C/C-SiC复合材料的导热性能及其影响因素
李专,肖鹏,熊翔,黄伯云
(中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:以炭纤维针刺毡为预制体,采用化学气相渗透法和熔融渗硅法相结合制得C/C-SiC复合材料;研究C/C-SiC材料在室温至1 300 ℃之间的导热性能以及预制体结构、基体炭结构和石墨化处理对其热扩散率的影响。研究结果表明:C/C-SiC材料的比热容随着温度的升高不断增大,在700 ℃时达到最大值2.18 J/(g·K),随后降至1 300℃时的0.57 J/(g·K),其导热系数在1 300 ℃时为3.95 W/(m·K);C/C-SiC材料的热扩散率在室温时为0.12 cm2/s,随着温度的升高不断降低并趋于常量,平行摩擦面方向的热扩散率明显比垂直于摩擦面方向的大;以全网胎为预制体的C/C-SiC材料其垂直和平行摩擦面的热扩散率相当,树脂炭质量分数增大及石墨化处理均可显著提高C/C-SiC材料的热扩散率。
关键词:C/C-SiC复合材料;导热系数;熔融渗硅;炭纤维
中图分类号:TB 331;TH 117.3 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2013)01-0040-06
Thermal conductivity of C/C-SiC composites and its influence factors
LI Zhuan, XIAO Peng, XIONG Xiang, HUANG Boyun
(State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Carbon fibre reinforced carbon and silicon carbide dual matrix composites (C/C-SiC) were fabricated by the combination of chemical vapor infiltration (CVI) with liquid silicon infiltration (LSI). The effects on thermal conductivity of C/C-SiC composites were investigated. The results show that the specific heat capacity of C/C-SiC increases with the increase of temperature and reaches the highest value of 2.18 J/(g·K) at 700 ℃, and decreases to 0.57 J/(g·K) at 1 300 ℃. At the same temperature, the thermal conductivity of C/C-SiC is 3.95 W/(m·K). The thermal diffusivity of C/C-SiC decreases to constant with the increase of temperature. The thermal diffusivity parallel to friction surface is obviously larger than that perpendicular to friction surface. The thermal diffusivity paralled to friction surface is quite to that of perpendicularity of C/C-SiC using the preform as web, and the thermal diffusivity significantly increases with the increase of mass fraction of the resin carbon and the treatment of graphitization.
