曝气强度与回流比对UCT-MBR工艺运行效能与膜污染的影响
王朝朝1,李军1,李佟1, 2,高金华2,常江2
(1. 北京工业大学 建筑工程学院,北京市水质科学与水环境恢复工程重点实验室,北京,100124;
2. 北京城市排水集团有限公司,北京,100176)
摘要:采用UCT-MBR工艺处理合成市政污水,考查不同曝气强度与回流比的运行条件对该工艺在营养物去除效能及膜污染方面的影响。研究结果表明:曝气强度与回流比的变化对该工艺在COD (chemical oxygen demand, COD)及NH4+-N去除效能影响不大,平均去除率分别保持在89.4%和99.7%,出水质量浓度维持在31.8和0.2 mg/L左右;在进水ρ(COD)/ρ(N)/ρ(P)为49.1/8.3/1.0的条件下,回流比的增加(r1由200%提高到400%)强化了反硝化除磷的效果,其中在低曝气强度条件(100~125 L/h,ρ(DO)=1~2 mg/L),回流比为400%的条件下, 反硝化除磷菌(denitrifying poly-phosphate accumulating organisms, DPAOs)占聚磷菌(poly-phosphate accumulating organisms,PAOs)的数量比例达到最大值,稳定在50.7%左右;曝气强度的增加 (250~300 L/h,ρ(DO)=2~3 mg/L),对缺氧除磷率(Rano-p), 总磷(total phosphorus,TP)及总氮(total nitrogen, TN) 的去除效能均具有一定的抑制作用,分别由93.0%,92.6%和79.6%降至78.0%,77.0%及70.0%,且发现出水中TN与TP的含量及TN与TP的去除率具有一定的正相关性(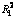 =0.636 0;
=0.636 0;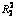 =0.678 6)。此外,曝气强度的增加虽然使得结合型胞外聚合物(bound extracellular polymeric substances,Bound-EPSs)的含量增加,但气水两相流的刮刷作用明显地降低了滤饼层的污染阻力;增大回流比(r1由200%提高到400%)可增加对污泥的剪切作用,导致污泥粒径的减小及溶解性微生物代谢产物(soluble microbial productions, SMPs)的增加,是导致膜孔内部阻力增加的主要原因;红外光谱对膜表面污染物质的分析表明曝气强度与回流比的变化并没有造成其组成成分的变化。
=0.678 6)。此外,曝气强度的增加虽然使得结合型胞外聚合物(bound extracellular polymeric substances,Bound-EPSs)的含量增加,但气水两相流的刮刷作用明显地降低了滤饼层的污染阻力;增大回流比(r1由200%提高到400%)可增加对污泥的剪切作用,导致污泥粒径的减小及溶解性微生物代谢产物(soluble microbial productions, SMPs)的增加,是导致膜孔内部阻力增加的主要原因;红外光谱对膜表面污染物质的分析表明曝气强度与回流比的变化并没有造成其组成成分的变化。
关键词:膜生物反应器;回流比;反硝化除磷;曝气冲刷;膜污染
中图分类号:X703 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2014)07-2509-08
Influences of aeration intensity and recirculation ratios on process performance and membrane fouling in a UCT-type submerged membrane bioreactor
WANG Zhaozhao1, LI Jun1, LI Tong1, 2, GAO Jinhua2, CHANG Jiang2
(1. Key Laboratory of Beijing for Water Quality Science and Water Environment Recovery Engineering,
College of Architecture and Civil Engineering, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing 100124, China;
2. Beijing Drainage Group Co. Ltd., Beijing 100176, China)
Abstract: A bench-scale UCT-type submerged membrane bioreactor was operated to treat synthetic municipal wastewater regarding the influences of aeration and recirculation ratios on process performance and membrane fouling. The results show that variations of aeration intensity and recirculation rations in UCT-MBR process have no effects on the COD and NH4+-N removals, with removal efficiencies of COD (chemical oxygen demand) and NH4+-N stabilizing at 89.4% and 99.7% on an average and with effluent concentrations of 31.8 and 0.2 mg/L respectively. In the feed condition of ρ(COD)/ρ(N)/ρ(P) at 49.1/8.31/1.0, the increase of recirculation ratio (r1 from 200% to 400%) strengthens the denitrifying phosphorus removal, during which in the condition of lower aeration intensity (100-125 L/h, ρ(DO)=1-2 mg/L) and the recirculation ratio of 400%, the ratio of DPAOs to PAOs reaches the maximum value, and stabilizes at about 50.7%. The increase of the aeration intensity (250-300 L/h, ρ(DO)=2-3 mg/L) inhibits anoxic phosphorus removal efficiency (Rano-p) and removal efficiencies of TP and TN, decreasing to 78.0%, 77.0% and 70,0% from 93.0%, 92.6% and 79.6% respectively. Furthermore certain positive correlations between effluent concentrations of TN and TP, removal efficiencies of TN and TP are observed (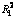 =0.636 0;
=0.636 0; 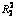 =0.678 6). In addition, the increase of the aeration intensity induces the increase amount of Bound-EPSs (bound extracellular polymeric substances, Bound-EPSs), whereas the scouring effect of the gas-water two-phase flow significantly reduces the resistance of the cake layer; the increase of recirculation ratio (r1 from 200% to 400%) also increases shear stress for activated sludge resulting in the decrease in particle size and the increase of SMPs (soluble microbial productions, SMPs), which become the main reason for the increased resistance of deep pore clogging. FT-IR (Fourier translation infrared spectroscopy, FT-IR) analysis of the membrane foulants shows that the variations of aeration intensity and the recirculation ratios have no effects on their compositions.
