具有可见光光催化活性N掺杂纳米二氧化钛的制备和表征
彭 兵,刘立强,齐萨仁,柴立元,刘云超,李国良
(中南大学 冶金科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘 要:以廉价的TiOSO4为原料,通过水解法制备正钛酸前驱体,然后,向正钛酸前驱体中加入尿素作为氮源,经煅烧制备氮掺杂纳米二氧化钛。用X射线衍射、紫外-可见吸收光谱、热重-差热分析和X射线光电子能谱等方法对制备的样品进行表征,考察煅烧温度、煅烧时间及Ti与N配比等对光催化活性的影响。研究结果表明:制备的样品均为锐钛矿,氮掺杂使二氧化钛在可见光区的光吸收明显增强;煅烧温度和Ti与N配比对光催化性能影响显著;于400 ℃制备的样品中存在1个最佳的Ti与N配比,所对应的可见光催化活性最强,甲基橙降解实验15 min时脱色率达到97%。
关键词:硫酸氧钛;氮掺杂TiO2;尿素;可见光;光催化
中图分类号:TQ134.11 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2009)04-0944-06
Preparation and characterization of N-doped TiO2 nano-powder with visible light photocatalytic activity
PENG Bing, LIU Li-qiang, QI Sa-ren, CHAI Li-yuan, LIU Yun-chao, LI Guo-liang
(School of Metallurgical Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The nano-meter particle of TiO2 precursor was prepared by hydrolysis with industrial titanic solution, and then urea was added as the source of nitrogen. The mixture was calcined to obtain N-doped TiO2. The prepared samples were then characterized using X-ray diffractrometry, UV-Vis absorption spectra, TG-DTA and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The effects of calcination temperature, time and mole ratio of Ti to N on the photocatalytic activity were investigated. The results show that all catalysts are anatase, and the doping of nitrogen leads to an obvious increase in optical absorption intensity in the visible-light region. The calcination temperature and mole ratio of Ti to N has significant influence on photoctalytic activity. There exists an optimal mole ratio of Ti to N for the catalysts calcined at 400 ℃, which results in the highest visible-light photoctalytic activity. In the experiment of degradation of methyl orange, the degradation rate reaches 97% in 15 min.
