土工格栅加筋高路堤边坡稳定性的弹塑性有限元分析
范臻辉, 王永和
(中南大学 土木建筑工程学院, 湖南 长沙, 410075)
摘要: 在研究路堤填土施工过程和土体的非线性应力应变关系的基础上, 建立了土工格栅加筋高路堤边坡的有限元分析模型, 并利用该模型对土工格栅加筋高路堤边坡的受力情况、 位移和破坏机理进行研究, 分析土工格栅的长度、 刚度以及铺设间距等参数对路堤变形的影响。 实验结果表明, 选择模量高, 延伸率适宜的土工格栅对减少路堤侧向位移和提高高路堤的稳定性具有明显效果; 随着路堤填土高度的增加, 每层土工格栅所受拉力的最大峰值逐渐移向路堤内部; 土工格栅所受的拉力从下往上逐渐减小, 最大拉力出现在堤底第2层上; 当路堤边坡较陡时(坡率为1∶m, m≤1.0), 土工格栅的加筋长度宜取5.5~8 m; 土工格栅的铺设间距宜为60 cm。
关键词: 土工格栅; 高路堤; 弹塑性有限元分析
中图分类号:TU472.3 文献标识码:A 文章编号: 1672-7207(2005)05-0904-07
Elastic-plastic finite element analysis of reinforcing geogrids applied in high embankment slope
FAN Zhen-hui, WANG Yong-he
(School of Civil and Architectural Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410075, China)
Abstract: Considering the relationship of the embankment filling construction and the non-linear constitutive of the soil, a finite element analytical model for the high embankment slope reinforced with geogrids was set up. Based on this model, this paper analyzed the behavior, displacement and destruction mechanism of such a slope, as well as the effect of the length, stiffness and laying distance of geogrids on the deformation of the embankment. The results show that geogrids with high elastic modulus and proper extensibility will apparently reduce the lateral displacement and improve the stability of the high embankment. In addition, the increasing height of the embankment filling will result in the gradual movement of the strongest peak tension from each layer of geogrids towards the inside of embankment, and the tension imposed on geogrids decreases gradually from the top down, with the strongest one occurring at the second layer from the bottom. In the case of comparatively steep embankment slope (ratio of slope 1∶m, m≤1.0 ), the reinforcement length of geogrids is supposed to be 5.5-8 m, and the laying distance 60 cm.
