文章编号:1004-0609(2007)05-0693-06
TiO2纳米管阵列的制备、热处理及光催化性能
陶海军,秦 亮,王 玲,陶 杰
(南京航空航天大学 材料科学与技术学院,南京 210016)
摘 要:采用恒压直流阳极氧化法制备具有规则排列的TiO2纳米管阵列,并研究其在空气热处理过程中的晶型转变,同时用甲基橙的降解过程表征其光催化性能。结果表明:电解液采用0.5%(质量分数)HF水溶液时,电压在10~20 V之间,时间5 min以上才能形成TiO2纳米管阵列;随着氧化电压的提高,纳米管的平均管径和管长都增大;随着氧化时间的延长,纳米管管长明显增长,平均管径变化不大;纳米管阵列在空气中热处理时,280 ℃左右出现锐钛矿相,400 ℃左右出现金红石相,680 ℃左右锐钛矿相向金红石相的转变结束,600 ℃纳米管阵列结构仍然保持完整。光催化实验表明,在氧化电压为20 V、氧化时间为20 min时获得的纳米管阵列经过400 ℃热处理后,在40 min的光照时对甲基橙的光催化降解率高达99.6%。
关键词:TiO2纳米管阵列;阳极氧化;光催化
中图分类号:TG 146; TQ 153.6; X 703.1 文献标识码:A
Fabrication, anneal and photocatalysis applications of
self-organized TiO2 nanotubes
TAO Hai-jun, QIN Liang, WANG Ling, TAO Jie
(College of Materials Science and Technology, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,
Nanjing 210016, China)
Abstract: Self-organized TiO2 nanotube arrays were fabricated by anodic oxidation of a pure titanium sheet at constant potential. The results show that TiO2 nanotube arrays are regularly obtained when anodizing voltages ranges from 10 to 20 V, anodizing time keeps more than 5 min and HF concentration is 0.5%. The average diameter and length of the tube increase with increasing anodizing voltage. And the length of tube increases with longer anodization time obviously. After annealing for 3 h in ambient atmosphere, the anatase phase emerges at about 280 ℃, the rutile phase emerges at about 400 ℃, anatase transforms completely to rutile at about 680 ℃ and nanotube architecture can be preserved till 600 ℃. Furthermore, TiO2 nanotubes, fabricated at anodizing voltage of 20 V for 20 min and then annealed at 400 ℃, possess better photo-catalytic activity, i.e. the decolourisation of methyl orange irradiated for 40 min is 99.6%.
Key words: TiO2; nanotube arrays; anodic oxidation; photo-catalytic activity
