抗菌仿生多孔钛植入体的成骨性能
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2017年第9期
论文作者:王国慧 付华 赵颜忠 周科朝 朱晒红
文章页码:2007 - 2014
关键词:抗菌功能;表面改性;多孔钛植入体;骨整合;冷冻铸造
Key words:antibacterial function; surface modification; porous titanium implant; osseointegration; freeze-casting
摘 要:采用冷冻铸造和热氧化法制备一种新型兼具抗菌功能和良好骨整合性能的表面改性仿生多孔钛植入体。通过细胞增殖实验、碱性磷酸酶(AKP)活性水平测定实验、X线检测及骨硬组织切片等体内外成骨实验方法评价多孔钛植入体的骨整合性能。结果显示,随着植入体与体外细胞共培养时间的延长,表面纳米改性后多孔钛实验组的体外细胞增殖、分化活性水平较未表面纳米改性的多孔钛和致密钛对照组明显升高(P<0.05);随着在动物体内植入时间的延长,处理和未处理多孔钛实验组孔隙中有骨长入和成骨现象,而且成骨细胞在处理组孔隙中分化程度更加成熟。抗菌仿生多孔钛植入体能与骨组织形成牢固的生物性骨嵌合,具有良好的骨整合性能。
Abstract: A novel antibacterial biomimetic porous titanium implant with good osseointegration was prepared by freeze-casting and thermal oxidation. Bone integration properties of the porous titanium implant were evaluated by cell proliferation assay, alkaline phosphatase activity assay, X-ray examination and hard bone tissue biopsy. The in vitro cell proliferation and the level of differentiation of the group with a modified nano-porous implant surface were significantly higher than those in the group without surface modification and the dense titanium control group (P<0.05). In vivo, bone growth and osteogenesis were found in the experimental groups with modified and unmodified porous titanium implants; osteoblasts in the modified group had more mature differentiation in the pores compared to the unmodified group. Such implants can form solid, biologically compatible bone grafts with bone tissues, exhibiting good osseointegration.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 27(2017) 2007-2014
Guo-hui WANG1, Hua FU1, Yan-zhong ZHAO1, Ke-chao ZHOU2, Shai-hong ZHU1
1. The Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha 410013, China;
2. State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 25 May 2016; accepted 16 September 2017
Abstract: A novel antibacterial biomimetic porous titanium implant with good osseointegration was prepared by freeze-casting and thermal oxidation. Bone integration properties of the porous titanium implant were evaluated by cell proliferation assay, alkaline phosphatase activity assay, X-ray examination and hard bone tissue biopsy. The in vitro cell proliferation and the level of differentiation of the group with a modified nano-porous implant surface were significantly higher than those in the group without surface modification and the dense titanium control group (P<0.05). In vivo, bone growth and osteogenesis were found in the experimental groups with modified and unmodified porous titanium implants; osteoblasts in the modified group had more mature differentiation in the pores compared to the unmodified group. Such implants can form solid, biologically compatible bone grafts with bone tissues, exhibiting good osseointegration.
Key words: antibacterial function; surface modification; porous titanium implant; osseointegration; freeze-casting
1 Introduction
Titanium and titanium alloys, as bone substitute materials, have good biocompatibility, mechanical properties, and many other advantages. However, in vivo titanium and titanium alloy implants only mechanically but not biologically integrate with bone tissues after an operation. In particular, loosening, peripheral bone inflammation, and severe complications caused by bacterial growth on the implant surface increase the risk of failure after bone implantation [1,2].
New bone implants require a special response and interaction with living cells of the bone tissue, thereby inducing osteoblast development into viable new bone tissue or organs in the physiological environment, i.e., good osseointegration [3,4]. Structures with anisotropic gradient distribution of porous metals prepared by freeze-casting are very similar to natural human skeletal materials. Optimization of freeze-casting may change the pore morphology and size of a porous titanium implant, rendering them similar to human bone tissues [5-7]. Our previous study has shown that thermal oxidation helps the formation of nanoscale, nanospike structures on the porous surface of titanium implants that effectively avoid bacterial growth [8]. But osseointegration of these implants requires verification.
