文章编号:1004-0609(2008)10-1872-07
熔体快淬非晶Fe-Si-B-Cu合金的晶化行为
赵仲恺1,周海涛1,周 啸2,严 彪3,钟建伟1,李庆波1
(1. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 江西理工大学 材料与化学工程学院,赣州341000;
3. 同济大学 上海市金属功能材料重点实验室,上海200092)
摘 要:采用差热扫描量热分析(DSC)、X射线衍射分析(XRD)以及透射电镜技术(TEM)对熔体快淬非晶薄带Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2的晶化行为进行研究。结果表明:在不同升温速率下的DSC曲线中出现两个放热峰,晶化表观激活能分别为369.177和430.162 kJ/mol;经500~680 ℃、1 h等温退火后,发现晶化时发生α-Fe(Si)相的形核长大以及Fe3B和Fe2B相的析出;在500 ℃退火后获得的α-Fe(Si)平均晶粒尺寸最小;α-Fe(Si)的晶格常数起初增大,在560 ℃达到最大值后缓慢降低;在500 ℃等温退火,随着时间的延长,α-Fe(Si)的晶粒尺寸及晶格常数逐渐增大,在等温退火1 h时,晶粒尺寸约为20 nm。
关键词:非晶合金;纳米晶;相变;晶粒尺寸;晶格常数
中图分类号:TB 31; TB 34 文献标识码: A
Crystallization behavior of melt-spun amorphous alloy Fe-Si-B-Cu
ZHAO Zhong-kai1, ZHOU Hai-tao1, ZHOU Xiao2, YAN Biao3, ZHONG Jian-wei1, LI Qing-bo1
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. School of Materials Science and Chemical Engineering, Jiangxi University of Science and Technology,
Ganzhou 341000, China;
3. Shanghai Key Laboratory of D&A for Metal-Functional Materials, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China)
Abstract: The crystallization process of the amorphous soft magnetic alloy Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2 was investigated by DSC, XRD and TEM. The DSC curves show two exothermal peaks, of which the crystallization activation energy Ea are 369.177 kJ/mol and 430.162 kJ/mol in average for the first peak and second one, respectively. This can be explained by the crystallization mechanism, that is, grain nucleation and growth process of α-Fe(Si) and the precipitation of Fe3B and Fe2B phases. Annealing at 500 to 680 ℃ for 1 h, the nano-grain size of α-Fe(Si) is minimate at 500 ℃, and the lattice parameter of α-Fe(Si) solid solution increases with rising temperature at the beginning, reaches the maximum value at 560 ℃ and goes down slightly. Moreover, both of the grain size and the lattice parameter increase with the annealing process continuing at 500 ℃ and the average grain size is about 20 nm for 1 h.
