挤压铸造和重力铸造T4态Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金的低周疲劳行为
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2015年第11期
论文作者:郑成坤 张卫文 张大童 李元元
文章页码:3505 - 3514
关键词:Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金;挤压铸造;重力铸造;显微组织;力学性能;低周疲劳
Key words:Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy; squeeze casting; gravity die casting; microstructure; mechanical properties; low cycle fatigue
摘 要:研究重力铸造和挤压铸造制备的Al-7.0Zn-2.5Mg-2.1Cu合金(T4态)的显微组织、力学性能和低周疲劳行为。结果表明:挤压铸造制备的合金铸造缺陷较少,二次枝晶间距较小,其静态力学性能明显优于重力铸造制备合金的;挤压铸造制备的合金具有优异的疲劳性能。在较低总应变幅下(小于0.4%),两种方法制备的合金均呈循环稳定特征;在较高总应变幅下均呈循环硬化特征,且挤压铸造制备的合金循环硬化程度高于重力铸造制备合金的。在重力铸造条件下,疲劳裂纹主要起源于缩松、缩孔处,并且易于沿着这些铸造缺陷扩展;在挤压铸造条件下,裂纹起源于表面和靠近表面处的滑移带、共晶相以及夹杂。
Abstract: Gravity die casting (GC) and squeeze casting (SC) T4-treated Al-7.0Zn-2.5Mg-2.1Cu alloys were employed to investigate the microstructures, mechanical properties and low cycle fatigue (LCF) behavior. The results show that mechanical properties of SC specimens are significantly better than those of GC specimens due to less cast defects and smaller secondary dendrite arm spacing (SDAS). Excellent fatigue properties are obtained for the SC alloy compared with the GC alloy. GC and SC alloys both exhibit cyclic stabilization at low total strain amplitudes (less than 0.4%) and cyclic hardening at higher total strain amplitudes. The degree of cyclic hardening of SC samples is greater than that of GC samples. Fatigue cracks of GC samples dominantly initiate from shrinkage porosities and are easy to propagate along them, while the crack initiation sites for SC samples are slip bands, eutectic phases and inclusions at or near the free surface.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25(2015) 3505-3514
Cheng-kun ZHENG, Wei-wen ZHANG, Da-tong ZHANG, Yuan-yuan LI
School of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China
Received 29 December 2014; accepted 22 April 2015
Abstract: Gravity die casting (GC) and squeeze casting (SC) T4-treated Al-7.0Zn-2.5Mg-2.1Cu alloys were employed to investigate the microstructures, mechanical properties and low cycle fatigue (LCF) behavior. The results show that mechanical properties of SC specimens are significantly better than those of GC specimens due to less cast defects and smaller secondary dendrite arm spacing (SDAS). Excellent fatigue properties are obtained for the SC alloy compared with the GC alloy. GC and SC alloys both exhibit cyclic stabilization at low total strain amplitudes (less than 0.4%) and cyclic hardening at higher total strain amplitudes. The degree of cyclic hardening of SC samples is greater than that of GC samples. Fatigue cracks of GC samples dominantly initiate from shrinkage porosities and are easy to propagate along them, while the crack initiation sites for SC samples are slip bands, eutectic phases and inclusions at or near the free surface.
Key words: Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy; squeeze casting; gravity die casting; microstructure; mechanical properties; low cycle fatigue
1 Introduction
The Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy is a kind of the high- strength and light-mass structural materials, which is now being widely used in aviation and aerospace fields [1-3]. It is well known that 7000 series alloys are developed mainly as wrought alloys and are unsuitable for conventionally produced castings [4]. To improve the mechanical properties of cast 7000 series aluminum alloys, attempts have been made to produce aluminum alloy components by various methods. The process of squeeze casting (SC) is one kind of such methods, which allows the production of gas and shrinkage free castings [4-6]. WILLIAMS and FISHER [7] demonstrated that the tensile properties of squeeze cast 7075 alloys in the T6 and T73 temper conditions fell between the typical transverse and longitudinal values of the forged alloys. CHADWICK and YUE [4,8] reported that the mechanical properties of squeeze cast 7010 alloy were comparable to those found in the wrought form of the alloys.
