文章编号:1004-0609(2012)04-1156-07
C/LiFePO4动力蓄电池的热行为
李文成,卢世刚
(北京有色金属研究总院 动力电池研究中心,北京 100088)
摘 要:为了明确圆柱形C/LiFePO4动力蓄电池放电过程中的温度特性及其产热机理,利用自动充放电仪对其在不同倍率放电过程中表面温度的变化进行研究,并对该电池在放电过程中的产热率进行计算。结果表明:相同放电时间的表面温度增加与放电电流呈抛物线关系,放电结束时表面温度增加则与放电电流呈线性关系;电池内部的热效应主要为不可逆阻抗热和电池反应的可逆热效应,0.3C、1C、2C和3C放电时,不可逆阻抗热的平均产热率分别是总平均产热率的85.0%、98.0%、99.4%和99.6%,电池反应的可逆热效应所占比例很小;小电流放电时,电池表面温度的下降与电池反应的可逆热效应有关。
关键词:LiFePO4;锂离子动力电池;温度特性;热行为
中图分类号:TM912.9 文献标志码:A
Thermal behavior of C/LiFePO4 power secondary battery
LI Wen-cheng, LU Shi-gang
(Research and Development Center for Vehicle Battery and Energy Storage,
General Research Institute for Nonferrous Materials, Beijing 100088, China)
Abstract: In order to investigate the temperature characterize and heat generation mechanism of a cylindrical power secondary battery using graphite and LiFePO4 as anode and cathode, its surface temperature change at different discharge rates were studied by a automatic charge and discharge device. Moreover, its heat generation rate during discharge was calculated. The results show that, at the same discharge time, the relationship between the surface temperature rising and the discharge current is parabolic, whereas at the end of discharge, the surface temperature rising is a liner relationship with the discharge current. The irreversible resistive heating and reversible entropic heat are the major heat generation sources inside the battery. The average rates of the irreversible resistive heating at 0.3C, 1C, 2C and 3C rate are about 85.0%, 98.0%, 99.4% and 99.6% of that of the total heat generation, respectively. The proportion of reversible entropic heat is very small. At low discharge current, the surface temperature drop is dominated by reversible entropic heat.
Key words: LiFePO4; Li-ion power battery; temperature characterize; thermal behavior
锂离子动力电池具有比功率和比能量高、循环寿命长、安全性好等特性,在电动汽车中具有广泛的应用前景。从电化学原理看,电池的充放电过程是一个电能和化学能相互转化的过程。在这个过程中,会伴随电池热行为的发生,即一部分能量转化为热能导致电池自身温度发生变化。温度是影响电池寿命[1-4]和安全性能[5-9]的关键因素。电池温度过高会加剧电池内部副反应,缩短电池的寿命,严重时会引发电池的热失控,造成电池起火或爆炸等安全问题。研究锂离子动力电池,应当分析电池的热行为及其影响因素。
