DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2018.10.003
钢中非金属夹杂物对时频域超声参量的影响
肖会芳1,陈丹2,徐金梧2
(1. 北京科技大学 机械工程学院,北京,100083;
2. 北京科技大学 钢铁共性技术协同创新中心,北京,100083)
摘要:通过建立包含夹杂物的二维金属板超声测量数值分析模型,研究超声信号随夹杂物的深度、厚度和类型等属性特征的变化规律,并通过超声显微镜和扫描电镜实验验证模型的有效性。研究结果表明:纵波声速随夹杂物厚度的增加呈线性递增,含有Al2O3夹杂物的声速最大且增速最快,含有MnS夹杂物的声速最小且增速最慢,纵波声速可以作为判定内部是否存在夹杂物的参量;不同超声参量随入射波长的变化关系曲线,可用于判定夹杂物的厚度;当夹杂物深度位于钢板厚度的中间时,衰减系数最大,且含有MnS夹杂物引起的声波幅值衰减最严重,含有TiN夹杂物的声波幅值衰减最小。
关键词:非金属夹杂物;超声参量;数值仿真;多值域;影响特性
中图分类号:TH14 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2018)10-2381-10
Effect of embedded inclusion in steel on ultrasonic parameters in time frequency domain
XIAO Huifang1, CHEN Dan2, XU Jinwu2
(1. School of Mechanical Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China;
2. Collaborative Innovation Center of Steel Technology,University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China)
Abstract: A numerical analytical model of two-dimensional isotropic plate with embedded inclusion was established, and the variation of ultrasonic signals with the depth, thickness and type of inclusions was studied. The validity of the model was verified using experimental results from ultrasonic microscope measurement and scanning electron microscope. The results show that the longitude sound velocity increases linearly with the thickness of inclusion. The Al2O3 inclusion has the largest sound velocity and the fastest increasing rate, while the sound velocity of MnS inclusion has the smallest sound velocity and the slowest rising rate. The longitudinal sound velocity can be used to determine the existence of inclusion. The relationship between different ultrasonic parameters and incident wavelength can be used to determine the thickness of inclusions. When the inclusion is at the center of the steel plate, the attenuation coefficient has the maximum value, and the attenuation of MnS inclusion is the maximum, while the attenuation of TiN inclusion is the minimum.
