文章编号:1004-0609(2013)08-2190-10
工业纯钛的高温热氧化行为
李 旭1, 4,彭小燕1, 4,段雨露1, 4,张履国2,赵以容2,王学文3,徐国富1, 4
(1. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 遵义钛业股份有限责任公司,遵义 563004;
3. 中南大学 冶金科学与工程学院,长沙 410083;
4. 中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,长沙 410083)
摘 要:采用原子力显微镜(AFM)、扫描电镜(SEM)和X射线衍射仪(XRD)研究工业纯钛经600、700和800 ℃热氧化后硬化层的形貌、粗糙度和相结构,分析热氧化过程中氧原子的扩散机制、渗氧层的形成和氧化膜的分层现象。结果表明:随着氧化时间的延长和温度的升高,硬化层表面粗糙度增大,氧化物颗粒迅速长大,主要物相为TiO2、Ti2O、Ti3O、Ti6O;钛的氧化过程是氧原子通过气相/氧化膜及氧化膜/金属基体的渗透过程;氧化膜随着氧化反应的加剧和自身的分解,其结构和性质发生变化而导致分层现象。
关键词:工业纯钛;氧化膜;高温氧化;扩散机理
中图分类号:TG 146 文献标志码:A
Thermal oxidation behavior of commercial purity titanium at high temperature
LI Xu1, 4, PENG Xiao-yan1, 4, DUAN Yu-lu1, 4, ZHANG Lü-guo2, ZHAO Yi-rong2, WANG Xue-wen3, XU Guo-fu1, 4
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Zunyi Titanium Industry Co. Ltd., Zunyi 563004, China;
3. School of Metallurgy Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
4. State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The morphologies, roughness and phase structure of hardened layer of commercial purity titanium (CP-titanium) after thermal oxidation at 600, 700 and 800 ℃ were investigated by AFM, SEM and XRD. The diffusion mechanism, formation of oxygen-diffusion zone and stratification during the thermal oxidation treatment were analyzed. The results show that the roughnesses of hardened layer increase and the oxide particles grow up continually with the