Key words: C/C-SiC composites; thermal conductivity; liquid silicon infiltration; carbon fibre
炭纤维增强炭和碳化硅双基体(C/C-SiC)复合材料最早于20世纪90年代中期开始应用于刹车材料领域。C/C-SiC刹车材料与传统半金属基与粉末冶金刹车材料相比,具有密度低、耐高温、制动平稳、摩擦因数高、磨损少和使用寿命长等优点[1-3]。与C/C材料相比,由于C/C-SiC刹车材料中引入了SiC陶瓷相作为基体,不仅有效提高了材料的抗氧化性和摩擦因数,而且显著改善了其摩擦性能对外界环境介质(潮气、霉菌和油污等)的稳定性。经过10多年的发展,C/C-SiC刹车材料已经成为高性能轻质刹车材料的一个主要研究方向[4-6]。刹车材料在使用过程中不仅需要具有优良的摩擦性能,而且需要承受极大的机械载荷和热载荷,是一种典型的结构-功能一体化材料。为了衡量材料的刹车性能水平,通常采用刹车功率(单位面积承受的能载)进行定量表征[7]。随着刹车速度和刹车压力的增加,刹车功率不断提高,摩擦表面的温度也越高。对于确定的材料体系,摩擦功率具有1个额定的临界值。在刹车能量低于该临界值时,材料的摩擦因素能维持在比较稳定的状态;而当能量超过该临界值时,摩擦面会出现局部过热现象并出现闪点温度(高达1 000 ℃),从而导致摩擦性能衰减[8]。提高材料体系的导热系数和比热容是提高材料摩擦功率临界值的有效途径。在确定材料体系的情况下,提高垂直于摩擦面的导热系数能显著提高摩擦因素的稳定性。针对C/C-SiC刹车材料,提高其垂直于摩擦面导热系数的具体措施有[9-11]:(1) 使用热导率高的碳纤维(如高模量的纤维);(2) 增加纤维与摩擦面之间的夹角;(3) 增大C/C-SiC材料中基体的含量;(4) 引入高导热金属元素或者基体合金化。通过使用高弹性模量的纤维来提高材料的导热系数,会导致材料制造成本大幅度提高。增加纤维与摩擦面之间的夹角,可以通过纤维预制体的设计来实现。增加材料中基体含量或者基体合金化会导致纤维体积分数越低,材料的强度和断裂韧性下降。本文作者采用改变预制体结构、改变基体炭结构和石墨化处理工艺的措施来改善C/C-SiC材料的导热性能。以针刺炭纤维毡为预制体,采用化学气相渗透与熔融渗硅相结合的方法制得C/C-SiC复合材料,研究C/C-SiC复合材料在室温至1 300 ℃之间的导热性能,以及预制体结构、基体炭结构和石墨化处理对其热扩散率的影响。
1 实验
1.1 C/C-SiC材料的制备
采用日本东丽公司(Toray)生产的PAN型T700(12K)炭纤维。将炭纤维分别制成无纬布和网胎,将单层0°无纬布、网胎、90°无纬布、网胎依次循环叠加,然后,采用接力式针刺的方法在垂直于铺层方向引入炭纤维束制得炭纤维整体毡,或者只将多层胎网叠加后针刺制得炭纤维全网胎。在1 600 ℃对预制体进行高温热处理后,采用化学气相渗透法增密得到C/C多孔体,最后,将硅粉熔融浸渗C/C多孔体制得7组C/C-SiC复合材料。在CVI增密工艺中,以C3H6为反应气,H2为稀释气,于1 000 ℃沉积。
1.2 C/C-SiC材料的热物理性能测试
C/C-SiC复合材料的导热性能测试在德国Netszch公司生产的LFA 427激光导热仪上进行,试样直径×高为12.7 mm×2 mm。测试时,热流方向为垂直摩擦面方向,测量温度范围从室温到1 300 ℃,升温速度为3 ℃/min。在测试过程中,以Ar为保护气,流量为100 mL/min。本项测试在西北工业大学进行。
