DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2015.08.036
塔里木盆地致密砂岩气储层微观孔隙结构
孟智强1, 2,郭和坤2, 3,刘强1, 2,姜柏材1, 2,李海波2, 3
(1. 中国科学院大学,北京,100190;
2. 中国科学院渗流流体力学研究所,河北 廊坊,065007;
3. 中国石油勘探开发研究院廊坊分院,河北 廊坊,065007)
摘要:为研究塔里木盆地库车坳陷储层储集条件及其微观孔隙结构,应用核磁共振技术测定不规则岩样核磁孔隙度与核磁渗透率,应用高速离心实验标定岩样T2截止值,划定可动流体饱和度与不同喉道半径控制的可动流体体积分数,应用低温氮气吸附实验,深入分析岩样微观孔隙结构,建立致密砂岩储层渗透率、可动流体饱和度与微观孔隙特征之间的关系。研究结果表明:库车坳陷J1a层位致密砂岩气藏在深度4~5 km的储层占主要部分,平均渗透率0.021×10-3~3.982×10-3 μm2,平均孔隙度2.96%~7.17%;平均比表面1.83~2.35 m2/g,为页岩的1/10;该储层中半径为50 nm以下喉道控制孔隙占总孔隙60%左右,半径50 nm以下孔隙以介孔为主,平均占总孔隙的33.03%。当渗透率由0.1×10-3 μm2以下逐渐增大至1×10-3 μm2以上时,砂岩孔隙形状由墨水瓶孔为主逐渐变为平行板状孔,再逐渐变为V型孔。库车坳陷致密砂岩气物性较差,占总孔隙27%的由半径50 nm以下喉道控制的较大孔隙可以作为致密砂岩气藏进一步开发突破点。
关键词:库车坳陷;致密砂岩;核磁共振;氮气吸附;孔径分布;孔隙结构
中图分类号:TE311 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2015)08-3032-08
Microscopic pore structure for tight sandstone gas reservoirs in Tarim Basin
MENG Zhiqiang1, 2, GUO Hekun2, 3, LIU Qiang1, 2, JIANG Bocai1, 2, LI Haibo2, 3
(1. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China;
2. Institute of Porous Flow and Fluid Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Langfang 065007, China;
3. Branch of Research Institute of Petroleum Exploitation,
China National Petroleum Corporation, Langfang 065007, China)
Abstract: In order to investigate the reservoir conditions and microscopic pore structure in the Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin, the NMR porosity and permeability were analyzed by using the nuclear magnetic resonance technology for the irregular rock sample. T2 cutoff of the rock sample was calibrated and the movable fluid saturation and movable fluid percentage controlled by different throat radius were delimited by using the centrifugal experiment method. Simultaneously, the cryogenic nitrogen adsorption was applied to analyze the microscopic pore structure, and the relations between the tight sandstone reservoir permeability characteristics, the movable fluid saturation and microscopic pores were established. The results show that the Kuqa depression J1a layers of tight sandstone gas reservoirs in 4-5 km depth accounts for the major part, the average permeability is 0.021×10-3-3.982×10-3 μm2, the average porosity is 2.96%-7.17%, and the average surface area is 1.83-2.35 m2/g, which is 1/10 of the shale. The pore is controlled by throats whose radius is less than 50 nm, which accounts for about 60% of total pore. The pore whose radius is below 50 nm accounts for about 33% of the total porosity. When the permeability increases from less than 0.1×10-3 μm2 to more than 1×10-3 μm2, the sandstone pore shape dominated by the inkbottle-like pores gradually becomes parallel plate hole, and then gradually becomes V-shaped hole. Overall tight sandstone reservoirs properties are relatively poor. The large pores, about 27% of the total pore, are controlled by the throats below 50 nm, which can serve as a breaking point for development of tight sandstone gas reservoirs.