Fatigue failure in metals accounts for 90% of all in-service failure due to mechanical causes [9]. Nowadays, most of the researches on fatigue behavior of cast aluminum alloys are concentrated on Al-Si series alloys, especially A356 alloys [10-16]. Only a few articles about the fatigue properties of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys have been reported. JIAN et al [17] investigated the fatigue fracture of wrought Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys (T7451) and demonstrated that the fatigue damage preferably incubated at the fractured inclusion particles at or near the specimens’ free surfaces. YUE [18] studied the fatigue behavior of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys (7010-T6) in the form of squeeze and chill castings and rolled plate, and reported that the fatigue strength of squeeze cast material was found to lie between those of the gravity cast and plate material. However, the fatigue properties of squeeze cast Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy in T4 heat-treated condition have never been reported. In this paper, Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys were prepared by squeeze casting and gravity die casting. In order to obtain better comprehensive mechanical properties, especially the elongation, T4 heat treatment was adopted. Various test techniques were used to examine the microstructures, mechanical properties and low cycle fatigue behavior of the alloys.
2 Experimental
Highly pure Al (99.95%), pure Zn, pure Mg and Al-50Cu master alloy were used to prepare the experimental alloys and the chemical compositions analyzed by an optical emission spectrometer are shown in Table 1. The raw materials were melted at 1053 K in a graphite crucible using an electric resistance furnace. About 10 kg melt was degassed to minimize the hydrogen content. Then, the melt was poured into a cylindrical die under the applied pressure of 0 and 75 MPa. The die temperature was set at approximately 493 K and the pouring temperature was set at 983 K. Finally, the samples were obtained with sizes of 85 mm in height and 68 mm in diameter. The samples were solution-treated at 743 K for 24 h, and then quenched into water at room temperature (T4).
Table 1 Chemical composition of experimental alloys (mass fraction, %)

The tensile test was carried out on a SANS CMT5105 standard testing machine and the reported values were tested for at least three samples, both as-cast and T4-treated samples were tested. Total strain- controlled low cycle fatigue (LCF) test was carried out on a computer-controlled servo-hydraulic testing machine MTS809-25KN at room temperature in air with pull-push loading at a constant strain rate of 8×10-3 s-1 with zero mean strain (R=-1). Only T4-treated samples were tested. The specified strain amplitudes were from 0.2% to 0.6% and specimens were tested up to failure. Digital microhardness tester HVS-1000 was used to test the hardness of α(Al) matrix. The density test was carried out on a Sartorius BS-224B electronic balance.
Samples for metallographic observation were cut in the gauge length part from the selected tensile specimens. Metallographic samples were etched with 1 mL HF + 199 mL H2O solution for 30 s. A Leica optical microscope equipped with the image analysis software Leica materials workstation V3.6.1 was used to quantitatively analyze the α(Al) dendrite size. The microstructures of fatigue specimens were analyzed using a Quanta 2000 SEM equipped with an energy-dispersive X-ray analyzer (EDX) and a JEOL JEM-3010 transmission electron microscope (TEM) at 200 kV.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructures and mechanical properties
Figure 1 shows the microstructures of the as-cast samples prepared by GC and SC process, respectively. The microstructures of the as-cast alloys are typical dendrites with non-equilibrium eutectic phases, h(MgZn2) and T(Al2Mg3Zn3), distributing among the grain boundaries and secondary dendrite boundaries. A lot of shrinkage porosities are seen in GC samples, while nearly no shrinkage porosities are observed in SC samples. The mean secondary dendrite arm spacing (SDAS) was 15-25 μm for SC samples and 25-35 μm for GC samples. These differences in microstructural characteristics are considered to be due to different solidification speeds. The research by CHADWICK and YUE [4] suggests that the applied pressure in the process of solidification can reduce the air gap between the mold and casting and improve the interface heat transfer coefficient, which fastens the cooling rate of castings.
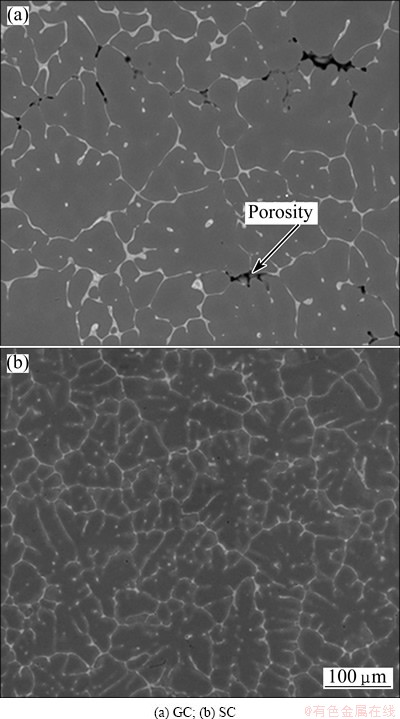
Fig. 1 Microstructures of Al-7.0Zn-2.5Mg-2.1Cu samples under as-cast condition
The density of SC samples (2.8383 g/cm3) is higher than that of GC samples (2.7943 g/cm3). The research by HASHEMI et al [19] shows that all samples prepared by squeeze casting with pressures above 50 MPa are fully dense. Therefore, the porosity percentage of the GC samples can be estimated by the following equation (regard the 75 MPa samples as fully dense) [20]:
 (1)
(1)
where f is the porosity percentage, rGC is the density of GC sample, and rSC is the density of SC sample. Thus, the porosity percentage of the GC sample is about 1.55%.
