DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2016.01.046
硫酸根自由基降解氟喹诺酮抗生素动力学模型构建
郭洪光1, 2,高乃云2,张永丽1,付垚1,何波辉3
(1. 四川大学 建筑与环境学院,四川 成都,610065;
2. 同济大学 水污染与控制国家重点实验室,上海,200092;
3. 四川省医学科学院 四川省人民医院,四川 成都,610072)
摘要:针对水环境中广泛残留的氟喹诺酮类抗生素污染问题,采用热激活过硫酸盐方式降解3种典型氟喹诺酮抗生素(环丙沙星、诺氟沙星、恩诺沙星),考察其在不同pH下的降解情况,构建相关自由基动力学氧化模型,并将数学模型与实验数据相耦合计算体系中特征自由基的浓度及目标物拟二级动力学反应常数。研究结果表明:建立的模型能够较好地描述氟喹诺酮微观反应动力学,反应体系中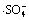 及·HO浓度受pH影响较大,环丙沙星、诺氟沙星、恩诺沙星与
及·HO浓度受pH影响较大,环丙沙星、诺氟沙星、恩诺沙星与 反应的二级动力学常数分别为6.96×107±2.31,2.52×107±4.47和8.55×107±1.98 L/(mol·s)。
反应的二级动力学常数分别为6.96×107±2.31,2.52×107±4.47和8.55×107±1.98 L/(mol·s)。
关键词:热激活;硫酸根自由基;氟喹诺酮抗生素;动力学模型;反应常数
中图分类号:X131.2 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2016)01-0338-06
Establishment and analysis of kinetic models for degradation of fluoroquinolones antibiotics by sulfate radical
GUO Hongguang1, 2, GAO Naiyun2, ZHANG Yongli1, FU Yao1, HE Bohui3
(1. College of Architecture and Environment, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610065, China;
2. State Key Laboratory of Pollution Control and Resources Reuse, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China;
3. Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences & Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, Chengdu 610072, China)
Abstract: To solve the pollution issue caused by the pervasive residual of fluoroquinolones antibiotics, thermally activated persulfate was used to degrade three typical fluoroquinolones (i.e., ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, enrofloxacin). The effect of pH on the degradation was investigated and kinetic oxidation models for free radicals were established. By coupling oxidation models with experimental results, the concentration of free radicals and the pseudo-second-order reaction constants for targets were calculated. The results show that the established high ordered equations can well describe the microreaction kinetics and pH has a significant effect on the concentrations of 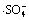 and ·HO. Meanwhile, the pseudo-second-order reaction constants with
and ·HO. Meanwhile, the pseudo-second-order reaction constants with 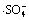 are 6.96×107±2.31,2.52×107±4.47 and 8.55×107±1.98 L/(mol·s) for ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and enrofloxacin, respectively.
are 6.96×107±2.31,2.52×107±4.47 and 8.55×107±1.98 L/(mol·s) for ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and enrofloxacin, respectively.
