DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-37916
CuMg0.4合金切向微动磨损行为研究
袁新璐,张晓宇,李 根,蒲 建,任平弟
(西南交通大学 机械工程学院摩擦学研究所,成都 610031)
摘 要:本文开展了CuMg0.4合金的切向微动磨损试验,详细研究了CuMg0.4合金的切向微动运行特性和损伤机理,建立了其运行工况微动图(RCFM)和材料响应微动图(MRFM)。结果表明,CuMg0.4合金的微动运行特性被分为部分滑移机制(PSR),混合滑移机制(MSR)和完全滑移机制(GSR)。在PSR中,接触中心以弹性变形为主,接触边缘只发生轻微擦伤。在MSR中,黏着区发生强烈的塑性变形,滑移区以表面疲劳磨损和磨粒磨损为主。此外,裂纹在黏-滑边界处萌生并向金属基体内部扩展,次表层的塑性应变累积促进裂纹在此处形核,并最终扩展至接触表面造成剥层。在GSR下,接触表面被严重氧化的第三体层覆盖,磨损机理主要为初始阶段的黏着磨损,稳定阶段的表面疲劳磨损,磨粒磨损。
关键词:微动磨损;CuMg0.4合金;接触状态;微动图
文章编号:1004-0609(2021)-xx-- 中图分类号:TH117.1 文献标志码:A
引文格式:袁新璐,张晓宇,李 根, 等. CuMg0.4合金切向微动磨损行为研究[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2021, 31(x): xxxx-xxxx. DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-37916
YUAN Xin-lu, ZHANG Xiao-yu, LI Gen, et al. Study on tangential fretting wear behavior of CuMg0.4 alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2021, 31(x): xxxx-xxxx. DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-37916
中国高速铁路(以下简称高铁)在近十年取得飞速发展,现已建成世界最大的高铁运营网[1]。悬挂在高速铁轨之上的接触网长期服役在振动、冲击和拉压载荷条件下,其关键零部件的紧配合表面不可避免地发生微动磨损,随着服役年限的增长,微动损伤不断累积,导致接触网零部件失效的频率日益增加,成为高铁安全运营的重要隐患之一[2-3]。铜镁合金不但具有较高的机械强度和耐腐蚀性能,还有良好的导电性[4-5],是接触网系统中绞线类零部件(如接触线、承力索、吊弦、弹性吊索等)的重要制备材料。但由于其较弱的抗耐磨性,铜镁合金零部件在整个接触网系统中的微动损伤最为严重[6-7]。目前针对铜镁合金的研究主要集中在制备工艺[8]和微观组织与性能[9-10]方面,而对铜镁合金微动损伤的研究鲜有报道。魏超等[11]通过铜镁合金弯曲微动疲劳试验,建立了疲劳寿命S-N曲线,揭示了其弯曲微动疲劳损伤特性及演变规律。薛博凯 等[12]讨论了载流条件对铜镁合金的弯曲微动疲劳的影响,结果显示载流会降低铜镁合金的微动疲劳寿命。微动磨损会造成接触表面磨损和裂纹形核,是导致零部件疲劳断裂的重要原因之一[13],但目前关于铜镁合金微动磨损的研究至今未见报道。
本文开展了铜镁合金在不同法向载荷和位移幅值条件下的微动磨损试验,旨在建立铜镁合金运行工况微动图,分析其在不同运行机制下的损伤机理。研究成果为改善铜镁合金的微动磨损问题提供基础数据及理论,对保障我国高速铁路安全运营具有重要意义。
1 试验部分
1.1 试验材料
微动试验材料选用CuMg0.4合金,牌号为JTMH,它是目前高速铁路接触网绞线类零部件最
常用的材料之一。测得室温条件下σ0.2=263 MPa,σb=273 MPa,材料金相组织见图1,化学成分见表1。试样尺寸为10 mm×10 mm×3 mm的方块,选取10 mm×10 mm平面作为磨损试验表面,用水砂纸逐渐研磨后抛光至粗糙度Ra小于0.02 μm。微动试验的对偶件选取相同材料的CuMg0.4合金,目的是探究接触网铜镁合金绞线内部存在的微动磨损行为,对偶件的尺寸为直径12 mm的球体,表面粗糙度Ra小于0.02 μm。所有试验样品制备完成后用无水乙醇在超声波中清洗15 min以去除表面油污,然后放置恒温干燥箱中存储备用。
