文章编号:1004-0609(2012)1-0216-08
过渡金属对Mg2Ni氢化物电子结构和热力学稳定性影响:第一性原理研究
陈捷狮,曾 含,王 路,蓝志强,郭 进
(广西大学 物理科学与工程技术学院,南宁 530004)
摘 要:采用基于密度泛函理论(DFT)的平面波赝势(PW-PP)方法,计算并分析了Mg2Ni1-xMx(M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, x=0.25)合金及其氢化物Mg2Ni1-xMxH4的电子结构和热力学稳定性。计算结果表明:Mg2NiH4和Mg2Ni1-xMx的晶胞参数与实验值吻合较好。对Mg2Ni1-xMxH4的电子结构分析发现:氢化物中的Ni—H和M—H键为共价键、Mg—H键为离子键,且Ni—H与M—H键的相互作用强于Mg—H键的。Mn、Fe和Co的部分替代对Ni—H键的相互作用影响较小,而Cu的替代则减弱了Ni—H键的相互作用,这可能是Cu替代后氢化物结构稳定性降低的一个原因。计算了Mg2Ni0.75M0.25H4 (M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu )的生成焓,分别为-57.7、-61.5、-61.4、63.4和41.6 kJ/mol,与实验值吻合较好。
关键词:Mg2Ni;第一性原理;电子结构;热力学稳定性
中图分类号:O641 文献标志码:A
Effects of transitional metal on electronic structure and thermodynamic stability of Mg2Ni hydride: A first-principle investigation
CHEN Jie-shi, ZENG Han, WANG Lu, LAN Zhi-qiang, GUO Jin
(College of Physical Science and Technology, Guangxi University, Nanning 530004, China)
Abstract: The electronic structures and thermodynamic stabilities of Mg2Ni1-xMx (M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, x=0.25) alloys and their hydrides Mg2Ni1-xMxH4 were investigated by plane-wave pseudo-potential approach based on the density functional theory. It is found that the calculated cell parameters of Mg2NiH4 and Mg2Ni1-xMx alloy are in good agreement with the experimental results. For Mg2Ni1-xMxH4, the interaction between Mg—H bonds is ionic bond, while the interactions between Ni—H and M—H are covalent bonds, which are stronger than that of Mg—H bonds. The Ni—H bond strength is almost unchanged when Ni is partially replaced by Mn, Fe and Co, and the Ni—H bond strength is weakened when Ni is partially substituted by Cu, which may be one of the reasons for causing the reduced structure stability of Mg2Ni0.75Cu0.25H4. The calculated formation enthalpies of Mg2Ni0.75M0.25H4 (M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu) are -57.7, -61.5, -61.4, 63.4 and 41.6 kJ/mol, respectively, which are in good agreement with the experimental results.