The formation of a good bone-implant interface is the key to successful grafting, and osteoblasts are critical components of that interface. Studies on the interaction between osteoblasts and implant materials, as well as the impact of implant materials on the biological properties of osteoblasts, can directly reflect the effectiveness of implant materials for osseointegration [9,10]. In the present work, freeze- casting and thermal oxidation were used to prepare a novel, surface-modified biomimetic porous titanium implant with good antibacterial properties and osseointegration. In vivo and in vitro osteogenic assays were used to evaluate the osseointegration of the implant to determine its feasibility for future clinical applications.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials
Specimens in the two experimental groups were porous titanium with surface modification (i.e., the modified experimental group) and porous titanium without surface modification (i.e., the unmodified experimental group). Dense titanium was used as specimen in the control group.
2.2 Preparation of porous titanium and nanospike surface modification
Titanium powder with a particle size of <25 μm (Sigma-Aldrich, USA) and camphene (Fisher Scientific, UK), a solvent medium, were magnetically stirred in a water bath for 2 h at a temperature of 60 °C and a stirring rate of 800 r/min. Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) was used as binder. The stirring vessel was covered to reduce solvent evaporation. The volume fraction of titanium powder in the slurry was 10%. The mold was placed in the water bath for precooling for 30 min at 20 °C, after which the prepared slurry was slowly poured into a precooled cylindrical mold with a thermally insulated top and bottom. After being cured for 4 h, the mold was placed overnight at -20 °C for further cooling. Then, the samples were demolded and transferred to a vacuum freeze drying oven for sublimating for 24 h. The dried body was then put into the sintering furnace, where it was sintered firstly in vacuum at a heating rate of 1 °C/min until furnace temperature reached 400 °C, and then in argon atmosphere at a heating rate of 10 °C/min until furnace temperature reached 1200 °C. After being sintered for 1 h, the dried body was naturally cooled down to room temperature, and then the preparation of the porous titanium was thereafter completed.
Samples were placed in the centre of a horizontal alumina tube furnace. After Ar was purged into the tube, the temperature of tube was increased to 850 °C at 15 °C/min. After reaching 850 °C, the Ar flow was diverted through a bubbler bottle containing acetone at 25 °C with the Ar flow rate of 300 mL/min. The temperature was kept at 850 °C for 45 min, after which the tube was allowed to cool under a flow of Ar of 500 mL/min. To remove the carbon from the as-synthesized nanospikes, the samples were heated to 600 °C at a rate of 10 °C/min.
2.3 Porous structures and mechanical properties
The porous structures (porosity, degree of interconnection) of the porous Ti scaffolds were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM, JSM-6330F, JEOL Techniques, Tokyo, Japan). The pore size was also analyzed from the SEM images of the samples prepared by infiltrating the porous Ti scaffolds with epoxy resin. The compressive strength of the porous Ti scaffolds with a diameter of 16 mm and a height of 20 mm was examined using a screw-driven load frame at a crosshead speed of 5 mm/min. The stress and strain responses of the samples were monitored during the compressive strength tests. Five samples were tested to obtain the mean values and the standard deviation.
2.4 Proliferation and differentiation of in vitro human osteosarcoma cells, MG63
2.4.1 Detection of human MG63 osteosarcoma cell proliferation
Porous titanium specimens in the modified and unmodified experimental groups, as well as dense titanium specimens in the control group, were transferred into 24-well culture plates after sterilization and drying. Each group contained three parallel samples. RPMI- 1640 culture medium (500 μL) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) was added into each well. After hydrating the specimens for 24 h, the culture medium was discarded followed by gently rinsing the specimens twice in phosphate buffered saline (PBS). Trypsinized and passaged human MG63 osteosarcoma cells were diluted to a density of 1×104 cells/μL per well, and the cell suspension was slowly transferred dropwise into each well on the specimen surface, followed by incubating at 37 °C in an incubator containing 5% CO2 and 95% humidity for 8 h. Once the cells began to grow, 1 mL culture medium was added slowly into each well. The cells were further incubated with the medium changed once every two days.