Key words: geogrids; high embankment; elastic-plastic finite element analysis
随着国家西部大开发战略的实施, 对各种基础设施尤其是交通设施的需求越来越迫切, 但在西部各省的高山深谷地区进行交通建设, 经常会遇到路堤高填深挖的问题。
在高填土路堤中加入抗拉强度较高的土工格栅比无筋路堤具有加快施工速度、 增加承载力、 节约经费等优点, 因此, 得到工程界的广泛重视。 目前, 土工格栅加筋边坡的工程实践超前于理论研究[1]。 在现有的研究中[2-10], 对土工格栅加筋边坡进行了较详细的试验分析, 而在理论分析上多采用基于圆弧滑动的极限平衡法。 由于加筋后的土体性质和无筋土体有较大区别, 仍然沿用无筋土体的假定往往和实际不符, 使理论值和实测值不吻合, 有时甚至得出和实际值完全相反的结论。 边坡侧向位移值逐渐被工程界所重视, 在分析边坡稳定性时常作为衡量边坡是否发生侧向过量位移破坏的重要指标; 而边坡坡面竖向位移即坡面沉降是工程技术要求的又一重要指标。 本文作者采用非线性有限元方法, 对土工格栅加筋高路堤边坡的受力性状、 破坏机理等进行研究, 讨论路堤边坡位移特性与土工格栅的长度、 刚度及铺设间距的关系。
1 计算模型
1.1 土体单元模型
土是一种复合体, 具有极为复杂的力学行为。 尽管土的线性模型和非线性弹性模型(如邓肯-张模型)用得较多, 但土体在外力的作用下, 不仅产生弹性变形而且还会产生不可恢复的塑性变形。 本文将土体视为弹塑性体, 采用Druck—Prager屈服准则[11]:
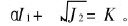
其中: I1为应力张量第一不变量; I1=σ11+σ22+σ33; J2为应力偏量第二不变量, 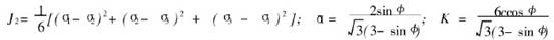 ;
;
c为土的粘聚力; 为土的内摩擦角。
1.2 土工格栅单元模型
把格栅单元看成只能受拉, 不能受压, 不具有抗弯刚度, 只能沿轴向变形的一维单元, 位移函数是线性的, 用增量形式表示的单元刚度矩阵为[12]:
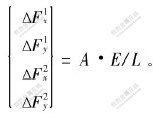
式中, E为格栅单元的弹性模量, kN/m; A为格栅的横截面积, m2; L为格栅单元的长度, m; α为单元与x轴的夹角。
土工格栅的厚度实际上是无法准确测定的, 格栅在做拉伸试验时, 所得到的应力实际上也是格栅单元宽度上受到的力。 因此, 本文中, 格栅单元成为一种薄膜单元, 采用的格栅单元刚度矩阵为:
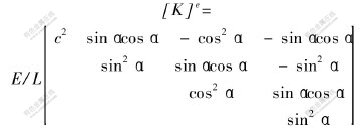
在岩土工程结构中, 当2种相邻材料的变形性能相差较大时, 在一定的受力条件下, 可能会在它们之间的接触面上产生错动、 滑移或开裂。 古德曼(Goodman)等人提出了岩石节理单元, 对土工格栅-土界面的模拟中, 被广泛地用作接触面单元[13-15]。
土工格栅是由横肋、 纵肋和孔眼组成, 其与土体的相互作用机理非常复杂。 但通过室内拉拔试验发现, 土工格栅与填土的咬合力非常大, 在土工格栅被拉出前就已被拉断, 故在土工格栅-土之间不采用接触单元。
2 计算实例
某土工格栅试验段高10.5 m, 左右边坡坡比为1∶0.75, 分17层铺设土工格栅, 层间距0.6 m, 除上面4层采取沿路堤横向通长布置外, 其余各层长度为6.5 m。 路堤填土的密度为1.96 g/cm3, C=12 kPa, =16; 地基土的密度为1.99 g/cm3, C=11.9 kPa, =29; 土工格栅的弹性模量为419.05 kN/m。
