

DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2021.04.031
高速铁路双线隧道内列车风分布及流场特性
王磊1, 2,骆建军1, 2,李飞龙1, 2,高立平1, 2
(1. 北京交通大学 城市地下工程教育部重点实验室,北京,100044;
2. 北京交通大学 结构风工程与城市风环境北京市重点实验室,北京,100044)
摘要:为研究高速列车非对称通过标准高速铁路双线隧道引起的列车风分布规律及列车周围流场分布特性,基于有限体积法理论,采用数值计算方法模拟CRH380A高速列车通过双线隧道全过程,应用滑移网格技术模拟列车与周围环境相对运动。研究结果表明:隧道内气动压力系数计算结果与国内现场实测结果变化规律基本一致;列车车头、车尾通过时,纵向、横向列车风风速均突然增大,在列车通过阶段,纵向列车风经历正向—负向—正向流动,横向列车风由背离列车向指向列车转变;列车两侧空间纵向列车风风速在车尾通过之后达到最大,车顶上方空间的纵向风速在车头经过后达到最大;车尾通过之前,横向列车风变化规律基本相同,车尾经过后,横向列车风波动程度增加,而纵向列车风在车头通过之前变化规律相同,车头通过后,风速波动程度增加;车头、车尾及车身表面存在较大的速度梯度,近隧道侧纵向列车风速较远隧道侧的风速大;中间列车周围速度分布基本一致,而列车尾部尾流效应对近隧道侧列车风影响非常显著;列车头部、尾部附近流场结构变化严重,中间列车周围流场分布规律基本稳定;环状空间内纵向列车风与到列车表面距离的关系呈指数函数变化。
关键词:高速铁路;双线隧道;数值模拟;列车风;流场特性
中图分类号:U25 文献标志码:A 开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID)
文章编号:1672-7207(2021)04-1346-12
Train-induced wind distribution and flow field characteristics in high-speed railway double-track tunnel
WANG Lei1, 2, LUO Jianjun1, 2, LI Feilong1, 2, GAO Liping1, 2
(1. Key Laboratory of Urban Underground Engineering of the Ministry of Education, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing 100044, China;
2. Beijing's Key Laboratory of Structural Wind Engineering and Urban Wind Environment, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing 100044, China)
Abstract: In order to study the law of train-induced wind distribution and the characteristics of the flow field around a train caused by high-speed train passing through a standard high-speed railway double-track tunnel asymmetrically, the whole process of CRH380A high-speed train passing through a double-track tunnel based on the finite volume method theory was simulated through numerical method. Sliding mesh method(SMM) was used to simulate the relative movement of the train and surroundings. The calculation results of the aerodynamic pressure coefficients in a tunnel were basically consistent with those of the field measurement. The results show that the longitudinal and transverse train-induced wind speeds increase sharply when the head car and rear car of the train pass. When the train passes, the longitudinal train-induced wind direction undergoes positive-negative-positive changes, while the transverse train-induced wind changes from diverging trains to pointing train. The speed of longitudinal train-induced wind reaches the maximum after the rear car passes on both sides of the train, while the speed of the longitudinal wind in the roof reaches the maximum after the head car passes through. Before the tail passes, the lateral train-induced wind changes basically the same and after the tail passes, the lateral wind fluctuation increases, while the longitudinal wind changes before the head passes and the longitudinal wind speed increases after the head passes. Furthermore, large velocity gradients exist on the head, rear and train body surface, and the longitudinal train-induced wind near the tunnel side is larger than that on the far tunnel side. The velocity distribution around the intermediate cars is basically the same, and the wake effect of the tail of the train has a significant effect on the wind of the train near the tunnel. The flow structures at the head and tail of the train changes severely, and the distribution of the flow field of the middle trains is basically stable. The relationship between the longitudinal train-induced wind and the distance to the train surface in the annular space conforms to an exponential function.
