乙酸在方解石表面吸附的密度泛函研究
来源期刊:中南大学学报(自然科学版)2019年第5期
论文作者:刘月田 柴汝宽 杨莉 辛晶 徐万里 马晶
文章页码:1252 - 1263
关键词:密度泛函理论;CaCO3(104)表面;乙酸;吸附机理
Key words:density functional theory; CaCO3(104) surface; acetic acid; adsorption mechanism
摘 要:为了探究乙酸在方解石表面的吸附机理,利用密度泛函方法研究乙酸的反应活性特征及其在CaCO3(104)表面吸附过程中的电子转移以及化学键形成特征。研究结果表明:乙酸前线轨道主要分布于乙酸中重原子之上,其中O(1)原子为反应活性中心;乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面的最稳定吸附位处于穴位和短桥位之间即2个Ca原子之间;乙酸以解离态吸附,其中乙酸根趋向于以双齿桥键合模式吸附于CaCO3(104)表面,H(4)原子与CaCO3(104)表面O(3)原子形成羟基;乙酸与CaCO3(104)表面之间存在电子的转移和化学键的形成,其中Ca(1)—O(1)和Ca(2)—O(2)形成离子键,H(4)—O(3)形成共价键,H(4)—O(2)形成氢键。
Abstract: To explore the adsorption mechanism of acetic acid on CaCO3(104) surface, the active sites of acetic acid, the electron transfer and chemical bond formation during the adsorption process were studied using density functional methods. The results show that the frontier orbital of acetic acid distributes over the heavy atom, in which O(1) atom is the reactive center. The most stable adsorption site is between hollow and short bridge sites, namely between two Ca atoms. The acetic acid is adsorbed in a dissociated state, in which the acetate tends to adsorb on the CaCO3(104) surface by a bridging bidentate mode and H(4) tends to form a hydroxyl groups with O(2) of CaCO3(104) surface. Meanwhile, there exist transfer of electrons and formation of chemical bonds between the acetic acid and the CaCO3(104) surface. Among them, Ca(1)—O(1) and Ca(2)—O(2) form ionic bond, H(4)—O(3) forms covalent bonds and H(4)—O(2) forms hydrogen bond.
DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2019.05.030
柴汝宽1,刘月田1,杨莉2,辛晶1,徐万里1,马晶1
(1. 中国石油大学(北京) 油气资源与探测国家重点实验室,北京,102249;
2. 中海油研究总院 开发研究院,北京,100028)
摘要:为了探究乙酸在方解石表面的吸附机理,利用密度泛函方法研究乙酸的反应活性特征及其在CaCO3(104)表面吸附过程中的电子转移以及化学键形成特征。研究结果表明:乙酸前线轨道主要分布于乙酸中重原子之上,其中O(1)原子为反应活性中心;乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面的最稳定吸附位处于穴位和短桥位之间即2个Ca原子之间;乙酸以解离态吸附,其中乙酸根趋向于以双齿桥键合模式吸附于CaCO3(104)表面,H(4)原子与CaCO3(104)表面O(3)原子形成羟基;乙酸与CaCO3(104)表面之间存在电子的转移和化学键的形成,其中Ca(1)—O(1)和Ca(2)—O(2)形成离子键,H(4)—O(3)形成共价键,H(4)—O(2)形成氢键。
关键词:密度泛函理论;CaCO3(104)表面;乙酸;吸附机理
中图分类号:O647 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2019)05-1252-11
CHAI Rukuan1, LIU Yuetian1, YANG Li2, XIN Jing1, XU Wanli1, MA Jing1
(1. State key Laboratory of Petroleum Resources and Prospecting, China University of Petroleum, Beijing 102249, China;
2. Development Research Department, China National Offshore Oil Corporation Research Institute, Beijing 100028, China)
Abstract: To explore the adsorption mechanism of acetic acid on CaCO3(104) surface, the active sites of acetic acid, the electron transfer and chemical bond formation during the adsorption process were studied using density functional methods. The results show that the frontier orbital of acetic acid distributes over the heavy atom, in which O(1) atom is the reactive center. The most stable adsorption site is between hollow and short bridge sites, namely between two Ca atoms. The acetic acid is adsorbed in a dissociated state, in which the acetate tends to adsorb on the CaCO3(104) surface by a bridging bidentate mode and H(4) tends to form a hydroxyl groups with O(2) of CaCO3(104) surface. Meanwhile, there exist transfer of electrons and formation of chemical bonds between the acetic acid and the CaCO3(104) surface. Among them, Ca(1)—O(1) and Ca(2)—O(2) form ionic bond, H(4)—O(3) forms covalent bonds and H(4)—O(2) forms hydrogen bond.
