Al-Cu合金的显微组织及其晶体生长方向
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2015年第5期
论文作者:陈体军 李向威 郭海洋 郝 远
文章页码:1399 - 1409
关键词:Al-Cu合金;定向凝固;晶体生长方向;金属型铸造;显微组织
Key words:Al-Cu alloy; directional solidification; crystal growth direction; permanent mould casting; microstructure
摘 要:研究金属型铸造(PMC)和定向凝固(DS)不同Cu含量Al-Cu的显微组织和晶体生长方向,同时,探讨浇铸温度对纯Al的显微组织和晶体生长方向的影响。结果表明,纯Al晶体并非始终保持胞状,而是随着浇铸温度的升高从胞状晶变为具有发达晶臂的柱状树枝晶,且晶体的生长方向也随之改变。Cu 元素对PMC和DS Al-Cu合金显微组织的影响相似:随着Cu含量的增加,α(Al)晶体均从胞状晶依次转变为柱状晶、柱状树枝晶和发达的等轴晶。随着Cu含量的增加,PMC合金晶体的生长方向逐渐逼近á110?方向,但所形成的á110?向的晶体并不属于羽毛状晶体。在所有DS Al-Cu合金中也未发现羽毛状晶体。
Abstract: The microstructures and crystal growth directions of permanent mould casting (PMC) and directionally solidified (DS) Al-Cu alloys with different contents of Cu were investigated. Simultaneously, the effects of pouring temperature on the microstructure and crystal growth direction of permanent mould casting pure Al were also discussed. The results indicate that the α(Al) crystals in the pure Al do not always keep common columnar grains, but change from the columnar grains to columnar dendrites with developed arms as the pouring temperature rises. The growth direction also varies with the change of pouring temperature. Cu element has similar effects on the microstructures of the PMC and DS casting Al-Cu alloys and the α(Al) crystals gradually change from columnar crystals in turn to columnar dendrites and developed equiaxed dendrites as the Cu content increases. The crystal growth direction in the PMC alloys gradually approaches á110? orientation with increasing Cu content. But the resulting crystals with growth direction of á110? do not belong to feathery grains. There are also no feathery grains to form in all of the DS Al-Cu alloys.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25(2015) 1399-1409
Ti-jun CHEN, Xiang-wei LI, Hai-yang GUO, Yuan HAO
State Key Laboratory of Advanced Processing and Recycling of Nonferrous Metals, Lanzhou University of Technology, Lanzhou 730050, China
Received 18 June 2014; accepted 9 October 2014
Abstract: The microstructures and crystal growth directions of permanent mould casting (PMC) and directionally solidified (DS) Al-Cu alloys with different contents of Cu were investigated. Simultaneously, the effects of pouring temperature on the microstructure and crystal growth direction of permanent mould casting pure Al were also discussed. The results indicate that the α(Al) crystals in the pure Al do not always keep common columnar grains, but change from the columnar grains to columnar dendrites with developed arms as the pouring temperature rises. The growth direction also varies with the change of pouring temperature. Cu element has similar effects on the microstructures of the PMC and DS casting Al-Cu alloys and the α(Al) crystals gradually change from columnar crystals in turn to columnar dendrites and developed equiaxed dendrites as the Cu content increases. The crystal growth direction in the PMC alloys gradually approaches <110> orientation with increasing Cu content. But the resulting crystals with growth direction of <110> do not belong to feathery grains. There are also no feathery grains to form in all of the DS Al-Cu alloys.
Key words: Al-Cu alloy; directional solidification; crystal growth direction; permanent mould casting; microstructure
1 Introduction
Compared with ZA27 alloy, the melting point of 10% Si (volume fraction) particle reinforced ZA27 in situ composite (Sip/ZA27 composite) is significantly raised from 497 °C to 625 °C [1]. Its pouring temperature thereby is raised correspondingly. However, the pouring temperature rise leads to the primary α(Al) dendrites to change from original small equiaxed dendrites to very developed columnar dendrites, even to feathery grains with large anisotropic morphology as the temperature is raised to 750 °C [2]. Feathery grain is a kind of specific columnar dendrite that is often found in Al alloys [3]. Due to its strong anisotropy and nonuniform aspect, this kind of microstructure is highly undesirable in Al manufacturing. The investigation indicates that the mechanical properties of the Sip/ZA27 composite are obviously impaired due to this microstructure [1]. To avoid the feathery grains, it is of importance to verify their formation conditions.