Key words: high-speed railway; double-track tunnel; numerical simulation; train-induced wind; flow field characteristics
自1997年起,中国铁路经过6次大提速,我国进入高铁时代。2010年11月,京沪高铁试运行最高速度达到486.1 km/h,刷新世界最高运营铁路试验速度记录。然而,随着铁路运行速度不断提高,高速列车空气动力学效应包括气动阻力、气动噪声、隧道效应、侧风效应和列车风等日益显现[1]。由于空气黏性效应和列车表面摩阻作用,列车带动周围空气一起运动形成列车风。受隧道壁面和道床限制,隧道内空气流动受到严重限制,列车运动引起的滑流比露天情况下引起的滑流比更加严重[2],对隧道内轨旁作业人员和设备设施造成严重不利影响。研究初期,国外学者多采用现场实测手段对隧道内列车风进行研究[3-7]。由于现场试验成本高、周期长、易受周围环境影响等,越来越多的学者采用室内试验和数值模拟方法对隧道内列车风进行研究。BELL等[8-9]利用风洞试验研究了不同尾车形状对列车尾流及列车风的影响。SUZUKI等[10]通过研究发现列车前部涡结构尺寸较小,列车中后部涡结构尺寸不断增大。费瑞振等[11]分析了列车在隧道内运行时列车风分布特点及列车风作用下的人员安全性。施成华等[12]研究了隧道内接触网在列车风反复作用下的安全性。GUO等[13]就CRH380A高速列车附属设备和列车长度对列车风的影响进行了研究。其中,文献[11-13]均采用滑移网格技术对列车风效应进行研究。
目前,对列车风的研究主要以列车在明线行驶为研究对象,对列车在隧道内行驶产生的列车风研究较少。并且受试验设备条件限制和数值计算成本影响,通常采用短编组(国内通常采用三车编组)进行研究。然而,已有研究表明列车长度对隧道内列车风有显著影响[14],短编组列车试验结果不能真实反映实际情况。为此,本文作者采用数值模拟方法,运用流体力学软件Fluent建立隧道-列车-空气模型,对真实编组列车通过隧道过程进行数值模拟,并采用专业后处理软件Tecplot对计算结果进行绘制等值线图、流线图等处理,分析隧道内纵向和横向列车风分布规律,并对不同列车位置断面上列车周围流场特性进行研究。
1 列车风产生机理
在隧道内运动的列车可视为一个移动压源,隧道内的气体流动就是压源(列车)与周围环境共同作用的结果。列车在隧道内行驶时,列车与周围空气通过复杂作用实现列车与气体间的能量交换,气体获得能量为活塞风压力,在隧道内形成列车风。列车风风速不仅受阻塞比、列车运行速度、列车外形、列车与隧道壁面粗糙程度和隧道长度的影响[12, 15],而且要受到周围自然风的附加影响[16]。
根据列车运动位置变化,列车通过隧道过程中的列车风变化过程可分为3个阶段:1) 列车完全驶入前为列车风发展阶段,车头前方空气受压缩作用引起压力升高,形成较大的压力梯度,车头前方空气沿列车纵向向隧道出口流动;随着列车驶入隧道长度不断增大,引起车头前方压力持续升高,气流速度越来越大。由于从隧道出口排出的空气体积远小于列车车体所占据的隧道空间体积,导致大部分空气沿隧道-列车之间的环状间隙由隧道入口处排出;当尾车进隧道后,在尾涡区真空效应作用下,隧道入口处空气沿列车前进方向流入隧道。2) 列车完全进入隧道后为列车风稳定阶段,列车周围流场为与时间无关的定常流动。3) 车头驶出隧道后为列车风衰减阶段,列车风风速逐渐减小。列车驶出后,由于气流惯性作用,隧道内气体保持运动状态,随列车驶出隧道时间增加而逐渐变化到与自然风状态一致。列车风的时变特性已通过足尺试验验证[17-18]。
2 数值模型
根据已有研究成果[19],列车编组长度为200 m、运行速度为300~350 km/h的高速列车单车通过隧道的最不利隧道长度在400~700 m之间,因此,本文选取长度为500 m的隧道进行计算。基本计算条件见表1,测点布置见图1。为了方便表述,列车距离隧道壁面小的一侧为近隧道侧,反之为远隧道侧。
以列车高度为特征长度,当列车以350 km/h速度行驶时,雷诺数Re=2.3×107。列车在隧道内运行时产生非定常、可压缩、三维、紊态流动[20]。本文采用非定常、黏性、可压缩N-S方程和标准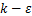 双方程湍流模型进行仿真模拟[21-23]。采用流体计算软件Fluent进行计算,控制方程通过有限体积法进行离散求解。流体压力和速度耦合问题采用PISO算法求解。采用二阶迎风格式用于对流-扩散项离散,采用PRESTO!算法对压力修正方程进行离散,采用一阶隐式方法对时间导数进行离散[24]。本次计算时间步长为0.001 s,迭代次数为40次。