Figure 2 shows the microstructures of the T4-treated samples produced by GC and SC, respectively. A vast of non-equilibrium eutectic phases dissolve into α(Al) matrix. The volume fraction of eutectic phases decreases apparently compared with that of the as-cast condition.
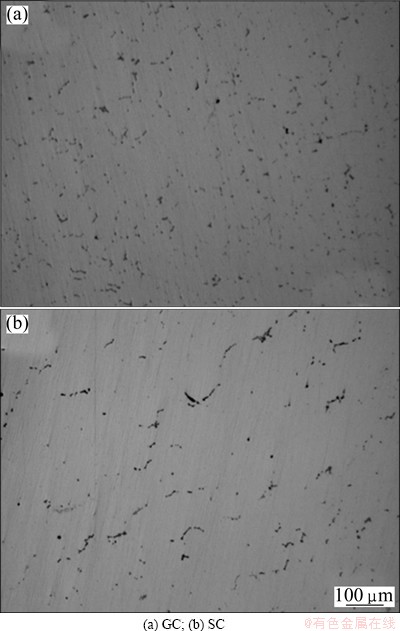
Fig. 2 Microstructures of samples under T4 condition
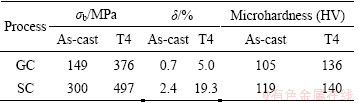
The static mechanical properties of GC and SC alloys are presented in Table 2. The ultimate tensile strength and elongation are improved significantly after T4 heat treatment. This is contributed to solution strengthening. So, only T4-treated alloys are considered in present study. Furthermore, the ultimate tensile strength and elongation of SC samples are higher than those of GC samples under both as-cast and T4 conditions. Under T4 condition, the ultimate tensile strength and elongation are improved by 32.2% and 286% respectively by SC processing. This is mainly attributed to the decrease of the secondary dendrite arm spacing, disappearance of the casting defects such as shrinkage porosities after squeeze casting processing.
What’s more, the microhardness values of samples produced by two casting methods are also listed in Table 2. It can be seen that a higher hardness is obtained for SC samples, which is about 13.3% higher under as-cast condition and 2.9% higher under T4 condition than that of GC samples. The difference of the hardness of α(Al) matrix between GC and SC samples can be attributed to different SDASs and solid solubilities.
Table 2 Static mechanical properties of GC and SC alloys
3.2 Cyclic hysteresis loop
Figure 3 shows the engineering stress-strain hysteresis loops of the T4-treated experimental alloys prepared by GC and SC at total strain amplitudes of 0.3%, 0.4% and 0.5%, respectively. The plastic strain range (Dep) is determined from the width of hysteresis loop by subtracting the elastic stain range (Dee) from the total strain range (Det). At the first cycle, there is nearly no Dep for both GC and SC samples at total strain amplitudes of 0.3% and 0.4%, while a small Dep is observed when the total strain amplitude is up to 0.5%. At half-life cycle, nearly no Dep can be observed for both SC and GC samples at all specified total strain amplitudes. Therefore, the experimental alloys can be regarded as exhibiting elastic cyclic fatigue under the specified total strain amplitudes. The same phenomenon also occurred in 7050-T7451 alloys studied by CHEN [21].
3.3 Cyclic hardening behavior
Cyclic stress response curve exhibits the change of stress with cycle timely in the process of cyclic loading. Figure 4 shows the cyclic stress response curves of GC and SC samples at total strain amplitudes of 0.3%, 0.4% and 0.5%, respectively. At low total strain amplitudes (0.3%, 0.4%), the stress amplitudes remain essentially constant for SC and GC alloys as cyclic deformation is progressed. At a total strain amplitude of 0.5%, SC and GC alloys exhibit continuously serious cyclic hardening to 200 cycles followed by cyclic stabilization. In addition, under the same total strain amplitudes, the maximum value of cyclic hardening of SC samples is greater than that of GC samples.

