深过冷K4169高温合金凝固组织演变和力学性能的关系
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2016年第7期
论文作者:张可人 谢发勤 胡锐 吴向清
文章页码:1885 - 1891
关键词:K4169高温合金;深过冷;Laves相;力学性能;显微组织
Key words:K4169 superalloy; undercooling; Laves phase; mechanical properties; microstructures
摘 要:采用循环过热与熔融玻璃净化相结合的方法使K4169 高温合金获得了14~232 K过冷度。采用透射电子显微镜(TEM)、扫描电子显微镜(SEM)和光学显微镜等手段研究过冷K4169高温合金枝晶形貌以及相组成。研究发现,枝晶形貌、晶粒尺寸和晶间相都会随着过冷度的增加而发生明显改变。同时,系统研究过冷K4169高温合金凝固组织与力学性能之间的关系。实验结果表明,晶粒尺寸和晶间相含量的减小以及Laves相的均匀分布提高了合金的抗拉强度和伸长率,并且当过冷度达232 K时,合金具有最优力学性能,抗拉强度为932.2 MPa,伸长率为6.5%。
Abstract: Various undercoolings 14-232 K of bulk K4169 superalloys were obtained by the method of molten glass fluxing combined with superheating cycling and the mechanical properties of undercooled K4169 with as-solidified state were tested. Microstructures and phases composition in undercooled bulk K4169 superalloy were identified by transmission electron microscope (TEM), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and optical microscopy (OM). The morphology of dendrites, grain size and intergranular phase all change with the increased undercooling. Meanwhile, the relationship between microstructure of undercooled K4169 superalloy and tensile properties was investigated. The experimental results show that the uniform distribution of Laves phase and the decrease of grain size and intergranular phase content are favorable for the improvement of mechanical properties. The maximum tensile strength and elongation obtained at undercooling of 232 K are 932.2 MPa and 6.5 %, respectively.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 26(2016) 1885-1891
Ke-ren ZHANG1, Fa-qin XIE2, Rui HU1, Xiang-qing WU2
1. State Key Laboratory of Solidification Processing, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710072, China;
2. School of Aeronautics, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710072, China
Received 25 June 2015; accepted 25 February 2016
Abstract: Various undercoolings 14-232 K of bulk K4169 superalloys were obtained by the method of molten glass fluxing combined with superheating cycling and the mechanical properties of undercooled K4169 with as-solidified state were tested. Microstructures and phases composition in undercooled bulk K4169 superalloy were identified by transmission electron microscope (TEM), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and optical microscopy (OM). The morphology of dendrites, grain size and intergranular phase all change with the increased undercooling. Meanwhile, the relationship between microstructure of undercooled K4169 superalloy and tensile properties was investigated. The experimental results show that the uniform distribution of Laves phase and the decrease of grain size and intergranular phase content are favorable for the improvement of mechanical properties. The maximum tensile strength and elongation obtained at undercooling of 232 K are 932.2 MPa and 6.5 %, respectively.
Key words: K4169 superalloy; undercooling; Laves phase; mechanical properties; microstructures
1 Introduction
The fine-grain microstructure of Ni-based superalloys has lots of advantages, such as refined grain, carbides, and precipitates [1]. The fine-grain process was developed to improve the strength, creep and fatigue life of discrotors, turbine blades, and integral wheels working [2-4]. Compared with the fine granular grains produced by conventional solidification (e.g., magnetic and mechanical stirring, copious nucleation induced by grain refiner, etc.), the grain refinement of undercooled melts occurs spontaneously [5]. Meanwhile, the solidification rate is no longer controlled only by the external heat extraction if an alloy melt is substantially undercooled prior to nucleation, which makes high undercooling become an effective technique to produce refined grain bulk rapid solidified alloys [6]. Actually, the microstructure obtaining from undercooled melt is different with the cast microstructures, due to the rapid solidification process and the fragment of dendrites. Up to now, most of these investigations about undercooled metal by fluxing technique mainly focus on the crystal nucleation and grain growth. Nevertheless, few works have been done on the relationship between mechanical properties and undercooling microstructures in bulk multicomponent alloys.