按GB 11108—89标准,利用激光脉冲法在国产JR-3激光导热仪上测试不同C/C-SiC试样的常温热扩散率测试,分别取垂直和平行于C/C-SiC复合材料摩擦面2个方向的试样,直径×高为10 mm×3 mm。
1.3 测试与分析
采用阿基米德排水法测试C/C-SiC试样的密度和开孔率;利用Rigaku-3014型X线衍射仪对试样进行物相组成分析;采用日本JSM-6360LV型扫描电子显微镜和德国Leica MeF3A金相显微镜观察C/C-SiC试样在不同尺度下的显微结构。
2 结果与分析
2.1 材料物相和组织结构分析
试样1是以整体毡为预制体制备的C/C-SiC复合材料,其密度为1.89 g/cm3,开孔率为17.9%,XRD分析结果和物相组成如图1所示。由图1可见:在浸渗过程中,液硅与热解炭反应生成了β-SiC,同时还残留有部分未反应完全的Si。为了得到各成分的质量分数,也同时为了能观察物相界面的显微形貌,采用质量分析法处理C/C-SiC材料[12],测得试样1中C,SiC和Si的质量分数分别为58%,35%和7%。
试样1的显微形貌如图2所示。从图2(a)可以看出:C/C-SiC材料是典型的非均质材料,无纬布和网胎相互交替排布,具有明显的亚结构单元。能谱分析表明其中深色部分为炭纤维和热解炭,浅色部分为β-SiC及残留Si。因为无纬布层纤维排列整齐紧密, Si只能渗入纤维束间或沿着针刺纤维附近的孔隙渗入,而胎网层是由短纤维随机杂乱排列而成,孔隙孔径大而且数量多,液Si很容易渗入孔隙中:因此,在熔融渗硅过程中,液Si渗入到这些孔隙中,与接触到的热解炭和纤维束外部的炭纤维反应生成SiC,并有部分Si残余(如图2(b)所示),同时材料中还有部分孔隙没有填充。
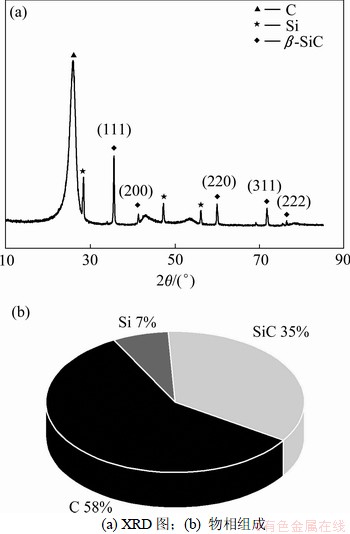
图1 C/C-SiC复合材料的XRD图及物相组成(质量分数)
Fig.1 XRD pattern and phase compositions of C/C-SiC composite (mass fraction)
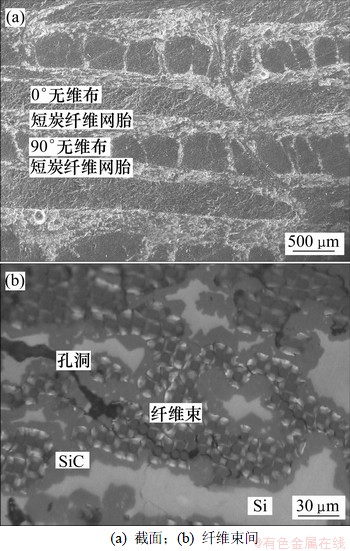
图2 C/C-SiC复合材料的显微形貌
Fig.2 Typical SEM micrographs of C/C-SiC composites
2.2 C/C-SiC在室温至1 300 ℃之间的导热性能
试样1从室温到1 300 ℃范围内垂直于摩擦面方向的比热容、热扩散率及导热系数如图3所示。从图3(a)可见:C/C-SiC材料的比热容在室温为0.84 J/(g·K),随着温度的升高不断增大,在700 ℃时达到最大值2.18 J/(g·K),随后不断降低至1 300 ℃时的0.57 J/(g·K);热扩散率在室温为0.12 cm2/s,随着温度的升高不断降低,在9 00~1 100 ℃略微升高后继续下降,在1 400 ℃时为0.03 cm2/s。由图3(b)可知:随着温度的升高,试样1的导热系数在1 100 ℃之前保持稳定在15~21 W/(m·K),随后急剧下降至1 300 ℃时的3.95 W/(m·K)。
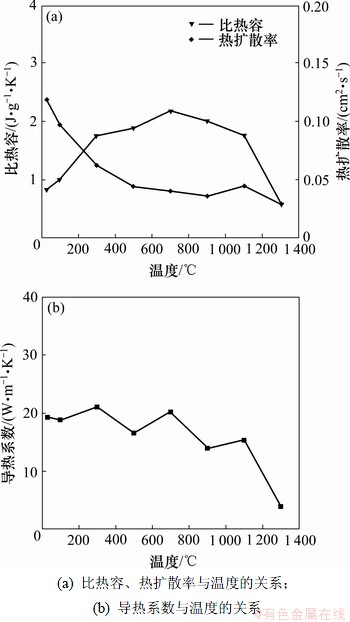
图3 C/C-SiC复合材料在不同温度下热物理性能
Fig.3 Thermal physical properties of C/C-SiC composites at different temperatures