In fact, the primary metal phase in the Sip/ZA27 composite is identical to that of Al alloys and both of them belong to α(Al) phase. So, it can be considered that the formation of feathery grains in the composite is similar to that of Al alloys. The existing investigations on Al alloys indicated that high temperature gradient and growth rate, the presence of fluid flow, the absence of nucleation agents and a given amount of certain solute elements with specific crystal structure can accelerate the formation of feathery grains [4-6]. That is to say, the composition of an alloy has large effects on the formation of feathery grains. The reason is that the solutes change the anisotropy of the solid-liquid interface and the adsorption kinetics of atoms, thus resulting in the formation of twins and the change of growth direction [3,7-9]. But a recent study has shown that the formation of feathery grains was not concerned with solute kind, but with its amount [10]. The investigation demonstrated that the formation actually depended on Zn content for Al-Zn alloy and <110> orientated feathery grains were clearly found above 60% Zn [11].
In order to verify the formation of feathery grains in the Sip/ZA27 composite, it is necessary to clarify the effects of all kinds of solutes. Cu is a main alloying element for the composite [12]. But the existing investigations have not involved the effect of Cu element on the microstructure, especially on the formation of feathery grains. The proposed structure of feathery grains is made of thin lamellar dendrites in the center of their trunk by a coherent (111) twin plane [3,7]. Twinned dendrite trunks always grow along <110> direction and have a highly complex branch morphology of <110> secondary arms [3,4]. The formation of the very anisotropic morphology is essentially attributed to the change of α(Al) growth direction from the isotropic growth along <100> to the anisotropic growth along <110>. The present work indicates that the growth direction of the α(Al) in Al-Cu alloy can change to <110> orientation under given Cu content and solidification conditions, but the resulting morphology is not so anisotropic.
Therefore, the study on the effect of Cu element on the microstructure of Al-Cu alloy is significant not only for verifying the microstructure of the Sip/ZA27 composite, but also for understanding the formation and structure of feathery grains in Al alloys. In the present work the effects of Cu content and directional solidification on the microstructure and crystal growth direction of Al-Cu alloy were mainly investigated. For comparison, the cases of permanent mould casting pure Al, especially the effects of pouring temperature were discussed.
2 Experimental
The raw materials used in this work are pure Al and Al-50Cu master alloy. According to the compositions of target alloys, the raw materials were melted in a resistance furnace at 790 °C, then degassed using C2Cl6 and poured into a permanent mould with a cavity of d16 mm × 130 mm at 740 °C. The mould temperature was at room temperature prior to pouring. The Cu content in the ZA27 alloy is always limited within 2%-2.5%, but to verify the effects of Cu content on the microstructures and growth directions of primary α(Al) crystals (including those in the ZA27 alloy and Cu- containing Al alloys), the range of Cu content should be chosen as wide as possible. So, the employed Cu content was selected within the range from 0 to 23%. The investigation indicated that feathery grains could form in the ZA27 alloy when pouring temperature was elevated to 650 °C or above [13]. So, the pouring temperature of 740 °C was employed in this work. A given amount of pure Al was also remelted and poured into the same mould at different temperatures ranging from 680 °C to 830 °C to investigate the effect of pouring temperature on the microstructure and crystal growth direction. A specimen with dimensions of d16 mm×10 mm was cut from the bottom end of each casting rod away for 50 mm. Then, each specimen was sectioned into two small specimens along axial direction. The cross-section of one of them was finished and polished. For the Al-Cu specimens, the cross-sections were etched by 1% HF aqueous solution and for the pure Al specimens, they were etched by 15% NaOH aqueous solution at 70-80 °C. They were observed with an optical microscope (OM) and analyzed by energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS) on a scanning electron microscope (SEM). Finally, some typical specimens were finished and polished again, and then vibrating-polished and analyzed on the SEM by electronic back scattered diffraction (EBSD).