TiO2已被广泛地应用于光催化剂[1-3]、气敏传感 器[4-5]、光电材料[6-7]和染料敏化太阳能电池(DSSC)[8-11]。随着人们对环境问题的日趋重视,有关TiO2光催化降解废水和有害气体方面的研究也逐渐成为热点[12]。TiO2作为光催化剂有许多种存在形式,例如纳米薄膜、纳米颗粒、纳米线等,制备这些不同形式纳米结构的目的是获得尽可能大的比表面积,从而提高TiO2的光催化性能。这就促使更大比表面积的纳米结构不断出现,其中具有高度规则结构的纳米管阵列引起了学者的广泛兴趣。目前为止,纳米管的制备方法有模板法[13]、水热法[14]、高温气固反应法和阳极氧化法[15-18],其中阳极氧化法方法简单、成本低廉、易于实现工业化并且可以获得大面积的纳米管阵列结构。因此,本文作者采取恒压阳极氧化法制备TiO2纳米管阵列,研究了TiO2纳米管阵列的形成过程、热处理时的晶型转变、升温时的结晶过程,同时还表征了其对甲基橙的光催化降解性能。
1 实验
1.1 TiO2纳米管阵列的制备
高纯度(99.6%)钛箔(25 mm×30 mm×0.1 mm),经丙酮、二次蒸馏水超声洗净后在HF与HNO3体积比为1?1的混合溶液中化学抛光,取出后立刻用二次蒸馏水洗净,在室温下用N2吹干备用。
TiO2纳米管阵列的制备采用两电极体系,电源采用恒压直流电源,与试样片等面积的Pt为对电极,两电极间距离保持在5 cm,电解液为0.5%的氢氟酸水溶液,整个实验在室温下进行并始终伴随磁力搅拌。实验中通过改变阳极氧化电压和氧化时间,研究TiO2纳米管阵列的形成过程。
1.2 TiO2纳米管阵列的热处理
将表面具有纳米管阵列膜的钛箔平放在Al2O3陶瓷片上,在马弗炉中进行热处理。整个热处理过程由程序控制,先以15 ℃/min速度升温,达到所需温度后控温保持3 h,最后试样随炉冷却到室温后取出备用。实验中通过改变热处理温度,研究TiO2纳米管阵列在此种热处理工艺下的结晶过程和晶型转变。
1.3 TiO2纳米管阵列光催化性能表征
以10 mg/L甲基橙水溶液为目标降解物,具体过程为:取热处理后的试样片浸入10 mL目标降解物溶液中, 置于图1所示的光催化反应器里。每隔一定的光照时间将甲基橙溶液取出, 采用惠普上海分析仪器有限责任公司的6010紫外-可见光分光光度计测定甲基橙在最大吸收波长463.5 nm处的吸收度A,根据Beer定律计算去除率。
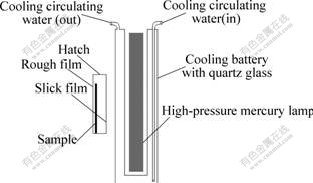
图1 光催化反应装置示意图
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of photo-catalytic reactor
纳米管阵列微观形貌的表征采用LEO-1530VP场发射扫描电镜,管阵列结晶行为的表征采用BRUKER D8 Advance多晶X射线衍射仪(Cu Kα)。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 TiO2纳米管阵列的形成
前期的研究[19-20]表明:在含有一定量HF的水溶液中,通过改变阳极氧化条件可以获得纳米多孔膜或者纳米管阵列。进一步的研究证实,除了氧化电压会影响纳米管阵列的形成(由文献[20]知,电解液为0.5%HF水溶液时,纳米管阵列在10~20 V范围出现),氧化时间对管阵列的形成也有重要的影响,即纳米管阵列的出现存在一个渐进演变的过程(图2)。
图2所示为20 V氧化电压下,纳米管阵列的形成过程。氧化时间(图2(a))为30 s时,氧化膜表面呈现纳米级颗粒小岛状分布。随着时间的延长,表面岛状结构逐渐被纳米孔(图2(b))和纳米管(图2(c))所取代。由宏观图可以看出,时间的延长使氧化膜表面更加干净,纳米管的结构也更加明显,如图2(d)所示。
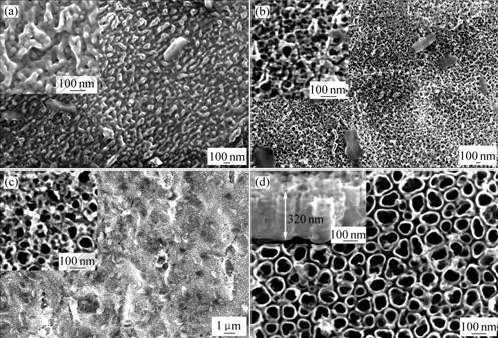
图2 20 V电压下不同氧化时间形成的TiO2膜的表、截面形貌
Fig.2 FE-SEM top and cross-sectional images of TiO2 films anodized under 20 V for different time: (a) 0.5 min; (b) 1 min; (c) 2 min; (d) 5 min
大量实验证明,对于不同的电解液体系,形成纳米管阵列所需的特定电压范围都是不同的。对于HF水溶液体系的电解液,HF的含量越高,形成纳米管阵列所需的电压越低。这就要求我们对于不同的电解液体系,都要掌握获得纳米管阵列的特定氧化条件。
2.2 氧化参数对纳米管阵列形貌的影响
氧化电压除了影响纳米管阵列的产生与否,还会影响其微观形貌。由图3看出,随着电压的增大,纳米管的平均管径和管长都明显的增大。当电压由10 V 增加到20 V时,平均管径由50 nm增大到100 nm,纳米管的长度也由170 nm增加到390 nm。