Fig. 3 Cyclic hysteresis loops of GC and SC alloys at first cycle and half-life cycle
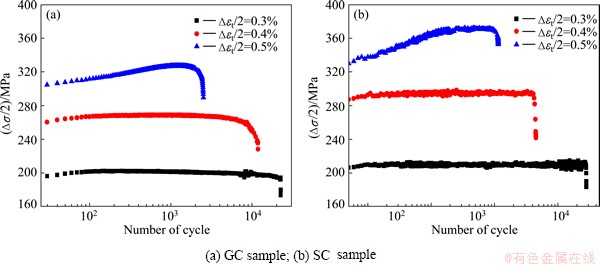
Fig. 4 Cyclic stress response curves of GC and SC samples at total strain amplitudes of 0.3%, 0.4% and 0.5%
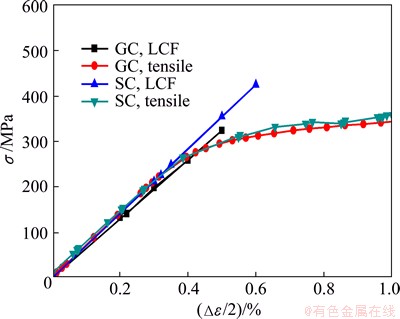
Fig. 5 Cyclic stress-strain curves of T4-treated GC and SC samples
Figure 5 shows the cyclic stress-strain curves of T4-treated GC and SC samples. For comparison, the static tensile curves are also plotted. For GC and SC samples, the cyclic stress-strain curves almost coincide with the tensile curves at low total strain amplitudes (below 0.4%). This indicates that the alloys exhibit cycling stabilization at low total strain amplitudes. At higher total strain amplitudes such as 0.5% and 0.6%, the cyclic stress values are significantly higher than the static tensile stress values, which demonstrates that the alloys exhibit cyclic hardening at higher total strain amplitudes. This phenomenon is consistent with the cyclic stress response curves.
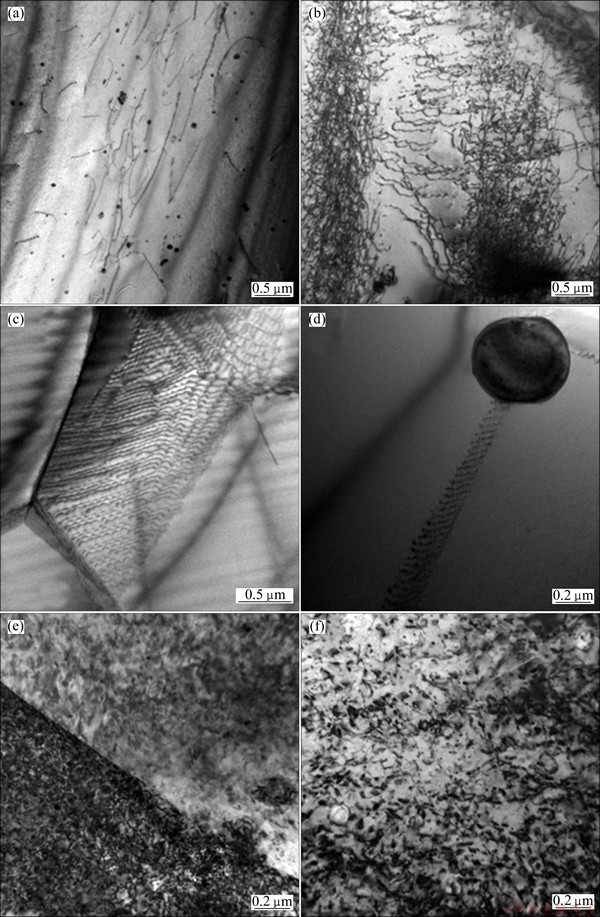
Fig. 6 TEM images of T4-treated SC samples without cyclic loading (a) and with cyclic loading at total strain amplitudes of 0.3% (b, c, d) and 0.5% (e, f)
The cyclic hardening behavior is the result of dislocation entanglement, dislocation accumulation and dislocation interaction with the second phases. In consideration of the same cyclic hardening behavior of SC and GC alloys as mentioned above, only SC samples were used for TEM analysis. TEM images of SC samples (T4) without cyclic loading and with cyclic loading at total strain amplitudes of 0.3% and 0.5% are shown in Fig. 6. Under T4 heat treatment condition without cyclic loading, a few quenching dislocations and nearly no precipitated phase in α(Al) matrix are observed (Fig. 6(a)).