双方程湍流模型进行仿真模拟[21-23]。采用流体计算软件Fluent进行计算,控制方程通过有限体积法进行离散求解。流体压力和速度耦合问题采用PISO算法求解。采用二阶迎风格式用于对流-扩散项离散,采用PRESTO!算法对压力修正方程进行离散,采用一阶隐式方法对时间导数进行离散[24]。本次计算时间步长为0.001 s,迭代次数为40次。
表1 基本计算条件
Table 1 Basic condition of calculation
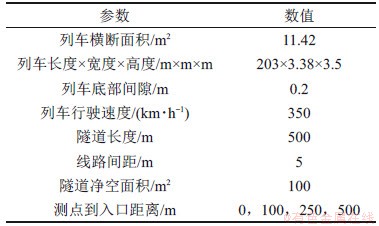
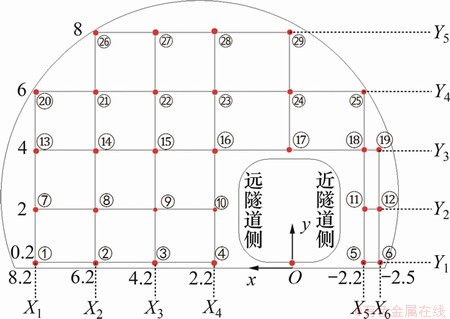
图1 测点位置
Fig. 1 Locations of measuring points
忽略受电弓、转向架等细部结构,模型为光滑车体。为保证流场充分发展,避免边界条件对列车周围流场结构的影响,以列车高度H为特征长度,隧道入口侧计算域长、宽和高分别取113H,57H和15H;隧道出口侧计算域长、宽和高分别取57H,57H和15H,如图2所示。车头初始位置距离隧道入口100 m。计算域采用六面体结构网格进行离散,最小网格尺寸为0.1 m[25]。在隧道洞口处网格进行加密处理,计算模型离散后六面体单元不少于1 500万个,见图3。
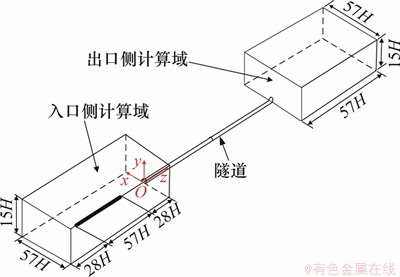
图2 高速列车通过隧道计算域
Fig. 2 Calculation domain of high speed train passing through tunnel
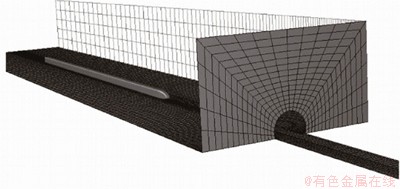
图3 计算模型网格示意图
Fig. 3 Schematic diagram of calculation model mesh
列车驶入隧道之前,环境风对隧道内空气流动速度和压力变化有很大影响。本文不考虑环境风因素,因此,认为气体初始状态是静止、不产生相对流动的。假定列车表面及隧道壁面法向速度为零,列车表面及地面采用无滑移壁面边界条件,即压力梯度法向分量为零。计算域外边界采用压力出口边界条件,压力取为标准大气压即101 325 Pa。采用滑移网格技术模拟列车与周围环境之间的相对运动,隧道壁面粗糙高度取5 mm,列车表面粗糙高度取9.2 mm[21]。
3 数值计算验证
为验证本文数值方法的正确性,采用武广高铁海棠隧道气动效应实车试验进行验证。海棠隧道为双线单洞隧道,长度为2 908 m,线间距5 m,为武广高铁长度最大的隧道。试验列车采用8车CRH380A列车编组,与数值模型中采用列车编组相同,列车运行速度均为350 km/h(97.22 m/s)。沿隧道长度方向不同位置设置气动压力测点,对列车通过阶段的气动压力变化进行监测。
为方便空气动力学研究研究,一般采用量纲一的形式进行分析。气动压力采用压力系数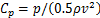 表示,其中
表示,其中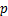 为气动压力,
为气动压力,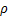 为空气密度,
为空气密度,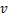 为列车速度。图4所示为距离隧道入口230 m处列车通过隧道过程中的气动压力系数实测与数值计算曲线。通过对比,气动压力系数实测结果与计算结果变化规律基本一致,具有良好的吻合性,表明本文采用的计算方法能够反映真实情况,可以采用此方法进行后续分析研究。
为列车速度。图4所示为距离隧道入口230 m处列车通过隧道过程中的气动压力系数实测与数值计算曲线。通过对比,气动压力系数实测结果与计算结果变化规律基本一致,具有良好的吻合性,表明本文采用的计算方法能够反映真实情况,可以采用此方法进行后续分析研究。
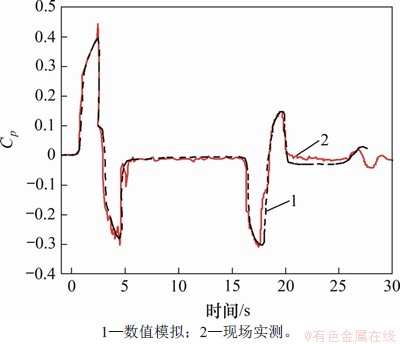
图4 距离隧道入口230 m处气动压力实测与计算曲线
Fig. 4 Measured and calculated curves of aerodynamic pressure at 230 m away from tunnel entrance
4 结果分析
图5所示为隧道入口处测点10列车风速度分量时程曲线。从图5可知:不同列车风速度分量出现峰值时间不同;车头通过时,垂向和横向速度分量达到最大值,而纵向速度分量在车尾通过之后一段时间才达到最大;此外,各列车风速度分量最大值差别显著,垂向、横向及纵向分量最大值分别为2.5,10.7和10.8 m/s,垂向速度分量不到纵向、横向速度分量的1/4;纵向速度分量和合速度曲线变化规律相似,合速度最大值为11.6 m/s,两者仅相差8.4%,表明纵向风速对列车风起主导作用。故在后文分析中将不考虑垂向风速对结果的影响,以分析横向和纵向列车风为主。
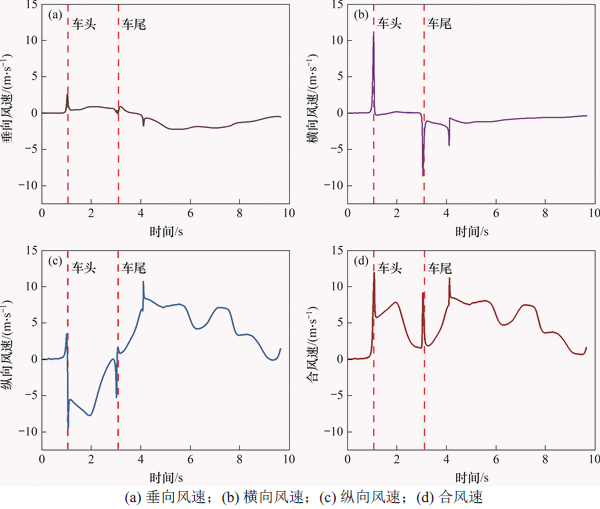
