现代大型铝电解槽内复杂物理场的仿真计算与优化
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报2011年第10期
论文作者:李劼 张红亮 徐宇杰
文章页码:2594 - 2606
关键词:铝电解槽;电热场;热应力场;电磁流场;数值仿真
Key words:aluminium reduction cell; electro-thermal field; thermal-stress field; electro-magneto-flow field; numerical simulation
摘 要:总结了国内外在铝电解槽电热场、热应力场及电磁流场方面的研究进展,指出当前多物理场仿真计算算法的不足,介绍了最新开发的“液(电解质)-液(铝)-气”和“液-气-固(颗粒)”两类三相流模型、多物理场(电、磁、热、流、力、浓度分布场等)、磁流体稳定性和电流效率三维耦合仿真模型与算法,并提出基于多相-多场耦合仿真的大型铝电解槽结构与生产工艺综合优化方法,发现大型铝电解槽在3.7~3.9 V低电压下高效、低电耗、低排放、稳定运行的状态空间,并确立相应的工艺实现条件。
Abstract:
The electro-thermal fields, thermal-stress fields and electro-magneto-flow fields of aluminium electrolysis cells were concluded, and the weaknesses of the current multi-physical field computation were pointed out. On the basis of this, the two kinds of latest developed “liquid(electrolyte)-liquid(melt metal)-gas” and “liquid-gas-solid(particles)” three-phase models and the 3D simulation coupling models and algorithms of multi-physical field (electric, magnetic, thermal, flow, stress and concentration distribution fields, etc), magneto hydrodynamics (MHD) stability and current efficiency were introduced, and the comprehensive optimization of structure and production process for large-scale cells based on multiphase and multifield coupled simulation was put forward. The state space of large-scale cells steadily operating under the low voltage of 3.7-3.9 V with high current efficiency, low energy consumption and less emission was found, and the corresponding technology realizing condition was established.
文章编号:1004-0609(2011)10-2594-13
李 劼,张红亮,徐宇杰
(中南大学 冶金科学与工程学院,长沙 410083)
摘 要:总结了国内外在铝电解槽电热场、热应力场及电磁流场方面的研究进展,指出当前多物理场仿真计算算法的不足,介绍了最新开发的“液(电解质)-液(铝)-气”和“液-气-固(颗粒)”两类三相流模型、多物理场(电、磁、热、流、力、浓度分布场等)、磁流体稳定性和电流效率三维耦合仿真模型与算法,并提出基于多相-多场耦合仿真的大型铝电解槽结构与生产工艺综合优化方法,发现大型铝电解槽在3.7~3.9 V低电压下高效、低电耗、低排放、稳定运行的状态空间,并确立相应的工艺实现条件。
关键词:铝电解槽;电热场;热应力场;电磁流场;数值仿真
中图分类号:TF821;O441.4 文献标志码:A
LI Jie, ZHANG Hong-liang, XU Yu-jie
(School of Metallurgical Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The electro-thermal fields, thermal-stress fields and electro-magneto-flow fields of aluminium electrolysis cells were concluded, and the weaknesses of the current multi-physical field computation were pointed out. On the basis of this, the two kinds of latest developed “liquid(electrolyte)-liquid(melt metal)-gas” and “liquid-gas-solid(particles)” three-phase models and the 3D simulation coupling models and algorithms of multi-physical field (electric, magnetic, thermal, flow, stress and concentration distribution fields, etc), magneto hydrodynamics (MHD) stability and current efficiency were introduced, and the comprehensive optimization of structure and production process for large-scale cells based on multiphase and multifield coupled simulation was put forward. The state space of large-scale cells steadily operating under the low voltage of 3.7-3.9 V with high current efficiency, low energy consumption and less emission was found, and the corresponding technology realizing condition was established.
