Al-Sc和Al-Ti靶材在高速撞击下的动态响应以及数值模拟
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2015年第2期
论文作者:张伟贵 何良菊 李培杰 叶益聪 冯 雪 L. S. NOVIKOV
文章页码:559 - 570
Key words:Al-Sc alloy; Al-Ti alloy; Al3Sc; high-speed impact; dynamic response; numerical simulation
摘 要:研究Al-Sc和Al-Ti半无限靶材在高速弹体撞击下的动力学响应,弹体的撞击速度分别为0.8、1.0、1.2和1.5 km/s。结果表明:Al-Sc靶材具有更优异的抗高速撞击能力。研究发现,不同的显微组织结构,包括晶粒大小、基体中析出的沉淀相粒子,导致Al-Sc和Al-Ti合金具有不同的抗撞击能力。同时,讨论Al-Sc合金中的纳米级Al3Sc粒子的尺寸效应对抗撞击能力的影响。此外,通过数值模拟对高速撞击后弹坑形状/几何尺寸进行仿真,并与实验结果进行对比验证。仿真分析结果较准确地复现了实验结果,在此基础上通过外推的方法将弹体速度推广到超高速范畴(>5 km/s)进行分析。在超高速撞击作用下,弹坑表面发生熔化和凝固现象。
Abstract: Al-Sc and Al-Ti semi-infinite targets were impacted by high-speed projectiles at velocities of 0.8, 1.0, 1.2 and 1.5 km/s, respectively. It is found that the Al-Sc targets demonstrate more excellent ability to resist high-speed impact. It is concluded that different microstructures of Al-Sc and Al-Ti alloys, including different grain sizes and secondary particles precipitated in the matrix, result in their greatly different capabilities of resisting impact. Furthermore, the effect of the size range of nanoscale Al3Sc precipitate in Al-Sc alloy on the resistance of high-speed impact was investigated. In addition, computer simulations and validation of these simulations were developed which fairly accurately represented residual crater shapes/geometries. Validated computer simulations allowed representative extrapolations of impact craters well beyond the laboratory where melt and solidification occurred at the crater wall, especially for hypervelocity impact (>5 km/s).
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25(2015) 559-570
Wei-gui ZHANG1, Liang-ju HE2, Pei-jie LI1, Yi-cong YE3, Xue FENG2, L. S. NOVIKOV4
1. Department of Mechanical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China;
2. School of Aerospace Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China;
3. College of Aerospace Science and Engineering, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China;
4. Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics, Moscow State University, Moscow 119992, Russia
Received 8 January 2014; accepted 5 March 2014
Abstract: Al-Sc and Al-Ti semi-infinite targets were impacted by high-speed projectiles at velocities of 0.8, 1.0, 1.2 and 1.5 km/s, respectively. It is found that the Al-Sc targets demonstrate more excellent ability to resist high-speed impact. It is concluded that different microstructures of Al-Sc and Al-Ti alloys, including different grain sizes and secondary particles precipitated in the matrix, result in their greatly different capabilities of resisting impact. Furthermore, the effect of the size range of nanoscale Al3Sc precipitate in Al-Sc alloy on the resistance of high-speed impact was investigated. In addition, computer simulations and validation of these simulations were developed which fairly accurately represented residual crater shapes/geometries. Validated computer simulations allowed representative extrapolations of impact craters well beyond the laboratory where melt and solidification occurred at the crater wall, especially for hypervelocity impact (>5 km/s).
Key words: Al-Sc alloy; Al-Ti alloy; Al3Sc; high-speed impact; dynamic response; numerical simulation
1 Introduction
Necessitated by the research needs in defense and aviation/aerospace fields, high-speed impact experiments have been carried out on a wide range of materials systems or targets since 1950s [1-5]. More recent interests are focused on the developments of high-speed collisional shields and the long-term response of structural materials in earth orbits and more general extended space environments [6,7]. Aluminum (Al) alloys are widely used as structural materials for airplanes and space vehicles, due to their low density, high specific strength and high specific modulus. Because of the importance of Al alloys in spacecraft and the inescapability of high-speed impacts between spacecraft and micrometeoroids or space debris, the studies of dynamic impact behaviors of Al alloys have always been carried out [8,9]. In general, such studies can be divided into the following three categories: 1) crater penetration depth and diameter [10,11]; 2) microstructural phenomena, such as microbands and shear bands, grain size effects, dynamic recrystallization [12] as well as deformation mechanisms and damage behavior [13,14]; 3) protection structure design aspect, including thin Al plate [5], Al-Whipple shield [15], Al matrix composite materials [16] and Al honeycomb [17].