As one of the most widely used superalloys in modern industry, K4169 superalloy (similar with Inconel718C) shows outstanding performances at elevated temperature environment, and it is widely used as the critical structural components in gas-turbine engines. Most of the studies [7,8] considered that Laves phase precipitated in cast K4169 superalloy is harmful to the mechanical properties at ambient temperature, because Laves phase with AB2 type is common type of topologically close-packed (TCP) structures which has low ductility and brittle fracture characteristics. However, dispersion of Laves phase at grain boundary (GB) can improve the ductility and shows high strength at high temperatures [9-11] which may inhibit the dislocation motion and strengthen the grain boundary. Thus, the uniform distribution of Laves phase obtained by highly undercooled K4169 superalloy may improve the strength at ambient temperature.
Most investigations about undercooling focus on the nucleation and grain growth. However, the microstructure dependent mechanical properties of the bulk undercooled K4169 superalloys need to be investigated for potential applications. So, this work aimed to investigate the effect of Laves phases on mechanical properties obtained by undercooled K4169 superalloy.
2 Experimental
Commercial K4169 superalloy was chosen (Table 1) in the undercooling experiment, which was conducted by glass fluxing method in a high frequency induction unit with a coil mounted in atmosphere. The glass flux was B2O3 which had been dehydrated at 1073 K for 5 h in advance. In each experiment, 100 g bulk K4169 superalloy was placed in the quartz crucible of 20 mm in diameter and covered with B2O3 powder on the top and bottom. Then, the crucible was placed in the coil of the high frequency induction unit. Firstly, the sample was heated to 773-873 K until completely enwrapped by the molten B2O3. Then, the temperature increased to 1821-1881 K which was 200-260 K above the liquidus temperature (TL) of K4169 superalloy and held for 3-5 min. After that the temperature decreased to TL+ 30 K and held for 3-5 min. The process was cycled 2-3 times to generate different undercoolings (△T).
Table 1 Composition of K4169 super alloy (mass fraction, %)
The specimen used in this experiments was cut from the as-solidified ingot along the longitudinal direction. The tensile specimens had a length of 24 mm, width of 8 mm, and thickness of 0.6 mm. In the present work, the tensile tests were carried out at room temperature with the strain rate of 1×10-3 s-1 by using InstronMicroTester machine and the ultimate tensile strength (σb) and the elongation (δ) can be obtained. Any normal property was represented by the average value of three measurements.
The solidified samples were cut along the longitudinal section, polished and etched using a solution of 10 g CuCl2 +100 mL HCl +100 mL alcohol. The solidification microstructures and the fracture morphologies of different undercoolings were observed by means of Olympus-PMG3 optical microscope (OM) and JSM-6460 scan electron microscope (SEM). The intergranular phase with 232 K undercooling was tested by Tecnai F30 transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and the grain size was expressed by the equivalent diameter using Image-Pro Plus software.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Structural transition with undercooling
In previous investigations, similar microstructure evolution in undercooled melts has been detected, i.e., from granular crystals to dendrites and then to granular crystals again [11-13]. Within an overall transformation (including undercooled solidification and solid-state grain growth), the as-solidified state of undercooled melt actually acts as the initial state of the subsequent grain growth [14]. CHEN et al [15] indicated that the first grain refinement at small △T was induced by the concurrent of dendrite fragmentation and at high △T was induced by recrystallization of dendrites. Generally, the fluid flow can act as the driving force for dendrite fragmentation deformation [15]. In the present work, the as-solidified samples are cooled down after recalescence at different undercoolings to show the effect of cooling history on the microstructure.