Key words: aluminium reduction cell; electro-thermal field; thermal-stress field; electro-magneto-flow field; numerical simulation
自1886年Hall-Héroult发明电解铝工艺以来,铝电解的主题结构一直未发生太大的变化。在当前普遍采用的铝电解槽结构中(见图1),强大的直流电由阳极母线,经阳极导杆、阳极炭块、电解质、铝液、阴极炭块,并由阴极底部的水平钢棒从两侧导出,再经阴极母线汇集至下一槽的立柱母线[1]。
在电解槽内外分布着形状各异的几十种媒质材料,在强大的直流电(160~500 kA)作用下,体系中形成气(阳极气体)、液(电解质熔体和铝溶体)、固(加入的原料及凝固电解质等)三相共存,并在体系中形成多种物理场,如电场、磁场、热场(即温度场)、流场、应力场、浓度场等[4-5]。
从宏观上来看,铝电解槽中电场、磁场、流场、热场(温度场)、应力场以及浓度场相互耦合。电场(电流与电势分布)是电解槽运行的能量基础,是其他物理场形成的根源。电流的磁效应产生磁场,电流的热效应(焦耳热)产生热场;磁场与电场作用产生的电磁力及其阳极气体的浮力带动熔体在槽膛内流动与波动(流场);电解质与铝液的运动导致氧化铝和金属的扩散与溶解(浓度场),同时影响槽帮的形成;温度场的分布不仅是形成稳定槽帮、保证电解过程得以进行的基础,也是影响能量平衡的重要影响因素,其与化学侵蚀作用共同促使槽体结构发生变形(应力场),此外,对熔体的运动及物质扩散也将产生影响。这些物理场之间的耦合关系十分复杂,其综合作用效果决定了电解槽的电流效率、直流能耗和槽寿命[7]。

图1 传统预焙铝电解槽结构示意图
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of prebaked aluminum reduction cell: 1—Feeder; 2—Anode stell claw; 3—Carbon anode; 4—Al2O3 cover; 5—Frozen ledge; 6—Electrolyte; 7—Molten aluminium; 8—Carbon cathode block; 9—Cathode steel bars; 10—Lining
目前,对于铝电解槽的多相多场耦合计算主要集中在电、热、应力、磁及两相稳态流场仿真上。由于新型铝电解槽及特大型铝电解槽已成为未来铝电解槽的发展方向,目前的这些算法以及不能满足电解槽设计与优化的需要,为此,本文作者在已有基础上,开发了“液(电解质)-液(铝)-气”和“液-气-固(颗粒)”两类三相流模型以及多物理场(电、磁、热、流、力、浓度分布场等)、磁流体稳定性和电流效率三维耦合仿真模型与算法,在此基础上,对控制算法进行了深入优化。
1 铝电解槽多相多场数值仿真计算
1.1 电热场耦合仿真
高强电流流过铝电解槽,产生大量的焦耳热,使槽内温度高达960 ℃,而外围环境温度仅为几十摄氏度,可见,槽内存在显著的温度梯度。为保证铝电解过程顺利高效地进行,电解槽需要达到良好的热平衡,使熔体保持高温,炉帮形状规整[1]。国内外学者围绕着槽帮形状和热平衡计算等方面开展了大量的研究工作,为电解槽内衬结构的设计提供理论依据。
关于槽膛内形的计算,HAUPIN[2]最早于1971年提出了1D传热模型,KRYUKOVSKY和SCHERBININ[3]也采用1D模型计算了电解槽的温度分布;PFUNDT等[4]采用2D模型计算槽帮形状;BRUGGEMAN和DANKA[5]在2D模型的基础上考虑了许多材料在Z方向上的不连续性,对材料属性进行了修正;KASEB等[6]在2D模型中考虑了槽帮与熔体之间界面的相变,在数学控制方程中增加了相变热。
TOMASINO等[7]在2D模型中考查了电解槽周围的散热情况,槽外自然对流和辐射均引入到模型中,结果与实测值较吻合。LASZLO和VERONIQUE[8]提出了3种计算槽帮形状的热阻模型,比较之后选出比最优的模型,在此基础上建立2D模型计算不同热收入下的槽膛内形。
随着计算机硬件设备和软件技术的不断发展,铝电解槽电热场的3D仿真计算和参数优化已经逐步实现。3D模型更加真实地反映实际问题,计算结果更加精确,是物理场仿真的必然方向。DUPUIS等[9-12]率先采用有限元商业软件ANSYS建立了3D半阳极模型、阴极切片模型、全槽切片模型、单阴极模型、阴极角部模型、四分之一电解槽模型、二分之一电解槽模型和全槽模型。SAFA等[13]采用3D铝电解槽全槽模型进行了电-热-磁-流场的耦合计算,得到了槽膛形状,计算中不仅考虑了电热场对槽帮形状的影响,流场对槽帮的冲刷作用也考虑在内。
在国内,仿真技术起步较晚,但发展迅猛,也获得了较多的成果。本文作者及其课题组在这一领域开展了大量的工作:李相鹏等[14]在ANSYS商业软件平台上通过循环迭代,计算出了槽膛内形,计算结果与实测结果吻合较好;李劼等[15-18]分别对不同容量的预焙铝电解槽进行了3D电热场耦合计算,均取得比较好的结果,并采用2D槽帮计算与3D电热场计算相结合的方式对两种5 kA级惰性阳极铝电解槽进行了系统的仿真计算,确定较合理化的槽结构;CUI等[19]采用3D电热耦合模型在ANSYS商业平台上计算了3D槽帮形状,同时考察其温度分布以及各部分电压降,结果表明槽帮形状在小面厚度大于大面,而在角部处槽帮最厚,与实际情况相符。
1.2 电热应力场耦合仿真
经过长期的生产实践和统计分析,发现电解槽寿命主要受到以下4个主要因素的影响[20]:结构设计(20%)、筑炉工艺(20%)、选用材料(10%)和焙烧方法(25%)。应力场研究与以上4个方面均紧密相关,对优化电解槽结构、延长槽寿命和降低成本具有重要意义。综合而言,对铝电解槽应力场的研究重点集中在槽壳应力场和阴极应力场两方面。
1.2.1 槽壳应力
槽壳为电解槽内衬砌体外部的钢壳和加固结构,起到盛装内衬砌体、支持电解槽质量和克服内衬材料在热应力和化学应力作用下的变形等作用。为保证槽壳和摇篮架结构强度可靠,同时钢材用量节省,国内外学者进行了很多的现场测试和仿真研究。
对槽壳应力场的测量,通常先现场测量槽壳的变形数据,再反推内壁压力值。MITTAG等[21]对槽焙烧后24个月内的应力变化进行了测量,数据表明,短边应力值为0.50 MPa,长边应力值为0.45 MPa。伍洪泽和文丕华[22]针对180 kA级铝电解槽测量了大量槽壳变形和温度变化数据,根据反求应力的半解析方法,反求槽壳的应力分布,确定槽壳的应力载荷为:短边750 kN/m,长边375 kN/m。SAYED等[23-24]采集电解槽运行90 d和615 d后的位移数据并反推内壁压力分别为0.7 MPa和1.17 MPa。