C/C-SiC复合材料由晶体SiC和Si以及晶体非晶体炭组成,其导热主要是靠声子(即晶格振动的格波)的运动来实现,不同的结构对声子散射的贡献存在非常大的差别[13]。材料的热扩散率随声子平均自由程(l)增大而增大。在声子间的交互作用中,声子平均自由程对温度非常敏感。随着温度的升高,声子振动能量加大,频率加快,碰撞次数增多,所以,l减小,材料热扩散率下降。由于自由程减小有一定限度,在高温下,最小自由程为几个晶格间距,所以,高温时热扩散率趋于常量;另一方面,前期C/C-SiC复合材料的氧化实验研究结果表明[14]:700 ℃左右为C/C-SiC中单质Si氧化成SiO2的起始氧化温度点,1 100 ℃左右为SiC基体的氧化起始点。Si氧化成SiO2是一个质量增加的过程,而SiC的氧化是一个质量降低的过程:因此,C/C-SiC材料随着温度升高,SiC发生氧化,使得材料变得疏松,开孔率增大,导热系数急剧下降。
2.3 C/C-SiC导热性能的影响因素
2.3.1 预制体结构
炭纤维预制体结构是C/C-SiC复合材料热性能的主要影响因素。分别以整体毡和全网胎为预制体,采用LSI制备2组C/C-SiC复合材料,其基本参数如表1所示。由表1可知:以整体毡为预制体的试样2和以全网胎为预制体的试样3相比,试样2的开孔率较高;试样2在垂直摩擦面方向(⊥)的热扩散率较比试样3的低,而平行摩擦面方向(∥)则比试样3的高。
预制体结构、材料组分含量和孔隙率是导致导致上述差异的主要原因。首先,试样2是以整体毡为预制体,纤维含量高(预制体密度高达0.57),其长纤维无纬布平行摩擦面方向,而其垂直摩擦面方向只有Z向针刺纤维,因此,其平行摩擦面方向的热扩散率要高得多。试样3以全网胎为预制体,炭纤维含量低,短纤维呈短程杂乱、远程均匀分布,因此,其垂直摩擦面方向与平行摩擦面方向的热扩散率相当,同时,其平行摩擦面方向的热扩散率比试样2的低。
对比试样2和试样3的C/C多孔体密度和C/C-SiC密度可知:试样3含有更多的SiC基体。在垂直摩擦面方向,主要依靠基体和Z向针刺纤维导热,由于两者的Z向纤维相当,因此,陶瓷基体越多,热扩散率也就越高。
CVI后试样3的C/C密度较低,在LSI过程中有更多液Si渗入并与炭反应生成SiC,导致试样3的开孔率(0.6)比试样2的开孔率(5.4)相差近1个数量级。垂直于摩擦面的热扩散方向与纤维排布方向垂直,因此,热扩散系数反映了基体的热扩散能力。对于同一种微观结构的C/C-SiC摩擦材料,孔隙度增大,意味着宏观缺陷增多。孔隙中的空气可看作一弥散相,气孔能引起声子散射,降低声子的平均自由程,因此,气孔降低了材料的导热能力。根据欧根(Eucken)公式[13]:

 (1)
(1)
对于垂直摩擦面方向,由于热流垂直无纬纤维布平面,导热主要依靠基体,由于λs远大于λa,式(1)可简化为
 (2)
(2)
式中:λp为有孔隙材料总的导热系数(W/(m·K);λs为有孔隙材料固相的导热系数(W/(m·K));λa为空气的导热系数(W/(m·K)); 为孔隙体积分数(%)。由式(2)可知:当孔隙度增大时,C/C-SiC复合材料导热系数降低。该理论能很好地解释实验现象,Klett等[15]对C/C复合材料的研究也证明了这一点。
为孔隙体积分数(%)。由式(2)可知:当孔隙度增大时,C/C-SiC复合材料导热系数降低。该理论能很好地解释实验现象,Klett等[15]对C/C复合材料的研究也证明了这一点。
2.3.2 基体炭结构
以整体毡为预制体,分别采用CVI和(或)树脂浸渍/炭化制得基体炭,然后,利用LSI制得3组不同基体炭C/C-SiC复合材料,其基本参数如表2所示。由表2可知:随着树脂炭质量分数的提高,材料的热扩散率不断增大,试样5的热扩散率为试样2的近3倍。
表1 预制体结构对LSI法制备C/C-SiC材料热扩散率的影响
Table 1 Thermal properties of C/C-SiC composites with different structures of perform
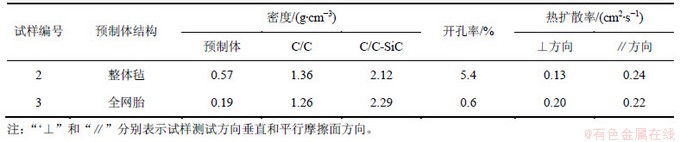
表2 基体炭结构对LSI法制备C/C-SiC材料热扩散率的影响