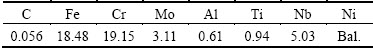
When the undercooled K4169 superalloy melt solidifies, dendrites are formed due to the interface instability induced by thermal and solute diffusion [16]. When △T is less than 80 K, the microstructure consists of dendritic crystals with coarse branching arms (Fig. 1(a)) and the grain size is about 46 μm. The dendrite growth velocity is slow, and dominantly controlled by the solute diffusion [17]. As △T reaches 80 K, dendrite arms are disintegrated to granular grains (Fig. 1(b)) and the grain size is about 42 μm. The dendrite growth velocity is still not high so that the solute concentrates in the liquid discharge from the dendrite, which inevitably improves the interface energy of liquid-solid interface and then leads to the fragileness of the root of dendrite [16]. The model proposed by SCHWARZ et al [18] described the whole fragmentation process. Thus, the dendrites can be remelted to generate granular grain. In the undercooling range of 80-232 K, the microstructure becomes dendrites again which is refined significantly (Fig. 1(c)) and the grain size is about 25 μm at 178 K undercooling. Thermal diffusion predominantly controls the dendrite growth process, which indicates a transition from the equilibrium of a solidification controlled by the solute gradient to a thermally controlled growth owing to a relaxation of diffusional equilibrium at the solid-liquid interface [19]. Thus, the dendrite tip radius decreases derived by thermal diffusion in this undercooling range. When △T>232 K, aforementioned dendrite structure disappears and transforms into granular grain with average size only about 13 μm (Fig. 1(d)). In this undercooling range, high stresses are accumulated in the dendrite skeleton during the extremely rapid solidification process [20], which leads to the dendrite network collapse and fragment, originating from solidification shrinkage and pressure differential driving fluid flow.
With increased undercooling, however, the L/S interface advances rapidly, and thus Nb atoms can be overtaken by the advancing interface. Recalescence effect leads to the grain growth, and then solute segregation of trapped Nb to GBs, which has been detected in Fig. 2. Thus, when the composition of Nb reaches 19.1% in the GBs, it is considered that the eutectic γ+Laves phase can be formed at L/S interface [21]. Meanwhile, an anomalous eutectic can be formed due to rapid nucleation and growth of γ and Laves phases at high △T [22]. For △T<80 K, microstructure exhibits coarse dendrite pattern and intergranular phases are regular γ+Laves eutectic structure (Fig. 2(a)), and growth velocities of γ and Laves phases are similar. Thus, when the eutectic growth begins, γ phase grows associated with the Laves phase, which achieves coupled growth [23], and regular lamella eutectic phase can be found.
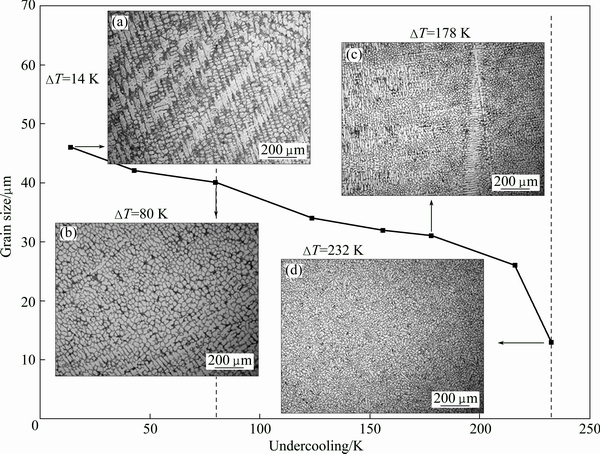
Fig. 1 Grain size and solidification morphology of K4169 superalloy at different undercoolings
For 80 K <△T<232 K, growth velocities of eutectic two phases increase rapidly and gradually show difference due to the different crystal structures of γ and Laves phases. The high growth velocity breaks the symmetry of lamella eutectic γ+Laves phase [24], thus some Laves phases can grow independently. In this undercooling range, microstructure of regular lamella eutectic and single Laves phases are formed (Fig. 2(b)).