利用所获得的内壁压力,对槽壳结构进行仿真优化设计。曹国法[25]采用有限元法建立了简化的膜杆模型,计算了160 kA电解槽槽壳的应力分布,认为热载是槽壳变形的重要因素之一,在结构设计时应引起重视。DUPUIS等[26]建立了65 kA电解槽应力场计算的有限元模型,模型中考虑了槽壳的弹塑性问题,结果表明,端部加强筋可以消除了端部应力集中。
梁利[27]针对200 kA铝电解槽槽壳及摇篮架进行了静态的等效应力和变形相应分析,结果显示材料的本构关系对有限元计算结果的影响大于接触对其的影响。王长成和蒙培生[28]以及王泽武等[29]在ANSYS软件平台上建立了3D槽壳应力场计算模型,模型中考虑了材料和结构的非线性,并预设了槽壳温度梯度和大小面设计压强,计算结果表明,槽壳和摇篮架分别发生了屈服应变和弹性应变。
1.2.2 阴极应力
LARSEN和S?rlie[30]建立了阴极炭块的2D热应力计算有限元模型,探讨了阴极底部炭块纵面内的应力及应变分布受阴极炭块种类、捣固料的弹性、端部内衬的刚度、钢棒放置位置、燕尾槽形状等的影响情况。DUPUIS[31]进行铝电解的3D电热-应力顺序耦合计算,先进行电热场解析,再将温度结果作为应力场计算的热载荷,在结构模型中,考虑了捣鼓糊在不同温度下状态不同这一特性,并且考虑了不同材料对炭块的作用。
学者们对钠膨胀进行了大量的实验研究[32-35],一般认为,随着阴极炭块石墨化程度的提高,金属钠的渗透降低,钠的膨胀量与其浓度呈正比关系,钠扩散过程服从Fick第二定律。ZOLOCHEVSKY等[36]测定了炭块中的钠扩散以及钠膨胀,并建立3D有限元模型进行仿真计算,仿真结果和试验测定值吻合较好。
在阴极内衬研究上,本文作者及其课题组在国内较早的开展了相关研究,其中,邓星球[37]在ANSYS软件平台上建立了铝电解槽电-热-应力稳态计算的3D有限元模型,研究了阴极炭块种类对炭块位移、应变、应力等的影响,并用相应的强度理论判断其安全状况,分析表明,石墨含量越高,对电解槽的应力分布越有利。张钦菘[38]针对铝电解槽焙烧过程中阴极内各种应力随时间的演变进行了研究,结果表明,垂直方向的正应力一直占主导地位;同时考查了不同石墨含量阴极炭块的热应力分布,结果表明,石墨化炭块应力分布较优。伍玉云[39]建立3D单阴极模型计算钠扩散,根据计算得到的钠浓度计算结果,计算热应力和钠膨胀应力的共同作用下,电解槽启动30 d后的应力分布情况,并比较不同炭块对电解槽应力分布的影响,结果表明,采用纯石墨化炭块对延长槽寿命有利。
1.3 电磁流场耦合仿真
在铝电解槽中,强大的直流电自立柱母线流入,经阳极横母线、阳极导杆、阳极、电解质、铝液、阴极、阴极钢棒经阴极母线收集流入串联的下一台铝电解槽。为得到铝电解槽内外导体的电流分布情况,优化电解槽结构配置,前人进行了较多的研究工作。
ZIEGLER等[40]使用1D有限差分法、2D和3D有限元法研究了阳极结构、电导率、电解质电导率等对阳极电流密度的影响,通过阳极结构的优化可降低局部电流密度,使槽寿命提高。贺志辉等[41]通过2D模型,研究了槽膛内形对铝液内水平电流分布的影响,结果表明,过长或过短的伸腿都会产生水平电流,应将铝液控制在阳极投影以下。FRASER等[42]和曾水 平[43]分别采用2D和3D模型考察了电流分布受槽膛内形和非均匀阳极电流边界的影响,认为大面和小面方向的水平电流都很重要,计算结果可用于磁流体的计算。DUPUIS[9]最早在ANSYS软件平台上开发了铝电解槽的3D电场计算模型,并将计算结果用于热平衡和磁场的计算。目前,铝电解槽3D电场的建模仿真计算已经比较成熟。
随着铝电解槽的大型化,其母线设计日趋重要。在早期,母线是单独建模研究的。TVEDT等[44]针对铝液和下游槽阳极之间的电路,根据串并联关系等效为电阻网格,应用数值计算方法迭代计算出电场分布。BUIZA[45]通过1D线单元进行母线模拟,对母线进行设计和优化。将母线导体与槽主体结构部分一起建模研究在近年来已经逐步发展成熟。DUPUIS和BOJAREVICS[46]在ANSYS软件计算平台上分别开发了整槽3D实体母线模型和简化的1D线单元母线模型,并优化了500 kA级电解槽的母线设计方案。
对铝电解槽内导体及槽外母线的电场进行研究,既可为铝电解槽生产和母线设计提供建议,又可为后续的热平衡和磁场计算提供数据。电场分布是铝电解槽内其他物理场分布的源头,对其分析是多物理场研究的初级工作。与电场计算相比,铝电解槽内的磁场计算则更为复杂,究其原因是槽内外分布着大量自由电流和槽壳、钢梁、钢爪等铁磁材料。近年来,铝电解槽不断向大型化发展,磁场分布对铝电解槽稳定性的作用日益重要,磁场计算与设计逐渐成为铝电解槽设计的热点和难点。一般而言,槽内熔体是铝电解槽磁场研究的主要分析区域,其磁场主要有两部分构成:1) 槽内的电极电流、熔体电流、槽外的母线电流以及临槽、临车间等电流导体产生的一次磁场;2) 铁磁体在源电流作用下磁化而产生的二次磁场。
磁场的计算大致可以分为4类[47],即图解法、模拟法、解析法和数值计算法。其中,数值计算法极大拓展了磁场分布边值问题的求解范围,具有很强的实用性和较高的计算精度。常用的磁场数值计算方法包括积分方程法、表面磁荷法、磁偶极子法、有限元法等。计算机技术的不断发展和成熟有限元软件的出 现,为采用有限元法解决复杂的工程问题带来了极大的便利。大多数情况下,有限元法进行磁场计算是与标量磁位法结合使用的。根据麦克斯韦方程,在恒定磁场的无电流区域内有![]() (H是磁场强度),标量磁位
(H是磁场强度),标量磁位![]() 满足
满足![]() ,但
,但![]() 仅适用于无自由电流区域。
仅适用于无自由电流区域。
为了避免矢量计算,同时能够应用标量磁位计算有电流区域的磁场分布,有学者提出了多种计算方法,如简化标量磁位法、全标量磁位法、差分标量磁位法,来计算磁介质和有源空气域内的磁场分布,均已集成在ANSYS软件计算中[48]。简化标量位法数学模型简单,其有限元计算过程亦简单,但是计算结果在铁区误差较大[49];双标量位法在铁区和非铁区分别定义了标量位,克服了这一缺点,但由于不同区域两个位函数的存在,在交界面上两位函数不连续,给计算和分析带来了困难;为避免这些缺陷,MAYERGOYZ等[50]最早提出了差分标量位法,能够解决前二者计算方法存在的问题,能够很好解决单连通铁区的磁场问题;但对于铝电解槽问题,即有电流源又有多连通铁区,全标量位法能够很好解决这一类问题,GYIMESI 等[51-52]提出了GP ψ-DP标量位法分3步求解磁场,适合铝电解槽磁场问题的求解。