To investigate the effect of Cu content on the microstructure and growth direction of the Al-Cu alloy under directional solidification conditions, casting Al-Cu rods with a diameter of 10 mm and with the same compositions (0-23% Cu) to those of the alloys employed in the above experiments were first prepared. Then each of the rods was put into a quartz tube with a diameter of 10.5 mm, remelted and directionally solidified on a zone-melted directional solidification device. The employed solidification rate was 30 μm/s. All of the solidified rods were cut into two parts along their axis direction. One of them was used for metallographic observation and analysis. The preparation processes of metallographic specimens and EBSD specimens, and the observation and analysis methods are same as those of the above permanent mould casting specimens.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Effects of pouring temperature on microstructure and crystal growth direction of permanent mould casting pure Al
Figure 1 gives the microstructures of the pure Al poured at different temperatures. It can be found that the primary grains are in columnar form at 680 °C (Fig. 1(a)). Then, the columnar crystals generate branches (Fig. 1(b)) and the branches gradually evolve into dendritic arms as temperature rises (Fig. 1(c)). The crystals thereby become into columnar dendrites at 740 °C (Fig. 1(c)). The dendritic arms become more and more developed and the crystals change into the developed columnar dendrites when the temperature is further elevated (Fig. 1(d)). Simultaneously, both the length of the columnar crystals or columnar dendrite region and the primary dendritic arm spacing (PDAS) increase as the temperature rises, which can be more clearly seen from the quantitative results shown in Fig. 2. In addition, the columnar crystals, especially the columnar dendrites are refined as they grow towards the casting rod center and thus the primary trunk spacing decreases (Fig. 1). In view of the variation of the primary trunk spacing with the distance from the casting rod edges, it should be noted that the results shown in Fig. 2(b) are obtained by examining the microstructures near the rod edges.

Fig. 1 Microstructures of pure Al poured at 680 °C (a), 710 °C (b), 740 °C (c) and 830 °C (d)

Fig. 2 Variations of length of columnar dendrite region (a) and primary dendritic arm spacing (b) of pure Al with pouring temperature
For the present casting rods, their length (130 mm) is far larger than their diameter (16 mm). So, it is reasonably suggested that the heat released after pouring conducts mainly along the radial direction and the heat flow along the axial direction can be ignored, as shown in Fig. 3. The directional heat flow is the reason for the formation of the columnar crystals or columnar dendrites. Under twin-roll casting conditions, columnar dendrites and equiaxed dendrites can form for pure Al [14]. It can be expected that the temperature difference between the melt and the mould increases, and thus the temperature gradient in the melt increases as the pouring temperature rises. The increase of the temperature gradient must enhance the directional growth of crystals. So, the length of the columnar crystal region or columnar dendrite region increases as the temperature rises (Figs. 1 and 2(a)). Figures 1(d) and 2(a) indicate that the length of the columnar dendrite region is up to 8 mm and thus the whole cross section is composed of columnar dendrites. The melt does not begin to solidify until its temperature is cooled below the melting point, whatever the pouring temperature is. But as the pouring temperature rises, the temperature of the mould, especially the part close to the melt, is elevated during solidification. So, the cooling rate in this region decreases, the resulting columnar dendrites thereby are coarsened and the PDAS increases (Figs. 1 and 2(b)).

Fig. 3 Schematic of solidification behavior of cross-section of casting rod
Theoretically, the planar growth of a pure metal should always be maintained if the temperature gradient in the front of solid-liquid interface is positive and the resulting microstructure is always composed of planar crystals [15]. But the pure Al used in this work has Al content of 99.9% and there are about 0.1% impurities. In addition, some impurities on the tools used for melting can enter into the melt during melting. Figure 1 shows that there are lots of black structures at the grain boundaries, which demonstrates that quite large amount of impurities really exist in the pure Al. The EDS result indicates that the impurities mainly include Fe, Si and Mn. The impurity content in the front of solid-liquid interface will increase as the columnar crystals grow towards the rod center. Simultaneously, the temperature gradient in the growing front also decreases. So, a constitutional supercooling may generate when the cellular or columnar crystals grow to a degree and the supercooling degree increases as the crystals further grow. Subsequently, renucleation will occur and equiaxed dendrites will form in the center region of the rods.
As described above, the temperature of the mould close to the melt is elevated as the pouring temperature rises. Thus, the temperature gradient in the melt close to the mould wall is decreased. So, the possibility of forming constitutional supercooling increases as the pouring temperature rises. In addition, no temperature gradient exists theoretically along the circumferential direction shown in Fig. 3. Therefore, constitutional supercooling is easy to form in the side fronts of the columnar crystals. Side branches thereby generate around the columnar crystals and they gradually evolve into developed dendrite arms as the temperature rises. Similarly, more and more branches or dendrite arms can form as the columnar dendrites grow towards the center region due to the increased constitutional supercooling. This is the reason why the columnar dendrites are refined as they grow towards the center (Fig. 1).