increase of oxidation time and temperature, and the main phases are TiO2, Ti2O, Ti3O and Ti6O. The oxidation process of CP-titanium is that oxygen atom passes the gaseous phase/oxidation film and oxidation film/metallic matrix. The structure and property of oxidation film change and lead to stratification due to the acceleration of oxidation reaction and the decomposition of oxidation film.
Key words: commercial purity titanium; oxidation film; high temperature oxidation; diffusion mechanism
工业纯钛是含有少量碳、氮、氧、铁和其他杂质的α-Ti合金,具有优异的耐蚀性、良好的力学性能和焊接性能,可以作为重要的耐蚀结构材料,广泛用于化工设备、滨海发电装置、海水淡化装置和舰艇零部件[1]。常温下,工业纯钛在空气中能自发形成极薄的致密氧化膜,厚度约为0.5~7 nm。热处理氧化法(TO)是在含氧气氛中对钛合金加热一段时间,使其表面生成一层氧化膜。热处理氧化法能够使钛表面生成高结晶度的金红石型厚氧化物膜,该氧化膜相比于钛金属基体,具有更优异的耐腐蚀性、耐磨性和生物相容性。金泰来等[2]研究了工业纯钛在超高温(1 000 ℃以上)短时间内的氧化动力学特性,严伟等[3]、魏寿庸等[4]以及朱月秀等[5]对热氧化处理钛表面渗氧层的显微硬度进行了测试分析。目前,对热加工生产温度范围内(600~1 000 ℃)工业纯钛氧化过程中硬化层形貌尺寸和物相结构的分析不够充分,对氧化机制和规律的揭示不够全面,热加工氧化导致的产品缺陷无从得知。因此,本文作者对工业纯钛在600、700和800 ℃的氧化行为进行研究,全面地分析表面硬化层的形貌尺寸、元素分布和物相结构,深入地研究硬化层的生长、分层机制和氧化规律。
1 实验
实验材料采用5 mm厚的工业纯钛退火板材,其化学成分为(质量分数,%):Fe 0.02、C 0.008、N 0.005、H 0.005、O 0.042,余量为Ti。组织为α等轴晶粒。将板材加工成10 mm×10 mm的方形试样,在金相预磨机上将试样用水磨砂纸打磨成平整的表面,将预磨后的试样在金相抛光机上进行精抛,直至表面光亮无划痕。抛光好的试样放入乙醇中,在超声清洗仪中震荡清洗10 min后取出晾干。电阻炉热氧化温度分别为600、700和800 ℃;依据热加工时实际的加热时间,设定对应每个温度的氧化时间分别为0.5、2、6、12、18、24、36和48 h。到氧化时间后,试样取出进行空冷。使用Dimension Icon原子力显微镜对氧化膜的三维形貌和粗糙度进行分析。利用Sirion 200场发射扫描电镜及附带的Gensis60能谱分析仪进行氧化膜形貌观察和成分分析,加速电压为20 kV。试样的物相分析在D/max 2500型X射线衍射仪上进行,扫描速度为1 (°)/min。使用MDI Jade 5.0软件对所得的XRD衍射谱进行分析。