=0.678 6). In addition, the increase of the aeration intensity induces the increase amount of Bound-EPSs (bound extracellular polymeric substances, Bound-EPSs), whereas the scouring effect of the gas-water two-phase flow significantly reduces the resistance of the cake layer; the increase of recirculation ratio (r1 from 200% to 400%) also increases shear stress for activated sludge resulting in the decrease in particle size and the increase of SMPs (soluble microbial productions, SMPs), which become the main reason for the increased resistance of deep pore clogging. FT-IR (Fourier translation infrared spectroscopy, FT-IR) analysis of the membrane foulants shows that the variations of aeration intensity and the recirculation ratios have no effects on their compositions.
Key words: membrane bioreactor; recirculation ratio; denitrifying phosphorus removal; aeration scouring; membrane fouling
膜生物反应器(membrane bioreactors, MBRs)是将传统生物污水处理与膜分离有机结合而成的工艺技术,并以其优质的出水成为市政污水回用及工业废水强化处理的重要技术手段[1-2]。在水体富营养化日益加剧的情况下,以脱氮/除磷或者同步脱氮除磷为目的的膜生物反应器工艺层出不穷,其中强化生物除磷膜生物反应器(enhanced biological phosphorus removal membrane bioreactor, EBPR-MBR)工艺构型逐渐成为了市政污水处理中的主流模式[3-6]。然而,膜污染问题始终伴随在MBRs的广泛应用中,并成为影响其可持续运行的重要的障碍之一。对于不同构型的膜生物反应器,其膜污染的特性与机制又具有一定的差别;即使是在同一构型的膜生物反应器中,不同的运行条件也会影响其膜污染的特性[7-9]。在EBPR-MBR工艺中,以强化脱氮除磷为目的的工艺运行条件与有效抑制膜污染的运行模式存在着一定的冲突,因此,在优化脱氮除磷效果运行模式的同时考虑其对膜污染的影响是至关重要的。本文作者针对同步脱氮除磷膜生物反应器(university of cape town membrane bioreactor, UCT-MBR)工艺中的2个关键的运行参数(曝气强度与回流比)进行试验,主要考查这2个因素对UCT-MBR 工艺在脱氮除磷效能方面的影响,重点分析曝气强度与回流比对反硝化除磷特性方面的影响,以及在不同运行阶段下反硝化除磷菌在聚磷菌群落结构中的分布及缺氧除磷率的变化;同时考查曝气强度与回流比对UCT-MBR膜污染特性的协同影响,分析这2个因素对污泥理化特性及其代谢产物的影响,并探究膜污染各部分阻力的形成机制。
1 试验材料与方法
1.1 试验装置与工艺流程
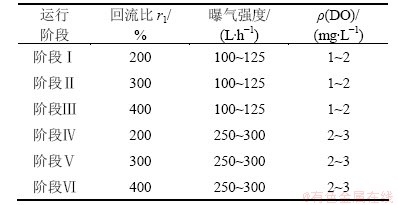
