文章编号: 1004-0609(2006)07-1184-06
纳米Ti(CN)基金属陶瓷烧结过程中的组织结构演变
周书助1, 2, 王社权2, 王零森2, 丁泽良1
(1. 湖南工业大学 无机非金属材料工程技术湖南省重点实验室, 株洲 412007;
2. 中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室, 长沙 410083)
摘 要: 用分段真空烧结、 背散射扫描电镜、 透射电镜和能谱分析等手段研究纳米Ti(CN)基金属陶瓷在烧结过程中的组织结构演变。 结果表明: 纳米Ti(CN)粉末金属陶瓷在1200℃以后开始发生剧烈的固相反应, 纳米Ti(CN)粉末与M反应形成富M (M=Mo, W, Ta)的(Ti, M)(CN)固溶体为核, 贫M的(Ti, M)(CN)固溶体为环的“亮芯黑环结构”, 在1350℃即可获得致密的合金。 而微米金属陶瓷中Ti(CN)粉末颗粒很少参与固溶反应而成为核, 富钨和富Mo的固溶体为环, 形成“黑芯亮环结构”, 烧结温度在1400℃以上才能获得致密合金。
关键词: 纳米Ti(CN); 金属陶瓷; 显微组织; 演变
中图分类号: TG148 文献标识码: A
Evolution of microstructure of
nano-Ti(CN) base cermets in sintering
ZHOU Shu-zhu1, 2, WANG She-quan2, WANG Ling-sen2, DING Ze-liang1
(1. Key Laboratory of Inorganic and Nonmetal Materials Engineering Technology of Hunan Province,
Hunan Industry University, Zhuzhou 412007, China;
2. State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University,
Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Using SEM/BSE, TEM/EDX and vacuum sintering in step temperature, the evolution of the microstructure of nano-Ti(CN) base cermets in sintering process was studied. The result indicates that nano-cermets begin solid state reaction acutely at 1200℃, nano-Ti(CN) powder reacts with Mo to form (Ti, M)(CN) solid solution which is rich in M (M=Mo, W, Ta) and is the core of surrounding structure, (Ti, M)(CN) which is poor in M is the rim, it is “bright core dark rim surrounding structure”. The dense nano-cermets can be gained at 1350℃. But the micron-Ti(CN) powder grains take part in solid reaction rarely and become core of surrounding structure, the solid solution which is rich in W and Mo is the rim, it is “dark core bright rim surrounding structure”. The dense micro-cermets can be gained above 1400℃.