Key words: Mg2Ni; first principle; electronic structure; thermodynamic stability
A2B型Mg2Ni储氢合金具有储氢量(3.6%,质量分数)大、价格低廉、资源丰富等突出优点,是最具应用前景的储氢合金之一。但是,Mg2Ni合金放氢温度高,反应动力学和热力学性能较差,阻碍了其实际应用[1-2]。近年来,为了提高Mg2Ni合金的综合性能,国内外学者在实验和理论上进行了大量的研究。如YANG等[3]通过球磨的方法合成了Mg2Ni0.75M0.25合金 (XRD相结果显示Mg2Ni0.75M0.25合金为六边形结构),并指出Mg2Ni0.75M0.25合金经氟化处理后具有良好的储氢性能。吕光烈等[4]研究了以Al和Ti取代Mg2Ni合金中的Mg原子,发现元素替代后Mg2Ni形成Mg3MNi2(M=Ti, Al)的立方晶系,且同Mg2Ni相比,Mg3MNi2的吸放氢温度明显降低,循环寿命也得到改善。在理论上,TAKAHASHI等[5]采用DV-Xa方法研究了高温相Mg2NiH4的团簇模型,指出在Mg2Ni合金中Mg—Ni的相互作用占支配地位,且 Ni—H的相互作用明显强于Mg—H的。SETTEN等[6]采用从头算方法研究了过渡金属掺杂对低温相Mg2NiH4的影响,发现Cu或Fe取代一个Ni原子后,氢化物的分解焓大约减少了9.6 kJ/mol,但是Co的替代却增加了氢化物的分解焓。JASEN等[7]采用密度泛函理论方法对低温相Mg2NiH4的电子结构进行了研究,发现Ni—H的相互作用明显大于Mg—H的,且其主要表现为H 1s与Ni 4s3p轨道电子的成键作用。目前,对Mg2Ni合金的研究还在开展中,但是一系列过渡金属分别替代Mg2Ni合金中的部分Ni原子对合金及其氢化物的晶体结构、电子结构和热力学稳定性的理论研究还较 少。研究其电子结构和热力学稳定性为提高Mg2Ni1-xMxH4 (M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, x=0.25)的吸放氢动力学性能提供一定的理论指导。密度泛函理论已被广泛应用于材料模拟研究中[8-9],本文作者采用基于密度泛函理论(DFT)的平面波赝势(PW-PP)方法,系统考察了一系列过渡金属M(=Mn, Fe, Co, Cu)分别替代Mg2Ni合金中部分Ni原子对Mg2Ni及其氢化物结构、电子结构和热力学稳定性的影响。
1 计算方法与模型
1.1 计算方法
计算采用基于广义梯度近似(GGA)的密度泛函理论,选用PBE泛函描述电子关联能[10]。从第一性原理出发,将晶体的多电子方程转化为Kohn-Sham方程,选择超软赝势[11](Ultrasoft pseudopotentials)描述电子和离子的相互作用。用CASTEP模块[12]进行结构优化和电子总能计算,平面波截止能取350 eV,简约布里渊区采用Monkhors-Pack方法[13]取适量K点,Mg2Ni及其替代合金K点取为6×6×2,Mg2NiH4及其替代氢化物K点取为4×4×4,M(=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu)单质的K点取为12×12×12,H2分子的K点取为 3×3×3。结构优化的收敛指标: 总体能量变化小于1.0×10-5 eV·atom-1,每个原子的受力小于0.05 eV·?, 自洽迭代收敛能量为1.0×10-6 eV·atom-1,公差偏移小于0.001 ?,应力偏差小于0.05 GPa。建立a=10 ?简单立方模型来计算H2分子的能量,同时对内坐标进行结构优化。
1.2 晶体结构及模型
Mg2Ni的晶胞模型及在298 K下的Mg2NiH4晶胞模型及替代后的Mg2Ni1-xMxH4 (M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, x=0.25)原胞模型如图1所示。