Key words: amorphous alloy; nano-grain; phase transformation; gain size; lattice parameter
纳米晶材料通常是指拥有晶粒尺寸5 nm到50 nm的单相或者多相的多晶体材料[1]。在磁性功能材料方面,Fe-Si-B系的非晶态合金由于其具有优越的软磁性能,已经在热性能、晶化行为、磁性能、电化学腐蚀性能方面被广泛的研究[2-7]。但是,大多数研究集中在5%~10%Si、75%~78%Fe(摩尔分数)这一成分范围 内[8-12],较高Si含量的合金较少报道。YOSHIZAWA等[13]于1988年报道将Fe73.5Si13.5B9Cu1Nb3熔体快淬制成非晶薄带,并将非晶薄带在813 K等温退火,得到约10 nm的晶粒后,此材料具有优越的综合软磁性能。随后,德国真空熔炼公司的HERZER等[14]对该合金进行了深入研究,根据非晶合金的随机各向异性模型,建立了纳米晶软磁合金的随机各向异性模型,即著名的有效磁各向异性模型,发现与普通的软磁合金如硅钢的增大晶粒尺寸来提高软磁性能的机理恰恰相反。当晶粒尺寸减小到一定范围(约40 nm)时,纳米晶软磁合金呈现特殊的性能。按照此模型,减小晶粒尺寸,是提高纳米晶软磁材料软磁性能的重要途径。HONO等[15]采用原子探针对Fe73.5Si13.5B9Cu1Nb3的析出机理进行了深入的研究,发现在550 ℃退火初期,fcc Cu原子率先析出,聚集后形成Cu原子簇成为α-Fe(Si)粒子的不均匀形核的因素。NUDES等[6]和YOSHIZAWA等[13]的研究也表明,Nb在α-Fe(Si)粒子长大过程中起到抑制作用,可以减小α-Fe(Si)粒子的长大速率,有利于得到纳米晶。但是,曾桂仪等[16]指出,Nb的加入Fe73.5Si13.5B9Cu1Nb3退火后表现出较高的脆性,不利于实际应用。
对于不添加Nb并且Si含量大于10%(摩尔分数)类Finemet合金国内外研究较少,特别是有关此种非晶合金的晶化行为、析出相和结构演化的报道就更少。因此,本文作者对单辊快淬制备的非晶合金带Fe77.5Si13.5B8Cu2(摩尔分数,%)的晶化行为进行研究,包括晶化表观激活能的计算、析出相分析,主相α-Fe(Si)的晶粒尺寸和晶格常数随等温退火温度和时间的变化规律等。
1 实验
本实验采用单辊快淬法制备非晶态Fe77.5Si13.5B8- Cu2合金。首先,纯Fe(≥99.9%)、纯Si(≥99.8%)、纯B(≥99.5%)、纯Cu(≥99.9%)按照适当比例混合,在WK-IIB型真空电弧熔炼炉中熔炼,电磁搅拌均匀后制备母合金。采用单辊快淬法制备宽55 mm、厚40 μm的非晶合金带,铜辊滚面线速度为25 m/s,采用X射线衍射仪(XRD)检验其为非晶状态。利用TA Simultaneous DSC-TGA Q600热分析仪测量了该非晶态合金的非等温晶化曲线,采用的升温速率β分别为5、10、15、20和25 K/min,在Al2O3坩埚,通氩气保护条件下进行加热。而后,将试样截为宽为10 mm,长为55 mm的短条在真空条件下,在500~680 ℃的范围内,无磁场退火1 h后空冷至室温,温度精度为±2 ℃。随后采用Rigaku D/Max 2500型18 kW转靶X射线衍射仪测量X射线衍射谱,对不同条件下的退火样进行物相分析,以及平均晶粒尺寸和晶格常数的计算。最后,采用Hitachi H-800透射电镜对500 ℃温度退火不同时间的样品的微观结构进行观察,研究相演变 规律。
2 结果及讨论
2.1 非晶Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2合金的DSC研究
图1所示为不同升温速率下测得的非Fe75.5-Si13.5B9Cu2合金的DSC曲线。随着温度的升高,出现两个放热峰,并且随着升温速率β的提高,合金的晶化峰值温度Tp向高温方向移动。
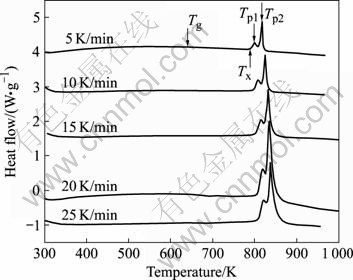
图1 不同升温速率下测得的非晶Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2晶化的DSC曲线