Figure 4 gives the pole figures of the columnar crystals or columnar dendrites of pure Al poured at different temperatures. Through comparing with the standard pole figures in the texture application software, it can be found that the crystal growth directions at 680 °C and 740 °C are 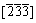 and
and  respectively (Figs. 4(a) and (b)) and that at 830 °C is towards
respectively (Figs. 4(a) and (b)) and that at 830 °C is towards  orientation (Fig. 4(c)). That is to say, the growth directions of the α(Al) crystals under different pouring temperatures are all not towards the theoretical orientation <100> and they vary with the pouring temperature. But no crystal grows along <110> direction, the typical growth direction of feathery grains [3,4]. So, it can be concluded that the pouring temperature has large effects on the crystal morphology and growth direction of pure Al, but there are no feathery grains to form, even if the resulting crystals have large anisotropic morphology. This is consistent to the existing viewpoint that a given amount of solute element is one of the main factors for forming feathery grains [4-6]. The solutes can change the anisotropy of solid-liquid interface and the adsorption kinetics of atoms, thus resulting in the formation of twins [3,7-9]. The twins then change the α(Al) growth direction from the isotropic growth along <100> to the anisotropic growth direction <110> and the crystals finally grow into feathery grains [3,4]. A previous investigation indicated that the (100) plane would preferentially grow towards the direction opposite to heat flow, but several (112) planes could grow along the direction having an angle of 10° with heat flow if this preferential growth direction was disturbed by other solute elements or vibrating [16].
orientation (Fig. 4(c)). That is to say, the growth directions of the α(Al) crystals under different pouring temperatures are all not towards the theoretical orientation <100> and they vary with the pouring temperature. But no crystal grows along <110> direction, the typical growth direction of feathery grains [3,4]. So, it can be concluded that the pouring temperature has large effects on the crystal morphology and growth direction of pure Al, but there are no feathery grains to form, even if the resulting crystals have large anisotropic morphology. This is consistent to the existing viewpoint that a given amount of solute element is one of the main factors for forming feathery grains [4-6]. The solutes can change the anisotropy of solid-liquid interface and the adsorption kinetics of atoms, thus resulting in the formation of twins [3,7-9]. The twins then change the α(Al) growth direction from the isotropic growth along <100> to the anisotropic growth direction <110> and the crystals finally grow into feathery grains [3,4]. A previous investigation indicated that the (100) plane would preferentially grow towards the direction opposite to heat flow, but several (112) planes could grow along the direction having an angle of 10° with heat flow if this preferential growth direction was disturbed by other solute elements or vibrating [16].

Fig. 4 Pole figures corresponding to columnar dendrite structures of pure Al poured at 680 °C (a), 740 °C (b) and 830 °C (c)
Therefore, it can be concluded that the crystal morphology of pure Al does not keep the common columnar form, but changes from columnar form to columnar dendrite shape with developed arms as the pouring temperature rises. The reasons that lead to this change should be attributed to the constitutional supercooling from impurities and the decreased temperature gradient. The growth direction does not also maintain the metallographic preferential direction of <100> and can vary with pouring temperature. But there are no feathery grains to form, even if the resulting crystals have large anisotropic morphology.
3.2 Effects of Cu content on microstructure and dendrite growth direction of permanent mould casting Al-Cu alloy
Figure 5 shows the microstructures of the Al-Cu alloys with different Cu contents. It indicates that the length of columnar dendrite region decreases with the increase of Cu content (Figs. 5(a)-(c)), just contrary to the change of pure Al with rising pouring temperature discussed in the above section. The columnar dendrite region completely disappears when the content increases to 17% and the whole microstructure is composed of equiaxed dendrites (Fig. 5(d)). But the changes of crystal morphology and PDAS are similar to those of pure Al with pouring temperature. The crystal morphology changes from columnar shape to columnar dendritic form with developed arms and the PADS increases. The quantitative variations of the length of columnar dendrite region and PADS can be seen in Fig. 6. The dendrite morphology does not obviously change when the content is over 17%. But the amount of eutectic structures increases and the number of dot-like or short rod-like arms that are separated from the dendrites also increases (comparing Figs. 5(d) and (e)).