Al alloys containing Sc represent a new generation of high-performance alloys that display numerous advantages over high strength Al alloys. Al alloys containing Sc are much stronger than other high strength alloys, exhibiting significant grain refinement, strengthening welds, and eliminating hot cracking in welds [18]. These Sc-containing Al alloys have been proved to be attractive materials for applications in the aerospace industry. However, until now, little is known about the dynamic impact response of Al-Sc alloy. Only in recent studies, LEE et al [19-21] studied the impact deformation behavior of several Al-Sc alloys by employing the compression split Hopkinson pressure bar (SHPB). Impact deformation behavior and microstructural evolution were investigated and the constitutive equations of Al-Sc alloys were set up in their works. However, SHPB test cannot substitute the hypervelocity impact test. Lately, the residual microstructures and impact responses of Al-Sc alloys have been investigated and compared with Al-Ti alloys using the hypervelocity impact test [22,23]. Nevertheless, the influence of the size range of nanoscale Al3Sc particles on the dynamic impact behavior was not involved. In addition, numerical simulation of high-speed impact was not carried out either.
Due to the limited velocity range and high cost of physical testing, the numerical simulation of hypervelocity impacts is becoming increasingly important. Maximum impact velocities seldom exceed 7 km/s even for very light projectiles such as soda-lime glass. In this regard, valid computer simulations are necessary in extending the implications of experimental impact crater phenomena beyond the laboratory, and making the implications more consistent with the actual environments of low-earth orbit and aspects of deeper space. Hereby, the residual crater sizes are especially important if the associated microstructures and properties are to be investigated and utilized as a basis for valid computer simulations.
The present study aimed to reveal the dynamic impact response of Al-Sc alloy by comparing the results of Al-Ti alloy. A particular focus of this research was the validation of computer simulations and the extrapolation of impact phenomena to the hypervelocity regime using the validated simulations.
2 Experimental procedures and simulation methods
2.1 Impact experiment
Samples of Al-1.0%Sc alloy and Al-1.0%Ti alloy (mass fraction, referred to as Al-Sc and Al-Ti, respectively, in the following) were obtained by adding master alloys Al-2.12%Sc and Al-2.15%Ti to pure Al (99.99%), respectively, with annealing at 450 °C for 1 h after solution treatment at 600 °C for 3 h. The original target samples were cut and machined to ensure that the thickness along the impact axis was about 10 mm.
The projectiles were carefully selected stainless steel spheres with a density of 7.9 g/cm3 and a diameter of 0.8 mm, which is a typical size of space debris in the near earth space. These projectiles were launched from a two-stage light gas gun with impact velocities from 0.5 to 6 km/s. In the present study, craters were formed at impact velocities of 0.8, 1.0, 1.2 and 1.5 km/s (Table 1).
Table 1 Data of projectile target cratering system

2.2 Analysis methods
The samples were carefully cut and ground to produce one exact crater half-section. The crater geometries were measured from these half-sections. The samples with polished cross-sections were electropolished in a mixture of perchloric acid and acetic acid, anodized in Baker’s reagent and examined under polarized light to reveal the grain structure for optical metallography. Metallographic observation and analysis were performed using an NEOPHOT 32 microscope system. Thin foils for transmission electron microscopy (TEM) examination were prepared by grinding sections of samples to thin sheet and punching out discs with diameter of 3 mm, which were then electropolished in a solution of 30% nitric acid (volume fraction) in methanol at -30 °C and 16 V. The foils were examined by a 2011 TEM at 200 kV. Vickers microhardness was obtained using a THV-30S microhardness tester. The load of 1×10-2 N and a dwell time of 15 s were employed during the microhardness measurement.
2.3 Computer simulation methods
An LS-DYNA 2D hydrocode software was used in the impact crater simulations reported herein. The LS-DYNA hydrocode can produce numerous plots based on pressure, temperature, stress, strain, strain rate, etc. in addition to material grid plots. The Johnson-Cook constitutive relationship is applicable to the high rate deformation of many materials including most metals. Typical applications include explosive metal forming, ballistic penetration, and impact. Herein, the Johnson-Cook constitutive relationship was applied to the stainless steel projectiles as well as the Al-Sc and Al-Ti targets. The Johnson-Cook [24] constitutive relationship has the general form:
 (1)
(1)
where σ0, B, C, n and m are experimentally determined material constants, ε is the strain, 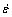 is the strain rate,
is the strain rate, 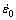 is the reference strain rate (usually equal to unity), and
is the reference strain rate (usually equal to unity), and
 (2)
(2)
where Tm is the melting temperature, Tr is a reference temperature at which σr is measured, and T is the temperature at which σ is calculated:
 (3)
(3)
The strain at fracture (εf) is given by
 (4)
(4)
where σ* is the ratio of hydrostatic pressure (p) to effective stress:
 (5)
(5)
 (6)
(6)
where σ1, σ2, σ3 are the principal stresses.