2 结果与分析
2.1 氧化膜的宏微观形貌
工业纯钛在空气中热氧化不同时间和温度后,用肉眼即可观察到试样表面颜色的变化。经过不同时间和温度处理后,工业纯钛表面生成的氧化膜厚度不同。氧化膜表面的反射光与氧化膜/钛界面内部的反射光发生光的干涉作用,由不同波长的色光相加混合而显色。氧化膜厚度不同,则氧化膜的光通量和对光的折射率、反射率均不同,因而产生不同的光的干涉效应,使光的混合比例产生改变,而呈现出不同的色彩[6-7]。对热氧化后工业纯钛表面颜色变化进行观察,其结果如表1所列。从试样表面形貌还可以看出,随着热氧化温度的升高或处理时间的延长,氧化膜与钛基体的结合力逐渐下降。当氧化温度为600 ℃和700 ℃时,即使氧化时间延长至48 h,所得氧化膜与钛基体的结合也很紧密牢固。在800 ℃热处理氧化2 h后,氧化膜与基体的结合紧密牢固;氧化6~18 h后,氧化膜开始出现局部脱落;氧化24~48 h后氧化膜开始出现严重脱落,未脱落的部分用指甲轻轻碰触即完全脱落,脱落的氧化膜厚而脆。
表1 工业纯钛在不同热处理条件下氧化膜的颜色
Table 1 Colors of oxide films on CP-titanium after different thermal oxidation treatments

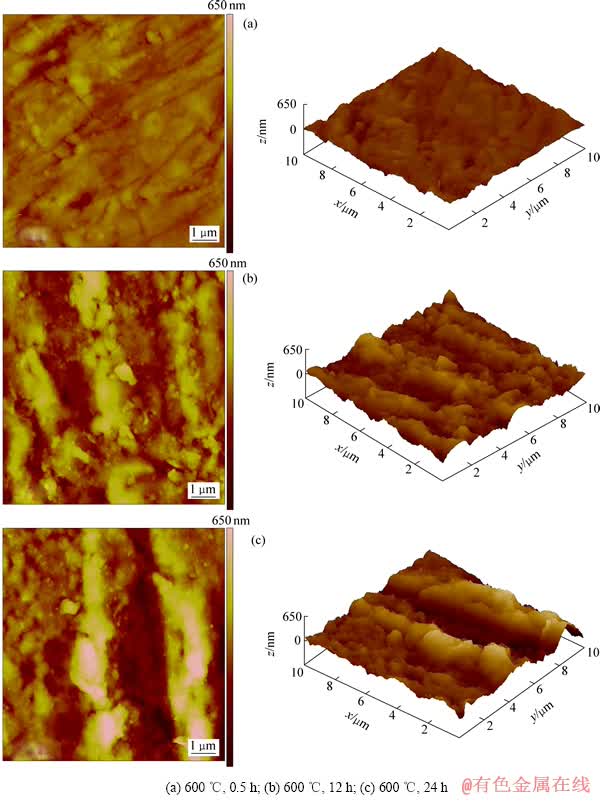
图1 工业纯钛热氧化后表面的AFM像
Fig. 1 AFM images of CP-titanium after oxidation
表2 工业纯钛热氧化后表面的粗糙度分析结果
Table 2 Roughness data of CP-titanium after different thermal oxidation treatments
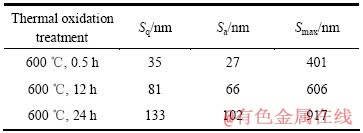
工业纯钛在热氧化过程中,钛原子和氧原子在不同位置的扩散速率不同,二氧化钛颗粒的长大速度也就不同,从而导致表面不平整而产生粗糙度。使用原子力显微镜对工业纯钛热氧化表面的三维形貌和粗糙度进行分析,结果如图1和表2所示。在600 ℃热氧化0.5 h后,试样表面平整,粗糙度指数Sq和Sa分别为35和27 nm,而整个100 μm2的图片面积中Smax为401 nm。从图1中还可看到细小的划痕,这是样品热氧化前磨抛导致的。随着氧化时间的延长,细小的划痕消失,领先长大的颗粒由于与氧原子充分接触、直接受热而长大极快,使得粗糙度显著增大。热氧化24 h后,Sq、Sa和Smax分别增加到133、102和917 nm。由于试样表面粗糙度增大,原子力显微镜频频发生撞针,故后面的试样不适合做原子力分析。
图2所示为工业纯钛在600、700和800 ℃热氧化不同时间后表面氧化物的形貌。从图2中可以清楚地观察到试样表面钛的氧化物颗粒呈多面体形状,随着氧化温度的升高和氧化时间的延长,颗粒尺寸逐渐增大。经600 ℃氧化24 h后,氧化物颗粒平均尺寸约为0.1 μm;经600 ℃氧化48 h后,颗粒尺寸稍微增大;样品在700 ℃热氧化,氧化速率显著增大;经氧化24 h和48 h后,氧化物颗粒比较均匀,平均尺寸分别约为0.3 μm和0.5 μm,且排列致密,几乎没有孔隙;样品经800 ℃氧化24 h后,一部分氧化物颗粒异常长大,尺寸达到0.7 μm左右,而另外一部分颗粒的尺寸则与经700 ℃氧化24 h后的相当;当氧化时间延长到48 h后,大颗粒继续长大,而小颗粒则长大不明显。