UCT-MBR的反应器装置如图1所示。装置各矩形反应池由有机玻璃构成,总有效体积为28 L,V厌氧池:V缺氧池-1:V缺氧池-2:V好氧膜池为1:1:1:2。该装置由可编程逻辑控制器(PLC)控制,采用恒通量过滤间歇抽吸方式进行产水,膜通量保持在20 L/(m2·h),抽吸周期为10 min,9 min抽吸,停1 min。通过液位计对厌氧池液位的监控,控制进水泵1的启停,跨膜压差数值通过记录仪在线存储。污水依次经过厌氧池、缺氧池1、缺氧池2、好氧池膜池,最后通过产水泵实现出水,水力停留时间(HRT)维持在15.56 h左右。为保持处于悬浮状态,在厌氧池、缺氧池1和缺氧池2配备搅拌桨。好氧膜池采用穿孔曝气,孔径为5 mm,通过空气压缩机对其进行鼓风,一方面是为了形成气水剪切流,减缓污泥在膜组件上的沉积;另一方面是为了保证好氧池微生物自身需要和降解有机物的生化需氧曝气量。膜组件为1片氯化聚乙烯的平板微滤膜(Kubta公司制造),膜孔径为0.4 μm,膜面积为0.1 m2。反应器温度通过加热棒控制在20 ℃左右,通过便携式WTW Multi 340i检测仪对好氧膜池的DO进行监控。试验期间的其他运行参数如表1所示。
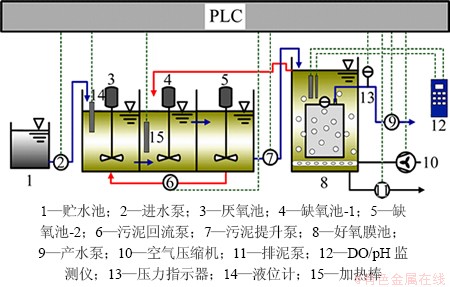
图1 UCT-MBR工艺流程图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of UCT-MBR
表1 试验运行阶段的工艺参数
Table 1 Operational parameters during different phases
1.2 污泥的接种与驯化及进出水特性
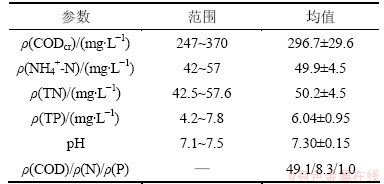
试验的接种污泥取自高碑店污水处理厂A/O脱氮工艺的二沉池的回流污泥,具有良好的脱氮性能。系统的污泥停留时间(SRT)维持在20~25 d,好氧膜池的污泥(mixed liquor suspended solids, MLSS)质量浓度在5 000 mg/L左右,厌氧池、缺氧池1、缺氧池2、好氧池的污泥量占总反应器污泥总量的14%,19%,20%和47%。试验用水为合成废水,配方如下:CH3COOH 0.2~0.6 mL/L,NH4Cl 190~195 mg/L,KH2PO4 20~22 mg/L,NaHCO3 340~350 mg/L,FeCl3·6H2O 4 mg/L,CaCl2 11 mg/L,MgSO4 11 mg/L,KCl 8 mg/L,NaCl8 mg/L,并且通过加入NaOH与稀盐酸来调节进水pH。不同阶段的进水水质特征如表2所示。
表2 试验运行阶段污水水质特性
Table 2 Feed wastewater characteristics during operational phases
1.3 分析项目及测定方法
1.3.1 CODcr,NH4+-N,TN,TP,MLSS和MLVSS含量的测定
采用水和废水监测分析方法(第4版)中的标准方法[10]测定上述指标;pH用便携式WTW Multi 340i检测仪测定;污泥粒径采用马尔文粒径仪测定(Worcestershire, UK)。
1.3.2 跨膜压差
采用在线的数据记录仪进行在线采集跨膜压差数据,并采用下式进行校正:
 (1)
(1)
在每一个阶段试验结束时,根据达西公式计算总污染阻力:
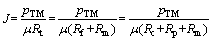 (2)
(2)
其中:μ为产水的黏度,Pa·s。将膜组件取出反应器,用海绵将膜表面的滤饼层轻微擦去,然后放在清水中在一定压力下进行过滤,并测定出水通量,根据式(2)计算得出膜孔内部阻力(Rp)和膜固有阻力(Rm)之和,其与Rm的差值为Rp;总污染阻力(Rt)与其差值即为滤饼层的阻力Rc。将膜组件浸泡在0.5%的次氯酸钠溶液中,使其渗透性恢复到95%以上,进入下一个试验阶段。
1.3.3 EPS与SMP的萃取与表征
EPS与SMP萃取:EPS的萃取采用离子交换树脂法,取50 mL好氧膜池的活性污泥,在12 000 r/min下离心15 min,然后收集上清液经过0.45 μm微滤膜后测定糖与蛋白质,分别记为 SMPc和SMPP,取其加和作为SMP,mg/L;将离心浓缩的污泥,用缓冲液(缓冲液由2 mmol/L Na3PO4, 4 mmol/L Na2HPO4, 9 mmol/L NaCl and 1 mmol/L KCl)补充到原来的体积。根据单位挥发性污泥(mixed liquor volatile suspended solids, MLVSS)质量加70 g的比例将强酸型Na+树脂(粒径为0.3~0.7 mm)和污泥缓冲液加入到锥形瓶当中,并使用磁力搅拌器将其控制在800 r/min下搅拌2 h。搅拌结束之后,使用离心机在12 000 r/min下离心15 min,取其上清液通过0.45 μm微滤膜,测定过滤液中的糖(硫酸蒽酮法)和蛋白质(考马斯亮蓝法),分别记为 EPSc和EPSp,单位MLVSS质量下糖和蛋白质的质量加和作为EPS的质量分数[11],mg/g。
