
Effect of traveling magnetic field on dendrite growth of Pb-Sn alloy during directional solidification
MIN Zhi-xian, SHEN Jun, WANG Ling-shui, LIU Lin
State Key Laboratory of Solidification Processing, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710072, China
Received 28 September 2010; accepted 24 June 2011
Abstract: The influence of melt convection on dendrite growth during the upward-directional solidification of Pb-33%Sn binary alloys was investigated. The melt convection was modulated by traveling magnetic field. When the direction of traveling magnetic field was changed from upward to downward, the primary dendrite spacing gradually increased, and the distribution peak of the primary dendrite spacing shifted to the field of narrower spacing. These result from the different intensities of melt convection, which are controlled by the traveling magnetic field. The effects of the traveling magnetic field on melt convection are similar to those of adjustment in the gravity level, thus, the primary dendrite spacing varies. When the intensity of the traveling magnetic field was 1 mT, and the drawing speed was 50 μm/s, the gravity acceleration reached 0.22g for the downward-traveling magnetic field and 3.07g for the upward-traveling magnetic field.
Key words: directional solidification; microstructure; Pb-Sn alloy; traveling magnetic field
1 Introduction
Dendrites are the most common patterns during directional solidification. Dendrite formation includes many characteristic properties and lengths, such as primary dendrite spacing, secondary dendrite spacing, and dendrite tip radius. In order to describe these lengths, detailed theoretical models were established under diffusive conditions [1]. In most experimental studies, however, the convection effects play an important role in terrestrial conditions, thus causing conflicts between the theoretical predictions and experimental results. Recent studies showed that convection has significant effects on dendrite spacing [2-3]. Many methods, such as the ACRT method [4] and capillary crucible method [5], and different types of magnetic fields, such as alternating magnetic field [6], rotating magnetic field [7] and traveling magnetic field [8], were used to investigate the effects of convection on the microstructure and solute distribution of solids during solidification.
The effect of magnetic fields as a remote method for controlling conductive melt convection during directional solidification was summarized [9]. Traveling magnetic fields have many advantages. For example, they interact more effectively with buoyancy-driven convection in conductive melts and are excellent tools for controlling macroscopic interface morphology. They were widely used for planar solid-liquid interfaces in crystal growth via the vertical Bridgman technique and vertical gradient freeze method for metallic alloys [8-9]. Few studies, however, focused on the effects of the traveling magnetic field on convection in “mushy” zones during directional solidification. The purpose of this work is to study the effects of a traveling magnetic field on dendrite growth in Pb-33%Sn alloys during directional solidification. The primary dendrite spacing and dendrite morphology are investigated to determine the influence of melt convection induced by the traveling magnetic field.
2 Experimental
Samples of Pb-33%Sn (mass fraction) binary alloy were prepared with 99.99% Pb, and 99.9% Sn, using an electrical resistance furnace under the conditions of mechanical stirring and argon atmosphere. The specimen was processed in an aluminum crucible with an inner diameter of 7 mm and a length of 80 mm. The samples were re-melted, directionally solidified in a vertical Bridgman-type furnace, and then cooled by liquid metal at (65±1) °C. Two K-type (NiCr-NiSi) thermocouples were used to determine the temperature gradient, which was measured to be about 140 K/cm. During directional solidification, the drawing speeds were selected at 5, 10, and 50 μm/s. The traveling magnetic field was supplied by an experimental apparatus, which consisted of three coaxial coils in a delta connection and a standard three-phase alternating-current with a frequency of 50 Hz and phase shift of 120°. A Gauss meter was used to measure the intensity of traveling magnetic field at a precision of ±0.1 mT. The primary arm spacing was measured on the transverse section by hand-counting the number of dendrites in a specific area, according to λ1=B(A/N)-1/2, where A is the area and B is a constant taken as 1. The distribution of primary dendrite spacing was based on statistics obtained by measuring the distances between adjacent dendrite cores in a transverse section. A Lecia DM4000M optical microscope was employed to characterize the dendrite morphologies and spacing.