X射线衍射实验表明[14]:Mg2Ni晶体为六方结 构,如图1(a)所示,其空间群为P6222(No. 180),晶胞参数为a=b=5.205 ?、c=13.236 ?、α=β=90°、γ=120°,Mg原子的空间位置为6f(0.5, 0, 0.1187)和6i(0.162, 0.324, 0),Ni原子的空间位置为3b(0, 0, 0.5)和3d(0.5, 0, 0.5)。计算取Mg12Ni6的单胞,在晶胞中Mg和Ni各有两种独立的位置,分别用Mn、Fe、Co和Cu取代Ni(3d)(取代Ni(3d),Ni(3b)两个位置,计算结果差别很小,且取代Ni(3d)处能量较低),接着,对Mg12Ni6晶胞及替代后Mg12Ni5M晶胞进行结构优化。Mg2Ni合金吸氢后首先迅速形成结构不变的Mg2NiH0.24[15],在298 K下,Mg2Ni合金吸氢后形成Mg2NiH4的单斜结构,如图1(b)所示,其空间群为C2/c(No.15),晶胞参数为a=14.343 ?、b=6.403 8 ?、c=6.483 0 ?、α=γ= 90°、β=113.52°,单胞有56个原子,其中,H原子有4种独立的位置,占据着晶格8f位,Mg原子有3种独立的位置分别占据着晶格的8f、4e和4e位,Ni原子只有一种独立的位置占据着晶格的8f位[16]。考虑Mg2NiH4晶胞特征,本文作者采用其原胞模型进行计算,分别用Mn、Fe、Co和Cu取代Mg8Ni4H16原胞中的一个Ni原子,如图1(c)所示,原胞由28个原子组成,包含8个Mg原子、3个Ni原子、1个M原子和16个H原子,最后,对Mg8Ni4H16及替代的Mg8Ni3MH16进行结构优化。
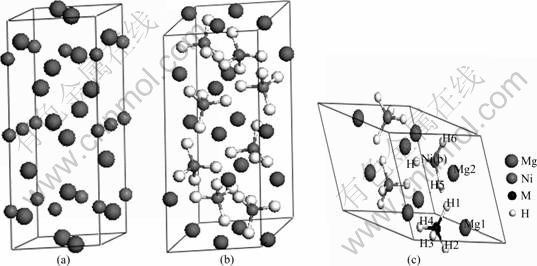
图1 Mg2Ni和Mg2NiH4的晶胞模型以及Mg2Ni0.75M0.25H4的原胞模型
Fig. 1 Cell models of Mg2Ni (a), Mg2NiH4 (b) and primitive cell model of Mg2Ni0.75M0.25H4(c)
2 计算结果与讨论
2.1 结构优化
表1所列为Mg2Ni1-xMx(M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, x= 0.25)优化后的晶胞参数。从表中看出,Mg2Ni晶胞参数的计算值与实验测定值很接近,其中,a、b轴的相对误差为0.36%,c轴的相对误差为0.15%,说明 Mg2Ni所选取的计算条件和参数是合理、可靠的。 Mn、Fe、Co和Cu 替代氢化物中部分Ni原子后使Mg2Ni晶胞的b和c轴都略有伸长,a轴变短,晶胞体积也发生了明显变化。图2所示为晶胞体积与替代元素的变化关系,替代后Mg2Ni1-xMx晶胞体积的计算值与实验 值[3]吻合较好。
表1 Mg2Ni1-xMx(M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, x=0.25)的晶胞参数
Table 1 Cell parameters of Mg2Ni1-xMx(M= Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, x=0.25)
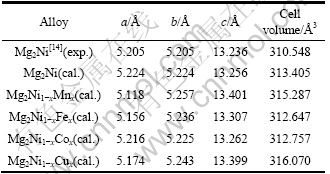

图2 Mg2Ni1-xMx(M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, x=0.25)晶胞体积的计算值和实验值
Fig. 2 Calculated and experimental unit cell volumes of Mg2Ni1-xMx(M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, x=0.25)
表2列出了Mg2Ni1-xMxH4(M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, x=0.25)结构优化后的晶胞参数。由表2可知, Mg2NiH4晶胞参数与实验值符合很好,其中,a、b轴的相对误差只有0.047%,c轴的相对误差也仅为0.8%。用Mn、 Fe、Co和Cu分别替代Mg2NiH4中部分Ni原子后,Mg2NiH4的晶胞参数发生了明显变化。Mn和Cu的替代导致Mg2NiH4的a轴变长,而Co和Fe的替代使Mg2NiH4的a轴变短,其中,Co的替代引起的a轴变化最明显,大约缩短0.72%。对于b轴,替代后晶胞的b轴都略微增大,其中,Mn替代引起的b轴变化最明显,大约增大2.7%。而对c轴影响最大的是Cu,Cu的替代使Mg2NiH4的c轴大约增长15.6%。M(=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu)替代后Mg2Ni1-xMxH4晶胞体积由大到小的顺序为V(Cu)、V(Ni)、V(Co)、V(Mn)和V(Fe)。
2.2 态密度