由于对称性, 将路堤对称划分为如图1所示的网格。 地基的计算范围: 竖向深度取路堤填土高度的2倍, 即21 m; 水平长度取距路堤中心线40 m。 共有1258个三角形土体单元, 170个土工格栅单元, 结点总数为687个, 其中X方向的约束结点数为44个, Y方向为33个。
计算过程分为19步: 第1步计算地基的初始地应力分布; 第2步至第18步模拟路堤施工(共分17层, 每层铺设一层土工格栅, 其中1至16层每层高度0.6 m, 第17层高度为0.9 m); 第19步按汽-20加载。
图 1 单元网格划分
Fig. 1 Division of element mesh
3 计算结果与分析
3.1 变形结果与计算
本文在文献[11]的基础上编制了土工格栅加筋边坡的有限元程序, 对上述土工格栅路堤和相同条件素填土路堤(即无土工格栅)进行对比计算。 图2和图3所示分别为土工格栅路堤的底部中心竖向位移和坡脚水平位移随填土高度的变化曲线。
当路堤填筑完毕, 土工格栅路堤底部中心的沉降为7.79cm, 坡脚的水平位移为16.44 mm。 再加上汽-20的荷载, 路堤底部中心的沉降达到8.06 cm, 坡脚水平位移达到18.19 mm。
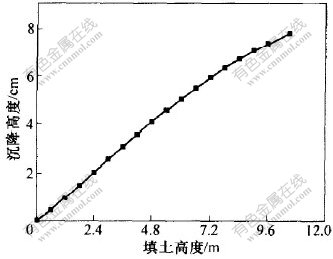
图 2 路堤底部中心沉降与填土高度关系
Fig. 2 Relation between settlement and height of fill
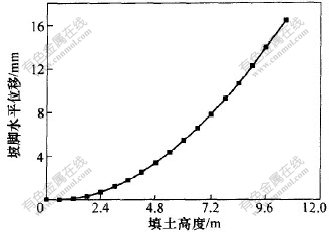
图 3 坡脚水平位移与填土高度关系
Fig. 3 Relation between lateral displacement and height of fill
而在对素填土路堤进行有限元分析时, 当路堤填筑到第15层(高度9.0 m)时, 计算结果不收敛, 即当不采取任何加固措施时, 路堤不能填筑到10.5 m的高度, 此时素填土路堤的坡脚水平位移为12.53 cm。 从图2可以看出, 加固后随着路堤填筑高度的增加, 路堤底部中心的沉降呈线性变化, 说明地基土仍处于弹性变形阶段, 地基土的承载能力较高, 能承受10.5 m高的路堤。 可见, 土工格栅的加入能有效地限制土体的侧向位移, 提高路堤的稳定性。
3.2 土工格栅的内力分布
图4所示为土工格栅路堤填筑完毕后第1层至第9层土工格栅内力分布图, 图5~7所示为第15至第17层土工格栅的内力分布图(土工格栅的编号采取从下往上的编号方式, 即第1层位于路堤底部, 第17层位于路堤顶部)。
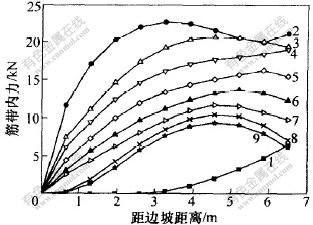
图 4 第1层至第9层土工格栅的内力分布
Fig. 4 Curves of geogrid’s tension from the first layer to the ninth layer
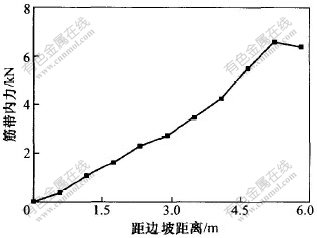
图 5 第15层土工格栅内力分布
Fig. 5 Curve of geogrid’s tension of the fifteenth layer
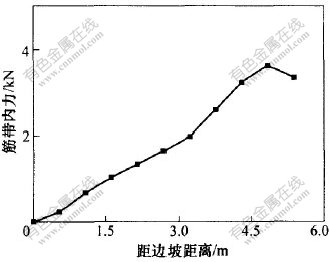
图 6 第16层土工格栅内力分布
Fig. 6 Curve of geogrid’s tension of the sixteenth layer
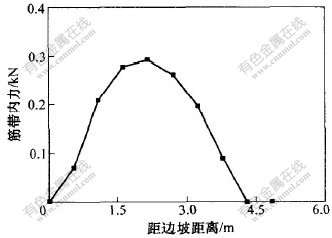
图 7 第17层土工格栅内力分布
Fig. 7 Curve of geogrid’s tension of seventeenth layer
从图4可以看出, 除第1层土工格栅外, 其余各层土工格栅所受的拉力从下往上逐渐减小, 最大拉力出现在第2层土工格栅上, 最大值为22.61 kN, 低于土工格栅的抗拉强度46.8 kN。