Key words: thermal activation; sulfate radical; fluoroquinolones; kinetic model; reaction constants
近年来, PPCPs(pharmaceuticals and personal care products)等新型环境污染物的迁移转化及其对生物所产生的毒害效应引起了人们的关注[1-4],其中大量用于人体及动物体的氟喹诺酮类抗生素在水环境中的残留受到了研究者的广泛重视[5-8]。研究表明,生活、工业及医药废水排放及农畜牧业的面源污染是造成氟喹诺酮类药物在水环境中“假持续”现象的主要原因[9-11]。世界上许多国家及地区在地表水及地下水中都检测到纳克及微克级别的氟喹诺酮类抗生素[4, 12-14]。而即使环境中较低浓度的该类抗生素,也会通过生物富集与内分泌干扰作用对人体健康以及整个生态系统构成长期潜在危害。由于氟喹诺酮类抗生素本身的抗药性和低浓度性使得现有常规水处理工艺对该类抗生素去除效果十分有限,因而亟需开发新型工艺以应对该类物质所产生的水环境污染[5, 15]。近年来,基于过硫酸盐激活的新型高级氧化工艺引起了水处理者的重点关注,其所产生的硫酸根自由基 (氧化还原电位E0=2.6~3.1 V)具有较强的氧化能力,使得其能够对环境中的多种有机物(如微囊藻毒素、2,4-二氯苯酚、阿特拉津、多氯联苯等)具有氧化降解作用[16-23]。然而,现行研究多集中于采用多种激活方式(热、光、波、过渡金属及活性炭等)考察该工艺对特定物质的降解效果及影响因素,对该工艺中的相关自由基生成及氧化模型鲜有报道。为此,本文作者采用热激活过硫酸盐方式降解水中3种典型氟喹诺酮抗生素,构建不同pH下基于自由基的氧化动力学模型,并以此计算该工艺体系中特定自由基的浓度与相关动力学常数,以期为该工艺的后续应用提供参考。
(氧化还原电位E0=2.6~3.1 V)具有较强的氧化能力,使得其能够对环境中的多种有机物(如微囊藻毒素、2,4-二氯苯酚、阿特拉津、多氯联苯等)具有氧化降解作用[16-23]。然而,现行研究多集中于采用多种激活方式(热、光、波、过渡金属及活性炭等)考察该工艺对特定物质的降解效果及影响因素,对该工艺中的相关自由基生成及氧化模型鲜有报道。为此,本文作者采用热激活过硫酸盐方式降解水中3种典型氟喹诺酮抗生素,构建不同pH下基于自由基的氧化动力学模型,并以此计算该工艺体系中特定自由基的浓度与相关动力学常数,以期为该工艺的后续应用提供参考。
1 实验
1.1 主要试剂
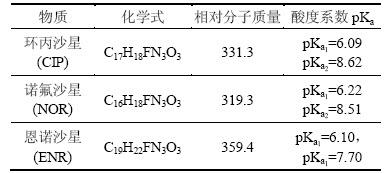
主要试剂有:盐酸环丙沙星(ciprofloxacin hydrochloride(CIP),质量分数>98%),诺氟沙星(norfloxacin (NOR),质量分数>98%),恩诺沙星(enrofloxacin (ENR),质量分数>98%),均购自日本TCI株式会社,其理化性质如表 1所示;分析用乙腈及甲醇,购自Sigma-Aldrich 公司;过硫酸钠、高氯酸、NaOH、硫代硫酸钠等,均采用分析纯(国药集团化学试剂有限公司),使用时未经进一步纯化。试验中所用溶液均采用Milli-Q 超纯水配置。
1.2 分析方法
根据实验要求设定水浴温度,采用0.1 mol/L的HClO4或NaOH调节200 mL抗生素储备液pH至设定值。加上聚四氟乙烯瓶塞后放入恒温水浴中预热30 min,并保持转速160 r/min,使溶液温度与水浴温度保持一致。根据试验设定向抗生素反应液中加入定量的过硫酸钠储备液,并同时开始计时,在固定时间节点上定时取样并迅速加入 100 μL CH3OH淬灭,在24 h内进行定性及定量分析。
表1 典型氟喹诺酮抗生素性质参数
Table 1 Properties of typical fluoroquinolone antibiotics
环丙沙星与诺氟沙星浓度分析采用先前研究方 法[6]进行分析,仪器为Waters e2695-2489高效液相色谱仪、UV/Vis紫外可见光检测器。使用Waters XBridgeTM C18反相色谱柱(填料粒径为3.5 μm,直径为4.6 mm,长度为150 mm),流动相为乙腈及体积分数为0.1%的甲酸水溶液,乙腈与甲酸体积比V(乙腈)/V(甲酸)=20/80,流速为0.8 mL/min,柱温为40 ℃,检测波长为280 nm,检测时间为10 min。
恩诺沙星浓度采用高效液相色谱串联质谱仪(LC-MS-MS)进行分析。使用Thermo Scientific C18反相色谱柱(填料粒径为5.0 μm,直径为2.1 mm,长度为100 mm);液相检测流动相为乙腈及体积分数为0.1%的甲酸水溶液,V(乙腈)/V(甲酸)=10 /90,流速为0.3 mL/min,柱温为40 ℃。样品进样量为 10 μL。质谱分析方法为:在正离子模式下(ESI+),采用二级碰撞解离模式,碰撞能量为19 eV,管径电压(Tube lens)为 131 V,载气为高纯氮气(纯度>99%),碰撞气为氩气(纯度为99.999%),碰撞气压为0.199 5 Pa;循环周期为5.0 s;采用SRM(选择离子)扫描模式,母离子质量数为360.20,特征子离子质量数为316.30,扫描时间为7 min,喷雾电压为3.5 kV,鞘气压力为2.8×105 Pa,毛细管温度及喷雾器温度分别为270 ℃和300 ℃。
2 不同pH下氟喹诺酮抗生素降解分析
作为典型的两性有机物,该类抗生素具有的喹诺酮基团及哌嗪基团可在不同的pH下分别具有酸性和碱性的电离特性,且在不同条件下溶液中的氧化活性物质并不相同[6]。基于此,首先考察pH对热激活降解氟喹诺酮抗生素的影响。试验中目标有机物初始浓度为0.013 mmol/L,反应温度为50 ℃,Na2S2 O8投加量与目标物摩尔比为80:1,分别考察在不同初始pH下对3种氟喹诺酮抗生素的降解影响,实验结果如图 1所示(其中,c(O, CIP/NOR/ENR)为CIP/NOR/ENR初始时刻浓度;c(t,CIP/NOR/ENR)为CIP/NOR/ENR t时刻浓度)。