图3所示为Mg2Ni1-xMxH4(M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, x=0.25)的总态密度图。图中以费米能级(EF)为能量的参考点。从总态密度(TDOS)图可知,Mn、Fe、Co和 Cu分别替代Mg2NiH4中部分Ni原子后的总态密度主峰都下降, 其中,Mn和Cu的替代下降最明显;同 时,替代后的Mg2Ni1-xMxH4 (M=Mn, Fe, Co, Cu, x=0.25)各总态密度的主峰都向深势阱方向移动,其中,Mg2Ni0.75Cu0.25H4的偏移最明显。
表2 Mg2Ni1-xMxH4(M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, x=0.25)的晶胞参数
Table 2 Cell parameters of Mg2Ni1-xMxH4 (M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, x=0.25)
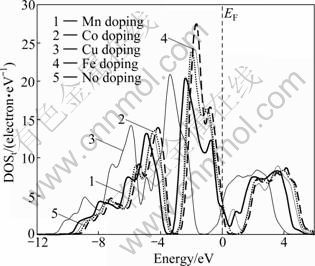
图3 Mg2Ni1-xMxH4(M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, x=0.25)的总态密度图
Fig. 3 Total density of states (DOSt) of Mg2Ni1-xMxH4 (M= Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, x=0.25)
由于替代后态密度的整体变化趋势大体相同且Cu变化最明显,所以,进一步研究Cu替代前后总态密度及分波态密度情况。图4所示为Mg2NiH4和Mg2Ni0.75Cu0.25H4的总态密度及分波态密度。由图 4(a)可得,Mg2NiH4的导带和价带间的禁带宽度为 1.72 eV,这与BROEDERSZ等[17]的计算值接近,表明Mg2NiH4具有明显的非金属性。在费米能级(EF)以下,总态密度主要由3个成键峰构成,其中,位于-8.8~-6.2 eV能量范围内的总态密度峰主要由Mg 3s、Ni 4s与H 1s轨道的电子贡献;位于-6.2~-3.7 eV能量范围内的总态密度峰主要由Mg 2p,Ni 3p(3d)及H 1s轨道的电子贡献;位于-2.7~0 eV能量范围内的总态密度峰主要由Mg 3s2p、Ni 3p(3d)及H 1s轨道的电子贡献。同时,H原子和Ni原子的态密度在价带部分有较大重叠,而Mg原子和H原子的态密度在价带部分重叠则较小。Cu替代Mg2NiH4中部分Ni原子后的总态密度发生了明显的变化(见图4(b)),其主要特征如下:1)在费米能级(EF)下,比替代前多了一个位于-5.2~-4.8 eV的成键峰,这个成键峰主要由替代元素Cu 3d轨道的电子贡献。2)替代后的总态密度相对替代前总态密度峰值下降很多,表明Cu的替代使Mg、Ni和H原子参与成键的电子数减少。3)位于-10.5~-7.9 eV能量范围内的总态密度峰主要由Mg 3s、Ni 4s、Cu 4s与H 1s轨道的电子贡献;位于-7.9~-5.2 eV能量范围内的总态密度峰主要由Mg 2p、Ni 3p3d、 Cu 3p3d及H 1s轨道的电子贡献;位于-4.2~-1.8 eV能量范围内的总态密度峰主要由Mg 3s2p、Ni 3p3d、Cu 3p及H 1s轨道的电子贡献。4)在费米能级(EF)以下,Cu原子和H原子的态密度重叠区域比Ni原子和H原子的态密度重叠区域大,说明在Mg2Ni0.75Cu0.25H4中Cu原子和H原子的成键电子数多于Ni原子和H原子的成键电子数。
2.3 电荷等密度和原子间键序
图5所示为Mg2Ni1-xMxH4(M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, x=0.25)的电荷等密度图。其中,图5(a)和(b)所示分别为Mg2NiH4两个不同截面的电荷等密度图;图5(c)和(d)所示分别为Mg2Ni0.75Cu0.25H4对应于图5(a)和(b)的两个电荷等密度图;图5(e)、(f)和(g)分别表示Mg2- Ni0.75Mn0.25H4、Mg2Ni0.75Fe0.25H4 和Mg2Ni0.75Co0.25H4 对应于图5(a)的电荷等密度图。从图5可知,在氢化物Mg2Ni1-xMxH4中,H原子和Mg原子的电子云重叠不明显,而H原子与Ni、M(M=Mn, Fe, Co, Cu)原子的电子云存在较大的重叠,这说明H原子和Ni、M原子具有很强的相互作用。比较图5(a)和(c)的可知,Ni原子和H原子的电子云重叠明显少于Cu原子和H的电子云重叠。比较图5(b)和(d)图可知,Cu的替代使Ni(b)—H的电子云重叠减少,说明Cu的替代会减弱Ni(b)和H原子的相互作用。这与态密度图反映的情况一致。