第15至17层土工格栅为沿宽度通长布置, 从图5至图7可以看出, 土工格栅所受的拉力同样从下往上逐渐减小。
图8所示为第2层土工格栅的内力分布与填土高度的关系曲线, 填筑高度分别为1.8, 3.6, 5.4, 7.2, 9.0和10.5 m。 从图中可见, 随着填土的逐渐增加(或所承受的荷载逐渐增加), 土工格栅拉力的最大峰值逐渐移向位于路堤里面的部分(末端处), 即路堤土体承受拉力的范围逐渐扩大, 土工格栅也逐渐发挥作用。
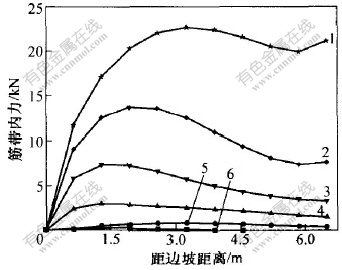
图 8 第2层土工格栅内力分布与填土高度关系
Fig. 8 Relation between geogrid’s tension of the second layer and height of fill
4 土工格栅加筋效果的影响因素
4.1 土工格栅长度
以前述的路堤为例, 土体参数不变, 改变土工格栅的长度, 当施加汽-20级荷载时, 土工格栅长度与坡脚水平位移的关系如图9所示。
从图9可知, 当路堤边坡较陡时(如本文中坡率为1∶0.75), 土工格栅的加筋长度宜大于5.5 m, 否则对路堤的变形稳定性作用不大; 另一方面, 加筋长度超过一定数值后, 坡脚水平位移不再随长度明显减小, 即水平位移数据趋于稳定。 因此, 当土工格栅长度达到8 m以后, 再增加长度效果不大。
当土工格栅长度分别为5.5, 6.5, 7.5和8.5 m时, 在汽-20级荷载作用下, 路堤内部塑性区如图10中阴影部分所示。
从图10可以看出, 当土工格栅长度为5.5 m时, 路堤内部的塑性区是贯通的, 此时路堤进入初期破坏; 当土工格栅长度大于或等于6.5 m时, 塑性区已被分隔, 从这一点可以看出, 本路堤土工格栅的加筋长度至少为6.5 m。
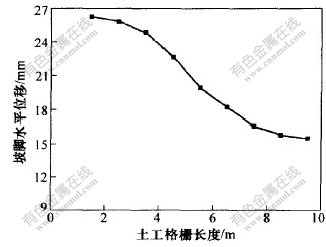
图 9 土工格栅长度与坡脚水平位移关系
Fig. 9 Relation between geogrid’s length and lateral displacement
4.2 土工格栅弹性模量
以前述的路堤为例, 土体参数不变, 土工格栅的长度为6.5 m, 土工格栅的弹性模量分别为100, 419.05和1000 kN/m, 当施加汽-20级荷载时, 计算结果如表1所示。
表 1 土工格栅弹性模量对路堤变形的影响
Table 1 Effect of different elastic modulus of geogrids on embankment’s deformation
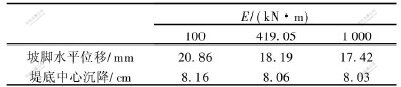
由于土中的加筋必须能承担一定的拉力才能发挥作用, 因此, 加筋的弹性模量(抗拉模量)对加筋效果有一定的影响。 从表1可以看出, 模量越大, 能够加强加筋的效果, 加强了对水平位移和沉降的抑制作用。
4.3 土工格栅间距
以前述路堤为例, 土体参数不变, 土工格栅的长度为6.5 m, 弹性模量为419.05 kN/m, 铺设间距分别为30, 45, 60, 75以及90 cm。 当施加汽-20级荷载时, 路堤的坡脚水平位移及堤底中心沉降的计算结果如表2所示。
表 2 土工格栅铺设间距对路堤变形的影响
Table 2 Effect of different laying distance of geogrids on embankment’s deformation
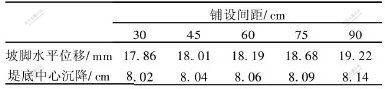
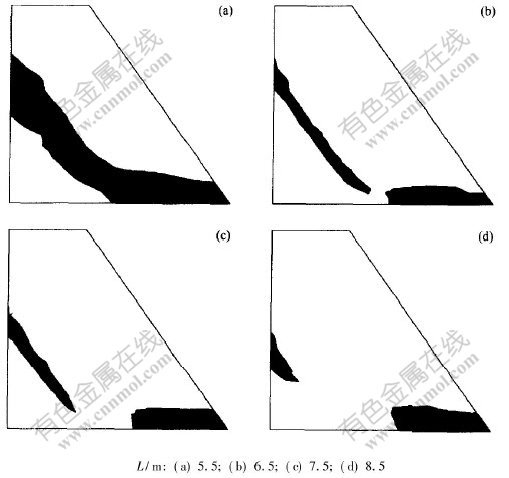
图 10 不同长度土工格栅路堤塑性开展区
Fig. 10 Plastic zone of embankments with different length of geogrids