1.3.4 红外光谱(FT-IR)
每个运行阶段完成后,将膜表面的污染物质收集并进行真空烘干,将粉末状的污染物质按照质量比为1:10加入溴化钾进行压片,然后采用傅里叶红外光谱仪(FT-IR 6700,Nicolet公司)进行透射扫描,扫描范围为400~4 000 cm-1,数据采集之后采用 origin 8.0软件进行处理。
1.3.5 DPAOs和PAOs的动力学试验与缺氧除磷率的计算
DPAOs占PAOs的数量比例按照Wachtmeistr等[12]的方法进行测定,采用单位MLSS质量下的最大缺氧吸磷速率Kano与最大好氧吸磷速率Kaer的比值来表征DPAOs与PAOs的数量比例(fDPAOs/PAOs)。
缺氧除磷率Rano-p计算公式为
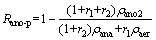 (3)
(3)
式中:ρana为厌氧池末端的磷质量浓度,mg/L;ρano2为缺氧池2末端的磷质量浓度,mg/L;ρaer为好氧池末端的磷质量浓度,mg/L;r1为好氧膜池到缺氧池-1的回流比;r2为缺氧池-2到厌氧池的回流比。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 回流比与曝气强度对UCT-MBR工艺脱氮除磷效能的影响
2.1.1 回流比与曝气强度对COD去除效能的影响
图2所示为不同阶段UCT-MBR工艺对COD的去除效果。由图2可知:进水ρ(COD)在247.0~370.0 mg/L之间变动,经过厌氧,缺氧池及好氧池之后,降为42.0 mg/L;膜组件对COD的截留维持在10.0 mg/L 左右,COD的平均去除率为 89.4%。在阶段Ⅰ~Ⅲ 和阶段Ⅳ~Ⅵ运行条件时,回流比对COD的去除影响较小。但在曝气量的增加到其2~3倍时,膜池上清液的COD质量浓度有少许增加的趋势,COD质量浓度在阶段 Ⅳ~Ⅵ 比阶段Ⅰ~Ⅲ时高10.0 mg/L 左右,去除率同比降低3%左右。
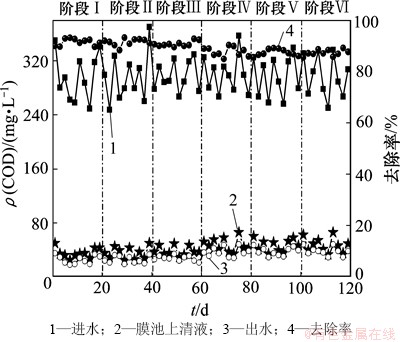
图2 不同阶段UCT-MBR工艺对COD的去除效果
Fig. 2 Performance of COD removal in UCT-MBR process during different phases
2.1.2 回流比与曝气量对N去除效能的影响
图3所示为不同阶段UCT-MBR工艺对NH4+-N和TN的去除效果。由图3可知:进水ρ(NH4+-N)质量浓度在42.0~57.0 mg/L之间变动,出水质量浓度平均为0.2 mg/L左右,去除率基本稳定在99.7%。即使阶段 Ⅳ~Ⅵ 的曝气强度高于阶段Ⅰ~Ⅲ的曝气强度,但是在阶段Ⅰ~Ⅲ运行条件下,溶解氧完全满足硝化所需的DO量,然而,TN的去除效果则明显受到曝气强度与回流比的协同影响。在阶段Ⅰ~Ⅲ时,进水ρ(TN)平均为50.5 mg/L,出水为 14.5 mg/L,去除率为 71.6%;在此相同曝气强度的运行下,随着回流比由200%增加到400%,TN的去除率逐渐增加,由64.0%提高到79.5%,出水由18.1 mg/L降至10.2 mg/L。而在阶段Ⅳ~Ⅵ,TN的去除率均低于阶段Ⅰ~Ⅲ的去除率。高DO是影响脱氮效果的主要因素,缺氧环境的破坏是由于膜池高DO的缘故。在相同回流比下,高曝气强度明显抑制了UCT-MBR工艺的脱氮效能。后3个运行阶段较前3个运行阶段,高DO对脱氮效能的抑制程度分别达到了6.9%,5.4%和9.1%。Tan等[13]在研究前置反硝化膜生物反应器工艺时发现,在相同回流比下,高DO会消耗更多的可利用碳源,从而减少了反硝化所补给的电子供体,进而影响整体脱氮的效能。
2.1.3 回流比与曝气量对P去除效能的影响
TP的去除效果也明显受到曝气强度与回流比的协同影响。图4所示为不同阶段UCT-MBR工艺对TP的去除效果。由图4可知:在阶段 Ⅳ-Ⅵ 运行下,TP的去除率均比阶段Ⅰ~Ⅲ的低。具体而言,在阶段Ⅰ~Ⅲ 进水ρ(TP) 分别为6.06,5.95和6.10 mg/L,出水分别为2.54,1.57和0.49 mg/L,去除率分别达到了58.0%,73.5%和92.6%。可以看到在低曝气强度下,随着回流比的增加,TP的去除率随之增加。在6个阶段中,阶段 Ⅲ 的TP的去除率达到最高,为92.6%,而在相同回流比下,提高曝气强度后TP的去除率降为77%。这说明高DO质量浓度对TP的去除率也具有一定的抑制作用。而回流比对TP的去除效能始终起促进作用。在高溶解氧及低回流比下使得TP的去除率达到最低,为41.1%(阶段Ⅳ)。