为了分析Mg2Ni1-xMxH4(M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, x=0.25)的成键作用,采用下列表达式[18]计算氢化物中部分原子单位键长的键序BOs(scale bond order):
BOs=BO/BL (1)
式中:BO和BL分别表示原子间的电荷布居和键长。键序BOs可用来定性评价结构中两原子相互作用的强弱,若BOs为正且键序值越大,说明两原子是共价键结合且相互作用越强;若键序值为负,说明两原子之是离子键结合[18]。Mg2Ni0.75M0.25H4 (M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu)键序与替代元素的计算结果如图6所示。图中, M—H表示M与周围所对应4个氢原子(即它周围四面体上的4个氢原子)的平均键序;Ni—H表示氢化物原胞中所有Ni原子和H原子的平均键序;Mg2—Ni(b)、Mg1—H2和M—Mg1分别代表单个原子间的键序(具体原子位置见图1(c))。观察键序随M的变化可以发现:Ni—H、Mg2—Ni(b)和Mg1—H2的键序随M变化较小,而M—H和Mg1—M的键序随M变化却很明显,且M—H键的相互作用越强,对应的 Mg1—M键的相互作用就越弱。TAKAHASHI等[5]通过DV-Xa法对Mg2NiH4团簇模型进行研究时也发现了同样的情况。比较各键序大小发现,Ni—H和 M—H的键序始终为正,Mg1—H2的键序为负,且 Ni—H和M—H的键序值较大,这说明氢化物中的Ni—H和M—H键为共价键,Mg1—H2键为离子键,并且Ni—H和M—H键存在较强的相互作用。所 以,Mg2Ni1-xMxH4放氢困难的一个主要原因Ni—H和M—H键的强相互作用。观察Ni—H的键序随M的变化可知,Mn、Fe和 Co分别替代Mg2NiH4中部分Ni原子后对氢化物中的Ni—H的影响较小,而Cu替代则减弱了Ni—H键的相互作用。
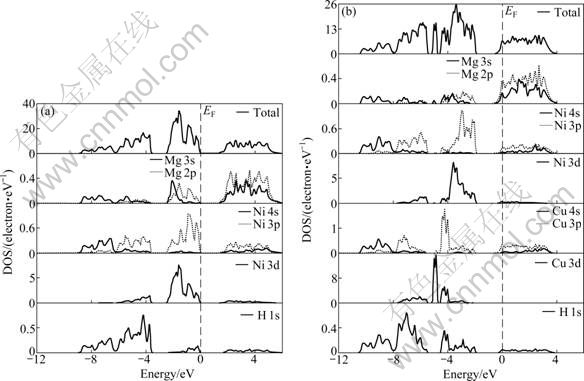
图4 Mg2NiH4和Mg2Ni0.75Cu0.25H4的总态密度及分波态密度
Fig. 4 Total and partial density of states of Mg2NiH4 (a) and Mg2Ni0.75Cu0.25H4 (b)
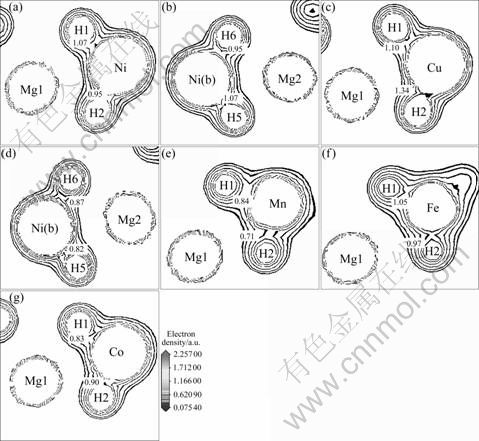
图5 Mg2Ni1-xMxH4(M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, x=0.25)的电荷等密度图
Fig. 5 Contour maps of electron density of Mg2NiH4 ((a), (b)), Mg2Ni0.75Cu0.25H4 ((c), (d)), Mg2Ni0.75Mn0.25H4 (e), Mg2Ni0.75Fe0.25H4 (f) and Mg2Ni0.75Co0.25H4 (g)
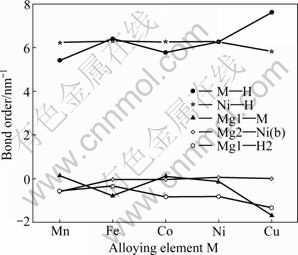
图6 Mg2Ni1-xMxH4(M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, x=0.25)键序与替代元素的变化关系
Fig. 6 Relationship between bond order and substituting element for Mg2Ni1-xMxH4 (M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, x=0.25)
2.4 热力学稳定性
生成焓?H是研究储氢材料热力学稳定性的重要参数,其表达式为生成物的总能量减去反应物的总能量[17]:
 (2)
(2)
若生成焓?H的值为负,表明该反应是放热反应;且反应过程放出的热量越多,生成物的结构就越稳 定[19]。一般情况下,Mg2Ni合金吸氢过程的反应式如下[20]:
Mg2Ni+2H2=Mg2NiH4 (3)
通过式(3)可得Mg2NiH4的生成焓?H表达式为
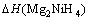 =
=
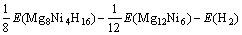 (4)
(4)
元素替代后,Mg2Ni合金吸氢过程的反应式可表示为[21]
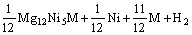 =
=
 (M=Mn, Fe, Co, Cu) (5)
