
DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2021.05.028
生活水箱内封装相变材料超声波强化传热研究
庹晓糠1,严中俊1,王姜1,李水生2,俞准1,张国强1
(1. 湖南大学 土木工程学院,湖南 长沙,410082;
2. 中国建筑第五工程局有限公司,湖南 长沙,410014)
摘要:现有生活水箱中封装相变材料强化换热方法主要包括添加翅片或石墨等,这些方法会导致封装结构蓄能密度降低,且石墨等高导热剂会在蓄能过程中发生沉降等,为此,提出将超声波技术应用于生活水箱中封装相变材料,在不降低封装结构蓄能密度的同时,利用超声波在液态介质中会发生空化和声流效应的特性实现相变材料熔化过程的强化换热,并以当前应用最广泛的圆柱型结构封装相变材料为例,通过可视化实验分析其在不同热水温度和不同频率超声波下的强化传热性能。研究结果表明:超声波的应用可显著加快相变材料的熔化,且随着加热时间推移,超声波的强化作用更加明显;当加热温度为60 ℃时,与无超声波作用相比,28 kHz超声波作用下相变材料液相体积分数的强化效率可由10 min时的12.7%提升至95 min时的40.8%;就超声波频率而言,受空化作用发生频率和声压衰减作用的影响,单纯增加超声波频率并不会持续增加相变材料的熔化性能;当超声波频率从20 kHz增大为28 kHz和40 kHz时,相变材料完全熔化时间先减少再增大;热水温度升高会使液相相变材料温度升高和空化阈值降低,从而增强超声波的空化作用;当热水温度为55,58和60 ℃时,与无超声波作用相比,28 kHz超声波作用下相变材料完全熔化时熔化速率的强化效率分别为42%,44%和48%。
关键词:相变材料;生活水箱;超声波;频率;强化传热
中图分类号:TU83 文献标志码:A 开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID)
文章编号:1672-7207(2021)05-1673-08
Study on heat transfer enhancement of phase change material encapsulated in domestic water tank using ultrasound wave
TUO Xiaokang1, YAN Zhongjun1, WANG Jiang1, LI Shuisheng2, YU Zhun1, ZHANG Guoqiang1
(1. School of Civil Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China;
2. China Construction Fifth Engineering Bureau Co. Ltd., Changsha 410014, China)
Abstract: Existing methods for enhancing heat transfer of phase change material(PCM) encapsulated in domestic water tanks mainly include the addition of fins or graphite, but these methods reduce the energy storage density of the encapsulation, and sedimentation may occur during the melting process of the PCM for the high thermal conductivity additions such as graphite. In order to solve these problems, the ultrasonic wave which could generate effects of cavitation and acoustic streaming in the liquid medium was proposed to enhance the heat transfer of cylindrically encapsulated PCM in domestic water tanks without reducing its energy storage density. In order to evaluate its effect, a visualization experiment with different ultrasonic frequencies and different heating temperatures were conducted. The results show that the ultrasound wave significantly accelerates the melting rate of PCM, and its effect increases with the increase of the heating time. At the heating temperature 60 ℃, the enhancement efficiency of 28 kHz ultrasound wave on the liquid phase volume fraction of PCM is 12.7% at 10 min and 40.8% at 95 min compared to those without ultrasound. As for the ultrasonic frequency, under the influence of cavitation frequency and attenuation effect of sound pressure, the increase of the ultrasonic frequency does not necessarily result in the increase of the enhancement. As the ultrasonic frequency increases from 20 kHz to 28 kHz and 40 kHz, the complete melting time of PCM first decreases and then increases. In addition, the increase of heating temperature can increase the temperature of the liquid phase change material and decrease the effect of cavitation, benefiting the usage of the ultrasonic wave. When the heating temperatures are 55, 58 and 60 ℃, compared to the efficiency without ultrasonic wave, the enhancement efficiency of melting rate with 28 kHz ultrasonic wave are 42%, 44% and 48%, respectively, when the PCM is completely melted.
