新型抗热腐蚀镍基高温合金K44的高温低周疲劳行为
李志军, 周兰章, 郭建亭, 姚 俊
(中国科学院 金属研究所 高温合金部, 沈阳 110016)
摘 要: 研究了K44合金900℃低周疲劳性能和断裂行为。 研究结果表明, 该合金在循环形变过程中, 首先表现出起始循环硬化或软化, 随后循环稳定及最终失稳断裂三阶段。 高应变幅下位错切割γ′相形成层错, 降低变形阻力, 合金表现出循环软化行为; 低应变幅下位错在γ′相前塞积造成位错可动性降低, 合金表现出循环硬化行为。 疲劳裂纹主要萌生于试样表面或近表面缺陷处, 以穿晶方式扩展; 合金基体中块状碳化物对裂纹扩展起阻滞作用。
关键词: 抗热腐蚀高温合金; K44; 低周疲劳; 循环应力响应; 疲劳裂纹 中图分类号: TG172.6
文献标识码: A
Low cycle fatigue behavior of corrosion-resistant nickel base superalloy K44
LI Zhi-jun, ZHOU Lan-zhang, GUO Jian-ting, YAO Jun
(Superalloys Division, Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenyang 110016, China)
Abstract: Low cycle fatigue(LCF) property and fracture behavior for alloy K44 at 900℃ were investigated. The results show that the LCF property of alloy K44 under various strain amplitudes can be characterized by three stages: the stage of initial cyclic hardening or softening behavior, the stage of continuous cyclic stability, and then the stage of rapid fracture. TEM observations show that, at high strain amplitudes the softening behavior can be attributed to the formation of stacking faults from dislocation cutting in γ′ particles, while at low strain amplitues the hardening behavior results from the decrease of mobility of dislocations due to the piling up of dislocations before γ′ particles. SEM observations show that the fatigue cracks initiate dominantly on the surface and/or at cast defects near the surface, and propagate in transgranular manner. The existence of block carbides in the matrix can retard effectively crack propagation.
Key words: corrosion-resistant superalloy; K44; low cycle fatigue; cyclic stress response; fatigue crack
K44合金是一种新型的燃气轮机用铸造镍基高温合金, 具有优异的抗高温氧化和抗热腐蚀性能[1]; 同时, 合金含有较高体积分数的γ′强化相, 具有相当优异的高温强度和良好的蠕变抗力[2, 3], 用于制作在900℃以下工作的涡轮叶片和其它高温部件。 在实际服役条件下, 这些构件长期承受高温及交变载荷的作用, 同时, 受其他相关构件的尺寸限制而导致产生以应变控制的疲劳损伤, 因此高温应变疲劳所造成的损伤成为影响此类构件使用寿命的一个不容忽视的因素[4-7]。 前人研究结果表明, 温度、应变速率、载荷保持时间和波形等实验参数是影响镍基高温合金高温低周疲劳寿命的主要因素[6, 8-10]。 高温合金在循环形变过程中, 循环应力—应变响应可能表现为循环硬化或循环软化, 甚至还可能表现为初期硬化随后软化或反之[9-13], 而合金具体呈现何种循环特性则主要取决于其本身的组织结构。 对高温合金在高温低周疲劳条件下的断裂行为研究发现, 疲劳裂纹的萌生、扩展与高温蠕变和环境的作用以及循环形变机制密切相关[14-20]。