y耳热和电化学动力电池的寿命和安全性非常重要近年来,随着LiFePO4正极材料商业化的成功,C/LiFePO4体系的锂离子电池的热行为成为研究热点之一。YANG等[10]研究了一种方形C/LiFePO4电池(额定容量为8 A·h,电池尺寸为80 mm×26 mm×92 mm,钢壳)的表面温度特性,发现放电过程中电池表面的最高温度和平均温升速率都随放电电流增加而线性增大。FORGEZ等[11]利用能量平衡定律发展了一个集中参数热模型,模拟了22650型LiFePO4电池充放电(脉冲或持续电流)过程中表面和内部的温度变化。根据该模型LiFePO4电池的内部产热主要来自不可逆阻抗热(Irreversible resistive heating)和电池反应的可逆热效应(Reversible entropic heat)。以上研究主要关注了LiFePO4电池在大倍率充放电时电池的热行为,本文作者重点研究了一种大容量圆柱形LiFePO4动力电池在小于3C倍率放电过程中的表面温度的变化规律,并计算了不同倍率放电过程中不可逆阻抗热和电池反应的可逆热效应的产热率。
1 实验
试验电池的额定容量为13 A·h,尺寸为d 42 mm×175 mm,质量为0.43 kg。其正极和负极活性物质分别为磷酸铁锂(M121,台湾立凯电能科技股份有限公司生产)和石墨(CMB-340,天津贝特瑞新能源材料有限责任公司生产),电解液为1 mol/L LiPF6/EC+EMC+DMC(体积比为1:1:1)/添加剂(JN908-6,天津金牛电源材料有限责任公司生产)。
1.1 电池表面温度测试
为了确保安全及减少外界环境对测量的影响,将电池放在一个600 mm×400 mm×400 mm的铁箱(内壁绝缘)内。使用Arbin BT2000充放电测试仪测试电池的倍率性能。测试制度如下:室温下,以0.3C恒流充电至3.7 V,转恒压充电,当电流降至10%时,充电结束,静置3 h。电池充分冷却后分别以0.3C、1C(13 A)、2C、3C放电,至电压2.5 V时放电结束,然后再静置3 h。在充放电过程中,把设备自带的T型热电偶固定在电池的中间位置,测量电池表面的温度变化。
1.2 开路电压的测量
采用HT-V60C20D40-4型电池测试仪(广州擎天实业有限公司)对电池充放电。室温((25±5) ℃)下,以0.5C恒流充电至3.7 V,转恒压充电,当电流降至10%时,充电结束;电池搁置2 h后以0.5C放电,每放出10%的额定容量,电池搁置2 h,测得电池在不同放电状态(Depth of discharge,DOD)下的开路电压。
1.3 开路电压的温度系数(dUavg/dT)的测量
充放电设备及充电制度同1.2节。满电态电池充分冷却后将其放入高低温箱(GDW-50,无锡市兰博试验设备有限公司生产)中,按照25、15、5、35和25 ℃的顺序每3 h变换一次温度,测量电池开路电压随温度的变化。然后在室温下0.5C放出电池额定容量的10%,搁置5 h后继续测量开路电压随温度的变化,依次测试电池在不同DOD状态下的温度—电压曲线,然后求得在不同DOD状态下的dUavg/dT。具体计算方法参照文献[11]。
2 结果与讨论
LiFePO4锂离子电池放电时,锂离子从石墨负极脱出,经过电解液的传输过程,然后嵌入到LiFePO4正极中,反应如下:
 (1)
(1)
整个放电过程的产热主要有两部分:不可逆阻抗热和电池反应的可逆热效应。不可逆阻抗热是电池放电时电池反应偏离平衡态时所产生的热;电池反应的可逆热效应是指电池反应在平衡态时电池放出(或吸收)的热。
2.1 电池表面温度的变化
图1所示为不同倍率放电时电池壳体表面温度随时间的变化曲线,图中竖线代表放电结束。由图1可以看出,电池表面温度受放电电流的影响较大。随着放电电流的增加,温度上升速度加快温度不断升高。放电结束后,温度还继续上升一段时间,3C放电时约持续了40 s。随后温度下降。0.3、1、2和3C放电的电池表面最高温度分别为27.0、30.1、35.6和40.5 ℃。
值得注意的是,大电流(如2C、3C)放电时,温度几乎呈直线上升;电流减小至1C,与放电初期和末期相比,在放电中期温度上升较慢;0.3C放电时,大约在1~2 h(大约29%~58%DOD)之间表面温度则有一个明显的下降过程,3 h(87%DOD)左右时,温度增加又变缓慢。
HALLAJ等[12]通过测试MCMB/LiCoO2体系的锂离子电池小电流放电时的温度特性,在23%DOD和95%DOD处也观测到温度下降的类似现象。本文作者分析认为,电池温度的下降与电池反应的可逆热效应有关。
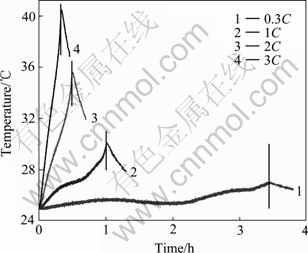
图1 不同倍率放电时电池壳体表面温度随时间的变化曲线
Fig. 1 Change curves of surface temperature with time during discharge at different rates
图2所示为不同倍率放电电压和电池表面温度变化的速度随时间变化曲线。由图2可以看出,0.3C放电曲线上3.29、3.25和3.14 V 3个电压平台清晰可见,与之相对应的温度变化的速度下降。在3.25 V电压平台处,其速度甚至降为负值,表明在第二个平台处可能有吸热发生。随着放电电流的增加,2个电压平台之间的界限逐渐变得模糊,相对应的温度变化速度的2个下降峰之间也逐渐分辨不清。