As shown in Fig. 3, there is nearly no macroscopic plastic strain at a total strain amplitude of 0.3%. However, plastic deformation has occurred in some grains. It is clear that a few dislocations occur in the alloys under a total strain amplitude of 0.3% as the plastic strain is very small. As shown in Fig. 6(b), the dislocation density is low, only slight entanglements are observed. Figure 6(c) shows the accumulation of dislocations formed by wave-slipping at the grain boundary. Figure 6(d) shows that dislocations pile up in the bulky undissolved second phase.
As shown in Figs. 3 and 4, at a total strain amplitude of 0.5%, there is a small plastic strain at the first cycle. Dislocation in α(Al) matrix proliferates vastly in cyclic loading. With the increase in the number of cycle, dislocation density, dislocation entanglement, dislocation accumulation and interaction between dislocations and grain boundaries increase continuously. So, the alloys exhibit cyclic hardening at higher total strain amplitudes, such as 0.5%.
What’s more, TEM micrograph (Fig. 6(f)) of the T4-treated specimen subjected to a total strain amplitude of 0.5% shows stress-induced precipitation and a continuous increase in dislocation density with the increase in number of cycles. VENKATESH et al [22] also found this phenomenon in T4-treated AA6061 alloys. It is universally acknowledged that the precipitated phase is h′(MgZn2). In the process of cyclic loading, the movement of dislocation leads to the fact that some small dispersion phases precipitate from the supersaturated solid solution. The second phases are so small that it is very difficult for dislocations to cut through, so they cause the pinning effect. A lot of dislocations move around the tiny second phases and tangle mutually, and then dislocation dipoles offset and dislocation loops form near the tiny precipitated phases. This is also one of the important reasons for cyclic hardening behavior at a total strain amplitude of 0.5%.
Compared with the microstructures of the GC samples, the dendrites and secondary dendrite arm spacing of SC samples are smaller, and the free path of dislocation slip is shorter under cyclic loading. Therefore, the degrees of dislocation accumulation and entanglement are greater, so does the interaction between dislocations and grain boundaries or second phases. As a consequence, SC samples show greater degree of cyclic hardening behavior.
3.4 Fatigue life
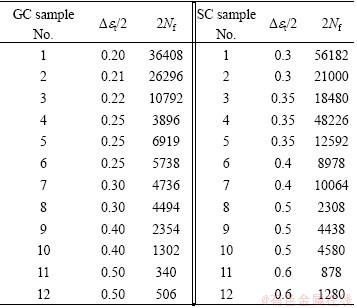
The fatigue lives of GC and SC samples are listed in Table 3. It is clear that excellent fatigue properties are obtained for SC alloy compared with GC alloy.
The total strain amplitude can be expressed as elastic strain amplitude (Δεe/2) and plastic strain amplitude (Δεp/2) [9], i.e.,
 (2)
(2)
It is universally known that low cycle fatigue life is often described by Mason-Coffin equation [9]:
 (3)
(3)
where E is the elastic modulus, Nf is the fatigue life or number of cycles to failure, s′f is the fatigue strength coefficient, b is fatigue strength exponent, ε′f is the fatigue ductility coefficient and c is the fatigue ductility exponent.
From the hysteresis loops discussed above, there is nearly no plastic strain amplitude (Δεp/2) at the half-life
Table 3 Low cycle fatigue lives of GC and SC alloys
cycle for both SC and GC alloys, so, Eq. (3) can be modified as Eq. (4) by ignoring small plastic strain amplitudes (Δεp/2) at high total strain amplitudes.
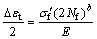 (4)
(4)
To obtain the fatigue parameters required for the calculation of fatigue life, curves of Δεt/2 vs 2Nf are plotted in Fig. 7. It is clear that the experimental data fit with Eq. (4) well and the relevant parameters are summarized in Table 4.
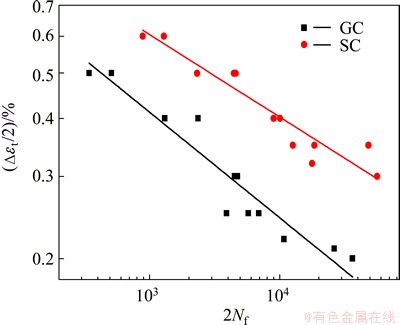
Fig. 7 Plots of total strain amplitude (Δεt/2) vs number of reversals to failure (2Nf)
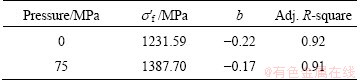
Table 4 Low cycle fatigue parameters for GC and SC alloys
3.5 Failure characteristics
Figures 8 and 9 show the fracture surfaces of GC and SC samples after fracture by cyclic loading. From the observation at low magnifications, three fracture zones are obvious for SC samples, corresponding to crack initiation sites, crack propagation zone and final rapid fracture zone, while the crack propagation zone and final rapid fracture zone are hard to distinguish for GC samples. What’s more, the fracture surfaces of GC samples are rough and a lot of shrinkage porosities can be observed, while the fracture surfaces of SC samples are relatively smooth and several secondary cracks can be seen.
