文章编号:1004-0609(2008)07-1237-05
电流密度对铬青铜/黄铜载流配副表面温度和
摩擦学特性的影响
上官宝1, 2,张永振2,邢建东1,孙乐民2,丘 明2,牛永平2,侯 明2
(1. 西安交通大学 材料科学与工程学院,西安 710049;
2. 河南科技大学 材料科学与工程学院,洛阳 471003)
摘 要:在自制的销盘式载流摩擦磨损试验机上,采用热电偶测量法检测不同电流密度下销试样的表面温度;研究滑动速度和电流密度对配副摩擦磨损性能的影响,采用扫描电镜观察载流磨损后黄铜表面形貌。结果表明:电流密度对铬青铜/黄铜配副的摩擦学特性和表面温度有显著影响;在载流条件下,摩擦表面的温度比无电流时明显升高,电流密度越大,表面温度越高;滑动速度较低时,电流密度对材料表面温度的影响更为显著;随电流密度的增加,铬青铜/黄铜配副的摩擦因数降低,黄铜销试样的磨损率升高;磨损表面存在电弧侵蚀,电弧的存在加剧材料的磨损。
关键词:铬青铜/黄铜配副;电流密度;表面温度;摩擦学特性
中图分类号:TH 117.3 文献标识码:A
Effect of current density on surface temperature and
tribology behavior of chromium bronze/brass couple
SHANGGUAN Bao1, 2, ZHANG Yong-zhen2, XING Jian-dong1, SUN Le-min2,
QIU Ming2, NIU Yong-ping2, HOU Ming2
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, China;
2. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang 471003, China)
Abstract: By using self-made pin-disk tester, the surface temperature of pins were measured under different current densities by thermocouple. The effects of velocity and current density on the frictional wear behavior of chromium bronze/brass couple were investigated. The surface microstructure of brass pin was observed by SEM. The results show that the tribological behavior of the chromium bronze/brass and surface temperature of the brass greatly depends on the current density. The surface temperature of brass pin increases remarkably as the electrical current passes through the pins and disk. The increase of current results in an increase in surface temperature and mass loss of brass and decrease in friction coefficient of the couple. Current density exists better effect on the surface temperature at low velocity specially. Electrical arc corrosion exists on the worn surface; the mass wear of the brass pin is increased by electrical arc corrosion.
Key words: chromium bronze/brass couple; current density; surface temperature; tribology behavior