Fracture occurs when the damage parameter D reaches the value of 1.
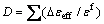 (7)
(7)
where εeff is the effective plastic strain, and εf is the fracture strain.
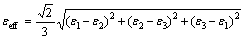 (8)
(8)
where ε1, ε2, ε3 are the principal strains.
The Mie-Grüneisen equation of state was used to describe the volumetric behavior of all materials. According to manual of LS-DYNA, for compressed materials, the Mie-Grüneisen equation of state defines pressure (p) for compressed materials as:
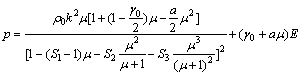 (9)
(9)
where C is the intercept of the vs-vp curve, S1, S2 and S3 are the coefficients of the slope of the vs-vp curve, γ0 is the Grüneisen gamma, a is the first order volume correction to γ0, and μ=ρ/ρ0-1. Note that vs and vp are shock wave velocity and particle velocity, respectively. The vs-vp curve is automatically calculated by LS-DYNA.
The input parameters into LS-DYNA for the velocity range used in this study (1 to 6 km/s) were set up in an identical manner for each specific crater simulation. A matrix of the most important input variables for the projectiles and targets are provided in Table 2. The parameters of Johnson-Cook constitutive relationship were obtained by standard SHPB test.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Impact craters in samples
Figure 1 shows cross-sections of the Al-Sc and Al-Ti targets impacted by the stainless steel projectile at velocities of 0.8, 1.0, 1.2 and 1.5 km/s. It is consistent with the former reported results [25], there is a protuberance around the crater of the target. If the projectile is hard and has a comparatively high melting temperature while the target is comparatively soft, a whole projectile can be found in the crater after the impact with a comparatively low velocity of ~1 km/s. For instance, if the projectile was made to impact the Cu target with a velocity of ~1 km/s, the hole was found in the crater and the size of the projectile is close to that of the hole [26]. The projectile was used to impact the Al alloy in this research with the impact velocity of lower than 2 km/s. Therefore, the projectile was found in the crater in most of the circumstances. There was no projectile in Figs. 1(a) and (g) because the projectile fell off during the sample preparation procedures. Actually, after high-speed impact, these two samples contained projectile in their craters.
Table 2 Input parameters for projectile and targets used in simulations
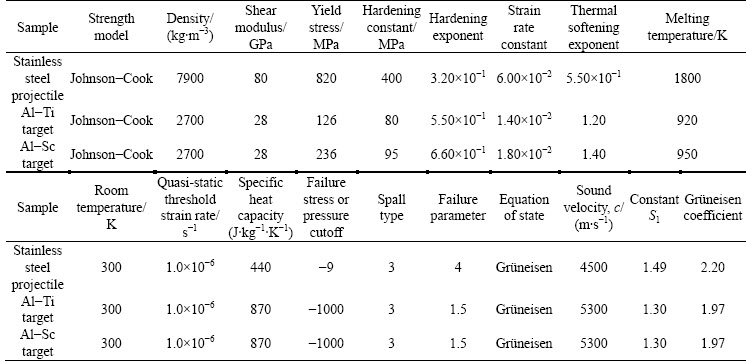

Fig. 1 Transverse (half-sectional) view comparisons of impact craters in Al-Sc and Al-Ti targets impacted by stainless steel projectiles with diameter of 0.8 mm
According to the definition of the crater depth in Fig. 2 [27], the parameters of the craters of the samples were measured and listed in Table 1. According to the data in Table 1, the relationship between the crater depth and the impact velocity was obtained (see Fig. 3). As shown in Figs. 1 and Fig. 3, under the same impact velocity, the crater depth of Al-Sc target is smaller than that of Al-Ti target. And as the impact velocity increases, the increase of the crater depth for Al-Sc target is smaller than that of Al-Ti target. Therefore, it is concluded that the resistant ability to high-speed impact of the Al-Sc target is higher than that of the Al-Ti target in this experiment.
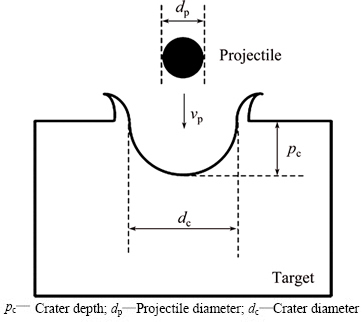
Fig. 2 Definitions of parameters of impact and crater

Fig. 3 Dependence between crater depth (pc) and impact velocity (v0)
3.2 Discussion of different capabilities of resisting impact of types of alloys
3.2.1 pc/dp formula
Plenty of experimental work on examinations of impact crater shapes has been reported [28]. These studies usually adapt metallic projectiles as impact bullets and Al alloy as targets which have practical consequences in structural materials in space. Correspondingly, a wide range of empirical cratering equations has also been developed (largely based on Al targets). Among the formulas, Eq. (10) is a typical one [29]:
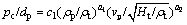 (10)
(10)
where ρp is the density of the projectile, ρt is the density of the target, vp is the velocity of the projectile, Ht is the hardness of the target, and a1, a2 and c1 are constants.