(M=Mn, Fe, Co, Cu) (5)
所以,通过下式可得Mg2Ni1-xMxH4(M=Mn, Fe, Co, Cu, x=0.25)的生成焓?H表达式为
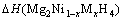 =
=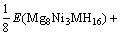
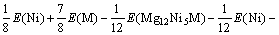
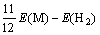 (6)
(6)
Mg12Ni6及其替代合金,Mg8Ni4H16及其替代氢化物,还有计算过程要用到的Mn、Fe、Co、Ni、Cu单质和H2能量如表3所列。将表3的能量代入式(4)和(6), 可算出Mg2Ni0.75M0.25H4(M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu)的生成焓(见表4)。
比较Mg2Ni1-xMxH4(M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, x=0.25)生成焓的计算值和实验值可以发现,生成焓的计算值和实验值[3,22]符合得较好。在所研究的替代元素中,Fe和Co分别替代Mg2NiH4中的部分Ni原子对Mg2NiH4结构稳定性影响较小,而Mn和Cu替代则较好地降低了Mg2NiH4的结构稳定性,尤其是Cu的替代使Mg2NiH4结构稳定性下降最明显。TAKAHASHI等[5]也指出,Cu的添加可以很好地降低Mg2NiH4的结构 稳定性。Mg2Ni0.75Cu0.25H4结构稳定性下降的一个原 因可能是Cu的替代使氢化物中Ni—H键减弱引起的。
表3 金属、金属间化合物和氢化物的能量计算值
Table 3 Calculated energies of metals, intermetallics and hydrides
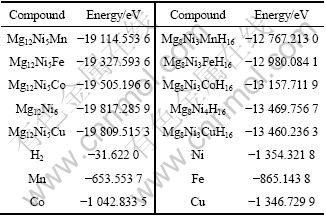
表4 Mg2Ni1-xMxH4(M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, x=0.25)生成焓的计算值和实验值
Table 4 Calculated and experimental formation enthalpies of Mg2Ni1-xMxH4 (M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, x=0.25)

2.5 氢化物的解离能
为了考察Mn、Fe、Co和Cu替代Mg2NiH4中的Ni原子前后体系的放氢性能,计算了Mg2Ni0.75M0.25H4晶胞中Ni(b)原子周围解离出最邻近的两个氢原子(即去除图1(c)中H5和H7原子)所需的能量,计算采用的表达式如下[23]:
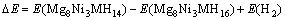 (7)
(7)
其中:?E表示Mg2Ni0.75M0.25H4晶胞中Ni(b)原子 周围解离出最邻近的两个氢原子所需的能量;E(Mg8Ni3MH16)和E(Mg8Ni3MH14)则分别表示Mg2Ni0.75M0.25H4解离两个氢原子前后的总能量;E(H2)表示氢气分子的能量,其值为-31.622 0 eV,计算结果如表5所列。计算结果表明:Mg2Ni0.75Cu0.25H4的解离能最小,这说明Cu替代Mg2NiH4中部分Ni原子可以提高Mg2NiH4的放氢性能。SELVAM等[22]也指出,Cu的添加可以提高Mg2NiH4的放氢性能。
表5 Mg2Ni0.75M0.25H4(M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu)氢化物解离能的计算值
Table 5 Calculated dissociated energies of Mg2Ni0.75M0.25H4 (M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu)

3 结论
1) 采用基于密度泛函理论(DFT)的平面波赝势(PW-PP)方法对Mg2Ni1-xMx(M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, x= 0.25)合金及其对应的氢化物Mg2Ni1-xMxH4(M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, x=0.25)的结构进行优化,计算结果和实验值基本符合。