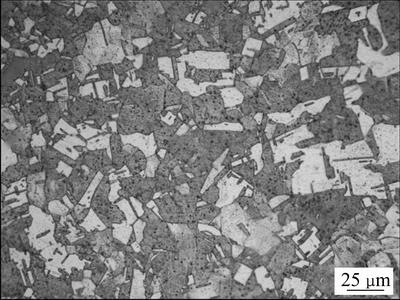
图1 CuMg0.4合金金相组织
Fig. 1 Microstructure of CuMg0.4 alloy
表1 CuMg0.4合金化学成分含量表
Table 1 Chemical composition of CuMg0.4
1.2 试验方法
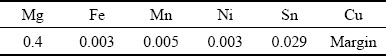
试验以平面/球接触方式在研制的微动磨损试验机(型号为MFC-01)上进行,其结构原理图如图2所示。压电陶瓷触动器输出正弦运动的微动位移,并由高精度电容式位移传感器测定;法向载荷施加在水平连杆上,通过应变式压力传感器测得。球试样被紧固在上夹具中,并跟随连杆在切向方向上做往复运动。平面试样被锁紧在下夹具中,而后将其固定在光滑的导轨组件上。下夹具与基座之间通过一个压电式力传感器相连,以监测微动过程中的摩擦力。试验过程中,计算机数据采集系统同时记录切向力和位移信号,并将分别将摩擦系数和切向 力-位移曲线图(Ft-D曲线)实时显示在计算机屏幕上。
微动试验在常温大气环境下进行,环境温度为20~25℃,相对湿度为50%~60%,试验参数设置如下:法向载荷P范围为10~100 N;位移幅值D范围为1~60 μm,微动循环次数N恒定为3×104次,运动频率f保持5 Hz不变。试验完成后,用光学显微镜(OM, MV 3000)以及扫描电子显微镜(SEM, Quanta 2000)对磨痕形貌及损伤机理进行分析,并结合EDX能谱仪(EDAX-7760/68M)对磨损区域进行能谱氧化程度分析。利用三维形貌仪(Contour GT)测定磨痕三维形貌及磨损体积。
图2 微动试验机原理图
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of fretting tester (Unit: mm)
2 结果与讨论
2.1 接触状态
HERTZ[14]在1982年对两个弹性体受正压力P作用下的接触问题进行了研究,得到了其接触半径和压应力分布。Mindlin[15]在1949年解决了两个弹性体同时施加正压力P和切向力T条件下的接触问题,给出了接触区域压应力和切应力的分布(见图3),这为研究微动接触状态提供了重要基础。如图3(a)所示,当施加的切向力T小于临界滑动摩擦力时,两个弹性接触体不发生相对滑动,只在一部分接触界面上产生微滑,该滑动区域被定义为滑移区(Slip zone);而在其余部分只发生弹性变形,被定义为黏着区(Stick zone)。随着切向力增加(仍小于临界值),黏着区减小而滑移区向内扩展,如图3(b)所示。这种接触中心黏着而接触边缘发生微滑的接触状态被定义为部分滑移状态(Partial slip state),在此种状态下,切应力在黏着区和滑移区的边界处出现应力奇点。当施加的切向力超过临界值时,整个接触区域发生相对滑动,如图3(c)所示,切应力等于摩擦应力,它是接触区位置r的连续函数。这种整个接触发生相对滑移的接触状态被定义为完全滑移状态(Gross slip state)。
图4所示为CuMg0.4合金在不同位移幅值下的磨痕光镜图及对应的摩擦力曲线。从图中可以看出,当位移幅值分别为2.5、5、20 μm时,如图4(a),(b),(c)所示,接触磨痕都可以被细分为两个区域,即中心的黏着区和环绕在其周围的微滑区,表明微动接触状态都处在部分滑移状态。对应的摩擦力曲线都呈现正弦演化特征(位移以正弦形式施加在接触体上),表明接触表面之间没有相对滑动,施加的微动位移主要通过接触区的弹塑性变形来协调。此外,从图中还可以看出随着位移幅值的增加,黏着区收缩而滑移区向内扩张且黏着区出现严重的塑性变形,表明随着位移幅值的增加,接触界面之间的摩擦力增加,黏着区由弹性变形向塑性变形转变。当位移幅值为50 μm时,如图4(d)所示,整个接触表面发生相对滑移,摩擦力曲线经过一个快速增加后,在一段时间内保持相对恒定,表明接触状态处在完全滑移状态。摩擦力的近似线性增长过程对应着接触区的弹塑性变形阶段,而摩擦力保持相对恒定的阶段对应着接触表面之间的相对滑动过程。