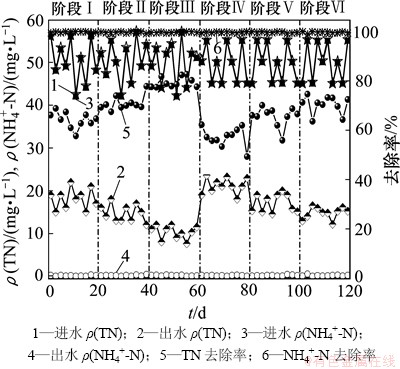
图3 不同阶段UCT-MBR工艺对NH4+-N和TN的去除效果
Fig. 3 Performance of NH4+-N, TN removal in UCT-MBR process during different phases
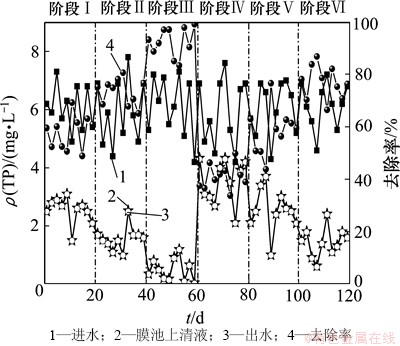
图4 不同阶段UCT-MBR工艺对TP的去除效果
Fig. 4 Performance of TP removal in UCT-MBR process during different phases
图5所示为不同阶段缺氧吸磷和好氧吸磷动力学特性。由图5可见:不同曝气强度与回流比对缺氧除磷的影响较大。由缺氧吸磷与好氧吸磷速率可知,在阶段Ⅰ~Ⅲ,PAOs与DPAOs的吸磷速率均增加,说明随着试验的进行,PAOs与DPAOs的种群在随之增长并富集。但在回流比增加的驯化下,DPAOs的富集速率比PAOs的快,fDPAOs/PAOs由31.0%提高到了50.7%,缺氧除磷率也由38.0%提高到93.0%。而在阶段 Ⅳ~Ⅵ 下,DPAOs的富集速率较在低DO的条件下则有所下降,fDPAOs/PAOs由26.6%提高到了40.2%,且缺氧除磷率由24.0%提高到78.0%。
图6所示为UCT-MBR工艺中TN与TP去除效能的相关性。由图6可见:出水ρ(TN) 随着ρ(TP)增加而出现增加趋势,TN的去除率随着TP去除率的增加也出现增加的趋势。TP与TN的质量浓度以及TN与TP的去除率具有一定的正相关性,具体相关性分析如式(4)和(5)所示。
ρ(TNeff)=2.762 8 ρ(TNeff)+10.455,  =0.636 0 (4)
=0.636 0 (4)
ρ(TNre)=3.579 1ρ(TPre)+44.114, 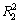 =0.678 6 (5)
=0.678 6 (5)
在同步脱氮除磷的工艺中,TN与TP的去除存在着碳源的竞争,并且两者在反硝化除磷的生化作用下得以缓解,因此,TN与TP的去除效果与反硝化除磷的特性相辅相成。DPAOs在强化的同时,会同步提高TN与TP的去除率,反之亦然。
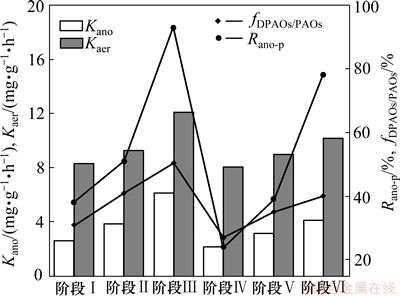
图5 不同阶段缺氧吸磷和好氧吸磷动力学特性
Fig. 5 Kinetic activities of PAOs and DPAOs during different phases
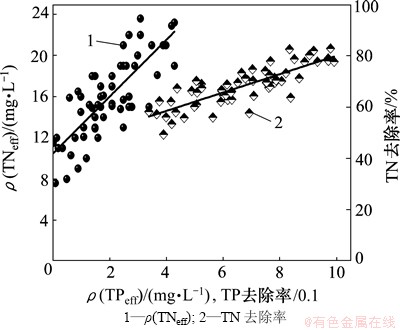
图6 UCT-MBR工艺中TN与TP去除效能的相关性
Fig. 6 Correlation between TN and TP removal efficiencies in UCT-MBR process
2.2 回流比与曝气强度对UCT-MBR工艺膜污染的影响
2.2.1 回流比与曝气强度对膜污染特性的影响
不同阶段UCT-MBR工艺的膜污染特性见图7,膜污染阻力分布见表3。从图7与表3可见:在运行的6个阶段中,阶段Ⅰ~Ⅲ在低曝气强度下膜污染速率均比阶段Ⅳ~Ⅵ的高,在阶段Ⅲ时污染阻力达到最大,为91.9×1011 m-1,因此,曝气强度的增加对于滤饼层阻力的减小是显而易见的。在阶段Ⅰ~Ⅲ 和阶段Ⅳ~Ⅵ,随着回流比的增加,膜污染速率也随之增加。同时,随着回流比的增加,膜孔内部的阻力在增加,且膜孔内部阻力在总阻力的组分也随之增加,也进一步表明膜孔内部阻力逐渐成为影响总阻力的重要因素。这也是由于动力剪切力提高使得污泥代谢产物及胶体物质增加,从而使得膜孔内部阻力加速。
图7 不同阶段UCT-MBR工艺的膜污染特性
Fig. 7 Membrane fouling characteristics in UCT-MBR process during different phases
2.2.2 回流比与曝气强度对污泥粒径的影响