针对铝电解槽磁问题的有限元求解,国内外学者做了大量的研究工作。DUPUIS等[53]最早在ANSYS软件平台上建立了铝电解槽电磁场模型,模型采用实体单元描述槽内实体,线单元描述槽周母线与相邻槽,计算结果表明,ANSYS软件具有较好的电磁场耦合 计算能力,能将所有导体内的电场结果耦合到磁场计算中。SEVERO等[54]以ALGOR软件为前处理器、ANSYS软件为求解器对240 kA级预焙铝电解槽进行了磁场研究,可见与DUPUIS的模型描述大体类似,并采用大于槽自身空间尺寸的空气包以解决空气漏磁的问题。
姜昌伟等[55]在ANSYS软件计算平台上建立了154 kA级铝电解槽磁场计算模型,并将计算结果与实测值进行比较,验证了模型的正确性。但该模型考虑的空气漏磁空间较小,槽壳以里内衬的连续网格剖分没有给出,且磁标量条件位置的选取存在不合理之处。
刘伟等[56-57]开发了3台槽相连的槽内导体与母线电磁场计算模型,如图2所示,中间槽为待研究主体槽,该计算模型考虑了前槽和后槽对主体槽结构的电场和磁场的影响。电场计算和磁场计算共用有限元模型,当电场计算时设置周围空气包单元为空,磁场计算时重新定义为实体单元,二者依次计算,达到电磁场计算的顺序耦合。该方法的计算精度较高,模型考虑的因素较多,能较准确地反应电解槽磁场分布情况。
除ANSYS软件外,其他有限元软件也在磁场计算中得到很好的应用。ZIEGLER和KOZAREK等[58]使用Bell高斯计和电压表对美铝P225型槽进行了3D磁场分布的测量,利用MAGNUM有限元软件求解了磁场分布,模型对槽长轴和垂直方向的预测值与实测值较符合,而短轴方向可比性差。KACPRZAK等[59]利用JMAG STUDIO软件建立了200 kA级铝电解槽磁场有限元模型,分析了槽中心、大面两侧垂直磁场的分布情况。计算结果表明,通过补偿母线的设计可使垂直磁场降低约7 mT。各大铝业公司也都开发了各自的计算软件包,如俄罗斯铝业公司的BLUMS软件[60]、加拿大铝业公司的ALUCELL软件[61],但由于技术保密的原因,很难从文献获得这些软件包的具体细节。

图2 3台槽相连的铝电解槽电场和磁场计算模型示意图[56]
Fig.2 Schematic diagram of electric and magnetic model with three solid cells and bus bar circuit: (a) Electric model; (b) Magnetic model[56]
自20世纪80年代以来,随着计算流体力学(CFD)和仿真技术的快速发展,铝电解CFD研究也迅速展开。TARAPORE[63]最先在研究185 kA槽时,将电磁力引入到Navier-Stokes方程中,结合湍流k-ε模型对2D稳态流场进行了计算。BLANC和ENTNER[64]通过对电解槽理想分布电磁力的讨论,认为电磁力旋度的垂直分量是熔体运动的量度,在此基础上定义了铝液流动的4种基本形式。AI[62]把电解质-铝液体系分成3个区域,根据各自的特征尺寸参数与物性参数进行了无量纲准数分析,阐述了不同区域的控制因素,并对两相流、传质传热、波动等现象进行了定性分析。周萍[65]在CFX软件平台上,以磁场、电场与热场综合解析的结果为基础,采用标准k-ε模型、低雷诺数J-L k-ε模型以及RNG模型分别对82 kA、156 kA和200 kA 3种电解槽的铝液流场进行了仿真计算,认为从收敛性与适用性的角度出发,标准k-ε模型更适于铝液流场的计算。PURDIE等[66]使用FLUENT软件研究了半阳极在气泡搅动下的电解质流动,结果表明,电流密度和阳极的几何形状对气泡生成方式和电解质的流动有重要影响,但模型中未引入电磁力因素。DOHEIM 等[67]在FLUENT中建立了208 kA电解槽的电解质流场2D模型,采用欧拉-拉格朗日方法、标准k-ε湍流模型分别计算了槽内电解质在仅阳极气体作用、仅电磁力作用、电磁力和阳极气体共同作用下的电解质流动情况。夏小霞[68]以CFX4.3为计算平台,建立了156 kA预焙槽电解质3D流场计算模型,同样分析了电磁力、阳极气体对电解质流动的影响,认为阳极气体对电解质流场起主要作用。
综上所述,国内外研究者在铝电解稳态流场研究上进行了大量工作,这些工作归纳起来可分为以下3类:1) 建立铝液流场模型,研究电磁力作用下的铝液流动;2) 建立电解质流场模型,研究电解质在电磁力、气泡搅动分别作用下或共同作用下的流动情况;3) 建立铝液-电解质流场模型,在只考虑电磁力而忽略气泡相的条件下研究熔体运动。
2 基于物理场仿真的铝电解槽的工艺优化与实现
2.1 多相多场耦合仿真
对于现代大型铝电解槽,由于电流强度大,导致体系中不同相之间、不同场之间以及多相-多场之间的耦合作用以及它们对电解槽运行特性的影响非常强烈,因此,必须建立更精确的模型对多相-多场给予更深入的研究才能为大型铝电解槽结构、工艺和控制技术的优化奠定基础。
为此,本文作者针对大型铝电解槽多相及多场交互作用强烈的特点,提出了多相-多场耦合建模方法,建立了“液(电解质)-液(铝)-气”和“液-气-固(颗粒)”三相流模型以及多物理场(电、磁、热、流、力、浓度分布场等)、磁流体稳定性和电流效率三维耦合仿真模型与算法,为大型铝电解槽状态分析与优化提供了先进可靠的技术手段。本文作者所建立的多相-多场铝电解槽仿真体系如图3所示。

图3 铝电解槽多相-多场耦合仿真模型
Fig.3 Multiphase-multifield coupled simulation model of aluminium reduction cell
与传统技术相比,本文作者及其团队所建立的多相-多场耦合仿真体系的主要特点为:
1) 首次将两类三相流、6种物理场和两种最重要的电解槽特性参数(磁流体稳定性、电流效率)的计算机三维耦合仿真集成于一体,并充分考虑了它们之间的复杂耦合关系。
2) 该场仿真体系中,建立了“液(电解质)-液(铝)-气”和“液-气-固(氧化铝颗粒)”两类三相流耦合仿真模型与算法,更加精确地实现了全域流场、铝液-电解质界面分布的一体化数值解析,为多相-多场耦合仿真的实现,特别是为低电压(低极距)下的电解槽流场等物理场的优化、阳极气泡排放优化等提供了新的技术手段。应用“液(电解质)-液(铝)-气”三相流模型所计算得到的电解槽流场如下图4所示。
3) 建立了基于上述两类三相流耦合仿真的浓度场(氧化铝浓度分布)仿真模型,更加精确地实现了对电解槽下料过程中氧化铝颗粒瞬态分散与传质过程规律的仿真研究,为下料策略优化提供了新的技术手段。计算得到的氧化铝浓度演变如图5所示。