图3 Mindlin接触模型的应力分布[15]
Fig. 3 Stress distribution of Mindlin contact model[15]

图4 CuMg0.4合金在不同位移幅值下的磨痕光镜图片(P=60 N)
Fig. 4 Optical microscope pictures of wear scars of CuMg0.4 alloy under different displacement amplitudes (P=60 N)
图5所示为CuMg0.4合金微动接触状态的演化模型。当微动处在部分滑移状态时,接触区域分为中心黏着区和环状滑移区。当接触表面的切向力较小时,黏着区主要发生弹性变形,随切向力的增加,黏着区由弹性变形转变为塑性变形且黏着区缩小而滑移区向内扩张。当接触表面的切向力超过临界值时,整个接触表面发生相对滑移,微动进入完全滑移状态。
2.2 微动运行机制
图6所示为CuMg0.4合金在不同试验条件下的摩擦力(Ft)-位移幅值(D)-循环次数(N)曲线图(Ft-D-N曲线),它记录了微动动态运行过程。根据Ft-D-N曲线演化特性可以定义三种微动运行机
制[16]。当位移幅值处在较低水平时(D= 1、2、2.5μm),3种法向载荷条件(P=20、40、60 N)下的Ft-D曲线一直保持近似直线状,如图6(a),(d),(g)所示,表明整个微动过程一直处在部分滑移状态,接触区主要以弹性协调为主,被定义为部分滑移机制(Partial slip regime, PSR)。当位移幅值较大时(D=30、40、50 μm),3种法向载荷条件(P=20、40、60 N)下的Ft-D曲线基本都呈现为平行四边形,如图6(c),(f),(i)所示,表明接触表面一直存在相对滑移,被定义为完全滑移机制(Gross slip regime, GSR)。但是,当位移幅值处在PSR和GSR之间时,如图6(b),(e),(h)所示,Ft-D曲线由初期的平行四边形逐渐转化为椭圆形并保持到微动结束,表明接触状态由初始阶段的完全滑移逐渐转变为部分滑移。这种接触状态出现一次或多次转变的动态运行特性被定义为混合滑移机制(Mixed slip regime, MSR)。

图5 CuMg0.4合金接触状态演化模型
Fig. 5 Contact state evolution model of CuMg0.4 alloy

图6 CuMg0.4合金在不同试验条件下的Ft-D-N曲线图
Fig. 6 Ft-D-N curves of CuMg0.4 alloy under different test conditions
图7所示为在位移幅值1~50 μm及法向载荷20~80 N条件下建立的CuMg0.4合金运行工况微动图(Running condition fretting map, RCFM)。从图中可以看出,PSR主要发生在极小位移幅值或较大法向压力条件下,微动被一直保持在部分滑移状态,接触区主要以弹性变形为主;与之相反,GSR主要发生在较大位移幅值或较小法向压力下,完全滑移始终发生在接触表面;MSR处在两者之间,微动接触状态由初期的完全滑移逐渐转化为部分滑移,接触表面发生塑性变形。此外,当法向载荷恒定时,随着位移幅值的增加,运行机制由PSR向MSR和GSR转化;当位移幅值恒定时,随着法向载荷的增加,运行机制由GSR向MSR和PSR转化。由此可以看出,法向载荷和位移幅值是影响CuMg0.4合金微动运行过程的关键因素。
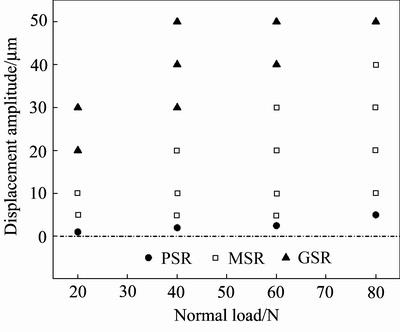
图7 CuMg0.4合金的运行工况微动图
Fig. 7 RCFM of CuMg0.4 alloy
2.3 摩擦系数演化