图1 pH对热激活过硫酸盐降解氟喹诺酮抗生素的影响
Fig. 1 Effect of different initial pH on degradation by thermally activated persulfate
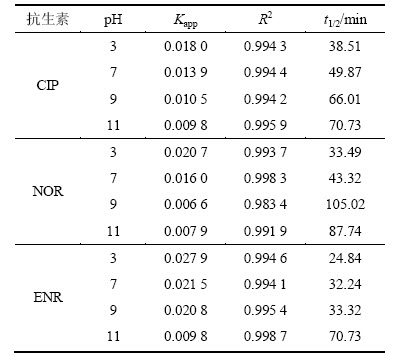
在不同pH(3,7,9和11)下热激活过硫酸盐降解氟喹诺酮抗生素的拟一级表观动力学常数Kapp、线性回归系数R2及反应半衰期T1/2如表 2所示。
表2 不同pH下氟喹诺酮抗生素降解的拟一级动力学模型拟合参数
Table 2 Fitting parameters of pseudo first-order kinetics model on degradation of fluoroquinolone antibiotics under different pH
3 氧化动力学模型的建立
基于 的高级氧化工艺在水中存在如下多个链式反应[16, 24-26]:
的高级氧化工艺在水中存在如下多个链式反应[16, 24-26]:
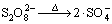 ,k1=5.7×10-5 s-1 (1)
,k1=5.7×10-5 s-1 (1)
 ,
,
k2=6.5×107 L/(mol·s) (2)
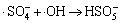 ,k3=1×1010 L/(mol·s) (3)
,k3=1×1010 L/(mol·s) (3)
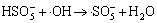 ,
,
k4=1.7×1010 L/(mol·s) (4)
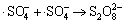 ,k5=3.1×108 L/(mol·s) (5)
,k5=3.1×108 L/(mol·s) (5)
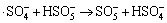 ,k6<105 L/(mol·s) (6)
,k6<105 L/(mol·s) (6)
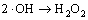 ,k7=5.5×10 9 L/(mol·s) (7)
,k7=5.5×10 9 L/(mol·s) (7)
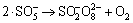 ,k8=1×108 L/(mol·s) (8)
,k8=1×108 L/(mol·s) (8)
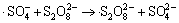 ,
,
k9=6.1×105 L/(mol·s) (9)
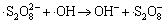 ,
,
k10=1.2×107 L/(mol·s) (10)
 ,
,
k11,CIP=(5.94±1.72)×109 L/(mol·s)
k11,NOR=1.00×109 L/(mol·s);
k11,ENR=(7.95±0.23)×109 L/(mol·s) (11)
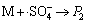 ,k12 (12)
,k12 (12)
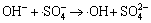 ,
,
k13 =6.5×107 L/(mol·s) (13)
式中:M代表水中存在的有机污染物;P1和P2代表其生成的产物。在有机污染物的存在下,中间态自由基使得反应动力学趋于复杂,但可以用拟一级动力学常数kapp来表征反应的表观速率及与底物反应的多种氧化剂的综合作用结果。kapp可以通过各种氧化剂的二级动力学关系得到:

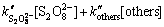 (14)
(14)
作者先前研究表明,过硫酸钠与氟喹诺酮药物在常温下不反应(数据未显示),而除 及·HO外的其他活性物质对该氧化体系的贡献亦较小,故3种氟喹诺酮类抗生素的降解速率可简化为
及·HO外的其他活性物质对该氧化体系的贡献亦较小,故3种氟喹诺酮类抗生素的降解速率可简化为

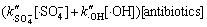 (15)
(15)
式中:“[ ]”表示浓度,mol/L。在酸性条件下, 在反应液中占主导作用[17, 27],故式(15)可以简化为
在反应液中占主导作用[17, 27],故式(15)可以简化为
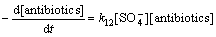 (16)
(16)
综合考虑反应液中的各种反应(式(1)~(13))及有效活性基团,Na2S2 O8、 浓度变化满足:
浓度变化满足:
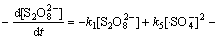
 (17)
(17)
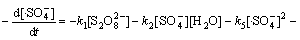
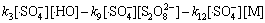 (18)
(18)
由于本实验中的Na2S2 O8均为过量(为底物浓度的80倍),在稳态条件下,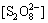 及
及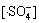 均为固定常数。且如前所述,在酸性条件下·HO参与反应的量很小,近似为0 mol/L,故式(17)与式(18)满足:
均为固定常数。且如前所述,在酸性条件下·HO参与反应的量很小,近似为0 mol/L,故式(17)与式(18)满足:
 (19)
(19)
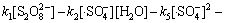
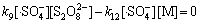 (20)