According to Eq. (10), the hardness of the target (Ht) plays a more important role in influencing the capability of resisting high-speed impact. Reference [30] summarized the depth of cavities and craters of many projectile/target systems including glass, plastic and metal projectiles and metal, rock, ice, foam, sheet-stack, and aerogel targets. Their studies also indicate that pc/dp depends on Ht. It is suggested that there are two main factors leading to the notable difference in strength between the Al-Sc and Al-Ti targets, which will be discussed later.
3.2.2 Different grain sizes
Generally speaking, as the crystalline grains of the material decrease, the crystal boundaries which prevent glide increase, and the strength and hardness of the material are enhanced correspondingly. The general relationship between hardness and grain size is as follows:
 (11)
(11)
where HV is the Vickers hardness, A and B are constants, and d is the average grain diameter. Obviously, the alloy hardness is dependent on the grain size. The microstructures of the Al-Ti and Al-Sc samples are shown in Fig. 4, in which the great difference in grain sizes between these two alloys is obvious. The grain sizes of the Al-Ti and Al-Sc targets are 85 and 25 μm, respectively. The grain size of Al-Sc target is much finer than that of Al-Ti target, which results in a higher hardness value compared with the Al-Ti target.

Fig. 4 Grain structures of original samples
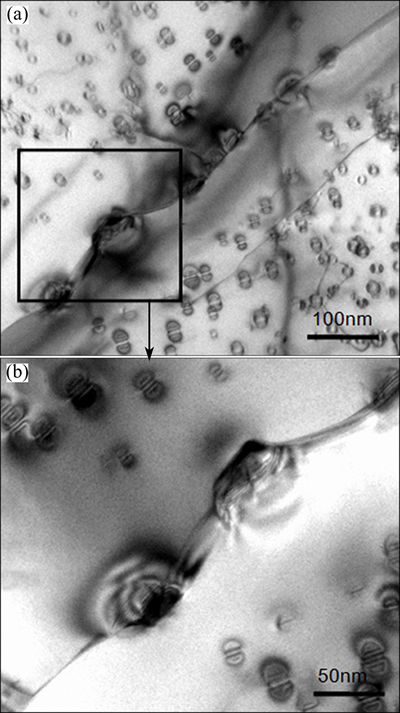
Fig. 5 TEM images of Al-Sc target before impact
3.2.3 Different microstructures
TEM micrographs of the Al-1.0%Sc alloy annealed at 450 °C for 1 h (before impact) show that there are a great deal of fine second-phase particles in the Al-Sc matrix (Fig. 5), while, no such particles were found in Al-Ti target. The particles in Al-Sc target were proved to be secondary Al3Sc, which was also confirmed in our previous studies [22]. The strength of Al alloys is mainly due to age-hardening mechanisms. Sc is supersaturated in Al solid solution formed during ingot casting and supersaturated solid solutions decompose on ageing at elevated temperature, precipitating the A13Sc (L12) phase. Owing to the similarity between the crystal lattices of the Al matrix and the Al3Sc phase in terms of structure and dimension, the Al3Sc phase particles precipitate homogeneously with a very high density as stable spherical particles fully coherent with the matrix, which provides a considerable increase in strength to Al alloys. From Fig. 5, it can be seen that secondary Al3Sc particles distribute uniformly in the Al matrix after annealing. The average diameter of Al3Sc particles is approximately 18 nm and the space between adjacent particles is small, which has a strong effect on dispersion strengthening. Measured by Vickers hardness, the hardness values of Al-Sc and Al-Ti targets before impact are HV 67 and HV 30, respectively.