如图8(a)所示,摩擦系数被定义为一次循环过程中平均切向力与法向载荷P的比值。图8(b)所示为恒定法向载荷40 N时不同位移幅值下的摩擦系数曲线。从图中可以看出,当位移幅值D=2 μm时,微动运行在PSR中,摩擦系数一直处在较低水平且保持恒定。当位移幅值分别为D=10 μm, D=20 μm时,微动过程受MSR控制,摩擦系数从一个较低值迅速增加,但经历大约3000次循环后,摩擦系数基本保持恒定,此时微动进入了稳态阶段;此外,位移幅值为20 μm时的稳态摩擦系数明显高于位移幅值为10 μm,说明了位移幅值越大,黏着区域的塑性变形越剧烈,摩擦阻力越大。当位移幅值D=40 μm时,微动处在GSR,摩擦系数从低水平迅速上升,达到一个峰值1.4后开始下降至0.66附近,然后又开始缓慢攀升,当循环次数达到约4000次时,摩擦系数不再发生明显波动,微动进入动态稳态阶段。
图8(c)所示为法向载荷60 N时不同位移幅值下的摩擦系数曲线图,虽然曲线的稳态值和峰值存在一些差异,但它与图8(b)呈现出几乎相同的演化特征。上述结果表明,当微动运行在PSR时,接触界面的摩擦力非常小,接触中心一直保持在黏着状态且主要以弹性变形为主;当微动运行在MSR时,稳态阶段的接触表面仍然保持在黏着状态,且位移幅值越大,黏着区塑性变形越剧烈,稳态摩擦系数越大;当微动运行在GSR时,接触表面由二体作用逐渐过渡到三体作用,摩擦系数先上升后下降,当第三体(磨屑层)的产生和从表面溢出保持动态平衡时,摩擦系数保持相对稳定。
2.4 损伤机理
2.4.1 PSR
本文对不同运行机制下的磨损形貌与损伤机理进行了详细分析。图9所示为PSR的典型损伤特征。从图9(a)所示的磨痕全貌图来看,接触中心几乎未发生损伤,而接触边缘呈现一个轻微的摩擦环。对摩擦环局部放大后观察,图9(b)所示,接触表面有滑动摩擦的痕迹,只造成轻微的擦伤。磨痕三维形貌图(见图9(c))和轮廓曲线图(见图9(d))进一步看出,微动对接触体并未造成明显的损伤,只在接触表面留下一个较浅的压痕。因此,当微动运行在PSR时,接触中心在黏着状态下发生弹性变形而接触边缘只发生轻微擦伤,它们对基体造成的损伤几乎可以忽略不计。
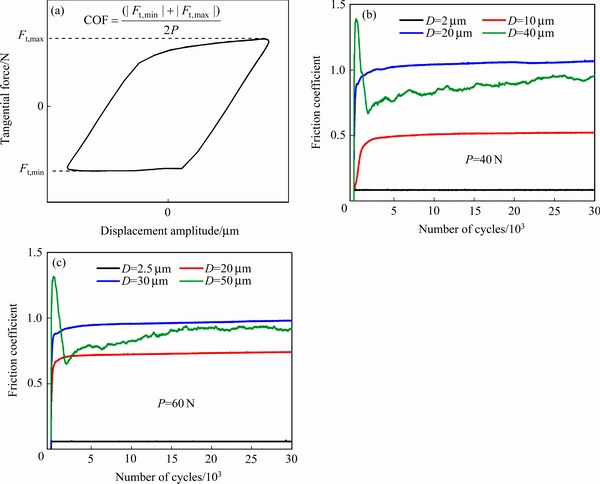
图8 不同运行机制下摩擦系数的演化特性
Fig. 8 Evolution characteristics of friction coefficient under different running regimes

图9 运行在PSR下的损伤特性(P=60 N, D=2.5 μm)
Fig. 9 Damage characteristics in PSR (P=60 N, D=2.5 μm)
2.4.2 MSR
图10所示为MSR控制下典型的损伤特征。磨痕全貌(见图10(a))仍然呈现出一个中心黏着区和环绕在其周围的滑移区。在黏着区内,图10(b)所示,观察到了黏着结合点在分离时留下“酒窝”状特征,且其周围发生了明显的塑性变形,这说明在相同材料配副的情况下,黏着更容易在金属表面发生且具有较强的黏结强度,这使得应力集中在黏着结点周围产生,在切应力反复作用下黏着结点周围留下了明显的塑性应变的痕迹。此外,在黏着区边缘还发现一个明显的断裂面,这是接触表面材料发生疲劳剥层后留下的断裂面。大量黏着结点在宏观上引起较大的塑性变形阻力,使得黏着区产生巨大的切应力,这不但会引起黏着区和滑移区边界出现严重的应力集中,还会导致塑性应变在次表层累积[17],从图10(c)中可以清楚地观察到在次表层中塑性应变累积留下的“鱼鳞”状特征。在往复微动过程中,微裂纹分别在黏-滑边界和次表层的塑性变形层上萌生并扩展,当这两类裂纹扩展连通至接触表面时,大块材料从表面剥离,留下图10(b)中明显的断裂面特征。从黏着区剥落的材料并未被迅速转移到接触区外,而是在滑移区被进一步挤压变形,形成塑性变形层覆盖在滑移区表面,如图10(d)所示。微动产生的循环应力会导致塑变层局部发生表面疲劳,剥离的片状磨屑在伴随氧化的摩擦过程中被破碎成细小的氧化物颗粒,这些硬质的氧化物颗粒在滑移区表面滚动,留下较深的沟槽,导致滑移区表面磨粒磨损。从磨痕三维形貌图(见图10(e))也可以清楚地观察到中心黏着区与边缘滑移区明显的分界,黏着磨损的部分磨屑堆积在黏着区的边界,滑移区被覆盖了一层塑性变形的磨屑。根据磨痕轮廓曲线图,黏着区大块材料脱离后留下一个巨大的“V”形凹陷,黏着区黏着磨损以及滑移区表面疲劳留下的小凹坑也在图中被观察到。

图10 运行在MSR下的损伤特性(P=60 N, D=30 μm)