2) 在氢化物Mg2Ni0.75M0.25H4中,Ni—H和M— H键表现为共价键,Mg—H键表现为离子键,且Ni—H和M—H键的相互作用大于Mg—H键的相互作用,这说明Mg2Ni0.75M0.25H4吸放氢性能主要取决于Ni—H和M—H键的强相互作用。Mn、Fe和Co的部分替代对Ni—H键的相互作用影响较小,而Cu的替代则减弱了Ni—H键的相互作用,这可能是Cu替代后氢化物结构稳定性降低的一个原因。
3) 生成焓的计算结果表明:Mg2Ni0.75M0.25H4 (M= Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu )的生成焓分别为-57.7、-61.5、 -61.4、63.4和41.6 kJ/mol,与实验值符合得较好。
REFERENCES
[1] GROCHALA W, EDWARDS P P. Thermal decomposition of the non-interstitial hydrides for the storage and production of hydrogen[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2004, 104(3): 1283-1316.
[2] SCHLAPBACH L, ZUTTEL A. Hydrogen-storage materials for mobile applications[J]. Nature, 2001, 414: 353-358.
[3] YANG Hua-bin, YUAN Hua-tang, JI Jing-tao, SUN Hua, ZHOU Zuo-xiang, ZHANG Yun-shi. Characteristics of Mg2Ni0. 75M0. 25 (M=Ti, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu and Zn) alloys after surface treatment[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2002, 330: 640-644.
[4] 吕光烈, 陈林深, 胡秀荣, 王连邦, 袁华堂. Mg3MNi2(M=Ti, Al)的晶体结构[J]. 金属学报, 2001, 37(5): 459-462.
L? Guang-lei, CHEN Lin-shen, HU Xiu-rong, WANG Lian-bang, YUAN Hua-tang. The crystal structure of new hydrogen storage Mg3MNi2(M=Ti, Al) alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2001, 37(5): 459-462.
[5] TAKAHASHI Y, YUKAWA H, MORINAGA M. Alloying effects on the electronic structure of Mg2Ni intermetallic hydride[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1996, 242(1/2): 98-107.
[6] van SETTEN M J, de WIJS G A, BROCKS G. Ab initio study of the effects of transition metal doping of Mg2NiH4[J]. Physical Review B, 2007, 76(7): 75125-75133.
[7] JASEN P V, GONZALEZ E Z, BRIZUELA G, NAGEL O A, GONZALEZ G A, JUAN A. A theoretical study of the electronic structure and bonding of the monoclinic phase of Mg2NiH4[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2007, 32(18): 4943-4948.
[8] 罗湖斌, 胡青苗, 杨 锐. 合金化对β钛合金热膨胀系数的影响: 第一性原理研究[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(s1): 399-403.