Key words: phase change materials; domestic water tank; ultrasonic wave; frequency; heat transfer enhancement
太阳能生活热水系统可以利用太阳能为用户提供生活热水,目前已在我国得到广泛应用。由于太阳辐射具有间歇性和不稳定性,导致太阳能热水系统热水供应和用户需求之间往往存在不匹配问题。在蓄热和放热过程中,相变材料具有温度恒定且相变潜热量大的特点,将其封装后应用于太阳能生活水箱中可通过错时用能有效解决上述不匹配的问题,同时可增大水箱蓄热密度并降低水温波动。然而,相变材料(如石蜡和有机酸等)导热系数较低,导致其封装后在水箱中应用时存在蓄放热速率较慢的缺点,往往难以满足实际需求,阻碍了其在工程实际中的应用和推广。针对该问题,国内外学者通常在封装结构内部添加翅片[1-3]以增加换热面积,或直接在相变材料中掺入石墨[4-5]和金属颗粒[6-7]等高导热剂以提高导热系数,从而实现强化传热。然而,添加翅片或高导热剂会增大封装相变材料的有效体积,从而降低其蓄热密度,且部分高导热剂如石墨等往往会在相变材料蓄放能过程中发生沉降,其长期传热强化效果难以保证。
不同于上述强化传热方法的机理,将超声波技术应用于液态介质时,可通过空化效应和声流效应等作用产生强化流体传热的效果。KIANI等[8]研究了超声波对铜球与乙二醇溶液单相对流传热的影响,并分析了声强和超声波换能器与铜球的距离对传热的影响,发现超声波所引起的空化效应和声流效应可强化单相对流传热,且传热效果随声强增加和超声波换能器与铜球之间的距离减小而增强。BARTOLI等[9]研究了超声波对浸没在蒸馏水中的铂丝在过冷沸腾条件下传热特性的影响,发现超声波可以在流体中引起湍流从而提高对流系数,使用超声波技术后的传热强化倍率可达到1.57。就封装相变材料在生活水箱中的应用而言,由于封装结构内四周相变材料在被加热时会同时熔化并在浮升力作用下产生自然对流运动,且对流传热在大部分熔化时间段内占据主导作用[10],将超声波技术应用于生活水箱中封装相变材料时也可通过空化效应和声流效应增强其熔化过程中的对流,从而实现强化换热。需强调的是,由于超声波可由超声波换能器在封装结构外部产生,将超声波应用于封装相变材料强化换热时可克服传统方法导致封装结构内蓄热密度降低或高导热剂容易沉降等缺点,是一种极具应用潜力的强化相变传热方法。
然而,迄今为止,尚未见相关文献就超声波对生活水箱内封装相变材料强化传热性能进行研究。考虑到相变材料的熔化特性与现有相关研究中其他液体介质有所不同,且超声波对生活水箱四周加热条件下封装相变材料的强化传热效果及不同因素(如超声波频率和热水温度)的影响尚不明确,有必要对上述问题进行深入研究,以实现超声波强化传热技术在相变蓄热生活水箱中的应用和推广。基于此,本文作者提出在生活水箱中采用超声波技术作为封装相变材料强化传热的方法,并以当前应用最广泛的圆柱型封装相变材料为例[11],通过可视化实验研究并对比分析超声波对相变材料固-液相界面的演变以及温度变化情况的影响。此外,考虑到超声波频率和热水温度对超声波产生的空化效应有很大影响,在上述研究基础上进一步探究超声波频率和热水温度对相变材料熔化性能的影响。
1 实验系统
1.1 实验装置
