文章编号:1004-0609(2010)11-2221-07
玻璃基底上纳米银粒子的原位生长及其表面增强拉曼散射活性
易 早1, 2, 李 恺1, 韩尚君1,牛 高1, 易有根2, 陈善俊1, 3, 罗江山1, 唐永建1, 3
(1. 中国工程物理研究院 激光聚变研究中心,绵阳 621900;
2. 中南大学 物理科学与技术学院,长沙 410083;3. 四川大学 原子与分子物理研究所,成都 610065)
摘 要:利用预处理-化学沉积法在玻璃基底表面原位生长形貌各异的纳米银粒子, 获得高活性的表面增强拉曼散射(SERS)基底。采用SEM、XRD和UV等测试手段对样品进行分析和表征, 并考察纳米银粒子的形貌对其薄膜基底表面增强拉曼散射活性的影响。结果表明:随着反应液中硝酸银与乙二胺的摩尔比以及反应温度的改变,纳米银粒子的形貌发生变化。当反应温度为30 ℃、硝酸银与乙二胺的摩尔比为1?5时,制备出的由纳米银薄片组成的薄膜具有最强的紫外吸收光谱红移,可红移至800 nm;并且以此条件得到的表面增强拉曼散射活性基底具有最强的表面增强拉曼散射信号,拉曼增强因子达到258.4。
关键词:表面增强拉曼散射基底; 化学沉积; 银纳米粒子; 拉曼增强因子
中图分类号:TG146 文献标志码:A
In-situ growth of silver nanoparticle on glass substrates and its surface-enhanced Raman scattering
YI Zao1, 2, LI Kai1, HAN Shang-jun1, NIU Gao1, YI You-gen2, CHEN Shan-jun1, 3, LUO Jiang-shan1, TANG Yong-jian1, 3
(1. Research Center of Laser Fusion, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang 621900, China;
2. School of Physical Science and Technology, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
3. Institute of Atomic and Molecular Physics, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610065, China)
Abstract: A novel solid substrate with high surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) activity was fabricated through in-situ growth of silver particles with variant morphology on glass substrates by pretreatment electroless. The effect of surface morphology of thin films of silver nanoparticles on the SERS activity of the substrate was studied by SEM, XRD and UV-Vis spectroscopy. The results show that the morphology of silver nanoparticles changes with the change of the molar ratio of AgNO3 and ethylenediamine in reaction solution and the reaction temperature. The film containing nano flake of silver has the strongest UV absorption spectra at 800 nm with red-shift when the reaction temperature is 30 ℃ and the molar ratio of AgNO3 to ethylenediamine is 1?5. The strongest SERS signal of SERS-active substrate is obtained under the same condition, and the Raman enhancement factor reaches 258.4.