另外,在0.3C、1C、2C和3C放电的初期和末期,温度的变化速度均快速上升,在放电末期速度达到最高,分别为2.3、26.9、92.3和114.0 ℃/h。放电过程中温度变化的平均速度分别为0.6、4.9、21.1和45.4 ℃/h。
图3所示为相同放电时间的电池表面温度的增加与电流的关系曲线。由图3可以看出:相同放电时间下,温度的增加与电流基本呈抛物线(ΔT∝I2Rt)关系。放电0.1、0.2和0.3 h时,温度的增加与电流的关系式分别为:y=0.002 56x2、y=0.005 18x2、y=0.007 41x2。当电流大于1C时,拟合结果与试验结果接近,基本表现出不可逆阻抗热的特征,表明电流较大时,电池内部产热可能以不可逆阻抗热为主。ZHANG[13]测试了一个容量为3A·h的锰酸锂电池在1.7C放电时的产热率,发现电池不可逆阻抗热约为总产热率的70%。0.3C放电时拟合结果与试验结果偏差略大一些,说明小电流放电时,不可逆阻抗热所占的比例可能有所减小。

图2 不同倍率放电电压和电池表面温度的变化速度随时间变化曲线
Fig. 2 Change curves of voltage and temperature rising rate with time during discharging at different rates: (a) 0.3C; (b) 1C; (c) 2C; (d) 3C

图3 相同放电时间时电池表面温度的增加与电流关系
Fig. 3 Relationship between temperature rising and discharge current at same discharge time
图4所示为整个放电过程中电池表面温度的增加与电流的关系曲线。由图4可以看出,温度的增加与电流基本为线性关系。这主要是由于整个放电过程中的放电时间与电流为反比关系(ΔT∝(13×3 600)IR, I=13×3 600/t),电流与放电相互抵消所致。在8A·h方形C/LiFePO4电池[10]和26650型C/LiMn2O4电池[13]的测试中,本文作者也得到了相似的结果。

图4 放电结束时的电池表面温度的增加与电流关系
Fig. 4 Relationship between temperature rising and discharge current at end of discharge
2.2 电池放电时的热行为分析
在自然对流环境下,当电池的长度与直径的比(L/D)在3~4之间时,毕奥数(Bi)小于0.1,可以认为电池内部的温度是均匀的[14]。对本研究中电池的L/D=3.69,因此,在后面的分析中不考虑电池内部温度的差异,同时假定电池的热容为定值。
根据能量守恒定律,锂离子电池在放电过程中的能量平衡公式可表示为[11]
 (2)
(2)
式中:cp是电池的定压比热容,J/K;Tsurf为电池表面温度,K;t为时间,s;h为与外界的换热系数,W/K;Tamb为铁箱内的温度,K;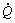 为电池的放热率或吸热率,W。根据文献[15],
为电池的放热率或吸热率,W。根据文献[15],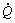 可表示为
可表示为

 (3)
(3)
其中:I为放电电流,A,放电时取负值;V为电池电压,V;U为电池处于平衡态时的端电压,V,在本实验中用电池的开路电压Uavg近似为平衡态的端电压;T为温度,K; 为化学反应i的焓变,J/mol;ri为反应i的速率,mol/s;
为化学反应i的焓变,J/mol;ri为反应i的速率,mol/s; 为物质j的偏摩尔焓,J/mol;cj为物质j的浓度,mol/m3;t为时间,s;v为体积,m3;上标avg代表是在体积平均浓度下的评估值。
为物质j的偏摩尔焓,J/mol;cj为物质j的浓度,mol/m3;t为时间,s;v为体积,m3;上标avg代表是在体积平均浓度下的评估值。
式(3)中右边第1项为不可逆阻抗热,该项为正值。在放电过程中,其变化趋势与-(V-Uavg)一致。图5所示为在不同倍率下电池放电电压与开路电压的差在不同DOD状态下的变化曲线,可以看出放电初始电池电压快速偏离开路电压,随后基本不变,放电末期电池电压与开路电压的差又急剧加大,随着电流的增加,电池电压与开路电压之间的差值逐渐增大。
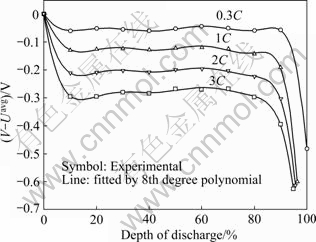
图5 不同倍率放电时电池电压与开路电压的差随DOD的变化曲线
Fig. 5 Changing curves of differences of cell voltage and open-circuit potential vs DOD at different discharge rates
式(3)中右边第2项为电池反应的可逆热效应,电池放电时该项可正可负。图6所示为不同放电状态下开路电压的温度系数变化曲线,可以看出开路电压的温度系数与DOD的状态有关,在0~70% DOD之间,开路电压的温度系数大于0;大于70% DOD后,开路电压的温度系数小于0。表明电池放电时,电池反应在0~70% DOD之间是吸热反应,大于70% DOD后是放热反应。