Table 2 Thermal properties of C/C-SiC composites with different structures of carbon matrix
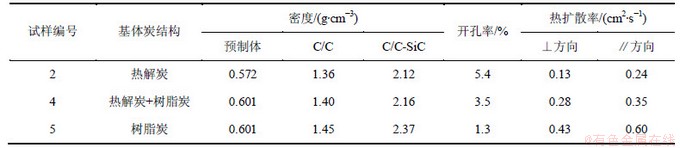
研究表明:由热固性树脂裂解得到的玻璃炭的热扩散率比CVI热解炭的低[16],而试样2,4和5中树脂炭质量分数逐渐增大,热解炭质量分数降低,扩散率理应不断降低。其原因是:(1) 试样2,4和5中基体炭质量分数不断增大,试样5中SiC质量分数比其他2个试样的高,而在平行于摩擦面的方向,材料的热扩散能力主要靠基体体现,因此,基体质量分数越高,则其热扩散也越高;(2) 试样2,4和5的开孔率不断降低,特别是试样5经过多次增密后其开孔率仅为1.3%;开孔率越大,其热扩散率越低。同时平行于摩擦面方向(无纬布层方向)的热扩散率明显比垂直于摩擦面方向的热扩散率大。这是因为对于垂直摩擦面方向的热传导,炭纤维的热导率很低,因此,复合材料在该方向上传热的主要通道为基体,此时,基体中的裂纹、界面对热传导的阻碍作用显得尤为明显。
2.3.3 石墨化处理
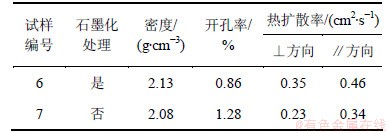
以整体毡为预制体,试样6在进行熔融渗硅后于2 100 ℃进行石墨化热处理,而试样7没有经过石墨化热处理,2组试样的基本参数如表3所示。由表3可知:热处理后的试样6其垂直和平行摩擦面方向的热扩散率与试样7的相比均有很大提高。这是由于经过石墨化处理后,材料的微晶层间距减小,石墨化度提高,微晶的平均尺寸变大,声子的平均自由程也随之增大,因此,热扩散率提高。此外,热处理使得材料中位错、交联、层面乱排、锥的边界等缺陷逐渐被去掉,减少了材料中的晶格缺陷,使影响声子散射的因素减弱,这也是热扩散率提高的原因之一。
表3 石墨化处理对LSI工艺制备C/C-SiC材料热扩散率的影响
Table 3 Thermal properties of C/C-SiC composites with high temperature treatment (HTT)
3 结论
(1) 采用整体毡为预制体的C/C-SiC材料的比热容在室温为0.84 J/(g·K),随着温度的升高不断增大,在700 ℃时达到最大值2.18 J/(g·K),随后不断降低至1 300 ℃时的0.57 J/(g·K)。C/C-SiC材料的导热系数在1 100 ℃之前稳定在15~21 W/(m·K),随后下降至1 300 ℃时的3.95 W/(m·K)。
(2) 以整体毡为预制体的C/C-SiC材料的热扩散率在室温为0.12 cm2/s,随着温度的升高不断降低,并趋于常量;同时平行于摩擦面方向(无纬布层方向)的热扩散率明显大于垂直于摩擦面方向的热扩散率。
(3) 采用全网胎为预制体的C/C-SiC材料其垂直和平行摩擦面的热扩散率相当,C/C-SiC材料的热扩散率随树脂炭质量分数的增大而增大,石墨化处理能显著提高C/C-SiC材料的热扩散率。
参考文献:
[1] Krenkel W, Heidenreich B, Renz R. C/C-SiC Composites for advanced friction systems[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2002, 4(8): 427-436.
[2] XIAO Peng, LI Zhuan, XIONG Xiang. Microstructure and tribological properties of 3D needle-punched C/C-SiC brake composites[J]. Solid State Sciences, 2010, 12(4): 617-623.