Key words: surface-enhanced Raman scattering; electroless deposition; silver nano particle; Raman enhancement factor
表面增强拉曼光谱(SERS)是研究分子在金属表面吸附的有力工具,它能提供大量的振动光谱信息,可用来确定吸附分子的种类、吸附状态和取向等。同时,巨大的增强因子使其具有亚单分子层的检测灵敏度。在一些纳米银粒子的表面上,某些分子的SERS信号灵敏度可与荧光光谱媲美,甚至超过荧光光谱。通常情况下荧光谱峰的宽度比拉曼谱峰宽10~100倍,因而,其光谱选择性要大大优于荧光光谱。这无疑为SERS在生物分子的结构和构象、分子界面行为和性质、分子与标记金属微粒表面的相互作用奠定了良好的基础[1-3]。
拉曼信号的增大主要是由于入射激发光与粗糙金属表面电子相互作用, 形成表面等离子激发, 导致金属表面电磁场增强(物理增强);其次,是由于所谓的电荷转移增强(化学增强),即金属表面电子和吸附分子间电子相互转移。其中,电场增强效应起决定性作用, 因此,表面增强拉曼效应必须以表面粗糙的金属为基底。从实际应用的角度出发,为了将SERS作为一种常规、在线的分析工具,一个理想的SERS基底应该具有增强能力巨大、稳定、易于制备以及SERS信号重现性好等优点,因此,关于SERS基底的制备研究一直是科学家们的一个重要的研究方向。目前, 活性金属膜层的制备方法有多种, 包括旋涂法[4]、电化学法[5]、真空蒸发沉积法[6]、平版印刷法[7]、自组装纳米金属胶体[8]和原位化学还原法[9]等。前几种方法依次需要旋涂机、电化学仪器、真空室和反应离子刻蚀配套等设备,而后2种方法的操作过程复杂且不易控制。为了克服以上不足,本文作者借鉴YOSHIO等[10]以及SABAHUDIN等[11]的方法,采用乙二胺为络合剂,并且借助其弱还原性在玻璃基底上制备出形貌各异的纳米银粒子。
1 实验
1.1 主要试剂与仪器
主要试剂:乙二胺(Ethylenediamine,en)、盐酸、硝酸银、二水合氯化亚锡、锡粒,所有药品均为分析纯,水为二次去离子水,基底为普通玻璃载玻片(切成4 cm×1 cm的长方形待用)。
仪器:XD-98型X射线衍射仪,UV-3802型紫外-可见分光光度计,Leica Cambridge S440扫描电镜(SEM)。
1.2 SERS活性基底的制备
将载玻片依次用洗衣粉水、乙醇和丙酮超声清洗30 min,经纯水洗干净后,再经过N2吹干,置于由质量分数为98%的浓硫酸和30%的双氧水以7?3的体积比配制而成的Piranha洗液中,于85 ℃煮沸2 h,取出,充分水洗后吹干。将6.85 g SnCl2·2H2O加入100 mL 6 mol/L的盐酸溶液中配制成溶液,并加入0.2 g锡粒,防止Sn2+氧化成Sn4+。溶液搅拌30 min后陈化12 h, 将玻璃基片浸没敏化液中静止2 h。室温下,取新制备的0.1 g/L的AgNO3 溶液2 mL加入到100 mL 锥形瓶中,缓慢滴加10 mL en水溶液,之后用去离子水将反应液稀释至100 mL。最后将敏化好的基片浸没于反应液中,静止反应2 h,反应结束后,取出基片用去离子水清洗干净,干燥后真空保存。
1.3 SERS活性测试
首先,将5 μmol/L R6G的甲醛溶液用微量移液枪取1 μL分别滴加在6种不同形貌的固体SERS基底上,等自然干燥后进行SERS 活性探测, 分析不同形貌纳米银粒子组成SERS基底活性的优劣, 寻找最优的制备条件。SERS用的共聚焦拉曼光谱仪为英国Renishaw公司生产的Renishaw-1000型光谱仪,激发光源为空气制冷氩离子激发器( Spectra-Physics Model 163-C4260), 激发波长为514.5 nm , 最大输出功率为20 mW。测量时激发功率为4.0 mW,积分时间均为10 s,单次测量。在每个基片上取5点进行测量,取平均值。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 反应机理分析