3 Results and discussion
Figure 1 shows the primary dendrite arm spacings of a Pb-33%Sn binary alloy with various traveling magnetic fields at different drawing speeds during upward-directional solidification under the condition of 1g gravity. The figure shows that different directions of traveling magnetic field cause a variety of primary dendrite spacings. As compared to the condition where no traveling magnetic field was applied, the primary dendrite spacing decreased for an upward-traveling magnetic field of 1 mT and increased for the same magnitude of downward-traveling magnetic field. Figure 2 shows the transverse microstructures of the Pb-33%Sn alloy during directional solidification at a drawing speed of 50 μm/s. Figure 3 shows the distributions of primary dendrite spacing obtained from Fig. 2. The dotted lines represent the Gaussian fit through the data points in Fig. 3, which give the corresponding Gaussian fit parameters as: H the peak height, A the center, and W the width. The center of the dotted lines shows that the primary dendrite spacing decreases from 113.98 μm at downward- to 74.715 μm at upward-traveling magnetic fields. The peak of distribution of primary dendrite spacing shifts to the field with narrower spacing, and the maximum primary dendrite spacing (λmax) remains almost unaltered. The minimum primary dendrite spacing (λmin) sharply decreases. The ratio of the maximum primary dendrite spacing to the minimum one (λmax/λmin) was found to be 2.2 for 1 mT downward- traveling magnetic field. The same ratio was found to be 3.75 for 1 mT upward- traveling magnetic field.
The above results indicate that the traveling magnetic field exerts significant effects on primary dendrite spacing and its disorder for Pb-33%Sn alloys during upward-directional solidification. Adjusting the direction of traveling magnetic field can induce a forced flow which has an amplitude and direction that can be conveniently and remotely controlled, respectively. The forced flow takes on the form of a single axisymmetric loop whose direction has a significant effect on buoyancy-driven convection [10]. This means that the flow intensity in the melt can be controlled by the traveling magnetic field. When the forced flow is induced by a traveling magnetic field and has the same magnitude as natural convection, the forced flow, coupled with buoyancy-driven convection, enhances the upward-traveling magnetic field in the melt. On the other hand, buoyancy-driven convection can be counteracted for a downward-traveling magnetic field. Buoyancy- driven convection is generated by density inversion coupled with gravity within the inter-dendritic region during the upward directional solidification of hypo-eutectic Pb-Sn alloys [3]. The primary dendrite spacing is reduced by buoyancy-driven convection and controlled by local solidification conditions. The mechanism for decreasing primary dendrite spacing has been pointed out in the previous reports [11]. The new primary arm is formed from a secondary arm with increasing inter-dendritic constitutional supercooling. Thus, the primary dendrite spacing is reduced.
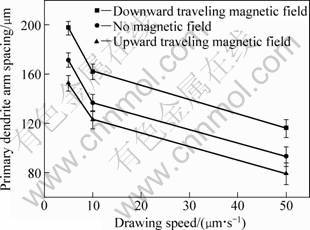
Fig. 1 Primary dendrite arm spacings of directionally solidified Pb-33%Sn alloy with different traveling magnetic fields
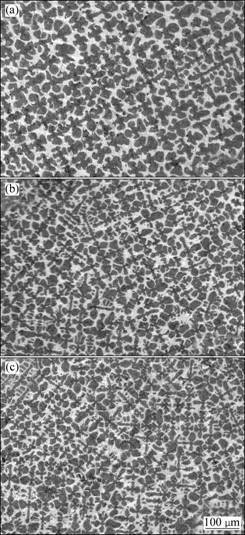
Fig. 2 Transverse microstructures of directionally solidified Pb-33%Sn at temperature gradient of 140 K/cm and with drawing speed of 50 μm/s and different parameters of TMF: (a) Downward, 1 mT; (b) Without magnetic field; (c) Upward, 1 mT
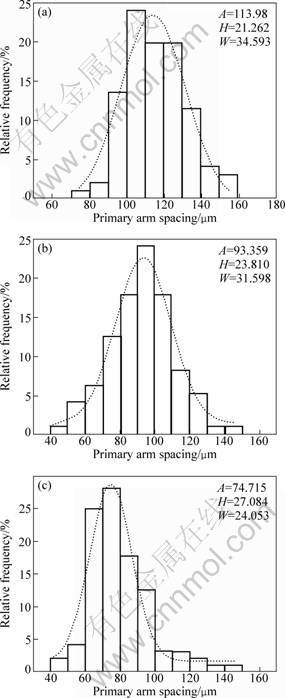
Fig. 3 Distribution of primary dendrite spacings of Pb-33%Sn binary alloy directionally solidified at drawing speed of 50 μm/s under different parameters of TMF: (a) Downward, 1 mT; (b) Without magnetic field; (c) Upward, 1 mT
