间能够使合金具有良好的力学性能。但是,镍铝青铜在热处理过程中还通常伴随着很多缺陷,其中包括缩孔、疏松、成分偏析和应力集中[9-10]。因此,对镍铝青铜进行一系列的表面改性是十分必要的。
目前对镍铝青铜进行表面改性的方法主要包括制备激光熔凝、激光熔覆、电镀、火焰喷涂和摩擦搅拌焊接[11-13]。TANG等[13]在锰镍铝青铜表面进行激光熔凝,激光熔凝使得合金表面形成均匀的单相组织,从而使得其耐腐蚀性能提高。NI等[14-15]使用摩擦搅拌焊在镍铝青铜表面形成变形层,一方面,由于焊接过程中晶粒细化使得其硬度、强度、塑性和耐腐蚀性能得到提升;另一方面,由于表层晶粒中存在较大的应力应变,使得其电化学腐蚀性能下降。
激光喷丸(Laser peening,LP)作为一种新型的表面强化处理技术[16],其特点是在试样表面形成较深的残余压应力层,从而提高其性能,该技术已广泛应用于钛合金[17]、铝合金[16, 18]以及镁合金[19]等金属材料。然而,激光喷丸用于强化镍铝青铜的报道较少。因此,研究激光喷丸对于镍铝青铜组织演变和腐蚀性能变化规律是十分必要的。本文作者以镍铝青铜为实验材料,研究了激光喷丸对于镍铝青铜的强化机理以及对其腐蚀性能的影响。
1 实验
1.1 实验材料
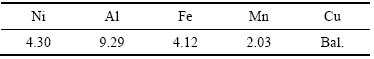
试验材料为铸态镍铝青铜,其型号为ZCuAl9Fe4Ni4Mn2,其具体成分见表1。在激光喷丸处理前,板材通过线切割加工成10 mm×10 mm×2 mm的大小,用不同型号的SiC砂纸打磨试样表面并进行抛光,然后用丙酮进行超声清洗,最后放入干燥箱待用。
表1 铸态镍铝青铜合金的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of as cast NAB alloy (mass fraction, %)
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 激光喷丸
本试验中采用西安天瑞达有限公司所生产的YD60-M165型激光冲击强化设备(见图1(a))。试验采用的激光脉冲波长为1064 nm,光斑直径3 mm,激光脉冲能量分别为3 J和6 J,光斑搭接率50%,激光喷丸路径如图1(b)所示。
1.2.2 物相分析和显微硬度测量
通过荷兰帕纳科公司生产的X'Pert PRO X型X射线衍射仪进行分析激光喷丸前后的物相,测试用靶材为Cu Kα,管电流为40 mA,管电压为40 kV。分别采用以下两种扫描方式:1) 扫描范围为20°~90°,扫描速度为10 (°)/min;2) 扫描范围42°~43.5°,扫描速度为1 (°)/min,并计算出试样表面的晶粒尺寸以及显微畸变。激光喷丸后试样的表面以及横截面的显微硬度测试采用DHV-1000型硬度计进行测量,加载力选用0.98 N,保荷时间为15 s。
1.2.3 残余应力和显微硬度测量
采用X射线应力衍射仪测定机械喷丸试样表面的残余应力,采用电压为25 kV,电流2.0 mA,扫描角度2θ范围为138°~148°。此外,采用剥层法喷丸试样的应力随层深的分布情况,采用的腐蚀液为磷酸酒精溶液。激光喷丸后试样的表面以及横截面的显微硬度测试采用DHV-1000型硬度计进行测量,加载力选用0.98 N,保荷时间为15 s。
1.2.4 显微结构表征
激光喷丸处理前后的试样经过不同型号的砂纸打磨、抛光后,采用3 g FeCl3+2mL HCl+96 mL酒精溶液对其进行腐蚀,通过 Quanta 200型扫描电子显微镜观察喷丸前后的显微组织。激光喷丸试样在进行EBSD测试前,应首先对其进行打磨、抛光,采用10%(体积分数)磷酸酒精溶液进行电解,并在扫描电子显微镜下进行观察、利用电子背散射衍射技术(EBSD)测定激光喷丸处理后样品的晶粒取向信息以及晶界角度分布。通过Tecnai G230 型透射电子显微镜观察喷丸前后表层的位错分布。