Key words: industrial titanium sulphate solution; N-doped TiO2; urea; visible light; photocatalysis
自从1972年Fujishima等[1]发现TiO2单晶电极在光的作用下可分解水以来,人们就致力于对半导体材料光催化技术的研究[2]。二氧化钛以其成本低、化学稳定性强、安全无毒、无二次污染等优点成为光催化领域研究的热点。但是,目前困扰二氧化钛光催化剂的应用有两大难题:一是由于二氧化钛的禁带较宽(Eg=3.2 eV),只能响应波长在387.5 nm以下的紫外光(约占太阳能8% ),而太阳光谱中占绝大多数的可见光(能量约占45%)则未能被有效利用[3];二是纳米TiO2的光生电子和空穴容易复合,导致光量子效率很 低。因此,缩小催化剂的禁带宽度使吸收光谱向可见光扩展及抑制光生电子与空穴的复合成为目前研究的热点[4]。过去几十年里人们通过各种手段对二氧化钛进行改性,以寻求提高二氧化钛的光催化效率,比较典型的有复合半导体[5-6]、过渡金属离子掺杂[7]、表面贵金属沉积[8]、染料敏化[9]等。掺杂过渡金属大多会导致TiO2的热稳定性下降,载流子的复合中心增多,并降低其紫外光活性,或者需要昂贵的离子注入设备;贵金属沉积对降解污染物存在选择性;染料敏化剂在近红外区吸收很弱,其吸收光谱不能与太阳光谱很好匹配[10]。而非金属(N,C,S,B和F等)掺杂可以使激发光由紫外区转移到可见区,能够直接利用太阳能中绝大部分的可见光降解、矿化污染物,具有广阔的应用研究前景。而在非金属掺杂中,氮掺杂又被认为是目前最有前景的手段之一[11]。在此,本文作者以廉价的硫酸氧钛为钛源[12]、尿素为氮源,在正钛酸前驱体中加入尿素,经过煅烧制备氮掺杂纳米二氧化钛。以甲基橙溶液为活性评价体系,研究氮掺杂对二氧化钛光催化性能的影响,以期获得在以硫酸氧钛为原料,以尿素为氮源的制备条件下的最佳工艺。
1 实 验
1.1 原 料
原料为:硫酸氧钛溶液(实验室自制);尿素(分析纯);NaOH(分析纯);甲基橙(分析纯);浓盐酸(分析纯);BaCl2(分析纯)。
1.2 制备方法
1.2.1 纯二氧化钛的制备
将1 mol/L NaOH溶液逐滴加入到一定浓度的TiOSO4溶液中,至pH值为6~8,得到白色正钛酸前驱体。用去离子水对前驱体洗涤,直至用5% BaCl2溶液检测不到硫酸根的存在。烘干后置于马弗炉中在400 ℃煅烧1 h,得到白色的纳米二氧化钛粉末。
1.2.2 氮掺杂二氧化钛的制备
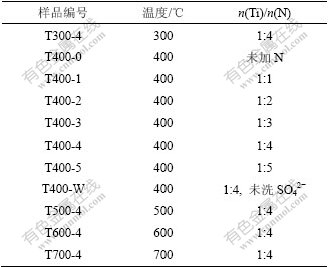
向去离子水洗涤后的正钛酸前驱体中按一定的Ti/N配比(摩尔比)加入尿素,置于80 ℃的烘箱中烘干,研磨,分别在不同温度300,400,500,600和700 ℃煅烧1 h,得到黄色的氮掺杂纳米二氧化钛粉末。另外,向未用去离子水洗涤的正钛酸前驱体中加入一定量的尿素,烘干,研磨,煅烧得到参比样。实验样品的编号见表1。
表1 供试样品的实验条件
Table 1 Experimental conditions of the tested samples
1.3 表征
采用日本生产的Rigaku D/max 2550VB+18KW型X射线衍射仪(40 kV/300 mA,步长0.02(?),Cu靶,λ= 0.154 06 nm,10?≤2θ≤85?)对粉体的晶型结构进行测
定。采用日本JSM-5600LV型扫描电镜SEM(Scanning electron microscope)对复合粉体的形貌进行分析。采用SDT-Q600热重差热分析仪进行TG-DTA测试。XPS分析采用英国VG公司MK-Ⅱ电子能谱议,选用Al阳极靶,X射线为Al Kα射线。紫外-可见漫反射吸收光谱采用日本岛津UV-2550PC型紫外可见分光光度计检测,测定波长范围为200~800 nm。
1.4 光催化活性评价