图8所示为不同运行阶段下膜池污泥粒径的分布。由图8可知:在相同的曝气强度下,随着回流比的增加,污泥粒径逐渐变小;在相同回流比下,随着曝气强度的增加,污泥粒径也呈减小趋势。回流比与曝气强度增加均增大对活性污泥的剪切。在6个阶段中,阶段Ⅰ时的污泥粒径最大,为 73.4 μm,阶段 Ⅵ 时的粒径减小为 27.4 μm。在阶段Ⅰ~Ⅲ 和阶段Ⅳ~Ⅵ时,随着回流比由200%提高到400%,污泥粒径分别降低31.6%和40.6%。由于污泥混合液可以分为颗粒物、胶体物质及溶解性物质。随着粒径的减小,污泥的胶体类物质含量和溶解性物质的含量增加,这2类物质也是造成膜孔堵塞的主要因素。
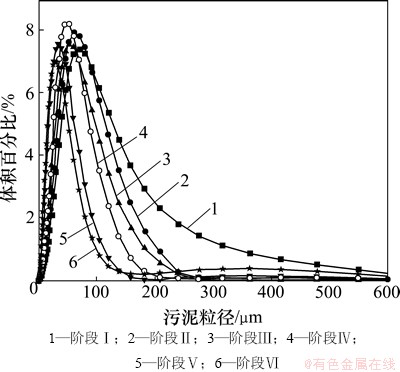
图8 不同运行阶段下膜池污泥粒径的分布
Fig. 8 Particle size distributions of activated sludge in aerobic-membrane tank during different phases
2.2.3 回流比与曝气强度对污泥代谢产物的影响
图9所示为不同运行阶段下好氧膜池污泥EPS的特性。由图9可见:阶段Ⅳ~Ⅵ的污泥当中的w(EPS)均比阶段Ⅰ~Ⅲ的高,可知随着曝气强度的增加污泥当中的w(EPS)随之增加。也有研究表明,w(EPS)增加会提高污泥滤饼层的阻力[11],因此,在阶段Ⅰ~Ⅲ和阶段Ⅳ~Ⅵ下滤饼层阻力分别增加。然而,阶段Ⅳ~Ⅵ的滤饼层阻力比阶段Ⅰ~Ⅲ的低,这主要是由于曝气强度增加,在膜表面的剪切力增加,因此,膜表面滤饼层阻力是污泥EPS与曝气剪切的综合作用的结果。在相同曝气量下,回流比的增加也使得污泥的w(EPS)增加。在阶段Ⅰ~Ⅲ和阶段Ⅳ~Ⅵ时,随着回流比由200%提高到400%,w(EPS)也分别提高22.8%和24.8%,而w(EPSc)/w(EPSp) 却分别由4.66和4.50降低到3.77和3.54,表明随着剪切力的增加使得EPS中蛋白质组分所占的比例有所升高。
表3 试验运行不同阶段膜污染阻力分布
Table 3 Distributions of membrane filtration resistances during different operational phases
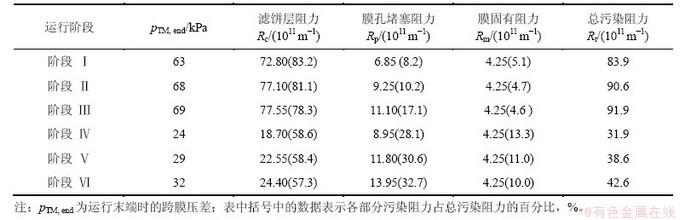
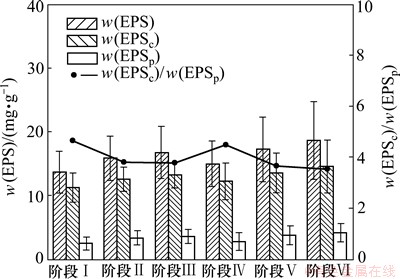
图9 不同运行阶段下好氧膜池污泥EPS的特性
Fig. 9 Variations of EPSs of activated sludge in aerobic-membrane tank during different phases
SMP的变化规律与EPS的变化规律类似。不同运地阶段下好氧膜池污泥SMP的特性见图10。由图10可见:在阶段Ⅰ中污泥中的SMP的存在以糖类为主,因此,糖类成为膜孔堵塞的主要因素。阶段Ⅳ~Ⅵ下污泥的SMP含量均比阶段Ⅰ~Ⅲ的大,因此,在阶段Ⅳ~Ⅵ下膜孔堵塞的阻力均比阶段Ⅰ~Ⅲ的大,ρ(SMPc)与ρ(SMPP)分别平均高10.9%和40.7%,其中以阶段Ⅵ时膜孔堵塞的阻力最大,这是由于此时曝气强度与回流比均达到运行工况的最大。Meng等[14]也在研究中发现:随着曝气量的增加,污泥的代谢溶解性产物明显增加,从而加速了膜孔堵塞速率及增加了其污染阻力在总污染阻力的比例。
2.2.4 回流比与曝气量对膜污染物质组成的影响
膜表面污染物质的红外光谱的特性如图11所示。红外光谱通过分析膜污染物质的官能团,从而鉴别膜污染物质的组成。由图11可知:在阶段Ⅰ~Ⅵ时的膜污染物质在红外透射时,在相同的波长点处同时出现吸收峰,表明各个阶段下膜污染物质在化学组成上一致。由图11还可知:污染物质分别在3 416 cm-1附近有1个较宽的吸收峰,这是由羟基官能团中O—H键伸缩导致;在2 924 cm-1处出现尖锐的吸收峰,这是由芳香族类的C—H键伸缩导致;在1 654,1 546和1 383 cm-1附近也分别出现了不同程度的吸收峰,表明存在蛋白质类二级结构物质;在1 047 cm-1处可以看到1个较宽的吸收峰,表明存在多糖及多糖类物质。此外,在指纹区内673 cm-1也发现了吸收峰值。Wang等[15]在研究EPS的红外图谱时发现其在上述相应的波长附近处也存在吸收峰,可以推测膜表面的污染物质主要是在膜分离过程中EPS在膜表面的积累所致。
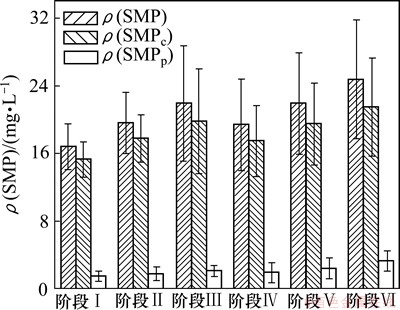