[3] Naslain R. Design, preparation and properties of non-oxide CMCs for application in engines and nuclear reactors: An overview[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2004, 64: 155-170.
[4] 张立同, 成来飞, 徐永东. 新型碳化硅陶瓷基复合材料的研究进展[J]. 航空制造技术, 2003(1): 24-32.
ZHANG Litong, CHENG Laifei, XU Yongdong. Progress in research work of new CMC-SiC[J]. Aeronautical Science and Technology, 2003(1): 24-32.
[5] Vaidyaraman S, Purdy M, Walker T, et al. C/SiC material evaluation for aircraft brake applications[C]//Proceedings of 4th International Conference on High Temperature Ceramic Matrix Composites(HT-CMC 4). Germany: Wiley VCH, 2001: 802-808.
[6] 肖鹏, 熊翔, 张红波, 等. C/C-SiC陶瓷制动材料的研究现状与应用[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2005, 15(5): 668-674.
XIAO Peng, XIONG Xiang, ZHANG Hongbo, et al. Progress and application of C/C-SiC ceramic braking materials[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 15(5): 668-674.
[7] Breuer B, Dausend U. Advanced brake technology[M]. Warrendale, USA: SAE International, 2003: 37-50.
[8] Panier S, Dufrenoy P, Weichert D. An experimental investigation of hot spots in railway disc brakes[J]. Wear, 2004, 256(7/8): 764-773.
[9] 贺福, 王茂章. 碳纤维及其复合材料[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1995: 23-32.
HE Fu, WANG Maozhang. Carbon fiber and composite[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1995: 23-32.
[10] 田广来, 徐永东, 范尚武, 等. 高性能碳/碳化硅刹车材料及其优化设计[J]. 复合材料学报, 2008, 25(2): 101-108.
TIAN Guanglai, XU Yongdong, FAN Shangwu, et al. High performance C/SiC brake materials and optimizing design[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2008, 25(2): 101-108.
[11] 范尚武, 张立同, 成来飞. 三维针刺C/SiC刹车材料的热物理性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2011, 28(3): 56-62.
FAN Shangwu, ZHANG Litong, CHENG Laifei. Thermal physical properties of 3D needled C/SiC brake materials[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2011, 28(3): 56-62.
[12] 姜四洲, 李专, 熊翔, 等. 温压-原位发应法制C/C-SiC复合材料及显微结构分析[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2011, 42(6): 1588-1592.
JIANG Sizhou, LI Zhuan, XIONG Xiang. Preparation and microstructure of C/C-SiC composites fabricated by warm compressed-in situ reacted process[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2011, 42(6): 1588-1592.
[13] 黎婉棠, 吴英凯. 固体物理学[M]. 北京: 北京师范大学出版社, 1990: 134-136.
LI Wantang, WU Yingkai. Solid state physics[M]. Beijing: Beijing Normal University Press, 1990: 134-136.
[14] 李专. C/C-SiC摩擦材料的制备、结构和性能[D]. 长沙: 中南大学粉末冶金研究院, 2010: 95-103.
LI Zhuan. Preparation, microstructure and properties of C/C-SiC Braking composite[D]. Changsha: Central South University. Research Institute of Powder Metallurgy, 2010: 95-103.
[15] Klett J W, Edie D D. Flexible towpreg for the fabrication of high thermal conductivity carbon/carbon composites[J]. Carbon, 1995, 23: 1485-1503.
[16] Luo R Y, Liu T, LI Jinsong, et al. Thermal physical properties of carbon/carbon composites and physical mechanism of thermal expansion and thermal conductivity[J]. Carbon, 2004, 42: 2887-2895.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期:2011-12-12;修回日期:2012-03-05
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51205417, 51072231);中国博士后科学基金资助项目(20110491278);中南大学自由探索计划项目(2011QNZT43))
通信作者:李专(1982-),男,湖南涟源人,在站博士后,从事高性能陶瓷基摩擦材料的研究;电话:13574842740;E-mail: li_zhuan@yahoo.com.cn