可见光催化实验在自制的光催化反应器中进行。反应器外壁为不锈钢冷却钢筒,中间为置放光源(175 W金卤灯)的玻璃冷阱,冷阱外设置夹层,中间填充2 mol/L NaNO2溶液,滤去波长λ<390 nm的紫外光[13];使用曝气装置进行曝气,提供体系矿化反应所需溶解氧;底部用磁力搅拌装置进行搅拌,以防止催化剂沉淀。
将0.3 g二氧化钛光催化剂粉末加入到300 mL的甲基橙浓度为10 mg/L的溶液中,暗态吸附30 min,以使催化剂充分分散并达到吸附平衡。在降解过程中定时抽取悬浊液,经过2次转速为10 000 r/min的离心分离出清液,然后,采用756型分光光度计在464 nm处测定降解后溶液的吸光度,最终计算甲基橙水溶液的降解率ρ/ρ0,其中,ρ0和ρ分别为反应前、后甲基橙的质量浓度。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 XRD分析
图1所示为于不同温度下,Ti与N的物质的量之比n(Ti)?n(N)=1?4,保温时间为1 h时样品的XRD谱。可见,于300,400,500,600和700 ℃所制备的的氮掺杂TiO2光催化剂均为锐钛相,未出现金红石相。其中于300 ℃煅烧得到的样品中晶型不完整,有部分板钛矿存在。随着温度的升高,衍射峰的强度逐渐增强,表明二氧化钛的锐钛矿晶型逐渐完整。图中未出现 N—O和Ti—N衍射峰。根据谢乐公式计算各温度下样品的平均粒径为:8.8,10.3,10.7,18.3和22.9 nm。说明随着煅烧温度的增加,样品的粒径逐渐增大。这是由于随着煅烧温度增加,样品发生了团聚。
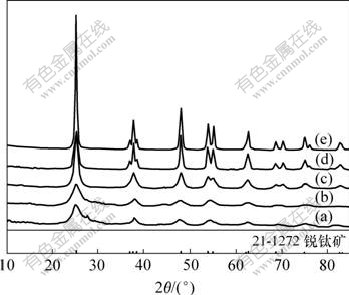
样品:(a) T300-4; (b) T400-4; (c) T500-4;
(d) T600-4; (e) T700-4
图1 不同煅烧温度下氮掺杂TiO2的XRD谱
Fig.1 XRD patterns of N-doped TiO2 calcined at different temperatures
2.2 紫外-可见漫反射吸收光谱
图2所示为于不同温度下,n(Ti)?n(N)=1?4,保温时间为1 h时样品的紫外-可见漫反射吸收光谱。
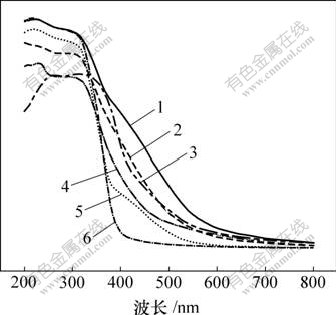
样品:1—T400-4; 2—T500-4; 3—T400-W; 4—T300-4;
5—T600-4; 6—T400-0
图2 不同温度下制备的氮掺杂TiO2和纯TiO2的紫外-可见吸收光谱
Fig.2 UV-Vis absorption spectra of nitrogen-doped TiO2 and undoped TiO2 calcined at different temperatures
由图2可以看出,对比空白样T400-0中,几乎所有氮掺杂样品在400~600 nm波长范围的可见光均被明显吸收。T400-4样品的吸收最明显,说明氮掺杂使二氧化钛的吸收光范围发生明显的变化,实现了向可见光红移。这是由于在氮掺杂后,N 2p和O 2p轨道发生混杂形成新的价带,价带位置向导带位置迁移,禁带宽度减小,电子在光激发的情况下由价带跃迁到导带的能量降低,所以,N掺杂TiO2样品的吸收向可见光方向发生红移[11]。同时,于400 ℃未洗SO42-样品T400-W的光吸收率较样品T400-4的光吸收率有所下降,原因可能是前驱体表面吸附了大量的SO42-,对氮掺杂过程产生了一定的阻碍作用;同时,样品中含有少量Na2SO4,对样品的光吸收性能产生一定的影响。由图2可以看出,400 ℃以后,随着煅烧温度的增加,样品对可见光的吸收逐渐减弱。结合热重-差热分析可知,这是由于随着温度升高,样品中部分进入晶格的掺杂氮重新逸出,氮掺杂量降低引起的。
2.3 热重-差热分析
将按 n(Ti)?n(N)=1?4(摩尔比)加入尿素的正钛酸前驱体于80 ℃干燥,然后,进行TG-DTA分析,结果见图3。