K44合金是一种新型抗热腐蚀镍基高温合金, 其应变控制下的高温低周疲劳行为尚未见报道。 本文作者对K44合金进行了900℃低周疲劳性能测试, 对其循环应力—应变响应行为、疲劳寿命—应变关系以及断裂机制进行了研究, 揭示了该合金高温低周疲劳的微观变形机理、 失效方式及影响疲劳寿命的主要因素, 为对该合金高温构件的疲劳设计和定寿、延寿工作提供有效的理论依据。
1 实验
实验合金在真空感应炉内重熔并浇注成d9mm×104mm的毛坯试棒。 其化学成分为(质量分数, %): 0.05C, 15.89Cr, 10.80Co, 5.61W, 1.99Mo, 3.07Al, 4.49Ti, 0.21Nb, 0.24Hf, Ni余量。 毛坯试棒热处理(1170℃, 4h, A.C.+1050℃, 4h, A.C.+850℃, 16h, A.C.)后加工成直径为6mm, 标距段为12mm的棒状疲劳试样。 疲劳实验在EHF-EG100KN-20L型疲劳机上进行, 用轴向引伸计控制试样的总应变, 加载波形为三角波, 应变比为R=-1, 实验频率为0.125~0.167Hz。 实验数据的采集和处理均由计算机完成, 各个实验均进行至试样断裂为止。 分别用扫描电镜和透射电镜观察疲劳断口和疲劳试样中的位错组态。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 K44合金组织特征
图1所示为K44合金显微组织。 合金铸态组织为典型的枝晶形貌, 枝晶干发达, 枝晶间分布γ/γ′共晶和白色块状碳化物, 如图1(a)所示, 箭头所指为放大的共晶和碳化物; 可见合金主要由γ′相、 γ/γ′共晶和碳化物组成。 经热处理后, 合金组织中析出大量的方形γ′相, 这些γ′相均匀分布在基体上, 体积分数约为50%, 尺寸在0.2~0.5μm之间。 同时, 在晶界析出少量链状碳化物, 能谱分析表明是富W、Cr的M23C6型碳化物, 如图1(b)所示。
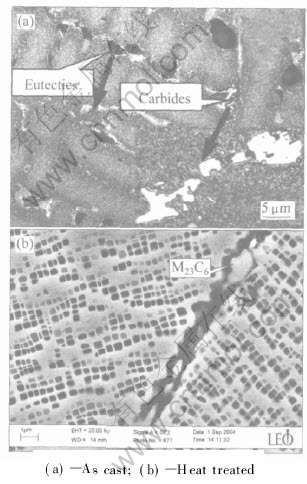
图1 K44合金显微组织
Fig.1 Microstructures of alloy K44
2.2 循环应力—应变行为
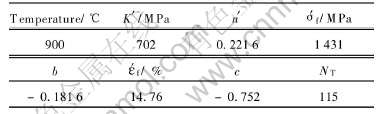
材料的循环应力—应变性能是低周疲劳研究的一个重要方面, 反映了材料在低周疲劳条件下的真实应力—应变特性, 通常用循环应力—应变曲线来表示。 图2所示为K44合金在900℃下应力—应变关系曲线, 符合Δσ/2=K′(Δεp/2)n′规律[7, 21]。 式中Δσ/2是循环应力幅, Δεp/2是塑性应变幅, K′是循环强度系数, n′是循环应变硬化指数。 对应力—应变数据进行线性回归分析, 确定出K′和n′(见表1)。 合金应力—应变关系曲线为:
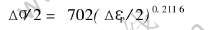
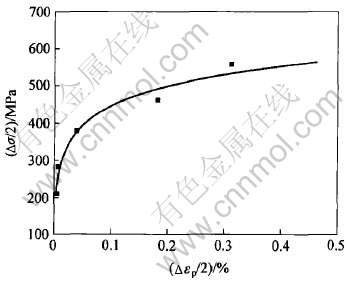
图2 K44合金900℃下应力—应变关系曲线
Fig.2 Cyclic stress—strain curve of alloy K44 at 900℃
表1 K44合金的应变疲劳参数
Table 1 Strain fatigue parameters of alloy K44
2.3 应变疲劳寿命
对于由应变控制的低周疲劳实验, 材料的应变疲劳寿命通常用Coffin-Manson公式[7, 21]来表示, 即
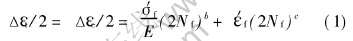
式中 σ′f为疲劳强度系数, ε′f为疲劳延性系数, 2Nf为断裂时的应力反向次数, b为疲劳强度指数, c为疲劳延性指数。
图3所示为K44合金在900℃下的应变幅—寿命关系曲线, 根据式(1)并由线性回归分析方法对应变—寿命数据进行分析, 确定出与高温低周疲劳寿命有关的各个参数(见表1)。 对应的Coffin-Manson方程如下:

Coffin[20]把塑性应变幅恰好等于弹性应变幅时(即图3中Δεt/2-2Nf曲线与Δεp/2-2Nf曲线的交点)所对应的疲劳寿命定义为过渡疲劳寿命(NT), 并指出影响过渡疲劳寿命的主要因素是材料的强度和延性。 一般地, 当Nf〈NT时, 塑性应变对疲劳的贡献大于弹性应变的贡献; 当Nf>NT时, 弹性应变则起主要作用。 通常材料的强度越高延性越低, 其过渡疲劳寿命也越低。 由图3可以看出, K44合金900℃的过度疲劳寿命仅约115周, 循环寿命大于过渡疲劳寿命, 弹性应变对疲劳寿命起主要作用, 说明合金疲劳寿命主要取决于合金的强度。