Fig. 10 Damage characteristics in MSR (P=60 N, D=30 μm)
进一步对磨痕剖面进行观察,图11所示为MSR磨痕的剖面特征。从图11(a)中可以明显观察到,一个较大的裂纹在黏着区和滑移区边界处形成并向基体内部扩展,表明黏-滑边界处的应力集中最终导致了疲劳裂纹在此处萌生并向基体内部扩展。在图11(b)中发现了黏着区的次表层有一个明显的塑性应变层,微裂纹在该层萌生并向接触表面扩展。接触区的最大剪应力不是在接触表面,而是在距离表面一定距离处的次表面,所以塑性应变最先在次表面累积并形成大量位错,这为裂纹的形成创造了良好条件[18],在微动引起的循环应力作用下,导致了裂纹在该层萌生并向接触表面扩展。此外,在图11(c)中还观察到,在中心黏着区有一些细小的裂纹,这些裂纹主要在黏着结点附近形成,因为黏着结点有较强的结合强度,使应力集中在结点周围产生,促进了微裂纹在此处萌生。
上述结果表明,当微动处在MSR时,接触表面的损伤主要以黏着磨损和塑性变形为主,但应力集中在该机制中最为严重。黏着区的宏观应力集中会导致裂纹在黏-滑边界处萌生,黏着结点处的局部应力集中会导致微裂纹的形成。此外,次表层的塑性应变累积也促进了裂纹此处形核,并最终扩展至接触表面造成材料剥落,这通常被称之为剥层磨损[19]。
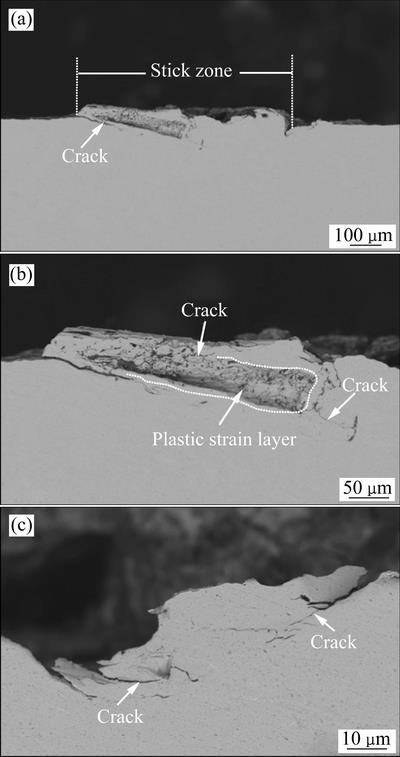
图11 运行在MSR的裂纹特征(P=60 N, D=30 μm)
Fig. 11 Crack characteristics in MSR (P=60 N, D=30 μm)
2.4.3 GSR
图12所示为GSR典型形貌特征。从全貌图可以看出(见图12(a)),整个接触区被覆盖一层较厚的塑性变形层,也被称之为“第三体层”。初始阶段黏着磨损产生的磨屑在有限的微动位移下难以排出接触区,在反复挤压变形后覆盖在接触表面,摩擦和氧化过程使其表面变得相对光滑,起到了固体润滑的作用[20]。对磨痕中心放大观察,如图12(b)所示,发现多个磨屑塑性变形的边界,这是因为在不同的循环次数下,磨屑的变形程度不一致(这也是摩擦系数曲线的波动的原因之一),新产生的磨屑被挤压变形后覆盖在原有的磨屑层上,从而留下了多个变形边界。此外,还观察到从接触表面脱离的片层状磨屑和多条沿微动方向的犁削凹槽,说明被氧化的磨屑颗粒在接触界面间充当磨粒的作用,对表面产生犁削效应造成磨粒磨损。从图12(c)可以更清楚地塑性变形层覆盖在基体表面,大部分磨屑呈颗粒状,但也有一部分磨屑呈团状堆积在接触边缘,这些团状磨屑可能是由于一些体积较大的磨屑在转移过程中未被完全破碎而形成的。从图12(d)中也发现了由于接触疲劳导致的剥落坑和磨粒磨损导致的犁沟,表明接触边缘也发生了一定程度的表面疲劳和磨粒磨损。磨痕的三维形貌图(见图12(e))显示,接触区发生了十分严重的材料损失,最大磨损深度接近52 μm。轮廓曲线图(见图12(f))呈现一个“M”形状,中间凹陷而两边隆起,这是因为中间区域有较大的摩擦应力,接触疲劳更容易发生,而塑性变形的磨屑使两边形成凸起。

图12 运行在GSR下的损伤特性(P=60 N, D=50 μm)
Fig. 12 Damage characteristics in GSR (P=60 N, D=50 μm)
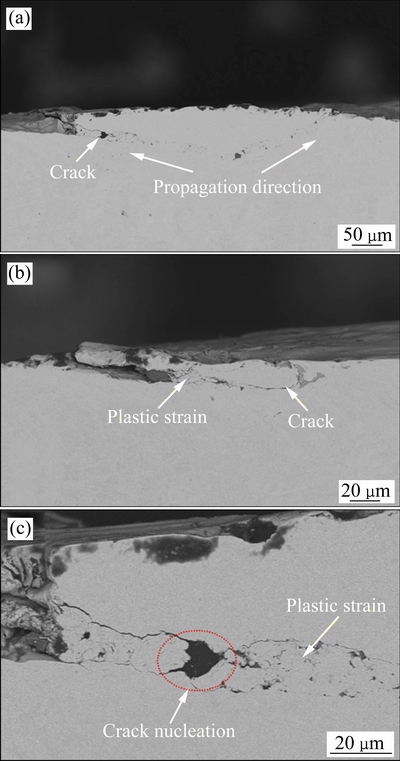
图13 运行在GSR的裂纹特征(P=60 N, D=50 μm)
Fig. 13 Crack characteristics in GSR (P=60 N, D=50 μm)
图13所示为GSR的剖面特征。从图中可以观察到次表层的裂纹从两侧向接触表面扩展,它们包围的材料即将从基体脱离形成大块磨屑。最大剪应力作用在次表层,导致位错和空洞在该区域形成,裂纹最先在此处形核,而后在循环应力下向接触表面扩展,最终引起接触表面发生疲劳剥层。上述结果表明,在接触区发生完全滑移时,磨损主要来自于四个方面:1) 初始阶段的黏着磨损。它产生的磨屑并没有迅速排出接触区,而是形成第三体层覆盖在接触表面,这反而阻止黏着磨损进一步发生。2)表面疲劳磨损。摩擦氧化使第三体层表面脆化,在循环应力作用下表面发生局部接触疲劳,片层磨屑从表面脱离,引起材料损失。3) 磨粒磨损。疲劳磨损产生的磨屑被进一步破碎成硬质氧化物颗粒,它们在接触表面之间滚动对基体表面造成犁削,引起磨粒磨损。4) 剥层磨损。裂纹在次表层最先形成,而后扩展至接触表面引起大块材料从基体剥离,与其他三种磨损相比,这一过程造成的材料损失最大。