(20)
由式(19)和式(20)联立方程组解得到:
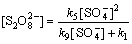 (21)
(21)
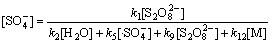 (22)
(22)
则式(16)可以转化为
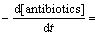
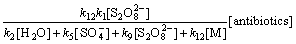 (23)
(23)
而在中性及碱性条件下,抗生素的降解速率满足
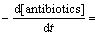
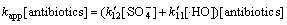 (24)
(24)
综合考虑反应液中的各种作用,Na2S2O8、 与·HO满足式(17),(18)及下式:
与·HO满足式(17),(18)及下式:

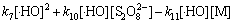 (25)
(25)
在稳态条件下,溶液中的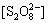 ,[
,[ ]及[·HO] 均为固定常数,即满足下式:
]及[·HO] 均为固定常数,即满足下式:
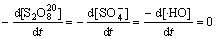 (26)
(26)
联立式(18)及式(25)可得到:
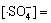
 (27)
(27)
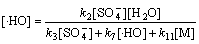 (28)
(28)
则式(24)可转化为
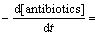

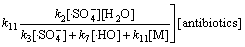 (29)
(29)
依据以上模型,根据式 (21),(22),(27)及式(28),按照不同pH下反应的表观速率常数试验值、Na2S2 O8初始浓度及抗生素浓度,可以间接计算不同工况条件下溶液中 及·HO的浓度和3种氟喹诺酮抗生素与
及·HO的浓度和3种氟喹诺酮抗生素与 反应的二级动力学常数。
反应的二级动力学常数。
以环丙沙星的氧化试验为例,在酸性条件下,试验初始Na2S2 O8浓度为1.04 mmol/L,反应温度为50 ℃,则根据式(21)可得
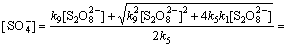 2.05×10-6 mol/L (30)
2.05×10-6 mol/L (30)
反应初始 10 min得到的环丙沙星初始表观速率常数kapp为0.0180 min-1=3×10-4 s-1,则有
 =3×10-4 (31)
=3×10-4 (31)
为保证Na2S2 O8浓度满足稳态条件,试验选取反应的前10 min作为研究对象。式中:[M]为10 min时的环丙沙星浓度,为0.0108 mmol/L。将k1,k2,k5,k9,k12及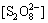 代入式(31)可得(酸性条件下k2[H2O]<2×10-3 s-1):k12=8.87×107 L/(mol·s)。
代入式(31)可得(酸性条件下k2[H2O]<2×10-3 s-1):k12=8.87×107 L/(mol·s)。
在碱性及中性条件下,其他条件保持不变,式(27)分母中的k2[H2O] 被k13[HO-]所替代,则根据式(27)及式(28)可知:
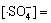
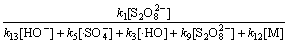 (32)
(32)
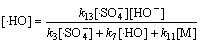 (33)
(33)
当pH=7.0时,反应初始 10 min得到的环丙沙星表观速率常数kapp=0.0139 min-1=2.32×10-4 s-1,则满足
2.32×10-4=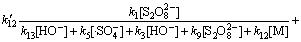
 (34)
(34)
将k1,k5,k7,k9,k11,k12,k13及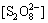 与t= 10 min时的[M]浓度代入式 (32)~(34)。其中[HO-]据溶液pH计算,采用Matlab 7.0编程和单变量法求解上述方程组可得到:
与t= 10 min时的[M]浓度代入式 (32)~(34)。其中[HO-]据溶液pH计算,采用Matlab 7.0编程和单变量法求解上述方程组可得到:
[ ] =3.66×10-8 mol/L;[·HO] =1.01×10-7 mol/L;
] =3.66×10-8 mol/L;[·HO] =1.01×10-7 mol/L;
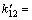 7.44×107 L/(mol·s)
7.44×107 L/(mol·s)
按照上述构建的数学模型,在不同pH下,3种氟喹诺酮类抗生素的自由基浓度[ ],[·HO]及
],[·HO]及 与有机物反应的动力学常数如表3所示。
与有机物反应的动力学常数如表3所示。
表3 不同pH下热激活过硫酸盐降解氟喹诺酮类抗生素的相关动力学参数
Table 3 Fitting parameters of fluoroquinolone antibiotics degradation ubder different pH by thermally activated persulfate

4 结论
1) 基于热激活过硫酸盐的新型高级氧化工艺下对水中的氟喹诺酮类抗生素具有较好的降解效果。
