


Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) 725-730
Mineralogical characterization of tin-polymetallic ore occurred in Mengzi, Yunnan Province, China
XU Yang-bao1, 2, QIN Wen-qing1, 2, LIU Hui1, 2
1. School of Minerals Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Biometallurgy of Ministry of Education, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 2 April 2011; accepted 15 July 2011
Abstract: A detailed mineralogical characterization of a tin-polymetallic ore from Mengzi, Yunnan Province, China, was undertaken by automated electron microprobe-based mineral mapping and quantitative analysis methods. The results show that the most valuable metal is Sn (0.98%, mass fraction). The main tin minerals are cassiterite and stannite, which account for 94.90% of total tin. Other metals, such as Cu (0.261%), Zn (0.612%) and Pb (0.296%) can also be seen as valuable metal to be recovered. Minerals such as pyrrhotite, pyrite, arsenopyrite, sphalerite, galena and chalcopyrite are disseminated in the ore. Quartz, sericite and dolomite are the main gangue. The optimal grinding fineness should be chosen as 0.037 mm to make sure that most of the tin minerals can be liberated from other minerals.
Key words: mineral characterization; tin minerals; cassiterite; stannite; particle size
1 Introduction
Tin is one of the earliest known metals in the history of world metallurgy [1]. With the development of history, tin becomes more and more important in human production and life [2]. China is an important tin productive country with most tin deposits being concentrated in south and southwest. The total tin reserves in Yunnan Province of China account for 28% of countrywide tin reserves. Previous mineralogical investigations showed that most of the tin occurs as cassiterite, while a fraction of tin occurs as stannite, kesterite, mawsonite, and other tin sulphides [3]. These tin sulphides have the similar behaviour to pyrite during the various stages of mineral processing [4]. Flotation is a cost-effective mineral processing method and is widely used to beneficiate sulphide minerals. Other methods, such as gravity concentration and magnetic separation [5], are also used to separate cassiterite from associated gangue minerals. However, recovery and concentrate grade by these methods are far from satisfaction [6]. Due to the reducing of high-grade ore in the world and increasing loss of mineral values during processing, it has become imperative to develop efficient and cost-effective processing routes to recover valuable minerals from ore [5,7,8]. However, it is not quite straightforward to process the ore, mainly because cassiterite as the main mineral of tin is fragile, and is easily overgound [9-11]. Fine cassiterite is difficult to recover by the methods mentioned above [12]. Other difficulties associated with this type of ore are linked to fine grain size, occurrence of minerals, and distribution in ore. Many earlier attempts have been made to develop techniques for concentration of fine cassiterite was limited to laboratory tests, which were lack of pilot plant study. Hence, the techniques met with very little commercial success. The problem lies in assuming the effectiveness of a technique irrespective of quality of the ore and lack of pilot plant study [13]. In other words, the characterization of the ore was not systematically investigated prior to processing of the ore. On this point, the present work involves sufficient characterization of the ore, which is essential for process selection through laboratory and pilot plant tests.
2 Experimental
In this work, a kind of ore from Mengzi, Yunnan Province, China, was investigated by chemical and mineralogical means. The ore was obtained from several deposits along the eastern margin of the basin on Bainiu Mountain. All of the samples represent composite prepared from ores collected during drill-core sampling programs. All the samples were examined by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD). Mineralogy was determined by collecting a series of maps showing the distribution of the elements. X-ray fluorescence (XRF) analyses of the bulk samples indicated the contents of different elements, and these elements were considered the minimum number required to delineate the major phases previously indicated by XRD analyses. Electron energy disperses spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy (Hitachi S-4000 equipped with the Kevex EDXA microanalysis system) were used for the mineral paragenesis and size distribution study [14,15]. It also allows us to identify areas of interest in the polished sections for further investigation. The mineral compositions were determined by EPMA analysis (CAMECA SX 50, France) [9].
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Chemical component of ore
Table 1 shows the result of multi-element analysis of the sample by X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy. The result indicates that the most valuable metal in the ore is Sn, while Cu, Zn and S can be used as the object of comprehensive utilization. Table 2 shows the result of chemical phase analysis of tin in the ore. It demonstrates that cassiterite and stannite are the main forms of tin mineral. The distribution rates of the two forms are 74.49% and 20.41% respectively. Tin in these two minerals accounts for 94.90%, which is the maximum theoretical recovery of tin.