2.2 工业纯钛硬化层的剖面元素分布和分层现象
工业纯钛在800 ℃下氧化2 h和12 h后的剖面元素线分布如图3(a)和(b)所示。从图3(a)和(b)中可以看出,氧化层部分氧含量较高,有连续的峰值;在氧化层与金属基体的交界处,氧含量急剧降低;深入到基体的内层,氧含量很低。样品在800 ℃氧化2 h后,形成了均匀、无孔隙的氧化层,厚度约为4 μm;而氧化12 h后,形成了由表面到钛基体之间的3层氧化层 ,厚度分别约为4、1和0.5 μm,且最外层中存在大量孔隙。钛在热氧化后,表面形成的氧化膜与金属基体之间是一个具有氧浓度梯度的过度层——渗氧层,可见1、2层为氧化层,3层为渗氧层。样品经800 ℃氧化24 h后,表层氧化膜完全脱落,去除表面氧化膜后,对暴露出来的新氧化表面进行SEM形貌观察,如图3(c)~(f)所示。新表面分为两层,两层氧化物颗粒的形貌都呈近球形,并没有形成规则的多面体,且排列松散。上层氧化物颗粒的尺寸比下层的略大。
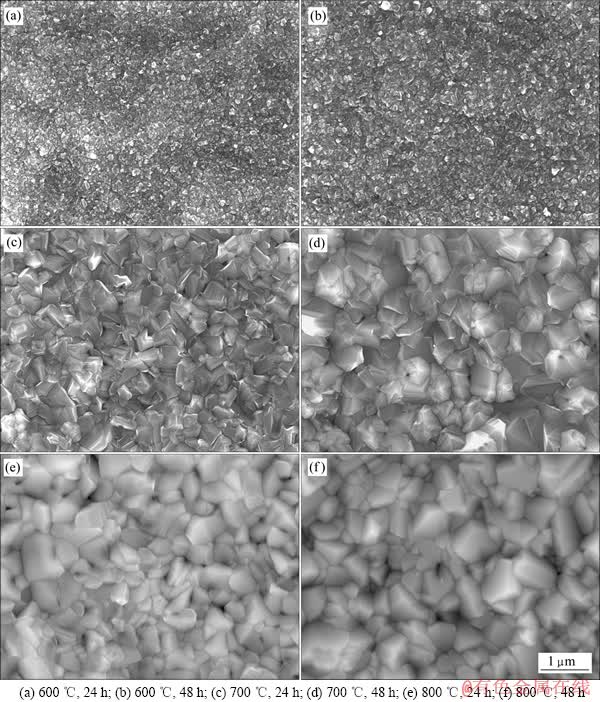
图2 工业纯钛热氧化后表面的SEM像
Fig. 2 SEM images of CP-titanium after oxidation
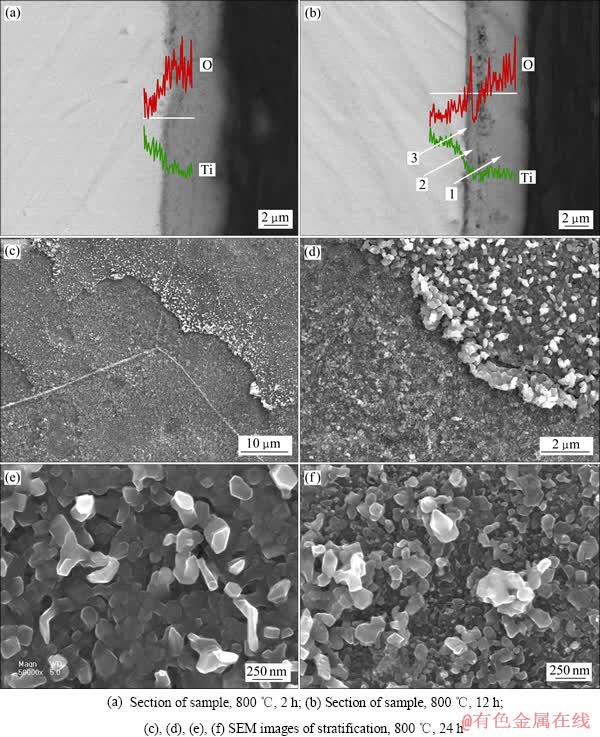

图3 工业纯钛热氧化后的分层现象和剖面元素分布
Fig. 3 Stratification phenomenon and element distribution of oxidation film section of CP-titanium after thermal oxidation
在热氧化过程中,工业纯钛的氧化物颗粒出现异常长大现象,如图4所示。在800 ℃热氧化过程中,氧化膜表面出现了氧化球,如图4(a)和(b)所示。氧化2 h后,氧化物颗粒聚集在一起,形成了直径约为4 μm的氧化球。当氧化时间延长到18 h时,氧化球长大到约7 μm,且球体规范致密。而时间延长到24 h以及更长后,氧化球消失。经800 ℃氧化12 h后,试样表面存在一些凹坑,凹坑中的氧化物呈四棱柱状,且排列松散,其尺寸较平整表面处颗粒小。
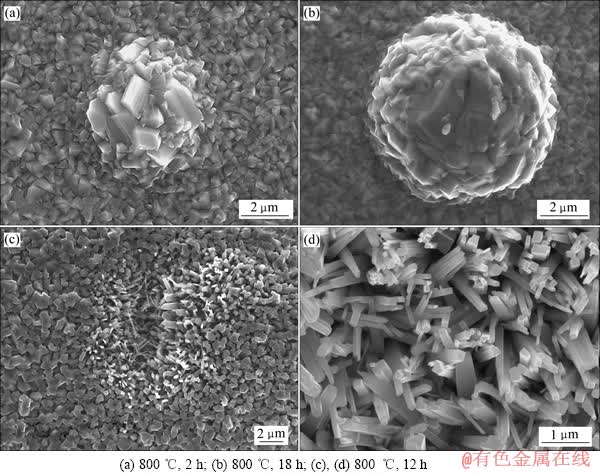

图4 工业纯钛热氧化过程中晶粒的异常长大现象
Fig. 4 Unusual grain-growth phenomenon of CP-titanium during thermal treatment
随着氧化时间的延长,凹坑逐渐变小直至消失。以上现象可根据氧化膜的形成过程来解释。氧化膜的形成过程分为4个步骤:1) 氧吸附在表面上;2) 氧化物形核;3) 晶核的侧向生长;4) 形成致密的氧化膜。形核处的氧化物颗粒由于优先形成,其长大速度较其他地方的快,从而形成颗粒聚集的氧化球。随着时间的延长,氧化球受钛原子供应限制而长大减慢甚至停止,而周边区域的晶粒持续长大,使得表面逐渐平整,氧化球消失。凹坑为晶核侧向生长的交汇处,由于该处晶粒后生长所致,随着晶粒的持续长大,最终凹坑变平整。
2.3 氧化膜的XRD物相分析