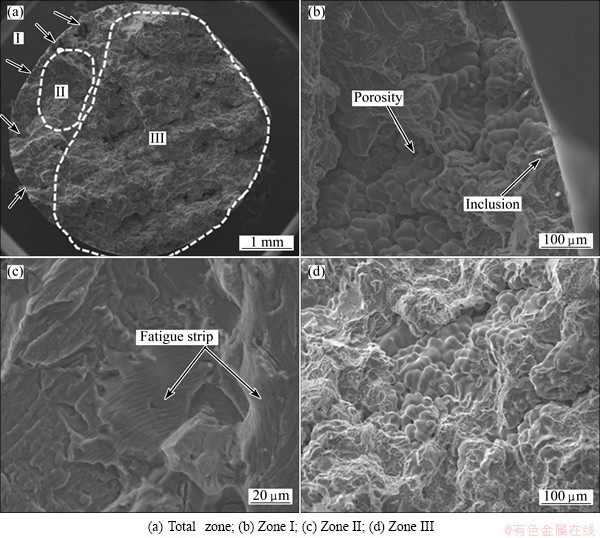

Fig. 8 SEM images of fracture surfaces of GC samples after fracture by cyclic loading at total strain amplitude of 0.3%
Black arrows indicate the locations of the fatigue crack initiation (FCI) sites on individual samples. GC and SC samples exhibit multi-source fatigue, but there are more fatigue crack initiation sites on GC samples than on SC samples. For GC samples, almost all fatigue cracks initiate from big shrinkage porosities, while there is nearly no shrinkage for SC samples and other defects become the fatigue crack initiation sites. As shown in Fig. 9, slip bands, eutectic phases and inclusions at or near the surface become the crack initiation sites of SC samples. The result coincides with the conclusion by COUPER et al [10] and WANG et al [12] that big shrinkage porosities are the most harmful defects for fatigue, when the sizes of porosities decrease to some critical values, and other defects like eutectic phases and inclusions become the possible crack initiation sites.
Striation-like formation can be seen clearly in the crack propagation zones of GC and SC samples. But the striation width of the SC samples, which indicates the fatigue crack propagation rate, is smaller than that of the GC samples. The smaller the width is, the slower the fatigue crack propagation rate is. This striation-like formation is created at different directions as indicated by the arrows in GC and SC samples which result from the variations in lattice orientation. What’s more, the cracks are easy to extend along shrinkage porosities for GC samples, while many broken second phases can be seen in the crack propagation zone of SC samples.
The fatigue crack propagation rate of SC samples is slower than that of GC samples, which mainly includes the following three reasons: 1) the matrix strength and plasticity are improved by SC processing as indicated by microhardness, so, the fatigue propagation resistance is larger; 2) the porosity percentage of GC samples is 1.55% and the fatigue cracks are easy to propagate along the porosities. This decreases the fatigue propagation resistance; 3) SC processing refines the dendrites, and the refined dendrite boundaries can alter the crack propagation path, so as to reduce the crack propagation rate.
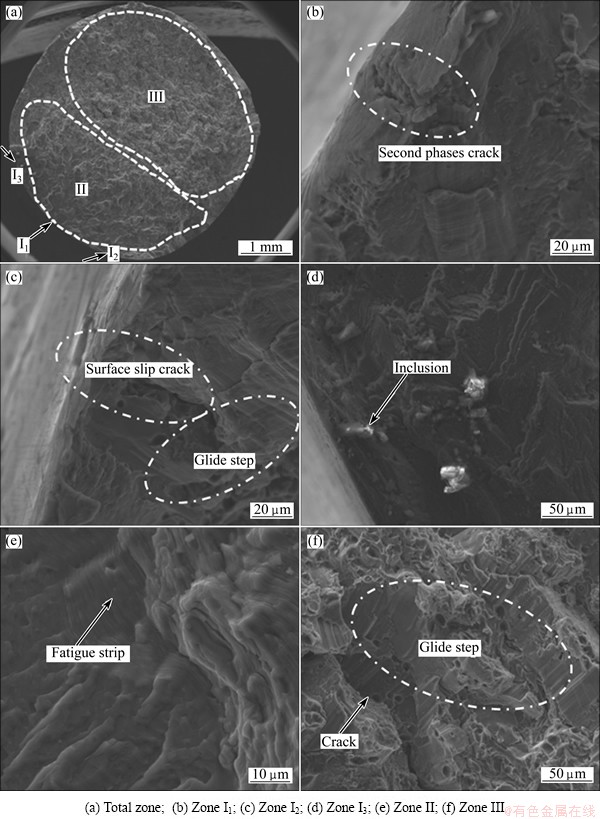
Fig. 9 SEM images of fracture surfaces of SC samples after fracture by cyclic loading at total strain amplitude of 0.3%
At the final fracture stage, the rugged fracture surfaces are observed for both GC and SC samples. For SC samples, a dimple-like fracture and some glide steps can be seen, whereas brittle rupture with a lot of shrinkage porosities is the main feature for GC samples.