图5 入口处测点10列车风速度分量及合风速
Fig. 5 Train-induced wind speed components and resultant speed at measuring point 10 at tunnel entrance
4.1 列车风纵向分布
列车车身完全进入隧道后,在列车前方、后方及列车-隧道之间的环状空间内会形成稳定的列车风。以t=4.5 s(列车第4节车厢中部达到隧道中部,车尾距入口137 m)为例进行分析。
图6所示为不同纵向位置测点10和测点11的纵向列车风变化曲线。从图6可知:当车头达到测点前,隧道内先产生与列车前进方向一致的纵向流动(正值);当车头经过测点时,气流方向迅速改变,与列车前进方向相反(负值),气体改变流向所需时间与流线型车头长度、列车速度有关;在列车车身经过阶段,纵向列车风风速先继续增大后迅速减小;当车尾通过测点时,纵向列车风第二次改变流向,与列车前进方向保持一致(正值)。相同测点在不同纵向位置的纵向列车风时程曲线变化规律基本相似。随着到入口距离的增加,纵向列车风风速逐渐增大,最大值出现在距离入口100 m处;远隧道侧和近隧道侧最大纵向风速值分别为15.1 m/s和20.9 m/s,均超过线路旁作业人员允许承受的14 m/s列车风风速的规定[26]。以隧道中心断面进行分析,远隧道侧和近隧道侧速度变化幅值分别为18.5 m/s和26.5 m/s,表面近隧道侧纵向列车风速度变化程度更加严重。当列车经过测点后,由于空气流动惯性作用,隧道内列车风仍会持续一段时间,最终降为零。
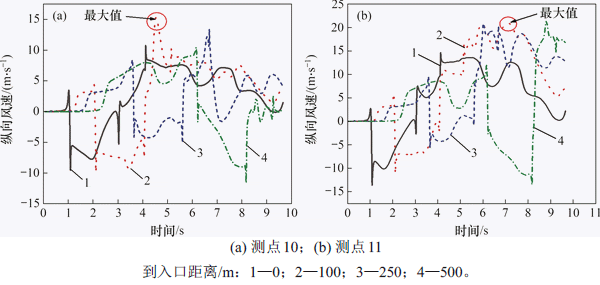
图6 到入口不同距离对称测点纵向列车风风速
Fig. 6 Longitudinal train wind speed at symmetrical measuring points at different distances from entrance
图7所示为测点10和测点11在不同纵向位置横向列车风变化曲线。由图7可知:与纵向列车风变化规律不同,当车头经过时横向风速突然增大,风向由列车指向隧道壁面,而车尾经过时横向列车风突然反向增大,由隧道壁面指向列车表面;在车身通过阶段远隧道侧横向风速变化相对较小,而近隧道侧横向风速缓慢增大,这是由于近隧道侧空间较小,测点11受列车表面边界层影响导致横向风速增加。列车表面边界层在列车中后部发展稳定,厚度基本不变,因此,近隧道侧横向列车风风速增加速率降低。测点10横向风速极大值相差不大,横向列车风正向最大值随着到入口距离增大而减小,在隧道入口、出口处横向列车风正向最大、最小值分别为10.8 m/s和9.8 m/s,相差10.2%。隧道中部(z=250 m)测点11在车尾通过后横向列车风达到最大值23.1 m/s,是测点10最大横向风速的2.1倍,表明列车在隧道内偏心运动时对列车-隧道距离较小侧的气体横向流动影响更加显著。
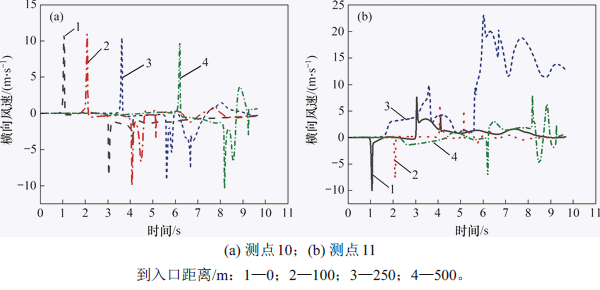
图7 到入口不同距离对称测点横向列车风
Fig. 7 Horizontal train wind at symmetrical measurement points at different distances from entrance
图8所示为距地表2.5 m水平面上列车周围纵向列车风分布云图。从图8可知:在列车表面、车头、车尾附近均存在很大速度梯度,并且沿列车车身风速等值线基本上均为平直线,表明车身-隧道形成的环状空间内纵向列车风基本处于稳定状态,并且近隧道侧纵向列车风风速比远隧道侧纵向风速大。
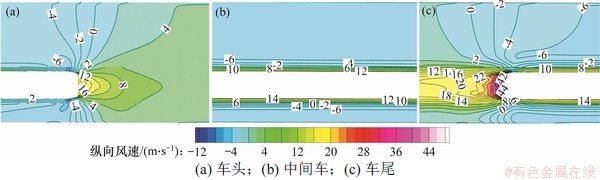
图8 列车周围纵向列车风分布
Fig. 8 Longitudinal wind distribution around train
4.2 列车风横向分布
图9所示为隧道中部不同测点横向、纵向列车风速变化曲线。测点11位于x轴负方向,为方便对比,对图9(a)中测点11的横向速度分量进行反向处理。经分析可知:列车车头、车尾通过时,测点横向风速均发生突变。这是因为车头通过前,车头将空气向外排出,流速增大,由列车表面流向隧道壁面;车尾通过时,由于车尾真空效应导致流速增大,周围空气由隧道壁面流向列车表面。当车身通过时横向风速变化很小,原因是车身截面形状变化不大。当列车尾部通过后,受涡流结构影响,横向风速波动明显加剧,到列车距离越小,波动程度越严重。测点11波动程度比测点10的更加剧烈。与列车两侧列车风不同,列车顶部测点17横向列车风较小,最大值仅为2.5 m/s。图10所示为相同断面测点的垂向速度分量。对比图9和图10可知:列车顶部气体以垂向流动为主;测点横向风速差异主要发生在车尾通过后,距车体距离越近气流波动越严重,并且在车尾通过之后风速波动程度迅速降低。距离列车较远处风速波动程度受列车尾通过影响较小,在车尾通过后一段时间横向风速波动程度才逐渐增大,表明隧道内气体流动具有明显滞后效性。