Fig. 5 Microstructures of Al-Cu alloys with 2% Cu (a), 7% Cu (b), 13% Cu (c), 17% Cu (d) and 23% Cu (e) poured at 740 °C

Fig. 6 Variations of length of columnar dendrite region (a) and primary dendritic arm spacing (b) with Cu content
It is known that under given solidification conditions, the higher the solute concentration, the larger the constitutional supercooling. So, it can be expected that the solid-liquid interfaces at the tips or sides of a columnar crystal become more and more instable as the Cu content increases. Then branches generate at these sites as the content increases to a given value and they gradually evolve into the developed arms as the Cu content further increases (Fig. 5). As the columnar dendrites grow towards the casting rod center, the Cu content in the front of solid-liquid interface becomes higher and higher, and thus both the constitutional supercooling degree and constitutional supercooling region increase. In addition, these two factors can also be enhanced with increasing the added Cu content. Based on these standpoints, the formation of the equiaxed dendrites in the casting rod center and the variation of the length of the columnar crystal region or columnar dendrite region with the Cu content can be easily understood.
According to the Al-Cu binary equilibrium diagram [17], when the pouring temperature is maintained at 740 °C, the superheating degree should increase as Cu content increases. So, it can be expected that the heat released prior to crystallizing increases, and thus the mould is heated to higher temperatures. This results in the decrease of the solidification rate and the increase of the PDAS. In addition, as discussed above, the dendrite arms become more and more developed as Cu content increases due to the increased constitutional supercooling. The more developed arms must result in longer distance between the primary trunks. That is to say, the increased constitutional supercooling is another reason that makes the PDAS increase. Furthermore, the solute agglomeration at the arm roots should also increase as Cu content increases, and the arms are easier to melt at their roots to form the dot-like or short rod-like grains that are not connected with the primary trunks (Fig. 5(e)).
As discussed in the above section, the growth direction of α(Al) in the pure Al poured at 740 °C is  , having an angle of 18.43° with direction <110>. The growth direction turns into [320] when 2% Cu is added, having an angle of 11.3° with direction <110> (Fig. 7(a)). As Cu content increases to 13%, the growth direction of most of the α(Al) crystals is
, having an angle of 18.43° with direction <110>. The growth direction turns into [320] when 2% Cu is added, having an angle of 11.3° with direction <110> (Fig. 7(a)). As Cu content increases to 13%, the growth direction of most of the α(Al) crystals is 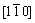 (Fig. 7(b)). So, it can be concluded that Cu element has large effects on the growth direction of α(Al) crystals, and the direction gradually approaches orientation <110> and even completely turns into <110> as Cu content increases. That is to say, the growth direction is same to that of feathery grains. But as shown in Fig. 5(c), the columnar dendrite region is quite narrow; the dendrite morphology is not so anisotropic with feathery grains and is also not in laminar form. So, it can be proposed that it is not sure that the α(Al) crystals which grow along <110> must belong to feathery grains. This result is consistent to that from the investigation on Al-23%Zn alloy, the direction of the primary trunks is <110> and the dendrite morphologies are also very anisotropic, but they are regular columnar grains and do not belong to feathery grains [10].
(Fig. 7(b)). So, it can be concluded that Cu element has large effects on the growth direction of α(Al) crystals, and the direction gradually approaches orientation <110> and even completely turns into <110> as Cu content increases. That is to say, the growth direction is same to that of feathery grains. But as shown in Fig. 5(c), the columnar dendrite region is quite narrow; the dendrite morphology is not so anisotropic with feathery grains and is also not in laminar form. So, it can be proposed that it is not sure that the α(Al) crystals which grow along <110> must belong to feathery grains. This result is consistent to that from the investigation on Al-23%Zn alloy, the direction of the primary trunks is <110> and the dendrite morphologies are also very anisotropic, but they are regular columnar grains and do not belong to feathery grains [10].
In summary, Cu content has large effects on the microstructure and crystal growth direction of Al-Cu alloy. The α(Al) crystals gradually change from columnar crystals to columnar dendrites and finally to equiaxed dendrites as Cu content increases. Simultaneously, the PDAS increases. All of these changes are attributed to the increased constitutional supercooling. The growth direction approaches the orientation <110> and even is completely along <110> as Cu content increases. But the crystals grown along <110> do not belong to feathery grains.