Key words: inclusion; ultrasonic parameters; numerical simulation; multi-domain; influence effect
钢中非金属夹杂物的存在破坏了材料的连续性,严重影响钢的加工性能,降低了钢的承载能力和疲劳寿命。对钢中夹杂物特征包括位置、尺寸、类型等的准确检测不仅能够反映钢的冶炼工艺,而且能为夹杂物的有效控制提供基础[1-7]。超声无损检测方法由于对样品没有破坏性,能够实现夹杂物的空间定位,同时能有效避免大型夹杂物的漏检,目前已被广泛应用于材料内部缺陷的检测[8-12]。要实现钢内部夹杂物的超声检测,最关键的问题是如何通过测量获得的回波信号或超声扫描图像辨识夹杂物的属性特征。但是,直接的超声回波信号只能较为准确地判断材料内部缺陷位置信息,而对夹杂物的类型难以确定,因而,明确夹杂物的类型、尺寸和深度等属性特征对超声测量信号的影响规律,对超声方法检测材料内部夹杂物具有重要的理论与实际意义。本文作者通过建立包含夹杂物的二维金属板超声测量模型,采用有限元数值计算的方法,对具有不同深度、不同厚度、不同类型夹杂物的材料内部超声波场进行计算,获得不同深度、不同厚度、不同类型夹杂物的回波信号,并分别计算其缺陷回波信号和底面回波信号的4个时域特征参量和2个频域特征参量,获得不同类型夹杂物的多值域超声参量随夹杂物厚度和深度的变化规律,并进行实验验证,为非金属夹杂物的超声检测提供参考。
1 含夹杂物的二维金属板模型
1.1 模型描述
研究内部夹杂物对超声参量影响规律的二维金属板超声测量模型示意图,如图1所示。超声检测采用水浸纵波脉冲回波法,即采用水作为耦合介质传递超声波,且仅有1个换能器同时激发和接收超声波信号。二维矩形金属板的厚度为H,厚度为D、深度为h的夹杂物位于金属板内部。压电晶片半径为a,几何焦距为F的聚焦换能器产生的超声波垂直入射,经过耦合介质水传播至材料内部,并在水-钢界面发生折射在材料内部二次聚焦,聚焦深度为d。通过调整水程厚度Hw,保证换能器在材料内部的焦点位于夹杂物上表面,以获得最大的横向分辨率和声压强度,即d=h。
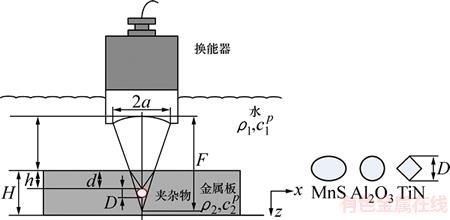
图1 含夹杂物的二维金属板超声测量模型示意图
Fig. 1 Ultrasonic measurement model a two-dimensional isotropic panel with embedded inclusion
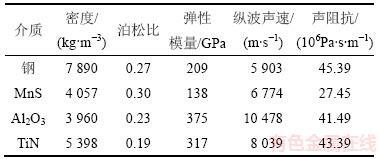
由于夹杂物的存在改变了金属板内超声波的传播特性,引起了缺陷反射回波和底面发射回波超声特征参量的变化,因而,回波的超声参量反映了夹杂物的特性信息。本文选取3种典型的夹杂物即塑性夹杂物MnS、脆性夹杂物Al2O3和高硬度夹杂物TiN进行分析。由于轧制过程中不同类型夹杂物的变形程度和形状不同,塑性夹杂物经轧制后通常为扁平的条状或片状、脆性夹杂物经轧制后一般为球状或链状、而高硬度夹杂物在轧制前后的形状不变,通常为立方体,因此,假设3种典型夹杂物的形状分别为椭圆形、球形和菱形[13]。不同类型夹杂物的材料参数和声参数如表1所示。对3种类型的夹杂物分别建立包含不同厚度和不同深度夹杂物的二维金属板超声测量模型,采用有限元方法,计算获得金属板上表面的反射回波曲线,并分别对缺陷回波和底面回波进行超声特征参量提取,获得超声特征参量随夹杂物厚度和深度的变化规律。计算中,钢板的厚度H=1.5 mm。
表1 不同介质的材料参数与声参数