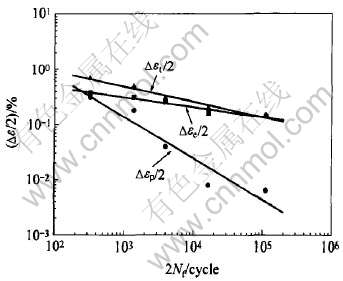
图3 K44合金在900℃下的应变幅—寿命曲线
Fig.3 Strain amplitude—fatigue life curves of alloy K44 at 900℃
2.4 循环应力响应行为
K44合金在900℃下的循环应力响应曲线如图4所示。 合金的循环应力响应曲线可分为3个阶段, 依次是初始表现出与外加总应变幅密切相关的循环硬化或循环软化阶段, 随后的循环稳定阶段及最终的失稳断裂阶段。 当总应变幅小于0.2%时, 合金初始呈现出循环硬化行为; 当总应变幅大于0.3%时, 合金初始则呈现出循环软化行为。 合金初始硬化/软化速率和外加总应变幅密切相关, 外加总应变幅大的硬化/软化速率大。 试样在最终断裂前表现出明显的应力快速下降是由于疲劳裂纹扩快展造成的。 循环响应应力随着应变幅的增加而升高, 主要是塑性应变分量的影响。 外加总应变幅增高, 其对应的塑性应变分量也将随之升高, 位错增殖速率增大, 从而导致位错间及位错与析出相间的强烈交互作用, 位错切割γ′相形成层错, 合金呈现出较强的循环软化效果。
图5所示为K44合金在900℃低周疲劳形变后的位错组态。 在低应变幅(〈0.2%)下, 位错在γ′相边界塞积和缠结使位错运动变得困难, 合金宏观上表现出循环硬化行为(图5(a))。 循环软化现象目前已经有多种解释。 Antolovich[5]和Hwang[22]等在对第二相强化的镍基高温合金的研究表明, 高温低周疲劳行为均造成合金的软化。 但是在软化的机制上持有不同的观点。 Hwang等认为合金的高温低周疲劳行为会使析出相与基体界面产生大量的错配位错, 从而造成析出相与基体共格性的损失而产生软化行为。 而Antolovich等则认为合金的软化是析出相在高温低周疲劳过程中发生粗化从而造成共格界面减少的结果。 杨富民等[7]在研究K40S合金的高温低周疲劳行为时指出, 合金900℃发生的软化现象是由于热激活条件下位错发生了攀移和交滑移, 同时, 随着响应应力的不断增加, 位错脱钉的几率增大, 合金中可动位错增殖, 在保持一定形变速率的前提下, 循环响应应力降低。 另外, 引起软化的原因还可能是实验温度高于合金时效温度, 有利于γ′质点长大, 同时由于连接着大小γ′质点的位错提供了容易扩散的通道, 材料经塑性变形将促进质点的快速长大, 而γ′质点的长大必将引起合金的软化[16-18]。 本实验温度虽然高于合金时效温度(850℃), 但是通过TEM观察, 发现在高应变幅(>0.3%)下γ′相并未粗化, 同时析出相γ′相与基体界面处也未产生错配位错, 而是典型的位错切割机制。 位错切割γ′相形成层错造成沉淀相的无序化(见图5(b)), 降低了材料的变形阻力, 合金宏观上表现出循环软化行为。 合金随后的循环稳定行为是由于高温下, 位错增殖的速率和湮灭速率之间达到了一个平衡, 强化和弱化效应彼此相抵消, 宏观上表现为循环稳定。
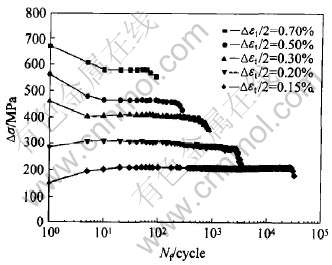
图4 K44合金在900℃下的循环应力响应曲线
Fig.4 Cyclic stress response curves of alloy K44 at 900℃

图5 K44合金900℃低周疲劳形变后的位错组态
Fig.5 Dislocations morphologies of alloy K44 after LCF deformation at 900℃
2.5 断口分析
K44合金高温低周疲劳断口一般较为粗糙, 其形成过程由裂纹萌生、裂纹扩展和裂纹失稳扩展直至瞬时断裂这3个阶段构成。 裂纹通常萌生于试样的表面处或近表面的疏松处(见图6(a)和6(b)), 且为多源断裂。 这是因为试样暴露在高温大气环境下, 表面发生了严重氧化, 位于表面的初生碳化物优先被氧化。 氧化造成表面疏松以及碳化物的退化, 与基体分离, 破坏了试样表面的连续性, 导致了疲劳裂纹源的形成。 可见, 高温氧化削弱了K44合金的抗高温疲劳破坏性能。 此外, 位于试样表面附近区域的疏松缺陷对承载较小总应变幅试样的疲劳寿命影响较大, 并使之降低, 但对承载较大总应变幅试样的疲劳寿命影响较小, 而连续的大面积的疏松缺陷使疲劳寿命明显降低。