1.2.5 浸泡腐蚀
激光喷丸前后试样浸泡在3.5% NaCl(质量分数)溶液中,浸泡时间达到240 h,后采用Quanta200型扫描电子显微镜观察表面形貌以及截面形貌,并通过Bruker型能谱仪 (EDS) 对腐蚀产物进行成分分析。采用500 mL HCl (ρ=1.19 g/mL)+1000 mL去离子水的混合液去除表面的腐蚀产物,随后采用电子天平称重后计算激光喷丸处理前后试样的均匀质量损失量(mL)和质量损失率(mLR),计算公式分别为式(1)和式(2)所示:
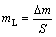 (1)
(1)
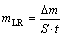 (2)
(2)
式中:mL为均匀质量损失量,g/mm2;mLR为均匀质量损失率,g/(mm2·h);Δm为质量损失,g;S为浸泡在腐蚀液中的样品面积,mm2;t为浸泡时间,h。
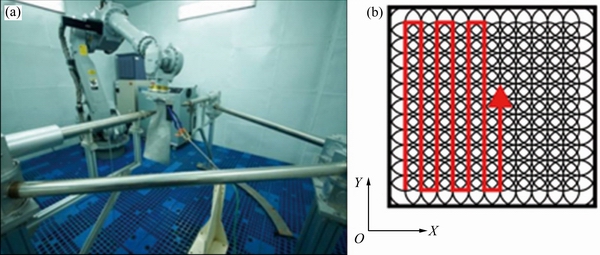
图1 激光喷丸设备照片和激光喷丸路径
Fig. 1 Laser shot peening equipment photo(a) and laser shot peening path (b)
2 结果与分析
2.1 XRD物相分析
图2所示为激光喷丸前后试样表面X射线衍射图谱。由图2(a)可见,激光喷丸处理后没有新相的产生,处理前后物相均有α-Cu和κ-(Al-Fe-Ni)两相组成。通过对比图2(b)中激光喷丸前后衍射峰的分布可以发现,处理后Bragg衍射峰变宽。通常认为,Bragg衍射峰宽化是由于晶粒细化和显微应变的共同作用[20]。通过Scherrer-Wilson[21]公式和Williamson Hall[22]公式分别计算出喷丸前后的晶粒尺寸和表面的显微应变,如式(3)和式(4)所示:
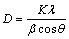 (3)
(3)
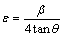 (4)
(4)
式中:D是平均晶粒尺寸;K是Scherrer常数,通常被认为0.89;λ是X射线波长;θ 是Bragg 角度;β是衍射峰半高宽; ε为显微应变。喷丸前后试样表面的晶粒尺寸以及显微应变如图3所示。由图3可以看出: 激光喷丸处理后,试样表面晶粒尺寸相对于未处理试样的晶粒尺寸明显降低,显微应变明显提升。当光斑能量为6J时,晶粒细化和显微畸变相比光斑能量为3J时更为显著。在激光喷丸过程中,激光轰击试样表面,能量部分被试样表面吸收,试样表面应变增大并发生塑性变形。因此,试样表层显微应变加剧且晶粒细化。而光斑能量加大,使得表层的变形更为严重,使得晶粒细化和显微应变的变化更为显著。
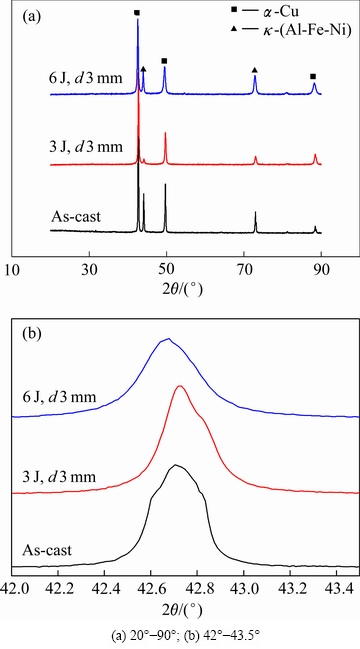
图2 激光喷丸前后试样表面XRD谱
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of NAB alloys before and after laser peening
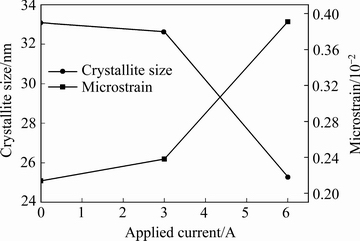
图3 试样表面平均晶粒尺寸以及显微应变随喷丸脉冲能量的变化
Fig. 3 Variation of average crystallite size and mean microstrain with treatment energy of laser peening in NAB alloy
2.2 显微结构表征
2.2.1 显微组织