Table 1 Element analysis of sample by X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (mass fraction, %)
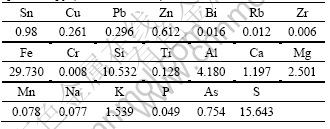
Table 2 Chemical phase analysis of tin in ore
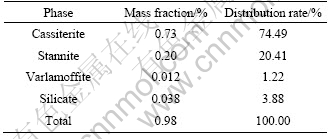
Table 3 Main mineral content in ore (mass fraction, %)
3.2 Mineral composition and content of ore
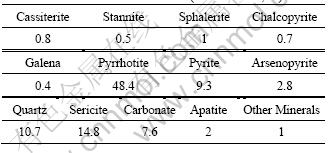
The fresh surface of the ores is gray black. The ores have veinlet and veinlet-disseminated structures. Because of high content of metal sulfides, the ores are compact and lumpy. Figure 1 shows the XRD pattern of raw ore. Table 3 shows the content of main minerals in the ores. Based on the analyses of XRD and SEM, cassiterite and stannite are the main forms of tin mineral while the content order of metal sulfides is pyrrhotite > pyrite > arsenopyrite > sphalerite > galena > chalcopyrite. There is also bismuthinite distributed sporadically in the ore. Gangue minerals are mainly quartz and sericite, with minor dolomite, ankerite, siderite, and chlorite.
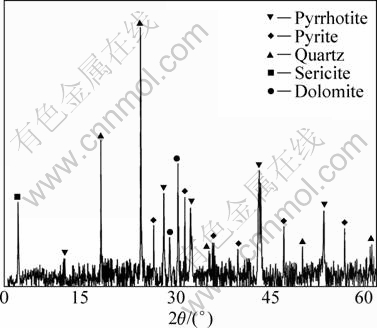
Fig. 1 XRD pattern of raw ore
3.3 Occurrence of main metallic minerals
3.3.1 Cassiterite
Figure 2 shows the SEM images of cassiterite combined with pyrrhotite. Cassiterite is the main mineral from which tin can be recovered. The mineral is unevenly distributed. It is relatively enriched in some part of the ores, and the volume content can reach 40% in a maximum. The cassiterite is euhedral column granular, light yellow or reddish brown in the transmitted light. Apart from individual crystal size up to 0.4 mm, most crystal size is smaller than 0.2 mm and some can even be smaller than 0.02 mm. Overall, most cassiterite in the ore shows disseminated output. According to the different patterns of embedding, it can be further divided into two patterns as the disseminated pattern and coated pattern. Cassiterite in disseminated pattern often fills along pyrite grain, while some distributes along the edge of sphalerite, pyrite or other metal sulfides, with little gangue minerals. Wraparound cassiterite which mainly distributes in the inner of pyrrhotite is not very close to the other metal sulfides, and it has the character like honeycomb of part enrichment. In these two embedded patterns of cassiterite, disseminated cassiterite can be found in a small number of ore blocks, while wraparound one distributes widely [3]. The ratio of mineral content is statistically about 40:60. Obviously, to recycle cassiterite from ore, the key point is to choose a proper grinding process to separate it from pyrrhotite completely. Figure 3 shows the result analyzed by EDS. It indicates that the chemical composition of cassiterite is stable and the impurity is mainly iron. There are 95.40% SnO2 and 4.22% FeO on average.