4) 建立了基于铝电解过程电流效率损失机理、相间传质理论、三相流耦合仿真和磁流体稳定性仿真的电解槽区域电流效率仿真模型,并在此基础上建立了铝电解槽主要技术经济指标(电流效率(Current efficiency, CE)、吨铝电耗和槽寿命)的理论计算与评估模型,从而在电解槽参数-多相流特性-多物理场特 性-技术经济指标之间建立起了直接的关系模型。计算得到的局部电流效率体分布如图6所示。
5) 完整的多相-多场耦合仿真模型克服了传统模型对“多相-多场”耦合性考虑不够(以往主要分别考虑“电-磁-流”耦合和“电-热-力”耦合)而无法精确考察电解槽各类参数间的复杂耦合关系与相互影响规律的问题,也克服了传统模型无法用于电解槽状态参数精确调控的问题,同时显著提高了电解槽物理场仿真的精度。

图4 300 kA电解槽电解质水平流速分布[48]
Fig.4 Horizontal velocity vectors of electrolyte layer in 300 kA cell: (a) Bath-bubble model; (b) Bath-metal model; (c) Three-phase model[48]
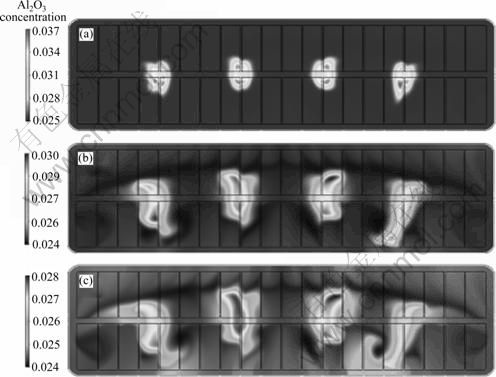
图5 下料周期氧化铝在电解质中分布
Fig.5 Al2O3 distribution of electrolyte during feeding period of 60 s: (a) t=20 s; (b) t=40 s; (c) t=60 s
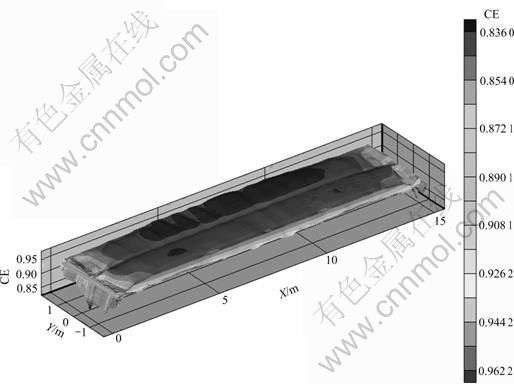
图6 300 kA铝电解槽槽内电流效率分布[48]
Fig.6 Calculated local current efficiency in 300 kA cell[48]
2.2 基于多相多场耦合的控制优化
由于铝电解槽的各种物理场分布特性及流体稳定性不仅取决于电解槽的结构参数和筑槽材料的物性参数,而且与电解槽的工艺参数密切相关,因此,过去设计优化、工艺优化和控制优化脱节的问题影响了整体优化结果。
本文作者应用基于多相-多场耦合仿真的大型铝电解槽结构、工艺与控制器综合优化方法,综合研究电解槽结构、工艺与控制器的综合优化。该综合优化方法的原理如图7 所示:将铝电解机理模型与多相-多场耦合仿真模型相结合,建立起模拟电解槽(数字化电解槽);以“多目标多环协同优化控制”模块为核心,建立一个可对模拟电解槽实施模拟控制并具有自寻优功能的模拟控制器;通过分别给模拟电解槽和模拟控制器给定相关参数(包括控制目标)并启动两者的模拟运行后,最终使两者的“运行”达到动态平衡;再建立一个参数综合评价与优化决策模块,用之对模拟电解槽和模拟控制器的输出参数进行综合评价并将优化决策结果分别反馈到两者的参数给定环节。
通过应用上述综合优化方法并结合现场试验,本文作者便可以寻找铝电解槽能在3.7~3.9 V的低电压下高效、低电耗、低排放、稳定运行的槽结构优化方案,并确立相应的工艺技术条件和控制器的相关控制参数。优化后的槽结构的最显著特征是,与传统设计方案相比,电解槽侧部一些部位的保温显著加强,同时底部的保温也适当强化,使电解槽在低电压条件下形成理想的槽膛。优化后的新工艺技术条件以“五 低-三窄-一高”(即:低温、低过热度、低氧化铝浓度、低槽电压、低阳极效应系数、窄物料平衡工作区、窄热平衡工作区、窄磁流体稳定性调节区、高电流密度)为主要特征,其中以“五低”追求电解过程的高电效、低电耗和低排放、以“三窄”追求电解过程的平稳性和电解槽长寿命,以“一高”追求电解过程强化增效并满足低电压下的热平衡要求,并在新型控制技术的保障下,这些技术条件良性互动,使槽况进入综合指标为最优的状态空间。
优化后的工艺技术条件的最显著特点是,电解槽的极距(即阴、阳极间距离)从过去的4.5 cm 左右降低到3.3~3.8 cm,对应的工作电压从过去的4.1 V 降低到3.7~3.9 V。这打破了电解槽的极距一般不能低于 4.0 cm(对应的槽电压一般不低于4.0 V)的传统认识。传统理论认为,若极距低于4.0 cm,则电解槽内的铝熔体(磁流体)稳定性会显著变差,从而引起电流效率显著降低,进而引起电解能耗升高或电解槽无法正常运行。但是,研究发现,引起磁流体稳定性和电流效率显著变差的极距“临界点”可以向低极距方向大幅度移动。因为降低极距所产生的对磁流体稳定性和电流效率的不利影响完全可以通过改变其他因素来抵消,例如,通过调整热平衡改变槽膛内形与适当强化电流的措施相结合不仅能使电解槽在低电压下达成新的稳定热平衡,而且能够显著提高阴极电流密度,从而形成有利于提高电流效率的条件,这在很大程度上抵消了极距降低对电流效率的不利影响;再配以将电解质温度、电解质过热度、氧化铝浓度和阳极效应系数等重要工艺参数也控制在尽可能低但尚可以控制的“临界点”附近,则处于“临界极距”附近的低电压不仅不会降低电流效率,而且可以提高电流效率。由于铝电解的吨铝直流电耗指标仅取决于平均槽电压和电流效率,因此在电流效率不变(甚至提高)的条件下实现槽电压的显著降低就可以实现吨铝直流电耗的大幅度降低。
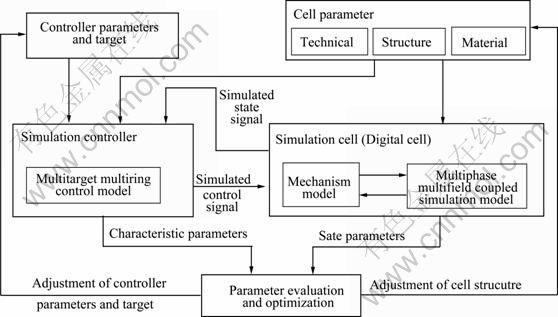
图7 基于多相多场耦合仿真的控制优化
Fig.7 Control optimization based on multiphase and multifield simulation
上述综合优化方法从有效降低电解槽“临界极距”的技术思路出发,辩证地解决了强化电流与降低极距(降低槽电压)的矛盾、以及降低极距与提高电解槽稳定性和提高电流效率的矛盾,可获得一种针对不同电解槽特性建立低电压高效节能新工艺的方法。该方法已经在全国多家铝厂推广应用,取得显著的节能减排效果。
电解槽的长寿命以“一高”追求电解过程强化增效并满足低电压下的热平衡要求。并且在新型控制技术的保障下,这些技术条件良性互动,使槽况进入综合指标为最优的状态空间。
3 结论与展望
1) 建立了“液(电解质)-液(铝)-气”和“液-气-固(颗粒)”两类三相流模型、多物理场(电、磁、热、流、力、浓度分布场等)、磁流体稳定性和电流效率三维耦合仿真模型与算法。
2) 基于多相-多场耦合仿真的大型铝电解槽结构与工艺综合优化方法,发现了大型铝电解槽在3.7~3.9 V低电压下高效、低电耗、低排放、稳定运行的状态空间,并确立了相应的工艺实现条件。
3) 未来铝电解槽仿真技术的发展,主要应集中在以下两个方面:一方面急需建立和完善更加可靠及精确的算法,对当前特大型铝电解(500 kA级以上)、新型铝电解槽(各类新型阴、阳级电解槽)及惰性电极铝电解槽开展相关物理场分析及机理研究;另一方面需要对当前传统电解槽的物理场(电-磁-热-流)的强耦合开展计算,并对生产实践中各类工艺条件进行研究,为电解槽节能降耗提供思路。
REFERENCES
[1] 田应甫. 大型预焙铝电解槽生产实践[M]. 长沙: 中南工业大学出版社, 1997.