从表2可以看出, 土工格栅的间距越大, 坡脚水平位移也越大, 当土工格栅的间距≤60 cm时, 坡脚水平位移减少的比较平缓, 可见, 当间距小于60 cm后, 土工格栅间距变化的加筋效果不太明显。
图11所示为5种铺设间距中拉力最大的土工格栅的内力分布图, 可见, 最大拉力出现在第2层土工格栅上。

图 11 土工格栅不同铺设间距最大拉力分布图
Fig. 11 The strongest tension of geogrids with different laying distance
从图11可以看出, 当铺设间距为90 cm时, 土工格栅的最大拉力为51.4 kN, 大于土工格栅的抗拉强度46.8 kN, 实际上土工格栅已被拉断; 当铺设间距为75 cm时, 土工格栅的最大拉力为44.53 kN, 已非常接近抗拉强度。 可见, 当土工格栅间距较大时, 土工格栅极易被拉断, 从安全角度考虑宜选取较小的铺设间距; 从铺设的经济角度来讲, 设置铺设间距为60 cm是比较合理的。
5 结 论
a. 高路堤陡坡采用土工格栅有利于减少路堤变形。 选用长度合适格栅的加筋能有效限制侧向位移, 提高路堤的稳定性。
b. 路堤中铺设的土工格栅所受的拉力从下往上逐渐减小, 最大拉力出现在堤底第2层上。 随着填土厚度的逐渐增加(所承受的荷载逐渐增加), 每层土工格栅拉力的最大峰值逐渐移向位于路堤里面的部分(末端处), 即路堤土体承受拉力的范围逐渐扩大, 土工格栅也逐渐发挥作用。
c. 当路堤边坡较陡时(坡率为1∶m, m≤1.0), 土工格栅的加筋长度宜大于5.5 m, 否则对路堤的变形约束作用不大; 另一方面, 加筋长度超过一定数值后, 坡脚水平位移不再随格栅长度明显减小而趋于稳定。 因此, 当土工格栅的加筋长度达到8 m以后, 再增加长度效果不大。
d. 土工格栅的抗拉模量越大, 加筋的效果越明显, 对水平位移抑制消减作用越大, 对沉降的抑制消减作用也有一定程度的加强。 所以, 工程中应在经济条件综合考虑下, 选择模量高、 延伸率适宜的加筋材料。
e. 土工格栅的所受的拉力随铺设间距的增加而增大, 从经济角度来讲, 铺设间距宜为60 cm左右。
参考文献:
[1]徐林荣, 华祖焜. 加筋边坡承载力和位移模型试验及结果分析[J]. 铁道学报, 1999, 21(1): 72-76.
XU Lin-rong, HUA Zu-kun. Model test and investigation on the bearing capacity and displacement of geogrid-reinforced slope[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 1999, 21(1): 72-76.
[2]Raju D M, Fannin R J. Monotonic and cyclic pull-out resistance of geogrids[J]. Geotechnique, 1997(2): 331-337.
[3]Huang C C, Meng F Y. Deep footing and wide-slab effects in reinforced sandy ground[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 1994(13): 281-293.
[4]朱湘, 黄晓明, 邓学钧. 土工格栅加筋路堤机理研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2000, 17(1): 1-4.
ZHU Xiang, HUANG Xiao-ming, DENG Xue-jun. Research of reinforced embank mechanism[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2000, 17(1): 1-4.