Buoyancy-driven convection influences solute transport in inter-dendritic melts, and in turn, inter- dendritic constitutional supercooling. The magnitude of buoyancy-driven convection is amplified by increasing levels of gravity. Therefore, the primary arm spacing decreases from low- to high-gravity portions of aircraft parabolas [12], the sketch of which is shown in Fig. 4. This indicates that the primary arm spacing decreases as the intensity of the melt convection is enhanced. The result of this work is in agreement with the previous findings. The primary dendrite spacing is not a unique value, even under diffusive conditions. Rather, it is a range of possible spacings (λcrit<λ<2λcrit). The λmax/λmin equal to 2.2 under 1 mT downward-traveling magnetic field approaches 2 under diffusive conditions. When buoyancy-driven convection occurs in the melt, steady-state dendrite growth cannot be achieved, even when the temperature gradient in the melt remains constant [13]. As the intensity of convection in the melt increases, the new primary arms continuously rise and grow along the longitudinal direction. Thus, the different stages of primary dendrites, e.g. the new primary arm with a smaller dendritic spacing and the steady primary arm with a larger dendritic spacing, appear in the same transverse section. Therefore, the value of λmax/λmin increases to 3.75 under 1 mT upward-traveling magnetic field.
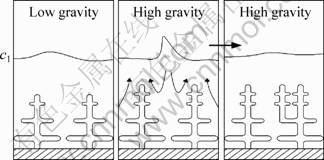
Fig. 4 Schematic for decreasing primary dendrite spacing during directional solidification from low- to high-gravity portion of aircraft parabolas
LEHAMANN [14] developed a model explaining the effect of convection on primary dendrite spacing with an order of magnitude analysis. The relationship between convection and primary dendrite spacing is shown as follows:
 (1)
(1)
where λ(gt) is the primary dendrite spacing under convective condition, which is the experimental data in this work; λ0 is the primary dendrite spacing under diffusive conditions, which can be calculated by Hunt-Lu model [15]; gt is a multiple of gravity acceleration g, which is equal to 9.81 m/s2; u is the fluid flow rate; and v is the drawing speed during solidification. According to Eq. (1), the value of fluid flow rate can be estimated. These values are 29.6 μm/s for downward-traveling magnetic field, 37.6 μm/s for no field and 46.1 μm/s for upward-traveling magnetic field. One can see that, the flow rate increases with the direction of traveling magnetic field changing from downward to upward.
The effect of the traveling magnetic field on the average primary dendrite spacing is similar to that of adjusting the gravity level. The scaling relationship between the primary dendrite spacing and gravity level is [16]
 (2)
(2)
where M is a parameter related to the Buoyancy-driven convection in inter-dendritic melts. Using Eq. (2), the gravity parameter gt reaches 3.07 and 0.22 for upward- and downward- traveling magnetic fields at 1 mT, respectively, by scaling relation at a drawing speed of 50 μm/s. Combined with the flow rate calculated by Eq. (1), we can see that the flow rate is increased as the gravity acceleration increases.
4 Conclusions
1) The average primary dendrite spacing and the distribution of primary dendrite spacing vary with changing traveling magnetic fields. This is due to that the intensity of the melt convection is modulated by traveling magnetic field.
2) The effects of traveling magnetic field on melt convection are similar to those from adjustment in gravity levels. When the intensity of the traveling magnetic field is 1 mT and the drawing speed is 50 μm/s, the gravity accelaration reaches 3.07g and 0.22g for the upward and downward traveling magnetic fields, respectively.
Reference
[1] FU Heng-zhi, GUO Jing-jie, LIU Lin, LI Jin-shan. Directional solidification and processing of advanced materials [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2008: 250-253. (in Chinese)
[2] QU Min, LIU Lin, TANG Feng-tao, ZHANG Jun, FU Heng-zhi. Effect of sample diameter on the primary dendrite spacing of directionally solidifed Al-4%Cu alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2009, 19(1): 1-8.