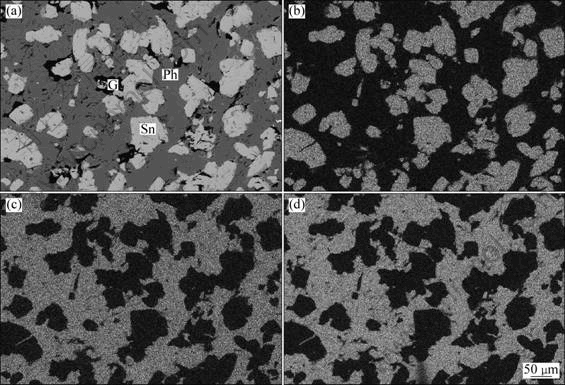
Fig. 2 SEM images of cassiterite combined with pyrrhotite: (a) Back-scattered electron image; (b) Sn element mapping; (c) Fe element mapping; (d) S element mapping (Ph—Pyrrhotite; G—Gangue)
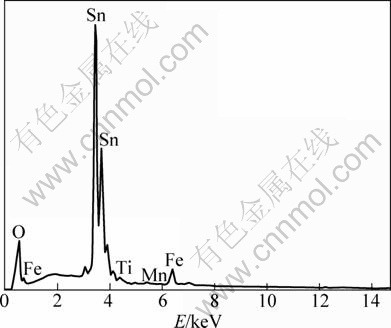
Fig. 3 EDS analysis of cassiterite in ore
3.3.2 Stannite
Figure 4 shows the image of irregular stannite disseminated in pyrrhotite in reflected light. By comparing with the cassiterite, there is fewer stannite in the ore, but it distributes more widely. In reflected light, it is grey or light green. Meanwhile, the double reflection and heterogeneity are distinct. Most of the stannite is in microgranular as the crystal size is usually smaller than 0.02 mm. The output form of stannite is similar to that of cassiterite. However, it has a higher degree of dispersion, and the particle size is relatively small. The intergrowth relationship with embedded mineral is complicated as it mainly presents as irregular serrated form. According to the difference of embedded mineral and dissemination distribution, it can be predicted that the degree of stannite liberation is lower than that of cassiterite under the same condition. Figure 5 shows the result by EDS.

Fig. 4 Image of irregular stannite disseminated in pyrrhotite in reflected light: St—Stannite; Ph—Pyrrhotite; G—Gangue
The result reveals that the chemical composition of stannite is stable. The contents of Cu, Fe and S are 27.90%, 12.46% and 32.3%, respectively. The average content of Sn is 28.13% in stannite, very similar to the theoretical value of Sn content in stannite.
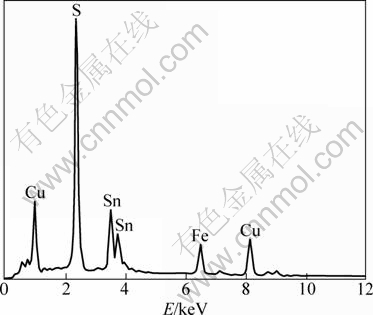
Fig. 5 EDS analysis of stannite in ore
3.3.3 Chalcopyrite
The distribution of chalcopyrite in the ore is not uniform as shown in Fig. 6. Chalcopyrite presents along voids or cranny with an irregular form. Some is scattered in the granular form with different sizes within massive pyrrhotite. Less can be seen as the fine veined aggregate by mixing with pyrrhotite filling along the crack of gangue. The relationship of chalcopyrite with galena and sphalerite is not very close. The particle size distribution is uneven. The diameter of coarse ones may be larger than 0.5 mm while the diameter of tiny ones is merely 0.02 mm. The common size is between 0.04 mm to 0.3 mm.
3.3.4 Galena
Galena is white in reflected light in this ore, as shown in Fig. 7. Apart from some tiny inclusion embedded in the pyrrhotite aggregate, most of the galena shows irregular granularity structure, or fine veined filling in the intergranule space, voids or crack of cataclastic pyrite and sphalerite. The particle size range is wide. Some coarse ones may be about 0.8 mm while the common size is smaller than 0.2 mm.