Table 1 Material and ultrasonic parameters of different mediums
采用多物理场仿真软件COMSOL求解超声波场,并计算获得回波曲线。换能器的激励载荷是中心频率fc=50 MHz,时间Δt=60 ns的压力载荷,如图2所示。其在钢中的纵波波长λ=0.12 mm。网格尺寸为λ/60,时间步长为0.2 ns。金属板的左右设置吸收边界,以消除计算模型宽度有限引入的边界反射效应对内部超声波场的影响[14-15]。计算时间t=1.9 μs,保证金属板上表面的回波信号中能够包含二次底面回波。
1.2 有限元计算方法有效性验证
采用有限元方法计算无夹杂物缺陷时的金属板内部声场分布,并与理论模型的计算结果进行对比,验证本文有限元模型的准确性。仿真计算获得的中心频率为50 MHz换能器在水-钢两相介质中的瞬态声场分布,如图3(a)所示。从图3(a)可知:在钢中传播的声波在焦点位置(z=0.75 mm)处汇聚,而被水-钢界面反射的声波以近似平面波的方式反向传播。提取焦平面处的径向声压分布,并与多元高斯声束模型(MGB)计算的径向声压分布对比,结果如图3(b)所示。其中,多元高斯声束模型的径向声压分布表达式为[16-17]
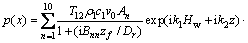
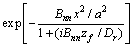 (1)
(1)
式中:T12为水-钢界面的透射系数,T12=2/[1+(ρ1/ρ2)(c1/c2p)],ρ1为水的密度,c1为水中声速,ρ2为钢的密度,c2p为钢中的纵波声速;v0为换能器表面的速度;zf为焦平面所在位置且zf=Hw+zcp/c1;Dr为瑞利距离且Dr=k1a2/2,k1=ω/c1为水中的波数,k1=ω/c2p为钢中的波数;Bnn=Bn+iDr/F为聚焦换能器的高斯声束系数,An和Bn分别为Wen和Breazeale系数[18]。从图3(b)可知:有限元计算获得的焦平面处径向声压分布与多元高斯声束模型得到的径向声压分布基本完全一致,说明了本文有限元方法的有效性。
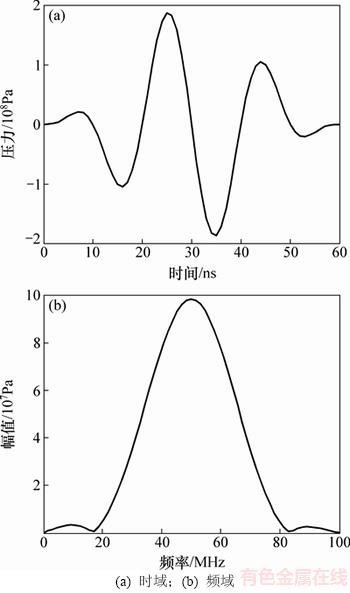
图2 激励载荷的时域和频域图
Fig. 2 Excitation signal in time and frequency domains
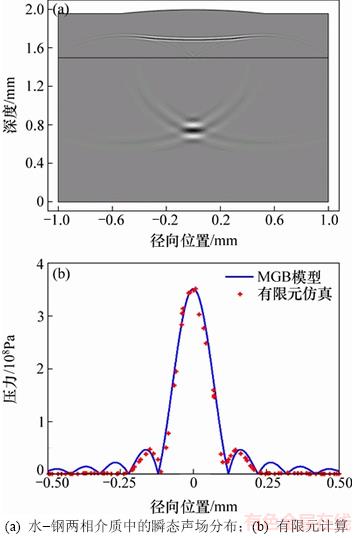
图3 水-钢两相介质中的瞬态声场分布和有限元计算的径向声压与MGB模型计算结果对比图
Fig. 3 Pressure distribution in water-solid mediums and comparison of radial pressure between FEM and MGB model
2 计算结果与分析
对含有不同厚度和不同深度夹杂物的反射回波,分别提取4个时域超声特征参量和4个频域特征超声参量,分析超声参量随夹杂物厚度和夹杂物深度的变化规律。由于2次回波的波形更为复杂,因此,主要采用1次回波进行超声特征参量计算。时域超声参量包括:纵波声速cp、衰减系数α、1次缺陷回波正峰值pd和1次底面回波正峰值pb。其中,纵波声速cp的表达式为
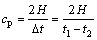 (2)
(2)
其中:H为金属板厚度;t1为界面波的峰值对应的时刻;t2为1次底面回波的峰值对应的时间。衰减系数α的表达式为[19]
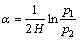 (3)
(3)
其中:p1为1次底面回波的正峰值;p2为二次底面回波的正峰值。衰减系数α越小,说明衰减越严重。缺陷回波正峰值pd表达式为
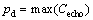 (4)
(4)
其中:Cecho为1次缺陷回波。底面回波正峰值pb表达式为
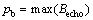 (5)