载电流(载流)摩擦磨损是指处于电场中的摩擦副在通电条件下的摩擦磨损行为,主要存在于高速铁路(包括轻轨)及城市公共交通中的有轨和无轨电车的电力传输系统[1?3]、发电机和励磁电机的电刷[4?5]等摩擦配副中。随着载流摩擦配副应用的日益广泛,载流摩擦问题引起国内外学者的重视,对其开展了深入的研究。由于电流的介入,配副的摩擦磨损性能将发生很大变化[6?8]。电流通过材料摩擦表面时会产生电阻热和电弧热,使表面温度升高,从而影响材料的摩擦学特性及表面形貌,尤其是电弧的产生,影响将更大[9?12]。但大多数研究均对载流条件下表面温度进行定性分析而未进行实际测量。材料的摩擦学性能和摩擦表面的温度密切相关[13?14],因此有必要了解摩擦表面的真实温度以分析材料的摩擦学特性。
本文作者采用热电偶测量法,检测不同电流密度下黄铜销试样的表面温度,研究速度和电流密度对配副摩擦磨损的影响,并对磨损表面形貌进行观察。
1 实验
本实验采用自制的销?盘摩擦磨损试验机,其结构简图如图1所示。实验所用摩擦配副材料:销试样是H68黄铜,摩擦盘材料是铬青铜QCr0.5。实验速度为3.6~10.0 m/s,载荷为0.19~0.32 MPa,电流密度0.61~1.53 A/mm2。磨损量采用失重法测量,采用感量为0.1 mg的BS210S电子分析天平测定试验前后销试样的磨损质量损失计算其磨损率。摩擦力经压力传感器输出至笔式记录仪,通过计算得到摩擦因数。采用K型热电偶,测量销试样离摩擦面2 mm处的温度,用英华达EN880显示记录仪(误差为1%)实时记录该点温度的变化曲线。采用JSM?5610LV型扫描电子显微镜和EDAX能谱分析仪对销试样磨损表面及纵剖面进行观察。
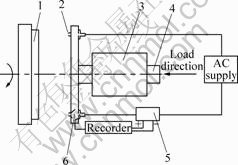
图1 销盘摩擦磨损试验机
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of pin-on-disc tester: 1―Pisk; 2―Pins; 3―Holder; 4―Axis; 5―Current collector; 6―Pressure sensor
2 结果和讨论
2.1 电流大小和滑动速度对销试样表面温度的影响
图2所示为载荷在0.29 MPa时,不同速度和电流条件下离摩擦面2 mm处销试样的温度变化。
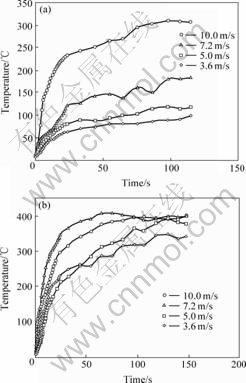
图2 不同速度条件下销试样的表面温度
Fig.2 Surface temperatures of pin at different speeds: (a) Without current; (b) At current density 1.15 A/mm2
从图2可以看出,无论有无电流,试样表面温度均随时间的延长而升高,最后达到稳定温度;滑动速度越大,表面温升越大。与无电流时相比,当有电流通过时,初期销试样表面温升的速度明显提高,且达到平衡时的温度显著高于无电流的同速度条件下的温度;速度较低时,有电流时表面温升的速率较快,温度升高更为显著,达到稳定温度时,不同速度间的温差小。如滑动速度为3.6和5.0 m/s时,在无电流时,表面温度达到稳定时分别为89和117 ℃,而在电流密度1.15 A/mm2,表面温度可达到340和377 ℃。这表明电流对试样表面温度的升高有重要影响。在滑动速度较低时,影响更为显著。这是由于在干滑动摩擦时,表面只产生摩擦热,滑动速度越高,产生的摩擦热越大,表面温度越高。而在载流摩擦时,摩擦表面除产生摩擦热外,还会产生电阻热和电弧热。由于摩擦热在产生的总热量中所占的比例较小,电流产生的电阻热和电弧热起主要作用[15],在低滑动速度时,造成有电流条件下材料表面温升显著。而在高速时,由于摩擦热在总热量中比例减少,因而在有电流时不同滑动速度间的表面温差小。
图3所示为速度7.2 m/s、载荷0.29 MPa时,不同电流密度条件下离摩擦面2 mm处销试样温度的变化曲线。由图可以看出,随时间延长,试样的表面温度增加,最后达到平衡温度。当电流密度增加时,试样初期的温升速度增加,稳定时的表面温度明显升高,电流密度越大,表面温度越高。这是由于除摩擦热以外,电流引起的电阻热和电弧热会增加摩擦表面的热量输入。电流强度越大,输入的热量越多,从而导致在有电流条件下,材料表面的温度明显提高。
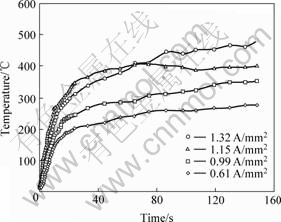