在疲劳裂纹扩展区可观察到明显的疲劳条纹(见图6(c))。 通常, 在高温低周疲劳加载条件下, 试样表面的晶界由于优先氧化而使其强度低于晶粒内部强度, 促进沿晶裂纹萌生。 但是, 该合金晶粒尺寸较大, 以致于在温度高达900℃时仍具有相当优异的蠕变抗力, 从而有效地避免了蠕变所引起的沿晶断裂, 疲劳源区和扩展区均以穿晶方式扩展(见图6(a), 6(b)和6(c))。 在裂纹扩展过程中, 裂纹尖端的应力集中导致碳化物本身或其与基体的相界面开裂, 产生二次裂纹(见图6(c), 箭头所指为放大的开裂碳化物), 二次裂纹的出现又有效地松弛了裂纹尖端的应力集中, 降低了裂纹扩展的驱动力, 延缓了疲劳裂纹的扩展。
裂纹扩展后期, 试样的有效承载面积减小, 而合金枝晶间的结合力相对较弱, 在循环载荷的作用下, 疲劳裂纹失稳扩展, 试样沿枝晶间被撕裂, 疲劳断口瞬断区呈现沿枝晶间断裂特征(见图6(d))。 
图6 K44合金900℃疲劳断口形貌
Fig.6 Morphologies of fatigue fracture surface of alloy K44 at 900℃
3 结论
1) K44合金在900℃下的低周疲劳应力—应变关系表达式为: Δσ/2=702(Δεp/2)0.2116。
2) K44合金的过渡疲劳寿命小于循环寿命, 说明合金形变以弹性应变为主, 合金的强度对疲劳寿命起决定作用。 其应变幅—寿命表达式为: Δεt/2=0.0097(2Nf)-0.1816+0.1476(2Nf)-0.752。
3) 在900℃低周疲劳加载条件下的循环形变起始阶段, 当应变幅小于0.2%时, 位错在γ′相前塞积造成位错可动性降低, K44合金呈现循环硬化行为; 当应变幅大于0.3%时, 位错切割γ′相形成层错, 降低了合金变形阻力, K44合金呈现循环软化行为。
4) K44合金在900℃下的疲劳裂纹主要萌生于试样表面或近表面缺陷处; 裂纹扩展过程中, 碳化物开裂延缓了疲劳裂纹扩展, 裂纹以穿晶方式扩展。
REFERENCES
[1]方龙, 刘学贵, 李云, 等. K44铸造镍基高温合金800℃氧化行为的研究[J]. 沈阳化工学院学报, 2004, 18(2): 121-124.
FANG Long, LIU Xue-gui, LI Yun, et al. Oxidation kinetics of cast Ni-base superalloy K44[J]. Journal of Shenyang Institue of Chemical Technology, 2004, 18(2): 121-124.
[2]Hou J S, Guo J T, Zhou L Z, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of cast Ni-base superalloy K44[J]. Mater Sci Eng, 2004, A374: 327-334.
[3]侯介山, 张玉龙, 郭建亭, 等. 镍基铸造高温合金K44的高温蠕变行为[J] . 金属学报, 2004, 40: 579-584.
HOU Jie-shan, ZHANG Yu-long, GUO Jian-ting, et al. High temperature creep behavior of cast nickel base superalloy K44[J]. Acta Metall Sinica, 2004, 40: 579-584.
[4]Gell M, Leverant G R. Mechanisms of high temperature fatigue[A]. Carden A E, McEvily A J, Wells C H. Fatigue at Elevated Temperature[C]. Philadelphia: ASTM STP 520, 1972. 37-67.
[5]Antolovich S D, Liu S, Baur R. Low cycle fatigue behavior of René 80 at elevated temperature[J]. Metall Trans, 1981, A12: 473-481.
[6]杨富民, 孙晓峰, 管恒荣, 等. K40S钴基高温合金的高温低周疲劳行为Ⅰ—疲劳性能[J]. 金属学报, 2002, 38(10): 1047-1052.
YANG Fu-min, SUN Xiao-feng, GUAN Heng-rong, et al.Low cycle fatigue behavior of K40S cobalt-base superalloy at elevated temperature[J]. Acta Metall Sinica, 2002, 38(10): 1047-1052.