(5)
其中:Becho为1次底面回波。
频域超声特征参量包括:一次底面回波峰值频率fp和一次底面回波-6 dB频谱带宽fb。其中,回波信号的峰值频率fP为幅频曲线最大幅值处对应的频率,回波信号-6 dB频谱带宽fb为幅频曲线最大幅值50%处的横线与频谱曲线2个交点之间的频率差。
2.1 不同厚度夹杂物的超声参量特性
保持夹杂物的深度h=0.75 mm不变,改变夹杂物的厚度D为0.05,0.08,0.11,0.14,0.17,0.20和0.23 mm,计算获得材料上表面反射回波并分别提取时域和频域超声参量。D=0.05 mm和D=0.17 mm的3种不同类型夹杂物,材料上表面接收到的反射回波信号,如图4所示。从图4可知:在界面波和一次底面回波之间、一次底面回波和二次底面回波之间,可以观察到明显的缺陷回波。二次缺陷回波和二次底面回波的幅值明显低于一次缺陷回波和一次底面回波幅值,且时间展宽增大,表明经过多次反射后,超声波发生了衰减和散射。从图4还可知:不同厚度的同类夹杂物,其缺陷回波和底面回波的幅值、波形均有所差异。
对3种类型夹杂物,计算获得的时域超声参量随夹杂物尺寸的变化关系曲线,如图5所示。其中,横坐标为夹杂物尺寸,定义为夹杂物厚度D与波长λ的比值。图5(a)中,含夹杂物钢材的理论声速计算公式为
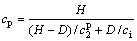 (6)
(6)
其中:ci为夹杂物中的纵波声速,如表1所示。从图5(a)可知:仿真计算获得的声速与理论计算结果基本完全一致,仿真结果稍大于理论值。这是由于式(6)的理论声速假设波遇到夹杂物时的传播路径为直线,而实际超声波遇到夹杂物时会绕射,传播路径为曲线,引起声速增大。
从图5(a)可知:不同类型夹杂物,纵波声速均随着夹杂物尺寸呈线性递增,夹杂物尺寸相同时,含有MnS夹杂物的声速最小,含有Al2O3夹杂物的声速最大。从表1可知:夹杂物的声速均大于钢基体的声速,且有cp(Al2O3)>cp(TiN)>cp(MnS),因此,当钢内部含有夹杂物时,通过超声回波计算的声速大于纯钢基体的声速且声速随着夹杂物尺寸增大而递增,含有Al2O3夹杂物的增速最快。因此,对于夹杂物的超声检测而言,当检测回波的纵波声速大于钢基体声速时,可以作为判定内部是否存在夹杂物的参考参量。
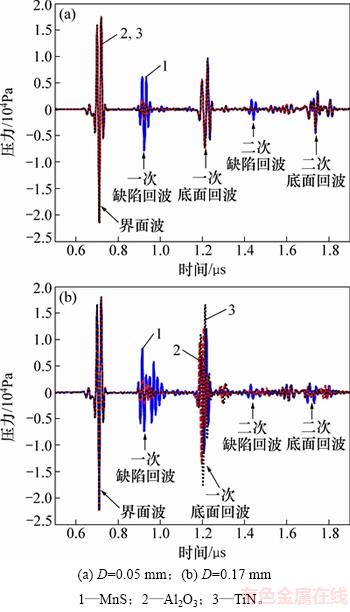
图4 D=0.05 mm和D=0.17 mm的不同类型夹杂物的反射回波信号
Fig. 4 Reflected pressure signals for different inclusion types with D=0.05 mm and D=0.17 mm
从图5(b)可知:当钢内含有MnS夹杂物时,衰减系数最小,引起的超声衰减量最大;TiN夹杂物的衰减系数最大,引起的超声衰减量最小。同时,不同类型夹杂物,衰减系数随夹杂物尺寸均呈先增大后减小的变化规律,存在最大值。对Al2O3和TiN夹杂物,最大衰减系数对应的夹杂物尺寸D/λ分别为1.42和1.66,即夹杂物厚度与声波波长的比值约为1.5。对MnS夹杂物,最大衰减系数对应的夹杂物尺寸D/λ=3.33,远比Al2O3夹杂物和TiN夹杂物的大。
从图5(c)可知:不同类型夹杂物的缺陷回波正峰值随夹杂物尺寸均呈先减小后增大的变化规律,存在最小值,最小值对应的夹杂物尺寸D/λ约为1,即当夹杂物厚度等于入射声波的波长时,缺陷反射回波的幅值最小;当夹杂物厚度等于入射声波的波长时,超声波的绕射现象最严重,反射能力最弱,引起缺陷反射回波幅值最小。对不同类型的夹杂物,MnS夹杂物的声阻抗与钢基体声阻抗差异最大,TiN夹杂物的声阻抗与钢基体的声阻抗差异最小,因而,MnS夹杂物的缺陷反射回波幅值最大,TiN夹杂物最小。从图5(d)可知:不同类型夹杂物,底面回波的正峰值随夹杂物尺寸增加递增,含TiN夹杂物的底面反射回波幅值最大,含MnS夹杂物的反射回波幅值最小。