值得注意的是,在10%~20%DOD之间,开路电压的温度系数有一个下降峰。这与FORGEZ等[11]测量的结果非常相似,认为这主要是由于放电时石墨负极由Ⅰ阶向Ⅱ阶结构的变化造成的。

图6 不同放电状态下开路电压的温度系数变化曲线
Fig. 6 Changing curves of temperature coefficient of open-circuit potential with DOD under different discharge conditions
式(3)中右边第3项为电池内部所有的化学反应热。在本实验电池的充放电曲线正常,3C放电容量约占0.3C放电容量的95%,可以认为电池内部副化学反应较少,因此化学反应热忽略不计;第4项是由电池内部离子浓度梯度的变化引起的混合热。一般认为电池的混合热是造成放电结束后电池表面温度继续上升的原因之一[15-16],电池3C放电结束后的温升仅为0.6 ℃,可以推断,放电电流小于3C的放电过程中的混合热也较少,也可忽略不计。因此,该LiFePO4电池产热主要以不可逆阻抗热和电池反应的可逆热效应为主,则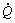 可简化为
可简化为
 (4)
(4)
将式(4)代入式(2),则式(2)变为
 (5)
(5)
电池壳体为厚度0.6 mm的铝壳,传热较快,因此假定电池内部卷芯的温度与壳体表面温度相等,则式(5)变为
 (6)
(6)
由于试验是在室温下自然对流环境中进行的,与外界的热交换系数不能精确测定,为此对式(6)做进一步变换:
 (7)
(7)
式中: ,当电流为0时(即放电结束后的静置过程),式(7)可简化为
,当电流为0时(即放电结束后的静置过程),式(7)可简化为
 (8)
(8)
将式(8)两边积分可得:
 (9)
(9)
式中:B为积分常数。测试过程中Tamb的变化较小,假定Tamb为常数。用式(9)拟合不同倍率放电结束后的温度曲线得到不同倍率放电时的k值分别为0.000 58、0.000 64、0.000 68和0.000 61 s-1,k值非常小。忽略式(7)右边的第1项,则
 (10)
(10)
图7所示为不同倍率放电的不可逆阻抗热、电池反应的热效应及总产热率随DOD的变化曲线,可以看出总产热率的趋势基本与电池表面温度变化的速度(见图2)的趋势相对应。比较图7(a)中的总产热率和电池反应的可逆热效应曲线,两者变化规律基本一致,这说明0.3C放电时电池表面温度的下降主要是电池反应的可逆热效应造成的。
比较总产热率与不可逆阻抗热两条曲线,两者大小基本相当。0.3C、1C、2C和3C放电时,不可逆阻抗热的平均产热分别为0.369、2.027、6.034和11.828 W,分别约为总平均产热的85.0%、98.0%、99.4%和99.6%,电池反应的可逆热效应所占比例很小。这与前文的分析结果一致。文献[13]计算的锰酸锂电池在1.7C放电时,电池反应的热效应约为总产热的30%,大于本实验的计算结果,这可能与LiFePO4比LiMn2O4材料更加稳定有关。
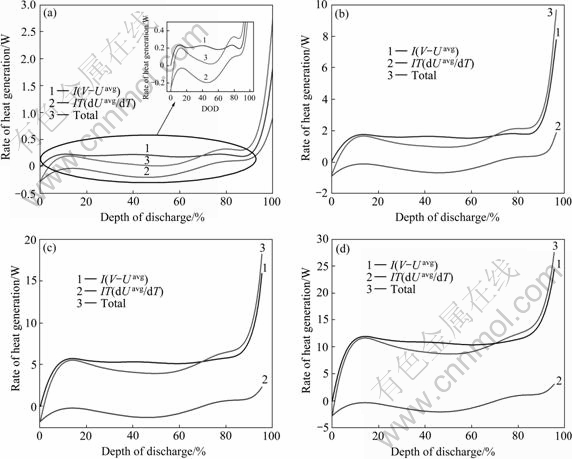
图7 不同倍率放电的不可逆阻抗热、电池反应的可逆热效应及总产热率随DOD变化曲线
Fig.7 Changing curves of rates of irreversible resistive heat, reversible entropic heat and total heat during discharge with DOD at different rates: (a) 0.3C; (b) 1C; (c) 2C; (d) 3C
3 结论
1) 室温下,将圆柱形C/LiFePO4动力蓄电池以0.3C、1C、2C和3C放电时,电池表面温度分别升高了2.0、5.1、10.6和15.5 ℃。在相同放电时间下,电池表面温度的增加与放电电流成抛物线关系,放电结束时电池表面温度的增加与电流呈线性关系。
2) 电池内部产热主要以不可逆阻抗热和电池反应的可逆热效应为主,0.3C、1C、2C和3C放电时,不可逆阻抗热的平均产热为0.369、2.027、6.034和11.828 W,分别约占总平均产热的85.0%、98.0%、99.4%和99.6%,电池反应的可逆热效应所占比例很小。小电流放电时,电池表面温度的下降与电池反应的可逆热效应有关。
PERFERENCES
[1] BROUSSELY M, HERREYRE S, BIENSAN P, KASZTEJNA P, NECHEV K, STANIEWICZ R J. Aging mechanism in Li ion cells and calendar life predictions[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2001, 97/98: 13-21.