3.3 Effects of Cu content on microstructure and dendrite growth direction of directionally solidified Al-Cu alloy
Figure 8 gives the microstructures of the Al-Cu alloys with different Cu contents solidified under a given directionally solidified condition. The solidification condition was determined by the criterion that columnar grains can form in the Al-13%Cu alloy, an alloy with a middle Cu content employed in this work. The result indicates that the microstructure of pure Al is composed of columnar grains on which there are lots of protruded particle-like secondary dendrite arms (Fig. 8(a)). The addition of 2% Cu makes the columnar grains branch (Fig. 8(b)) and the branches become closer and closer with the increase of Cu content (Figs. 8(c) and (d)). And the microstructure evolves into columnar dendrites with quite developed arms when Cu content increases to 21% (Fig. 8(e)). Simultaneously, the length of columnar crystal region decreases. As Cu content further increases, the columnar dendrites then turn into the developed equiaxed dendrites that are distributed randomly (Fig. 8(f)). In summary, the increase of Cu content causes the primary crystals to form branches, and the branches become more and more developed, finally, the crystals change from columnar crystals to the developed equiaxed dendrites.
From the existing investigations, it can be concluded that feathery grains are very easy to form under directional solidification conditions [10,11]. To judge if feathery grains generate in the present directionally solidified Al-Cu alloys, comparing the microstructures with those of the proposed feathery grains should be a useful method. Feathery grains consist of thin lamellar dendrites in the center of their trunk by a coherent (111) twin plane [3,7]. Twinned dendrite trunks always grow along <110> direction and have a highly complex branch morphology of <110> secondary dendrite arms [3,4]. The microstructure in the section parallel to the trunk growth direction is composed of continuous rows. The rows are alternatively separated by straight boundaries and wavy boundaries [3,4,7]. The transverse section also consists of continuous rows, but the boundaries between them are not so clear with those of the longitudinal section and the crystals in the rows are more equiaxed [10]. As shown in Fig. 8, the longitudinal sections of some Al-Cu specimens are composed of rows of columnar crystals or columnar dendrites, especially the pure Al and Al-21% Cu alloy have the straight trunk boundaries and the wavy boundaries resulted from the impingement of side branches (Figs. 8(a) and (e)). But the microstructure morphologies of the transverse sections are obviously different from those of feathery grains, which indicate that there are no feathery grains in all of the present Al-Cu alloys (including pure Al). From Fig. 9, it can be seen that in the transverse section, the crystals of pure Al are in round or polygon form (Fig. 9(a)), which is consistent with the characteristic of columnar crystals. For the Al-Cu alloys, the crystal morphologies change from the mixture of round and polygon forms of the pure Al to polygon shape (Fig. 9(b)) and equiaxed dendrite shape (Fig. 9(c)) as Cu content increases. The branches of equiaxed dendrites become closer and more developed as Cu content further increases (Figs. 9(d) and (e)). The polygon shape corresponds to the cross-section shape of columnar grains and the equiaxed dendrite shape matches that of columnar dendrites. In contrast, the growth anisotropy of the columnar crystals in the pure Al is more obvious than that in the Al-2%Cu alloy because the angle shown in Fig. 9(a) is sharper than that shown in Fig. 9(b). The reason is the higher constitutional supercooling resulted from Cu element for the Al-2%Cu alloy. For the Al-23%Cu alloy, the transverse section also consists of the developed equiaxed dendrites, similar to the longitudinal section shown in Fig. 9(f). That is to say, there are no feathery grains forming in the Al-Cu alloys in view of their microstructure morphologies.

Fig. 7 Pole figures corresponding to columnar dendrite structures of Al-2%Cu alloy (a) and Al-13%Cu alloy (b)
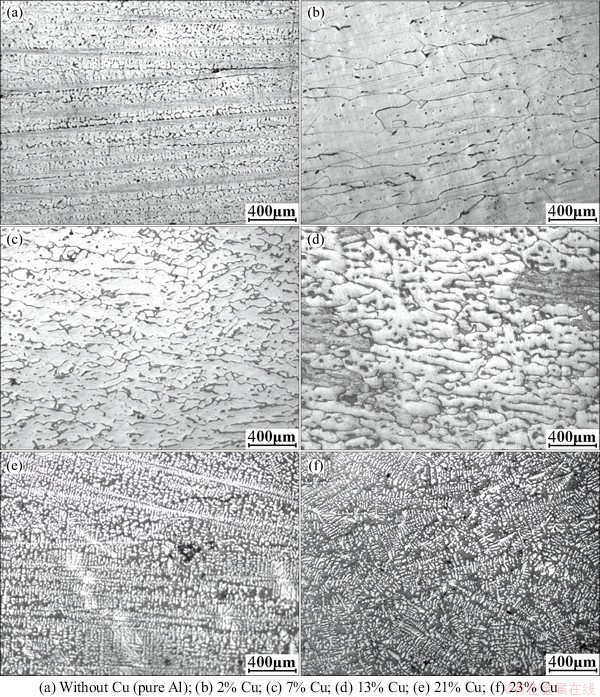
Fig. 8 Microstructures of Al-Cu alloys directionally solidified under certain conditions (parallel to solidification direction)
In addition, the crystal growth direction is another criterion for judging if the crystals belong to feathery grains as discussed in the above two sections. Figure 8(e) shows that the parallelly-distributed grains of the Al-21%Cu alloy have the most anisotropic morphologies and thus the crystal growth direction of this alloy was analyzed by EBSD. The result indicates that the crystals have  orientation growth direction (Fig. 10), different from the common growth direction <110> of feathery grains. WOOD et al [18] proposed that the growth direction of primary trunk in the twined feathery grains could change from <110> to <112>. Another investigation on directionally solidified Al-Cu alloy indicated that the primary trunk of feathery grains grew along <112> direction [19]. That is to say, the growth direction of feathery grains can be <112>. But from the microstructure morphology discussed in the above section, it is found that the grains in the Al-21%Cu do not belong to feathery grains.