对图4(a)所示D=0.05 mm的不同类型夹杂物反射回波信号中的一次缺陷回波和一次底面回波进行快速傅里叶变换后的频域曲线,如图6所示。从图6可知:对中心频率为50 MHz、频率范围在20~80 MHz的入射超声波,缺陷回波和底面回波的频率范围均为20~80 MHz,缺陷回波的峰值频率大于50 MHz,底面回波的峰值频率小于50 MHz。
对3种类型的夹杂物,分别对不同尺寸夹杂物底面回波的幅频曲线进行频域超声参量计算,获得的频域超声参量随夹杂物尺寸的变化关系曲线如图7所示。图7(a)和7(b)所示的底面回波峰值频率、底面回波带宽随夹杂物尺寸增加均呈先增大后减小的变化规律,存在最大值;最大值对应的夹杂物尺寸D/λ分别为1.15和0.90,即当夹杂物厚度约等于入射声波的波长时,底面反射回波的峰值频率和带宽均最大;对3种不同类型夹杂物,TiN夹杂物的峰值频率和带宽最大,MnS夹杂物最小,表明MnS夹杂物对入射声波中心频率和带宽范围频率成分衰减最显著。
上述时域和频域超声参量随夹杂物尺寸的计算结果显示:底面回波峰值、底面回波峰值频率和带宽均在夹杂物尺寸约为1时出现极值,即当夹杂物厚度与入射声波波长相等时,超声参量出现极值。该特性可以为超声准确测定夹杂物厚度提供基础。在实际检测过程中,可以采用不同中心频率的探头测量获取多个回波曲线,绘制不同的超声参量随入射波长的变化曲线,曲线的极值点对应的波长即为夹杂物的厚度。
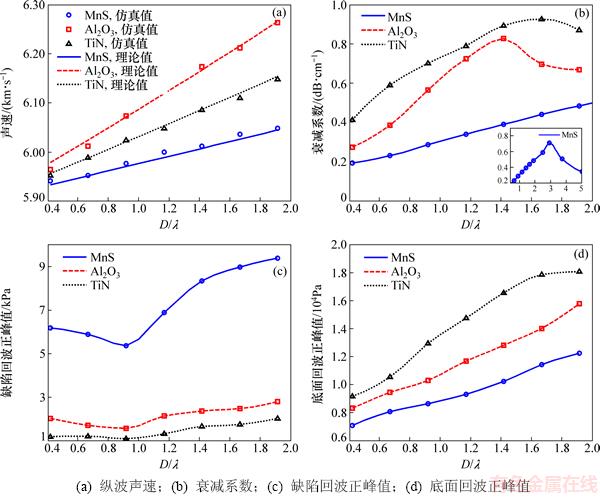
图5 时域超声参量随夹杂物尺寸的变化关系曲线
Fig. 5 Plots of time domain ultrasonic parameters versus inclusion size

图6 D=0.05 mm的不同类型夹杂物的幅频曲线
Fig. 6 Plots of amplitude-frequency relationship for different inclusion types with D=0.05 mm
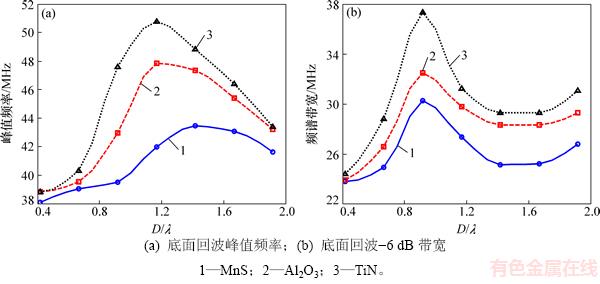
图7 频域超声参量随夹杂物尺寸的变化关系曲线
Fig. 7 Plots of frequency domain ultrasonic parameters versus inclusion size
2.2 不同深度夹杂物的超声参量特性
保持夹杂物的厚度D=0.10 mm不变,改变夹杂物深度h为0.45,0.55,0.65,0.75,0.85和0.95 mm,计算获得金属板上表面反射回波并分别提取时域和频域超声参量。对于深度h=0.45 mm和h=0.75 mm的3种不同类型夹杂物,金属板上表面接收到的反射回波信号如图8所示。从图8可知:当夹杂物深度变化时,缺陷回波到达的时间不同。根据缺陷回波与界面波的时间间隔,可以计算缺陷的深度位置。
对3种类型的夹杂物计算获得的时域超声参量随夹杂物深度的变化关系曲线,如图9所示。其中,横坐标为夹杂物深度与钢板厚度的比值。从图9(a)可知:夹杂物深度变化时,纵波声速保持不变。从图9(b)可知:衰减系数随夹杂物深度变化呈先减小再增大的变化规律,最小值出现在h/H=0.5,即当夹杂物位于板厚的中间时,衰减系数最小,衰减最严重;随着夹杂物深度向上和向下偏离中心厚度,衰减系数逐渐增大,与图5(b)所示结果一致,含TiN夹杂物时的衰减系数最大,含MnS夹杂物时的衰减系数最小,即MnS夹杂物引起的声波幅值衰减最严重。从图9(c)和9(d)可知:缺陷回波正峰值和底面回波正峰值均随夹杂物深度的增加递增,MnS夹杂物的缺陷回波幅值最大,而底面回波幅值最小,TiN夹杂物的缺陷回波幅值最小,而底面回波幅值最大。
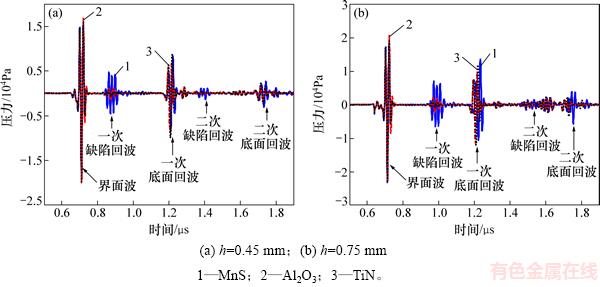
图8 h=0.45 mm和h=0.75 mm的不同类型夹杂物的反射回波信号
Fig. 8 Reflected pressure signal for different inclusion types with h=0.45 mm and h=0.75 mm

图9 时域超声参量随夹杂物深度的变化关系曲线