由图可见,在100~700 ℃范围内,TG曲线有4个质量损失平台。从50 ℃至150 ℃附近的质量损失比较缓慢,样品表面附着水损失,大约损失3%;加热至160 ℃时,粉体中大量尿素开始分解,产生氨气和氰酸,导致在160~223.5 ℃质量快速损失,粉体质量损失36.25%;从223.5~445.17 ℃,粉体中晶格水脱除,并且表面吸附的部分有机物分解,粉体质量损失19.07%;从445~706.55 ℃,粉体中的已掺杂氮元素随温度的升高开始逸出,粉体质量损失1.048%。
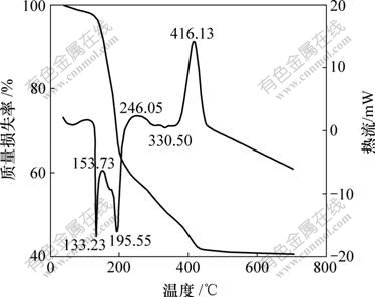
图3 氮掺杂TiO2的TG-DTA曲线
Fig.3 TG-DTA curves of N-doping TiO2
4个质量损失平台对应着3个吸热峰和3个放热峰。在133.23 ℃附近出现1个明显的吸热峰,这是尿素达到熔点熔化所致;在153.73 ℃附近出现1个放热峰,这是尿素分解成小分子氨气、氰酸等时放热所致;于196.55 ℃和246.05 ℃出现的峰分别对应吸热峰和放热峰,这是由于尿素的分解产物发生副反应所致;在333.50 ℃处出现1个吸热峰,被认为是晶格水脱除吸热产生的;在416.13 ℃出现的放热峰,是晶型转变,锐钛矿晶型的形成引起的[14]。
2.4 XPS分析
图4所示为样品T400-4的X射线光电子能谱。图4(a)中结合能399.40 eV处出现了N1s的特征峰,这说明TiO2煅烧过程确实实现了氮掺杂。一般认为[11, 15]N 1s在402和400 eV处的峰,代表氮的化学吸附;而在396 eV处的峰是Ti—N键。然而,最近很多研究也对此提出了质疑[16-17],认为N 1s谱中396~397 eV范围内的峰并不一定是N掺杂TiO2的惟一特征峰,N掺杂TiO2制备方法的不同可能导致掺杂N在TiO2晶格中存在的状态和位置不同。本文作者认为399.40 eV左右处的峰除了代表含氮化合物如NH4+,N2及NOx的化学吸附外,也可能是由于N取代TiO2中少量O后形成N—Ti—O结构。因为氧的电负性高于N,使得N—Ti—O中N电子云密度低于N—Ti—N中N的密度,从而可能引起N1s的结合能提高[15, 18-19]。另外,由XPS宽谱(c)计算得到样品的化学成分见表2 。 可以看出,样品中的Ti原子和O原子并不是按化学计量TiO2存在的。而O1s图谱(图4(b))在530.3 eV处出现峰值,这与TiO2中的O1s峰值529.8 eV有一定偏差,认为可能是非化学计量Ti2O3中O1s峰[20],这也进一步说明氧空位的存在,N—Ti—O结构形成的可能性。
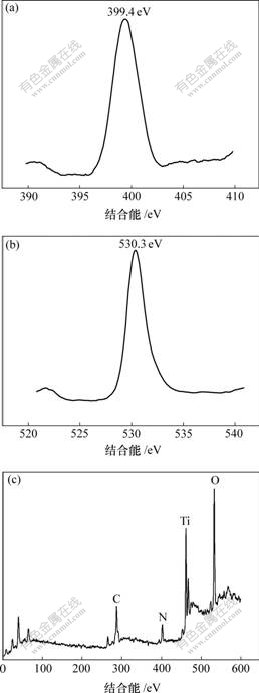
(a) N 1s;(b) O 1s;(c) 宽谱
图4 样品T400-4的XPS谱
Fig.4 XPS spectra of sample T400-4
表2 样品T400-4的化学成分
Table 2 Chemical composition of sample T400-4
摩尔分数/%
2.5 N掺杂TiO2的可见光光催化活性
研究了不同煅烧温度、不同n(Ti)/n(N)配比、不同保温时间得到的系列样品在可见光下对甲基橙的褪色效果,结果见图5。图5(a)所示是煅烧温度为400 ℃、保温1 h、不同n(Ti)/n(N)的系列样品。可见,于400 ℃煅烧温度下所制备的纯二氧化钛T400-0几乎没有可见光活性,而氮掺杂二氧化钛的降解效率均明显优于纯二氧化钛。随着Ti/N配比的增加,样品的光催化活性呈逐渐增加趋势,并且存在最佳的n(Ti)?n(N)=1?4。该样品在15 min内可使甲基橙脱色97%。结合前面的分析,本文作者认为,这是由于氮掺杂代替部分晶格氧,产生氧空位,氧空位随着氮掺杂量的增加会逐渐增多,但是,过多的氧空位的存在又会增加空穴和电子的重新复合几率[21],因此,氮掺杂量存在1个值与最佳光催化活性相对应。而随着n(Ti)/n(N)的增加,样品的光催化活性有所下降。