[3] TEWARI S N, SHAH R. Macrosegregation during dendritic arrayed growth of hypoeutectic Pb-Sn alloys: Influence of primary arm spacing and mushy zone length [J]. Metall Mater Trans A, 1996, 27: 1353-1362.
[4] WANG Tao, JIE Wan-qi, XU Yan-dong, ZHA Gang-qiang, FU Li. Characterization of CdZnTe crystal grown by bottom-seeded Bridgman and Bridgman accelerated crucible rotation techniques [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2009, 19(s3): s622-s625.
[5] HU Xiao-wu, LI Shuang-ming, GAO Si-feng, LIU Lin, FU Heng-zhi. Effect of melt convection on primary dendrite arm spacing in directionally solidified Pb-26%Bi hypoperitectic alloys [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(1): 65-71.
[6] STELIAN C, DELANNOY Y, FAUTRELLE Y, DUFFAR T. Solute segregation in directional solidification of GaInSb concentrated alloys under alternating magnetic fields [J]. J Cryst Growth, 2004, 266(1-3): 207-215.
[7] STEINBACH S, RATKE L. The effect of rotating magnetic fields on the microstructure of directionally solidified Al-Si-Mg alloys [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2005, 413-414: 200-204.
[8] YESILYURT S, MOTAKEF S, GRUGEL R, MAZURUK K. The effect of the traveling magnetic field (TMF) on the buoyancy-induced convection in the vertical Bridgman growth of semiconductors [J]. J Cryst Growth, 2004, 263: 80-89.
[9] RUDOLPH P. Travelling magnetic fields applied to bulk crystal growth from the melt: The step from basic research to industrial scale [J]. J Cryst Growth, 2008, 310(7-9): 1298-1306.
[10] MAZURUK K. Control of melt convection using traveling magnetic fields [J]. Adv Spce Res, 2002, 29 (4): 541-548.
[11] JACKSON K, HUNT J, UHLMANN D, SEWARD T. On the origin of the equiaxed zone in castings [J]. Trans AIME, 1966, 236: 149-154.
[12] CURRERI P, LEE J, STEFANESCU D M. Dendritic solidification of alloys in low gravity [J]. Mater Trans A, 1988, 19(11): 2671-2676.
[13] LI M, MORI T, IWASAKI H. Effect of solute convection on the primary arm spacings of Pb-Sn binary alloys during upward directional solidification [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 1999, 265: 217-223.
[14] LEHAMANN P, MOREAU R, CAMEL D, BOLCATO R. A simple analysis of the effect of convection on the structure of the mushy zone in the case of horizontal Bridgman solidification comparison with experimental results. [J] J Cryst Growth, 1998, 183: 190-704.
[15] HUNT J D, LU S Z. Numerical modeling of cellular/dendritic array growth: Spacing and structure predictions [J]. Mater Trans A, 1996, 27: 611-623.
[16] STEINBACH I. Pattern formation in constrained dendritic growth with solutal buoyancy [J]. Acta Mater, 2009, 57(9): 2640-2645.
行波磁场对定向凝固Pb-Sn合金枝晶生长的影响
闵志先,沈 军,王灵水,刘 林
西北工业大学 凝固技术国家重点实验室,西安 710072
摘 要:在1g的重力加速度条件下,研究熔体对流对向上生长的定向凝固Pb-33%Sn合金枝晶生长行为的影响。熔体对流由行波磁场进行调制。当行波磁场方向由向上转变为向下时,一次枝晶间距逐渐增大,一次枝晶间距的分布更加紧凑,且峰值趋于降低。分析表明:行波磁场对熔体对流的调制作用与改变重力加速度的效果类似,当抽拉速率为50 μm/s,行波磁场强度为1 mT时,在向上和向下的行波磁场作用下有效重力加速度分别为3.07g 和0.22g。
关键词:定向凝固;微观组织;Pb-Sn合金;行波磁场
(Edited by YUAN Sai-qian)
Foundation item: Project (50827102) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2010CB631202) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China; Project (28-TP-2009) supported by Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Solidification Processing (NWPU), China
Corresponding author: MIN Zhi-xian; Tel/Fax: +86-29-88494080; E-mail: zhixianmin@yahoo.com.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60959-X