To further understand the failure characteristics of GC and SC alloys, cross-sectional micrographs of the samples adjacent to fracture surfaces were performed. For GC samples, many porosities can be seen along the cross-section, which indicates that the cracks are prone to extend along them (Figs. 10(a) and (b)). For SC samples, some bulky broken eutectic phases can be observed and fatigue cracks are inclined to propagate along them (Fig. 10(c)). However, small second phases (about 10 mm) can alter crack propagation path, which increase crack propagation resistance (Fig. 10(d)). This is in favor of fatigue property.
From these observations, it is clear that different failure modes occur in SC and GC alloys, the crack initiation sites for SC samples are slip bands, eutectic phases and inclusions at or near the free surface, while fatigue cracks of GC samples dominantly initiate from porosities and are easy to propagate along them, and these are responsible for their different fatigue properties as indicated above.
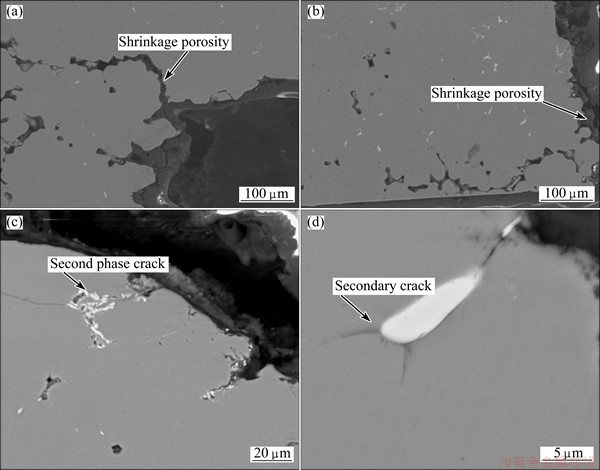
Fig. 10 Cross-sectional micrographs of GC (a, b) and SC (c, d) samples adjacent to fracture surfaces
4 Conclusions
1) The mechanical properties of squeeze cast (SC) Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy are significantly better than those of gravity die cast (GC) alloy due to less cast defects and smaller secondary dendrite arm spacing (SDAS).
2) Excellent fatigue properties are obtained for the SC alloys compared with the GC alloys. GC and SC alloys both exhibit cyclic stabilization at low total strain amplitudes (less than 0.4%) and cyclic hardening at higher total strain amplitudes. The degree of cyclic hardening of SC samples is greater than that of GC samples.
3) Different failure modes occur in the SC and GC alloys. Fatigue cracks of GC samples dominantly initiate from shrinkage porosities and are easy to propagate along them, while the crack initiation sites for SC samples are slip bands, eutectic phases and inclusions at or near the free surface.
References
[1] ZHAO P Z, TSUCHIDA T. Effect of fabrication conditions and Cr, Zr contents on the grain structure of 7075 and 6061 aluminum alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 499: 78-82.
[2] MAZZER E M, AFONSO C R M, GALANO M, KIMINAMI C S, BOLFARINI C. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy reprocessed by spray-forming and heat treated at peak aged condition [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2013, 579: 169-173.
[3] LIU Hong-liang, SHU Da, WANG Jun, SUN Bao-de. Research status on impurities in ultra high strength aluminum alloys [J]. Materials Review, 2011, 25(3): 84-88. (in Chinese)
[4] CHADWICK G A, YUE T M. Principles and applications of squeeze casting [J]. Metals and Materials International, 1989, 5: 6-12.
[5] MALEKI A, SHAFYEI A, NIROUMAND B. Effects of squeeze casting parameters on the microstructure of LM13 alloy [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2009, 209: 3790-3797.
[6] FAN C H, CHEN Z H, HE W Q, CHEN J H, CHEN D. Effect of the casting temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of the squeeze-casting Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2010, 504: L42-L45.