图1所示为玻璃基底上原位生长纳米银颗粒的过程示意图。玻璃基底表面一般带负电,通过静电吸附作用,Sn2+很容易吸附到基底表面。基底表面吸附的Sn2+很容易发生如下的氧化还原反应:
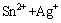 →Sn4++Ag (1)
→Sn4++Ag (1)
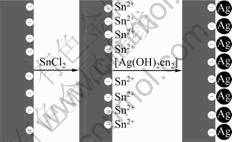
图1 玻璃基底上原位生长银纳米颗粒的过程示意图
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of in-situ growth of silver nanoparticle on glass substrate by electroless plating method
这样,银沉积在玻璃基底表面上形成一层均匀、细小的银颗粒。乙二胺在式(1)中作为一种络合剂,同时也作为一种较弱的还原剂,以小银颗粒为“成核点”,将AgNO3在小银颗粒上不断还原。在反应过程中,Ag+与en的络合和Ag+与氨的络合相似。当加入en之后,Ag+以[Ag(OH)2en]-的形式存在,反应如下:
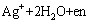
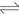
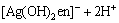 (2)
(2)
en与AgNO3形成络合物可以调节氧化还原电位差Δφ,Ag+以[Ag(OH)2en]-形式存在,可以很好地控制反应速率,使得反应稳定进行,有利于粒子的均匀生长。
2.2 产物的形貌分析
在不同实验条件下制备不同形貌的6个样品以探明基底上不同形貌的纳米Ag颗粒对拉曼增强效应的影响,具体制备条件如表1所列。
用SEM测得上述纳米Ag粒子薄膜形貌如图2所
示。从图2可以看出,采用化学镀的方式,通过改变实验条件,可以制备出形貌不同的纳米结构的Ag薄膜。
表1 样品的制备条件
Table 1 Preparation condition of samples
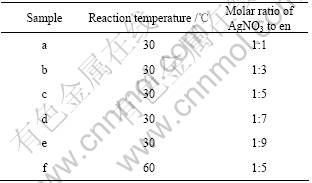
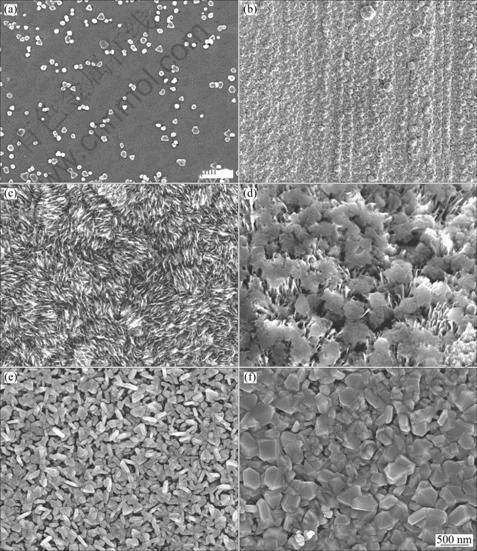
图2 不同制备条件下样品的SEM像
Fig.2 SEM images of samples prepared under different preparation conditions: (a) Sample a; (b) Sample b; (c) Sample c; (d) Sample d; (e) Sample e; (f) Sample f
随着反应条件的改变,纳米Ag薄膜呈现出不同的形貌:球形Ag粒子,平均粒径约为100 nm,在基底上单层排列,排列非常紧密(见图2(b));纳米Ag颗粒为薄片状,薄片边长约为500 nm,厚度为10 nm,排列较紧密(见图2(c));纳米Ag颗粒为薄片状,但是存在大量团聚现象,许多薄片粒子粘在一起(见图2(d));纳米Ag颗粒为不规则粒子,有片状、球状,单层排列(见图2(e));纳米Ag颗粒为不规则的多面体晶型结构(见图2(f))。图2(f)与(c)对应的样品形貌有很大差异,这是由于温度对产物形貌的影响主要作用在还原速度和晶型重整两个方面。当温度过高时,其反应进程会大大加快,使得还原得到的银原子来不及在特定晶面吸附生长就团聚到一起形成较大的、不规则的多面体晶型的纳米颗粒。
2.3 产物的结构分析