图4所示为激光喷丸处理前后截面的显微组织。由图4可见,激光喷丸处理前组织为典型的铸态组织形貌,如图4(a) 所示,主要为其主要包含α相和κ相。其中α相是Al溶于Cu9Al4基体中的固溶体,为面心立方结构,其塑性较好;κ相根据其成分,形态以及分布可以分为4种:其中κⅡ相是富铁相,呈球状或者玫瑰花状,分布于α相与β相的晶界处;κⅢ则为富镍相的金属间化合物,为成片状分布于晶界处;κⅣ则是从α相内部析出细小的颗粒状。铸态组织粗大,晶粒取向随机分布。激光喷丸处理后试样组织形貌如图 4(b)所示。由图4(b)可以发现,经过激光喷丸处理后,试样表层发生严重的塑性变形,形成了流线组织并由表及里逐渐减弱。这可能是由于在喷丸过程中,表面持续受到高速运动弹丸的轰击,导致表面显微畸变不断累积,从而导致塑性变形,形成流线型组织。
2.2.2 EBSD分析
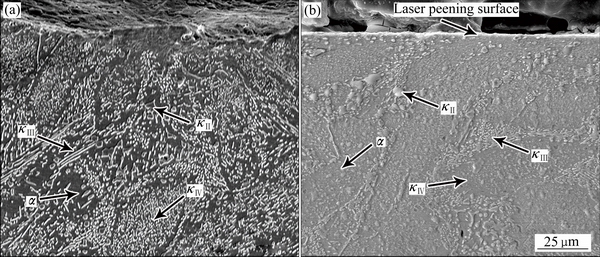
图4 激光喷丸前后试样截面的显微组织
Fig. 4 Cross-sectional SEM images of cast(a) and laser peened(b) NAB alloys
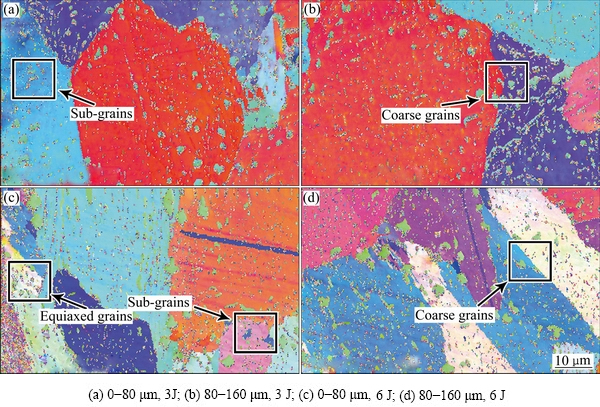
图5 激光喷丸后试样截面不同区域EBSD取向图
Fig. 5 EBSD orientation image maps in different regions for laser peened alloy
通过组织形貌可以发现,表层区域已经发生大量的塑性变形,但是其变形层由于存在较大的应力应变使得其的具体微观结构不清晰,因此采用EBSD技术对不同激光能量所处理后的试样截面进行图谱采集,从而分析其组织结构转变机理。图5所示为激光喷丸处理后试样截面的EBSD取向图,其中不同颜色代表不同的取向。从图5可知,当激光脉冲能量为3 J时,最表层粗大晶粒内部颜色不一,表示粗大的晶粒内部晶粒取向存在差异,这种差异是由于晶粒内部形成亚晶所导致的,亚晶区域的层深约为80 μm,内部则为原始粗大的晶粒(尺寸为30~50 μm);而当激光脉冲能量增大到6 J,最表层为细小的等轴晶(尺寸为2~5 μm),次表层形成亚晶,亚晶层深度达到距表面120 μm,内部为原始粗大的晶粒。CHEN等[23]在研究喷丸对于Ti-6Al-4V 合金中也发现喷丸处理能够细化晶粒,粗大的晶粒转变为亚晶和等轴晶,认为这是由喷丸过程中应变的累积所造成的,表层应变不断加大使得位错发生滑移,原始粗大的晶粒破裂从而细化晶粒。
在晶粒细化的过程中,其晶界的取向也会随着改变。图6(a)和图6(b)分别为3 J和6 J激光脉冲能量下激光喷丸处理后试样截面晶界角度分布,从图6可以发现,激光喷丸处理后,试样表层区域小角度晶界相对于内部较多,而大角度晶界则较少。喷丸处理时,表层粗大的晶粒破裂,形成亚晶或者等轴晶,这会使得大角度晶界向小角度晶界的转变。图7所示为激光喷丸处理后小角度晶界比例随深度的变化,由图7可以发现,激光喷丸处理后,小角度晶界的比例由表及里逐渐减弱,激光脉冲能量为6 J时,同区域小角度晶界的比例更大。小角度晶界的多少和其受变形的程度相关,当激光喷丸能量为3 J时,试样表面持续遭受弹丸的撞击,表层显微畸变不断累积使得原始粗大的晶粒破裂,形成亚晶,同时使得表层小角度晶界增多;而当激光喷丸能量增大至6 J,表层畸变进一步加深,从而使得小角度晶界的进一步增多。
2.2.3 TEM分析
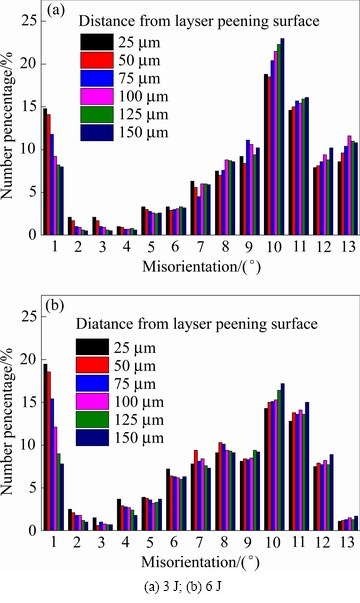
图6 不同激光脉冲能量喷丸处理后试样截面小角度晶界分布
Fig. 6 Misorientation angle distributions in different regions of laser peened NAB alloy with different treatment energies
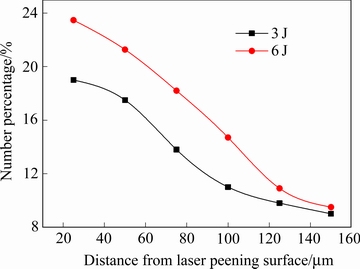