A significant characteristic of microstructure appears when the undercooling is above 232 K. The microstructure becomes granular grain again, and intergranular phase becomes the single Laves phase (Fig. 2(c)). Growth velocities of γ and Laves phases continue to increase so that high growth velocity makes solute diffusion more difficult. In this undercooling range, the dendrite growth is controlled by thermal diffusion and the enrichment of solute in the remained small quantity liquid provides an additional driving force. Due to the structure variance of γ and Laves phases, increasing undercooling would further promote variance of growth velocity. Therefore, γ and Laves phases tend to grow independently as free dendrites, which results in a transition from lamellar eutectic growth to divorced dendritic growth [25,26]. Thus, the interdendrite phase transforms from eutectic structure (γ+Laves phase) to single Laves phase.
Microstructures for undercooled melts are influenced by not only the undercooling method but also the cooling history [27]. The highly undercooled solidification predominantly influences the subsequent mode of grain growth. That is to say, the final microstructure is determined by successive contribution from grain refinement to subsequent solid-state grain growth. However, under the same cooling conditions, △T predominantly controls the microstructure and mechanical properties of alloys. Thus, the relationship among mechanical properties, subsequent S/S transformation and microstructure of K4169 superalloy obtained at different undercoolings can be simplified to the relationship between mechanical properties and microstructure.
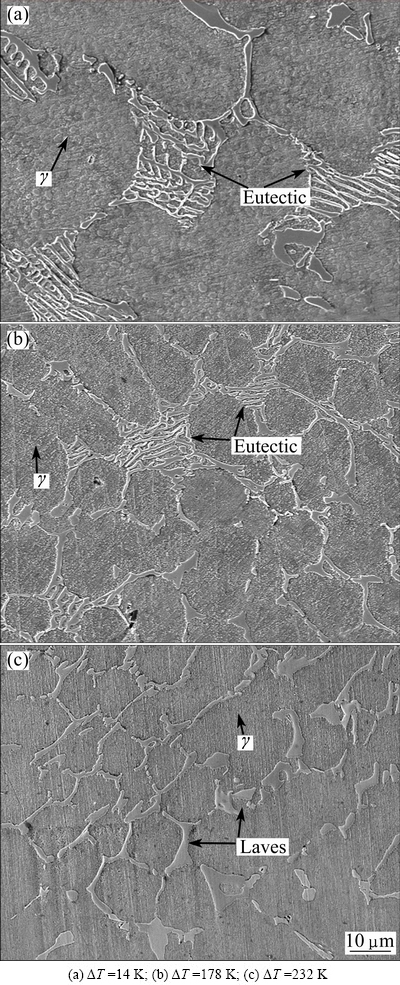
Fig. 2 SEM images of K4169 superalloys at different undercoolings
Figure 3 shows the microstructure of intergranular phase (Fig. 3(a)) and its TEM diffraction patterns (Fig. 3(b)) at undercooling of 232 K. The intergranular phase can conform to be Laves phase with HCP structure [28], whose atomic arrangement and lattice constant are a=0.4831nm, c=0.7881nm. The occurrence of Laves phase can be explained by the pseudobinary phase diagram [29]. In the Nb-rich pseudobinary phase diagram, the equilibrium Laves phase at ambient temperature has hexagonal C14 structure. The room temperature brittleness of the Laves phases is most likely due to their complex TCP structure and the resistance to dislocation motion [30]. Plastic deformation in Laves phases occurs only at temperature above two-thirds of the melting point by the “synchroshear” mechanism, which involves the simultaneous motion of atoms on adjacent atomic planes [31]. This mechanism is difficult at low temperatures, explaining the brittle behavior observed at room temperature [32].