根据X射线衍射理论,对X射线衍射峰进行多重峰分离,并对分离出的衍射峰进行线性分析,把由仪器因素引起的几何宽化和由尺寸和微观应变等物理因素引起的物理宽化分开,最后扣除几何宽化,对衍射线性函数进行Warren-Averbach傅里叶变换,求得样品的晶粒尺寸。图3所示为样品的X射线衍射谱。在XRD谱中出现了4个衍射峰,与衍射卡片组(PDF—040836)的数据进行比较,衍射线的4个衍射峰均为Ag的特征峰,共有4个晶面,对应的晶面指数由里到外依次为(111)、(200)、(220)、(311),为面心立方结构。由图3可见,5条谱线的峰位和峰形基本一致,根据上述理论以及已有的数据,计算出样品的平均晶粒尺寸分别为3.75 nm(b),3.74 nm(c),3.75 nm(d),3.76 nm(e)和3.77 nm(f),得到的晶粒尺寸基本一致。该曲线衍射峰相当尖锐,表明产品结晶性能良好[12]。
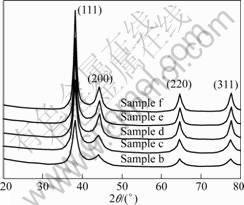
图3 样品的XRD谱
Fig.3 XRD patterns of samples
2.4 产物的紫外-可见吸收光谱分析
金属纳米粒子在紫外可见区的吸附带或者吸附区,是由价带电子与电磁场的相互作用产生的连续振动,即表面等离子体共振(Surface plasmons resonance, SPR)而产生的。这是小粒子尺寸效应的表现,吸收峰的位置和形状与粒子大小、形状和团聚状态有关[13]。图4所示为样品的紫外吸收光谱图。金属纳米粒子的表面等离子体共振吸收由粒子表面导带电子受外光电场驱动发生集体振荡所致,吸收峰位受粒子形貌和尺度、周围介质的介电常数、粒子表面偶联分子的性质、粒子间的聚集程度等因素的影响。5个样品均在430~450 nm区间有一个缓和的肩峰,这是基底上不规则状的银纳米粒子产生的SPR特征吸收峰。各基底均在更长波长处出现一个强而宽的吸收峰,样品b和d的谱线由于该峰与球形纳米银粒子的SPR峰较接近,故区分不明显。在样品d、e和c的谱线中由于出现片状银纳米结构,其紫外吸收峰在近红外区域产生强的吸收。随着银纳米片的变薄,其红移程度加强(见样品e和c的谱线),机理类似于三角形银纳米片引起红移的增强[14]。当样品主要为片状银纳米结构时,紫外吸收峰红移最为明显,可达800 nm(见样品c的谱线)。当纳米薄片部分出现团聚并且粘附在一起时,SPR峰出现蓝移。具体SPR峰位移动情况可见图4中箭头方向。这些均可从SEM像得到验证。
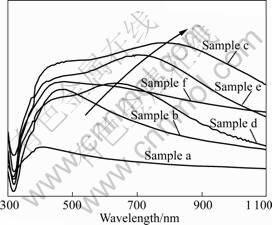
图4 样品的紫外光谱图
Fig. 4 UV-Vis absorption spectra of samples
2.5 SERS活性
实验时,在样品c的表面和玻璃基底上分别滴一滴(5 μL)浓度为5 μmol/L的R6G甲醇溶液,溶剂蒸发后,在2个基底表面形成了直径为20 mm左右、大小基本一致的R6G薄膜。假设在20 mm直径范围内分子是均匀分布的,通过计算,可以得到R6G分子在这一区域内的密度为6.38×1012 cm-2,因此,每个分子所占的面积为877 ?2。GUPTA和WEIMER[15]用半经验分子轨道模型(Semi-empirical molecular orbital model)对R6G分子的结构进行优化,得到每个R6G分子在表面上所能占有的最大面积为222 ?2。所以,在这个实验中,R6G分子在2种基底表面的覆盖度约为25%,是亚单层膜。然后,用同一台拉曼光谱仪分别测纳米粒子表面的R6G的SERRS谱和玻璃基底上R6G的荧光光谱(见图5)。在图5(a)中,荧光信号在1361 cm-1处的强度为1 213 cps,而在经过基线校正除去荧光背景的R6G的SERRS谱图中,相应位置的谱峰强度约为200 cps,即拉曼信号约为荧光信号强度的20%。NIE和EMORY[16]对R6G分子在514.5 nm激发波长下的荧光截面进行了计算,得到的数值为2.5×10-16 cm2,而其拉曼信号的散射截面为荧光截面的20 %即5×10-17cm2,在没有增强的情况下,R6G的拉曼散射截面为10-30 cm2,所以,在514.5 nm激发波长下纳米粒子对R6G的增强能力为1013,除去共振的影响(大概在104[16]),这种纳米粒子实际的增强能力约为109。