Key words: nano-Ti(CN); cermets; microstructure; evolution
Ti(CN)基金属陶瓷以其较高的化学稳定性, 抗粘结磨损能力, 在高速切削条件下显示出优异的性能, 是钢材高速精加工和半精加工较为理想的刀具材料[1-4]。 同时, Ti(CN)基金属陶瓷的原料和组织结构远比一般硬质合金的成分复杂, 而这些成分在烧结过程中发生复杂的反应和变化[5-8]。 粗颗粒的金属陶瓷更易于产生更多的裂纹, 由于其不均匀的结构和较高的孔隙, 因此, 它的韧性较差[9]。 尽管微米金属陶瓷原料粉末经过强化球磨破碎, 粒度可以细化, 但微米Ti(CN)粉末的破碎主要以解理破碎为主, 混合料中Ti(CN)硬质相粉末粒径多数在1μm以上, 个别的达到3~4μm。 造成金属陶瓷合金组织结构的不均匀, 组织中出现很多条状和片状Ti(CN)芯部。
与较粗Ti(CN)基金属陶瓷相比, 纳米Ti(CN)、 WC的位错密度比传统尺寸原料粉末颗粒低, 没有夹杂, 纳米Ti(CN)基金属陶瓷表现出更加均匀的结构。 纳米复合物在粘结相中具有更高的W含量和C含量, 增加了粘结相的体积比, 而粘结相钴中具有更高的FCC/HCP比例, 强化了粘结相。 由于细化的结构和强化的粘结相, 其硬度的增加并不进一步降低它的断裂韧性[10, 11]。 纳米粉体以其奇特的表面效应和尺寸效应, 表现出与微米粉体完全不同的烧结特性。 要想获得优异的合金性能, 必须对金属陶瓷组织结构中的环形结构进行设计[12]。 因此, 研究纳米Ti(CN)基金属陶瓷在烧结过程中显微组织结构的演变具有十分重要的意义。
1 实验
为了更好研究纳米Ti(CN)原料粉末的烧结性能, 以微米Ti(CN)原料粉末的烧结性能为参考, 进行对比研究。 分别以等离子体气相法生产的纳米Ti(CN)粉末和以碳(氮)热还原法生产的微米Ti(CN)粉末为主要成分, 它们的颗粒形貌见图1。 按50%Ti(CN)+10%WC+10%TaC+10%Mo2C+10%Co+10%Ni分别配成两种混合料。 原料粉末经球磨混合, 压制成试条。 将2种试条压坯经脱胶后, 分别在600、 800、 900、 1000、 1100、 1200、 1250、 1300、 1350、 1400、 1450、 1520℃下烧结, 并保温1h。 用背散射扫描电镜分别观察在不同烧结温度下合金的组织结构。

图1 Ti(CN)粉末的形貌
Fig.1 SEM images of Ti(CN) powders
2 结果与分析
从图1可以看出, 纳米Ti(CN)粉末的平均粒径为50~100nm, 粒度均匀且基本为球形。 微米Ti(CN)粉末的平均粒径为1.5μm左右, 粒度分布比较宽。 分别用纳米Ti(CN)粉末和微米Ti(CN)粉末为主要原料制备的两种混合料, 混合料压坯分别在不同温度下烧结后合金的显微组织见图2和图3。
由于背散射电子对原子序数十分敏感, 样品上原子序数较高的区域中由于收集到的背散射电子数量较多, 图像就越亮, 故利用背散射电子进行形貌分析, 可以观察出组织结构中成分的变化。 从图2不同烧结温度下纳米Ti(CN)基金属陶瓷的组织结构, 来分析纳米Ti(CN)基金属陶瓷刀具材料的组织结构演变过程。 在1100℃以前, 原子扩散比较慢, 压坯收缩很小, 压坯基本上没有强度而不能制作出理想电镜试样, 在1200℃时, 由于原子扩散加速, 纳米金属陶瓷压坯已开始收缩, 压坯开始有一点强度。 图2(a)中只有粘结相、 埋在粘结相中的纳米Ti(CN)颗粒和纳米WC-Co复合粉团粒。 WC在1250℃开始消失, 图2(b)中, 原子扩散加速, 收缩加快, 开始看到明显的固溶反应, 部分纳米Ti(CN)颗粒的颜色变灰, 或接近消失, 并开始出现颗粒边界层。 图2(c)中, 在1300℃时, 液相还没有出现, 但固相反应(1)~(4)早已发生。 由于粘结相并非纳米颗粒, 很多粘结相颗粒仍然单独存在。 但原子扩散加速, 在纳米Ti(CN)颗粒周围已经形成一层很薄的扩散层。