Fig. 3 TEM observations of K4169 superalloys at undercooling of 232 K
3.2 Solute segregation
Solute segregation in solid originates from the nonequilibrium crystallization. Driving force for crystallization is accumulated when the melt is cooled below the equilibrium melting temperature. As a consequence, the undercooled melt will first undergo a rapid solidification stage in which the concentrated release of the latent heat leads to the temperature recalescence of the system. The recalescence makes the dendrite skeleton in the superheated state immediately as soon as they form. The solidus content has to change toward the equilibrium solidus concentration. Intergranular phase is formed from remained melt between dendrite skeletons after recalecence, thus the solute segregation will form. With the increase of undercooling, nucleation rate increases and growth velocity gets faster, which may increase the content of primary solid phase and decrease the fraction of remained melt. Thus, the liquid fraction (fLR) of remained melt is calculated in this study. It is assumed that the recalescence occurs in adiabatic condition, and the solid and the liquid are in equilibrium at the maximum recalescence temperature (TR). The relation below can be derived according to the mass and the energy conservation laws [6]. fLR can be expressed as
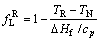
where ΔHf is the enthalpy of fusion; cp is the liquid specific heat; TN is nucleation temperature; fSR +fLR =1, fSR and fLR are the mass fractions of solid and liquid, respectively.
The fLR is calculated by using the thermophysical data of K4169 superalloy [29], as shown in Fig. 4. In Fig. 4, the fLR decreases with increased undercooling, indicating a shortened solidification time and an increased primary γ dendrites. Thus, the content of intergranular phase will decrease with the increased undercooling. In addition, the solute segregation is suppressed because of the multi-solute trapping [33]. So, the deviation of the solute concentration at boundaries from the average value becomes lightened.
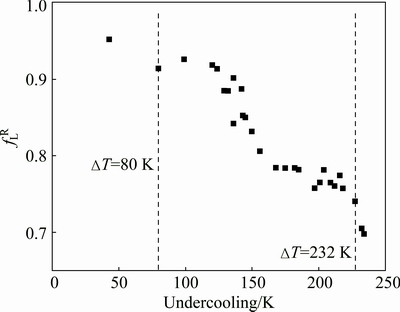
Fig. 4 Liquid fraction (fLR) after recalescence for undercooled K4169 superalloy
3.3 Correlation between microstructure and tensile properties
Figure 5 shows the mechanical properties for undercooled K4169 superalloy at ambient temperature and every property is obtained by the average value of three measurements. For ΔT<80 K, tensile strength is less than 800 MPa. For ΔT>80 K, the tensile strength rises rapidly. The maximum tensile strength (σb) is up to 939.2 MPa when undercooling reaches 232 K. This excellent tensile strength is higher than that of formal cast K4169 superalloy used in an industrial application superalloy [34]. Meanwhile, the values of elongation (δ) rise gradually with the increased undercooling and the largest value is up to 6.5%. Generally, the undercooled alloy possesses high strength and low elongation, which results in poor ductility. The mechanical properties can be affected by different undercooling degrees.
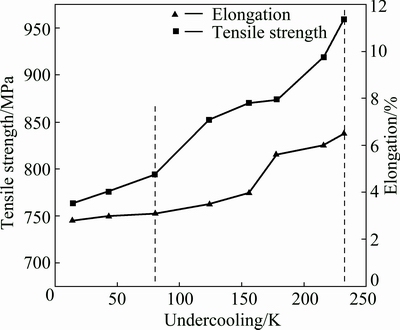
Fig. 5 Mechanical properties of K4169 superalloys at different undercoolings
When undercooling is lower than 80 K, the microstructures are coarse dendrites and γ+Laves eutectic intergranular phase as mentioned above. Due to complex crystal structure of Laves phase [9] and high intergranular phase content, it is hard for dislocation to slip, which leads to crack nucleating and extending from intergranular phase. Meanwhile, the coarse dendrites have straight grain boundary which is conducive to the spread of crack, and the uneven micro deformation concentrated at the grain boundary makes it possible that the dendrite morphology can still be observed on the fractograph, which shows that cracks occur mainly along GB. Thus, the strength and elongation are not high in this case. A similar fractograph is shown at the undercooling of 124 K (Figs. 6(a) and (b)), indicating a typical intergranular fracture.