Key words: density functional theory; CaCO3(104) surface; acetic acid; adsorption mechanism
近年来,有机物与方解石晶体反应机理研究引起广泛的关注,这是因为有机物与方解石晶体的相互作用涉及生物化学和地球化学等多个领域[1],直接影响晶体生长[2]、矿物浮选[3]和提高采收率[4]等过程。以提高采收率研究为例,原油作为有机混合物吸附于碳酸盐岩储层矿物表面,原油与方解石晶体的相互作用方式及强度直接决定储层润湿性以及润湿性改变的程度,进而影响油藏采收率[5-6]。因此,研究有机物与方解石表面的相互作用具有重要意义。SUBHAYU等[7]利用原子力显微镜研究不同组分对储层润湿性的影响,提出疏水反应影响非极性组分吸附造成润湿性反转;LIU等[8]借助化学力显微镜研究不同极性组分在疏水和亲水表面的吸附强度,提出二者对不同极性组分具有相反的吸附规律;王业飞等[9]研究了原油组分对石英表面润湿性的影响,提出沥青质吸附影响表面润湿性;陈晨等[10]研究了盐水组成对原油中酸、碱极性组分在石英表面吸附的影响,提出极性组分在石英表面的吸附机理。在实验研究中,由于尺度限制难以获得有机分子与矿物晶体表面作用过程中的物理化学反应的详细信息,如有机分子与晶体表面的成键特征、电子转移特征等,即不能在机理上解释吸附过程[11-12]。量子化学方法能够通过计算原油中的有机分子的前线轨道分布、吸附能和电荷转移等参数,分析分子的反应活性和吸附性质[13-16],从原子水平揭示有机分子与矿物晶体表面的相互作用,解释储层润湿性形成及变化的原因。SANCHEZ等[17]利用密度泛函理论研究了丙酸分子在方解石和白云石表面吸附机理,解释了低矿化度水驱机理;ALVIM 等[18]根据第一性原理研究了沥青在方解石表面的吸附机理;ATAMAN等[19-20]通过密度泛函理论研究羧酸类、醇类和醛类等在方解石表面的吸附,对比研究不同官能团吸附差异。当前的研究往往基于吸附能等参数评价不同组分的吸附强度,并未系统地分析不同组分与方解石表面之间具体电荷转移以及成键特征。本文作者基于密度泛函理论,从原子尺度解释乙酸在方解石表面的吸附机理。首先,通过前线轨道分析和分子局部反应活性分析确定乙酸活性吸附位点;而后,通过吸附构型、吸附能以及Mulliken电荷布居、体系态密度和电子局域函数等分析乙酸在方解石表面的稳定吸附构型和二者之间电荷转移以及化学键形成特征,探究乙酸在方解石表面吸附的微观机理。
1 计算模型及方法
采用Materials Studio中的CASTEP模块完成结构优化和能量计算,采用广义梯度近似(GGA)中的PW91[21]描述电子交换相关作用,采用超软赝势(USPP)[22]描述离子实与价电子之间的相互作用。选取平面波的截断能为400 eV,Brillouin区x,y和z这3个方向上K点数分别为4,4和3个,自洽场单原子的收敛标准设定为1.0×10-6 eV,所有计算均在倒易空间进行。几何构型优化采用Broyden-Fletcher- Goldfarb-Shanno算法,收敛标准如下:体系的总能量变化为1.0×10-5 eV,原子间最大作用力为0.3 eV/nm,原子最大位移为1×10-4 nm。模拟计算中有关原子赝势计算选择的价电子分别为Ca 4s2,O 2s22p4,C 2s22p2和H 1s1。利用上述计算参数对CaCO3晶体进行结构优化得到结构参数:晶体轴长 a=b=0.504 93 nm,c=1.720 02 nm;晶体轴角α=β=90°,γ=120°,这与文献[23]中的结果(a=b=0.503 nm,c=1.717 nm)和X线衍射实验结果(a=b=0.499 nm,c=1.706 nm)相符[24]。乙酸在长×宽×高为1.6 nm× 1.4 nm×2.0 nm的立方晶格中利用上述参数进行结构优化,结构示意图如图1所示。由图1可知:乙酸优化结构与文献[25-26]中的结果相符,验证了模拟计算参数选择的准确性。

图1 乙酸结构示意图
Fig. 1 Structural diagram of acetic acid
本文选择CaCO3晶体中结构最为稳定的(104)表面[27-29]进行研究。为保证足够大的吸附面积,构建具有周期性边界的表面积为1.619 nm×1.497 nm的超晶胞模型进行表面模拟。通过原子层数和真空层厚度测试,CaCO3(104)表面取4层原子,真空层厚度取为2 nm。表面模型的结构优化和能量计算采用与体相一致的交换关联函数、赝势方法、截断能和收敛标准。此外,在进行几何结构优化和能量计算时,冻结CaCO3 晶胞中最底部的2层原子作为衬底结构,其余2层原子和乙酸不固定并进行自由弛豫。
利用Dmol3模块在不施加任何对称性限制的条件下对完成优化的乙酸进行能量计算,计算其轨道属性、Mulliken电荷分布和Fukui指数。采用广义梯度近似(GGA)中的PBE描述电子交换相关作用,采用加极化函数展开的双数值基组(DNP)[30]处理价电子波函数,体系中所有原子进行全电子计算;热拖尾效应和实空间的截断半径分别为0.005 Ha和0.48 nm,用以加速收敛。自洽场中原子的收敛标准为1.0×10-6 eV/个。
2 乙酸最优构型及反应活性中心
2.1 分子前线轨道分布
分子的前线轨道[31-32]包括最高已占有轨道(HOMO)和最低未占有轨道(LUMO)。最高已占有轨道是分子中电子占据的最外层轨道,其能量表示分子提供电子的能力;最低未占有轨道是分子中电子未占据的最内层轨道,其能量反映分子得到电子的能力。根据前线轨道理论[33]:分子的许多性质取决于分子的前线轨道,化学反应中反应物间的相互作用仅发生在分子前线轨道之间,HOMO和LUMO决定分子的反应活性,因此,分子的前线轨道对分子间的化学反应有着至关重要的作用。