图14所示为不同微动运行机制下的磨损体积测量。PSR下的体积损失极小,几乎可以忽略不计,MSR和GSR都造成了较大的材料损失,但GSR的磨损总量高于MSR。PSR下接触表面以弹性变形为主,边缘的微滑摩擦对表面造成的损伤也十分有限,所以磨损体积也是微不足道。MSR控制下,黏着磨损引起的材料损失有限,但由次表层裂纹引起的剥层磨损导致了严重的体积损失。GSR下,黏着磨损,表面疲劳磨损,磨粒磨损和剥层磨损的共同作用下,引起了较大的材料损失。
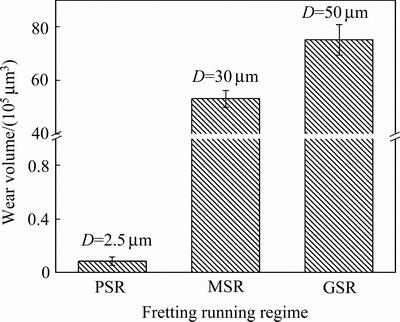
图14 不同微动运行机制下的磨损体积(P=60 N)
Fig. 14 Wear volume under different fretting running regimes (P=60 N)
综合上述分析,图15总结了CuMg0.4合金在不同运行机制下的损伤简化模型。当微动处在PSR时,接触中心以弹性变形为主,接触边缘的微滑只对表面产生轻微的擦伤。当微动处在MSR时,接触区仍然存在一个中心黏着区和边缘滑移区,但黏着区内的黏着结点遭受严重的塑性变形,滑移区被覆盖一层塑性变形的磨屑,其表面发生表面疲劳磨损和磨粒磨损。黏着区的宏观应力集中会导致裂纹在黏-滑边界处萌生,黏着结点处的局部应力集中也会导致微裂纹形成。此外,次表层的塑性应变累积也促进裂纹在此处形核,并最终扩展至接触表面造成剥层磨损。当微动处在GSR时,整个接触表面被第三体磨屑层覆盖。黏着磨损,表面疲劳磨损,磨粒磨损和剥层磨损的共同作用下,引起了较大的材料损失。
图16给出了CuMg0.4合金材料响应微动图,它将不同位移幅值和法向载荷条件下的材料损伤分为三个区域:轻微损伤区,黏着裂纹区以及严重磨损区,分别对应着微动运行工况图的PSR,GSR和GSR。该图对指导实际工程应用具有重要价值,在实际设计中,应尽量避免使微动处在黏着裂纹区和磨损区,应采取措施将其向轻微退化区转化。

图15 不同微动运行机制的损伤模型
Fig. 15 Damage models under different fretting running regime
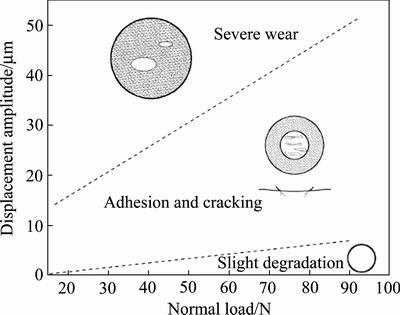
图16 CuMg0.4合金材料响应微动图
Fig. 16 MRFM of CuMg0.4 alloy
3 结论
1) CuMg0.4合金存在部分滑移和完全滑移两种接触状态。在部分滑移状态下,接触区域可以被细分为中心黏着区和环状的滑移区;随着位移幅值的增加,接触表面切向力增加,黏着区由弹性变形主导逐渐转化为塑性变形主导。当切向力超过临界值时,整个接触表面发生相对滑移,微动进入完全滑移状态。
2) CuMg0.4合金微动运行工况图(RCFM)由部分滑移机制(PSR),混合滑移机制(MSR)和完全滑移机制(GSR)组成。PSR主要发生在极小位移幅值或较大法向压力条件下,而GSR与之相反,MSR处在两者之间。
3) PSR下的微动损伤非常轻微,接触中心以弹性变形为主,接触边缘只发生轻微擦伤。MSR下,黏着区发生黏着磨损,滑移区被覆盖一层磨屑,磨损机理主要为表面疲劳磨损和磨粒磨损。裂纹在黏-滑边界处萌生并向金属基体内部扩展。次表层的塑性应变累积促进裂纹在此处形核,并最终扩展至接触表面造成剥层磨损。GSR下,接触表面被严重氧化的第三体层覆盖,磨损在该机制下占主导地位,磨损机理主要为初始阶段的黏着磨损,稳定阶段的表面疲劳磨损,磨粒磨损。
REFERENCES
[1] 谭德强, 莫继良, 彭金方, 等. 高速接触网零部件失效问题研究现状及展望[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2018, 53(3): 610-619.