Fig.1 DSC curves of amorphous Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2 alloy crystallizated at different heating rates
非晶态合金晶化的表观激活能是指原子从非晶态结构转变成晶态结构所需要的平均能量。按照晶化动力学原理,当T=Tp时, ,采用Bansal修正的Kissinger模型[17],
,采用Bansal修正的Kissinger模型[17],
 利用ln(
利用ln( /β)对1/Tp作图,将得到1条斜率为Ea/R的直线,进而可以得到表观激活能Ea。图2所示为晶化峰1和晶化峰2的ln(
/β)对1/Tp作图,将得到1条斜率为Ea/R的直线,进而可以得到表观激活能Ea。图2所示为晶化峰1和晶化峰2的ln( /β)—1/Tp之间的关系,随后可求得2个晶化峰的表观激活能,分别为371.926 kJ/mol和434.164 kJ/mol。
/β)—1/Tp之间的关系,随后可求得2个晶化峰的表观激活能,分别为371.926 kJ/mol和434.164 kJ/mol。
通过Doyle-Ozawa[18]法计算晶化表观激活能Ea:

按lgβ—1/T作图为直线关系,斜率为-0.456 7 Ea/R,也可以求得两个晶化峰的表观激活能,分别为366.428 kJ/mol和426.160 kJ/mol。

图2 非晶Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2合金晶化过程的 /β—1/Tp曲线
/β—1/Tp曲线
Fig.2 Curves of  /β vs 1/Tp for amorphous Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2 alloy crystallization: (a) Peak 1; (b) Peak 2
/β vs 1/Tp for amorphous Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2 alloy crystallization: (a) Peak 1; (b) Peak 2
表1所列为采用Kissinger方法和Doyle-Ozawa方法计算的非晶合金Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2晶化表观激活能。通过比较可知,两种方法计算的表观激活能结果相差不大,因此,可以表示为非晶合金Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2的表观晶化激活能。此外,第2个放热峰的晶化激活能大于第1个峰的表现激活能,因此产生二次晶化较难,且速率较慢,并且由于fcc Cu形成几个纳米尺度的团簇在晶化初期充当非均匀形核的因素而导致第一个晶化过程的表观激活能小于不含Cu的Fe-Si-B的表观激活能[19]。
表1 晶化表观激活能
Table 1 Crystallization activation energy
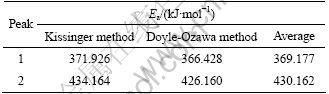

图3 非晶Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2合金两步晶化过程的lg β-1/T曲线
Fig.3 Curves of lg β vs 1/T for amorphous Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2 alloy crystallization: (a) Peak 1; (b) Peak 2
2.2 非晶Fe77.5Si13.5B8Cu2合金的XRD研究