图1所示为本文所搭建的实验系统示意图。从图1可见该系统主要由恒温水箱(2个)、圆柱型封装相变材料、超声波装置、温度测量装置、相机以及数据采集终端组成,其中,恒温水箱由方形容器和电加热系统组成。方形容器边长为300 mm,为便于观察,其正面和背面的材质为玻璃,其余面为不锈钢;电加热系统包括容器底部功率为2 kW的环形电加热器、容器侧面的不锈钢铠装T型热电偶以及温度控制器,采用PID控制来保持水箱中水温恒定,控制精度为±0.5 ℃。将在进行圆柱型封装后,相变材料垂直放置于恒温水箱中。为便于观察,封装结构侧壁采用透明聚碳酸酯管(内径为76 mm,高为144 mm,厚度为2 mm),底部和顶部为不锈钢圆头封装。超声波装置由超声波发生器和超声波换能器组成,超声波换能器紧贴在封装结构底面并固定在水箱底部。为了测量相变材料在熔化过程中的温度变化,在封装结构中轴线上以30 mm间距均匀布置T1,T2和T3共3个T型热电偶测点。实验开始前采用冰水混合物统一对热电偶传感器进行标定,标定精度误差为±0.5 ℃。所有传感器均与数据采集仪(Agilent 34972A)连接以采集温度数据。考虑到月桂酸具有无毒、化学稳定性较强以及相变温度适中等优点,本文选用相变温度为43~45 ℃的月桂酸作为实验用相变材料。
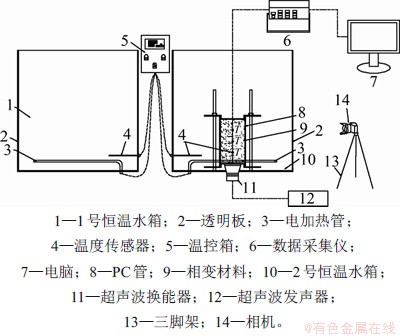
图1 实验系统示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of experimental system
1.2 实验工况及步骤
考虑到生活水箱热水温度设置在实际工程中往往有所不同,本文在参考相关技术标准和文献调研的基础上[12-13],选择55,58和60 ℃这3种常用的热水温度作为典型参数进行实验,分析不同水温对超声波性能的影响;同时,为了探究不同超声波频率对水箱中相变材料熔化过程的影响,在无超声波和现有相关文献研究中最常用的3种频率超声波(20,28和40 kHz)条件下[14],对圆柱型封装相变材料的熔化过程进行测试。具体实验步骤如下。
1) 实验开始前将圆柱型封装相变材料置于1号恒温水箱内。水箱中热水温度设定在25 ℃,静置24 h以保证相变材料的初始温度均匀一致且稳定在25 ℃。
2) 调节温控箱的设定温度,将2号恒温水箱中的水加热到指定温度(55,58或60 ℃),接着将1号恒温水箱中25 ℃的水换成2号恒温水箱中的水,再通过调节超声波发生器的开闭和频率来设定超声波的不同频率(无超声波,20 kHz,28 kHz或40 kHz),然后开始实验测试。
3) 通过Agilent 34972A多功能数字数据采集仪采集热电偶测量的温度,时间间隔为1 min,并记录在电脑终端;同时,用相机记录封装结构内相变材料在熔化过程中固-液相界面的变化,直至封装结构内的相变材料完全熔化为止。
2 结果和讨论
2.1 超声波对相变材料熔化过程的影响
为了研究超声波技术对圆柱型封装结构内相变材料熔化性能的影响,以60 ℃热水温度和28 kHz超声波频率工况为例,对未使用和使用超声波时的相变材料熔化过程中固-液相界面、液相体积分数以及温度变化进行对比分析。
2.1.1 相变材料固-液相界面和液相体积分数变化分析
图2所示为加热时间达到10,40,70和95 min时相变材料固-液相界面图和对应的由MATLAB边缘检测算法[15]计算出的液相体积分数。从图2(a)和图2(e)可见:当加热到10 min时,靠近容器加热壁面的固体相变材料由于离热源较近,其温度快速上升并熔化形成明显的液体层;此外,图2(a)中容器四周的液体层厚度基本相等,其原因是该液体层相变材料同时受到加热壁面和相变材料固体界面对其的黏滞力,从而处于静止状态(传热机制主要为热传导)。与图2(a)相比,图2(e)中底部液体层的厚度相对于顶部和侧面液体层的厚度明显较大,其原因是超声波换能器安装在封装结构的底部,从而底部液体层中的相变材料受到超声波的作用较强。需强调的是,在实验过程中观测到底部液相相变材料在超声波空化效应作用下产生大量微小气泡,这些气泡不断膨胀、压缩直至爆裂形成射流,从而增强了底部液相相变材料的自然对流和传热。就相变材料液相体积分数而言,其从无超声波时的15.0%提高到有超声波时的16.9%,超声波的相应强化效率为12.7%。

图2 有超声波和无超声波作用时相变材料固-液相界面随时间的变化