图7 激光喷丸处理后NAB合金小角度晶界比例随深度变化曲线
Fig. 7 Percentage low-angle boundaries of laser peened NAB alloy
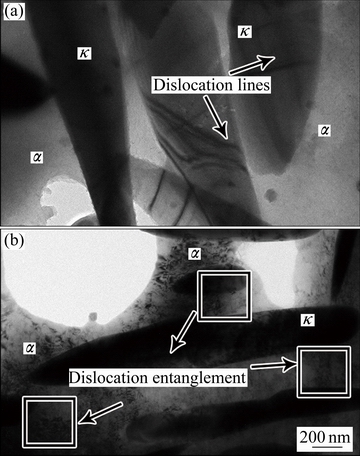
图8 激光喷丸处理前后后NAB合金表层区域的TEM像
Fig. 8 TEM images of NAB alloy before (a) and after (b) laser peening
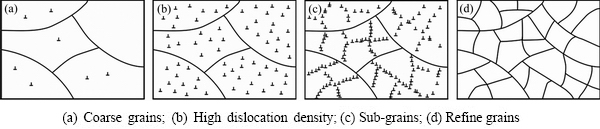
图9 激光喷丸过程中组织演变原理图
Fig. 9 Schematic diagrams of microstructures evolution during laser peening
由TEM暗场像(见8(a))可以看出,铸态基体中存在少量的位错,位错线随机分布,没有观察到位错缠结。少量位错的存在可能是由热处理过程中不均匀冷却导致的。激光喷丸处理后,图8(b)中所示位错密度显著提升,并且发生位错缠结,进一步证实了EBSD的结果。基于EBSD和TEM中的结果,得出镍铝青铜在激光喷丸过程中组织转变原理图如图9所示。 激光喷丸处理前,基体中晶粒粗大,位错较少且随机分布(见图9(a));在激光喷丸过程中,高速运动的弹丸撞击试样表面,使得表面应变不断提高。当应变累积到一定程度,滑移系被激活,同时使得位错密度不断增加(见图9(b));其次,随着应变的进一步增大,高密度位错移动发生缠结,形成亚晶界(见图9(c));最后,应变进一步增大,发生再结晶转变为细小等轴晶(见图9(d))。
2.3 残余应力和显微硬度分布
激光喷丸前后NAB合金的残余应力随层深的分布如图10所示。结果表面,喷丸处理前,试样表面的残余应力约为52 MPa。激光喷丸处理在表面均能够引入残余压应力,随距表面深度的增大,残余压应力的变化趋势为先增大后减小,最后转变为残余拉应力。激光喷丸处理时,当脉冲能量从3 J增至6 J时,喷丸表面残余应力变化不明显,但最大残余应力由-180.7 MPa增大到-210 MPa,增幅达到16.2%;但其残余压应力层深由280 μm增大到520 μm。
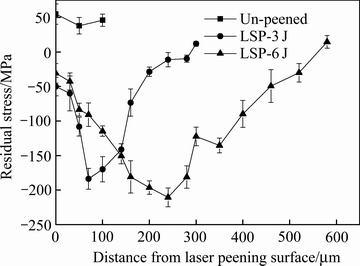
图10 喷丸前后镍铝青铜合金残余应力随深度分布
Fig. 10 Residual stresses distribution of NAB alloy with and without shot peening along depth from top surface
在喷丸过程中,弹丸以一定速度轰击加工表面,使得试样表层形成弹性变形区和塑性变形区,同时,在表层引入残余压应力和显微畸变。激光喷丸过程中,随着能量的增大,试样表面被打击的力度增大,使得表层形变程度加深,因此,LSP-6J试样相对于LSP-3J试样的激光脉冲能量处理后试样具有更大的残余压应力和更深的残余压应力层。
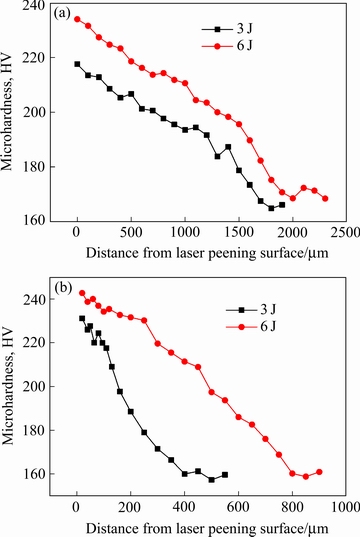
图11 激光喷丸处理后试样表面硬度和截面硬度分布
Fig. 11 Surface microhardness(a) and cross-section microhardness distribution(b) of NAB alloy after laser peening
图11(a)所示为激光喷丸后试样的表面硬度分布。从图11(a)可以看出,激光喷丸后表面硬度相对有较大的提升,距离光斑中心越近,提升效果越明显。当激光脉冲能量为3 J,光斑中心硬度可达到217 HV,相对于基体硬度(约为165 HV)提升了31.5%;激光脉冲能量为6 J时,光斑中心硬度为234 HV,相对于基体提高了41.8%。图11(b)所示为激光喷丸处理后截面硬度分布,可以看出,激光喷丸可以形成一定深度的硬化层,硬度提升效果由表及里逐步降低。当脉冲能量为3 J,影响层深约为400 μm;脉冲能量增大至6 J,影响层深增大至750 μm。