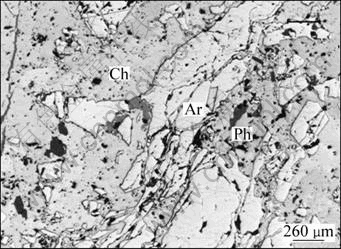
Fig. 6 Image of irregular chalcopyrite in reflected light: Ch—Chalcopyrite; Ph—Pyrrhotite; Ar—Arsenopyrite

Fig. 7 Image of irregular galena in reflected light: Ph—Pyrrhotite; Ga—Galena; G—Gangue
3.3.5 Sphalerite
Sphalerite is more widely distributed than chalcopyrite or galena in the ore, but it only exists in part of ore blocks. The isotropic body of sphalerite is caesious in reflected light, while it is bronze in transmission light. It indicates that there is higher content of ferrum in sphalerite. Figure 8 shows the image of irregular spalerite in reflected light. According to the particle size, sphalerite can be divided into two forms as fine size and microgranular size. The former is the main target mineral in zinc comprehensive recovery and enrichment. It exists in an irregular aggregate in the gangue or is embedded in pyrrhotite, pyrite and other metal sulfides. The particle size range is wide. Some coarse ones may be about 1.5 mm, while the common size is 0.05-0.5 mm. Microgranular sphalerite occurs less frequently, which accounts for about 5% of the total sphalerite. It is highly euhedral and mostly disseminates along the edge of pyrrhotite in the form of single crystals. Particles are commonly tiny, in the range of 0.02-0.05 mm. It is obvious that microgranular sphalerite is hard to liberate in milling process.
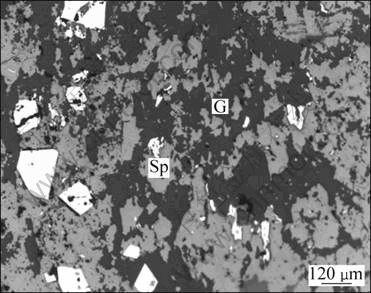
Fig. 8 Image of irregular spalerite in reflected light: Sp—spalerite; G—gangue
3.4 Particle size of tin minerals disseminated in ore
The composition and particle size distribution of valuable mineral play an essential role in determining the grinding fineness and the methods of mineral processing. Figure 9 shows the size distribution of tin mineral (cassiterite and stannite). It indicates that cassiterite and stannite in the ore are fine-grained. Compared with cassiterite, the size of stannite is finer. 76.77% of cassiterite is over 0.074 mm while only 62.46% of stannite is over 0.074 mm.
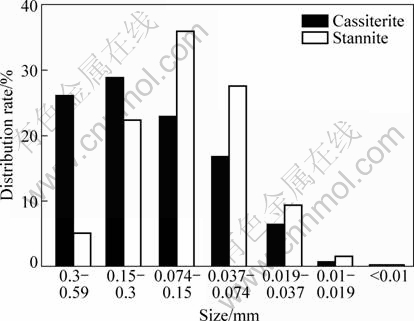
Fig. 9 Size distribution of cassiterite and stannite
In order to increase liberation, particles need to be broken as fine as possible. However, with decreasing particle size, energy costs substantially increase, and it becomes more difficult to separate fine particles. According to the analysis of size distribution [12], the optimal grinding fineness is chosen to be 0.037 mm to make sure that 90% of cassiterite and stannite can be liberated from other minerals.
4 Conclusions
1) The most valuable metal in the ore is Sn, while Cu, Zn and S can be used to synthetically recover. Cassiterite and stannite are the main forms of tin mineral existing in the ore. The distribution rates of the two forms are 74.49% and 20.41%, respectively. Tin in these two minerals accounts for 94.90%, which is the maximum theoretical recovery of tin.
2) The order of metal sulfides content is pyrrhotite> pyrite > arsenopyrite > sphalerite > galena > chalcopyrite. The ores have veinlet and veinlet- disseminated structures. Cassiterite and stannite in the ore are fine-grained dissemination.
3) In order to separate the tin mineral well from gangue, the optimal grinding fineness is chosen to be 0.037 mm.
References
[1] WANG Y W, WANG J B, WANG L J, CHEN Y Z. Tin mineralization in the Dajing tin-polymetallic deposit, Inner Mongolia, China [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2006, 28(4-6): 320-331.
[2] SREENIVAS T, PADMANABHAN N P H. Surface chemistry and flotation of cassiterite with alkyl hydroxamates [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2002, 205: 47-59.
[3] BENZAAZOUA M, MARION P, PINTO A, MIGEON H, WAGNER F E. Tin and indium mineralogy within selected samples from the Neves Corvo ore deposit (Portugal): A multidisciplinary study [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2003, 16(11): 1291-1302.