Key words: Kuqa Depression; tight sandstone; NMR; nitrogen adsorption; pore size distribution; pore structure
近年来,非常规油气资源勘探开发进入高速发展时期,中国致密气可采资源量为8.8×1012~12.1×1012 m3[1-2],而且是目前中国天然气增储上产的最为现实的待开发非常规油气资源。邹才能等[3-5]认为:致密气藏储集空间主体为纳米级孔喉系统,局部发育微米级至毫米级孔隙,并且储层孔喉直径为40~700 nm;与页岩气形成过程相比,致密砂岩气藏一般为储集层,经过一次运移或短距离二次运移[6];就成因类型来说,塔里木盆地库车坳陷依南2侏罗系气藏为“致密深盆气藏”,即致密储层形成之后充注天然气,而迪那2气藏古近系成因类型为“致密常规气藏”,即致密储层形成之前,天然气已大量充注[7-10]。致密砂岩气藏不同的地质形成过程和成因类型使天然气在砂岩中吸附、聚集的形式不同,由此形成的储层结构和孔隙特性也影响气体储集和运移的方式。致密岩心微观孔隙特征分析技术包括核磁共振、氮气吸附、高压压汞和扫描电镜等[11],核磁共振作为岩心孔隙特征分析技术,适用范围广,对于低孔低渗岩心可以达到较好效果;氮气吸附对分析致密岩心孔容、孔径分布和孔隙形态等具有较好效果。本文作者采用核磁共振技术结合离心实验对库车坳陷6口井40块不规则岩样与8块规则柱塞样核磁渗透率进行测量,并通过高速离心技术确定半径为50 nm以下喉道控制的孔隙占总孔隙的比例;通过低温氮气吸附实验脱附线对致密砂岩岩心半径50 nm以下孔隙孔容分布进行分析,并确定半径50 nm控制孔隙占总孔隙的比例;通过等温吸附线与迟滞回线类型对致密砂岩岩心孔隙形状进行分析,并首次将致密砂岩岩心孔隙度、渗透率、可动流体饱和度与孔容、比表面、孔隙形状等建立关系,为库车坳陷致密砂岩气藏进一步开发提供依据。
1 实验样品与方法
1.1 实验样品
实验样品共48块取自塔里木盆地库车坳陷J1a层,其中44块岩心样品取心深度为4 038.80~5 012.10 m,4块岩心样品取心深度为965.70~1 678.30 m,岩性绝大多数为粗砂岩,其中有些含有砾石,极少量为泥质粉砂岩,大部分岩心取心地层深,而且岩心孔隙度、渗透率都很小,岩心资料表见表1。
1.2 实验仪器与方法
核磁共振实验仪器采用中石油勘探开发研究院廊坊分院自主研发的RecCore04型低磁场核磁共振岩心分析仪,可以对长度不大于5 cm,直径2.5 cm岩心含水信号量进行精确扫描,在反演得到的T2谱中,通过标定岩心T2截止值时间,可以得到岩心束缚水饱和度和可动流体饱和度,进而计算得到核磁孔隙度与渗透率。
表1 致密砂岩气藏6口井岩心资料
Table 1 Tight sandstone gas reservoir core data from six wells
低温氮气吸附实验采用美国Quantachrome公司生产的 自动等温吸附仪,采用温度在77.4 K(液氮温度)下以氮气(纯度为99.99%)为吸附介质,在相对压力0.01~1.00之间测定吸附等温线,测试孔隙直径范围为0.35~100.00 nm,最低可测的比表面积为5×10-4 m2/g,最小检测孔体积为0.01 mm3/g。在低温氮气吸附实验测试前,为了消除样品中残留的束缚水和毛细管水分以及杂质,所有样品都在300 ℃经过3 h高温抽真空预处理。
自动等温吸附仪,采用温度在77.4 K(液氮温度)下以氮气(纯度为99.99%)为吸附介质,在相对压力0.01~1.00之间测定吸附等温线,测试孔隙直径范围为0.35~100.00 nm,最低可测的比表面积为5×10-4 m2/g,最小检测孔体积为0.01 mm3/g。在低温氮气吸附实验测试前,为了消除样品中残留的束缚水和毛细管水分以及杂质,所有样品都在300 ℃经过3 h高温抽真空预处理。