激光喷丸使得试样表层硬度提升可能归功于晶粒细化和位错强化的共同作用。根据WANG等[24]的研究,材料的硬度和实际晶粒尺寸之间存在如下关系
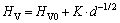 (5)
(5)
式中:HV为材料硬度;HV0为与晶粒大小不相关的材料硬度;K为常数;d为晶粒尺寸大小。从式(5)可以看出,材料硬度和晶粒尺寸是负相关的,晶粒尺寸越小,材料的硬度增大。除此之外,根据XU等[25]的研究,材料硬度和位错密度之间也存在相互作用关系,其公式如下:
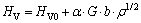 (6)
(6)
式中:HV为材料硬度;HV0为与晶粒大小不相关的材料硬度;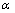 ,G,b均为和材料相关的常数;
,G,b均为和材料相关的常数;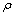 为位错密度。从式(6)可以看出,位错密度越高,材料的硬度越大。激光喷丸强化使得表层位错密度显著增大,位错缠结,原始大晶粒内部出现较多的亚晶。当光斑能量为6 J时,表层出现等轴晶,晶粒大小约为2~5 μm,相对于基体粗大的晶粒细化明显。晶粒细化和位错增多使得硬度提升,此外,喷丸后合金表层残余压应力的存在能够抵消部分显微硬度测量时压头施加给合金表面的压力,从而提高材料的抗塑性变形能力,测量时压痕变小最终提高表面硬度。光斑能量越大,晶粒细化和位错增多更为明显,且残余压应力的层深加大,因此表层硬度更大,硬化层深更高。
为位错密度。从式(6)可以看出,位错密度越高,材料的硬度越大。激光喷丸强化使得表层位错密度显著增大,位错缠结,原始大晶粒内部出现较多的亚晶。当光斑能量为6 J时,表层出现等轴晶,晶粒大小约为2~5 μm,相对于基体粗大的晶粒细化明显。晶粒细化和位错增多使得硬度提升,此外,喷丸后合金表层残余压应力的存在能够抵消部分显微硬度测量时压头施加给合金表面的压力,从而提高材料的抗塑性变形能力,测量时压痕变小最终提高表面硬度。光斑能量越大,晶粒细化和位错增多更为明显,且残余压应力的层深加大,因此表层硬度更大,硬化层深更高。
2.4 浸泡腐蚀实验
图12所示为试样在3.5% NaCl(质量分数)溶液中浸泡过程中的质量损失量和损失率随时间的关系曲线。从图12可以发现以下3个规律:1) 喷丸处理前后试样质量损失量均随着浸泡时间增加而增大;2) 喷丸处理前后试样质量损失率均随着浸泡时间增大而减小;3) 激光喷丸处理后合金质量损失量和质量损失率均小于未处理试样,说明激光喷丸处理能够改善合金的耐腐蚀性能。
为了进一步了解激光喷丸对于NAB合金浸泡腐蚀性能的影响机制,通过扫描电镜对浸泡后试样的截面形貌和表面形貌进行了观察。图13所示为未喷丸试样在3.5% NaCl溶液中浸泡240 h后的截面形貌,如图13(a)所示,未喷丸试样浸泡240 h后腐蚀深度达到6.7 μm,其中α+κⅢ 相所组成的共析区域腐蚀最为严重,为典型的选相腐蚀现象;激光喷丸后腐蚀层厚度明显减小,仅为2.8 μm,如图13(b)所示。这说明激光喷丸处理能够一定程度地改善合金的耐腐蚀性能,这结果和质量损失曲线所反映的结果是一致的。
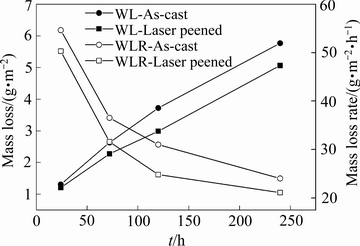
图12 激光喷丸前后试样浸泡过程中质量损失与质量损失率
Fig. 12 Mass loss and mass loss rates of cast and laser peened samples
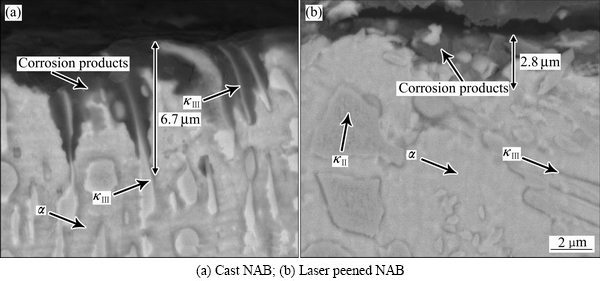