When undercooling reaches 232 K, the microstructure is completely fine granular grain which can increase the density of GB to enhance the deformation reinforcement. At the same time, intergranular phase transforms from eutectic structure to single Laves phase, and the intergranular phase content decreases significantly. The grain boundary is no longer a favorable way for the spread of crack, which makes the decrease of crack initiation. Laves phase distributes uniformly which can inhibit the dislocation motion and result in strengthening the alloy. Observation of the crack surface at under cooling of 232 K shows that cracks appear on the GB and grain interior (Figs. 6(c) and (d)). Therefore, the strength and elongation are improved in this undercooling range and fracture mechanism of undercooled K4169 superalloys varies from the intergranular fracture to a mixture of transcrystalline and intergranular fracture.
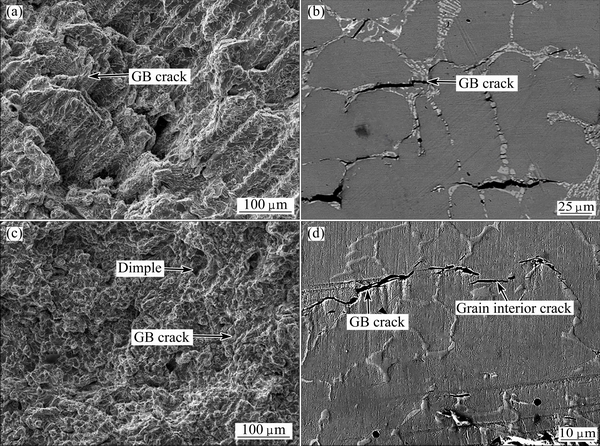
Fig. 6 Microstructures of fracture surface (a) and longitudinal section at ΔT =124 K undercooling (b), microstructures of fracture surface (c) and longitudinal section at ΔT =232 K undercooling (d)
The strength is improved at ambient temperature by the uniform distribution of Laves phase which shows high strength and high creep resistance at high temperatures [7,35]. The strength obtained at the undercooling of 232 K has the same level with fine-grain casting, but may have high strength at high temperature.
4 Conclusions
1) 100 g bulk K4169 superalloy can achieve high undercooling of 232 K by using glass fluxing combined with superheating cycling method and a sequence of microstructure changes emerge at different undercoolings. At the undercooling of 80 K or above 232 K, granular grain appears, whereas the melts undercooled at 14-80 K and 80-232 K solidify to columnar dendritic crystals. The grain size decreases with the increased undercooling.
2) The intergranular phase transforms from regular γ+Laves eutectic phase to single Laves phase at undercooling of 232 K and the content of intergranular phase decreases with the increased undercooling.
3) The uniform distribution of Laves phase and the decrease of grain size and intergranular phase content with undercooling are favorable for the improvement of mechanical properties. The fracture mechanism of undercooled K4169 superalloys varies from the intergranular fracture to a mixture of transcrystalline and intergranular fracture.
References
[1] LIAO J H, BOR H Y, WEI C N, CHAO C G, LIU T F. Influence of microstructure and its evolution on the mechanical behavior of modified MAR-M247 fine-grain superalloys at 871 °C [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2012, 539: 93-100.
[2] SIMS C T, STOLOFF N S, HAGEL W C. Superalloys Π [M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1987: 420-426.
[3] WEI C N, BOR H Y, CHANG L. The effects of carbon content on the microstructure and elevated temperature tensile strength of a nickel-base superalloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 527: 3741-3747.
[4] LIU L, HUANG T, XIONG Y, YANGA M, ZHAOZ L, ZHANG R, LI J S. Grain refinement of superalloy K4169 by addition of refiners: Cast structure and refinement mechanisms [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 394: 1-8.