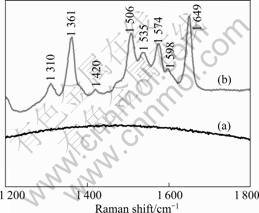
图5 R6G分子在玻璃基底上的荧光光谱以及R6G分子在样品c上的拉曼光谱
Fig.5 Fluorescence spectrum of R6G on glass substrates (a) and Raman spectrum of R6G on sample c (b)
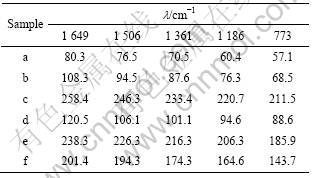
分别用上述样品作为SERS的衬底材料,采用5 μmol/L的罗丹明6G为探针分子,得到罗丹明6G的增强Raman散射信号,并将5 μmol/L的罗丹明6G直接滴加到普通玻璃上的Raman信号作为对比,如图6所示。从图6可以清晰地看出:将被稀释的探针罗丹明6G滴在玻璃基片上时,其Raman 散射信号强度很弱,几乎没有峰值;在基底上获得了高信噪比的R6G的SERS光谱, 与苯环相关的一系列C=C双键伸缩振动特征谱[17] (1 310、1 361、1 506、1 574、1 649 cm-1)以及与苯环相关的面内、面外变形振动特征谱610、773、1 186 cm-1均获得了明显增强。上述结果证实这些基底的SERS活性较高,需要指出的是并不是以上6种基底都具有这样优良的SERS活性, 只有当基底表面的纳米银颗粒出现活性点位时才具有SER活性,并且活性点位的数量对荧光猝灭的能力和拉曼增强效果也不同, 并呈现出一定的规律。对不同基底上R6G进行SERS比较测定, 每一基底各取5个不同位置进行SERS检测后取平均值, 得到不同形貌纳米银粒子组装基底的SERS活性特点。对照样品的SEM像有,当基片表面的球形纳米银颗粒分布相对稀疏时,基底表面粗糙度不够,以致SERS效果不理想, 大部分位置的SERS活性较差, 仅在少许“热点”位置才测得SERS, 且荧光背景高、信噪比差, SERS 活性点位分布表现出明显的不均匀性(见图6(a))。当基片表面的球形颗粒排列紧密时,基底表面粗糙度随之变大,SERS活性增强(见图6(b))。当基底表面纳米Ag颗粒为薄片状时(见图2(c)), 表面各位置SERS活性较均一, 荧光较好地被猝灭,获得了最佳的表面拉曼增强效果。而当表面粒子依旧为薄片状,但是存在大量团聚现象时,SERS活性减弱,SERS仅在一些“热点”处测得(见曲线图6(d))。这是因为在该区域,片状银颗粒的连续絮状分布将会致使该区域银颗粒分布过度致密, 膜粗糙度降低(见图2(d))。 当基片表面纳米Ag颗粒为不规则粒子时,形貌同时存在片状和球状(见图2(e)),SERS活性介于球状与薄片状之间(见图6(e))。当基片表面纳米Ag颗粒为不规则的多面体晶型结构,且其粒径较大时(见图2(f)),SERS活性减弱,如图6(f)所示。
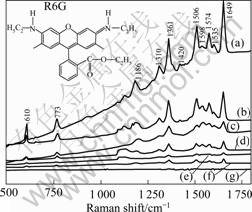
图6 R6G分子在样品以及玻璃基底上的拉曼光谱
Fig.6 Raman spectra of R6G on samples and on glass substrate: (a) Sample c; (b) Sample e; (c) Sample d; (d) Sample f; (e) Sample b; (f) Sample a; (g) Glass substrate
要确定一种基底的增强能力,就必须计算出吸附在粒子表面上的分子吸附信号的表面增强因子。普遍的认识是物理增强和化学增强同时存在,只是对于不同分子,其在SERS中所占的比例不同。不管是从物理增强还是从化学增强考虑,对SERS有贡献的主要是吸附在银粒子表面的单分子层。因此,在实验中需要尽量保证吸附在基底表面的有机分子为单层膜的结构。现在普遍接受的方法是采用吸附分子的SERS信号与其荧光信号或与其常规拉曼信号的比值作为增强因子大小的衡量依据。这里采用的是前面一种方法,通过将R6G分子在活性基底上的拉曼散射截面与其在玻璃基底上测得的荧光散射截面进行比较即可得到增强因子[18]。