2 核磁共振实验
岩心渗透率、可动流体饱和度和不同半径喉道控制的可动流体体积分数是划分储层类型、评价储层性质、选择开发方式重要的参数。由于岩心不完整,常规气测渗透率实验无法进行,核磁共振技术可以通过标定平行岩样T2截止值,得到待测岩心束缚水饱和度(或者可动流体饱和度),进而通过Coates-cutoff模型[12-14]计算得到待测岩心渗透率;由于标定岩心在2.76 MPa下进行离心,通过离心力与控制喉道半径的转换关系[15-17],所标定岩心控制喉道半径为50 nm,可以计算在半径为50 nm以下喉道控制孔隙占总孔隙的体积分数。如表2所示为所测的各井岩心核磁孔隙度、渗透率、束缚水饱和度(对半径为50 nm以下喉道控制孔隙占总孔隙的体积分数)与可动流体孔隙度(半径为50 nm以上喉道控制孔隙的孔隙度)数据。如图1所示为库车坳陷依南2井~克孜1井区5口井所选代表岩心与明南1井中3个岩心的核磁共振T2谱线。
由表2可知:所测的核磁孔隙度与表1中的水测孔隙度基本一致,说明核磁孔隙度测试结果准确。前5口井平均核磁孔隙度在2.40%~6.58%之间,为低渗透砂岩孔隙度(10%~15%)的一半,平均核磁渗透率在0.021×10-3~3.982×10-3 μm2之间,第6口井平均核磁孔隙度为16.69%,平均核磁渗透率为15.67×10-3 μm2;48块岩心中最小渗透率为1.56×10-7 μm2,渗透率小于0.1×10-3 μm2的岩心为16块(依南2与依南4井占11块),占所测岩心的1/3;从孔隙度和渗透率参数来看,该1~5口井储层属于典型致密气藏储层。
表2 6口井岩心核磁共振分析结果
Table 2 NMR analysis results of the core from 6 wells
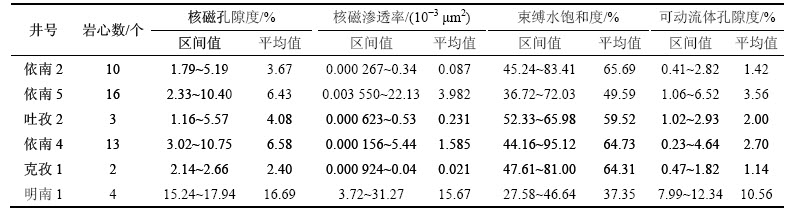

图1 8个致密砂岩气藏岩心核磁共振T2谱
Fig. 1 NMR T2 spectrum of 8 tight sandstone gas reservoir cores
由表1可知:地层深度大于4 km的前5口井岩心视密度平均在2.47 g/cm3以上,且前5口井T2谱明显呈现双峰形态,说明岩心内大孔与小孔孔隙半径有明显界限,孔径分布分散,T2弛豫时间10 ms以下孔隙占总孔隙一半左右,说明黏土微孔较多。第6口井岩心T2谱呈现单峰形态,说明岩心内孔径分布较集中,而且T2弛豫时间在10 ms以上占主要部分,说明岩心内孔隙半径较大,以粒间孔为主。从表2也可以看出:地层深度与岩心渗透率有一定关联;前5口井孔隙度约为第6口井的1/4,而且束缚水饱和度是第6口井的2倍。
由表2可以看出:前5口井岩心束缚水饱和度为50%~65%,即半径为50 nm以下喉道控制孔隙占总孔隙60%左右,平均可动流体孔隙度在3%左右,开发难度较大。
3 低温氮气吸附实验
低温氮气吸附实验利用氮气分子在低温下在固体表面易吸附的特点,分析岩心内极微小空隙。利用静态体积法[18],将已知量的气体通到自动恒定在吸附温度的样品管内,气体在样品表面发生吸附,固定空间内的气体压力不断降低,直到吸附质与吸附物质达到平衡。平衡压力下吸附质的量就是供气量与残留在气相中的吸附物质的量之差,实验过程中需要测量系统的压力、温度和体积。岩心比表面积通过Brunauer,Emmett和Teller推导出的BET方程计算,在相对压力0.05~0.35内作BET 直线图[19-20],求得单分子层饱和吸附量,从而计算样品的BET比表面积。岩心孔径分布通过Barret,Joyner和Halenda方法计算,孔体积和平均孔径由相对压力约为1时的氮气吸附量计算得到[21],由于BJH方法主要针对岩心介孔进行分析,所测的岩心孔隙直径基本都分布在0~50 nm之间。图2所示为6个岩心的等温吸附曲线,图3所示为岩心孔径分布图,表3所示为岩心所有孔隙的比表面积、孔隙半径在50 nm以下岩心的平均孔隙半径、孔隙率(孔隙半径50 nm以下孔隙体积占岩心总体积的比例)、孔隙百分数(孔隙半径为50 nm以下的孔隙占总孔隙比例)。