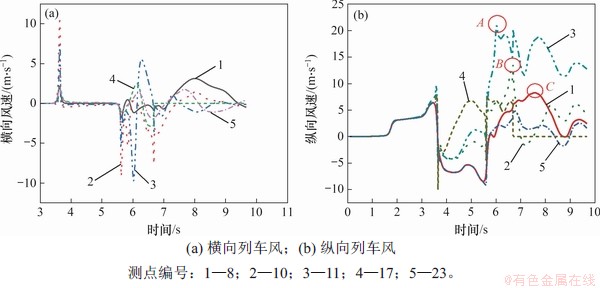
图9 隧道中部横断面测点纵向速度分量
Fig. 9 Longitudinal velocity component at measuring point of central cross section of tunnel
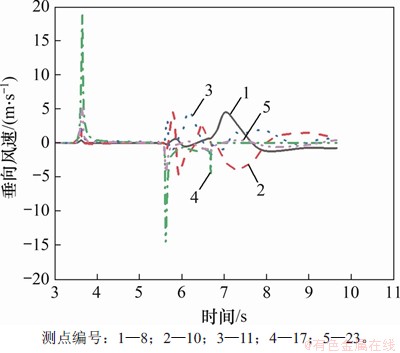
图10 隧道中部横断面垂向速度分量
Fig. 10 Vertical velocity component of central cross
由图9(b)可知:车头到达之前,气体流动方向与列车前进方向一致,纵向风速变化规律相同;当车头通过时,纵向风速达到极大值,且流向迅速改变,与列车运动方向相反;在列车车身通过阶段,受列车表面、隧道壁面摩阻力和列车附面层影响,纵向风速均有继续增大趋势;在车尾通过测点前,各测点纵向风速迅速负向增大,并在车尾通过瞬间几乎同时达到负向最大值。车尾通过后空气流动方向迅速改变与列车前进方向一致;在尾车通过后,列车两侧的测点(测点8,10和11)纵向列车风峰值及达到峰值所需时间不同,测点10和测点11峰值分别为13.4 m/s和20.6 m/s,相差53.7%;测点8达到峰值时刻(点C)比测点10(点B)和测点11(点A)分别迟0.9 s和1.6 s,表明隧道内纵向气体流动与空间位置有密切关系,具有显著空间效应。与列车两侧测点纵向风速变化规律不同,车顶正上方测点(测点17和23)纵向风速在车头通过时刻达到最大值,而不是车尾通过以后。
由上可知,列车通过对横向、纵向列车风影响规律不同。在车尾通过之前,不同位置处的横向列车风曲线变化规律基本一致,车尾通过之后横向列车风波动情况才逐渐加剧。与横向列车风不同,不同位置的纵向列车风在车头经过之后波动程度逐渐增大,在车尾通过以后纵向列车风波动程度最为剧烈。
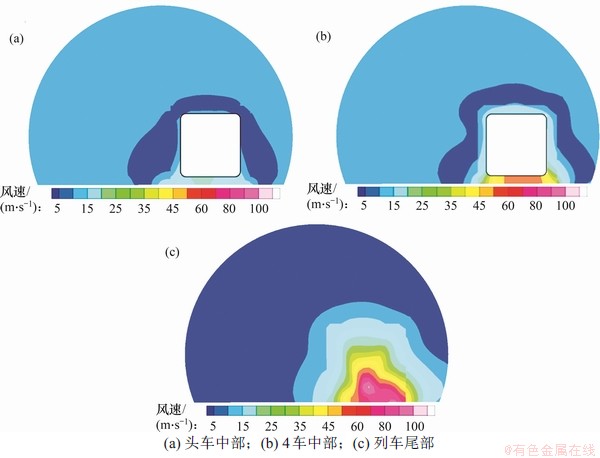
图11 隧道内横断面列车风云图
Fig. 11 Cross-sectional views of train in tunnel section of tunnel
图11所示为第4节车厢中部位于隧道中央时(t=4.5 s)隧道内不同位置横断面上列车风速度分布云图。从图11可知:中部列车周围速度分布规律基本一致,而车尾通过时产生的尾流对近隧道一侧列车风影响非常显著。
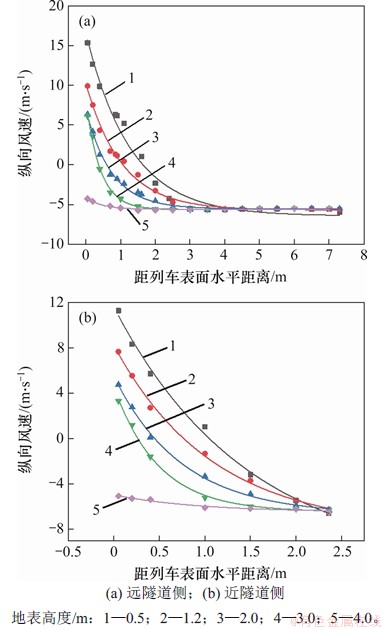
图12 列车两侧纵向分布曲线
Fig. 12 Longitudinal distribution curve of both sides of train
图12所示为距离地表分别为0.5,1.2,2.0,3.0和4.0 m时,列车两侧纵向列车风与到列车侧面水平距离关系变化曲线。从图12可知:在相同水平距离时,纵向列车风风速随着高度增大而减小,纵向风速降低速率先增大后迅速减小,并且在距地表3.0 m时纵向列车风降低速率最大;在相同地面高度时,随着到列车表面水平距离增加,纵向列车风迅速减小至零,然后开始反向增大。经过对不同类型函数拟合效果进行对比,最终采用指数函数对纵向风速与到列车水平距离之间的关系进行回归分析。远隧道侧不同地面高度下的拟合关系式分别为式(1)~(5),相关系数分别为0.980 39,0.991 10,0.992 93,0.994 23和0.957 03,见图12(a)。
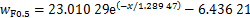 (1)
(1)
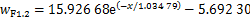 (2)
(2)
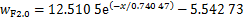 (3)
(3)
 (4)
(4)
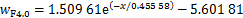 (5)
(5)
近隧道侧拟合关系式分别为式(6)~(10),相关系数分别为0.996 38,0.997 75,0.997 68,0.997 42和0.949 04,见图12(b)。对比图12(a)和12(b)可知:在相同高度下,远隧道一侧纵向列车风衰减速度比近隧道侧纵向列车风风速快,这是因为近隧道侧受隧道壁面限制,列车风只能沿隧道长度方向扩散,而远隧道侧空间远大于近隧道一侧空间,列车风可以向各个方向扩散,从而导致远隧道侧列车风衰减速度更快。
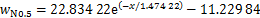 (6)
(6)
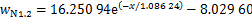 (7)
(7)
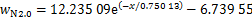 (8)
(8)