图13 激光喷丸前后样品在3.5%氯化钠溶液中浸泡240 h后的高倍背散射电子像
Fig. 13 High magnified backscattered electron images of cross sectional of samples after exposure to 3.5% NaCl solution for 240 h

图14 激光喷丸前后样品在3.5%氯化钠溶液中浸泡不同时间后的表面形貌
Fig. 14 SEM images of surface of samples after exposure to 3.5% NaCl solution for different time
图14所示为试样浸泡在3.5% NaCl溶液中不同时间的表面形貌。对于未喷丸试样,当浸泡24 h后,如图14(a)所示,表面已经遭受较为严重的腐蚀,腐蚀产物分布不均匀,试样表面局部区域出现了尺寸大小为5~10 μm的腐蚀坑;而对于激光喷丸处理后的试样浸泡24 h后(见图14(b)),表层已经被致密的腐蚀产物所覆盖,腐蚀表面较为均匀,通过EDS能谱分析表面主要为Cu的氧化物。浸泡240 h后,基体表面大多数腐蚀产物已经脱落,稀疏分布的腐蚀产物余留在合金表面(见图14(c)),通过能谱分析证实表面为Cu和Al的氧化物。除此之外,α+κⅢ 共析区域中的富铜的α相被溶解,从而形成孔洞;而激光喷丸试样浸泡240 h,表层Cu的氧化物不再致密,部分Cu的氧化物已经脱落(见图14(d)),但内部Al的氧化物仍未脱落,致密Al的氧化物存在能够缓解合金进一步腐蚀,从而改善合金的耐腐蚀性能。
镍铝青铜合金优良的耐腐蚀性能是由于其在腐蚀过程中所形成的保护性的腐蚀层,这种腐蚀层主要包括外层的Cu2O和内层的Al2O3[15]。但是由于铸态NAB合金微观组织较为复杂以及各相的成分不均,容易发生选相腐蚀。特别是由α+κⅢ 相所组成的共析区域,α与κⅢ成层片状紧密排布,其中富铜的α相电势较高,而富Al的κⅢ 相电势较低,两者之间形成电势差为选相腐蚀提供驱动力,使得此区域最容易遭受选相腐蚀。这就使得NAB合金在3.5% NaCl溶液中浸泡240 h后共析区域的富铜α相被溶解从而形成孔洞,如图14(c)所示。
激光喷丸处理后,通过EBSD结果表面表层晶粒细化,从而减弱了NAB合金选相腐蚀倾向;且在腐蚀过程中腐蚀层更为均匀,更为致密的腐蚀产物缓解了合金的进一步腐蚀,从而使得浸泡过程中的质量损失量以及质量损失率低于铸态NAB合金。
3 结论
1) 镍铝青铜合金在激光喷丸过程中没有产生新相,但其原始大晶粒显著细化,当激光脉冲能量为3 J时,表层形成亚晶;而激光脉冲能量增大至6 J时,表层出现细小的晶粒,尺寸为2~5 μm。除此之外,NAB合金在激光喷丸过程中表层应变增大,小角度晶界增多,位错密度显著提高,且脉冲能量越大,提高效果更为明显。
2) 激光喷丸处理能够显著提高镍铝青铜合金的表面硬度,并形成一定深度的硬化层,当脉冲能量为3 J,影响层深约为400 μm;脉冲能量增大至6 J,影响层深增大至750 μm。这主要是晶粒细化、位错增值和残余压应力场的共同作用所导致的。
3) 激光喷丸处理能够改善镍铝青铜合金在3.5% NaCl溶液耐腐蚀性能,浸泡时间为240 h时,激光喷丸强化后试样的腐蚀层深度仅为2.8 μm,远低于铸态镍铝青铜腐蚀层深度(6.7 μm)。这是由于激光喷丸处理后晶粒细化,使得表面的腐蚀产物分布更为均匀,缓解了铸态镍铝青铜选相腐蚀倾向。
REFERENCES
[1] CULPAN E A, ROSE G. Microstructural characterization of cast nickel aluminium bronze[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1978, 13(8): 1647-1657.