所选6个岩心为48个岩心中等温吸附脱附曲线具有普遍特征的岩心,根据国际纯粹与应用化学联合会(IUPAC)提出的物理吸附等温线分类[22],以上6个岩心都属于IV型等温线,典型特征是等温线的吸附曲线与脱附曲线不一致,可以观察到迟滞回线。从图2可以看到,相对压力P/P0(其中P为当前压力,MPa;P0为-196.15 ℃下的氮气饱和蒸汽压,约为0.101 MPa)在0~0.8范围内,等温吸附线氮气吸附量上升缓慢,当相对压力P/P0在0.8~1.0的区间时,氮气吸附量有一个迅速升高的过程,而且迟滞回线突变点[23]在相对压力为0.4附近,说明P/P0>0.4时,发生毛细管凝聚现象。
由于氮气在同一孔内凝聚与解聚现象发生在不同压力,所以出现迟滞回环,等温线回环形状与固体颗粒的孔形有关。分别对比3组岩心(图2(a)和2(b),图2(c)和2(d),图2(e)和2(f))迟滞回线有显著区别,依南2井1号样,依南5井6号样,明南1井2号样和明南1井3号样岩心按照IUPAC分类为H3型迟滞回线,在较高相对压力区域没有表现出任何吸附限制,表明该岩心孔隙主要为缝形孔;但是明南1井2号样和明南1井3号样岩心等温脱附与吸附线几乎重合,说明脱附过程吸附量随压力减小下降很快,接近等温吸附线III型,孔径分布主要以较大介孔为主,孔隙结构以V型孔和产生少量迟滞回线的平行板状孔为主。依南2井8号样和吐孜2井2号样岩心为H2型迟滞回线,孔径分布比H1型更宽,突变点下降陡峭,孔隙结构主要以平行板状孔与细颈广体墨水瓶孔为主。
由图2可知:渗透率小于0.1×10-3 μm2的依南2井8号样和吐孜2井2号样岩心,迟滞环普遍较宽,说明其孔隙结构墨水瓶型孔隙数量多,岩心内存在大量微孔瓶颈,最大吸附量为3.3 cm3/g,是大渗透率岩心吸附总量的66%;而随着渗透率的增大(如依南2井1号样、依南5井6号样、明南1井2号样和明南1井3号样),迟滞环宽度逐渐减小,吸附量增大,最大吸附量为5 cm3/g。可以看出:岩心孔隙结构与岩心渗透率有密切的关系,渗透率小于0.1×10-3 μm2时,砂岩岩心孔隙以墨水瓶孔隙为主,0.1×10-3~1×10-3 μm2之间以平行板状孔为主,大于1×10-3 μm2以V型孔和产生少量迟滞回线的平行板状孔为主。
图3中4个致密砂岩心孔容分布结果取自48块实验岩心中具有普遍特征的岩心,从图3可以看出:渗透率小于0.1×10-3 μm2的岩心,孔隙半径1.67~2.14 nm的孔隙体积最多,即微孔较多,占半径50 nm以下孔隙总体积的50%左右;0.1×10-3~1×10-3 μm2的岩心孔隙半径在1.67~2.14 nm与半径大于8.24 nm的孔隙体积占主要部分,占半径50 nm以下孔隙总体积的55%左右;渗透率大于1×10-3 μm2的岩心微孔基本不发育,而主要孔隙空间由较大介孔构成,孔隙半径大于8.24 nm的孔隙占半径50 nm以下孔隙总体积的75%。

图2 6个致密砂岩岩心等温吸附曲线
Fig. 2 Isothermal adsorption curves of 6 tight sandstone core
表3 6口井氮气吸附分析结果
Table 3 Nitrogen adsorption analysis results of 6 wells