图2所示为乙酸前线轨道的等值面图(其中,EHOMO为最高占有分子轨道能量,ELUMO为最低未占有分子轨道能量)。由图2(a)可知:乙酸HOMO轨道主要出现在O(1)原子,而在C(1),O(2),H(1)和H(2)原子处分布较少;由图2(b)可知:LUMO轨道主要分布于O(1)原子和C(2)原子,C(1)和O(2)原子处分布较少,H(1)和H(2)原子处分布最少。由此可见,乙酸的前线轨道分布几乎覆盖了乙酸中的重原子。

图2 乙酸前线轨道的等值面图
Fig. 2 Frontier orbital isosurfaces of acetic acid
2.2 乙酸局部反应活性分析
通过上述对乙酸前线轨道分析可知:乙酸前线轨道覆盖了分子中的重原子。若确定分子的活性位点,则需要综合考虑乙酸中各原子的电荷分布情况、Fukui 指数以及各原子对分子前线轨道的贡献等参数[31-32,34]。
Fukui指数[35]表征分子中各个原子活性以及得失电子的能力,能够有效确定分子的局部反应活性位点。f +和f -分别为亲核Fukui指数与亲电Fukui指数,前者表征原子得到电子的能力,后者表征原子失去电子的能力。对于任一分子,组成分子的每个原子的前线轨道系数平方和与构成分子的所有原子的前线轨道系数平方和之比,即为该原子对分子相应前线轨道的贡献,其数值越大,表明贡献越大。
表1所示为乙酸中各原子的Mulliken电荷、Fukui指数及其对前线轨道的贡献。由表1可知:乙酸中O(1)原子带有的负电荷最多,f +和f -均较大,对HOMO和LUMO的贡献也较大,所以,O(1)原子既是亲电活性中心,又是亲核活性中心。O(2)原子带有一定负电荷,对HOMO和LUMO的轨道有一定的贡献,所以,O(2)原子带有一定的亲核和亲电特性。C(2)分子带有0.466 e的正电荷,f +较大,对LUMO轨道的贡献较大,所以,C(2)原子具有较强的亲核活性。
表1 乙酸中各原子的Mulliken电荷布居、Fukui指数及其对前线轨道的贡献
Table 1 Mulliken charge, Fukui exponent and the contribution to frontier orbital of each atom in acetic acid

综上可知,乙酸前线轨道分布于乙酸中的重原子之上,其中O(1)原子既是亲电活性中心又是亲核活性中心,所以,在乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面吸附过程中O(1)原子优先吸附于CaCO3表面。
3 乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面的吸附
通过本文第2节的分析可知乙酸的反应活性位点为O(1)原子。因此,以O(1)原子为反应位点构建乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面的4个高对称吸附位(顶位、穴位、短桥位和长桥位)的初始吸附构型,如图3所示。下面对体系结构优化进行研究并对能量进行计算。

图3 乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面不同高对称吸附位的初始吸附构型
Fig. 3 Initial adsorption configuration of acetic acid on different high symmetry adsorption sites of CaCO3(104) surface
3.1 乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面稳定吸附
3.1.1 吸附能分析
为了分析乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面不同高对称吸附位的稳定性,计算乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面的吸附能Eadsorption[22-24]:
Eadsorption=Etotal-(Eacetic-acid+ECaCO3(104)) (1)
式中:Eadsorption 为分子吸附能;Etotal为平衡吸附体系总能量;Eacetic-acid为乙酸单点能;ECaCO3(104)为清洁CaCO3(104)表面能量。其中,Eadsorption为负值,表示发生放热反应,吸附体系稳定;Eadsorption越小,表示吸附体系越稳定;Eadsorption为正值,表示发生吸热反应,吸附体系不稳定[13]。
表2所示为乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面的4个高对称吸附位的吸附能。由表2可知:乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面4个吸附位的吸附能从小到大依次为穴位、短桥位、长桥位和顶位。其中,乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面的穴位的吸附能最小,为-1.045 0 eV;短桥位吸附能次之,为-0.991 7 eV;长桥位的吸附能为-0.897 3 eV;顶位的吸附能最大,为-0.607 2 eV。由此可见,乙酸在顶位的吸附作用最弱,在穴位和短桥位的吸附作用较强且二者差距较小。因此,需要结合平衡吸附构型确定乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面最稳定吸附位。此外,乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面4种高对称位的吸附能均小于-0.62 eV[25],说明乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面为化学吸附,存在电子的交换和化学键的形成。