图4所示为非晶Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2在500~680 ℃分别退火1 h后的XRD谱,其中图4(a)所示为单辊快淬的原始样,可以发现没有出现明显的晶体衍射峰;而在37?~55?处出现1个非晶漫散峰,这表明该材料为全部的非晶结构。经500 ℃退火后,在45 ?左右原非晶漫散峰的基础上出现1个晶化峰;进一步升高退火温度,峰的强度增大,并在65.64?和82.77?又析出2个较弱的晶化峰。根据这3个峰的位置和强度关系,可以判定为α-Fe(Si)固溶体的衍射峰。所以,DSC曲线中的第一个放热峰是发生非晶→α-Fe(Si)的晶化转变,并且随着退火温度的升高,α-Fe(Si)的衍射峰强度增大,而且明显高于其他的衍射峰,这说明该α-Fe(Si)为非晶Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2的晶化主相,由于α-Fe(Si)相为性能优良的软磁相[19],因此,增加α-Fe(Si)的体积分数对提高该合金的软磁性能具有重要意义。
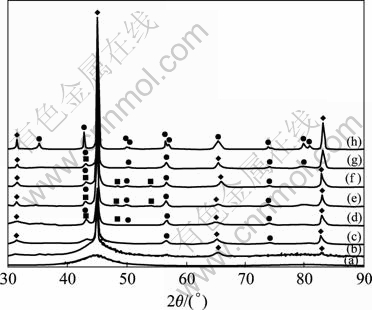
图4 非晶Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2不同温度退火1 h的XRD谱
Fig.4 XRD patterns of amorphous Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2 alloy annealed at different temperatures for 1 h: (a) As-quenched; (b) 500 ℃; (c) 520 ℃; (d) 540 ℃; (e) 550 ℃; (f) 560 ℃; (g) 600 ℃; (h) 680 ℃
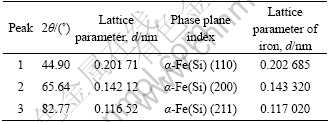
表2列出上述3个峰的角度、晶面指数、晶面间距等参数。可见,和纯铁的晶面间距对比,α-Fe(Si)的相的晶面间距略小于纯铁,这是由于该相中溶入了Si原子所致。
表2 500 ℃退火后X射线衍射谱的标定
Table2 XRD patterns index of alloy annealed at 500 ℃
在温度高于520 ℃退火时,在2θ = 43.12?和2θ = 56.20?处隐约出现2个强度微弱的峰。通过PDF卡片分析以及结合文献[18-20],分别对应为Fe3B相和Fe2B相,并且随着退火温度的升高,亚稳相Fe3B相起初析出,最后达到600 ℃以上时消失。在680 ℃退火1 h后,在2θ = 35.14?、43.12?、56.42?、57.00?、73.70?、79.78?、80.80?均出现Fe2B的衍射峰,说明随着温度的升高,有大量的Fe2B硬磁相产生。ZHANG[23]在研究Fe77.5Si13.5B9非晶合金晶化过程时发现,当温度升高到600 ℃以上时,同样发现Fe3B的消失过程,判定存在Fe3B→α-Fe(Si)+Fe2B的相变过程。这里可以推断,Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2的DSC曲线时认为第2个晶化峰是由发生了非晶→Fe3B晶化转变以及Fe3B→α-Fe(Si)+Fe2B相转变的竞相转化过程造成的,最终亚稳相在高温下将消失。
根据Scherrer公式,对不同温度退火1 h后的α-Fe(Si)平均晶粒尺寸进行计算,结果如图5(a)所示。因为添加的微量的Cu在非晶晶化的初期成为不均匀成核的中心,α-Fe(Si)平均晶粒尺寸在500~680 ℃成“S型”增长的趋势,晶粒尺寸单调增大,500 ℃晶粒最小,为13.7 nm,长大速率在540~560 ℃的区间内较大,在680 ℃时晶粒尺寸为42 nm。根据Herzer提出的有效磁各向异性理论[14],α-Fe(Si)晶粒尺寸越小,材料的有效磁各向异性越小,矫顽力将减小,同时材料的初始磁导率增大,对软磁性能有利,所以非晶在500 ℃退火1 h可以获得较佳的软磁性能。
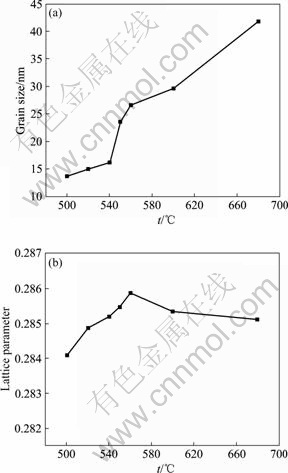
图5 α-Fe(Si)在不同温度下退火1 h后晶粒尺寸、晶格常数的变化
Fig.5 Relations between (a) grain size or (b) lattice parameter of α-Fe(Si) phase and annealing temperature for 1 h