Fig. 2 Solid-liquid interface of phase change materials at different time with ultrasonic wave and without ultrasonic wave
随着加热时间延长,固体相变材料进一步熔化,液体相变材料的厚度增大,此时,液体相变材料由于密度差引起的浮升力克服了其受到的壁黏力,其传热方式从热传导开始向自然对流转变。在自然对流作用下,高温液相相变材料沿加热壁面向上运动,而低温液相相变材料沿固体相变材料壁面向下运动,液体相变材料的温度在竖直方向上出现温度分层,从而导致与侧面和底部液体层相比,顶部液体层的厚度较大,如图2(b)和(f)所示。值得注意的是,与图2(b)中的液体层厚度相比,图2(f)中除了底部液态相变材料层厚度明显较大外,侧面和顶部的厚度也稍大,这主要是因为超声波的空化效应和声流效应在促进底部自然对流的同时,也推动了底部的液相相变材料向上运动,促进了侧面和顶部固态相变材料的熔化。在这种作用下,加热到40 min时相变材料的液相体积分数从未使用超声波时的39.0%提高到47.5%,超声波的相应强化效率为21.8%。
从图2(c)和图2(g)可见:当加热到70 min时,在固体相变材料的顶部出现了弯曲的固-液相界面,说明此阶段液相相变材料的传热方式以自然对流为主;此外,固体相变材料底部出现了不规则的固-液相界面(图2(g)),这是因为超声波作用效果随距离增大而减弱,导致离底部越近(远)的相变材料温度越高(低),底部液相区出现明显的温度分层,在浮升力作用下,液相相变材料在底部液相区形成多个自然对流单元。在这些对流单元冲刷下,与对流单元接触的固体相变材料快速熔化,从而导致固体相变材料不均匀熔化。就相变材料液相体积分数而言,此时未使用超声波和使用超声波这2种情况下相变材料液相体积分数分别为58.2%和79.9%,超声波的相应强化效率为37.3%。
由图2(d)和(h)可见:当加热到95 min时,在超声波作用下相变材料已完全熔化,与无超声波作用下的液相体积分数71.0%相比,其液相体积分数提升了40.8%。
由上述分析可知,超声波可显著加快相变材料的熔化,且随着加热时间推移,超声波强化效果更加明显。导致该现象的主要原因是,在加热过程中,液相相变材料的自然对流运动随着液体层厚度的增大不断增强,而超声波主要是通过增强自然对流来强化传热,因此,其效果会随着熔化的进行得到增强。
2.1.2 相变材料温度变化分析
图3所示为在无超声波和有超声波作用2种情况下T1,T2和T3这3个热电偶测点的温度随加热时间的变化情况。由图3可见:由于各测点的初始温度低于相变材料的相变温度,加热初始阶段为固态显热加热阶段,各测点的温度均快速升高;当温度达到相变材料的相变温度时,相变材料开始熔化,其温度进入相变平台期;当相变材料完全熔化后,相变材料的加热过程变成液态显热加热阶段,温度又快速上升。值得注意的是,与无超声波作用情况相比,有超声波作用时3个测点的温度上升速度更快,且其相变平台期明显较短,T1,T2和T3这3个测点的相变平台期分别缩短71,26和9 min,熔化速率分别提升51.4%,28.2%和12.5%,其主要原因是超声波强化了液相区相变材料的自然对流,加速了固体相变材料与液体相变材料在固液界面上的传热,从而缩短了测点周围相变材料完成相变的时间。
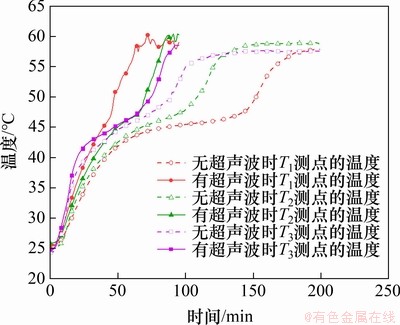
图3 有无超声波作用时不同测点温度变化
Fig. 3 Temperature change at different measuring points with and without ultrasonic wave