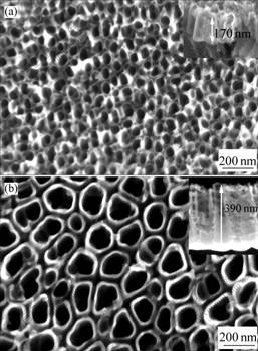
图3 不同电压下氧化20 min形成的纳米管阵列的表、截面形貌
Fig.3 FE-SEM top and cross-sectional images of nanotube arrays for 20 min under different voltages: (a) 10 V; (b) 20 V
由图2(d)、3(b)和图4可以明显的看出,氧化时间对纳米管的平均管径影响不大(随时间的延长稍有增大),但是对纳米管的长度有着重要的影响。纳米管的长度随着氧化时间的延长不断增大,具体表现为:氧化5 min时为320 nm;15 min时为340 nm;20 min时为390 nm;30 min时增加到490 nm。
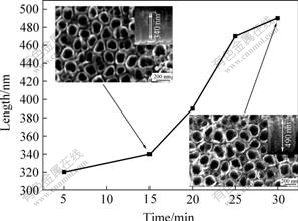
图4 氧化时间对纳米管长度的影响
Fig.4 Effect of anodization time on length of nanotube
综上所述,阳极氧化电压和时间对纳米管的平均管径和管长有着重要的影响,同时研究表明,不同的管长和平均内径对纳米管阵列的功能特性有着重要的影响。如Varghese等[5]研究发现,作为氢气传感器时,在290 ℃的工作温度下,内径为46 nm的管阵列比内径为76 nm的管阵列具有更高的氢气敏感度;Maca′k等[11]研究发现,作为染料敏化太阳能电池时,长2.5 μm左右的纳米管阵列在540 nm的单色光照下,其最大光电转换效率(IPCEmax)达到3.3%,而长500 nm左右的纳米管阵列在530 nm的单色光照下,其IPCEmax只有1.6%。因此,探求不同的阳极氧化工艺来制备不同结构参数(管长、平均管径、管壁厚度、阻挡层厚度)的纳米管阵列具有非常重要的实际意义。
2.3 热处理对纳米管阵列的影响
空气中的热处理对TiO2纳米管阵列的影响是两方面的:一是纳米管的形貌;二是TiO2的晶型。
由图5可以看出,热处理温度较低时(图5(a)和(b)),纳米管的平均孔径和表面并无变化;当热处理温度达到550 ℃时,纳米管表面沿着管壁在管口方向有环状结晶物,图5(d)更加明显。此外,由图5(c)、(d)也可明显看出,纳米管的中空部分在减小,TiO2晶体由管底部逐渐向管口生长。由这些形貌的变化可以推断纳米管的结晶过程大致如下:纳米管底部的晶体逐渐向上生长,管壁逐渐增厚,管口出现环状结晶物,直至最后纳米管状结构的消失。
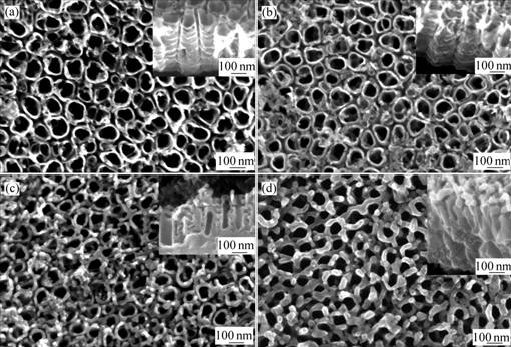
图5 热处理温度对纳米管表、截面形貌的影响
Fig.5 Effect of heat treatment temperature on surface and cross-sectional morphologies of nanotube arrays: (a) 350 ℃; (b) 400 ℃; (c) 550 ℃; (d) 600 ℃
由图5(d)还可以清楚地看到,在600 ℃热处理情况下,纳米管阵列仍然具有较好的结构稳定性,为其功能特性的发挥提供了保证。
众多学者研究认为,锐钛矿相的TiO2较金红石相的具有更好的光催化性能;但也有一部分学者研究认为锐钛矿相与金红石相体积比为7?3时,TiO2具有最好的光催化性能。因此探求TiO2晶型的转变过程具有重要的实际价值。由图6可以看出,具有钛基体的TiO2纳米管阵列在本实验所采用的热处理工艺下,280 ℃左右开始出现锐钛矿相((101)晶面),随着温度的提高,锐钛矿相的含量逐步增加;当温度提高到400 ℃左右时,金红石相((110)晶面)开始出现;直至温度达到680 ℃左右时,TiO2全部转变为晶体结构更加稳定的金红石相。由上述实验结果可看出,400 ℃热处理的纳米管阵列在具有较高锐钛相含量的同时,还具有一部分金红石相。本文作者认为此种晶型结构将具有较高的光催化活性,因此,选择400 ℃热处理的纳米管阵列作为光催化实验的试样。
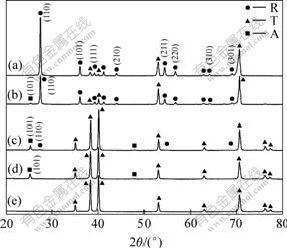
图6 纳米管阵列的晶型转变
Fig.6 Crystalline phase transition of nanotube arrays: (a) 680 ℃; (b) 650 ℃; (c) 400 ℃; (d) 280 ℃; (e) 240 ℃ (A and R represent anatase and rutile, T represents titanium)