图5(b)所示为α-Fe(Si)相的晶格常数在不同温度下退火1 h后的变化。由于Si原子溶入Fe的晶格中,形成bcc结构的α-Fe(Si)固溶体,其晶格常数小于纯bcc结构的α-Fe的0.286 64 nm。随着退火温度的升高,晶格常数起初增加,在560 ℃达到最大值0.285 871 nm后,缓慢降低。α-Fe(Si)相的变化规律与Fe73.5Cu1Nb3- Si13.5B9合金的情形不同,后者随退火温度的升高,晶格常数单调减小,最后达到1个稳定值[16]。但在Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2合金中,α-Fe(Si)的晶格常数在500~ 560 ℃的温度区间增大。USTINOVSHIKOV等[22]在研究Fe-Si有序合金的相变晶体学规律时发现,Fe与Si可以形成除B2和DO3两种有序结构相以及α-Fe(Si)的bcc无序固溶体结构以外的六边形的片状不稳定的化合物Fe5Si3(其颗粒与原基体形成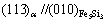 的取向关系),导致α-Fe(Si)的晶格常数的下降。但是,如果Si含量较少,由于能够观测DO3相、Fe5Si3相以及B2相的片层厚度的波长小于X射线的固定波长,所以DO3相、Fe5Si3相以及B2相在X射线衍射谱中的峰不存在。研究也表明[23]:在Fe与Si的摩尔比大于19%时,在X射线衍射图中,合金出现超结构的衍射峰,但它的衍射峰强度明显小于α-Fe(Si)的衍射峰。而本研究的合金成分Fe与Si的摩尔比小于19%,所以没有在X射线衍射图中发现DO3、Fe5Si3相和B2相的衍射峰,但是不可否认DO3、Fe5Si3和B2相的存在和转变。所以,在退火温度较低时,由于Si从α-Fe(Si)固溶体析出后形成Fe5Si3或Fe3Si化合物相,起初使α-Fe(Si)晶格常数增大。进而,随着退火温度的升高,亚稳相Fe5Si3的分解后Si原子回溶于α-Fe(Si)固溶体,以及Si在α-Fe(Si)固溶体中的固溶度增大,导致了α-Fe(Si)固溶体晶格常数的下降。
的取向关系),导致α-Fe(Si)的晶格常数的下降。但是,如果Si含量较少,由于能够观测DO3相、Fe5Si3相以及B2相的片层厚度的波长小于X射线的固定波长,所以DO3相、Fe5Si3相以及B2相在X射线衍射谱中的峰不存在。研究也表明[23]:在Fe与Si的摩尔比大于19%时,在X射线衍射图中,合金出现超结构的衍射峰,但它的衍射峰强度明显小于α-Fe(Si)的衍射峰。而本研究的合金成分Fe与Si的摩尔比小于19%,所以没有在X射线衍射图中发现DO3、Fe5Si3相和B2相的衍射峰,但是不可否认DO3、Fe5Si3和B2相的存在和转变。所以,在退火温度较低时,由于Si从α-Fe(Si)固溶体析出后形成Fe5Si3或Fe3Si化合物相,起初使α-Fe(Si)晶格常数增大。进而,随着退火温度的升高,亚稳相Fe5Si3的分解后Si原子回溶于α-Fe(Si)固溶体,以及Si在α-Fe(Si)固溶体中的固溶度增大,导致了α-Fe(Si)固溶体晶格常数的下降。
图6所示为α-Fe(Si)在500 ℃退火不同时间后平均晶粒尺寸和晶格常数的变化。可以看出,随着退火时间的延长,晶粒发生明显长大。在该温度下,退火1 h后得到平均晶粒尺寸为13.7 nm,当退火时间缩短到0.5 h时平均晶粒尺寸达到12.1 nm。这个平均晶粒尺寸比文献[13]中对Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si13.5B9材料给出最佳平均晶粒尺寸10 nm略大,这是因为含有Nb的Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si13.5B9非晶在晶化过程中抑制晶粒长大的缘故[19]。在退火时间低于1 h时,晶格常数变化平缓,随着时间的延长,晶格常数逐渐增大。这是由于Si从α-Fe(Si)固溶体析出后形成Fe5Si3或Fe3Si化合物相,使得α-Fe(Si)的晶格常数增大的缘故。但是,Fe5Si3是一种与成分和温度相关的不稳定相,随着等温退火的延续会发生分解,最后将导致α-Fe(Si)的晶格常数下降。
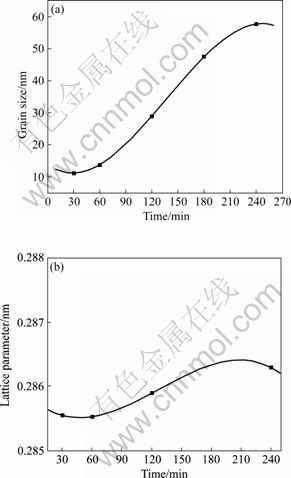
图6 在500 ℃退火不同时间后晶粒尺寸、晶格常数的变化
Fig.6 Relations between (a) grain size or (b) lattice parameter of α-Fe(Si)and annealing time at 500 ℃
2.3 非晶Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2合金的TEM分析