表2 乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面不同高对称吸附位的吸附能
Table 2 Adsorption energy of acetic acid on different high symmetry adsorption sites of CaCO3(104) surface Ev

3.1.2 平衡吸附构型分析
为进一步确定乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面的最稳定吸附位,结合体系平衡吸附构型对其进行分析。图4所示为乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面4个高对称吸附位(顶位、穴位、短桥位和长桥位)的稳定吸附构型。由图4可知:无论乙酸初始位于顶位、短桥位还是长桥位,体系达到新的平衡过程中乙酸都将在O(1)原子的牵引下向CaCO3(104)表面的穴位移动。最终,乙酸稳定吸附于CaCO3(104)表面的穴位和短桥位之间的位置,即2个Ca原子中间位置。

图4 乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面不同高对称吸附位的吸附平衡构型
Fig. 4 Equilibrium adsorption configuration of acetic acid on different high symmetry adsorption sites of CaCO3(104) surface
结合吸附能和吸附体系的平衡几何构型分析结果可知:乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面的最稳定吸附位在穴位和短桥位之间,即2个Ca原子之间。
3.2 吸附体系几何结构变化
统计乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面吸附前后二者几何结构的变化,分析吸附作用对乙酸和CaCO3(104)表面几何结构的影响。
表3所示为吸附前后乙酸几何结构的变化。由表3可知:乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面吸附前后的几何结构发生明显改变,其中C(2)—O(2)键长缩短0.003 9 nm;C(2)—O(1)键长拉长0.004 7 nm;O(1)—H(4)键长变化0.036 3 nm,被拉长至0.134 7 nm,远大于H和O原子半径之和0.098 0 nm,说明二者之间共价键已经断裂;与CaCO3(104)表面中O(3)新形成的O(3)—H(4)键长仅为0.110 9 nm,略大于0.098 0 nm,说明二者之间形成一定强度的共价键作用;C(1)—C(2)—O(1)和C(2)—O(1)—H(4)角度变化分别达到5.445°和5.138°。乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面吸附前后几何结构发生明显变化,说明二者之间的相互作用较强烈。
图5所示为CH3COOH/CaCO3(104)表面平衡吸附构型的几何结构图。由图5可知:体系稳定吸附构型中O(1)—Ca(1)和O(1)—Ca(1)的键长分别为0.265 8 nm和0.241 6 nm,这与Ca和O原子半径之和0.251 0 nm相近,说明O(1)—Ca(1)和O(1)—Ca(1)之间均形成一定强度的化学键,乙酸以双齿桥键合模式吸附于CaCO3(104)表面。
综上可知:乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面吸附过程中H(4)原子逐渐解离并吸附于CaCO3(104)表面O(3)原子之上形成羟基,羟基中H(4)原子和乙酸根中O(2)原子相互靠近形成氢键。与此同时,O(1)—Ca(1)和O(1)—Ca(1)之间均形成一定强度的化学键,乙酸根趋向于以双齿桥键合模式吸附于CaCO3(104)表面。
3.3 吸附体系电子结构变化
3.3.1 Mulliken电荷布居分析
Mulliken电荷布居[36]能够定量分析原子间的成键强弱,通过观察原子与原子间的电子云重新排布的情况,可以定性分析化学键的类型。通过分析乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面吸附前后的Mulliken电荷布居和成键布居的变化,得到乙酸与CaCO3(104)表面的成键以及电子的转移特征。

图5 平衡吸附构型的几何结构图
Fig. 5 Geometric structure of equilibrium adsorption configuration
表4所示为乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面吸附前后的Mulliken电荷布居,由表4可知:乙酸电荷布居由吸附前的-0.01 e变为吸附后的-0.21 e,即吸附过程中乙酸得到0.20 e。其中,H4原子得到0.11 e,电荷转移主要发生在s轨道;O(1)原子得到0.07 e,电荷转移主要发生在p轨道;C(2)原子得到0.03 e,主要发生在p轨道;O(2)原子失去0.03 e,C(1)得到0.05 e,H(1)失去0.01 e,H2和H3分别得到0.05 e和0.03 e。乙酸得到电子的同时CaCO3(104)表面失去等量的电子。其中,与乙酸临近的Ca(1)和Ca(2)原子分别失去0.01 e,与之对应的O(3),O(4)和O(5)分别失去0.04 e,0.01 e和0.01 e。统计4层CaCO3电荷布居数发现:4层原子总共失去0.20 e,每层电子转移程度差距较大。其中,第1层失去0.15 e,第2层失去0.23 e,第3层得到0.11 e,第4层得到0.07 e。因此,乙酸与CaCO3(104)表面发生相互作用促使CaCO3(104)表面失去电子,正电荷数增多,与此同时,乙酸得到电子,负电荷数增多。