[2] SHIM J, KOSTECKI R, RICHARDSON T, SONG X, STRIEBEL K A. Electrochemical analysis for cycle performance and capacity fading of a lithium-ion battery cycled at elevated temperature[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2002, 112(1): 222-230.
[3] BROUSSELY M, BIENSAN P, BONHOMME F, BLANCHARD P, HERREYRE S, NECHEV K, STANIEWICZ R J. Main aging mechanisms in Li ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2005, 146(1/2): 90-96.
[4] 李文成, 卢世刚, 庞静, 刘 莎, 王昌胤, 靳尉仁, 阚素荣, 吴国良. 高功率锂离子蓄电池制备与性能研究[J]. 电源技术, 2009, 33(4): 280-283.
LI Wen-cheng, LU Shi-gang, PANG Jing, LIU Sha, WANG Chang-yin, JIN Wei-ren, KAN Su-rong, WU Guo-liang. Preparation and performance of high power lithium secondary battery[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 33(4): 280-283.
[5] 胡 杨, 李 艳, 连 芳, 钟盛文, 李培植, 万新华, 刘庆国. 锂离子蓄电池热稳定性的机理[J]. 电源技术, 2006, 30(10): 833-836.
HU Yang, LI Yan, LIAN Fang, ZHONG Sheng-wen, LI Pei-zhi, WAN Xin-hua, LIU Qing-guo. The study of the thermal runaway of Li-ion batteries[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2006, 30(10): 833-836.
[6] 金慧芬, 王 荣, 高俊奎. 商业化锂离子电池的热稳定性研究[J]. 电源技术, 2007, 31(1): 23-25, 33.
JIN Hui-fen, WANG Rong, GAO Jun-kui. Study on thermal stability of commercial Li-ion battery[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2007, 31(1): 23-25, 33.
[7] SMITH K, KIM G H, DARCY E, PESARAN A. Thermal/electrical modeling for abuse-tolerant design of lithium ion modules[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2010, 34(2): 204-215.
[8] 王松蕊, 付亚娟, 卢立丽, 刘兴江. 锂离子电池温度变化热模拟研究[J]. 电源技术, 2010, 34(1): 41-44, 91.
WANG Song-rui, FU Ya-juan, LU Li-li, LIU Xing-jiang. Thermal simulation on temperature changes for lithium-ion cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2010, 34(1): 41-44, 91.
[9] 王 峰, 李茂德. 电池热效应分析[J]. 电源技术, 2010, 34(3): 288-291.
WANG Feng, LI Mao-de. Thermal performance analysis of batteries[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2010, 34(3): 288-291.
[10] YANG K, AN J J, CHEN S. Temperature characterization analysis of LiFePO4/C power battery during charging and discharging[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2010, 99(2): 515-521.
[11] FORGEZ C, DO D V, FRIENDRICH G., MORCRETTE M, DELACOURT C. Thermal modeling of a cylindrical LiFePO4/graphite lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2010, 195(9): 2961-2968.
[12] HALLAJ S A, VENKATACHALAPATHY R, PRAKASH J, SELMAN J R. Entropy changes due to structural transformation in the graphite anode and phase change of the LiCoO2 cathode[J]. Journal of Electrochemical Society, 2000, 147(7): 2432-2436.
[13] ZHANG X W. Thermal analysis of a cylindrical lithium-ion battery[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2011, 56(3): 1246-1255.
[14] HALLAJ S A, MALEKI H, HONG J S, SELMAN J R. Thermal modeling and design considerations of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 1999, 83(1/2): 1-8.
[15] THOMAS K E, NEWMAN J. Thermal modeling of porous insertion electrodes[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2003, 150(2): A176-A192.
[16] BERNARDI D, PAWLIKOWSKI E, NEWMAN J. A general energy balance for battery systems[J]. Journal of Electrochemical Society, 1985, 132(1): 5-12.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家高技术研究发展计划资助项目(2008AA11A103)
收稿日期:2011-03-20;修订日期:2011-06-21
通信作者:卢世刚,教授,博士;电话:010-82241199;E-mail: slu@grinm.com