[2] CULPAN E A, ROSE G. Corrosion behaviour of cast nickel aluminium bronze in sea water[J]. British Corrosion Journal, 1979, 14(3): 160-166.
[3] LORIMER G W, HASAN F, IQBAL J, RIDLEY N. Observation of microstructure and corrosion behaviour of some aluminium bronzes[J]. British Corrosion Journal, 1986, 21(4): 244-248.
[4] 孙飞龙, 李晓刚, 卢 琳, 万红霞, 杜翠薇, 刘智勇. 铜合金在中国南海深海环境下的腐蚀行为研究[J]. 金属学报, 2013, 49(10): 1211-1218.
SUN Fei-long, LI Xiao-gang, LU Li, WAN Hong-xia, LIU Zhi-yong. Corrosion behavior of copper alloys in deep ocean environment of South China Sea[J]. Acta Metall Sin, 2013, 49(10): 1211-1218.
[5] JAHANAFROOZ A, HASAN F, LORIMER G W, RIDLEY N. Microstructural development in complex nickel-aluminum bronzes[J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1983, 14(10): 1951-1956.
[6] FULLER M D, SWAMINATHAN S, ZHILYAEV A P, MCNELLEY T R. Microstructural transformations and mechanical properties of cast NiAl bronze: Effects of fusion welding and friction stir processing[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 463(1): 128-137.
[7] WU Z, CHENG Y F, LIU L, Lü W J, HU W B. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure evolution and erosion-corrosion behavior of a nickel-aluminum bronze alloy in chloride solution[J]. Corrosion Science, 2015, 98: 260-270.
[8] 李振亚, 杨丽景, 许 赪, 冒守栋, 宋振纶. 时效温度对镍铝青铜合金的硬质相演变的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(4): 766-772.
LI Zhen-ya, YANG Li-jing, XU Cheng, SONG Zhen-lun. Effect of aging temperature on hard phase evolution of nickel aluminum bronze[J]. Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2016, 26(4): 766-772.
[9] FONLUPT S, BAYLE B, DELAFOSSE D, HEUZE J L. Role of second phases in the stress corrosion cracking of a nickel-aluminium bronze in saline water[J]. Corrosion Science, 2005, 47(11): 2792-2806.
[10] AL-HASHEM A, RIAD W. The role of microstructure of nickel-aluminium-bronze alloy on its cavitation corrosion behavior in natural seawater[J]. Materials Characterization, 2002, 48(1): 37-41.
[11] HANKE S, FISCHER A, BEYER M, SANTOS J D. Cavitation erosion of NiAl-bronze layers generated by friction surfacing[J]. Wear, 2011, 273(1): 32-37.
[12] LUO Q, WU Z, QIN Z, LIU L, HU W B. Surface modification of nickel-aluminum bronze alloy with gradient Ni-Cu solid solution coating via thermal diffusion[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2017, 309: 106-113.
[13] TANG C H, CHENG F T, MAN H C. Effect of laser surface melting on the corrosion and cavitation erosion behaviors of a manganese-nickel-aluminium bronze[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 373(1): 195-203.
[14] NI D R, XUE P, WANG D, XIAO B L, MA Z Y. Inhomogeneous microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir processed NiAl bronze[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 524(1): 119-128.
[15] NI D R, XIAO B L, MA Z Y, QIAO Y X, ZHENG Y G. Corrosion properties of friction-stir processed cast NiAl bronze[J]. Corrosion Science, 2010, 52(5): 1610-1617.