为准确分析乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面吸附过程中二者之间成键特征,统计吸附前后体系的成键布居和键长变化,如表5所示。由表5可知:乙酸中成键布居和键长均发生较大变化。其中,C(1)—H(1)和C(1)—H(2)的成键布居分别增加0.01 e和0.02 e,键长变短,二者之间的共价键强度增大;C(1)—C(2)键布居增加0.03 e,共价键强度增大;C(2)—O(2)键布居从0.61 e增加到0.80 e,键长缩短0.004 75 nm,原子间相互作用增强;H(4)—O(2)的键布居数从0.49 e下降到0.26 e,键长伸长0.036 23 nm,吸附作用导致H(4)—O(2)共价键破裂转化为一定强度的氢键,乙酸发生解离吸附,这与几何结构分析结果一致;C(2)—O(1)成键布居由吸附前的1.10 e转变为吸附后的0.98 e,键长伸长0.038 6 nm,吸附作用导致C(2)—O(1) 之间相互作用减弱。CaCO3(104)表面的成键布居和键长同样发生明显变化。其中,Ca(1)—O(4)和Ca(2)—O(3)的成键布居分别降低0.06 e和0.07 e,同时键长分别伸长0.032 45 nm和0.005 7 nm,乙酸的吸附使CaCO3(104)表面的Ca—O离子键强度减弱。此外,吸附后新形成的H(4)—O(3)的成键布居为0.42 e,键长为0.110 93 nm,形成共价键作用较强的羟基。O(1)—Ca(1)成键布居为0.12 e,键长小于O(4)—Ca(1)和O(3)—Ca(2)的健长,仅为0.241 55 nm,即O(1)—Ca(1)形成强度较大的离子键,该键强度甚至强于CaCO3晶体内部部分Ca—O键强度。O(2)—Ca(2)键的布居数为0.10 e,键长为0.265 79 nm,二者之间形成一定强度的离子键。综上可知:乙酸吸附于CaCO3(104)表面过程中存在电子转移并伴随着分子内原有化学键结构的改变和新化学键的形成。
表3 吸附前后乙酸几何结构变化
Table 3 Changes of geometric structure of acetic acid before and after adsorption

根据平衡吸附体系的原子电荷布居和成键布居分析可知:乙酸吸附于CaCO3(104)表面过程中与CaCO3(104)表面原子之间存在电子交换和化学键的形成。吸附过程中乙酸发生解离,其中H(4)原子和CaCO3(104)表面的O(3)原子之间形成羟基[11,25],H(4)—O(2)共价键断裂转化为氢键。与此同时,乙酸根中的O(1)和O(2)原子与CaCO3(104)表面的Ca(1)和Ca(2)原子之间发生电子交换形成2个离子键。最终,乙酸根以双齿桥键合模式吸附于方解石表面,研究结果与体系几何结构分析结果一致。
表4 CH3COOH/CaCO3(104)表面吸附体系原子的Mulliken电荷布居
Table 4 Mulliken population of atoms in CH3COOH/CaCO3(104) adsorption system

表5 CH3COOH/CaCO3(104)表面吸附体系的Milliken成键布居
Table 5 Mulliken bonding population of CH3COOH/CaCO3(104) adsorption system
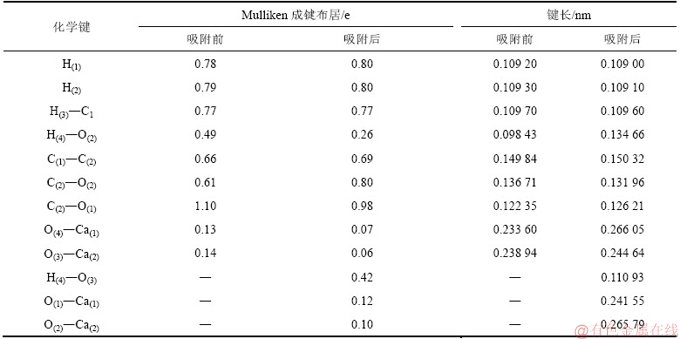
3.3.2 CH3COOH/CaCO3(104)表面吸附体系态密度
电子态密度[37]可以反映体系的电子结构及体系中各原子的电子态对总态密度的贡献,可定性分析体系中的电子杂化情况及掺杂效应,主要用于研究体系环境变化对其电子结构产生的影响。
通过对体系原子的电子态密度进行分析,研究乙酸与CaCO3(104)表面之间的成键本质。图6所示为乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面吸附前后的态密度。由图6可知:吸附前CaCO3(104)表面的最高占据态能量为-3.99~0.92 eV,主要是由O 2p和Ca 3d原子轨道贡献;吸附后体系最高占据态向深能级处移动约 0.7 eV,最高占据态能量为-3.29~0.36 eV。体系轨道能量降低、体系稳定性增强,说明乙酸已经与方解石晶体表面发生反应。此外,乙酸吸附后体系轨道在-17.0~22.83 eV和-37.24~39.32 eV处明显展宽并且伴随着态密度峰值不同程度地降低,表明吸附作用发生后体系能量降低,结构更加稳定。
图7所示为吸附体系中部分原子的分波态密度图。由图7可知:乙酸吸附于CaCO3(104)表面过程中CaCO3(104)表面的Ca和O原子以及乙酸中C,O和H原子的态密度均向深能级移动并伴随着态密度峰值降低。其中,O(3)和H(4)中态密度的变化最明显:O(3)向深能级移动1.39 eV,且其态密度峰值从15.85 eV下降到2.17 eV,H4态密度向深能级移动并伴随着态密度峰值从8.39 eV大幅度下降到0.46 eV。说明吸附作用发生时乙酸和CaCO3(104)表面的原子活性均不同程度地降低,体系稳定性增强。

图6 乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面吸附前后的态密度
Fig. 6 Total density of states of clean CaCO3(104) surface and CH3COOH/CaCO3(104) adsorption system