SERS的增强因子(Enhancement factor)定义为
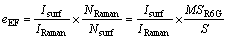 (3)
(3)
式中:Isurf为吸附在基底上探针分子的特征峰的积分面积;IRaman为溶液中探针分子特征峰的积分面积;S为样品上所有探针分子所占面积;SR6G 为单个探针吸附分子所占的表面积;M为探针分子总数量。增强因子越大,增强效应越强。
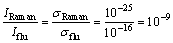 (4)
(4)
式中:σRaman和σflu分别为拉曼强度和荧光强度,根据图5及相关数据计算得其增强能力约为109。
依据公式(3)和(4)有下列式子:
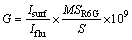 (5)
(5)
基于式(5),可以对样品的SERS增强因子进行计算,计算结果见表2。从表2可以看出,样品c对应的增强因子最大,增强效应最好,是最理想的SERS活性基底材料。
表2 样品的拉曼增强因子
Table 2 Enhancement factor of samples
3 结论
1) 以玻璃片为基底,采用预处理-化学镀法在其表面制备出形貌各异的纳米银粒子薄膜材料。随着反应液中AgNO3与乙二胺的摩尔比以及温度的改变,银纳米粒子的形貌发生改变。
2) 玻璃基底表面纳米银粒子薄膜由形貌各异、纯度很高和面心立方结构的纳米银粒子堆积而成。当反应温度为30 ℃、AgNO3与en的摩尔比为1:5时,制备出的由纳米银薄片组成的薄膜具有最强的紫外吸收光谱红移,可红移至800 nm。
3) 制备出的纳米银粒子薄膜具有很强的SERS活性,可以充当高SERS活性的固态基底材料。当纳米银粒子形貌不同时,SERS效应不同,且当活性基底由纳米银薄片组成时,增强因子最大,增强效应最好。
REFERENCES
[1] MORTON S M, JENSEN L. Understanding the molecule-surface chemical coupling in SERS[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2009, 131: 4090-4098.
[2] TIAN Zhong-qun, REN Bin, WU De-yin. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering: From noble to transition metals and from rough surfaces to ordered nanostructures[J]. J Phy Chem B, 2002, 37(106): 9463-9483.
[3] CANO T D, AROCA R, SAJA D J A, RODRIGUEZ-MENDEZ M L. Langmuir-blodgett mixed films of titanyl(Ⅵ) pthalocyanine and arachidic acid: Molecular orientation and film structure[J]. Langmuir, 2003, 19: 3747-3751.
[4] MICHAELS A M, NIRMAL M, BRUS L E. Surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy of individual rhodamine 6G molecules on large Ag nanocrystals[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 1999, 121: 9932-9939.