在1300~1350℃之间, 发生的变化最大, 液相出现, 原子在液相中的扩散速度大于在碳化物中的扩散速度几个数量级。 固相反应式(1)~(5)的反应产物(Mo, Ti)C、 (Ti, W)C、 (Ti, Ta)C、 (Ti, W, Ta, Mo)C中的小颗粒优先溶解, 反应(4)加速, 贫Mo、 W、 Ta的(Ti, Mo, W, Ta)(CN)相首先在未溶解的富Mo、 W、 Ta的(Mo, Ti)C、 (Ti, W)C、 (Ti, Ta)C、 (Ti, W, Ta, Mo)C颗粒表面析出, 随着Ti(CN)、 (Mo, Ti)C、 (Ti, W)C、 [CM(22](Ti, Ta)C、 (Ti, W, Ta, Mo)C颗粒不断溶解和
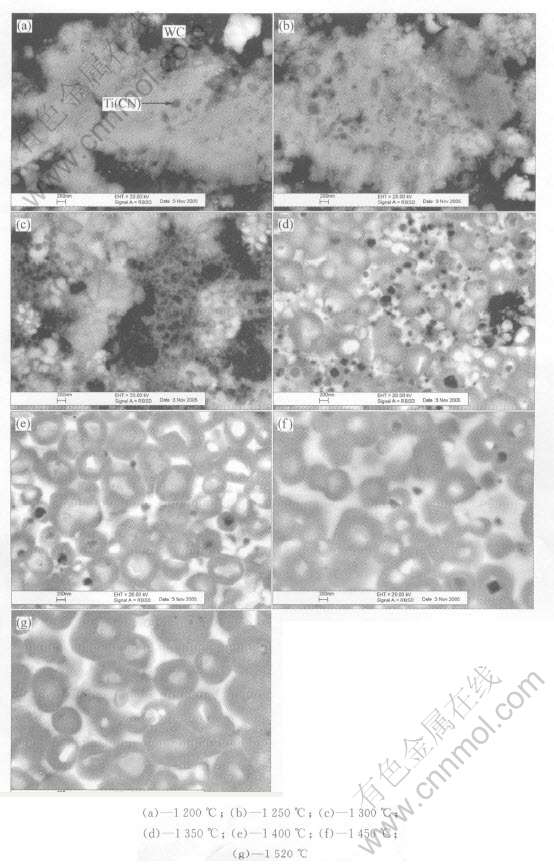
图2 纳米Ti(CN)基金属陶瓷混合料压坯经不同温度烧结后组织结构的演变过程
Fig.2 Microstructural evolution of nano-Ti(CN) base cermets green compacts after sintering at different temperatures
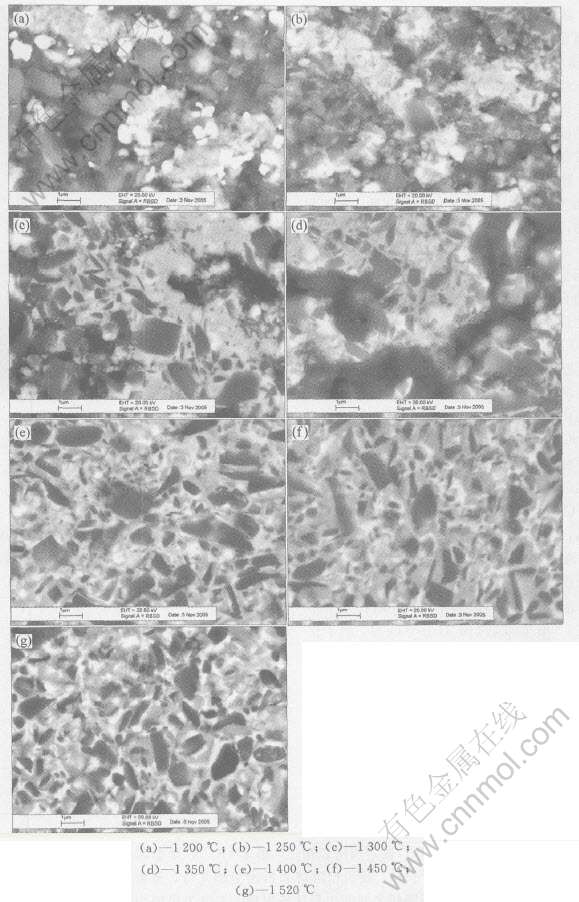
图3 微米Ti(CN)基金属陶瓷混合料压坯经不同温度烧结后组织结构的演变过程
Fig.3 Microstructural evolution of micro-Ti(CN) base cermets green compacts after sintering at different temperatures
贫Mo、 W、 Ta的(Ti, Mo, W, Ta)(CN)相析出, 包围大的未溶解的(Mo, Ti)C、 (Ti, W)C、 (Ti, Ta)C、 (Ti, W, Ta, Mo)C颗粒, 使之与液相隔开, 亮芯黑环结构析出。 另一方面, 如果析出的贫Mo、 W、 Ta的(Ti, Mo, W, Ta)(CN)相在((Mo, Ti)C、 (Ti, W)C、 (Ti, Ta)C、 (Ti, W, Ta, Mo)C颗粒一个有利成核位置成核, 或者以少数未溶解的Ti(CN)为有利成核位置, 在冷却过程中, 富Mo、 W、 Ta的液相形成富Mo、 W、 Ta的(Ti, Mo, W, Ta)(CN)亮环, 围绕贫Mo、 W、 Ta的芯或Ti(CN)芯, 亮环黑芯形成[13], 认为有不到20%的Ti(C, N)未溶解[14], 见图2(d)。 在1350℃以后, 从图2(e)~(g), 原子扩散, 溶解析出更充分, 组织结构更加均匀, 贫Mo、 W、 Ta的芯或Ti(CN)芯基本上消失。 在纳米原料粉末体系中可以固溶更多的WC、 TaC和Mo2C, 形成了细而均匀、 球形的晶粒结构和高体积分数的环形相[15]。
同样, 从图3所示微米Ti(CN)基金属陶瓷在不同烧结温度下的组织结构和图2比较, 分析微米Ti(CN)基金属陶瓷和纳米Ti(CN)基金属陶瓷刀具材料的组织结构演变过程的差别。 从1200℃开始, 金属陶瓷压坯已开始收缩, 原子扩散主要发生在小颗粒集中的区域和颗粒分散接触比较好的区域, 图3(a)中颗粒基本以原始颗粒聚集态出现。 图3(b)中, 原子扩散加速, 收缩加快, 部分Ti(CN)颗粒周围开始出现WC的包围, 有的包围是间断, 有的包围是连续的, 这些包围的WC就是内环相。 在图3(c)中, 在1300℃时, 液相还没有出现。 开始看到明显的固溶反应, 原子扩散加速, 内环相变厚, 局部区域开始合金化。 在1350℃时, 液相开始出现, 原子扩散速度大大加快, 压坯中的局部区域合金化。 在1400℃时, 液相增多, 颗粒重排, 收缩加快, 合金接近致密。 在1250~1400℃之间, 是组织结构演变的关键阶段, 首先是WC固态扩散形成环形结构的内环相, 在液相出现之前, 通过Ti原子向六方相Mo2C扩散, 富Mo的 (Mo, Ti)(CN)转变成立方相(Mo, Ti)(CN)。 