[5] HERLACH D M. Non-equilibrium solidification of undercooled metallic melts [J]. Materials Science and Engineering R, 1994, 12: 177-272.
[6] LI J F, ZHOU Y H, YANG G C. Mechanical properties of undercooled Cu70Ni30 alloy [J]. Journal of Material Science, 2000, 35(22): 5581-5585.
[7] QU Feng-sheng, LIU Xu-guang, XING Fei, ZHANG Kai-feng. High temperature tensile properties of laser butt-welded plate of Inconel 718 superalloy with ultra-fine grains [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(10): 2379-2388.
[8] MIAO Zhu-jun, SHAN Ai-dang, WU Yuan-biao, LU Jun, XU Wen-liang, SONG Hong-wei. Quantitative analysis of homogenization treatment of INCONEL718 superalloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(5): 1009-1017.
[9] KEITZ A V, SAUTHOFF G. Laves phase for high temperatures-Part Π: Stability and mechanical properties [J]. Intermetallics, 2002, 10: 497-510.
[10] LI Sheng, WANG Hai-feng, LIU Feng. Microstructure and microtexture evolution of undercooled Ni-15%Cu alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(11): 3265-3270.
[11] CHEN S W, ZHANG C, XIA Z X, ISHIKAWA H, YANG Z G. Precipitation behavior of Fe2Nb Laves phase on grain boundaries in austenitic heat resistant steels [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014, 616: 183-188.
[12] CHEN Zheng, WANG Hai-feng, LIU Feng, YANG Wei. Effect of nonlinear liquidus and solidus on dendrite growth in bulk undercooled melts [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20: 490-494.
[13] HERLACH D M, ECKLER K, KARMA A, SCHWARZ M. Grain refinement through fragmentation of dendrites in undercooled melts [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2001, 304-306: 20-25.
[14] CHEN Z, LIU F, ZHANG K, MA Y Z, YANG G C, ZHOU Y H. Description of grain growth in metastable materials prepared by non-equilibrium solidification [J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2010, 313: 81-90.
[15] CHEN Z, CHEN Q, SHEN C J, LIU F. Grain growth and thermal stability accompanying recrystallization in undercooled Ni-3at.%Sn alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 646: 983-989.
[16] LIU Feng. Rapid solidification and special coating of highly undercooled DD3 superalloy. [D]. Xi’an: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2001: 64-90. (in Chinese)
[17] LIU F, CAI Y, GUO X F, YANG G C. Structure evolution in undercooled DD3 single crystal superalloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2000, 291(1-2): 9-16.
[18] SCHWARZ M, KAMA A, ECKLER K, HERLACH D M. Physical mechanism of grain refinement in solidification of undercooled melts [J]. Physical Review Letters, 1994, 73(10): 1380-1383.
[19] LU Y P, LIU F, YANG G C, WANG H P, ZHOU Y H. Grain refinement in solidification of highly undercooled eutectic Ni-Si alloy [J]. Materials Letters, 2007, 61: 987-990.
[20] ZHOU S Y, HU R, LI J S, CHANG H, KOU H C, ZHOU L. Stress induced deformation in the solidification of undercooled Co80Pd20 alloys [J]. Materials Sciences and Engineering A, 2011, 528: 973-977.
[21] KNOROVSKY G A, CIESLAK M J, HEADLEY T J, ROMIG A D, HAMMEFTER W F. INCONEL 718: A solidification diagram [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1989, 20: 2149-2158.
[22] LIU Li, MA Xiao-li, HUANG Qi-sen, LI Jin-fu, CHENG Xian-hua, ZHOU Yao-he. Solidification process and microstructure evolution of bulk undercooled Co-Sn alloys [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(1): 289-293.
[23] AHMAD R, COCHRANE R F, MULLIS A M. The formation of regular αNi-γ(Ni31Si12) eutectic structures from undercooled Ni-25 at.% Si melts [J]. Intermetallics, 2012, 22: 55-61.