LOU Hu-bin, HU Qing-miao, YANG Rui. Effect of alloying on thermal expansion efficient of β titanium alloy: First principles study[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(s1): 399-403.
[9] 刘奕新, 梁 初, 蒋 龙, 黎光旭, 韦文楼, 郭 进. Li-Al-N-H 系络合物贮氢反应的第一性原理研究[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2009, 19(1): 108-113.
LIU Yi-xin, LIANG Chu, JIANG Long, LI Guang-xu, WEI Wen-lou, GUO Jin. Investigations on Li-Al-N-H complex for hydrogen storage by first principle[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 19(1): 108-113.
[10] MARLO M, MILMAN V. Density-functional study of bulk and surface properties of titanium nitride using different exchange-correlation functionals[J]. Physical Review B, 2000, 62(4): 2899-2907.
[11] VANDERBILT D. Soft self-consistent pseudopotentials in a generalized eigenvalue formalism[J]. Physical Review B, 1990, 41(11): 7892-7895.
[12] SEGALL M D, LINDAN PHILIP J D, PROBERT M J, PICKARD C J, HASNIP P J, CLARK S J, PAYNE M C. First-principles simulation: Ideas, illustrations and the CASTEP code[J]. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2002, 14(11): 2717-2744.
[13] MONKHORST H J, PACK J D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations[J]. Physical Review B, 1976, 13(12): 5188-5192.
[14] DARRIET B, SOUBEYROUX J L, PEZAT M. Structural and hydrogen diffusion study in the Mg2Ni-H2 system[J]. Journal of the Less Common Metals, 1984, 103(1): 153-162.
[15] NOREUS D, WERNER P. Structural studies of hexagonal Mg2NiHx[J]. Acta Chemica Scandinavica A, 1982, 36(10): 874-851.
[16] ZOLLIKER P, YVON K, JORGENSEN J, ROTELLA F J. Structural studies of the hydrogen storage material magnesium nickel hydride (Mg2NiH4): 2. Monoclinic low-temperature structure[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 1986, 25(20): 3590-3593.
[17] BROEDERSZ C P, GREMAUD R, DAM B, GRIESSEN R. Highly destabilized Mg-Ti-Ni-H system investigated by density functional theory and hydrogenography[J]. Physical Review B, 2008, 77(2): 24204-24214.
[18] ZHANG R J, WANG Y M, CHEN D M, YANG R, YANG K. First-principles calculations of LaNi4Al-H solid solution and hydrides[J]. Acta Materialia, 2006, 54(2): 465-472.
[19] LI S L, WANG P, CHEN W, LUO G, CHEN D M, YANG K. Hydrogen storage properties of LaNi3.8Al1.0M0.2(M=Ni, Cu, Fe, Al, Cr, Mn) alloys[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 485(1/2): 867-871.
[20] REILLY J J, WISWALL R H. The reaction of hydrogen with alloys of magnesium and Nickel and the formation of Mg2NiH4[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 1968, 7(11): 2254-2256.
[21] ZENG Yan-li, FAN Ke, LI Xiao-yan, XU Bao-en, GAO Xiao-zhen, MENG Ling-peng. First-principles studies of the structures and properties of Al- and Ag-substituted Mg2Ni alloys and their hydrides[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2010, 35(19): 10349-10358.
[22] SELVAM P, VISWANATHAN B, SWAMY C S, SRINIVASAN V. Studies on the thermal characteristics of hydrides of Mg, Mg2Ni, Mg2Cu and Mg2Ni1-xMx (M= Fe, Co, Cu or Zn; 0 [23] LI S, JENA P, AHUJA R. Dehydrogenation mechanism in catalyst-activated MgH2[J]. Physical Review B, 2006, 74(13): 132106-132109.
(编辑 陈卫萍)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50861003, 51071054);广西科学基金重点项目(2010GXNSFD013004);广西大学拔尖创新团队建设计划项目
收稿日期:2011-01-20;修订日期:2011-03-31
通信作者:郭 进,教授,博士;电话:0771-3232666;E-mail: guojin@gxu.edu.cn