Cells were assayed after 1, 3, and 5 days of incubation by discarding the culture medium and gently rinsing with PBS twice, followed by adding 500 μL RPMI-1640 culture medium containing 10% FBS and 50 μL cell counting kit (CCK)-8 reagent, and then cultured at 37 °C in the incubator for 4 h. Cell supernatants from wells co-cultured with corresponding specimens in the three different groups were transferred to a 96-well plate to measure the optical density in a microplate reader at 450 nm wavelength.
2.4.2 Detection of alkaline phosphatase (AKP) activity in human MG63 osteosarcoma cells
Cells were prepared in 24-well culture plates exactly as described in Section 2.4.1. Cell were assayed after 1, 3, and 5 days of incubation by discarding culture medium and gently rinsing with PBS twice, followed by adding 2.5 g/L trypsin to digest the cells for 2 min. Cell lysate (500 μL 0.2% TritonX-100) was added into each well to cover the cells, and then they were incubated overnight at 4 °C. An AKP assay kit (microtitration method) was used to calculate the AKP activity of the osteoblasts according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.5 Detection of in vivo osteogenic activity
Eighteen New Zealand rabbits (equal number of male and female) weighing (2.5±0.5) kg were provided by the Experimental Animal Center of the Third Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China. Animals were randomly divided into three groups, including 4-week, 8-week, and 12-week groups (six animals per group). After conventional hair removal, disinfection, and placement of a sterile surgical drape on the lateral femoral region of the high limbs, an incision of approximately 2.5 cm was made on the lateral proximal femur. A 3 mm diameter drill was used to drill through the cortex perpendicular to the long axis of the femur, followed by continuously rinsing the drill with 4 °C normal saline to prepare a d3 mm × 6 mm bone defect. The specimens of the experimental groups were implanted at one of the hind limbs, with the implants located slightly above the bone cortex surface. Dense titanium samples of the control group were implanted in the other hind limb of the same animal using the above methods.
The rabbits in the different groups were sacrificed at 4, 8, and 12 weeks after implantation for bilateral anteroposterior X-ray examination on the femurs with imaging conditions of 70 kV, 80 mA, and 32 ms to observe bone repair. Animals were dissected to collect specimens and peripheral bone tissues (within 0.5-1.0 cm). The collected materials were fixed in 80% ethanol for more than 48 h, followed by dehydrating in gradient ethanol solutions, polymethyl methacrylate embedding, coronal serial sectioning along the femurs using a Leica 2500 microtome (100 μm in thickness per section), a step-by-step grinding-based method to prepare the bone sections into 50-70 μm in thickness, and methylene blue Van Gieson’s staining and light microscopy to observe the histomorphology of the new bone growth and calcification around the implants.
2.6 Statistical analysis
SPSS19.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) software was used for statistical analysis. Experimental data are presented as means ± standard deviation  . Experimental data from two groups were compared using independent-sample Student’s paired t tests. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant. ANOVA was used to test significant differences between multiple groups.
. Experimental data from two groups were compared using independent-sample Student’s paired t tests. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant. ANOVA was used to test significant differences between multiple groups.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Porous structures and mechanical properties
When the volume fraction of titanium powder in slurry was set to be 10% and the porous specimen was sintered at 1200 °C for 1 h, the porosity, pore diameter, compression strength and elasticity modulus of the porous specimen were (58.32±1.08)%, (126.17± 18.64) μm, (58.51±20.38) MPa and (1.70±0.52) GPa, respectively. SEM image (Fig. 1(a)) showed that the morphology of porous titanium was radially distributed and concentrated in the middle of the cylinder. As shown in Fig. 1(b), nanospikes were evenly distributed on the pore wall surface after thermal oxidation treatment. The size of the nanospikes developed on the substrate of the pore wall was about 200 nm.