为了更深入地研究乙酸与CaCO3(104)表面的相互作用机理,分析乙酸中O(1),O(2)和H(4)原子和CaCO3(104)表面的Ca(1),Ca(2)和O(3)原子之间轨道分布特征。图8所示为平衡吸附体系中O(1)原子与Ca(1)原子的态密度。由图8可知:乙酸吸附于CaCO3(104)表面过程中,O(1)原子的2p轨道和Ca(1)原子的3d轨道在-8.2~0 eV重叠明显,即二者之间存在电子转移,形成一定强度的离子键。
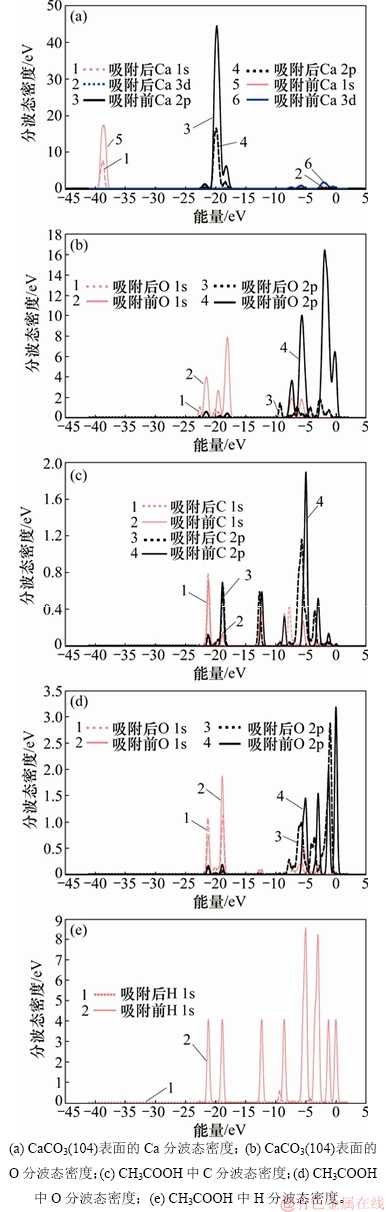
图7 乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面吸附前后部分原子的分波态密度图
Fig. 7 Partial density of states of atoms of acetic acid before and after adsorption on CaCO3(104) surface

图8 吸附体系中O(1)原子与Ca(1)原子的分波态密度
Fig. 8 Partial density of states of O(1) and Ca(1) in adsorption system
图9所示为吸附体系中O(2)原子与Ca(2)原子的态密度。由图9可知:乙酸吸附于CaCO3(104)表面过程中O(2)原子部分轨道与Ca(2)原子部分轨道存在明显的重叠即二者之间存在相互作用,形成一定强度的离子键。其中,O(2)原子的2p轨道和Ca(2)原子的3d轨道重叠明显,说明二者之间存在电子的转移和交换。

图9 吸附体系中O(2)原子与Ca(2)原子的分波态密度
Fig. 9 Partial density of states of O(2) and Ca(2) in adsorption system
图10为平衡吸附体系中O(3)原子与H(4)原子的态密度。由图10可知:乙酸吸附于CaCO3(104)表面过程中H(4)原子部分轨道与O(3)原子的部分轨道存在明显的重叠,说明二者之间形成一定强度的共价键。其中,H(4)原子的1s轨道和O(3)原子的2p轨道重叠明显。
通过对体系态密度分析可知:吸附作用发生后体系态密度向深能级移动约0.7 eV并且态密度峰值存在不同程度降低;乙酸吸附于CaCO3(104)表面过程中乙酸中的O(1),O(2)和H(4)的原子轨道分别与CaCO3(104)表面中的Ca(1),Ca(2)和O(3)原子轨道之间存在重叠并形成化学键。体系态密度分析结果与Mulliken电荷布居数分析结果一致。

图10 吸附体系中O(3)原子与H(4)原子的态密度
Fig. 10 Partial density of states of O(3) and H(4) in adsorption system
3.3.3 CH3COOH/CaCO3(104)表面体系电子局域函数
电子局域函数[38-39] (electron localization function, ELF,其变量用fELF表示)表征核外电子分布情况,用于描述原子间成键类型及性质。通过计算原子或分子中电子的核外分布,确定体系中电子近核区、结合成键区及孤对电子区分布,进一步分析化学键性质与类型。fELF范围为0~1.00,当0.75<fELF<1.00时,该区域电子呈现高度局域化,表现出较强的共价键;当 0.50<fELF≤0.75时,表现为金属键;当0<fELF≤0.50时,该区域为少电子区域,表现出较强的离子键。
图11所示为CH3COOH/CaCO3(104)稳定吸附体系的电子局域函数图。由图11(a)可得:乙酸的O(1)和O(2)原子以及Ca(CaCO3)表面的Ca(1)和Ca(2)原子之间的0<fELF<0.50为少电子区域,说明O原子和Ca原子之间形成一定强度的离子键。由图11(b)可见:乙酸的H(4)原子和O(2)原子之间电子云重叠微弱,fELF接近于0,结合键长可知二者之间的共价键已经断裂;与此同时,H(4)原子与CaCO3(104)表面的O(3)原子之间存在明显的电子云重叠,并且H(4)和O(4)的原子间距非常小,说明O(3)原子和H(4)原子之间形成一定强度的共价键,这与键布居数以及态密度分布分析结果一致。
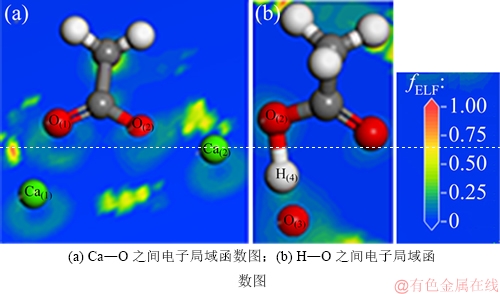
图11 CH3COOH/CaCO3(104)吸附体系电子局域函数图
Fig. 11 Electron localization function of CH3COOH/CaCO3(104) adsorption system
4 结论
1) 乙酸中O(1)原子既是亲电活性中心,又是亲核活性中心;O(2)原子带有一定的亲核和亲电特性。
2) 乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面的最稳定吸附位介于穴位与短桥位之间,即2个Ca原子之间;乙酸在CaCO3(104)表面发生解离吸附,其中H(4)原子和表面的O3原子之间形成羟基,伴随着H(4)—O(2)共价键断裂转化为氢键;与此同时,乙酸中的O(1)和O(2)原子以及CaCO3(104)表面的2个Ca(1)和Ca(2)原子之间发生电子交换形成离子键。最终,乙酸根以双齿桥键合模式吸附于方解石表面。
3) 乙酸吸附于CaCO3(104)表面过程中二者之间存在电子的转移和化学键的形成,其中,Ca(1)—O(1)和Ca(2)—O(2)形成离子键,H(4)—O(3)之间形成共价键,H(4)—O(2)之间存在氢键作用。
参考文献:
[1] AGUSTIN D A, MAURICIO M D, OSCAR G A, et al. Experimental-theoretical approach to the adsorption mechanisms for anionic, cationic, and zwitterionic surfactants at the calcite- water interface[J]. Langmuir, 2016, 32(11): 2608-2616.