3.3 High-speed impact results of Al-Sc and Al-Ti targets with different microstructures
According to Eq. (10), the calculated ratios of the crater depth of the Al-Sc to Al-Ti targets, pc(Al-Sc)/pc(Al-Ti), is 0.76. However, the actual ratios of pc(Al-Sc)/pc(Al-Ti) are 0.75, 0.74, 0.72 and 0.65, corresponding to the projectile impact velocity of 0.8, 1.0, 1.2 and 1.5 km/s, respectively. Setting Al-Ti target as a reference, the actual crater depth of the Al-Sc target is smaller than that calculated by empirical formula with increase of the impact velocity. Based on the law of the dynamic behavior of materials, it is inferred that the microstructure of material has a significant effect on the penetration of projectiles in target. In order to investigate the relationship between microstructure of material and impact behavior, comparative impact test of Al-Ti and Al-Sc targets under different heat treatment processes was carried out. Al-Sc and Al-Ti alloys with different microstructures can be obtained by adjusting alloy compositions, and changing the temperatures and time of the heat treatment. Then, the effects of the grain sizes and the secondary phase particles were examined. The partial impact parameters are listed in Table 3. The results of the impact experiments were plotted in the coordinates by making the dimensionless ballistic velocity as the x-axis and the crater shape factor as y-axis (see Fig. 6). By carefully examining the results, several conclusions can be obtained.
Table 3 Experimental impact crater parameters

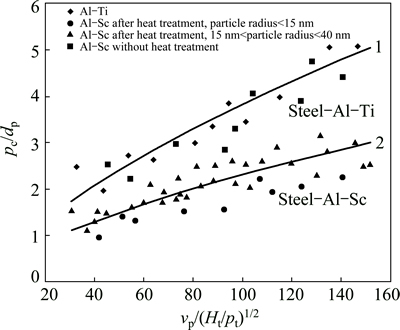
Fig. 6 Dependence between dimensionless crater depth (pc/dp) and dimensionless impact velocity (vp/(Ht/ρt)1/2)
1) Al-Sc alloys without heat treatment and Al-Ti alloys, which are no matter subjected to heat treatment, are all close to the fitted Curve 1. While, Al-Sc alloys, after heat treatment is close to the fitted Curve 2. The fitted Curves 1 and 2 are shown as follows:
Curve 1: 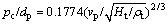 (12)
(12)
Curve 2:  (13)
(13)
It is obvious that Al-Sc alloys after heat treatment (Curve 2) represents higher ability to resist high-speed impact.
2) The samples corresponding to data points close to Curve 1 do not have secondary phase particles, and the differences between which are the grain sizes. The hardness differences resulted from different grain sizes are shown in x-axis. This demonstrates that the grain sizes show no direct influence on the depth of the hole produced in the impact process.
3) The samples corresponding to data points close to Curve 2, are all heat treated Al-Sc alloys, which show a common obvious characteristic of secondary Al3Sc precipitation strengthening. Curve 2 is entirely located below Curve 1, which demonstrates that the precipitation of the secondary Al3Sc particle shows more influence on enhancing the resistive abilities of the alloys than just on the hardness of the alloys, because the hardness effect has been shown in x-axis. The data points close to Curve 2 can be divided into two regions. The secondary Al3Sc particles with radius of 15-40 nm are distributed on both two sides of the curve or on the curve, and there are more data points above the curve than those under the curve. Most of the data points corresponding to the grains with radius smaller than 15 nm are underneath the curve. According to Ref. [31], the secondary Al3Sc particles in the radius range of 15-40 nm are transition particles. This means that in these particles, some just begin to lose coherency and some have lost coherency completely and turned into semi-coherency. The secondary Al3Sc particles with radius of smaller than 15 nm are all coherency with the matrix.
Obviously, different resistive abilities to impact of different target materials, are not only affected by their hardness, but also influenced by the second phase particles. In this experiment, as the sizes of the second phase particles decrease, the degree of dispersed precipitation increases, which demonstrates better resistive abilities to impact gradually. The role of secondary Al3Sc precipitate in the Al-Sc alloy in the impact process has been reported in our previous studies [22,23]. It is concluded that the secondary Al3Sc particles play a predominant role in the high-speed impact process in addition to the grain size. The secondary Al3Sc particles have two effects of stabilizing the matrix structure and acting as source of dislocation, which reduce deformation range and improve the alloy hardening in Al-Sc target. As a result, the capability of alloy to resist high-speed projectile impact is enhanced.
3.4 Numerical simulation of Al-Sc and Al-Ti target
An LS-DYNA 2D, PC-compatible hydrocode utilizing Lagrangian and Eulerian processors with a Johnson-Cook constitutive relationship has been applied to simulating impact craters. These impact craters were all experimentally developed by impacting Al-Sc and Al-Ti targets using stainless steel spheres (nominally 0.8 mm in diameter) at velocities ranging from 0.8 to 1.5 km/s.