[16] 罗新民, 王 翔, 陈康敏, 鲁金忠, 王 兰, 张永康. 激光冲击诱导的航空铝合金表层高熵结构及其抗蚀性[J]. 金属学报, 2015, 51(1): 57-66.
LUO Xin-ming, WANG Xiang, CHEN Kang-min, LU Jin-zhong, WANG Lan, ZHANG Yong-kang. Surface layer high-entropy structure and anti-corrosion performance of aero-aluminum alloy induced by laser shock processing[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2015, 51(1): 57-66.
[17] 罗新民, 赵广志, 张永康, 陈康敏, 罗开玉, 任旭东. Ti-6Al-4V激光冲击强化及其微结构响应分析[J]. 金属学报, 2012, 48(9): 1116-1122.
LUO Xin-ming, ZHAO Guang-zhi, ZHANG Yong-kang, CHEN Kang-min, LUO Kai-yu, REN Xu-dong. Laser shock processing of Ti-6Al-4V and analysis of its microstructure response[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2012, 48(9): 1116-1122.
[18] 罗新民, 陈康敏, 张静文, 鲁金忠, 任旭东, 罗开玉, 张永康. 纯Al和铝合金激光冲击表面改性的位错机制[J]. 金属学报, 2013, 49(6): 667-674.
LUO Xin-ming, CHEN Kang-min, ZHANG Wen-jing, LU Jin-zhong, REN Xu-dong, LUO Kai-yu, ZHANG Yong-kang. Dislocation mechanism of surface modification for commercial purity aluminum and aluminum alloy by laser shock processing[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2013, 49(6): 667-674.
[19] CARALAPATTI V K, NARAYANSWAMY S. Effect of high repetition laser shock peening on biocompatibility and corrosion resistance of magnesium[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2017, 88: 75-84.
[20] 刘莉莉, 揭晓华, 于 能, 麦永津. 45钢表面增压喷丸纳米化及其耐磨性研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2009, 38(14): 124-126.
LIU Li-li, JIE Xiao-hua, YU Neng, MAI Yong-jin. Study on surface nano-crystallization by adding pressure shot peening and its effect on wear resistance[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2009, 38(14): 124-126.
[21] GREGORY N W. Elements of X-ray diffraction[M]. Addison- Wesley Publishing Company Inc, 1956: 66.
[22] WILLIAMSON G K, HALL W H. X-ray line broadening from filed aluminum and wolfram[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1953, 1(1): 22-31.
[23] CHEN Guo-qing, JIAO Yan, TIAN Tan-yong, ZHANG Xin-hua, LI Zhi-qiang, ZHOU Wen-long. Effect of wet shot peening on Ti-6Al-4V alloy treated by ceramic beads[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(3): 690-696.
[24] WANG J T, ZHANG Y K, CHEN J F, ZHOU J Y, GE M Z, LU Y L, LI X L . Effects of laser shock peening on stress corrosion behavior of 7075 aluminum alloy laser welded joints[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2015, 647: 7-14.
[25] XU C, SHENG G M, WANG H D, JIAO Y J, YUAN X J. Effect of high energy shot peening on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg/Ti joints[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 695: 1383-1391.
Effect of laser peening on surface characterization and corrosion resistance of nickel aluminium bronze
CHENG Guang-kun, HU Shu-bing, ZENG Si-qi
(State Key Laboratory of Material Processing and Die and Mould Technology, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China)
Abstract: A fine grained layer formed on the surface of nickel-aluminum-bronze alloy (NAB) by laser peening. The microstructure was characterized by X-ray diffractometry (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The effect of laser shot peening on the corrosion resistance of NAB alloy was studied by immersion corrosion test. The results show that the laser peening results in the formation of equiaxed fine grains, and increases the low-angle boundaries and dislocation densities in the surface layer. When the laser spot energy is 3 J or 6 J, the surface hardness of the sample is 31.5% or 41.8% higher than that of the substrate, respectively. The increase in the hardness of the alloy surface is due to the combined effect of grain refinement, dislocation increment and residual compressive stress. Besides, the static immersion corrosion test indicates that laser shot peening can improve the corrosion resistance of NAB alloy, which may attributed to the grain refinement.
Key words: nickel aluminum bronze; laser peening; microstructure; hardness; corrosion resistance
Foundation item: Project(2014CB046704) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China
Received date: 2018-01-19; Accepted date: 2018-07-20
Corresponding author: HU Shu-bing; Tel: +86-13995667466; E-mail: hushubing@163.com
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(2014CB046704)
收稿日期:2018-01-19;修订日期:2018-07-20
通信作者:胡树兵,教授,博士;电话:13995667466;E-mail:hushubing@163.com