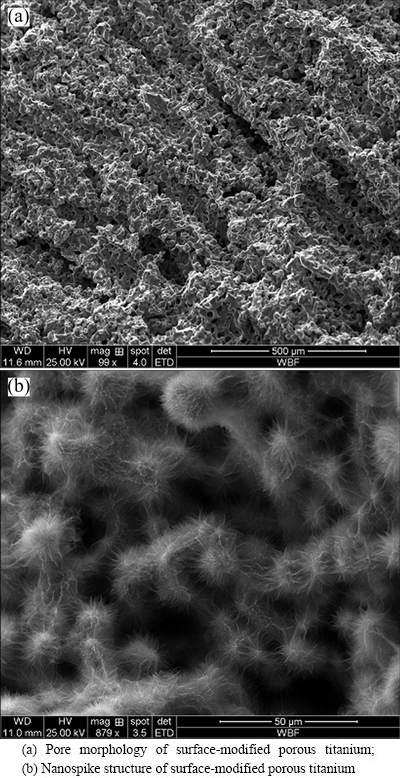
Fig. 1 SEM images of surface-modified porous titanium
3.2 Cell proliferation and differentiation of human MG63 osteosarcoma cells
3.2.1 Proliferation of human MG63 osteosarcoma cells
In vitro osteogenic assay is a relatively simple method to evaluate osseointegration. In addition, it has the advantage of allowing observation of the effects of a single factor via changes occurring after co-culturing of cells and implants [11]. Osteoblasts are the cells responsible in vivo for osteogenesis, and are responsible for synthesizing and secreting bone matrix and promoting mineralization to form bone tissue. Morphological analysis of the adhesion and chemotaxis of osteoblasts, and analysis of their proliferation and differentiation on implant materials, are required to verify the degree of osseointegration to determine if the materials are suitable for clinical application [12,13].
In this work, MG63 osteosarcoma cells were co-cultured with corresponding specimens from modified and unmodified experimental groups as well as the control group. Figure 2 indicated that the osteoblast adhesion and proliferation on the specimens of the three groups on days 1, 3, and 5 of co-culture were extensive. Extension of the co-culture time also increased cell proliferation for different groups. However, significant differences in cell proliferation were found between the two experimental groups and the control group on days 1 and 3 of co-culture (P<0.05), while no significant difference was found between the unmodified and modified experimental groups. Cell proliferation on the three groups of implant materials was the greatest on day 5 of co-culture and was significantly larger compared to that on day 1. Significant differences in cell proliferation on day 5 were found between the modified and unmodified experimental groups, as well as between the modified experimental groups and control group (P<0.05). Co-culture with the porous titanium specimens facilitated cell proliferation better than the dense titanium alloy, suggesting that porosity was the main factor affecting proliferation. Prolonged co-culture with the modified porous titanium specimen improved osteoblast proliferation better than that with either the unmodified porous specimens or the dense alloy. Nanostructures in the pores of implants are considered to promote cell adhesion and proliferation because of (1) their biomimetic effects, in which the structural size is very similar to the inorganic mineral size of normal bone, (2) the larger surface area of the nanostructures compared with traditional microstructures which allows more adhesion for osteocytes, and (3) nano-pores or tubular structures which allow cell filaments to extend into the structures and act as anchors to promote cell adhesion and growth [14-16].