2) 酸性条件有利于抗生素的降解。通过高次数学方程组构建的动力学模型能够较好地阐释不同pH条件下反应体系中 与·HO的变化规律,将该模型与实验数据有效结合可分析并计算获得溶液中不同pH时相关自由基的浓度及目标抗生素的二级反应动力学常数。计算得出
与·HO的变化规律,将该模型与实验数据有效结合可分析并计算获得溶液中不同pH时相关自由基的浓度及目标抗生素的二级反应动力学常数。计算得出 ·氧化降解环丙沙星、诺氟沙星与恩诺沙星的二级反应动力学常数分别为6.96× 107±2.31,2.52×107±4.47和8.55×107±1.98 L/(mol·s)。
·氧化降解环丙沙星、诺氟沙星与恩诺沙星的二级反应动力学常数分别为6.96× 107±2.31,2.52×107±4.47和8.55×107±1.98 L/(mol·s)。
参考文献:
[1] WANG P, HE Y L, HUANG C H. Oxidation of fluoroquinolone antibiotics and structurally related amines by chlorine dioxide: reaction kinetics, product and pathway evaluation[J]. Water Research, 2010, 44(20): 5989-5998.
[2] YAN Shuwen, SONG Weihua. Photo-transformation of pharmaceutically active compounds in the aqueous environment: A review[J]. Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts, 2014, 16(4): 697-720.
[3]  , FERRANDO-CLIMENT L, RODRIGUEZ- MOZAZ S, et al. Degradation of pharmaceuticals in non-sterile urban wastewater by trametes versicolor in a fluidized bed bioreactor[J]. Water Research, 2013, 47(14): 5200-5210.
, FERRANDO-CLIMENT L, RODRIGUEZ- MOZAZ S, et al. Degradation of pharmaceuticals in non-sterile urban wastewater by trametes versicolor in a fluidized bed bioreactor[J]. Water Research, 2013, 47(14): 5200-5210.
[4] LINDBERG R H, OSTMAN M, OLOFSSON U, et al. Occurrence and behaviour of 105 active pharmaceutical ingredients in sewage waters of a municipal sewer collection system[J]. Water Research, 2014, 58: 221-229.
[5] WAMMER K H, KORTE A R, LUNDEEN R A, et al. Direct photochemistry of three fluoroquinolone antibacteria: norfloxacin, ofloxacin, and enrofloxacin[J]. Water Research, 2013, 47(1): 439-448.
[6] GUO Hongguang, GAO Naiyun, CHU Wenhai, et al. Photochemical degradation of ciprofloxacin in UV and UV/H2O2 process: kinetics, parameters, and products[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2013, 20(5): 3202-3213.
[7] STURINI M, SPELTINI A, MARASCHI F, et al. Photolytic and photocatalytic degradation of fluoroquinolones in untreated river water under natural sunlight[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2012, 119: 32-39.
[8] 郭洪光, 高乃云, 张永吉, 等. 水中环丙沙星的UV 及UV/H2O2光化学降解[J]. 沈阳工业大学学报, 2011, 34(4): 468-475.
GUO Hongguang, GAO Naiyun, ZHANG Yongji, et al. UV and UV/H2O2 photochemical degradation of ciprofloxacin in aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Shenyang University of Technology, 2011. 34(4): 468-475.
[9] BOXALL A B A, RUDD M A, BROOKS B W, et al. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the environment: what are the big questions?[J]. Environmental Health Perspectives, 2012, 120(9): 1221-1229.