[5] LIU Guang-qiang, CAI Wei-ping, LIANG Chang-hao. Trapeziform Ag nanosheet arrays induced by electrochemical deposition on Au-coated substrate[J]. Cryst Growth Des, 2008, 8(8): 2748-2752.
[6] DRACHEV V P, NASHINE V C, THORESON M D, BEN-AMOTZ D, DAVISSON V J, SHALAEVET V M. Adaptive silver films for detection of antibody-antigen binding[J]. Langmuir, 2005, 21: 8368-8373.
[7] SMYTHE E J, DICKEY M D, BAO Ji-ming, WHITESIDES G M, CAPASSO F. Optical antenna arrays on a fiber facet for in situ surface-enhanced raman scattering detection[J]. Nano Lett, 2009, 9(3): 1132-1138.
[8] SUN Lan-lan, SONG Yong-hai, WANG Li, GUO Cun-lan, SUN Yu-jing, LIU Zhe-lin, LI Zhuang. Ethanol-induced formation of silver nanoparticle aggregates for highly active SERS substrates and application in DNA detection[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2008, 112: 1415-1422.
[9] SONG Wei, CHENG Yu-chuan, JIA Hui-ying, XU Wei-qing, ZHAO Bing. Surface enhanced Raman scattering based on silver dendrites substrate[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2006, 298: 765-768.
[10] YOSHIO K, VERO?NICA S M, LUIS M. Deposition of silver nanoparticles on silica spheres by pretreatment steps in electroless plating[J]. Chem Mater, 2001, 13: 1630-1633.
[11] SABAHUDIN H, LIU Ya-li, GARY E, FARID B, JOHN H T. New strategy for preparing thin gold films on modified glass surfaces by electroless deposition[J]. Langmuir, 2003, 19: 3958-3965.
[12] 魏丽丽, 徐盛明, 徐 刚, 陈崧哲, 李林艳. 表面活性剂对超细银粉分散性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2009, 19(3): 595-600.
WEI Li-li, XU Sheng-ming, XU Gang, CHEN Song-zhe, LI Lin-yan. Effects of surfactants on dispersive performance of ultrafine silver powder[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 19(3): 595-600.
[13] 易 早, 唐永建, 易有根, 李 恺, 罗江山, 李喜波, 张建波, 叶 鑫. 中空Ag纳米球壳的制备及性能表征[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2009, 21(9): 1354-1359.
YI Zao, TANG Yong-jian, YI You-gen, LI Kai, LUO Jiang-shan, LI Xi-bo, ZHANG Jian-bo, YE Xin. Preparation of hollow silver microspheres and their characterization[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2009, 21(9): 1354-1359.
[14] HE Yi, SHI Gao-quan. Surface plasmon resonances of silver triangle nanoplates: Graphic assignments of resonance modes and linear fittings of resonance peaks[J]. J Phys Chem B, 2005, 109: 17503-17511.
[15] GUPTA R, WEIMER W A. High enhancement factor gold films for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy[J]. Chem Phys Lett, 2003, 374(3): 302-306.
[16] NIE S M, EMORY S R. Probing single molecules and single nanoparticles by surface-enhanced Raman scattering[J]. Science, 1997, 275(2): 1102-1106.
[17] WEI Gang, ZHOU Hua-lan, LIU Zhi-guo, ZHUANG Li. A simple method for the preparation of ultrahigh sensitivity surface enhanced Raman cattering (SERS) active substrate[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2005, 240(4): 260-267.
[18] JIA Hui-ying, ZENG Jiang-bo, SONG Wei, AN Jing, ZHAO Bing. Preparation of silver nanoparticles by photo-reduction for surface-enhanced Raman scattering[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2006, 496(2): 281-287.
(编辑 杨 华)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(10804101);国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(2007CB815102);等离子体物理国防科技重点实验室基金资助项目(9140C6805020806)
收稿日期:2009-11-27;修订日期:2010-03-22
通信作者:唐永建,教授;E-mail: myyz1984@yahoo.cn