图10 不同运行阶段下好氧膜池污泥SMP的特性
Fig. 10 Variations of SMPs of activated sludge in aerobic-membrane tank during different phases
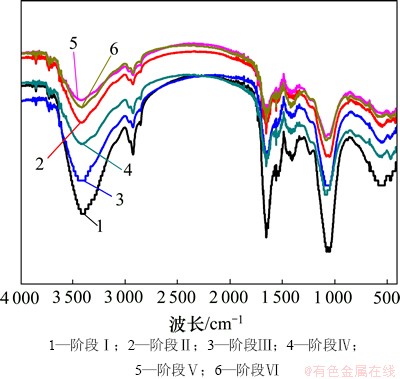
图11 不同运行阶段下膜表面污染物质的红外光谱
Fig. 11 FT-IR characterizations of membrane foulants during different phases
3 结论
(1) 曝气强度与回流比的变化对UCT-MBR工艺对COD及NH4+-N去除效能影响不大,平均去除率分别保持在89.4%和99.7%,出水质量浓度分别维持在31.8和0.2 mg/L。
(2) 在相同的曝气强度的条件下,回流比r1的增加(r1由200%提高到400%)强化了反硝化除磷的效果,其中在曝气强度为100~125 L/h,回流比为400%的条件下, DPAOs与PAOs的数量比例达到了最大值,稳定在50.7%左右;曝气强度的增加对缺氧除磷率、TP及TN的去除效能具有一定的抑制作用,去除率分别降至78.0%,77.0%及70.0%。
(3) 曝气强度的增加会使得EPS的含量增加,但曝气强度对滤饼层的形成起到明显的抑制作用;回流比的剪切作用使得污泥粒径减小及微生物代谢产物增加,是导致膜孔内部阻力增加的主要因素。曝气强度与回流比的变化并没有造成其组成成分的变化。
参考文献:
[1] MENG Fangang, Chae S R, Drews A, et al. Recent advances in membrane bioreactors (MBRs): Membrane fouling and membrane material[J]. Water Research, 2009, 43(29): 1489-1512.
[2] Judd S. The MBR book: Principles and applications of membrane bioreactors for water and wastewater treatment[M]. 2nd ed. London: Elsevier Press, 2010: 1-50.
[3] Monclús H, Sipma J, Ferrero G, et al. Optimization of biological nutrient removal in a pilot plant UCT-MBR treating municipal wastewater during start-up[J]. Desalination, 2010, 250(2): 592-597.
[4] Boris L, Regina G. Christian A. Process configurations adapted to membrane bioreactors for enhanced biological phosphorous and nitrogen removal[J]. Desalination, 2002, 149(1/2/3): 217-224.
[5] Lee H, Han J, Yun Z. Biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal in UCT-type MBR process[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2009, 59(11): 2093-2099.
[6] Kim M, Nakhla G. Phosphorus fractionation in membrane- assisted biological nutrient removal processes[J]. Chemosphere, 2009, 76(9): 1283-1287.
[7] Paetkau M, Cicek N. Comparison of nitrogen removal and sludge characteristics between a conventional and a simultaneous nitrification-denitrification membrane bioreactor[J]. Desalination, 2011, 283: 165-168.