[10] CALIMAN F A, GAVRILESCU M. Pharmaceuticals, personal care products and endocrine disrupting agents in the environment: A review[J]. Clean-Soil Air Water, 2009, 37(4/5): 277-303.
[11] GE Linke, CHEN Jingwen, WEI Xiaoxuan, et al. Aquatic photochemistry of fluoroquinolone antibiotics: kinetics, pathways, and multivariate effects of main water constituents[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(7): 2400-2405.
[12] VASCONCELOS T G, KLAUS K, HENRIQUES D M, et al. Ciprofloxacin in hospital effluent: Degradation by ozone and photoprocesses[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 169(1/2/3): 1154-1158.
[13] LI Bing, ZHANG Tong. Different removal behaviors of multiple trace antibiotics in municipal wastewater chlorination[J]. Water Research, 2013, 47(9): 2970-2982.
[14] RUTGERSSON C, FICK J, MARATHE N, et al. Fluoroquinolones and qnr genes in sediment, water, soil, and human fecal flora in an environment polluted by manufacturing discharges[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(14): 7825-7832.
[15] WEI Ruicheng, GE Fang, CHEN Ming, et al. Occurrence of ciprofloxacin, enrofloxacin, and florfenicol in animal waste water and water resources[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2012, 41(5): 1481-1486.
[16] ANTONIOU M G,DE LA CRUZ A A,DIONYSIOU D D. Degradation of microcystin-LR using sulfate radicals generated through photolysis, thermolysis and e- transfer mechanisms[J]. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2010, 96(3/4): 290-298.
[17] LIANG Chenju, SU H W. Identification of sulfate and hydroxyl radicals in thermally activated persulfate[J].Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2009, 48(11): 5558-5562.
[18] YANG Shiying, YANG Xin, SHAO Xueting, et al. Activated carbon catalyzed persulfate oxidation of azo dye acid orange 7 at ambient temperature[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2011, 186(1): 659-666.
[19] HAN Qiang, YANG Shiying, YANG Xin, et al. Cobalt catalyzed peroxymonosulfate oxidation: a review of mechanisms and applications on degradating organic pollutants in water[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2012, 24(1): 144-156.
[20] ANIPSITAKIS G P, DIONYSIOU D D. Transition metal/UV- based advanced oxidation technologies for water decontamination[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2004, 54(3): 155-163.
[21] AHMAD M, TEEL A L, WATTS R J. Mechanism of persulfate activation by phenols[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(11): 5864-5871.
[22] XIONG Xinmei, SUN Bo, ZHANG Jing, et al. Activating persulfate by Fe0 coupling with weak magnetic field: Performance and mechanism[J]. Water Research, 2014, 62: 53-62.
[23] FANG Guodong, GAO Juan, DIONYSIOU D D, et al. Activation of persulfate by quinones:free radical reactions and implication for the degradation of PCBs[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(9): 4605-4611.
[24] WOLS B A, HOFMAN-CARIS C H M. Review of photochemical reaction constants of organic micropollutants required for UV advanced oxidation processes in water[J]. Water Research, 2012, 46(9): 2815-2827.
[25] SANTOKE H, SONG Weihua, COOPER W J, et al. Free-radical-induced oxidative and reductive degradation of fluoroquinolone pharmaceuticals: Kinetic studies and degradation mechanism[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2009, 113(27): 7846-7851.
[26] HU Lanhua, STEMIG A M, WAMMER K H, et al. Oxidation of antibiotics during water treatment with potassium permanganate: reaction pathways and deactivation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(8): 3635-3642.
[27] LIANG Chenju, BRUELL C J, MARLEY M C, et al. Thermally activated persulfate oxidation of trichloroethylene(TCE) and 1,1,1-trichloroethane(TCA) in aqueous systems and soil slurries[J]. Soil & Sediment Contamination, 2003, 12(2): 207-228.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期:2015-01-10;修回日期:2015-03-08
基金项目(Foundation item):国家科技重大专项(2012ZX07403-001);四川省环保科技计划项目(2013HB08);中央高校基本科研业务费资助项目(2082604184026) (Project(2012ZX07403-001) supported by the National Major Project of Science & Technology of China; Project(2013HB08) supported by Sichuan Provincial Environment Protection Office; Project(2082604184026) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities)
通信作者:高乃云,教授,博士生导师,从事水处理理论与技术等研究;E-mail: gaonaiyun@sina.com