TIAN Ying-fu. Practice of large scale prebaked anode aluminum reduction cells[M]. Changsha: Central South University of Technology Press, 1997
[2] Haupin W E. Calculating thickness of containing walls frozen from melt[C]//Edgeworth T C. Light Metals 1971. New York, NY: Metallurgical Society of AIME, 1971: 188-194.
[3] Kryukovsky V A, Scherbinin S A. Mathematical modelling of heat transfer in pots lining materials for production of non-ferrous metals[C]//Rooy E L. Light Metals 1991. San Diego, CA: TMS, 1991: 557-562.
[4] Pfundt H, Vogelsang D, Gerling U. Calculation of the crust profile in aluminium reduction cells by thermal computer modelling[C]//Campbell P G. Light Metals 1989. Las Vegas, NV: Metallurgical Society of AIME, 1989: 371-377.
[5] Bruggeman J N, Danka D J. Two-dimensional thermal modeling of the Hall-Héroult cell[C]//Blckert C M. Light Metals 1990. Anaheim, CA: TMS, 1990: 203-209.
[6] Kaseb S, Ahmed H A, El-Refaie F A, El-Raghy S M, Bassuny Z. Thermal behavior of prebaked aluminum reduction cells: Modeling and experimental analysis[C]// Huglen R. Light Metals 1997. Orlando, FL: TMS, 1997: 395-401.
[7] Tomasino T, Martin C, Waz E, RENAUDIER S. Numerical modeling of heat transfer around an aluminum reduction pot shell[C]//Tabereaux A T. Light Metals 1997. Carlotte, NC: TMS, 2004: 433-438.
[8] Las?lo K, Veronique D. Freeze thickness in the aluminium electrolysis cells[C]//Deyoung David H. Light metals 2008. New Orleans, LA: TMS, 2008: 431-436.
[9] Dupuis M. Computation of aluminum reduction cell energy balance using ANSYS finite element models[C]//Welch B J. Light Metals 1998. San Antonio, TX: TMS, 1998: 409-417.
[10] Tabsh I, Dupuis M, Gomes A. Process simulation of aluminum reduction cells[C]//Hale W. Light Metals 1996. Anaheim, CA: TMS, 1996: 451-457.
[11] Dupuis M. Thermo-electric design of a 400 kA cell using mathematical models: A tutorial[C]//Peterson D R. Light Metals 2000. Nashville, TN: TMS, 2000: 297-302.
[12] Dupuis M. Thermo-electric analysis of the grande-baie aluminum reduction cell[C]//Mannweiler U. Light Metals 1994. San Francisco, CA: TMS, 1994: 339-342.
[13] Safa Y, Flueck M, Rappaz J. Numerical simulation of thermal problems coupled with magnetohydrodynamic effects in aluminium cell[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2009, 33(3): 1479-1492.
[14] 李相鹏, 李 劼, 薛铁鹏, 赖延清, 刘业翔. 大型预焙铝电解槽槽膛内形模拟计算[J]. 冶金自动化, 2003(4): 30-33.
LI Xiang-peng, LI Jie, XUE Tie-peng, LAI Yan-qing, LIU Ye-xiang. Simulation calculation of tank hearth profile in large scale prebaked aluminum electrolytic cell[J]. Metallurgical Industry Automation, 2003(4): 30-33.
[15] 李 劼, 程迎军, 赖延清, 周乃君. 大型预焙铝电解槽电、热场的有限元计算[J]. 计算物理, 2003, 20(4): 351-355.
LI Jie, CHEN Ying-jun, LAI Yan-qing, ZHOU Nai-jun. Numerical simulation of current and temperature fields of aluminum reduction cells based on ANSYS[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2003, 20(4): 351-355.
[16] 李 劼, 邓星球, 赖延清, 刘凤琴, 刘业翔. 160 kA预焙铝电解槽在低分子比和低温条件下的三维电热场[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2004, 35(6): 875-879.
LI Jie, DENG Xing-qiu, LAI Yan-qing, LIU Feng-qin, LIU Ye-xiang. 3D thermo-electric of 160 kA prebaked aluminum reduction cell at low cryolitic ratio and temperature[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2004, 35(6): 875-879.
[17] 李 劼, 王志刚, 张红亮, 赖延清, 徐宇杰. 5 kA级惰性阳极铝电解槽热平衡仿真[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2009, 19(2): 339-345.
LI Jie, WANG Zhi-gang, ZHANG Hong-liang, LAI Yan-qing, XU Yu-jie. Simulation of heat balance in 5 kA grade aluminum reduction cell with inert anodes[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 19(2): 339-345.
[18] 李 劼, 王志刚, 赖延清, 刘 伟, 徐宇杰. 5kA惰性阳极铝电解槽槽膛内形及热平衡[J]. 过程工程学报, 2008, 8(S1): 54-58.
LI Jie, WANG Zhi-gang, LAI Yan-qing, LIU Wei, XU Yu-jie. Cell profile and heat balance of 5 kA inert anode aluminum reduction cell[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2008, 8(S1): 54-58.