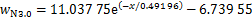 (9)
(9)
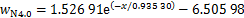 (10)
(10)
车顶上方气体流动特性对受电弓的气动性能影响很大,然而,当前关于列车顶部气动特性的研究鲜有报道。本文对列车顶部半宽处不同高度纵向风速进行分析。图13所示为列车顶部纵向风速曲线。由图13可知:在距离车顶1 m范围内,纵向列车风衰减速度极快,因此,需要特别关注顶部列车风风速剧变产生交变荷载对接触网系统产生的不利影响。当距离超过1 m后,纵向列车风风速变化很小,基本保持不变。类似地,采用指数函数进行拟合,可得到列车顶部纵向风速-到顶部距离的函数关系,见式(11),其相关系数为0.988 95。
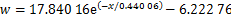 (11)
(11)
由此可知,当列车在隧道内高速运行时,环状空间内纵向列车风风速可采用以e为底的指数函数进行拟合,见式(12)。
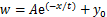 (12)
(12)
式中: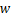 为纵向列车风风速;x为到列车表面的距离;
为纵向列车风风速;x为到列车表面的距离;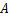 ,t和
,t和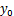 为与地面高度相关的系数。
为与地面高度相关的系数。
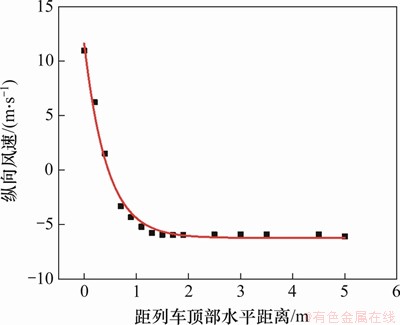
图13 列车顶部纵向列车风分布曲线
Fig. 13 Longitudinal wind distribution curve of train roof
5 列车周围流场分布
目前关于明线和侧风条件下列车周围流场分布规律研究很多,而对列车在隧道内运行情况研究较少。图14所示为隧道内不同横断面的流线图。由图14可知:当列车前方距车头鼻尖较远时,隧道内气体受到列车运动影响较小(见图14(a));随着到车头鼻尖距离越来越近,流线型车头将前方空气向上及两侧排开,导致空气流动程度增大(见图14(b));当距车头鼻尖后方13.25 m(头车中部)时,在列车远隧道侧上下拐角处开始形成漩涡(见图14(c));随着到头车鼻尖距离的增加,列车远隧道侧的流体结构得以充分发展,且近地表拐角处的漩涡逐渐脱落,并产生新的漩涡进行补充;此外,列车近隧道侧的拐角处也会产生漩涡,但漩涡尺寸要远小于远隧道侧的漩涡尺寸(见图14(d)~14(g));靠近列车尾部时,列车周围流场分布发生变化,气流由背离列车表面向流向列车表面转变,列车两侧拐角处的漩涡逐渐消失,在近隧道侧隧道壁面附近产生新的漩涡(见图14(h))。这是由于列车近隧道侧空间狭小且隧道壁面曲率变化较大,严重限制气体自由流动。在流线型车尾区域,由于横断面形状变化,漩涡不断从车体表面产生、脱落、合并,并向列车下游运动,在尾车后方产生一对纵向旋涡结构。随着到尾车鼻尖距离增加,漩涡结构尺寸不断增大、脱落,并且旋涡结构向近隧道一侧靠近(见图14(i)~14(l)),这就是近隧道列车风风速波动程度比远隧道侧更严重的原因。
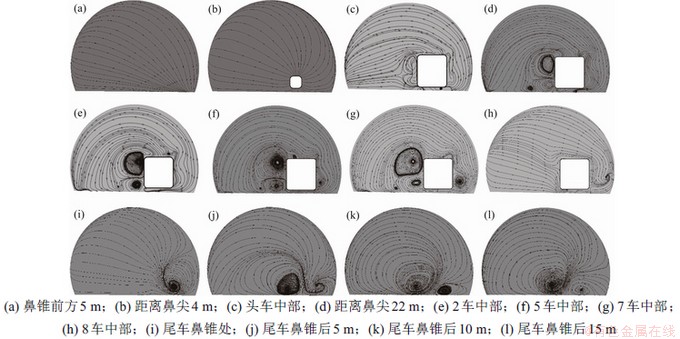
图14 隧道内不同横断面流线图
Fig. 14 Streamlines of different cross sections in tunnel
由此可知,当列车在隧道内行驶时,车头、车尾表面曲率变化较大,导致列车周围流场结构发生显著改变。随着到车头鼻尖距离增大,列车周围流场逐渐发展至稳定状态。因此,若以分析隧道内列车周围流场分布规律为主要研究目的,则可以采用三车(头车+中间车+尾车)或四车(头车+2中间车+尾车)短编组列车进行计算分析,可有效降低计算成本。
6 结论
1) 列车车头、车尾通过时,纵向、横向列车风风速均突然增大。在列车通过阶段,横向列车风风向经历背离列车—指向列车转变,纵向列车风风向经历正向—负向—正向流动。纵向列车风风速最大值出现在距离入口100 m断面处,远隧道侧与近隧道纵向风最大值分别为15.1 m/s和20.9 m/s,均超过线路旁作业人员允许承受的14 m/s列车风速的规定。
2) 不同空间位置纵向风速最大值出现时间不同。列车两侧空间位置在车尾通过一段时间后纵向列车风风速达到最大,车顶处在车头经过后纵向风速达到最大。
3) 纵向和横向列车风变化规律不同。在车尾通过之前,横向列车风变化规律基本相同,而风速波动程度在车尾经过后逐渐增加;在车头通过之前,纵向列车风变化规律相同,而风速波动程度在车头通过后显著增大。
4) 车头、车尾及车身表面存在较大的速度梯度,近隧道侧的纵向列车风较远隧道侧的大;中间列车周围速度场分布规律基本一致,而在列车尾部产生的尾流对近隧道一侧列车风影响非常显著。随着到地表、列车表面距离增大,环状空间内纵向列车风衰减速率逐渐减小,纵向列车风变化规律满足指数函数。