氧化反应在600和700 ℃下形成的氧化膜没有出现脱落现象,对其进行X射线衍射分析,如图5所示。由图5可看出,经600 ℃氧化24 h和48 h后,氧化膜的主要物相为TiO2、Ti3O、Ti6O、Ti。出现了钛的衍射峰,说明生成的氧化膜较薄,经700 ℃氧化24 h后,主要物相仍为TiO2、Ti3O、Ti6O、Ti,但时间延长到48 h后,钛的衍射峰消失,说明氧化膜明显增厚,X射线无法穿透。
在800 ℃下,产生的氧化膜大部分出现了脱落,将脱落的氧化膜以及去除表面氧化膜后的氧化层进行X射线衍射分析,如图6所示。由图6可见,经800 ℃氧化24 h和48 h后,脱落的氧化膜为TiO2,而去除表面氧化膜后的氧化层主要为TiO2、Ti2O、Ti3O。由此可见,在热加工温度范围内,氧化膜的物相主要是TiO2、Ti2O、Ti3O等低价的钛氧化物。
3 讨论
钛表面的硬化层结构由氧化膜和渗氧层组成,氧化膜为钛的多种氧化物组成的混合物,呈多孔状,性脆易脱落;而渗氧层为氧原子溶入钛的固溶体,与基体结合比较紧密,不易剥落。在600~1 000 ℃,钛的氧化由两个过程共同决定,氧化膜的生长和氧化膜的分解。常温下钛的氧化膜是致密的,透过氧化膜的传质过程是非常缓慢的,因此,钛的氧化膜在常温下具有保护作用。在高温下,钛的氧化很复杂,由于存在许多种稳定的氧化物以及具较大的氧溶解度,可形成多种稳定氧化物如Ti2O、TiO、Ti2O3、Ti3O5、TiO2等[8-9]。钛的氧化物生长因氧化温度及氧压的不同,或是以氧原子的内扩散为主或是以钛原子的外扩散为主进行。一般情况下,由于氧原子溶解及TiO2形成速度比低价钛的氧化物快得多,故钛在氧化过程中一般形成TiO2,但在高温特别是低氧压条件下也可形成低价的氧化物。
根据多层氧化膜生成理论[10-11],可以认为工业纯钛氧化过程是氧原子通过气相/氧化膜及氧化膜/金属基体的渗透过程。氧化初期,氧化膜比较致密,氧原子透过氧化膜的速度较慢;随着保温时间的延长,初期形成的致密氧化膜遭到破坏,氧化膜开裂并形成孔隙,氧原子沿着裂纹或者孔隙快速进入钛基体内部。此时氧原子通过这些微观或者宏观的裂纹和孔隙的传输是其主要的氧化机制,此外,高温下氧原子和钛原子的扩散速度加快,氧化速度势必会加快。尽管此时在疏松的外层氧化膜与钛基体之间形成相对致密的新氧化层,但是该层在高温下并不具有保护作用,因此,氧原子继续向钛基体内部渗透。氧原子作为溶质特别是在高温条件下很容易溶入钛中,渗氧层中氧浓度的分布是从表面向内呈梯度递减的。渗氧层中的氧原子主要有两个来源:一是大气中的氧原子通过氧化膜向内扩散,其中一部分氧原子在氧化膜/金属界面与金属反应生成氧化物,另一部分继续向金属内部扩散,以间隙原子的形式固溶于金属基体中,形成渗氧层;二是随着时间的延长和温度的升高,膜越来越厚,在钛表面形成了具有保护性的氧化膜,氧原子的扩散变得困难,但氧化膜/金属界面的氧浓度差使得氧化膜要源源不断地向金属提供氧原子,于是界面处的氧化物开始发生分解反应,随着处理时问的延长和温度的升高,分解程度越大,界面处氧化膜的钛氧比升高。当氧化膜内钛氧比升高到一定程度时,氧以间隙原子的形式固溶于金属基体中,形成渗氧层[12-13]。处理温度越高,时间越长,氧化膜分解得越多,所以,渗氧层的厚度增大。
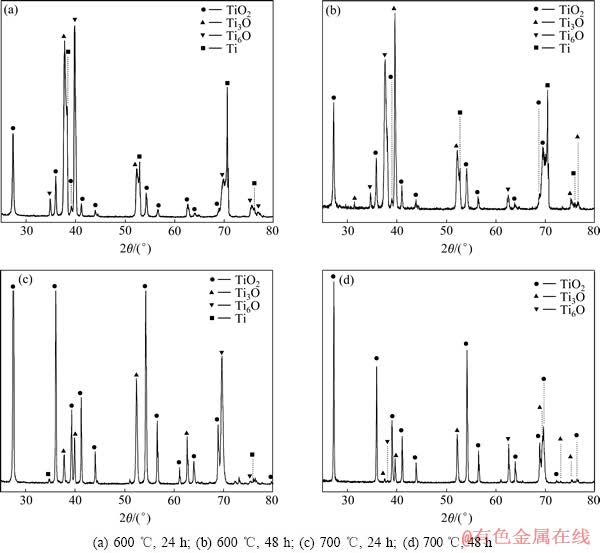