[8] Shin H, Kang S. Performance and membrane fouling in a pilot scale SBR process coupled with membrane[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2002, 47(1): 139-144.
[9] McAdam E, Judd S, Cartmell E, et al. Influence of substrate on fouling in anoxic immersed membrane bioreactors[J]. Water Research, 2007, 41(17): 3859-3867.
[10] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2004: 210-284.
State Environmental Protection Administration of China. National standard methods for water and wastewater quality analysis[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2004: 200-284.
[11] Malamis S, Andreadakis A. Fractionation of proteins and carbohydrates of extracellular polymeric substances in a membrane bioreactor system[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2009, 100(13): 3350-3357.
[12] Wachtmeister A, Kuba T, van Loosdrecht M C M, et al. A sludge characterization assay for aerobic and denitrifying phosphorus removing sludge[J]. Water Research, 1997, 31(3): 471-478.
[13] Tan T W, Ng H Y. Influence of mixed liquor recycle ratio and dissolved oxygen on performance of pre-denitrification submerged membrane bioreactors[J]. Water Research, 2008, 42(4/5): 1122-1132.
[14] MENG Fangang, YANG Fenglin, SHI Baoqiang, et al. A comprehensive study on membrane fouling in submerged membrane bioreactors operated under different aeration intensities[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2008, 59(1): 91-100.
[15] WANG Zhiwei, WU Zhichao, TANG Shujuan. Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) properties and their effects on membrane fouling in a submerged membrane bioreactor[J]. Water Research, 2009, 43(9): 2504-2512.
(编辑 杨幼平)
收稿日期:2013-07-31;修回日期:2013-10-17
基金项目:国家水体污染控制与治理科技重大专项(2008ZX07314-008)
通信作者:王朝朝(1985-),男,河北邯郸人,博士研究生,从事膜法污水处理技术与应用;电话:18303233729;E-mail:W-Z-Z@163.com