图3 不同电流密度条件下销试样表面温度
Fig.3 Surface temperature of pin at different current densities
2.2 速度和电流密度对配副摩擦磨损的影响
图4所示为速度7.2 m/s、载荷0.25 MPa时,不同电流密度与配副摩擦因数和销试样磨损率的关系曲线。
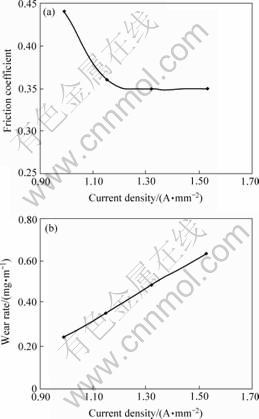
图4 电流密度对配副摩擦因数和销试样磨损率的影响
Fig.4 Influence of electrical current on friction coefficient and wear of pin
`由图4可知,随着电流密度的增大,配副的摩擦因数减小,当达到某一数值时(1.15 A/mm2),摩擦因数随电流密度的增加变化不大;销试样的磨损率随着电流密度的增大也逐渐增大。这是由于随着电流的增加,材料产生电阻热和可能产生电弧的几率增加,使摩擦表面温度升高,摩擦副的塑变抗力降低,微凸峰接触点之间的剪切抗力下降,因而摩擦因数变小。当电流达到某一数值时,材料表面达到较高的温度,使材料表面软化甚至熔化,因而摩擦因数随电流密度的增加变化不大。电弧热与电流成正比,电流密度增加,电弧烧蚀加剧,磨损率增加[16]。由于磨损时表面温度较高,试样表面受强烈的热作用影响,沿滑动方向产生塑性变形,组织产生弯曲变形(见图5),而材料表层中氧含量增加,锌含量降低(见图6和7)。
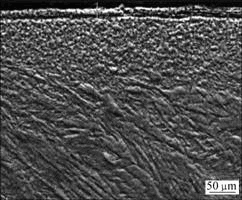
图5 黄铜销试样垂直切面的SEM形貌
Fig.5 SEM morphology of cross section of brass pin
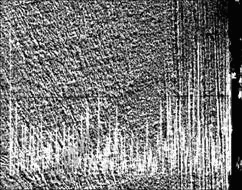
图6 黄铜销试样摩擦面垂直切面氧元素线的分布
Fig.6 Linear distribution of O element on cross section of brass pin
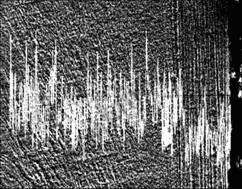
图7 销试样摩擦面垂直切面表层Zn元素分布
Fig.7 Linear distribution of Zn element on cross section of brass pin
2.3 磨损表面形貌
由于电流的存在,载流摩擦磨损除有一般磨损条件下存在的磨粒磨损和粘着磨损外,还有电弧侵蚀。由于盘表面的粗糙度, 在销盘相对滑动时会造成销盘的瞬时离合而产生电弧,大量电弧热使摩擦表面局部温度急剧升高而氧化,产生氧化龟裂(见图8)。当电弧造成销试样表面温度较高时,会在材料表面形成局部熔蚀坑(见图9)和局部熔化(见图10)。由此可见,电弧的存在加剧材料磨损。
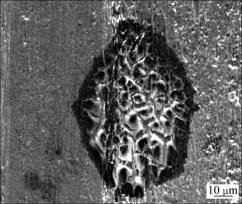
图8 电弧造成的氧化龟裂区的SEM形貌
Fig.8 SEM morphology of electrical arc eroded chap in worn surface
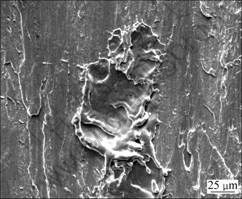
图9 电弧造成的材料局部熔蚀坑的SEM形貌
Fig.9 SEM morphology of electrical arc eroded pit in worn surface
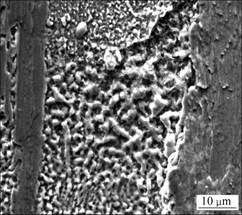
图10 电弧造成的材料局部熔化区的表面形貌
Fig.10 SEM morphology of melting zone in worn surface
3 结论
1) 在载流条件下,摩擦表面的温度明显升高,电流密度越大,表面温度越高。滑动速度较低时,电流对材料表面温度的影响更为显著。
2) 随电流密度的增加,铬青铜/黄铜配副的摩擦因数降低,黄铜销试样的磨损率降低。
3) 磨损表面存在电弧侵蚀,电弧的存在加剧材料磨损。
REFERENCES
[1] AZEVEDO C R F, SINATORA A. Failure analysis of a railway copper contact strip[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2004, 11: 829?841.