TAN De-qiang, MO Ji-liang, PENG Jin-fang, et al. Research and prospect on high-speed catenary component failure[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2018, 53(3): 610-619.
[2] LIU X Y, PENG J F, TAN D Q, et al. Failure analysis and optimization of integral droppers used in high speed railway catenary system[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2018, 91: 496-506.
[3] 谭德强, 莫继良, 罗 健, 等. 高速铁路接触网定位钩和定位支座失效分析[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2018, 39(5): 111-118.
TAN De-qiang, MO Ji-liang, LUO Jian, et al. Failure analysis of positioning hook and support for high speed railway catenary[J]. China Railway Science, 2018, 39(5): 111-118.
[4] GAO Y, JIE J C, ZHANG P C, et al. Wear behavior of high strength and high conductivity Cu alloys under dry sliding[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(7): 2293-300.
[5] TONG Y X, LI S Y, ZHANG D T, et al. High strength and high electrical conductivity CuMg alloy prepared by cryorolling[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2019, 29(3): 595-600.
[6] YUAN X, LI G, ZHANG X, et al. An experimental investigation on fretting wear behavior of copper-magnesium alloy[J]. Wear, 2020, 462/463: 203497.
[7] 陈时光, 王忠诚, 王凯强, 等. 高铁用整体吊弦线体断裂原因分析[J]. 铁道机车车辆, 2020, 40(1): 98-101, 19.
CHEN Shi-guang, WANG Zhong-cheng, WANG Kai-qiang, et al. Fracture analysis of the integated dropper string body for high-speed railway[J]. Railway Locomotive & Car, 2020, 40(01): 98-101, 19.
[8] 孙亚琴, 潘嘉祺, 陈建斌, 等. 工艺参数对上引连铸铜镁合金杆微观组织的影响[J]. 有色金属工程, 2017, 7(5): 16-19.
SUN Ya-qin, PAN Jia-qi, CHEN Jian-bin, et al. Influence of process parameters on microstructure of upward continuous casting Cu-Mg alloy rod[J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 2017, 7(5): 16-19.
[9] 韦大杰, 刘明星, 聂金凤, 等. 高速电气化铁路用铜合金接触线反复弯曲失效分析[J]. 热加工工艺, 2017, 46(1): 255-258, 61.