[2] RICCI M, SEGURA J J. ERICKSON B W, et al. Growth and dissolution of calcite in the presence of adsorbed stearic acid[J]. Langmuir, 2015, 31(27): 7563-7571.
[3] 张国范, 张佰发, 石晴. 油酸钠在闪锌矿表面的吸附机理[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 48(1): 16-24.
ZHANG Guofan, ZHANG Baifa, SHI Qing. Adsorption mechanism of sphalerite by sodium oleate[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2017, 48(1): 16-24.
[4] UKRAINCZYK M, GREDICAK M, JERIC I, et al. Interactions of salicylic acid derivatives with calcite crystals[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2012, 365(1): 296-307.
[5] SAND K K, STIPP S L S. The interaction of ethanol and water with the {10.4} surface of calcite[J]. Langmuir, 2010, 26(18): 14520-14529.
[6] KARIMI M, MAHMOODI M, NIAZI A, et al. Investigating wettability alteration during MEOR process, a micro/macro scale analysis[J]. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces, 2012, 95: 129-136.
[7] SUBHAYU B, SHARMA M M. Investigating the role of crude-oil components on wettability alteration using atomic force microscopy[J]. SPE Journal, 1997, 4(3): 235-241.
[8] LIU Fanghui, YANG Hui, WANG Jingyao, et al. Salinity- dependent adhesion of model molecules of crude oil at quartz surface with different wettability[J]. Fuel, 2018, 223: 401-407.
[9] 王业飞, 徐怀民, 齐自远, 等. 原油组分对石英表面润湿性的影响与表征方法[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 36(5): 155-159.
WANG Yefei, XU Huaimin, QI Ziyuan, et al. Effects of crude fractions on quartz surface wettability and characterization method[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum(Edition of Natural Science), 2012, 36(5): 155-159.
[10] 陈晨, 董朝霞, 高玉莹, 等. 盐水组成对极性组分在石英表面吸附的影响[J]. 石油学报, 2017, 38(2): 217-226.
CHEN Chen, DONG Zhaoxia, GAO Yuyin, et al. Effects of brine composition on quartz surface absorption of polar components[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2017, 38(2): 217-226.
[11] 王进明, 王毓华, 余世磊, 等. 十二烷基硫酸钠对黄锑矿浮选行为的影响及作用机理[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 44(10): 3955-3962.
WANG Jinming, WANG Yuhua, YU Shilei, et al. Flotation behavior and mechanism of cervantite with sodium dodecyl sulfate[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2013, 44(10): 3955-3962.
[12] TORRES A, AMAYA S J, RODRIGUEZ R E, et al. Adsorption of prototypical asphaltenes on silica: First-Principles DFT simulations including dispersion corrections[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2018, 122(2): 618-624.
[13] LAZAR P, KARLICKY F, JURECKA P, et al. Adsorption of small organic molecules on graphene[J]. Journal of American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(16): 6372-6377.
[14] PAVLOVA T V, ZHIDOMIROV G M, ELTSOY K N. First- Principle study of phosphine adsorption on Si(001)-2×1-Cl[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2018, 122(3): 1741-1745.
[15] 龙朝辉, 丁静, 邓博华, 等. 锂离子电池负极材料NiSi2嵌锂性质的第一性原理研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 49(2): 323-329.
LONG Chaohui, DING Jing, DENG Bohua, et al. First-principle study of Li-insertion properties of NiSi2 as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2018, 49(2): 323-329.
[16] COSTA D, RIBEIRO T, CORNETTE P, et al. DFT Modeling of corrosion inhibition by organic molecules: carboxylates as inhibitors of aluminum corrosion[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2016, 120(50): 28607-28616.
[17] SANCHEZ V M, MIRANDA C R. Modeling acid oil component interactions with carbonate reservoirs: A First-Principles view on low salinity recovery mechanisms[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2014, 118(33): 19180-19187.
[18] ALVIM R S, LIMA F C D A, SANCHEZ V M, et al. Adsorption of asphaltenes on the calcite (10.4) surface by first-principles calculations[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(97): 95328-95336.
[19] ATAMAN E, ANDERSSON M P, CECCATO M, et al. Functional group adsorption on calcite: I. oxygen containing and nonpolar organic molecules[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2016, 120(30): 16586-16596.