从图3还可看出:这3个测点中,超声波对底部测点T1的温度影响最大,其周围相变材料完成上述3个阶段的时间从180 min降低到62 min,经计算,熔化速率提升了65.6%,而顶部测点T3温度受到的影响最小,其完成时间从124 min降低到 88 min,熔化速率仅提升29.0%。考虑到超声波换能器安装在结构的底部且测点之间距离为30 mm,显然,超声波作用效果随距离增大而减弱较快。
2.2 不同频率超声波下相变材料液相体积分数变化
为了研究超声波频率变化对相变材料熔化性能的影响,在上述研究基础上,进一步对无超声波与20,28和40 kHz这3种频率超声波作用下的相变材料熔化过程液相体积分数随时间的变化进行比较,结果如图4所示。
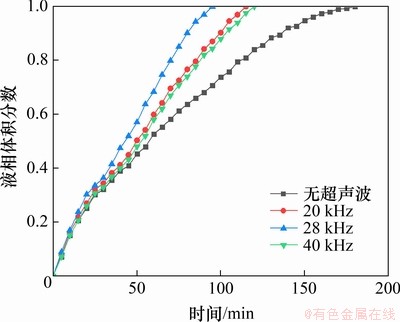
图4 不同超声波频率下液相体积分数随时间的变化
Fig. 4 Change of liquid volume fraction with time at different ultrasonic frequencies
由图4可见:就超声波作用下的熔化过程而言,在加热初始阶段,相变材料液相体积分数较低,超声波强化效果较弱,其液相体积分数-时间曲线与无超声波作用下的曲线基本重合;随着液相体积分数增大,超声波强化作用不断增强,该曲线与无超声波作用下的曲线开始分离,且其斜率明显大于无超声波作用下的曲线斜率。具体而言,当频率从20 kHz增加到28 kHz时,其曲线斜率增大,相变材料完全熔化时间(即液相体积分数达到1.0)从115 min降低到95 min,熔化时间降低17.4%;当频率从28 kHz增加到40 kHz时,其曲线斜率减小,相变材料完全熔化时间从95 min增加到120 min,熔化时间增加26.3%。
显然,随着超声波频率从20 kHz增大到40 kHz,超声波的强化效果先增大再减少;当频率从20 kHz增大到28 kHz时,随着频率增大,液相相变材料发生空化的频率加大,更多的气泡将在液相相变材料中产生,从而导致超声波的强化效果增强;当超声波频率从28 kHz增加到40 kHz时,尽管空化作用的频率增大,但由于超声波声压沿传播方向的衰减加快[16],离超声波换能器安装位置较远的液相相变材料由于声压降低到低于液相相变材料的空化阈值(空化阈值是克服液体的静压力和黏滞力发生空化的声压临界值,当超声波声压超过该阈值时,相应的液体就会发生空化效应[17]),液相相变材料发生空化作用的区域减少,从而导致超声波的强化效果下降。
由上述分析可知,受空化作用发生频率和声压衰减作用的影响,单纯增加超声波频率并不会使相变材料的熔化效率持续增加。需注意的是,相变材料的空化阈值与相变材料的黏滞力有关,因此,在工程实际中,应根据相变材料的具体性质选择合适的超声波频率,以提高超声波强化传热效果。
2.3 热水温度对超声波强化性能的影响
为了研究加热温度对超声波强化相变材料传热性能的影响,本文对热水温度分别为55,58和60 ℃,频率分别为20,28和40 kHz时的相变材料完全熔化时间进行比较,结果如图5所示。
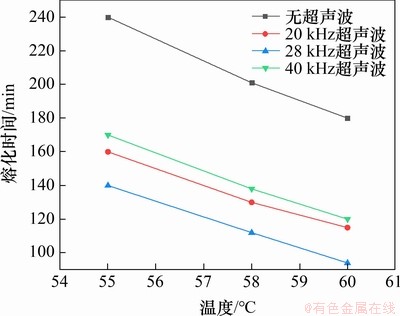
图5 完全熔化时间与热水温度的关系
Fig. 5 Relationship between complete melting time and water temperature
由图5可见:未使用超声波与使用20,28和40 kHz超声波时相变材料熔化时间-温度曲线基本平行,说明随着热水温度升高,与未使用超声波相比,在使用某一频率的超声波时相变材料完全熔化时间的减少量基本相等。此外,考虑到相变材料完全熔化时间随加热温度增大而减少,超声波对熔化速率的强化效率(即完全熔化时间减少量与无超声波作用下完全熔化时间之比)随加热温度升高而增大;当热水温度为55 ℃时,与不加超声波相比,28 kHz超声波频率下熔化速率的强化效率为42%;随着热水温度提高到58 ℃和60 ℃,该强化效率分别提升至44%和48%。其原因主要是热水温度升高会使得液相相变材料温度升高和空化阈值降低,从而增强超声波的空化作用[18]。