反应式(1)~(4)远没有纳米Ti(CN)颗粒那么明显, 液相出现, 早期的反应产物(Mo, Ti)C、 (Ti, W)C、 (Ti, Ta)C、 (Ti, W, Ta, Mo)C、 Ti(C, N)和(Mo, Ti)(C, N)的扩散, 在液相粘结相中溶解, 并在大的Ti(CN)颗粒表面析出, 形成以Ti(CN)为核, 富Ti的(Mo, Ti)(C, N)为环的结构, 芯部富N, 环形相几乎不含N[16]。 在1400℃以后(图3(e)~(g)), 原子扩散, 溶解析出更充分, 环形结构会有一些变化, 但整体组织结构变化不是特别明显。
图4所示为2种金属陶瓷的透射电镜照片。 表1为图4中金属陶瓷微区测量点的能谱分析。 从透射电镜照片和测量点的成分可以看出, 与微米Ti(CN)基金属陶瓷相比, 纳米Ti(CN)基金属陶瓷原子扩散、 硬质相溶解和析出更加充分, 显微组织中不同相之间的边界比较模糊, 表现为更加均匀的结构。 能谱成分分析结果与前面的分析是一致的。
由于纳米Ti(CN)和纳米WC-Co复合粉的高比表面积, 在粘结相中的溶解速度很快, 形成的环形相体积比也大。 在粘结相中具有更高的W含量和C含量, 增加了粘结相的体积比, 也强化了粘结相。 纳米Ti(CN)和添加的纳米WC-Co复合粉的位错密度比传统尺寸原料粉末颗粒低, 在结构中很多小颗粒的环形结构为“白芯黑环”或者没有明显的环形结构; 一些小的颗粒镶嵌在大颗粒的环形结构中, 保持部分共格而牢固结合, 强化和韧化了金属陶瓷。 另外, 粘结相的存在使得WC、 Mo2C等在较低的温度下与纳米Ti(CN)粉末形成固溶体。 与微米金属陶瓷合金相比, 纳米结构金属陶瓷的韧化机理不同; 纳米结构金属陶瓷由于细化的结构和强化的粘结相, 其断裂韧性提高[5, 17]。 而微米颗粒的金属陶瓷更易于产生更多的裂纹, 加上不均匀的结构, 它的韧性较差。
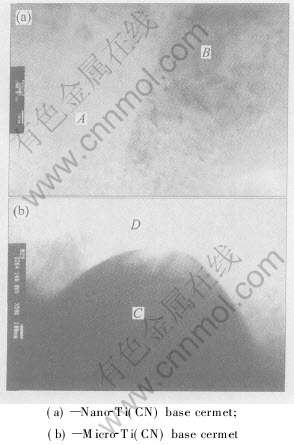
图4 金属陶瓷的透射电镜照片
Fig.4 TEM photos of cermets
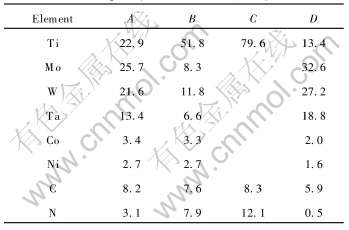
表1 图4中金属陶瓷微区测量点的能谱
Table 1 EDS results of measuring points in Fig.4 (mole fraction, %)
因此, 纳米Ti(CN)基金属陶瓷比微米金属陶瓷有望获得更高的断裂韧性, 能够在解决金属陶瓷韧性方面取得突破。 但是, 纳米Ti(CN)基金属陶瓷的研究还刚刚开始, 很多方面有待进一步深入的研究。 目前, 超细粉末原料的纯度比较低, 其合金的孔隙比较高, 制备工艺有待改进。
3 结论
1) 纳米Ti(CN粉末金属陶瓷由于其表面效应和尺寸效应, 原子扩散和烧结活性很高, 在1200℃以后开始发生剧烈的固相反应, 在1350℃即可获得致密的合金; 而微米Ti(CN)粉末金属陶瓷必须在1350℃以后出现液相, 在1400℃才能获得致密合金。
2) 纳米Ti(CN)粉末金属陶瓷在固相烧结过程中, 纳米Ti(CN)粉末与M(M=Mo, W, Ta)反应形成富M的(Ti, M)(CN)固溶体为核、 贫M的(Ti, M)(CN)固溶体为环的“亮芯黑环结构”, 显微组织表现为非常均匀的球形。 而微米金属陶瓷中Ti(CN)颗粒不能完全固溶而成为核, 富钨和富Mo的固溶体为环, 形成“黑芯亮环结构”。
REFERENCES
[1]ZHENG Yong, WANG Sheng-xiang, YOU Min, et al. Fabrication of nanocomposite Ti(C, N)-based cermet by spark plasma sintering[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2005, 92(1): 64-70.