各种纳米结构形式的TiO2的光催化活性不但与它的晶型、表面状态等有关,还与其比表面积有较大的关系(不同的比表面积吸附有机物的含量不同)。由图5(c)和(d)可以明显看出,随着热处理温度的提高,纳米管的中空部分的长度也在缩短,即其比表面积在减小。而由图5(b)可以看出,400 ℃热处理的纳米管阵列几乎不存在此种现象。这也是我们选用400 ℃热处理的试样做光催化实验的另一个原因。至于热处理温度、纳米管的比表面积、纳米管中TiO2的表面状态对光催化性能的具体影响将在其他论文中详细阐明。
2.4 TiO2纳米管阵列的光催化性能
本实验结合图6的XRD谱,对20 V电压下氧化20 min的纳米管阵列选取了400 ℃的热处理温度。
由图7可以看出,随着光催化时间的增长,甲基橙的降解率成指数增加。这是因为光生电子不断地被水中氧分子俘获,最终生成具有高活性的超氧负离子(·O2-) 和羟基自由基(·OH)。随着光催化时间的延长,此两种活性物质的量也增多,所以随着光催化时间的增长,光转化率降解逐渐升高。
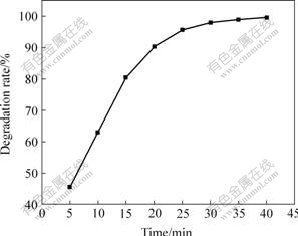
图7 TiO2纳米管阵列的光催化性能
Fig.7 Photocatalytic ability of TiO2 nanotube arrays
3 结论
1) 电解液为0.5%的HF水溶液,通过恒压阳极氧化法在电压为5~20 V、氧化时间为5 min以上时,可以在高纯钛箔表面制备出几百纳米厚的TiO2纳米管阵列膜。
2) TiO2纳米管阵列在空气中热处理会发生一系列的晶型转变:280 ℃左右出现锐钛矿相,400 ℃左右出现金红石相,680 ℃左右锐钛矿相向金红石相的转变结束,600 ℃时纳米管阵列结构仍然保持完整。
3) 纳米管的结晶过程由3个方向的生长过程组成:由底部到管口的向上生长过程、沿管口的环状结晶过程和管壁的结晶过程。其中由管底部向上的结晶过程最为明显,是整个管结构高温塌陷的主要原因之一。
4) 在氧化电压为20 V、氧化时间为20 min时获得的TiO2纳米管阵列经过400 ℃热处理后,在光照40 min时对甲基橙的光催化降解率高达99.6%。
REFERENCES
[1] Bahnemann D W, Kholuiskaya S N, Dillert R, et al. Photodestruction of dichloroacetic acid catalyzed by nano-sized TiO2 particles[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2002, 32(2): 161-169.
[2] LI Jing-yi, CHEN Chun-cheng, ZHAO Jin-cai, et al. Photodegradation of dye pollutants on TiO2 nanoparticles dispersed in silicate under UV-VIS irradiation[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2002, 37(4): 331-338.
[3] Sivalingam G, Nagaveni K, Hegde M S, Madras G. Photocatalytic degradation of various dyes by combustion synthesized nano anatase TiO2[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2003, 45(1): 23-38.
[4] Mor G K, Carvalho M A, Varghese O K, Pishko M V, Grimes C A. A room-temperature TiO2-nanotube hydrogen sensor able to self-clean photoactively from environmental contamination[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2004, 19(2): 628-634.