5) 由于列车截面形状变化较大,隧道内列车头部、尾部周围流场结构发生剧烈变化,而中间列车流场分布基本稳定。在远隧道侧上下拐角、近隧道侧下拐角处产生漩涡,并且远隧道侧漩涡要大于近隧道侧漩涡。
参考文献:
[1] RAGHUNATHAN R S, KIM H D, SETOGUCHI T. Aerodynamics of high-speed railway train[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2002, 38(6/7): 469-514.
[2] SUZUKI M, MAEDA T, ARAI N. Notes on Numerical Fluid Mechanics (NNFM)[M]. Wiesbaden: Vieweg+Teubner Verlag, 1996: 311-317.
[3] 何德昭, 徐鹤寿, 王厚雄. 列车通过隧道诱发的气动变化规律的试验研究[J]. 中国铁道科学, 1997, 18(4): 42-49
HE Dezhao, XU Heshou, WANG Houxiong. Research on the variation regularities of aerodynamic events in tunnels arising from passing trains[J]. China Railway Science, 1997, 18(4): 42-49
[4] 万晓燕, 吴剑. 时速200 km动车组通过隧道时空气动力学效应现场试验与研究[J]. 现代隧道技术, 2006, 43(1): 43-48.
WAN Xiaoyan, WU Jian. In-situ test and study on the aerodynamic effect of the rolling stock passing through tunnels with a speed of 200 km/h[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 2006, 43(1): 43-48.
[5] 刘堂红, 田红旗, 金学松. 隧道空气动力学实车试验研 究[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2008, 26(1): 42-46.
LIU Tanghong, TIAN Hongqi, JIN Xuesong. Experimental study of full-scale train on aerodynamics in tunnel[J]. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 2008, 26(1): 42-46.
[6] SAKUMA Y, SUZUKI M, IDO A, et al. Measurement of air velocity and pressure distributions around high-speed trains on board and on ground[J]. Journal of Mechanical Systems for Transportation and Logistics, 2010, 3(1): 110-118.
[7] SUZUKI M, SAKUMA Y. Pressure fluctuation characteristics of narrow gauge train running through tunnel[J]. Journal of Mechanical Systems for Transportation and Logistics, 2010, 3(3): 469-476.
[8] BELL J R, BURTON D, THOMPSON M C, et al. Moving model analysis of the slipstream and wake of a high-speed train[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2015, 136: 127-137.
[9] BELL J R, BURTON D, THOMPSON M C, et al. The effect of tail geometry on the slipstream and unsteady wake structure of high-speed trains[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2017, 83: 215-230.