WEI Da-jie, LIU Ming-xing, NIE Jin-feng, et al. Failre analysis of repeated bending of copper alloy contact wire for high speed electric railway[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2017, 46(1): 255-258, 61.
[10] 朱承程, 马爱斌, 江静华, 等. ECAP及后续退火对Cu-Mg合金组织与性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(5): 1331-1337.
ZHU Cheng-cheng, MA Ai-bin, JIANG Jin-hua, et al. Microstructure and properties of Cu-Mg alloys processed by ECAP and subsequent annealing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(5): 1331-1337.
[11] 魏 超, 彭金方, 刘曦洋, 等. CuMg0.4合金弯曲微动疲劳损伤特性研究[J]. 摩擦学学报, 2018, 38(6): 684-691.
WEI Chao, PENG Jian-fang, LIU Xi-yang, et al. Bending fretting fatigue damage characteristics of CuMg0.4 alloy[J]. Tribology, 2018, 38(6): 684-691.
[12] 薛博凯, 米 雪, 白崇成, 等. 电流作用对铜镁合金弯曲微动疲劳损伤特性的影响[J]. 摩擦学学报, 2020, 40(1): 107-116.
XUE Bo-kai, MI Xue, BAI Chong-cheng, et al. Effect of current strength on bending fatigue damage characteristics of copper-magnesium alloy[J]. Tribology, 2020, 40(1): 107-116.
[13] 张德坤, 葛世荣. 钢丝的微动磨损及其对疲劳断裂行为的影响研究[J]. 摩擦学学报, 2004, 24(4): 355-359.
ZHANG De-kun, GE Shi-rong. Fretting wear behavior of steel wire and the effect of fretting on its fatigue fracture behavior[J]. Tribology, 2004, 24(4): 355-359.
[14] HERTZ H. On the contact of elastic solids[J]. Journal für die rne und angewandte Mathematik (Crelles Journal), 1882, 92(156): 156-171.
[15] MINDLIN R D. Compliance of elastic bodies in contact[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1949, 16: 259-268.
[16] ZHOU Z R, VINCENT L. Effect of external loading on wear maps of aluminium alloys[J]. Wear, 1993, 162/164: 619-623.
[17] VINGSBO O, S DERBERG S. On fretting maps[J]. Wear, 1988, 126(2): 131-147.
[18] WATERHOUSE R B. The role of adhesion and delamination in the fretting wear of metallic materials[J]. Wear, 45(3): 355-364.
[19] SUH N P. An overview of the delamination theory of wear[J]. Wear, 1977, 44(1): 1-16.
[20] VARENBERG M, HALPERIN G, ETSION I. Different aspects of the role of wear debris in fretting wear[J]. Wear, 2002, 252(11): 902-910.
Study on tangential fretting wear behavior of CuMg0.4 alloy
YUAN Xin-lu, ZHANG Xiao-yu, LI Gen, PU Jian, REN Ping-di
(Tribology Research Institute, School of Mechanical Engineering, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu 610031, China)
Abstract: The tangential fretting wear tests of CuMg0.4 alloy were carried out in this paper. The tangential fretting running characteristics and damage mechanisms of CuMg0.4 alloy were studied in detail, and the running condition fretting map (RCFM) and material response fretting map (MRFM) were established. The results show that the fretting characteristics of CuMg0.4 alloy can be divided into partial slip regime (PSR), mixed slip regime (MSR) and gross slip regime (GSR). In the PSR, elastic deformation was dominant in the contact center, and only slightly scratch occurred at the contact edge. In the MSR, severe plastic deformation occurred in the stick zone, and surface fatigue wear and abrasive wear were dominant in the slip zone. In addition, the crack initiated at the stick-slip boundary and propagated into the metal matrix. The accumulation of plastic strain in the subsurface promoted cracks nucleation here, and these cracks finally extended to the contact surface, resulting in delamination. In the GSR, the contact surface was covered by anoxidized third-body layer, and the wear mechanism is mainly adhesive wear in the initial stage, surface fatigue wear and abrasive wear in the stable stage.
Key words: fretting wear; CuMg0.4 alloy; contact state; fretting map
Foundation item: Projects(U1534209, 51775459) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2020YFG0135) supported by the Key Research Development Program of Sichuan Science and Technology Department
Received date: 2021-03-10; Accepted date: 2021-07-14
Corresponding author: ZHANG Xiao-yu; Tel: +86-28-87603924; E-mail: zhangyu3035@126.com
(编辑 )
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(U1534209,51775459);四川省科技厅重点研发资助项目(2020YFG0135)
收稿日期:2021-03-10;修订日期:2021-07-14
通信作者:张晓宇,高级工程师,博士;电话:028-87603924;E-mail:zhangyu3035@126.com