[24] GOETZINGER R, BARTH M, HERLACH D M. Mechanism of formation of the anomalous eutectic structure in rapidly solidification Ni-Si, Co-Sb and Ni-Al-Ti alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 1998, 46(5): 1647-1655.
[25] YANG C L, LIU F, YANG G C, CHENY Z, LIU N, ZHOUY H. Microstructure and phase selection in bulk undercooled Fe-B eutectic alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2007, 441: 101-106.
[26] LI M, NAGASHIO K, KURIBAYASHI K. Reexamination of the solidification behavior of undercooled Ni-Sn eutectic melts [J]. Acta Materialia, 2002, 50: 3239-3250.
[27] CHEN Z, CHEN Q, LIU F, YANG X Q, FAN Y, ZHANG C H, LIU A M. The influence of solid-state grain growth mechanism on the microstructure evolution in undercooled Ni-10at.%Fe alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 622: 1086-1092.
[28] MANIKANDAN S G K, SIVAKUMAR D, RAO P K, KAMARAJ M. Laves phase in alloy 718 fusion zone-microscopic and calorimetric studies [J]. Materials Characterization, 2015, 100: 192-206.
[29] NASTAC L, STEFANESCU D M, Macrotransport-solidification kinetics modeling of equiaxed dendritic growth: Part П. Computation problems and validation on INCONEL 718 superalloy casting [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions, 1996, 27(12): 4075-4083.
[30] SCUDINO S, DONNADIEU P, SURREDDI K B, NIKOLOWSKI K, STOICA M, ECKERT J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Laves phase-reinforced Fe-Zr-Cr alloys [J]. Intermetallics, 2009, 17(7): 532-539.
[31] KURMAR K S, HAZZLEDINE P M. Polytypic transformations in Laves phases [J]. Intermetallics, 2004, 12: 763-770.
[32] HAZZLEDINE P M. Twinning by synchroshear in the cubic Laves phases [C]//Twinning in Advanced Materials. Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1994: 403.
[33] RUAN Y, DAI F P. Rapid dendrite growth subjected to multi-solute trapping in an undercooled Fe-based quaternary alloy [J]. Intermetallics, 2012, 25: 80-85.
[34] YANG A M. Study of structure refinement and optimization of mechanical proprieties for superalloy K4169 [D]. Xi’an: Northwestern polytechnical University, 2002: 80. (in Chinese)
[35] LEE S B, LIAW P K, LIU C T, CHOU Y T. Cracking in Cr-Cr2Nb eutectic alloys due to thermal stresses [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1999, 268(1-2): 184-192.
张可人1,谢发勤2,胡 锐1,吴向清2
1. 西北工业大学 凝固技术国家重点实验室,西安 710072;
2. 西北工业大学 航空学院,西安 710072
摘 要:采用循环过热与熔融玻璃净化相结合的方法使K4169 高温合金获得了14~232 K过冷度。采用透射电子显微镜(TEM)、扫描电子显微镜(SEM)和光学显微镜等手段研究过冷K4169高温合金枝晶形貌以及相组成。研究发现,枝晶形貌、晶粒尺寸和晶间相都会随着过冷度的增加而发生明显改变。同时,系统研究过冷K4169高温合金凝固组织与力学性能之间的关系。实验结果表明,晶粒尺寸和晶间相含量的减小以及Laves相的均匀分布提高了合金的抗拉强度和伸长率,并且当过冷度达232 K时,合金具有最优力学性能,抗拉强度为932.2 MPa,伸长率为6.5%。
关键词:K4169高温合金;深过冷;Laves相;力学性能;显微组织
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Foundation item: Project (2011CB610406) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China
Corresponding author: Rui HU; Tel: +86-29-88491764; Fax: +86-29-88460294; E-mail: rhu@nwpu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(16)64303-0