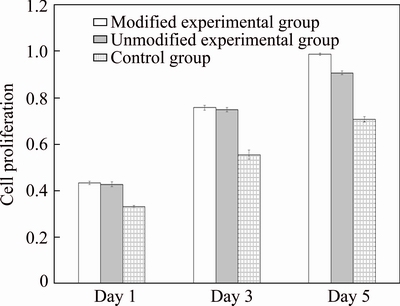
Fig. 2 Impacts of different materials on proliferation of human osteogenic sarcoma cell line MG63
3.2.2 AKP activity of human MG63 osteosarcoma cells
Good proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts accelerate the growth rate of the bone-implant interface and promote maturation of new bone tissues [9]. AKP is involved in the process of bone formation, metabolism and regeneration, and is an important protein for the early differentiation of osteoblasts. AKP activity reflects the differentiation activity and functional status of osteoblasts, especially newly formed osteoblasts. AKP activities of MG63 osteosarcoma cells in different groups were measured and it was found (Fig. 3) that prolonged co-culture with different specimens continually increased the AKP activities of the cells. AKP activities of osteoblasts co-cultured for 1 day with porous titanium in both experimental groups were significantly higher than those in the dense titanium implant control group (P<0.05). No significant difference in AKP activities was found between the two experimental groups. AKP activities for cells co-cultured for 3 and 5 days with porous titanium in both experimental groups were also significantly higher than those in the control group (P<0.05); in addition, AKP activity in the modified group was significantly higher than that in the unmodified group (P<0.05). These results suggested that the porous structure and tertiary nanostructure of the pore gaps affected the AKP activities of osteoblasts, as prolonged co-culture with nano-modified porous titanium showed the most enhanced AKP activity.
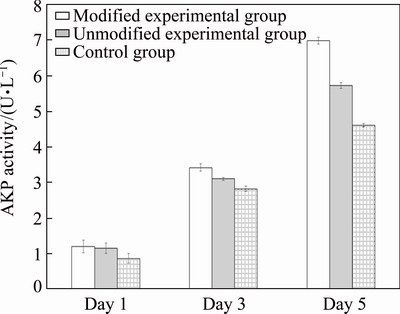
Fig. 3 AKP activity measured at different time after co-culturing of cells with different implant materials
3.3 In vivo osteogenic assay
The rabbits tested were in generally good health after the operations. Despite one animal with limb movement disorders, the remaining rabbits could walk, exercise, and eat normally after the operation without bone graft fractures or premature mortality. Postoperative wound healing was extensive, with no localized swelling, sinus formation, or pus secretion on the sutures. Specimens collected at different postoperative time after skin incision demonstrated no muscle necrosis, suppuration, or effusion of implant- adjacent tissues. Figure 4 demonstrates the in vitro coated periosteum in these three groups of implants with close integration with bone and no loosening.
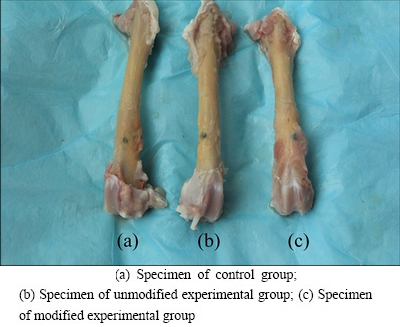
Fig. 4 Implant materials in different groups collected after postoperative 4 weeks
X-ray examinations after postoperative 4 weeks revealed no sign of bone dissolution or X-ray translucent areas in the implants of the two experimental groups and the control group. No obvious gap, but rather close integration, was found between the implants and adjacent bones. However, no significant signs of osteogenesis were found at the early stage of bone healing. X-rays taken after postoperative 8 weeks showed no significant changes in the dense titanium control group compared to 4 weeks; however, the integration between the modified and unmodified porous titanium and the implant-adjacent tissues was closer with new bone formation at 8 weeks compared to 4 weeks. Results after 12 weeks (Fig. 5) showed no loosening or bone resorption between these three groups of implant materials and their adjacent bone tissues. Bone density adjacent to implants of the modified and unmodified experimental groups was increased, but no significant increase of new bone mass was found.