Fig. 9 Plots of time domain ultrasonic parameters versus inclusion depth
对3种类型的夹杂物,计算获得的频域超声参量随夹杂物深度的变化关系曲线如图10所示。从图10(a)和(b)可知:随着夹杂物深度增加,底面回波的峰值频率和带宽均存在最小值,最小值对应的夹杂物深度h/H=0.5,即当夹杂物位于板厚的中间时,夹杂物对入射声波中心频率和带宽范围频率成分的衰减最显著,这与图9(b)所示的h/H=0.5对应最大衰减一致。
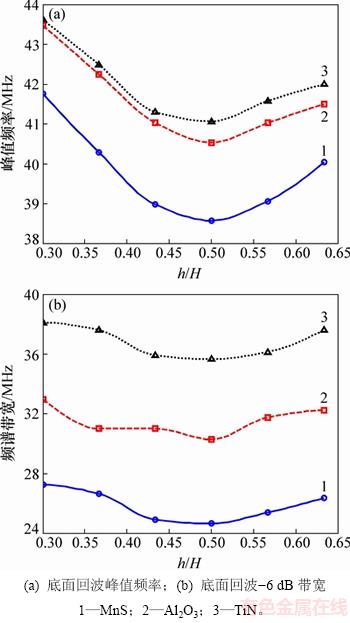
图10 频域超声参量随夹杂物深度的变化关系曲线
Fig. 10 Plots of frequency domain ultrasonic parameters versus inclusion depth
3 实验测试
为了进一步验证上述仿真计算结果的准确性,采用超声扫描显微镜装置PVA SAM300对厚度为1.5 mm的2个镀锌板样品进行超声扫描实验测试。与仿真计算条件保持一致,实验测试选取的探头为中心频率50 MHz,晶片直径3 mm,几何焦距10 mm的水浸式点聚焦探头。实验数据的采样频率为5 GHz,对应的时间间隔为0.2 ns,与仿真计算的时间步长0.2 ns相同。机械扫查机构的扫描步进精度为3 μm。样品1号内部不同深度检测到3个缺陷,不同深度缺陷的时域波形如图11所示。不同深度缺陷的缺陷回波与界面波之间的时间间隔(t)分别为0.231,0.304和0.382 μs,计算获得的缺陷深度(h)分别为0.66,0.87和1.04 mm。缺陷的深度和最大长度如表2所示。其中,缺陷的最大长度采用C扫图像的-6 dB下降法确定[20-21]。
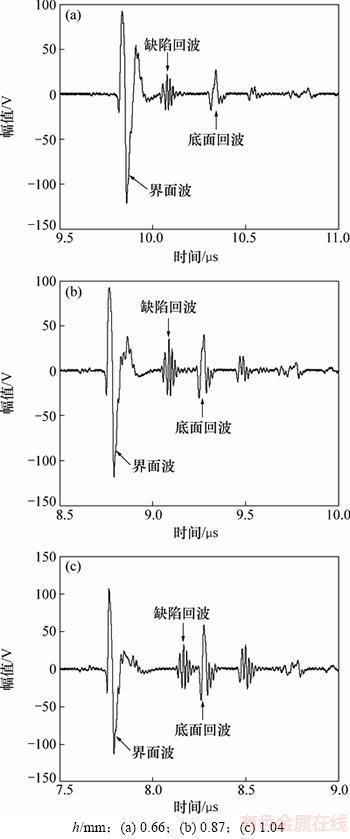
图11 不同深度缺陷的时域波形
Fig. 11 Measured time domain signal of crack with different depths
为了进一步验证超声检测的缺陷是否为夹杂物并判定夹杂物的类型,对超声检测后的样品进行切割、打磨和抛光处理,使缺陷暴露于表面,用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)观察并进行能谱分析,结果如图12所示。其中,Al元素和O元素的原子数分数分别为36.75%和52.21%,原子数之比约为2:3,能谱结果显示夹杂物的类型为Al2O3。
表2 1号样品实验测试的缺陷深度与最大长度
Table 2 The maximum length and depth of inclusions in experimental tests for sample one
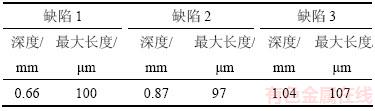
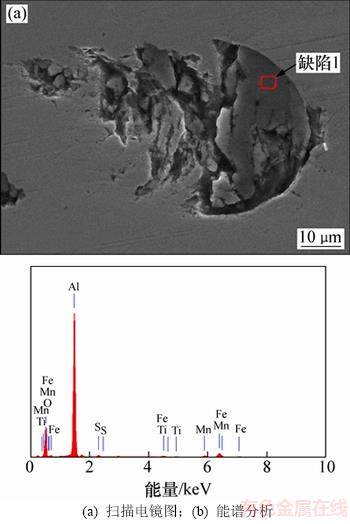
图12 缺陷1的扫描电镜图和能谱分析
Fig. 12 SEM image and energy spectrum of defect 1
从表2所示的实验结果可知:样品1号中检测到的3个夹杂物尺寸差异较小,而深度差异较大。因此,对样品1号不同深度Al2O3夹杂物的时域波形进行纵波声速特征值和衰减系数计算,并与图9(a)和9(b)的仿真计算结果进行对比,如图13所示。从图13可知:实验测试计算的声速和衰减系数与仿真计算结果具有较好的一致性,证明了仿真计算结果的正确性。同时,仿真计算获得的夹杂物的类型、厚度和深度等属性特征对超声测量信号的影响规律可为实际非金属夹杂物的超声检测提供基础与参考。
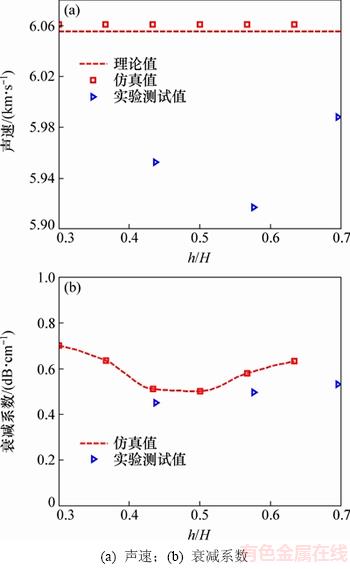
图13 仿真计算结果与实验结果对比
Fig. 13 Comparison between numerical and experimental results
4 结论
1) 当钢材内部存在夹杂物时,纵波声速随夹杂物尺寸的增加呈线性递增,而不随夹杂物的深度变化。含有Al2O3夹杂物的声速最大且增速最快,含有MnS夹杂物的声速最小且增速最慢,纵波声速可以作为判定内部是否存在夹杂物的参量。