[19] CUI Xi-feng, ZHANG Hong-liang, ZOU Zhong, LI Jie, LAI Yan-qing, XU Yu-jie, ZHANG He-hui. 3D freeze shape study of the aluminum electrolysis cells using finite element method[C]//Johnson J A. Light Metals 2010. Warrendale, PA: TMS, 2010: 447-452.
[20] S?rlie M, ?ye H A. Cathodes in aluminium electrolysis[M]. 2nd ed. Dusseldorf: Aluminium-Verlag, 1994.
[21] Mittag J, Bernhauser E, Friedli H. Sodium, its influence on cathode life in theory and practice[C]//Cutshall E R. Light Metals 1991. San Diego, CA: TMS, 1991: 789-793.
[22] 伍洪泽, 文丕华. 180 kA级铝电解槽槽壳应力数值计算方法[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 1995, 5(1): 30-33.
WU Hong-ze, WEN Pi-hua. Shell stress calculation of a 180 kA aluminum reduction cell using numerical computation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 1995, 5(1): 30-33.
[23] Sayed H S, Megahed M M, Omar H H, Ismael I M. Assessment of cathode swelling pressure using nonlinear finite element technique[C]//Hale W. Light Metals 1996. Anaheim, CA: TMS, 1996: 383-388.
[24] Sayed H S, Megahed M M, Dawi F M, Abdalla S. Identification of the nonlinear swelling pressure distribution of the aluminum reduction cell[C]//Huglen R. Light Metals 1997. Orlando, FL: TMS, 1997: 303-308.
[25] 曹国法. 大型铝电解槽槽壳热应力分析和上部结构设计[J]. 铝镁通讯, 1991(1): 23-30.
CAO Guo-fa. Shell thermal stress analysis of large scale aluminum reduction cell and Upper structure design[J]. Aluminum and Magnesium Communication, 1991(1): 23-30.
[26] Dupuis M, Asadi G V, Read C M, Kobos A M, Jakubowski A. Cathode shell stress modelling[C]// Blckert C M. Light Metals 1990. New Orleans, LA: TMS, 1990: 427-430.
[27] 梁 利. 200 kA铝电解槽非线性有限元结构分析[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2003.
LIANG Li. Structure nonliner finite element analysis of 200 kA aluminum reduction cell[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2003.
[28] 王长成, 蒙培生. 铝电解槽焙烧启动过程热应力有限元分析[J]. 华中科技大学学报: 城市科学版, 2006, 23(S2): 55-58.
WANG Chang-cheng, MENG Pei-sheng. Thermo-mechanical finite element analysis of aluminum reduction cell in baking process[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology: Urban Science Edition, 2006, 23(S2): 55-58.
[29] 王泽武, 蒙培生, 曾 青, 易小兵. 铝电解槽三维热应力场非线性有限元分析[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2007, 29(9): 948-952.
WANG Ze-wu, MENG Pei-sheng, ZENG Qing, YI Xiao-bing. Three-dimension thermo-mechanical field nonlinear finite element analysis of an aluminum reduction cell[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2007, 29(9): 948-952.
[30] Larsen B, S?rlie M. Stress analysis of cathode bottom blocks[C]//Campbell P G. Light Metals 1989. Las Vegas, NV: Metallurgical Society of AIME, 1989: 641-646.
[31] Dupuis M. Evaluation of thermal stress due to coke preheat of a Hall-Heroult[C]//Mannweiler U. San Francisco, CA: CIM, 1994: 15-23.
[32] Peyneau J M, Gaspard J R, Dumas D. Laboratory testing of the expansion under pressure due to sodium intercalation in carbon cathode materials for aluminum smelters[C]// Cutshall E R. Light Metals 1992. San Diego, CA: TMS, 1992: 801-808.
[33] Mikhalev Y, ?ye H A. Absorption of metallic sodium in carbon cathode materials[J]. Carbon, 1996, 34(1): 37-41.
[34] Zolochevsky A, Hop J G, Servant G, Foosn?s T, ?ye H A. Rapoport-Samoilenko test for cathode carbon materials I. Experimental results and constitutive modelling[J]. Carbon, 2003, 41(3): 497-505.
[35] Zolochevsky A, Hop J G, Servant G, FoosnAs T, ?ye H A. Creep and sodium expansion in a semi-graphitic cathode carbon[C]//Crepeau P N. Light Metals 2003. San Diego, CA: TMS, 2003: 595-602.
[36] Zolochevsky A, Hop J G, Foosnaes T, ?ye H A. Rapoport-Samoilenko test for cathode carbon materials Ⅱ. Swelling with external pressure and effect of creep[J]. Carbon, 2005, 43(6): 1222-1230.
[37] 邓星球. 160 kA预焙阳极铝电解槽阴极内衬电-热-应力计算机仿真研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2004.
DENG Xing-qiu. Structural-thermo-electric coupled simulation of the cathode lining in the 160 kA prebaked aluminum reduction cells[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2004.
[38] 张钦松. 160 kA预焙铝电解槽焦粒焙烧过程电-热-应力场计算机仿真研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2005.
ZHANG Qin-song. Study on structural-thermo-electric simulation for the coke preheating of 160 kA prebaked aluminum reduction cell[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2005.
[39] 伍玉云. 300 kA铝电解槽电热应力及钠膨胀应力的仿真优化研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2007.
WU Yu-yun. Study of simulation and optimization on the electro-thermo-stress field and sodium expansion stress field in 300 kA aluminum reduction cells[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2007.
[40] Ziegler D P. Current distribution modeling for novel alumina electrolysi[C]//Rooy E L. Light Metals 1992. New Orleans, LA: TMS, 1991: 363-374.
[41] 贺志辉, 陶光绪, 陈世玉. 铝电解槽槽膛内形对电流分布的影响[J]. 轻金属, 1987(6): 28-30.
HE Zhi-hui, TAO Guang-xu, CHEN Shi-yu. Influence of profile on the current distribution in aluminum reduction cell[J]. Light Metals, 1987(6): 28-30.
[42] Fraser K J, Billinghurst D, Chen K L. Some applications of mathematical modelling of electric current distributions in Hall Heroult cells[C]//Campbell P G. Light Metals 1989. Las Vegas, NV: Metallurgical Society of AIME, 1989: 219-226.
[43] 曾水平. 铝电解槽内电磁场计算及电流效率连续监测的研究[D]. 长沙: 中南工业大学, 1996.
ZENG Shui-ping. Field calculation of electric-magnetic in aluminum reduction cell and study of current efficiency continuous monitoring[D]. Changsha: Central South University of Technology, 1996.
[44] Tvedt T, Nebell H G. Newbus. A simulation program for calculation of the current distribution in the bus bar system of alumina reduction cells[C]//Boxall L G. Light Metals 1988. Phoenix, AZ: Metallurgical Society of AIME, 1988: 567-573.