[5]周志刚, 郑健龙, 宋蔚涛. 土工格栅加筋柔性桥台的机理分析[J]. 中国公路学报, 2000, 13(1): 18-21.
ZHOU Zhi-gang, ZHENG Jian-long, SONG Wei-tao. Analysis of mechanism of flexible abutment reinforced by geogrids[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2000, 13(1): 18-21.
[6]苏谦, 蔡英. 土工格栅、 格室加筋砂垫层大模型试验及抗变形能力分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2001, 36(2): 176-180.
SU Qian, CAI Ying. Geogrid- and geocell- reinforced sand blanket: model test and the ability to reduce deformation[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2001, 36(2): 176-180.
[7]李献民, 王永和, 律文田, 等. 土工格栅加固路桥过渡段的动测试分析[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 35(5): 860-864.
LI Xian-min, WANG Yong-he, L Wen-tian, et al. Dynamic test analysis on roadbed-bridge transition section reinforced by geogrid[J]. J Cent South Univ(Science and Technology), 2004, 35(5): 860-864.
[8]杨锡武, 徐积江, 王多银. 加筋高路堤陡边坡在渝长公路上的应用[J]. 重庆交通学院学报, 2000, 19(4): 55-58.
YANG Xi-wu, XU Ji-jiang, WANG Duo-ying. The application of reinforced steep soil slope to Chongqing Changsou express way[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong Institute, 2000, 19(4): 55-58.
[9]黄广军, 张千里, 俞锡健, 等. 加筋垫层对地基沉降控制效果的多方案比较[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2001, 23(5): 598-601.
HUANG Guang-jun, ZHANG Qian-li, YU Xi-jian, et al. Comparison of settlement control of reinforcement layer[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2001, 23(5): 598-601.
[10]闫澍旺, Barr B. 土工格栅与土相互作用的有限元分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 1997, 19(6): 56-61.
YAN Shu-wang, Barr B. Finite-element Modelling of soil-geogrid interaction with application to interpret the pullout behaviour of geogrids[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1997, 19(6): 56-61.
[11]欧文D R J, 辛顿E. 塑性力学有限元——理论与应用[M]. 曾国平, 刘忠, 徐家礼, 等译. 北京: 兵器工业出版社, 1989.
Owen D R J, Hinton E. Finite Elements in Plasticity—Theory and Practice[M]. ZENG Guo-ping, LIU Zhong, XU Jia-li, et al translate. Beijing: Press of Arms Industry, 1989.
[12]朱湘, 黄晓明. 有限元方法分析影响加筋路堤效果的几个因素[J]. 土木工程学报, 2002, 35(6): 86-92.
ZHU Xiang, HUANG Xiao-ming. Effects of reinforcements on embankment analyzed by finite element method[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2002, 35(6): 85-92.
[13]徐少曼, 洪昌华. 土工织物加筋堤坝软基的非线形分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 1999, 21(4): 438-443.
XU Shao-man, HONG Chang-hua. A non-linear analysis for soft cohesive subsoil under embankment reinforced by geotextile[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 1999, 21(4): 438-443.
[14]朱百里, 沈珠江. 计算土力学[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1990.
ZHU Bai-li, SHEN Zhu-jiang. Computational Soil Mechanics[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific and Technical Press, 1990.
[15]范臻辉. 加筋砂垫层加固软土地基的数值分析[D]. 长沙: 长沙铁道学院土木系, 1999.
FAN Zhen-hui. Numerical Analysis of Soft Ground Stabilized by Reinforced Sand Bed[D]. Changsha: Department of Civil Engineering, Changsha Railway University, 1999.
收稿日期:2004-12-15
基金项目: 铁道部科研基金资助项目(004594)
作者简介:范臻辉(1976-), 男, 湖南新化人, 讲师, 博士研究生, 从事桩及特殊土地基处理的研究
论文联系人: 范臻辉, 男, 讲师, 博士研究生; 电话: 0731-2654339(H); E-mail: fanzhenhui@126.com