[7]Suresh S. 材料疲劳[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 1998.
Suresh S. Fatigue of Materials[M] . Beijing: National Defence Industry Press, 1998.
[8]陈鸿均, Wever H. In738LC镍基高温合金高温低周疲劳性能的研究[J] . 材料工程, 2000, 11: 45-48.
CHEN Hong-jun, Wever H. Study on the low cycle fatigue property of a nickel based superalloy IN738LC at elevated temperature[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2000, 11: 45-48.
[9]陈立佳, 王中光, 姚戈, 等. 铸造Ni基高温合金K417的高温低周疲劳行为[J]. 金属学报, 1999, 35: 1144-1150.
CHEN Li-jia, WANG Zhong-guang, YAO Ge, et al. Investigation of high temperature low cycle fatigue properties of a casting nickel base superalloy K417[J]. Acta Metall Sinica, 1999, 35: 1144-1150.
[10]Chen L J, Wang Z G, Yao G, et al. The influence of temperature on low cycle fatigue behavior of nickel base superalloy GH4049[J]. Int J Fatigue, 1999, 21(8): 791-797.
[11]廖鄂斌, 郭建亭, 王淑荷. 定向凝固合金DZ17G的高温低周疲劳性能研究[J]. 金属学报, 1998, 34(3): 278-282.
LIAO E-bin, GUO Jian-ting, WANG Shu-he. LCF behavior of DS alloy DZ17G at high temperature[J]. Acta Metall Sinica, 1998, 34(3): 278-282.
[12]YE Du-yi, PING De-hai, WANG Zhen-lin, et al. Low cycle fatigue behavior of nickel-based superalloy GH4145/SQ at elevated temperature[J]. Mater Sci Eng, 2004, A373(1-2): 54-64.
[13]Yang F M, Sun X F, Guan H R, et al. On the low cycle fatigue deformation of K40S cobalt-base superalloy at elevated temperature[J].Materials Letters, 2003, V57(19): 2823-2828.
[14]姜文辉, 姚向东, 管恒荣, 等. DZ40M合金高温低周疲劳性能及其断口分析[J]. 金属学报, 1998, 34(4): 378-383.
JIANG Wen-hui, YAO Xiang-dong, GUAN Heng-rong, et al. High temperature low cycle fatigue of DZ40M cobalt-base superalloy[J]. Acta Metall Sinica, 1998, 34(4): 378-383.
[15]Clavel M, Levaillant C, Pineau A. Creep-Fatigue Environment Interactions[A]. Pelloux R M, Stlloff N, et al. Proc Symp on Creep-Fatigue-Environment Interactions[C]. Milwaukee, WI, TMS/AIME, 1980. 24-45.
[16]Guo J T, Ranucci D, Picco E. Low cycle fatigue behavior of case nickel-base superalloy IN738LC in air and in hot corrosive environments[J]. Mater Sci Eng, 1983, A58(1): 127-133.
[17]Guo J T, Ranucci D, Picco E, et al. Effect of environment on the low cycle fatigue behavior of cast nickel-base superalloy IN738LC[J]. Int J Fatigue, 1984, 6(2): 95-99.
[18]Guo J T, Ranucci D, Picco E. The effect of hot corrosion on the low cycle fatigue of IN738LC at elevated temperature[A]. Estratto, ATTI. X Convegno Nazionale AIAS[C]. Cosenza: Unversita Calabria Arcavacata Di Rende, 1982. 259-269.
[19]Matuszyk W, Camus G, Duquette D J, et al. Effects of temperature and environment on the tensile and fatigue crack growth of a Ni3Al-base alloy[J]. Metall Trans, 1990, A21: 2967-2975.
[20]Gayda J, Miner R V. Fatigue crack initiation and propagation in several nickel-base superalloys at 650℃[J]. Int J Fatigue, 1983, 5(3): 135-143.
[21]Coffin L F Jr. Fatigue at high temperature[A]. Carden A E, McEvily A J, Wells C H. Fatigue at Elevated Temperature[C]. Philadelphia: ASTM STP 520, 1972. 5-34.
[22]Hwang S K, Lee H N, Yoon B H. Mechanism of cyclic softening and fracture of an Ni-base γ′-strengthened alloy under low-cycle fatigue[J]. Metall Trans, 1989, A20: 2793-2801.
(编辑何学锋)
收稿日期: 2005-04-25; 修订日期: 2005-09-28
作者简介: 李志军(1978-), 男, 硕士
通讯作者: 郭建亭, 研究员; 电话: 024-23971917; E-mail: jtguo@imr.ac.cn