Figure 7 shows, in correspondence with Fig. 1, the simulated impact crater half-sections for the Al-Sc and Al-Ti targets at impact velocity ranging from 0.8 to 1.5 km/s. Note the projectile residual in Fig. 7 in comparison to the actual crater cross-section views in Fig. 1. The simulation results also show that the Al-Sc targets have more excellent ability to resist high-speed impact. The simulated crater geometries (pc, dc, and pc/dc) in Fig. 7 closely matched the experimental crater geometries, provided sufficient validation over the range of experimental impact velocities. Figure 8 shows the corresponding von Mises stress maps for the Al-Sc and Al-Ti targets at impact velocity ranging from 0.8 to 1.5 km/s. From Fig. 8, it is clear to see that the magnitude and range of the von Mises stress in Al-Sc target are smaller than those in Al-Ti targets, which indicated the more excellent ability of Al-Sc target to resist high- speed impact. The range of von Mises stress in target reflects a certain extent of the shock wave propagation range. The smaller the distribution of von Mises stress in target is, the smaller the shock wave propagation range is. Accordingly, the target will be more effective to resist impact. Validated computer simulations allowed relatively confident extrapolations into the hypervelocity regime. These extrapolations are illustrated in the computer simulations at impact velocities of 5 and 10 km/s for the Al-Sc target impacted by stainless steel projectile, as shown in Fig. 9. Figure 9 illustrates a somewhat more pronounced crater surface melt especially at 10 km/s (Fig. 9(b)). In addition, there are some obvious serrated characteristics on the crater surface as shown in Fig. 9(b). It is assumed that the serrated characteristics are caused by target melt.

Fig. 7 Comparison of computer simulated impact crater half-section for Al-Sc and Al-Ti targets: (Color keys next to Figs. (a)-(h) represent plastic strain of targets after high-speed impact)
The instantaneous Hugoniot shock pressure in the target is given by the shock Hugoniot equation [32]:
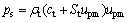 (14)
(14)
where ρt is the target density, ct is the bulk sound velocity in the target, St is the target material constant related to the Grüneisen parameter, and upm is the modified projectile velocity in the compressed region after impact and given by
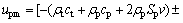
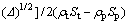 (15)
(15)
where

 (16)
(16)
and ρt and ρp are the target and projectile densities, ct and cp as well as St and Sp are the corresponding bulk sound velocity and Grüneisen parameters, respectively for the target (t) the projectile (p), and v is the projectile velocity at impact.

Fig. 8 Comparison of simulated distribution of von Mises stress in Al-Sc and Al-Ti targets (Color keys next to Figs. (a)-(h) represent von Mises stress in targets after high-speed impact)
In the hydrodynamic regime during crater formation, the steady-state pressure was calculated from the Bernoulli equation:
 (17)
(17)
The Bernoulli pressure is sometimes associated with the steady-state pressure at the crater bottom when the crater is actually formed, and represents an attenuation of the Hugoniot pressure [24].

Fig. 9 Impact crater simulations for Al-Sc target impacted by stainless steel projectile showing residual plastic strain contours and corresponding color key
In the present study, for the Al-Sc target impacted by the stainless steel projectile, the calculated instantaneous ps and steady-state pressures pB are 90.5 and 13.4 GPa, respectively, at the impact velocity of 5 km/s; and they are 259.9 and 53.8 GPa, respectively, at the impact velocity of 10 km/s. The calculated pressures here are very close to the data in Ref. [24], which calculated the instantaneous and steady-state pressures in the 1100 Al target impact by the stainless steel projectile at the same velocities. Temperatures generated in the cratering process are correlative with pressure. The high temperatures are caused by two main reasons. One is adiabatic temperature produced at the shock front, the other is residual temperature from the formed crater and heating of the target. For Al, adiabatic temperatures in the shock front will equal the melting temperature (~933 K) between 40 and 50 GPa [32]. However, the residual temperature rise will approach the melting temperature only when the instantaneous pressure exceeds about 90 GPa. In this study, the calculated pressures at 10 km/s far exceed those required for melting along with the crater wall. It is therefore concluded that the carter wall melt and the serrated characteristics shown in Fig. 9(b) are caused by crater surface melt.
The crater in Fig. 9(b) approaches an ideal, hypervelocity hemispherical-like shape, but pc/dc=0.83 is in contrast to an ideal hemisphere at pc/dc=0.5.
Table 4 summarizes the impact crater geometry data for the Al-Sc and Al-Ti targets impacted by stainless steel projectile with the velocity ranging from 0.8 to 1.5 km/s. It can be seen that the simulated crater parameters are in good agreement with the experimental data. The simulated data were obtained directly by LS-DYNA software and the measuring errors were estimated to be no more than 0.1%.