orientation growth direction (Fig. 10), different from the common growth direction <110> of feathery grains. WOOD et al [18] proposed that the growth direction of primary trunk in the twined feathery grains could change from <110> to <112>. Another investigation on directionally solidified Al-Cu alloy indicated that the primary trunk of feathery grains grew along <112> direction [19]. That is to say, the growth direction of feathery grains can be <112>. But from the microstructure morphology discussed in the above section, it is found that the grains in the Al-21%Cu do not belong to feathery grains.

Fig. 9 Microstructures of Al-Cu alloys directionally solidified under certain conditions (perpendicular to solidification direction)

Fig. 10 Pole figures corresponding to columnar dendrite structures of directionally solidified Al-21%Cu alloy
As for the microstructure variation with Cu content, it can be well interpreted by constitutional supercooling resulted from Cu element. It is known that under a given solidification condition, both the degree and region width of constitutional supercooling all increase as the solute amount of Cu increases [20]. These two increased parameters accelerate the formation of branches and make the branches closer and more developed. The crystals then change from original columnar grains in turn to columnar dendrites and equiaxed grains [20].
Generally, Cu element also has large effect on microstructure of the directionally solidified Al-Cu alloy and the primary phase changes from columnar grains in turn to columnar dendrites and developed equiaxed dendrites as the Cu content increases. There are also no feathery grains to form in all of the Al-Cu alloys employed in this work although the grains in some alloys have very anisotropic morphology, parallel distribution and growth direction of <112>.
4 Conclusions
1) The primary α(Al) crystals of pure Al do not maintain the common columnar crystals, but change from columnar crystals to columnar dendrites with developed arms as the pouring temperature rises. The growth direction of the primary crystals also does not maintain the metallographic preferential direction of <100> and can vary with the pouring temperature.
2) Cu content has large effects on the microstructure and crystal growth direction of the permanent mould casting Al-Cu alloy. The α(Al) crystals gradually change from columnar crystals to columnar dendrites and finally to equiaxed dendrites as Cu content increases, while the growth direction gradually approaches orientation <110> and is completely along <110> as Cu content increases to 13%. But the resulting crystals grown along <110> do not belong to feathery grains in view of their structures.
3) Cu element also has large effects on microstructure of the directionally solidified Al-Cu alloy and the primary phase changes from columnar crystals in turn to columnar dendrites and developed equiaxed dendrites as Cu content increases. There are also no feathery grains to form in all of the Al-Cu alloys although the crystals have <112> growth direction.
References
[1] CHEN T J, YUAN C R, FU M F, MA Y, LI Y D, HAO Y. In situ silicon particle reinforced ZA27composites. Part 1: Microstructures and tensile properties [J]. Mater Sci Technol, 2008, 24: 1321-1332.
[2] CHEN T J, LI X W, GUO H Y, HAO Y. Microstructure and dendrite morphology of Sip/ZA27 composite [J]. Mater Sci Technol, 2014, 30: 1783-1794.
[3] HENRY S, JARRY P, RAPPAZ M. <110> dendrite growth in aluminum feathery grains [J]. Metall Mater Trans A, 1998, 29: 2807-2817.
[4] TURCHIN A N, ZUIJDERWIJK M, POOL J, ESKIN D G, KATGERMAN L. Feathery grain growth during solidification under forced flow conditions [J]. Acta Mater, 2007, 55: 3795-3801.