图7所示为非晶Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2的透射电镜像及衍射花样。图7(a)所示为非晶Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2软磁合金在未做热处理时非晶的透射电镜像,从电子衍射花样中可以看到,衍射花样是由较宽的晕和漫散环组成,没有表征结晶态的任何斑点和条纹,透射电镜像下看不到晶粒边界以及晶粒的析出,只能看到单一的均匀的非晶相结构,可确定此时的软磁材料是完全的非晶结构。图7(b)所示为非晶Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2合金在500℃退火5 min后的透射电镜照片及衍射花样。从透射电镜图片中可以清楚地看到,等温晶化的初期有少量α-Fe(Si)晶粒从非晶中析出,且此时的晶粒较小,平均晶粒直径在5~10 nm之间,从衍射图样中可以看到清晰的(110)、(200)和(211)衍射环,与XRD衍射谱标定中看到的500 ℃退火后代表(110)、(200)和(211)晶面的衍射峰正好吻合。在晶化的初期,形核发生但不充分,α-Fe(Si)的形核和晶粒长大是由界面控制的[23]。非晶Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2合金在500 ℃退火30 min后,α-Fe(Si)晶粒析出急剧增多,弥散均匀的分布于非晶基体。虽然此时的晶粒尺寸很小,但是晶化分数明显还不够。500 ℃退火60 min后,晶粒大小大约为20 nm与Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si13.5B9[13]得到最佳的软磁性能的10 nm相比,晶粒尺寸略有增大,这是因为添加的Nb在Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si13.5B9中降低了Cu的溶解度,晶化初期形成的Cu原子簇尺寸小于不含Nb的Fe-Si-B-Cu合金的缘故[13]。通过上述观察结果,根据磁弹各向异 性Kσ:
Kσ=-3/2λsσ (8)
式中 λs为饱和磁致伸缩系数;σ为由于磁弹耦合而存在的机械应力。在Fe-Si-B系合金中,饱和磁致伸缩系数可以表示为
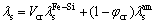 (9)
(9)
式中 φcr为α-Fe(Si)相的体积分数;α-Fe(Si)晶粒的饱和磁致伸缩系数 为负值(-6×10-6),而残余的非晶相基体的饱和磁致伸缩系数
为负值(-6×10-6),而残余的非晶相基体的饱和磁致伸缩系数 为正值(25×10-6)。由式(9)可知,要使得合金的饱和磁致伸缩系数为零,α-Fe(Si)的体积分数要足够大,约为70%~75%[15]。所以Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2合金在500 ℃退火60 min后,α-Fe(Si)的体积分数接近于70%,因此,可以获得较佳的软磁性能。
为正值(25×10-6)。由式(9)可知,要使得合金的饱和磁致伸缩系数为零,α-Fe(Si)的体积分数要足够大,约为70%~75%[15]。所以Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2合金在500 ℃退火60 min后,α-Fe(Si)的体积分数接近于70%,因此,可以获得较佳的软磁性能。
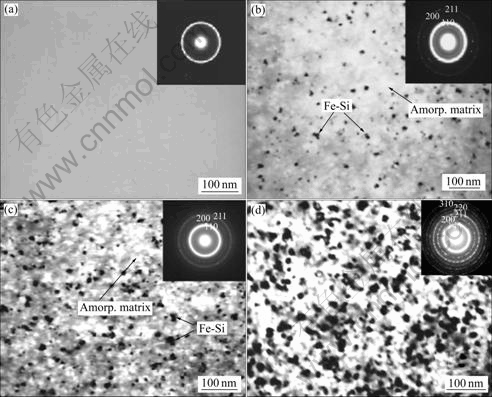
图7 非晶Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2的透射电镜照片及衍射花样
Fig.7 TEM morphologies and SAED patterns of amorphous Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2 alloy crystallization: (a) As-quenched; (b) 500 ℃, 5 min; (c) 500 ℃, 30 min; (c) 500 ℃, 60 min
3 结论