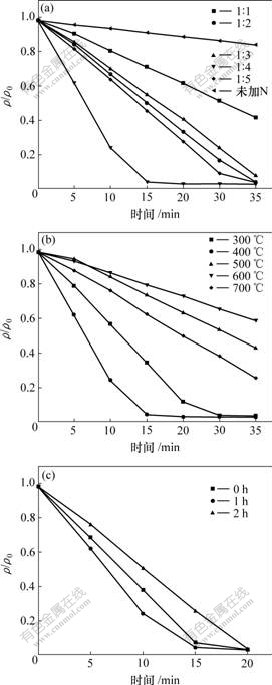
(a) 400 ℃,不同Ti/N;(b) 不同煅烧温度;(c) 不同煅烧时间
图5 甲基橙的光催化降解曲线
Fig.5 Photodegradation profiles of methyl orange
由图5(b)可以看出,随着煅烧温度的升高,氮掺杂二氧化钛的可见光活性呈现先增加后下降趋势,在400 ℃达到最大值。在400 ℃以后,随着煅烧温度的升高,样品的光催化性能逐渐下降。这与前面的紫 外-可见吸收光谱所得到的结果基本一致。
图5(c)所示为于400 ℃,n(Ti)?n(N)=1?4,煅烧不同时间的样品的光催化活性。可见,煅烧时间对催化剂的光催化性能的影响不大。煅烧1 h得到的催化剂的性能稍好于其他2个样品的性能。煅烧0 h的样品可能晶型还不太稳定,氮掺杂还不够充分;而煅烧2 h时,随着保温时间的增加,可能有部分掺杂氮重新逸出,导致光催化效果略有下降。
3 结 论
a. 以廉价的硫酸氧钛为钛源,尿素为氮源,通过向正钛酸前驱体中加入尿素,煅烧制备了氮掺杂纳米二氧化钛。在所有实验温度下得到的样品均为锐钛晶型。在400 ℃保温1 h时,存在1个最佳n(Ti)/n(N),即n(Ti)?n(N)=1?4。
b. 在煅烧过程中,氮取代TiO2中的晶格氧,导致氮掺杂样品较空白样品在可将光范围内均有明显的吸收,红移明显。
c. 在可见光下,氮掺杂TiO2对甲基橙具有较强的光催化活性,反应15 min可使甲基橙脱色率达到97%,而未掺杂TiO2几乎没有作用。
参考文献:
[1] Fujishima A, Honda K. Electrochemical photocatalysis of water at asemiconductor electrode[J]. Nature, 1972, 238(5789): 37-38.
[2] Wang R, Hashimoto K. Light induced amphiphilic surface[J]. Nature, 1997, 388(6641): 431-432.
[3] Burda C, LOU Yong-bing, CHEN Xiao-bo, et al. Enhanced nitrogen doping in TiO2 nanoparticles[J]. Nano Letters, 2003, 3(8): 1049-1051.
[4] 籍宏伟, 马万红, 黄应平, 等. 可见光诱导TiO2光催化的研究进展[J]. 科学通报, 2003, 48(21): 2199-2204.
JI Hong-wei, MA Wan-hong, HUANG Ying-ping, et al. Progress in visible light responding photocatalyst of TiO2[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2003, 48(21): 2199-2204.
[5] Vinodgopal K, Kamat Prashant V. Electrochemically assisted photocatalysis using nanocrystalline semiconductor thin films[J]. Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 1995, 38(1/4): 401-410.
[6] TONG Hai-xia, CHEN Qi-yuan, HU Hui-ping, et al. Preparation, characterization and photocatalytic behavior of WO3-TiO2/Nb2O5 catalysts[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2007, 14(6): 788-792.