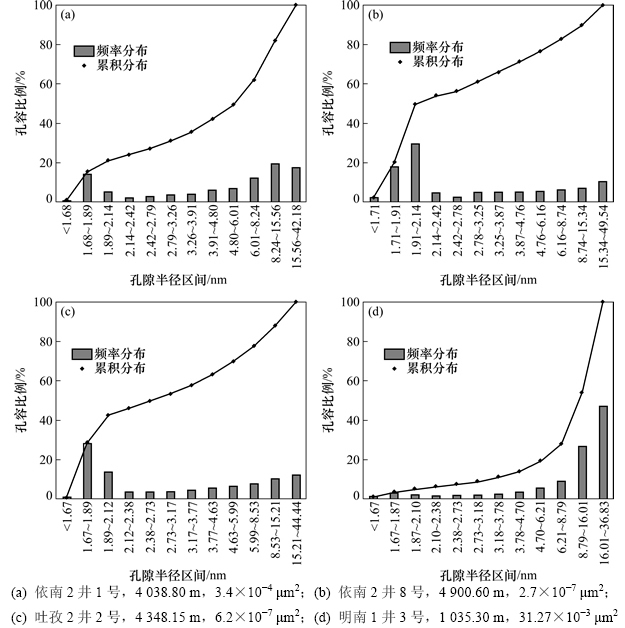
图3 4个致密砂岩岩心孔容分布
Fig. 3 Pore volume distribution of 4 tight sandstone cores
由表3可以看出:渗透率小的岩心平均比表面积大,平均在1.83~2.35 m2/g之间,而渗透率大的岩心比表面积较小,平均为1.57 m2/g,这是由于渗透率大的岩心微孔发育不足,孔隙主要由大孔构成,表面积较小[24]。六盘山盆地下白垩统乃家河组页岩[25]的比表面积可以达33.87 m2/g,平均为19.80 m2/g,是致密砂岩的10倍,说明致密砂岩气藏吸附作用储集天然气不明显,但是总体孔隙半径比页岩的大,仍有较好储集空间。
从孔容测试结果来看,这6口井的半径50 nm以下孔隙的平均孔容在4.48~7.51 mm3/g之间,平均孔隙率为1.15%~1.84%,平均孔隙百分数为9.30%~ 38.78%,渗透率较大的第6口井孔隙百分数最小,半径50 nm以下孔隙占岩心总孔隙比例明显较小,只有9.30%,说明该井以半径50 nm以上大孔为主,其他井中半径50 nm以下孔隙平均占岩心总孔隙的30%左右,最大达到54.08%。
从平均孔隙半径来看,这6口井半径50 nm以下孔隙平均孔隙半径为8.57~14.46 nm,说明储层中半径50 nm以下孔隙主要储集空间仍为介孔,与乃家河组页岩相比,页岩平均孔隙半径为3.687~4.294 nm,致密砂岩样平均孔隙半径是页岩的3倍。说明致密砂岩气藏孔隙相对页岩较大,对于气体在岩心中的渗流较有利。
4 结论
1) 核磁共振技术与离心实验分析得到库车坳陷J1a层位致密砂岩气藏4~5 km储层为典型致密砂岩储层,平均孔隙度为2.40%~6.58%,平均渗透率为0.021×10-3~3.982×10-3 μm2;渗透率小于0.1×10-3 μm2的岩心占所取岩样的33%,储层中半径50 nm以下喉道控制孔隙平均占总孔隙60%左右,开发难度较大。
2) 低温氮气吸附实验得出储层渗透率与孔隙结构相关性明显,渗透率小于0.1×10-3 μm2岩心孔隙结构主要由微孔构成,占半径50 nm以下孔隙总体积的50%左右,孔隙形状以墨水瓶孔为主,加上少量平行板状孔;渗透率在0.1×10-3~1×10-3 μm2之间的岩心孔隙结构由半径为1.67~2.14 nm和8.24~50 nm的孔隙构成,占半径50 nm以下孔隙总体积的55%左右,孔隙形状以平行板状孔为主;渗透率大于1×10-3 μm2的岩心孔隙结构主要以较大介孔为主,孔隙半径大于8.24 nm的孔隙占半径50 nm以下孔隙总体积的75%,孔隙形状以V型孔和产生少量迟滞回线的平行板状孔为主。
3) 与乃家河组页岩相比,致密砂岩气储层比表面是页岩的1/10,主要原因是致密砂岩微孔孔隙发育不足;半径50 nm以下孔隙平均孔容为4.48~7.51 mm3/g,平均孔隙半径在8.57~14.46 nm之间,是页岩的3倍,而且半径50 nm以下孔隙占总孔隙的30%左右,说明仍存在较大孔隙空间。总体来说,致密砂岩气藏由吸附作用储气不明显,但孔隙相对页岩较大,仍有较好储集空间,对气体的渗流有利。
4) 半径50 nm以下喉道控制孔隙占总孔隙百分数为60%,与低温氮吸附半径50 nm以下孔隙占总孔隙的33%相比,说明突破岩心半径50 nm以下喉道控制将能开发出喉道控制的半径50 nm以上的较大孔隙(较大孔隙占总孔隙的27%),该类孔隙可以作为库车坳陷致密砂岩气藏进一步开发突破点。
参考文献:
[1] 贾承造, 郑民, 张永峰. 中国非常规油气资源与勘探开发前景[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(2): 129-136.