图5 工业纯钛于600、700 ℃热氧化后氧化层的XRD谱
Fig. 5 XRD patterns of oxidation film of CP titanium at 600 and 700 ℃
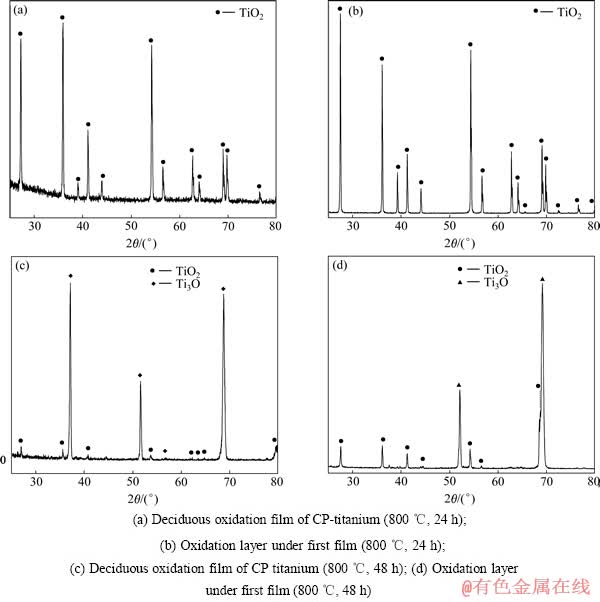
图6 工业纯钛800 ℃热氧化后的XRD谱
Fig. 6 XRD patterns of CP-titanium after thermal treatment at 800 ℃
实验表明,随着处理温度的升高和时间的延长,氧化膜的致密性也越来越差,经800 ℃处理12 h后,形成的氧化膜是疏松多孔的。这是由于致密的具有保护性的氧化膜生成后,氧原子通过氧化膜向内扩散较为困难。由于氧化膜中氧浓度明显高于与其接触的金属表面的氧浓度,在氧化膜/金属界面形成了氧浓度差,导致与金属接触的氧化膜发生了反应[14-15],分解得到的氧原子渗入金属基体中,成为渗氧层中一部分氧的来源,并在氧化膜中留下了空位。根据Ti-O相图,α-Ti的最大溶氧量为33%(摩尔分数),氧间隙固溶到晶格中,呈随机分布或者在六方系钛晶格中交替的(0002)晶面上有序分布[16-18],由于溶入氧导致晶格畸变,从而阻碍位错运动并造成材料脆化,使得氧化膜疏松易破损。根据HAUFFE[19]的结论,随着热氧化温度的升高和时间的延长,钛表面氧化膜由外向内的组成变化为TiO2-TiO2、TiO-TiO2、Ti2O3、TiO,从外向内钛氧比是逐渐升高的,越靠近渗氧层,氧化物的钛氧比越大。可以推测,随着温度的进一步升高或时间的进一步延长,氧化膜将大幅地转化为渗氧层。
金属的高温腐蚀理论指出[20-21],钛在低于400 ℃氧化时,质量增加与时间遵循对数规律;在400~600 ℃之间,先遵循对数规律,后转变成抛物线或立方规律;在600~700 ℃以上,氧化基本呈抛物线规律,并随着时间的延长,发生失稳氧化;在900~1 000 ℃以上,按线性规律氧化。高温长时氧化后钛的氧化膜往往呈片层状结构,片层与片层间的过渡区域结合弱,甚至为裂隙。这种片层状结构形成的原因如下:1) 根据KOFSTAD等[22]的研究,高温时在二氧化钛和钛之间将生成其他类型的氧化物,如TiO、Ti2O3。随着氧化物层数的增多,各层的热膨胀系数有差异,导致内应力增大,结合力降低;2) 随着处理温度的升高或处理时间的延长,氧化膜增厚,膜内生长应力增大,当应力超过膜内强度或膜与基体的结合力时,就会导致氧化膜的开裂剥落;3) 随着处理温度的升高和处理时间的延长,由于氧化膜发生了分解反应,形成了疏松多孔的氧化膜,导致氧化膜强度降低;4) 当表面形成了疏松多孔的氧化膜,金属阳离子可通过氧化膜向外扩散,使金属内部出现晶格缺陷,影响了氧化物与金属间的原子键,导致氧化膜剥落。与氧化膜分离后的钛又迅速被氧化,这一过程循环进行下去,钛的表面就会出现片层状的氧化膜。
4 结论
1) 工业纯钛在600、700和800 ℃热氧化过程中,随着热氧化时间的延长和温度的升高,氧化物颗粒迅速长大,氧化膜表面粗糙度增大,整个硬化层主要由氧化膜和渗氧层组成。在热氧化过程中,氧化物颗粒出现异常长大现象,呈球状和四棱柱状。经800 ℃热处理6 h后,氧化膜开始脱落,并且出现分层现象,整个硬化层的主要物相为TiO2、Ti2O、Ti3O、Ti6O等低价钛的氧化物。