[4] ROSENQVIST J, MACHESKY M L, VLCEK L, CUMMINGS P T, WESOLOWSKI D J. Charging properties of cassiterite (r-SnO2) surfaces in NaCl and RbCl ionic media [J]. Interface Science, 2009, 25(3): 10852-10862.
[5] KLEIN B, ALTUN N E, GHAFFARI H, MCLEAVY M. A hybrid flotation–gravity circuit for improved metal recovery [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2010, 94(3-4): 159-165.
[6] CHEN G, TAO D, REN H, QIAO J K. An investigation of niobite flotation with octyl diphosphonic acid as collector [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2005, 76(1-2): 111-122.
[7] SOMARIN A K. Ore mineralogy and mineral chemistry of the Glen Eden Mo-W-Sn greisen-breccia system, eastern Australia [J]. Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences, 2009, 104(6): 339-355.
[8] RODRIGUEZ-SANTIAGO V, FEDKIN M V, WESOLOWSKI D J, LVOV S N. Electrophoretic study of the SnO2/aqueous solution interface up to 260 ° C[J]. Langmuir, 2009, 25(5): 8101-8110.
[9] GERMANN K, LODERS V, BANKS D. Late Hercynian polymetallic vein-type base-metal mineralization in the Iberian Pyrite Belt: Fluid-inclusion and stable-isotope geochemistry [J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2003, 38(8): 953-967.
[10] SRIVASTAVA M. Characterization and processing of iron ore fines of Kiriburu deposit of India [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2001, 61(2): 93-107.
[11] MAMONTOV E, VLCEK L, WESOLOWSKI D J, CUMMINGS, P T, WANG W, ANOVITZ, L M, ROSENQVIST J, BROWN C M, GARCIASAKAI V. Dynamics and structure of hydration water on rutile and cassiterite nanopowders studied by quasielastic neutron scattering and molecular dynamics simulations [J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2007, 111(11): 4328-4341.
[12] GAY S. A liberation model for comminution based on probability theory [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2004, 17(4): 525-534.
[13] FANDRICH R, GU Y, BURROWS D, MOELLER K. Modern SEM-based mineral liberation analysis[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2007, 84(1-4): 310-320.
[14] RATERRON P, CARPENTER M, DOUKHAN J C. A TEM investigation of experimentally annealed sillimanite: New constraints for the SiO2-Al2O3 join [J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 2000, 64(2): 247-254.
[15] POWNCEBY M, SPARROW G, FISHERWHITE M. Mineralogical characterization of Eucla Basin ilmenite concentrates—First results from a new global resource [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2008, 21(8): 587-597.
[16] OKI T. Calculation of degree of mineral matter liberation in coal from sink–float separation data [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2004, 17(1): 39-51.
云南蒙自某锡多金属矿的工艺矿物学
徐阳宝1, 2,覃文庆1, 2,刘 慧1, 2
1. 中南大学 资源加工与生物工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 生物冶金教育部重点实验室,长沙 410083
摘 要:通过以自动化电子探针为基础的矿物扫描和定量分析,研究云南某锡多金属矿的工艺矿物学。结果表明,矿石中锡(0.98%)为最有回收价值的金属,锡石和黝锡矿为锡的主要矿物,占锡总量的94.90%;其他金属,如铜(0.261%)、锌(0.612%)和铅(0.296%)可作为有价金属回收。磁黄铁矿、黄铁矿、毒砂、闪锌矿、方铅矿、黄铜矿等矿物呈浸染状分布在矿石中。石英、绢云母和白云石为主要的脉石矿物。选择0.037 mm作为最佳的磨矿细度以确保锡矿物的单体解离。
关键词:工艺矿物学;锡矿物;锡石;黝锡矿;粒度
(Edited by YUAN Sai-qian)
Foundation item: Project (50774094) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2010CB630905) supported the National Basic Research Program of China
Corresponding author: QIN Wen-qing; Tel: +86-731-88830884; Fax: +86-731-88710804; E-mail: qinwenqing369@126.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61237-5