JIA Chengzao, ZHENG Min, ZHANG Yongfeng. Unconventional hydrocarbon resources in China and the prospect of exploration and development[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(2): 129-136.
[2] 戴金星, 倪云燕, 吴小奇. 中国致密砂岩气及在勘探开发上的重要意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(3): 257-264.
DAI Jinxing, NI Yunyan, WU Xiaoqi. Tight gas in China and its significance in exploration and exploitation[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(3): 257-264.
[3] 邹才能, 陶士振, 杨智, 等. 中国非常规油气勘探与研究新进展[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2012, 31(4): 312-322.
ZOU Caineng, TAO Shizhen, YANG Zhi, et al. New Advance in Unconventional Petroleum Exploration and Research in China[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2012, 31(4): 312-322.
[4] 邹才能, 朱如凯, 吴松涛, 等. 常规与非常规油气聚集类型、特征、机理及展望: 以中国致密油和致密气为例[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(2): 173-187.
ZOU Caineng, ZHU Rukai, WU Songtao, et al. Types, characteristics, genesis and prospects of conventional and unconventional hydrocarbon accumulations: Taking tight oil and tight gas in China as an instance[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(2): 173-187.
[5] 邹才能, 杨智, 陶士振, 等. 纳米油气与源储共生型油气聚集[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(1): 13-26.
ZOU Caineng, YANG Zhi, TAO Shizhen, et al. Nano-hydrocarbon and the accumulation in coexisting source and reservoir[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(1): 13-26.
[6] 柳广弟, 张厚福. 石油地质学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2010: 171-199.
LIU Guangdi, ZHANG Houfu. Petroleum geology[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2010: 171-199.
[7] 李卓, 姜振学, 庞雄奇, 等. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷致密砂岩气藏成因类型[J].地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2013, 38(1): 156-164.
LI Zhuo, JIANG Zhenxue, PANG Xiongqi, et al. Genetic Types of the Tight Sandstone Gas Reservoirs in the Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 2013, 38(1): 156-164.
[8] 何登发, 李德生, 何金有, 等. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷和西南坳陷油气地质特征类比及勘探启示[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(2): 201-218.
HE Dengfa, LI Desheng, HE Jinyou, et al. Comparison in petroleum geology between Kuqa depression and Southwest depression in Tarim Basin and its exploration significance[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(2): 201-218.
[9] 姜振学, 林世国, 庞雄奇, 等. 两种类型致密砂岩气藏对比[J]. 石油实验地质, 2006, 28(3): 210-214, 219.
JIANG Zhenxue, LIN Shiguo, PANG Xiongqi, et al. The Comparison of two types of tight sand gas reservoir[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2006, 28(3): 210-214, 219.
[10] 朱光有, 张水昌, 陈玲, 等. 天然气充注成藏与深部砂岩储集层的形成: 以塔里木盆地库车坳陷为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2009, 36(3): 347-357.
ZHU Guangyou, ZHANG Shuichang, CHEN Ling, et al. Coupling relationship between natural gas charging and deep sandstone reservoir formation: A case from the Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2009, 36(3): 347-357.
[11] 杨峰, 宁正福, 胡昌蓬, 等. 页岩储层微观孔隙结构特征[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(2): 301-311.
YANG Feng, NING Zhengfu, HU Changpeng, et al. Characterization of microscopic pore structures in shale reservoirs[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(2): 301-311.
[12] 彭石林, 叶朝辉, 刘买利. 多孔介质渗透率的NMR测定[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2006, 23(2): 271-282.
PENG Shilin, YE Chaohui, LIU Maili. Measurement of Permeability of Porous Rock Using NMR T2 Relaxation Distribution[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2006, 23(2): 271-282.