[5] Varghese O K, Gong D, Paulose M, et al. Hydrogen sensing using titania nanotubes[J]. Sensors and Actuators B, 2003, 93(1/3): 338-344.
[6] Ruan C, Paulose M, Varghese O K, Grimes C A. Enhanced photoelectrochemical-response in highly ordered TiO2 nanotube-arrays anodized in boric acid containing electrolyte[J]. Solar Energy Materials & Solar Cells, 2006, 90: 1283-1295.
[7] Paulose M, Mor G K, Varghese O K, Shankar K, Grimes C A. Visible light photoelectrochemical and water-photoelectrolysis properties of titania nanotube arrays[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 2006, 178: 8-15.
[8] Paulose M, Shankar K, Varghese O K, Mor G K, Hardin B, Grimes C A. Backside illuminated dye-sensitized solar cells based on titania nanotube array electrodes[J]. Nanotechnology, 2006, 17: 1446-1448.
[9] Mor G K, Shankar K, Paulose M, Varghese O K, Grimes C A. Use of highly-ordered TiO2 nanotube arrays in dye-sensitized solar cells[J]. Nano Letters, 2005, 6(2): 215-218.
[10] Paulose M, Shankar K, Varghese O K, Mor G K, Grimes C A. Application of highly-ordered TiO2 nanotube-arrays in heterojunction dye-sensitized solar cells[J]. J Phys D: Appl Phys, 2006, 39: 2498-2503.
[11] Maca’k J M, Tsuchiya H, Ghicov A, Schmuki P. Dye-sensitized anodic TiO2 nanotubes[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2005, 7: 1138-1142.
[12] 周武艺, 曹庆云, 唐绍裘, 罗 颖. 硫掺杂对纳米TiO2的结构相变及可见光催化活性的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16 (7): 1233-1238.
ZHOU Wu-yi, CAO Qing-yun, TANG Shao-qiu, LUO Ying. Effects of sulfur doping on structure phase transformation and visible-light photocatalytic activity of nano-TiO2[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16 (7): 1233-1238.
[13] Chu S Z, Wada K, Inoue S, Todoroki S. Fabrication of oxide nanostructures on glass by aluminum anodization and sol-gel process[J].Surface and Coatings Technology, 2003, 169-170: 190-194.
[14] Suzuki Y, Yoshikawa S. Synthesis and thermal analyses of TiO2-derived nanotubes prepared by the hydrothermal method[J]. J Mater Res, 2004, 19(4): 982-985.
[15] Gong D, Grimes C A, Varghese O K, et al. Titanium oxide nanotube arrays prepared by anodic oxidation[J]. J Mater Res, 2001, 16(12): 3331-3334.
[16] Mor G K, Varghese O K, Paulose M, et al. Fabrication of tapered, conical-shaped titania nanotubes[J]. J Mater Res, 2003, 18(11): 2588-2593.
[17] Mor G K, Varghese O K, Paulose M, et al. Transparent highly ordered TiO2 nanotube arrays via anodization of titanium thin films[J]. Adv Funct Mater, 2005, 15: 1291-1296.
[18] ZHAO Jian-ling, WANG Xiao-hui, CHEN Ren-zheng, LI Long-tu. Fabrication of titanium oxide nanotube arrays by anodic oxidation[J]. Solid State Communications, 2005, 134(10): 705-710.
[19] 陶海军,陶 杰,王 玲,王 炜. 纯钛及其合金表面纳米多孔TiO2膜的制备研究[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2005, 37(5): 597-602.
TAO Hai-jun, TAO Jie, WANG Ling, WANG Wei. Fabrication of nano-porous TiO2 films on pure titanium and its alloy[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 2005, 37(5): 597-602.
[20] TAO Hai-jun, TAO Jie, WANG Tao, WANG Ling, QIN Liang, XU Lu-lu. Fabrication of self-organized TiO2 nanotubes by anodic oxidation and their photocatalysis[J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2005, 15(S3): 462-466.
基金项目:江苏省自然科学基金资助项目(BK2004129);航空基金资助项目(04H52059)
收稿日期:2006-10-28;修订日期:2007-03-05
通讯作者:陶 杰,教授;电话:025-52112900; E-mail: taojie@nuaa.edu.cn
(编辑 龙怀中)