The morphology of the bone-implant interface has been used as the standard for evaluating osseointegration. In current studies on bone-implant interfaces, cutting/ grinding-based histological sectioning on undecalcified hard tissues is often used to prepare sections for analysis of bone formation, deposition and absorption. In the present work, light microscopy of Van Gieson’s stained hard tissue sections revealed connective tissues in blue, mature bone and trabecular bone in red, and peripheral tissues before calcification in purple. The results of morphological analysis are shown in Fig. 4. Van Gieson’s staining after postoperative 4 weeks showed the presence of a gap at the interface between the dense titanium implant and adjacent bone tissues, with blue connective tissues filling the inside of the gap (Figs. 6(a), (b) and (c)). Gaps were found in some regions between the porous titanium implants and bone tissues in the two experimental groups, with new bone tissue deposition and continuous growth from the bottom of the gap and bone wall surrounding the gap to the implant surface. Blue connective tissues growing into the pores were observed. Van Gieson’s staining after postoperative 8 weeks (Figs. 6(d), (e) and (f)) showed the disappearance of the gap at the interface between the dense titanium implant and adjacent bone tissues with close bone tissue integration. No other tissue filling was found at the bone-implant interface. The porous titanium implants of the two experimental groups were closely connected to their adjacent bone tissues, and the gaps were completely repaired by new bone tissue. No other tissue fillings were found at the bone-implant interfaces. The new bone tissue was gradually rebuilt, lamellar bone formed, and blue connective tissues were found to grow into the pores. After postoperative 12 weeks (Figs. 6(g), (h) and (i)), mineralization began to appear in some bone tissues adjacent to the dense titanium implant in the control group, with some areas showing vascular proliferation. In the porous titanium experimental groups, most of the bone-implant margin disappeared, mature bone plate tissues were found around the implants, and the bone growing into the pores began to mature and mineralize. The above findings suggested that the porous structure and surface nano-modification of implants affected the bone ingrowth. Bone deposited inside the pores of implants with surface nano-modification had more mature differentiation than that of unmodified implants, suggesting that the nanostructures promoted bone ingrowth and differentiation of osteoblasts, which might be associated with the physiological micro- vascularization inside the pores at the late stage. WILLIE et al [17] and CHRISTENSON et al [18] suggested that a moderate to late stage of osteogenesis and its stability are associated with vascularization, which is mainly affected by pore morphology and connectivity. Due to the complexity and variations of in vivo environments, factors affecting bone ingrowth due to nano-modification are relatively complex; therefore, further investigation and clarification of its direct impact factors will be necessary.
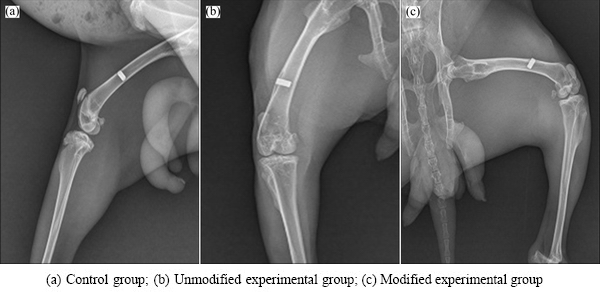
Fig. 5 X-ray images of different implant specimens after postoperative 12 weeks
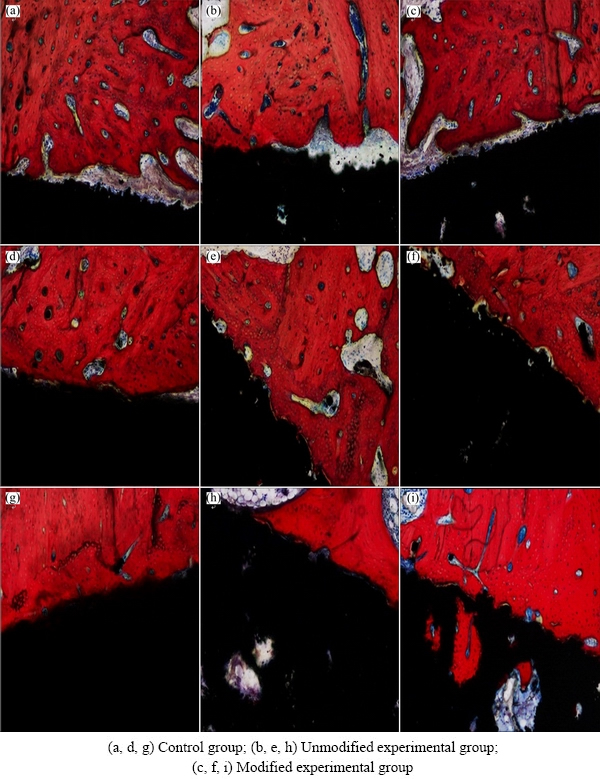
Fig. 6 Representative Van Gieson’s staining of hard tissue sections with different implant specimens after postoperative 4 (a-c), 8 (d-f), and 12 (g-i) weeks
4 Conclusions
1) Porous structures of the surface were modified with nanoscale nanospike biomimetic structures, and these structures affected the proliferation and differentiation capacity of in vitro osteoblasts.