[13] Taicher Z, Coates G, Gitartz Y, et al. A comprehensive approach to studies of porous media (rocks) using a laboratory spectrometer and logging tool with similar operating characteristics[J]. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 1994, 12(2): 285.
[14] Jerosch-Herold M, Thomann H. Permeability determination from NMR relaxation measurements for fluids in porous media[J]. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 1994, 13(6): XIV-XIV(1).
[15] 李海波, 朱巨义, 郭和坤. 核磁共振T_2谱换算孔隙半径分布方法研究[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2008, 25(2): 273-280.
LI Haibo, ZHU Juyi, GUO Hekun. Methods for Calculating Pore Radius Distribution in Rock from NMR T2 Spectra[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2008, 25(2): 273-280.
[16] 师调调, 孙卫, 何生平. 低渗透储层微观孔隙结构与可动流体饱和度关系研究[J]. 地质科技情报, 2012, 31(4): 81-85.
SHI Tiaotiao, SUN Wei, HE Shengping. Relationship between Micro-pore Structure and Movable Fluid Saturation in Low Permeability Reservoir[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2012, 31(4): 81-85.
[17] 杨胜来. 油层物理学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2004: 221-222.
YANG Shenglai. Petro-physics[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2004: 221-222.
[18] 陈诵英, 孙予罕, 丁云杰, 等. 吸附与催化[M]. 郑州: 河南科学技术出版社, 2001: 27-28.
CHEN Songying, SUN Yuhan, DING Yunjie, et al. Adsorption and catalysis[M]. Zhengzhou: Henan Science and Technology Press, 2001: 27-28.
[19] 田华, 张水昌, 柳少波, 等. 压汞法和气体吸附法研究富有机质页岩孔隙特征[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(3): 419-427.
TIAN Hua, ZHANG Shuichang, LIU Shaobo, et al. Determination of organic-rich shale pore features by mercury injection and gas adsorption methods[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(3): 419-427.
[20] 朱晓军, 蔡进功. 泥质烃源岩的比表面与有机质关系研究进展及意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2012, 33(3): 375-384.
ZHU Xiaojun, CAI Jingong. Progress and significance of research on relation between specific surface area and organic matter in argillaceous source rocks[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2012, 33(3): 375-384.
[21] 谢晓永, 唐洪明, 王春华, 等. 氮气吸附法和压汞法在测试泥页岩孔径分布中的对比[J]. 天然气工业, 2006, 26(12): 100-102, 202-203.
XIE Xiaoyong, TANG Hongming, WANG Chunhua, et al. Contrast of nitrogen adsorption method and mercury porosimetry method in analysis of shale pore size distribution[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2006, 26(12): 100-102, 202-203.
[22] Brunauer S, Deming L S, Deming W E, et al. On a theory of the van der Waals adsorption of gases[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1940, 62(7): 1723-1732.
[23] 巨文军, 申丽红, 郭丹丹. 氮气吸附法和压汞法测定Al2O3载体孔结构[J]. 广东化工, 2009, 36(8): 213-214+228.
JU Wenjun, SHEN Lihong, GUO Dandan. Nitrogen adsorption method and mercury injection method determination the pore structure of alumina carrier[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2009, 36(8): 213-214+228.
[24] 杨建, 康毅力, 李前贵, 等. 致密砂岩气藏微观结构及渗流特征[J]. 力学进展, 2008, 38(2): 229-236.
YANG Jian, KANG Yili, LI Qiangui, et al. Characters of Micro-structure and percolation in tight sandstone gas reservoirs[J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2008, 38(2): 229-236.
[25] 杨峰, 宁正福, 张世栋, 等. 基于氮气吸附实验的页岩孔隙结构表征[J]. 天然气工业, 2013, 33(4): 135-140.
YANG Feng, NING Zhengfu, ZHANG Shidong, et al. Characterization of pore structures in shales through nitrogen adsorption experiment[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2013, 33(4): 135-140.
(编辑 赵俊)
收稿日期:2014-06-19;修回日期:2014-09-20
基金项目(Foundation item):国家科技重大专项(2011ZX05013-002)(Project (2011ZX05013-002) supported by the National Science and Technology Major Program of China)
通信作者:郭和坤,高级工程师,从事渗流理论和核磁共振技术应用的研究;E-mail:nmrghk69@petrochina.com.cn