[7] 吴树新, 马 智, 秦永宁, 等. 掺杂纳米TiO2光催化性能的研究[J]. 物理化学学报, 2004, 20(2): 138-143.
WU Shu-xin, MA Zhi, QIN Yong-ning, et al. Photocatalytic redox activity of doped nanocrystalline TiO2[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Physics, 2004, 20(2): 138-143.
[8] 侯亚奇, 庄大明, 张 弓, 等. 磁控溅射制备Ag/TiO2复合薄膜的光催化降解性能[J]. 清华大学学报: 自然科学版, 2004, 44(5): 589-592, 608.
HOU Ya-qi, ZHUNG Da-ming, ZHANG Gong, et al. Photocatalytic degradation properties of Ag/TiO2 composite films prepared by magnetron sputtering[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University: Science and Technology, 2004, 44(5): 589-592, 608.
[9] YAN Xiu-ru, BAI Tian, HAN Fang, et al. The preparation of SO42-/TiO2-SiO2 and its photocatalyze degradation to methyl orange[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2003, 19(10): 1125-1128.
[10] WANG Zheng-peng, GONG Wen-qi, HONG Xiao-ting, et al. Preparation, characterization and visible light photocatalytic activity of nitrogen-doped TiO2[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology: Materials Science, 2006, 21(4): 71-73.
[11] Asahi R, Morikawa T, Ohwaki T, et al. Visible-light photocatalysis in nitrogen-doped titanium oxides[J]. Science, 2001, 293(5528): 269-271.
[12] YU Yan-fen, CHAI Li-yuan, PENG Bing, et al. Preparation of nanometer H3TiO3 by hydrolyzation with industrial titanic solution[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2006, 37(1): 52-57.
[13] Lettmann C, Hildenbrand K, Kisch H, et al. Visible light photo-degradation of 4-chlorophenol with a coke-containing titanium dioxide photocatalyst[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2001, 32(4): 215-227.
[14] Jimmy C, YU Jia-guo, Wingkei H, et al. Effects of F-doping on the photocatalytic activity and microstructures of nanocrystalline TiO2 powders[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2002, 14(9): 3808-3816.
[15] Saha N C, Tompkins H G. Titanium nitride oxidation chemistry: An X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1992, 72(7): 3072-3079.
[16] Diwald O, Thompson T L, Zubkov T, et al. Photochemical activity of ni-trogen-doped rutile TiO2(111) in visible light[J]. J Phys Chem B, 2004, 108(19): 6004-6008.
[17] Sano T, Negishi N, Koike K, et al. Preparation of a visble light-responsive photocatalyst from a complex of Ti4+ with a nitrogen-containing ligand[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2004, 14(3): 380-384.
[18] Yamada K, Nakamura H, Matsushima S, et al. Preparation of N-doped TiO2 particles by plasma surface modification[J]. Comptes Rendus Chimie, 2006, 9(5/6): 788-793.
[19] Gole J L, Stout J D, burda C, et al. Highly efficient formation of cisible light tunable TiO2-xNx pothocatalysts and their transformation at the nanoscale[J]. J Phys Chem B, 2004, 108(4): 1230-1240.
[20] 费贤翔, 熊予莹. 具有可见光活性的纳米掺氮TiO2制备和表征[J]. 功能材料与器件学报, 2005, 11(2): 223-227.
FEI Xian-xiang, XIONG Yu-ying. Preparation and characterization of nitrogen-doped TiO2 nano-powder absorbing visible light[J]. Journal of Functional Materials and Devices, 2005, 11(2): 223-227.
[21] Irie H, Watanabe Y, Hashimoto K. Nitrogen-concentration dependence on photocatalytic activity of TiO2-xNx powders[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2003, 107(23): 5483-5486.
收稿日期:2008-10-04;修回日期:2008-12-22
基金项目:湖南省科技厅科技计划项目(2007CK3075)
通信作者:彭 兵(1956-),男,湖南汩罗人,教授,从事冶金环境工程与环境材料研究;电话: 0731-88830875; E-mail: Pb@mail.csu.edu.cn