2) Prolonged co-culture with the modified porous titanium implant increased the proliferation, differentiation and adhesion activity of osteoblasts compared to the unmodified porous or dense titanium implants.
3) Porous structures and tertiary nanostructures inside the pores affected in vivo bone formation, deposition and calcification. Prolonged co-culture with these implants allowed for mature differentiation of osteoblasts inside the pores to form a solid biological bone chimera.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Professor SU Bo in School of Oral and Dental Sciences, University of Bristol, UK for carrying out nanospike surface- modification test.
References
[1] WANG Xiao-jian, XU Shan-qing, ZHOU Shi-wei, XU Wei, LEARY M, CHOONG P, QIAN M, BRANDT M, XIE Yi-min. Topological design and additive manufacturing of porous metals for bone scaffolds and orthopaedic implants: A review [J]. Biomaterials, 2016, 83: 127-141.
[2] RYAN G E, PANDIT A S, APATSIDIS D P. Porous titanium scaffolds fabricated using a rapid prototyping and powder metallurgy technique [J]. Biomaterials, 2008, 29: 3625-3635.
[3] ZHAO Ling-zhou, WEI Yan-ping, Li Jian-xue, HAN Yong, YE Rui-dong, ZHANG Yu-mei. Initial osteoblast functions on Ti-5Zr-3Sn-5Mo-15Nb titanium alloy surfaces modified by microarc oxidation [J]. J Biomed Mater Res A, 2010, 92: 432-440.
[4] DINAN B, GALLEGO P D, LEE H, HANSFORD D, AKBAR S A. Thermally grown TiO2 nanowires to improve cell growth and proliferation on titanium based materials [J]. Ceram Int, 2013, 39: 5949-5954.
[5] ULRIKE G K W, SCHECTER M, DONIUS A E, HUNGER P M. Biomaterials by freeze casting [J]. Phil Trans R Soc, 2010, 368: 2099-2121.
[6] SYLNAIN D. Freeze-casting of porous biomaterials: Structure, properties and opportunities [J]. Materials, 2010, 3: 1913-1927.
[7] PORTER M M, MCKITTRICK J, MEYERS M A. Biomimetic materials by freeze casting [J]. JOM, 2013, 65: 720-727.
[8] TERJS S, ANGELA H N, BO Su. Bactericidal nanospike surfaces via thermal oxidation of Ti alloy substrates [J]. Materials Letters, 2016, 167: 22-26.
[9] TORO R D, BETTI V, SPAMPINATO S. Biocompatibility and integrin-mediated adhesion of human osteoblasts to poly (DLlactide- co-glycolide) copolymers [J]. Eur J Pha rm Sci, 2004, 21: 161-169.
[10] ALCAIDE M, SERRANO M C, PAGANI R,  M T. Biocompatibility markers for the study of interactions between osteoblast sand composite biomaterials [J]. Biomaterials, 2009, 30: 45.
M T. Biocompatibility markers for the study of interactions between osteoblast sand composite biomaterials [J]. Biomaterials, 2009, 30: 45.