Table 4 Impact crater geometry data of simulations and experiments

4 Conclusions
1) Al-1.0%Sc and Al-1.0%Ti targets were impacted by high-speed projectiles with velocities of 0.8, 1.0, 1.2 and 1.5 km/s, respectively. The Al-Sc targets demonstrate more excellent ability to resist high-speed impact than Al-Ti targets. Different microstructures of Al-Sc and Al-Ti alloys, including different grain sizes and secondary particles precipitated in the matrix, result in greatly different capabilities of resisting impact. For the Al-Sc targets, Al-Sc alloy containing Al3Sc particles with size smaller than 15 nm exhibits the most excellent capability of resisting high-speed impact.
2) Computer simulations and validation of simulations were developed, which accurately represented residual crater shapes/geometries. By validating the computer simulations through matching crater shapes and geometries, crater simulations were extrapolated into the hypervelocity regime as an extension of the laboratory environment. These extrapolations were illustrated in the computer simulations at impact velocity from 5 to 10 km/s for the Al-Sc target, which illustrated a more pronounced crater surface melt especially at 10 km/s with shape factor, pc/dc=0.83, in contrast to an ideal hemisphere at pc/dc=0.5.
References
[1] STOCK T A C, THOMPSON K R L. Penetration of aluminum alloys by projectiles [J]. Metallurgical Transactions, 1970, 1(1): 219-224.
[2] HARRISON W, LOUPIAS C, OUTREBON P, TURLAND D. Experimental data and hydrocode calculations for hypervelocity impacts of stainless steel into aluminum in the 2-8 km/s range [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1995, 17(1-3): 363-374.
[3] MURR LE, FERREYRA E, PAPPU T S, GARCIA E P, SANCHEZ J C, HUANG W, RIVAS J M, KENNEDY C, AYALA A, NIOU C S. Novel deformation processes and microstructures involving ballistic penetrator formation and hypervelocity impact and penetration phenomena [J]. Materials Characterization, 1996, 37(5): 245-276.
[4] RIVAS J M, QUINONES S, MURR L E, NIOU C S, ADVANI A H, MANUEL D J, BIRUDAVOLU. Microstructural phenomena associated with micrometeoroid impact craters in aluminum and stainless steel [J]. Journal of Failure Analysis and Prevention, 2004, 4(3): 24-31.
[5] ZHANG Q, CHEN Y, HUANG F, LONG R. Experimental study on expansion characteristics of debris clouds produced by oblique hypervelocity impact of LY12 aluminum projectiles with thin LY12 aluminum plates [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2008, 35 (12): 1884-1891.
[6] MANDEVILLE J C, PERRIN J M, VIDAL L L. Experimental hypervelocity impacts: Implication for the analysis of material retrieved after exposure to space environment. Part I: Impacts on aluminum targets [J]. Acta Astronautica, 2012, 81: 532-544.
[7] RYAN S, CHRISTIANSEN E L. Hypervelocity impact testing of advanced materials and structures for micrometeoroid and orbital debris shielding [J]. Acta Astronautica, 2013, 83: 216-231.
[8] NISHIDA M, HAYASHI K, NAKAGAWA J, ITO Y. Influence of temperature on crater and ejecta size following hypervelocity impact of aluminum alloy spheres on thick aluminum alloy targets [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2012, 42: 37-47.
[9] LIANG X P, LI H Z, HUANG L, HONG T, MA B, LIU Y. Microstructural evolution of 2519-T87 aluminum alloy obliquely impacted by projectile with velocity of 816 m/s [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22: 1270-1279.
[10] BAKER J R. Hypervelocity crater penetration depth and diameter—A linear function of impact velocity [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1995, 17: 25-35.
[11] TANAKA K, NISHIDA M, OGAWA H, AKAHORI M, AIKAWA F. Hypervelocity crater formation in aluminum alloys at low temperatures [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2008, 35(12): 1821-1826.
[12] MURR L E, ESQUIVEL E V. Observations of common microstructural issues associated with dynamic deformation phenomena: Twins, microbands, grain size effects, shear bands, and dynamic recrystallization [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2004, 39(4): 1153-1168.
[13] ZHEN L, LI G A, ZHOU J S YANG D Z. Micro-damage behaviors of Al-6Mg alloy impacted by projectiles with velocities of 1-3.2 km/s [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 391(1-2): 354-366.
[14] ZHANG C, KALIA R K, NAKANO A, VASHISHTA P, BRANICIO P S. Deformation mechanisms and damage in α-alumina under hypervelocity impact loading [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2008, 103(8): 083508
[15] GONGSHUN G, PANG B J, WEI Z, YUE H. Crater distribution on the rear wall of Al-Whipple shield by hypervelocity impacts of Al-spheres [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2008, 35(12): 1541-1546.
[16] GUO Q, SUN D L, HAN X L, YANG W S, JIANG L T, WU G H. Damage behaviour of Al matrix composite reinforced with Ti-6Al-4V meshes under the hypervelocity impact [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2012, 535: 136-143.