[2] HE Da-hai, MANORY R. A novel electrical contact material with improved self-lubrication for railway current collectors[J]. Wear, 2001, 249: 626?636.
[3] 贾淑果, 刘 平, 田保红. 高强高导Cu-0.1Ag-0.11Cr 合金的强化机制[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(7): 1144?1148.
JIA Shu-guo, LIU Ping, TIAN Bao-hong. Strengthening mechanism in high-strength and high-conductivity Cu-0.1Ag- 0.11Cr alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(7): 1144?1148.
[4] 虞 澜. 金?稀土合金电刷丝的磨损机理研究[J]. 摩擦学学报, 2002, 22(4): 282?285.
YU Lan. Study on the wear mechanism of Au-rare earth alloy wires[J]. Tribology, 2002, 22(4): 282?285.
[5] 郑 冀, 欧阳锦林, 朱家佩. 真空长寿命自润滑电刷?滑环材料的研究[J]. 摩擦学学报, 1997, 17(2): 129?138.
ZHENG Ji, OUYANG Jin-lin, ZHU Jia-pei. Study on long life electrical brush slip-ring in acuum[J]. Tribology, 1997, 17(2): 129?138.
[6] LIU C P, VERHOEVEN J D, GIBSON E D. Gibson electritribological behavior of Cu-15vol.% Cr in situ composites under dry sliding[J]. Wear, 1997, 203/204: 28?35.
[7] ZHAO H, BARBER G C, LIU J. Friction and wear in high speed sliding with and without electrical current[J]. Wear, 2001, 249: 409?414.
[8] 凤 仪, 张 敏, 徐 屹. 外加载荷对碳纳米管银石墨复合材料电磨损性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2005, 15(10): 1484?1488.
FENG Yi, ZHANG Min, XU Yi. Effect of pressure on electrical wear of CNTs-Ag-G composites[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 15(10): 1484?1488.
[9] BOUCHOUCHA A, CHEKROUD S, PAULMIER D. Influence of the electrical sliding speed on friction and wear processes in an electrical contact copper-stainless steel[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2004, 223: 330?342.
[10] JIA S G, LIU P, REN F Z, TIAN B H, ZHENG M S, ZHOU G S. Wear behavior of Cu-Ag-Cr alloy wire under electrical sliding[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2005, 398: 262?267.
[11] KUBO S, KATO K. Effect of arc discharge on the wear rate and wear mode transition of a opper-impregnated metallized carbon contact strip sliding against a copper disk[J]. Tribology International, 1999, 32: 367?378.
[12] KUBO S, KATO K. Effect of arc discharge on wear rate of Cu-impregnated carbon strip in unlubricated sliding against Cu trolley under electric current[J]. Wear, 1998, 216: 172?178.
[13] DEGNAN C C, SHIPWAY P H, WOOD J V. Elevated temperature sliding wear behaviour of TiC-reinforced steel matrix composites[J]. Wear, 2001, 250/251: 1444?1451.
[14] CHANG C C, LIN J F, CHEN C Y, AI C F. The effect of under-layers and pre-test temperature on the tribological characteristics of TiN films rubbing against steel[J]. Wear, 2004, 256: 252?267.
[15] 戴利民, 林吉忠, 刘 越, 丁新华. 受电弓滑板受流摩擦中体温升的模拟计算分析[J]. 铁道学报, 2002, 24(5): 56?60.
DAI Li-min, LIN Ji-zhong, LIU Yue, DING Xin-hua. Calculation and study on strip cubage temperature of pantograph pan in sliding electric contact brasion[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2002, 24(5): 56?60.
[16] HE Da-hai, MANORY R R, GRADY N. Wear of railway contact wires against current collector materials[J]. Wear, 1998, 215: 146?155.
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(2007CB607603);国家自然科学基金资助项目(50432020;50775066)
收稿日期:2007-03-07;修订日期:2008-03-28
通讯作者:上官宝,副教授,博士研究生;电话:0379-64231723;E-mail: shanggb@mail.haust.edu.cn
(编辑 龙怀中)