[11] JEON O, BOUHADIR K H, MANSOUR J M, ALSBERG E. Photocrosslinked alginate hydrogels with tunable biodegradation rates and mechanical properties [J]. Biomaterials, 2009, 30: 2724-2734.
[12] ROHNER D, HUTMACHER D W, SEE P, TAN K C, YEOW V, TAN S Y, LEE S T, HAMMER B. Individually CAD-CAM technique designed, bioresorbable 3-dimensional polycaprolactone framework for experimental reconstruction of craniofacial defects in the pig [J]. Mund Kiefer Gesichtschir, 2002, 6: 162-167.
[13] ROTUNDA A M, NARINS R S. Poly-L-lactic acid: A new dimension in soft tissue augmentation [J]. Dermatol Ther, 2006, 19: 151-158.
[14] SATO M, SAMBITO M A, ASLANI A, KAIKHORAN N M, SLAMOVICH E B, WEBSTER T J. Increased osteoblast functions on undoped and yttrium-doped nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite coatings on titanium [J]. Biomaterials, 2006, 27: 2358-2369.
[15] SWAN E E, POPAT K C, GRIMES C A, DESAI T A. Fabrication and evaluation of nanoporous alumina membranes for osteoblast culture [J]. J Biomed Mater Res A, 2005, 72: 288-295.
[16] POPAT K C, LEONI L, GRIMES C A, DESAI T A. Influence of engineered titania nanotubular surfaces on bone cells [J]. Biomaterials, 2007, 28: 3188-3197.
[17] WILLIE B, YANG X, KELLY N, MERKOW J, GAGNE S, WARE R, WRIGHT T M, BOSTROM M P. Osseointegration into a novel titanium foam implant in the distal femur of a rabbit [J]. Journal of Biomedical Research: Applied Biometerials, 2010, 92: 479-488.
[18] CHRISTENSON E, ANSETH K, BEUCKEN J, CHAN C K, ERCAN B, JANSEN J A, LAURENCIN C T, LI W J, MURUGAN R, NAIR L S, RAMAKRISHNA S, TUAN R S, WEBSTER T J, MIKOS A G. Nanobiomaterial applications in orthopedics [J]. Journal of Orthopaedic Research, 2007, 25: 11-22.
王国慧1,付 华1,赵颜忠1,周科朝2,朱晒红1
1. 中南大学 湘雅三医院,长沙 410013;
2. 中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,长沙 410083
摘 要:采用冷冻铸造和热氧化法制备一种新型兼具抗菌功能和良好骨整合性能的表面改性仿生多孔钛植入体。通过细胞增殖实验、碱性磷酸酶(AKP)活性水平测定实验、X线检测及骨硬组织切片等体内外成骨实验方法评价多孔钛植入体的骨整合性能。结果显示,随着植入体与体外细胞共培养时间的延长,表面纳米改性后多孔钛实验组的体外细胞增殖、分化活性水平较未表面纳米改性的多孔钛和致密钛对照组明显升高(P<0.05);随着在动物体内植入时间的延长,处理和未处理多孔钛实验组孔隙中有骨长入和成骨现象,而且成骨细胞在处理组孔隙中分化程度更加成熟。抗菌仿生多孔钛植入体能与骨组织形成牢固的生物性骨嵌合,具有良好的骨整合性能。
关键词:抗菌功能;表面改性;多孔钛植入体;骨整合;冷冻铸造
(Edited by Bing YANG)
Foundation item: Projects (51290295, 51305464) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2016JJ6156) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China; Project (2016JC2064) supported by Key Research and Development Project of Hunan Province, China; Project (20130162120094) supported by Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education, China
Corresponding authors: Shai-hong ZHU; Tel: +86-731-88618234; E-mail: zhushaihong@medmail.com.cn; Yan-zhong ZHAO; Tel: +86-731-88618669;E-mail: yanzhongzhao@163.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(17)60225-5