显然,通过提高热水温度可提高超声波传热强化效果。然而,值得注意的是,热水温度提高同时也会导致水箱与环境的热损失增大,因此,在实际应用过程中,应根据热源和环境温度合理选择加热温度,在避免热损失过大基础上获得较高的超声波强化效果。
3 结论
1) 超声波可增强自然对流,显著加快相变材料的熔化,且随着加热时间推移,液相相变材料的自然对流随着液体层厚度增大而加强,因此,其强化作用更加明显。当加热温度为60 ℃时,与无超声波作用相比,在28 kHz超声波作用下,相变材料液相体积分数的强化效率可由10 min时的12.7%提升至95 min时的40.8%;此外,随着距离增大,超声波的作用效果减弱较快,其强化效率从30 mm时的65.5%降低到90 mm时的29.0%。
2) 受空化作用发生频率和声压衰减作用的影响,单纯增加超声波频率并不会使相变材料的熔化性能持续增强。当超声波频率从20 kHz增大为28 Hz和40 kHz时,相变材料完全熔化时间先减少再增大。考虑到相变材料发生空化作用的阈值与其受到的黏滞力有关,在工程实际中,应根据相变材料的具体性质选择合适的超声波频率,以获得较好的超声波强化传热效果。
3) 热水温度升高会使得液相相变材料温度升高和空化阈值降低,超声波声压将更容易达到空化阈值,发生空化效应的区域也会相应增加,从而增强超声波的强化传热作用。当热水温度为55,58和60 ℃时,与无超声波作用相比,在频率为 28 kHz的超声波作用下相变材料完全熔化时熔化速率的强化效率分别为42%,44%和48%。考虑到热水温度提高同时也会导致水箱与环境的热损失增大,在实际应用过程中,应根据热源和环境温度情况合理选择热水温度,在避免热损失过大基础上获得较高的超声波强化效果。
4) 在本文工作基础上,未来将建立封装结构内超声波场、速度场、温度场等多物理场耦合数值模型,以进一步研究不同参数(如超声波功率、相变材料热物性及封装结构几何尺寸)和超声波换能器的安装位置、角度等对超声波强化性能的影响,从而为超声波强化传热方法在相变蓄热生活水箱的应用和推广提供依据。
参考文献:
[1] 朱子钦, 肖胜蓝, 施松鹤, 等. 相变材料在含翅片球形容器内的约束熔化传热过程[J]. 科学通报, 2015, 60(12): 1125-1131.
ZHU Ziqin, XIAO Shenglan, SHI Songhe, et al. Constrained melting heat transfer of a phase change material in a finned spherical capsule[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2015, 60(12): 1125-1131.
[2] BEEMKUMAR N, KARTHIKEYAN A, SARAVANAKUMAR B, et al. Performance improvement of D-sorbitol PCM-based energy storage system with different fins[J]. International Journal of Ambient Energy, 2018, 39(4): 372-376.
[3] VELRAJ R, SEENIRAJ R V, HAFNER B, et al. Experimental analysis and numerical modelling of inward solidification on a finned vertical tube for a latent heat storage unit[J]. Solar Energy, 1997, 60(5): 281-290.