[5] LI L, ZHANG Y, ESLING C, ZHAO Z, ZUO Y, ZHANG H, CUI J. Formation of twinned lamellas with the application of static magnetic fields during semi-continuous casting of Al-0.24wt%Fe alloy [J]. J Crystal Growth, 2009, 311: 3211-3215.
[6] HENRY S, GRUEN G U, RAPPAZ M. Influence of convection on feathery grain formation in aluminum alloys [J]. Metall Mater Trans A, 2004, 35: 2495-2501.
[7] HENRY S, MINGHETTI T, RAPPAZ M. Dendrite growth morphologies in aluminium alloys [J]. Acta Mater, 1998, 46: 6431-6443.
[8] SEMOROZ A, HENRY S, RAPPAZ M. Application of the phase-field method to the solidification of hot-dipped galvanized coatings [J]. Metall Mater Trans A, 2000, 31: 487-495.
[9] LI L, ZHANG Y, ESLING C, ZHAO Z, ZUO Y, ZHANG H, CUI J. Formation of feathery grains with the application of a static magnetic field during direct chill casting of Al-9.8wt%Zn alloy [J]. J Mater Sci, 2009, 44: 1063-1068.
[10] Salgado-Ordorica M A, Rappaz M. Twinned dendrite growth in binary aluminum alloys [J]. Acta Mater, 2008, 56: 5708-5718.
[11] Gonzales F, Rappaz M. Dendrite growth directions in aluminum-zinc alloys [J]. Metall Mater Trans A, 2006, 37: 2797-2806.
[12] Prasad B K. Wear response of a zinc-based alloy containing silicon as influenced by material microstructure and test conditions [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2004, 367: 63-73.
[13] LI Xiang-wei. Study on crystal morphologies and structures of ZA27 alloy [D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology, 2010: 14-19. (in Chinese)
[14] CHEN Shou-dong, CHEN Jing-chao. Simulation of microstructures in solidification of aluminum twin-roll casting [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(6): 1452-1456.
[15] Dai Bin-yu. Liquid metal forming theory [M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2010. (in Chinese)
[16] Matsuishi F. Casting conditions of 6030 alloy DC growth twin crystals in aluminum and aluminum-base alloys [J]. Light Met, 1969, 19: 287-296.
[17] Yan X Y, Chang Y A, Xie F Y, Chen S L, Zhang F, Daniel S. Calculated phase diagrams of aluminum alloys from binary Al–Cu to multicomponent commercial alloys [J]. J Alloys Compd, 2001, 320: 151-160.
[18] Wood H J, Hunt J D, Evans P V. Modeling the growth of feathery crystals [J]. Acta Mater, 1997, 45: 569-574.
[19] Zhou Yao-he. Microstructure morphology of laminar crystals of directionally solidified Al alloy and mechanical properties [J]. J Northwest Polytechnical University, 1985, 3: 1-10. (in Chinese)
[20] Hu Han-qi. Theory of metal solidification [M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2007. (in Chinese).
陈体军,李向威,郭海洋,郝 远
兰州理工大学 省部共建有色金属先进加工与再利用国家重点实验室,兰州 730050
摘 要:研究金属型铸造(PMC)和定向凝固(DS)不同Cu含量Al-Cu的显微组织和晶体生长方向,同时,探讨浇铸温度对纯Al的显微组织和晶体生长方向的影响。结果表明,纯Al晶体并非始终保持胞状,而是随着浇铸温度的升高从胞状晶变为具有发达晶臂的柱状树枝晶,且晶体的生长方向也随之改变。Cu 元素对PMC和DS Al-Cu合金显微组织的影响相似:随着Cu含量的增加,α(Al)晶体均从胞状晶依次转变为柱状晶、柱状树枝晶和发达的等轴晶。随着Cu含量的增加,PMC合金晶体的生长方向逐渐逼近<110>方向,但所形成的<110>向的晶体并不属于羽毛状晶体。在所有DS Al-Cu合金中也未发现羽毛状晶体。
关键词:Al-Cu合金;定向凝固;晶体生长方向;金属型铸造;显微组织
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Project (51061010) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (NCET-10-0023) supported by the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University of China; Project (J201103) supported by the Program for Hongliu Outstanding Talents of Lanzhou University of Technology, China
Corresponding author: Ti-jun CHEN; Tel: +86-931-2976573; Fax: +86-931-2976578; E-mail: chentj1971@126.com; chentj@lut.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63739-6