1) 非晶Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2的晶化过程是两个放热过程,表观晶化激活能Ea分别为369.177和430.162 kJ/mol。
2) 非晶Fe75.5Si13.5B9Cu2晶化时,发生α-Fe(Si)相的形核长大以及Fe3B和Fe2B相的析出。
3) 在500 ℃随退火时间的延长,α-Fe(Si)的纳米晶粒析出增多,并呈长大趋势。
4) α-Fe(Si)相的晶格常数随退火温度的升高,呈先增大后减小的趋势,但随着退火时间的延长,该晶格常数呈增大的趋势。
REFERENCES
[1] MCHENRY M E, LAUGHLIN D E. Nano-scale materials development for future magnetic application[J]. Acta Mater, 2000, 48: 223-238.
[2] P?KALA M, JACHIMOWICZ M, FADEEVA V I, MATYJA H, GRABIAS A. Magnetic and structural studies of ball milled Fe78Si13B9[J]. J Non-Cryst Solid, 2001, 287: 380-384.
[3] CREMASCHI V, AVRAM I, PEREZ T, SIRKIN H. Electrochemical studies of amorphous, nanocrystallization, and crystalline FeSiB based alloys[J]. Scripta Mater, 2002, 46: 95-100.
[4] CHIRIAC H, MARINESCU C S. New position sensor based on ultraacoustic standing waves in FeSiB amorphous wires[J]. Sens Actuators A, 2000, 81: 174-175.
[5] YU Jin-qiang, ZHOU Yong, CAI Bing-chu, XU Dong. Giant magneto-impedance effect in amorphous magnetostrictive FeSiB thin films[J]. J Magn Magn Mater, 2000, 213: 32-36.
[6] NUDES E, PEREIRA R D, FREITAS J C C, PASSAMANI E C, LARICA C, FERNANDES A R, SANCHEZ F H. Thermo stability and magnetic properties of FeSiB amorphous alloy[J]. J Mater Sci Lett, 2006, 41: 1649-1651.
[7] RHO I C, YOON C S, KIM C K, BYUN T Y, HONG K S. Microstructure and crystallization Kinetics of amorphous metallic alloy: Fe54Co26Si6B14[J]. J Non-Cryst Solid, 2003, 316: 289-295.
[8] CHRISSAFIS K, MARAGAKIS M I, EFTHIMIADIS K G, POLYCHRONIADIS E K. Detailed study of the crystallization behavior of the metallic glass Fe75Si9B16[J]. J Alloys Compd, 2005, 386: 165-173.
[9] 陆 伟, 严 彪, 李志国, 黄文昱. 非晶Fe77.5Si8.5B14合金晶化动力学的非等温方法研究[J]. 同济大学学报, 2005, 33(4): 498-501.
LU Wei, YAN Biao, LI Zhi-guo, HUANG Wen-hai. Non-isothermal study of crystallization kinetics of Fe77.5Si8.5B14 amorphous alloys[J]. J Tongji Univ, 2005, 33(4): 498-501.