[20] ATAMAN E, ANDERSSON M P, CECCATO M, et al. Functional group adsorption on calcite: II. nitrogen and sulfur containing organic molecules[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2016, 120(30): 16597-16607.
[21] PACHECO-KATO J C, DEL-CAMPO J M, GAZQUEZC J L, et al. A PW91-like exchange with a simple analytical form[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2016, 651: 268-273.
[22] HANSEL R A, BROCKA C N, PAIKOFF B C, et al. Automated generation of highly accurate, efficient and transferable pseudopotentials[J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2015, 196: 267-275.
[23] MEDEIROS S K, ALBUQUERQUE E L, MAIA F F, et al. Electronic and optical properties of CaCO3 calcite, and excitons in Si@CaCO3 and CaCO3@SiO2 core-shell quantum dots[J]. Journal of Physics D Applied Physics, 2007, 40(18): 5747-5752.
[24] REEDER R J. Crystal chemistry of the rhombohedral carbonates[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy & Chemistry, 1983, 11: 1-48.
[25] JONES R E, TEMPLETON D H. The crystal structure of acetic acid [J]. Acta Crystallographica, 2010, 16(7): 657-661.
[26] COCKS I D, GUO Q, PATEL R, et al. The structure of TiO2(110) (1×1) and (1×2) surfaces with acetic acid adsorption: A PES study[J]. Surface Science, 1997, 390(1): 135-139.
[27] SILVERSTRI A, BUDI A, ARTAMAN E, et al. A quantum mechanically derived force field to predict CO2 adsorption on calcite {10.4} in an aqueous environment[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2017, 121(43): 24025-24035.
[28] CHEN H, PANAGIOTOPOULOS A Z, GIANNELIS E P. Atomistic molecular dynamics simulations of carbohydrate- calcite interactions in concentrated brine[J]. Langmuir, 2015, 31(8): 2407-2413.
[29] 柴汝宽, 刘月田, 王俊强, 等. 第一性原理研究H2O分子在CaCO3(104)表面吸附[J]. 原子与分子物理学报, 2018, 35(6): 1075-1082.
CHAI Rukuan, LIU Yuetian, WANG Junqiang, et al. First principles study on the adsorption of H2O molecule on CaCO3(104) surface[J]. Journal of Atomic and Molecular Physics, 2018, 35(6): 1075-1082.
[30] METHFESSEL M, PAXTON A T. High-precision sampling for Brillouin-zone integration in metals [J]. Physical Review B, 1989, 40(6): 3616-3621.
[31] KOVACEVIC N, KOKALJ A. DFT study of interaction of azoles with Cu(111) and Al(111) surface: role of azole nitrogen atoms and dipole-dipole interactions[J]. Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115(49): 24189-24197.
[32] 吴刚, 郝宁眉, 廉兵杰, 等. 吡啶类缓蚀剂及其在AI(111)表面吸附行为的密度泛函理论分析[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(7): 2565-2572.
WU Gang, HAO Ningmei, LIAN Bingjie, et al. Density functional theory analysis on pyridine corrosion inhibitors and adsorption behavior on AI(111)surface[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering (China), 2013, 64(7): 2565-2572.
[33] MENDIZABAL F, CONTRERAS R R, AIZMAN A J. Introduction of external field effects in the frontier molecular orbital theory of chemical reactivity[J]. International Journal of Quantum Chemistry, 1992, 44 (S26): 751-760.
[34] INAGAKI S, FUJIMOTO H, FUKUI K. Chemical pseudoexcitation and paradoxical orbital interaction effect[J]. Journal of American Chemical Society,1975,97(21): 6108-6116.
[35] LI Yan, Evans J N S. The fukui function: A key concept linking frontier molecular orbital theory and the hard-soft-acid-base principle[J]. Journal of American Chemical Society, 1995, 117(29): 7756-7759.
[36] HUZINAGA S, NARITA S. Mulliken population analysis and point charge model of molecules[J]. Israel Journal of Chemistry, 2013, 19 (1/2/3/4): 242-254.
[37] HEREMANS J P, JOVOVIC V, TOBERER E S, et al. Enhancement of thermoelectric efficiency in PbTe by distortion of the electronic density of states[J]. Science, 2008, 321(5888): 554-557.
[38] TSIRELSON V, STASH A. Determination of the electron localization function from electron density[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2002, 351(1): 142-148.
[39] 王鑫洋, 陈念科, 王学鹏, 等. 物理截断与电子局域函数结合法研究非晶态结构中的原子成键[J]. 物理学报, 2016, 65(17): 173101-1-173101-6.
WANG Xinyang, CHEN Nianke, WANG Xuepeng, et al. Bonding nature of the amorphous structure studied by a combination of cutoff and electronic localization function[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2016, 65(17): 173101-1-173101-6.
(编辑 伍锦花)
收稿日期:2018-06-20;修回日期:2018-09-10
基金项目(Foundation item):国家科技重大专项(2017ZX05032004-002);国家重点基础研究发展规划(973计划)项目(2015CB250905);中国石油重大科技专项(2017E-0405)(Project(2017ZX05032004-002) supported by the National Science and Technology Major Program of China; Project (2015CB250905) supported by National Basic Research Development Program(973 Program) of China; Project(2017E-0405) supported by China Major Program of Petroleum Science and Technology)
通信作者:刘月田,博士,教授,从事油气藏开发及提高采收率机理研究;E-mail: lyt51@163.com