[4] HEINZ A, STREICHER W. Application of phase change materials and PCM-slurries for thermal energy storage[C]// 10th International Conference on Thermal Energy Storage. Pomona, USA, 2006: 1-9.
[5] ZHANG Zhengguo, FANG Xiaoming. Study on paraffin/expanded graphite composite phase change thermal energy storage material[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2006, 47(3): 303-310.
[6] CHANDRASEKARAN P, CHERALATHAN M, KUMARESAN V, et al. Enhanced heat transfer characteristics of water based copper oxide nanofluid PCM(phase change material) in a spherical capsule during solidification for energy efficient cool thermal storage system[J]. Energy, 2014, 72: 636-642.
[7] EBADI S, HUMAIRA TASNIM S, ABBAS ALIABADI A, et al. Geometry and nanoparticle loading effects on the bio-based nano-PCM filled cylindrical thermal energy storage system[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2018, 141: 724-740.
[8] KIANI H, SUN Dawen, ZHANG Zhihang. The effect of ultrasound irradiation on the convective heat transfer rate during immersion cooling of a stationary sphere[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2012, 19(6): 1238-1245.
[9] BARTOLI C, BAFFIGI F. Effects of ultrasonic waves on the heat transfer enhancement in subcooled boiling[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2011, 35(3): 423-432.
[10] WU Yongke, LACROIX M. Melting of a PCM inside a vertical cylindrical capsule[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 1995, 20(6): 559-572.
[11] KENISARIN M, MAHKAMOV K. Solar energy storage using phase change materials[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2007, 11(9): 1913-1965.
[12] GB 50364—2018. 民用建筑太阳能热水系统应用技术标准[S].
GB 50364—2018. Technical standard for solar water heating system of civil buildings[S].
[13] XU Tianhao, CHIU J N, PALM B, et al. Experimental investigation on cylindrically macro-encapsulated latent heat storage for space heating applications[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2019, 182: 166-177.
[14] 李长达, 张伟, 李亚, 等. 超声波强化传热的研究进展[J]. 煤气与热力, 2016, 36(2): 7-12.
LI Changda, ZHANG Wei, LI Ya, et al. Research progress in enhancement of heat transfer by ultrasound[J]. Gas & Heat, 2016, 36(2): 7-12.
[15] 韩利利, 田益民, 齐千慧, 等. 基于MATLAB数字图像边缘检测算法的研究[J]. 北京印刷学院学报, 2019, 27(7): 98-101.
HAN Lili, TIAN Yimin, QI Qianhui, et al. Research on digital image edge detection algorithms based on MATLAB[J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Graphic Communication, 2019, 27(7): 98-101.
[16] 朱赞明. 大功率超声波防垢除垢系统的研究与设计[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2017: 41-42.
ZHU Zanming. Research and design of anti fouling system of high-power ultrasonic[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2017: 41-42.
[17] 荣兵兵. 基于超声技术的沉浸式换热器强化换热的研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2017: 8-9.
RONG Bingbing. Study on heat transfer enhancement of immersed heat exchanger based on ultrasonic technology[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2017: 8-9.
[18] 张鹏. 超声波对管板式换热器的强化传热试验研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2015: 30-34.
ZHANG Peng. Experimental study on heat transfer enhancement in tube-sheet heat exchanger by ultrasonic wave[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2015: 30-34.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期: 2020 -08 -10; 修回日期: 2020 -10 -21
基金项目(Foundation item):国家重点研发计划项目(2019YFD1101300) (Project (2019YFD1101300) supported by the National Key Research & Development Program of China)
通信作者:俞准,博士,教授,从事建筑耦合相变蓄能技术研究;E-mail:zhunyu@hnu.edu.cn
引用格式: 庹晓糠, 严中俊, 王姜, 等. 生活水箱内封装相变材料超声波强化传热研究[J].中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 52(5): 1673-1680.
Citation: TUO Xiaokang, YAN Zhongjun, WANG Jiang, et al. Study on heat transfer enhancement of phase change material encapsulated in domestic water tank using ultrasound wave[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2021, 52(5): 1673-1680.