2) 钛的氧化过程是氧原子通过气相/氧化膜及氧化膜/金属基体的渗透过程,氧原子通过氧化膜中的微观或者宏观的裂纹和孔隙传输是其主要的氧化机制。氧化膜随着氧化反应的加剧和自身的分解,其层数、内应力、致密度以及晶格发生变化而导致分层现象。
REFERENCES
[1] 周 廉. 美国、日本和中国钛工业发展评述[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2003, 32(8): 577-584.
ZHOU Lian. Review of titanium industry progress in America, Japan and China[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2003, 32(8): 577-584.
[2] 金泰来, 魏建峰, 顾兆林, 赵永庆, 常 辉. 工业纯钛在特高温度下的氧化行为研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2005, 34(12): 1998-2001.
JIN Tai-lai, WEI Jian-feng, GU Zhao-lin, ZHAO Yong-qing, CHANG Hui. Research on extreme high temperature oxidation behavior of commercial pure titanium[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2005, 34(12): 1998-2001.
[3] 严 伟, 王小祥. 热氧化处理钛表面渗氧层的组织与性能研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2005, 34(3): 471-473.
YAN Wei, WANG Xiao-xiang. Characterization of the surface oxygen-diffusion zone of the thermally oxidized titanium[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2005, 34(3): 471-473.
[4] 魏寿庸, 石卫民, 王鼎春, 王清江, 陈志勇, 刘建荣. 600 ℃时高温钛合金(Ti60)的组织与力学性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(S1): 801-806.
WEI Shou-yong, SHI Wei-min, WANG Ding-chun, WANG Qing-jiang, CHEN Zhi-yong, LIU Jian-rong. Microstructure and mechanical properties of high temperature titanium alloy Ti60 at 600 ℃[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(S1): 801-806.
[5] 朱月秀, 胡云展. 溅射-阳极氧化法在釉面砖上制备多彩TiO2膜[J]. 真空, 2001, 6: 26-28.