2) 当夹杂物厚度与入射声波波长相等时,时域和频域超声参量均出现极值。该特性可以为超声准确测定夹杂物尺寸提供基础。在实际检测过程中,可以采用不同中心频率的探头测量获取多个回波曲线,绘制不同超声参量随入射波长的变化曲线,曲线的极值点对应的波长即为夹杂物的厚度。
3) 当夹杂物深度位于钢板厚度的中间时,衰减系数和底面回波频域参量均出现极值,衰减系数最大,夹杂物对入射声波中心频率和带宽范围频率成分的衰减最显著,且含有MnS夹杂物引起的声波幅值衰减最严重,含有TiN夹杂物的声波幅值衰减最小。
参考文献:
[1] GIRAULT J M, M NIGOT S. Contrast optimization by metaheuristic for inclusion detection in nonlinear ultrasound imaging[J]. Physics Procedia, 2015, 70(1): 614-617.
NIGOT S. Contrast optimization by metaheuristic for inclusion detection in nonlinear ultrasound imaging[J]. Physics Procedia, 2015, 70(1): 614-617.
[2] MEISNER L L, MARKOV A B, PROSKUROVSKY D I, et al. Effect of inclusions on cratering behavior in TiNi shape memory alloys irradiated with a low-energy, high-current electron beam[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2016, 302: 495-506.
[3] 王新华, 李金柱, 姜敏, 等. 高端重要用途特殊钢非金属夹杂物控制技术研究[J]. 炼钢, 2017, 33(2): 50-56.
WANG Xinhua, LI Jinzhu, JIANG Min, et al. Investigation on technology of non-metallic inclusion control for high grade special steels of important uses[J]. Steelmaking, 2017, 33(2): 50-56.
[4] 马超, 罗海文. 扫描电镜和电解萃取法用于超洁净钢中夹杂物的表征[J]. 冶金分析, 2017, 37(8): 1-8.
MA Chao, LUO Haiwen. Inclusion particles of super-clean steel examined by both scanning electron microscope and electrolytic extraction[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2017, 37(8): 1-8.
[5] 陈兴富, 董国卿, 孙建勋, 等. 离心铸造高镍铬复合轧辊中夹杂物分析[J]. 铸造, 2017, 66(11): 1213-1219.
CHEN Xingfu, DONG Guoqing, SUN Jianxun, et al. Analysis of inclusions in high Nickel-chrome composite roll enhanced by centrifugal casting[J]. Foundry, 2017, 66(11): 1213-1219.
[6] 杨锋功, 杨华峰, 战东平, 等. 钢包软吹氩时间对GCr15 轴承钢中夹杂物的影响[J]. 材料与冶金学报, 2017, 16(4): 246-249.