[45] Buiza J I. Electromagnetic optimization of the V-350 cell[C]//Campbell P G. Light Metals 1989. Las Vegas, NV: Metallurgical Society of AIME, 1989: 211-214.
[46] Dupuis M, Bojarevics V. Busbar sizing modeling tools: Comparing an ansys [registered trademark] based 3D model with the versatile 1D model part of MHD-Valdis[C]//Galloway T J. Light Metals 2006. San Antonio, TX: TMS, 2006: 341-346.
[47] 冯乃祥, 孙 阳, 刘 刚. 铝电解槽热场、磁场和流场及其数值计算[M]. 沈阳: 东北大学出版社, 2001.
FENG Nai-xiang, SUN Yang, LIU Gang. Thermo field, magnetic field and flow field in aluminum reduction cell and its numerical calculation[M]. Shenyang: Northeastern University Press, 2001.
[48] LI Jie, XU Yu-jie, ZHANG Hong-liang, LAI Yan-qing. An inhomogeneous three-phase model for the flow in aluminium reduction cells[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2010, 8(9): 46-54.
[49] 石 生. 三维非线性磁场的标量磁位描述[J]. 电力学报, 1997, 12(4): 15-19.
SHI Sheng. The description for three demensional nonlinear magnetoseatic field using the scalar poteneial[J]. Journal of Electric Power, 1997, 12(4): 15-19.
[50] Mayergoyz I D, Chari M V K, D'Angelo J. A new scalar potential formulation for three-dimensional magnetostatic problems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 1987, MAG-23(6): 3889-3894.
[51] Gyimesi M, Lavers D, Pawlak T, OSTERGAARD D. Application of the general potential formulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 1993, 29(2): 1345-1347.
[52] Gyimesi M, Lavers J D. Generalized potential formulation for 3-D magnetoseatic problems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 1992, 28(4): 1924-1929.
[53] Dupuis M,
[54] Severo D S, Schneider A F, Pinto E C V, Gusberti V, Potocnik V, Consultant V P. Modeling magnetohydrodynamics of aluminum electrolysis cells with ANSYS and CFX[C]//Kvande H. Light Metals 2005. San Francisco, CA: TMS, 2005: 475-480.
[55] 姜昌伟, 梅 炽, 周乃君, 徐顺生. 用标量电位法与双标量磁位法计算铝电解槽三维磁场[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2003, 13(4): 1021-1025.
JIANG Chang-wei, MEI Chi, ZHOU Nai-jun, XU Shun-sheng. Computation of 3D magnetic field in prebaked cells using scalar voltage potential method and two scalar magnetic potentials method[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2003, 13(4): 1021-1025.
[56] 刘 伟. 铝电解槽多物理场数学建模及应用研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2008.
LIU Wei. Mathematical modeling of multiple physical fields and its application in aluminum reduction cells[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2008.
[57] 刘 伟, 李 劼, 赖延清. 铝电解槽电磁流场数学建模及应用[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2008, 13(5): 909-916.
LIU Wei, LI Jie, LAI Yan-qing. Development and application of electro-magneto-flow mathematic model of aluminum reduction cells[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 13(5): 909-916.
[58] Ziegler D P, Kozarek R L. Hall-Héroult cell magnetics measurements and comparison with calculations[C]//Rooy E L. Light Metals 1991. New Orleans, LA: TMS, 1991: 381-391.
[59] Kacprzak D, Gustafsson M J, Taylor M P. A finite element analysis of busbars and magnetic field of an aluminum reduction cell[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2006, 42(10): 3192-3194.
[60] Arkhipov G V. The mathematical modeling of aluminum reduction cells[J]. JOM, 2006, 58(2): 54-56.
[61] Martin O, Benkahla B, Ttomasino T, FARDEAU S, RICHARD C, HUGRON I. The latest developments of Alcan’s AP3X and ALPSYS technologies[C]//S?rlie M. Light Metals 2007. Orlando, FL: TMS, 2007: 253-258.
[62] Ai D K. Hydrodynamics of the Hall-Héroult cell[C]//Bohner H O. Light Metals 1985. New York, NY: Metallurgical Society of AIME, 1985: 593-607.
[63] Tarapore E D. Magnetic fields in aluminum reduction cells and their influence on metal pad circulation[C]//Peterso W S. Light Metals 1979. New Orleans, LA: Metallurgical Society of AIME, 1979: 541-550.
[64] Blanc J M, Entner P. Application of computer calculations to improve electromagnetic behaviour of pot[C]//McMinn C J. Light Metals 1980. Las Vegas, NV: Metallurgical Society of AIME, 1980: 285-295.
[65] 周 萍. 铝电解槽内电磁流动模型及铝液流动数值仿真的研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2002.
ZHOU Ping. A Research on mathematical models of electromagnetic hydrodynamics and numerical simulation of metal pad flow in aluminum reduction cells[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2002.
[66] Purdie J M, Bilek M, Taylor M P. Impact of anode gas evolution on electrolyte flow and mixing in aluminum electrowinning cells[C]//DAS S K. Light Metals 1993. Denver, CO: TMS, 1993: 355-360.
[67] Doheim M A, El-Kersh A M, Ali M M. Computational modeling of flow in aluminum reduction cells due to gas bubbles and electromagnetic forces[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2007, 38(1): 113-119.
[68] 夏小霞. 铝电解槽内电解质流场的数值模拟研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2005.
XIA Xiao-xia. Study on numerical simulation of electrolyte flow field in aluminum reduction cells[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2005.
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家科技支撑计划项目(2009BAE85B00);国家自然科学基金资助项目(50874020)
收稿日期:2011-05-10;修订日期:2011-07-20
通信作者:李 劼,教授,博士;电话:0731-88876454;E-mail: net_hotang@163.com
李劼教授简介
李 劼,1963年出生于湖南省汨罗市。1983年于中南矿冶学院获学士学位,1989年于中南工业大学获硕士学位,1993年于中南工业大学获博士学位,现为中南大学教授、博士生导师,校长助理,冶金科学与工程学院院长,难冶有色金属资源高效利用国家工程实验室常务副主任,先进电池材料教育部工程研究中心主任,中国有色金属学会轻金属学术委员会委员和铝电解专业委员会副主任委员,中国材料研究学会理事。一直从事铝冶金理论与工艺、计算机仿真与控制、新能源材料与电源系统等方面的研究。主持了多项国家级重点科研课题,取得了“铝电解智能控制系统”、“锂离子动力电池”等多项科研成果,发表SCI和EI收录论文200余篇,获得发明专利20余项,出版学术专著2部。