ZHU Yue-xiu, HU Yun-zhuan. Preparation of multi-colored TiO2 films on the ceramic substrate by sputtering-anodic oxidation method[J]. Vacuum, 2001, 6: 26-28.
[6] 张永德. 钛的着色工艺原理及其应用[J]. 表面技术, 2001, 30(2): 33-35.
ZHANG Yong-de. Coloring principle and application of titanium[J]. Surface Technology, 2001, 30(2): 33-35.
[7] 罗斌莉, 毛江虹, 林海峰, 曹继敏. TB2钛合金的热加工与热处理工艺[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(S1): 620-623.
LUO Bin-li, MAO Jiang-hong, LIN Hai-feng, CAO Ji-min. Heat processing and treatment technology of TB2 titanium alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(S1): 620-623.
[8] WAHLBECK P G, GILLES P W. Reinvestigation of the phase diagram for the system titanium-oxygen[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1966, 49(4): 180-183.
[9] KUMAR S, SANKARA N T S N, GANESH S R S, SESHADRI S K. Thermal oxidation of CP Ti-An electrochemical and structural characterization[J]. Materials Characterization, 2010, 61(6): 589-597.
[10] 朱日彰, 何业东, 齐慧滨. 高温腐蚀及耐高温腐蚀材料[M]. 上海: 上海科学出版社, 1995: 142-154.
ZHU Ri-zhang, HE Ye-dong, QI Hui-bin. High temperature corrosion and resistant material[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science Press, 1995: 142-154.
[11] 李 萍, 段园培, 薛克敏, 王晓溪, 甘国强. TB8钛合金的热变形组织与织构[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(5): 872-877.
LI Ping, DUAN Yuan-pei, XUE Ke-min, WANG Xiao-xi, GAN Guo-qiang. Microstructures and textures of TB8 titanium alloy after hot deformation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(5): 872-877.
[12] QI P Y, LI X Y. Characterisation of the palladium-modified thermal oxidation-treated titanium[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2002, 326(2): 330-342.
[13] GULERYUZ H, CIMENOGLU H. Effect of thermal oxidation on corrosion and corrosion-wear behaviour of a Ti-6Al-4V alloy[J]. Biomaterials, 2004, 25(16): 3325-3333.
[14] MUELLER Y, TOGNINI R, MAYER J, VIRTANEN S. Anodized titanium and stainless steel in contact with CFRP: An electrochemical approach considering galvanic corrosion[J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A, 82A(4): 936-946.
[15] SIVA R K D, BRAMA Y L, SUN Y. Thick rutile layer on titanium for tribological applications[J]. First International Conference on Advanced Tribology, 2007, 40(2): 329-334.
[16] MCKEE D W, HUANGS C. The oxidation behavior of gamma-titanium aluminide alloys under thermal cycling conditions[J]. Corrosion Science, 1992, 33(12): 1899-1914
[17] MOUSSA S O, EL-SHALL M S.Fabrication of nanostructured nickel and titanium aluminides starting from elemental nanopowders[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2008, 112(3): 1015-1020.
[18] GULERYUZ H, CIMENOGLU H. Surface modification of a Ti-6Al-4V alloy by thermal oxidation[J]. Surf Coat Technol, 2005, 192(2/3): 164-170.
[19] HAUFFE K. Oxidation of metals[M]. New York: Plenum Press, 1965: 201-209.
[20] 李美栓. 金属的高温腐蚀[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2001: 148-150.
LI Mei-shuan. The high temperature corrosion of metals[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2001: 148-150.
[21] 彭小敏, 夏长清, 王志辉, 黄 珍, 王金惠. TiAl基合金高温氧化及防护的研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(6): 1116-1130.
PENG Xiao-min, XIA Chang-qing, WANG Zhi-hui, HUANG Zhen, WANG Jin-hui. Development of high temperature oxidation and protection of TiAl-based alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(6): 1116-1130.
[22] KOFSTAD P, HAUFFE K. Oxydation von titanium[J]. Materials and Corrosion, 1956, 7(1): 642-649.
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家“十一五”科技支撑计划项目(2008BAE62B02);粉末冶金国家重点实验室开放基金资助课题
收稿日期:2012-11-09;修订日期:2013-04-10
通信作者:徐国富,教授,博士;电话:0731-88877217;E-mail: csuxgf66@csu.edu.cn