[2]LIU Ning, HAN Cheng-liang, YANG Hai-dong, et al. The milling performances of TiC-based cermet tools with TiN nanopowders addition against normalized medium carbon steel AISI1045[J]. Wear, 2005, 258(11-12): 1688-1695.
[3]Ishihara S, Shibata H, Goshima T, et al. Thermal shock induced microcracking of cermets and cemented carbides[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2005, 52(7): 559-563.
[4]ZHANG Hou-an, YAN Jian-hui, ZHANG Xin, et al. Properties of titanium carbonitride matrix cermets[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 2006, 24(3): 236-239.
[5]Park S, Kang S. Toughened ultra-fine (Ti, W)(CN)-Ni cermets[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2005, 52(2): 129-133.
[6]Jung J, Kang S. Effect of ultra-fine powders on the microstructure of Ti(CN)-xWC-Ni cermets[J]. Acta Materialia, 2004, 52(6): 1379-1386.
[7]ZHENG Yong, YOU Min, XIONG Wei-hao, et al. Valence-electron structure and properties of main phases in Ti(C, N)-based cermets[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2003, 82(3): 877-881.
[8]Kwon W T, Park J S, Kim S W, et al. Effect of WC and group Ⅳ carbides on the cutting performance of Ti(C, N) cermet tools[J]. International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture, 2004, 44(4): 341-346.
[9]Jeon E T, Joardar J, Kang S. Microstructure and tribo-mechanical properties of ultrafine Ti(CN) cermets[J].International Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 2002, 20(3): 207-211.
[10]Jia K, Fischer T E, Gallois B. Microstructure, hardness and toughness of nanostructured and conventional WC-Co composites[J]. Nanostructured Materials, 1998, 10(5): 875-891.
[11]Ehira M, Egami A. Mechanical properties and microstructure of submicron cermets[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 1995, 13(5): 313-319.
[12]Kim Y K, Shim J H, Cho Y W, et al. Mechanochemical synthesis of nanocomposite powder for ultrafine (Ti, Mo)C-Ni cermet without core-rim structure[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 2004, 22(2-3): 193-196.
[13]CHEN L M, Lengauer W, Ettmayer P, et al. Fundamentals of liquid phase sintering for modern cermets and functionally graded cemented carbonitrides(FGCC)[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2000, 18(6): 307-322.
[14]Lindahl P, Gustafson P, Rolander U, et al. Microstructure of model cermets with high Mo or W content[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 1999, 17(6): 411-421.
[15]Jung J, Kang S. Effect of ultra-fine powders on the microstructure of Ti(CN)-xWC-Ni cermets[J]. Acta Materialia, 2004, 52(6):1379-1386.
[16]Yang J K, Lee H C. Microstructural evolution during the sintering of a Ti(C, N)-Mo2C-Ni alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1996, 209(1-2): 213-217.
[17]ZHENG Yong, XIONG Wei-hao, LIU Wen-jun, et al. Effect of nano addition on the microstructures and mechanical properties of Ti(C, N)-based cermets[J]. Ceramics International, 2005, 31(1):165-170.
(编辑陈爱华)
基金项目: 国家高技术研究发展计划资助项目(2002AA331090); 湖南省科技厅重点科研攻关资助项目(04GK2010)
收稿日期: 2005-12-12; 修订日期: 2006-03-24
通讯作者: 周书助, 副教授; 电话: 0733-2889446; E-mail: zhoushuzhu@126.com