[10] EFTHIMIADIS K G, POLYCHRONIADIS E K, CHADJIVASILIOU S C, TSOUKALAS I A. Influence of Cu admixtures on the crystallization of amorphous Fe75Si9B16[J]. Mater Res Bull, 2000, 35: 937-944.
[11] ATALAY F, ATALAY S. Influence of hydrogen charging on magnetic and magnetoimpedance properties of FeSiB and CoFeSiB amorphous wires[J]. J Alloy Compd, 2005, 396: 69-73.
[12] KULIK T. Nanocrystallization of metallic glasses[J]. J Non-Cryst Solid, 2001, 287: 145-161.
[13] YOSHIZAWA Y, OGUMA S, YAMAUCHI K. New Fe-based soft magnetic alloys composed of ultrafine grain structure[J]. J Appl Phys, 1988, 64(10): 6044-6046.
[14] HERZER G. Soft magnetic nanocrystalline materials[J]. J Magn Magn Mater, 1996, 157/158: 133-136.
[15] HONO K, PING D H, OHNUMA M AND ONODERA H. Cu clustering and Si partitioning in the early crystallization stage of Fe73.5Si13.5B9Nb3Cu1 amorphous alloy[J]. Acta Mater, 1999, 47: 997-1006.
[16] 曾桂仪, 巴启先, 周广智. 退火温度对Fe72.5Cu1Nb2V2Si13.5B9软磁合金微结构的影响[J]. 金属学报, 1999, 35(11): 1178-1182.
ZENG Gui-yi, BA Qi-xian, ZHOU Guang-zhi. Effects of anealing temperature on microstructure of Fe72.5Cu1Nb2V2Si13.5B9 soft magnetic alloy prepared by melt-spinning[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 1999, 35(11): 1178-1182.
[17] 唐人剑, 严 彪, 陆 伟. 非晶态Finemet合金的纳米晶化动力学研究[J]. 同济大学学报, 2007, 35(1): 88-92.
TANG Ren-Jian, YAN Biao, LU Wei. A Study of nanocrystallization kinetics of amorphous Finemet alloy[J]. J Tongji Univ, 2007, 35(1): 88-92.
[18] RAVAL K G, KIRIT N L, PRATAP A, AWASTHI A M, BHARDWAJ S. Crystallization kinetics of a multicomponent Fe-based amorphous alloy using modulated differential scanning calorimetry[J]. Thermochimica Acta, 2004, 425: 47-57.
[19] ZHANG Y R, RAMANUJAN R V. Microstructural observations of the crystallization of amorphous Fe-Si-B based magnetic alloys[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2006, 505: 97-102.
[20] 陈文智. 超微晶Fe73.5Si13.5B9Nb3Cu1晶化的X射线研究[J]. 金属功能材料, 1996, 3: 90-93.
CHEN Wen-zhi. X-ray study of ultra-fine grain Fe73.5Si13.5B9Nb3Cu1 crystallization[J]. Metallic Func Mater, 1996, 3: 90-93.
[21] DOS SANTOS D S, DOS SANTOS D R. Crystallization kinetics of Fe-B-Si metallic glasses[J]. J Non-Cry Solid, 2002, 304: 56-63.
[22] USTINOVSHIKOV Y, SAPEGINA I. Morphology of ordering Fe-Si alloys[J]. J Mater Sci, 2004, 39: 1007-1016.
[23] ZHANG Y R, RAMANUJAN R V. A study of the crystallization behavior of an amorphous Fe73.5Si13.5B9 alloy[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2006, 416: 161-168
[24] LU Wei, YANG Lei, YAN Biao, HUANG Wen-hai. Nanocrystallization kinetics of amorphous Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si13.5B9 alloy[J]. J Alloys Compd, 2006, 420: 186-192.
收稿日期:2007-12-28;修订日期:2008-05-23
通讯作者:周海涛,博士,教授;电话:0731-8830257;E-mail: htzhou62@yahoo.com.cn
(编辑 陈爱华)