YANG Fenggong, YANG Huafeng, ZHAN Dongping, et al. Effect of ladle soft argon blowing time on inclusions of GCr15 bearing steel in tundish[J]. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2017, 16(4): 246-249.
[7] 刘浏, 范建文, 王品, 等. 轴承钢精炼中大型夹杂物来源的示踪[J]. 钢铁, 2017, 52(9): 34-41.
LIU Liu, FAN Jianwen, WANG Pin, et al. Generation mechanism of large inclusions during bearing steels refining process by tracer method[J]. Iron and Steel, 2017, 52(9): 34-41.
[8] MOGHADDAM S M, SADEGHI F, PAULSON K, et al. A 3D numerical and experimental investigation of microstructural alterations around non-metallic inclusions in bearing steel[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2016, 88: 29-41.
[9] MEZIL S, CHIGAREV N, TOURNAT V, et al. Evaluation of crack parameters by a nonlinear frequency-mixing laser ultrasonics method[J]. Ultrasonics, 2016, 69: 225-235.
[10] 陈振华, 史耀武, 赵海燕, 等. 微小缺陷的非线性超声检测及其成像技术[J]. 声学学报, 2010, 35(1): 9-13.
CHEN Zhenhua, SHI Yaowu, ZHAO Haiyan, et al. Nonlinear ultrasonic testing and imaging for tiny flaw[J]. Acta Acustica, 2010, 35(1): 9-13.
[11] 刘增华, 余锋祥, 于洪涛, 等. 基于群速度校准的超声导波技术及在复合材料缺陷检测中的应用[J]. 机械工程学报, 2012, 48(20): 8-15.
LIU Zenghua, YU Fengxiang, YU Hongtao, et al. Ultrasonic guided wave technology based on group velocity calibration and its application for defect detection in composite plates[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2012, 48(20): 8-15.
[12] 宋雨珂, 汪小凯, 华林. 轴类零件内部缺陷超声检测与重构方法研究[J]. 应用声学, 2016, 35(2): 109-115.
SONG Yuke, WANG Xiaokai, HUA Lin. Research on ultrasonic test and reconstruction method of the internal defects in shaft parts[J]. Journal of Applied Acoustics, 2016, 35(2): 109-115.
[13] 王国承. 钢中夹杂物尺寸控制理论与技术[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2015: 5-10.
WANG Guocheng. Size control theory and technology of inclusion in steel[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2015: 5-10.
[14] BELLIS C, BONNET M. Qualitative identification of cracks using 3D transient elastodynamic topological derivative: formulation and FE implementation[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2013, 253: 89-105.
[15] LI R, NATSUKI T, NI Q Q. A novel dynamic stress analysis in bimaterial composite with defect using ultrasonic wave propagation[J]. Composite Structures, 2015, 132: 255-264.
[16] KIM S J, SONG S J, SCHMERR L W. Modeling ultrasonic pulse-echo signals from a flat-bottom hole in immersion testing using a multi-Gaussian beam[J]. Journal of Nondestructive Evaluation, 2004, 23: 11-19.
[17] XIAO Huifang, SUN Yunyun, CHEN Dan, et al. Prediction of flat-bottom hole signals received by a spherically focused transducer for an ultrasonic pulse echo immersion testing[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2016, 27: 115001-1-11.
[18] WEN J J, BREAZEALE M A. A diffraction beam field expressed as the superposition of Gaussian beams[J]. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1988, 83(5): 1752-1756.
[19] NURUL I M, ARAI Y, ARAKI W. Initiation of fatigue crack growth in austenitic stainless steel detected by ultrasound: role of in-plane orientation[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2012, 556(11): 309-318.
[20] YANG S, YOON B, KIM Y. Using phased array ultrasonic technique for the inspection of straddle mount-type low-pressure turbine disc[J]. NDT & E International, 2009, 42(2): 128-132.
[21] SONG Yongfeng, WANG Yiling, NI Peijun, et al. Flaw sizing method based on ultrasonic dynamic thresholds and neural network[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2016, 1706: 180007-1-9.
(编辑 杨幼平)
收稿日期:2017-11-07;修回日期:2018-03-02
基金项目(Foundation item):国家“十二五”科技支撑计划项目(2015BAF30B00);国家自然科学基金资助项目(51775037)(Project(2015BAF30B00) supported by the National Science and Technology Program of China during the 12th Five-Year Plan Period; Project(51775037) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China)
通信作者:肖会芳,博士,副教授,从事材料超声无损检测技术研究;E-mail:huifangxiao@ustb.edu.cn