[17] WANG Z G, TIAN H Q, LU Z J, ZHOU W. High-speed axial impact of aluminum honeycomb—Experiments and simulations [J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2014, 56: 1-8.
[18] LATHABAI S, LIOYD P G. The effect of scandium on the microstructure, mechanical properties and weldability of a cast Al-Mg alloy [J]. Acta Materialia, 2002, 50(17): 4275-4292.
[19] LEE W S, CHEN T H. Dynamic deformation behaviour and microstructural evolution of high-strength weldable aluminum scandium (Al-Sc) alloy [J]. Materials Transactions, 2008, 49(6): 1284-1293.
[20] LEE W S, CHEN T H. Comparative study of dynamic impact properties and microstructures of weldable and unweldable aluminium-scandium (Al-Sc) alloys [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2009, 25(6): 711-724.
[21] LEE W S, CHEN T H, LIN C F, CHEN M S. Impact deformation behaviour and dislocation substructure of Al-Sc alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2010, 493(1-2): 580-589.
[22] YE Y C, LI P J, NOVIKOV L S, AVIKINA V S, HE L J. Comparison of residual microstructures associated with impact craters in Al-Sc and Al-Ti alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 2010, 58(7): 2520-2526.
[23] ZHANG W G, YE Y C, HE L J, LI P J, FENG X, NOVIKOV L S. Dynamic response and microstructure control of Al-Sc binary alloy under high-speed impact [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2013, 578: 35-45.
[24] VALERIO-FLORES O L, MURR L E, HERNANDEZ V S, QUINONES S A. Observations and simulations of the low velocity-to-hypervelocity impact crater transition for a range of penetrator densities into thick aluminum targets [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2004, 39(20): 6271-6289.
[25] MURR L E, QUINONES S A, FERREYRA T E, AYALA A, VALERIO O L, HORZ F, BERNHARD R P. The low-velocity-to- hypervelocity penetration transition for impact craters in metal targets [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1998, 256(1-2): 166-182.
[26] MURR L E, GARCIA E P, FERREYRA T E, NIOU C S, RIVAS J M, QUINONES S A. Microstructural aspects of hypervelocity impact cratering and jetting in copper [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1996, 31(22): 5915-5932.
[27] MURR L E, STAUDHAMMER K P, MEYERS M A. Metallurgical and materials applications of shock-wave and high-strain-rate phenomena [M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science, 1995.
[28] NISHIDA M, KUZUYA K, HAYASHI K, HASEGAWA S. Effects of alloy type and heat treatment on ejecta and crater sizes in aluminum alloys subjected to hypervelocity impacts [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2013, 54: 161-176.
[29] HERRMANN W, WIBECK J S. Review of hypervelocity penetration theories [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1987, 5(1-4): 307-322.
[30] KADONO T, FUJIWARA A. Cavity and crater depth in hypervelocity impact [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2005, 31: 1309-1317.
[31] IWAMURA S, MIURA Y. Loss in coherency and coarsening behavior of Al3Sc precipitates [J]. Acta Materialia, 2004, 52(3): 591-600.
[32] MEYERS M A. Dynamic behavior of materials [M]. New York: Wiley Interscience, 1994.
张伟贵1,何良菊2,李培杰1,叶益聪3,冯 雪2,L. S. NOVIKOV4
1. 清华大学 机械工程系,北京100084;
2. 清华大学 航天航空学院,北京100084;
3. 国防科技大学 航天科学与工程学院,长沙410073;
4. Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics, Moscow State University, Moscow 119992, Russia
摘 要:研究Al-Sc和Al-Ti半无限靶材在高速弹体撞击下的动力学响应,弹体的撞击速度分别为0.8、1.0、1.2和1.5 km/s。结果表明:Al-Sc靶材具有更优异的抗高速撞击能力。研究发现,不同的显微组织结构,包括晶粒大小、基体中析出的沉淀相粒子,导致Al-Sc和Al-Ti合金具有不同的抗撞击能力。同时,讨论Al-Sc合金中的纳米级Al3Sc粒子的尺寸效应对抗撞击能力的影响。此外,通过数值模拟对高速撞击后弹坑形状/几何尺寸进行仿真,并与实验结果进行对比验证。仿真分析结果较准确地复现了实验结果,在此基础上通过外推的方法将弹体速度推广到超高速范畴(>5 km/s)进行分析。在超高速撞击作用下,弹坑表面发生熔化和凝固现象。
关键词: Al-Sc合金;Al-Ti合金;Al3Sc;高速撞击;动态响应;数值模拟
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Corresponding author: Wei-gui ZHANG; Tel: +86-18210295008; E-mail: zwg11@mails.tsinghua.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63638-X