[10] SUZUKI M, IDO A, SAKUMA Y, et al. Full-scale measurement and numerical simulation of flow around high-speed train in tunnel[J]. Journal of Mechanical Systems for Transportation and Logistics, 2008, 1(3): 281-292.
[11] 费瑞振, 彭立敏, 杨伟超, 等. 高速铁路隧道空气动力效应对人员安全的影响研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2013, 23(7): 79-84.
FEI Ruizhen, PENG Limin, YANG Weichao, et al. Study on aerodynamic force effect on personnel safety in high-speed railway tunnel[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2013, 23(7): 79-84.
[12] 施成华, 杨伟超, 彭立敏, 等. 高速铁路隧道列车风作用下接触网安全性分析[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 43(9): 3652-3658.
SHI Chenghua, YANG Weichao, PENG Limin, et al. Analysis of catenary's safety under train wind action in high-speed railway tunnel[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2012, 43(9): 3652-3658.
[13] GUO Dilong, SHANG Keming, ZHANG Ye, et al. Influences of affiliated components and train length on the train wind[J]. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 2016, 32(2): 191-205.
[14] 牛纪强. 高速列车通过隧道时产生的列车风研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2015, 12(6): 1268-1276.
NIU Jiqiang. Research on gusts caused by high-speed trains passing through tunnel[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2015, 12(6): 1268-1276.
[15] 沈翔. 地下铁道活塞风特性的研究[D]. 上海: 同济大学机械与能源工程学院, 2004: 3-4.
SHEN Xiang. Research on wind characteristics of piston in underground railway[D]. Shanghai: Tongji University, School of Mechanical Engineering, 2004: 3-4.
[16] 王厚雄, 何德昭, 徐鹤寿. 准高速东风型列车风速度场特性初探[J]. 中国铁道科学, 1993, 14(2): 100-110.
WANG Houxiong, HE Dezhao, XU Heshou. An initial approach to the features of air flow field around quasi high speed train Dongfeng[J]. China Railway Science, 1993, 14(2): 100-110.
[17] PLANK J E. The relation between the size of plant and the spread of systemic diseases[J]. Annals of Applied Biology, 1948, 35(1): 45-52.
[18] POPE C W, GAWTHORPE R G, RICHARDS S P. An experimental investigation into the effect of train shape on the unsteady flows generated in tunnels[C]// Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on the Aerodynamics and Ventilation of Vehicle Tunnels. York, UK, 1982: 107-126.
[19] 轨道交通安全教育部重点实验室. 合武铁路、石太客运专线隧道气动效应试验研究报告[R]. 长沙: 中南大学轨道交通安全教育部重点实验室, 2009: 52-63.
Key Laboratory of Traffic Safety on Track of Ministry of Education. Research report of full-scale train tests for aerodynamics in tunnels on Wuhan-Hefei railway line[R]. Changsha: Central South University. Key Laboratory of Traffic Safety on Track of Ministry of Education, 2009: 52-63.
[20] BARON A, MOSSI M, SIBILLA S. The alleviation of the aerodynamic drag and wave effects of high-speed trains in very long tunnels[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2001, 89(5): 365-401.
[21] 谭鹏, 彭立敏, 施成华, 等. 城际铁路隧道列车风特性及对人员安全的影响分析[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 44(4): 1557-1563.
TAN Peng, PENG Limin, SHI Chenghua, et al. Characteristics of train wind and analysis of personnel security in inter-city railway tunnel[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2013, 44(4): 1557-1563.
[22] 李人宪, 赵晶, 张曙, 等. 高速列车风对附近人体的气动作用影响[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2007, 28(5): 98-104.
LI Renxian, ZHAO Jing, ZHANG Shu, et al. Influence of the aerodynamic force to human body near high-speed trains[J]. China Railway Science, 2007, 28(5): 98-104.
[23] HUR N, KIM S R, WON C S, et al. Wind load simulation for high-speed train stations[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2008, 96(10/11): 2042-2053.
[24] 骆建军. 高速地铁隧道内扩大段和通风竖井对压力波的影响研究[J]. 现代隧道技术, 2016, 53(4): 22-28.
LUO Jianjun. The influences of enlarged sections and ventilation shafts on pressure waves in high-speed metro tunnels[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 2016, 53(4): 22-28.
[25] 骆建军, 吴尽, 陈鹏飞. 高速铁路并联隧道横通道对隧道内压力变化的影响[J]. 北京交通大学学报, 2015, 39(1): 8-13.
LUO Jianjun, WU Jin, CHEN Pengfei. Pressure change from the cross aisle when the train passing through parallel tunnel of high-speed railway[J]. Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University, 2015, 39(1): 8-13.
[26] 田红旗. 中国列车空气动力学研究进展[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2006, 6(1): 1-9.
TIAN Hongqi. Study evolvement of train aerodynamics in China[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2006, 6(1): 1-9.
(编辑 杨幼平)
收稿日期: 2020 -06 -23; 修回日期: 2020 -08 -12
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(51678036) (Project(51678036) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China)
通信作者:骆建军,博士(后),教授,从事高速铁路隧道空气动力学研究;E-mail:jjluo@bjtu.edu.cn
引用格式: 王磊, 骆建军, 李飞龙, 等. 高速铁路双线隧道内列车风分布及流场特性[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 52(4): 1346-1357.
Citation: WANG Lei, LUO Jianjun, LI Feilong, et al. Train-induced wind distribution and flow field characteristics in high-speed railway double-track tunnel[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2021, 52(4): 1346-1357.