[7] WILLIAMS G, FISHER K M. Squeeze forming of aluminum-alloy components [J]. Metals Technology, 1981, 8: 263-267.
[8] YUE T M, CHADWICK G A. Squeeze casting of light alloys and their composites [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 1996, 58: 302-307.
[9] DIETER G E, BACON D. Mechanical metallurgy [M]. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1986.
[10] COUPER M J, NEESON A E, GRIFFITHS J R. Casting defects and the fatigue behaviour of an aluminum casting alloy [J]. Fatigue & Fracture Engineering Materials & Structures, 1990, 13(3): 213-227.
[11] LEE F T, MAJOR J F, SAMUEL F H. Effect of silicon particles on the fatigue crack growth characteristics of Al-12 wt pct Si-0.35 wt pct Mg-(0 to 0.02) wt pct Sr casting alloys [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transaction A, 1995, 26: 1553-1570.
[12] WANG Q G, APELIAN D, LADOS D A. Fatigue behavior of A356-T6 aluminum cast alloys. Part I: Effect of casting defects [J]. Journal of Light Metals, 2001(1): 73-74.
[13] CONLEY J G, HUANG J L, ASADA J, AKIBA K. Modeling the effects of cooling rate, hydrogen content, grain refiner and modifier on microporosity formation in Al A356 alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2000, 285: 49-55.
[14] YI J Z, GAO Y X, LEE P D, LINDLEY T C. Microstructure-based fatigue life prediction for cast A356-T6 aluminum-silicon alloys [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2006, 37: 301-311.
[15] SONG Mou-sheng, RAN Mao-wu, KONG Yuan-yuan, YAN Deng-yang. Low cycle fatigue behavior of cast A356 aluminum alloys [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(3): 538-545. (in Chinese)
[16] LIU Zhong-xia, SONG Mou-sheng, LI Ji-wen, WENG Yong-gang, WANG Ming-xing, SONG Tian-fu. Low cycle fatigue behavior and plastic strain energy of A356 alloys [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(2): 260-267. (in Chinese)
[17] JIAN Hai-gen, JIANG Feng, WEN Kang, JIANG Long, HUANG Hong-feng, WEI Li-li. Fatigue fracture of high-strength Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2009, 19(5): 1031-1036.
[18] YUE T M. Comparison of the fatigue behaviour of an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy (7010) in the form of squeeze and chill castings and rolled plate [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1990, 25: 175-182.
[19] HASHEMI H R, ASHOORI H, DAVAMI P. Microstructure and tensile properties of squeeze cast Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2001, 17: 639-644.
[20] MASOUMI M, HU H. Influence of applied pressure on microstructure and tensile properties of squeeze cast magnesium Mg-Al-Ca alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 528: 3589-3593.
[21] CHEN Yin-zhen. Investigation on the effects of mean strain on low-cycle fatigue behavior of aluminum alloy 7050-T7451 [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2012. (in Chinese)
[22] VENKATESH C V, RAMAN S G S, CHAKKINGAL U. Characterization of AA6061 alloy processed by equal channel angular pressing and subjected to low cycle fatigue [J].Transactions of the Indian Institute of Metals, 2013, 66(2): 147-154.
郑成坤,张卫文,张大童,李元元
华南理工大学 机械与汽车工程学院,广州 510640
摘 要:研究重力铸造和挤压铸造制备的Al-7.0Zn-2.5Mg-2.1Cu合金(T4态)的显微组织、力学性能和低周疲劳行为。结果表明:挤压铸造制备的合金铸造缺陷较少,二次枝晶间距较小,其静态力学性能明显优于重力铸造制备合金的;挤压铸造制备的合金具有优异的疲劳性能。在较低总应变幅下(小于0.4%),两种方法制备的合金均呈循环稳定特征;在较高总应变幅下均呈循环硬化特征,且挤压铸造制备的合金循环硬化程度高于重力铸造制备合金的。在重力铸造条件下,疲劳裂纹主要起源于缩松、缩孔处,并且易于沿着这些铸造缺陷扩展;在挤压铸造条件下,裂纹起源于表面和靠近表面处的滑移带、共晶相以及夹杂。
关键词:Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金;挤压铸造;重力铸造;显微组织;力学性能;低周疲劳
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Project (2015A030312003) supported by the Guangdong Natural Science Foundation for Research Team, China; Project (51374110) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: Wei-wen ZHANG; Tel: +86-20-87112272; Fax: +86-20-87112111; E-mail: mewzhang@scut.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63992-9

