氧分子与黄铁矿、白铁矿和磁黄铁矿表面作用的第一性原理计算
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2016年第2期
论文作者:赵翠华 陈建华 李玉琼 陈晔 李伟洲
文章页码:519 - 526
关键词:硫化矿;氧吸附;表面氧化;第一性原理
Key words:iron sulfide; O2 adsorption; surface oxidation; first-principle
摘 要:为了获得黄铁矿、白铁矿和磁黄铁矿的氧化机制,采用第一性原理方法研究氧分子与这三种矿物表面的作用。计算结果表明:氧分子在磁黄铁矿表面的吸附能最大,在白铁矿表面的吸附能次之,在黄铁矿表面的吸附能最小。氧分子在黄铁矿、白铁矿和磁黄铁矿表面都发生了解离。氧原子与黄铁矿、白铁矿和磁黄铁矿的表面原子具有不同的键合结构。由于白铁矿和磁黄铁矿表面与氧作用的原子数较多,因此,氧分子在白铁矿和磁黄铁矿表面的吸附能比在黄铁矿表面的吸附能大。磁黄铁矿表面相对较大的O—Fe键布局值导致氧分子在磁黄铁矿表面的吸附能比在白铁矿表面的吸附能大。
Abstract: The interaction of O2 with pyrite, marcasite and pyrrhotite surfaces was studied using first-principle calculations to obtain the oxidization mechanisms of these minerals. The results show that the adsorption energy of O2 on pyrrhotite surface is the largest, followed by that on marcasite surface and then pyrite surface. O2 molecules adsorbed on pyrite, marcasite and pyrrhotite surfaces are all dissociated. The oxygen atoms and surface atoms of pyrite, marcasite and pyrrhotite surfaces have different bonding structures. Due to more atoms on pyrrhotite and marcasite surfaces interaction with oxygen atoms, the adsorption energies of O2 on pyrrhotite and marcasite surfaces are larger than that on pyrite surface. Larger values of Mulliken populations for O-Fe bond of pyrrhotite surface result in relative larger adsorption energy compared with that on marcasite surface.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 26(2016) 519-526
Cui-hua ZHAO1, Jian-hua CHEN2, Yu-qiong LI2, Ye CHEN2, Wei-zhou LI1
1. College of Materials Science and Engineering, Guangxi University, Nanning 530004, China;
2. Guangxi Colleges and University Key Laboratory of Minerals Engineering, Guangxi University, Nanning 530004, China
Received 7 March 2015; accepted 4 August 2015
Abstract: The interaction of O2 with pyrite, marcasite and pyrrhotite surfaces was studied using first-principle calculations to obtain the oxidization mechanisms of these minerals. The results show that the adsorption energy of O2 on pyrrhotite surface is the largest, followed by that on marcasite surface and then pyrite surface. O2 molecules adsorbed on pyrite, marcasite and pyrrhotite surfaces are all dissociated. The oxygen atoms and surface atoms of pyrite, marcasite and pyrrhotite surfaces have different bonding structures. Due to more atoms on pyrrhotite and marcasite surfaces interaction with oxygen atoms, the adsorption energies of O2 on pyrrhotite and marcasite surfaces are larger than that on pyrite surface. Larger values of Mulliken populations for O-Fe bond of pyrrhotite surface result in relative larger adsorption energy compared with that on marcasite surface.
Key words: iron sulfide; O2 adsorption; surface oxidation; first-principle
1 Introduction
Iron sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula of FeS, and exists in several distinct forms, which differs in the ratio of sulfur to iron and properties. Common iron sulfides include pyrite (FeS2), marcasite (FeS2), pyrrhotite (FexS1-x) and so on. The structures of pyrite and marcasite have been well characterized and described in detail elsewhere, and the structural relationships between pyrite and marcasite were also studied [1-3]. According to BROSTIGEN and KIEKSHUS [3], the pyrite (001) and the marcasite (101) planes show the same atomic arrangement. Pyrrhotite is an unusual iron sulfide mineral with a variable iron content. Pyrrhotite is also called magnetic pyrite because the color is similar to that of pyrite and it is weakly magnetic. Pyrrhotite exists in a hexagonal or monoclinic form. The iron content ranges from 46.5% to 46.8% (mole fraction) in monoclinic pyrrhotite and from 47.4% to 48.3% in hexagonal forms [4]. The formula of pyrrhotite minerals can also be expressed as Fen-1Sn with n≥8 to give structures from Fe7S8 to Fe11S12. The most Fe-deficient end member, Fe7S8, has a monoclinic symmetry, whereas the intermediate (Fe1-xS) and equimolar (FeS) members have hexagonal and orthorhombic structures, respectively [5,6]. The bulk sulfides have been well studied and displayed different electronic structures and properties [7-10].
The surface chemistry of sulfides plays a large role in the commercially important processes of mineral benefaction and the separation of sulfides. The floatability of minerals depends on the wettability at solid particle surfaces. However, many studies show that O2 has large effect on the floatability of minerals [11,12]. It has been increasingly acknowledged that the oxidation of sulfide minerals themselves is fundamentally significant during flotation. Xanthates are often used in flotation operation as a collector for sulfide minerals, which attaches to the mineral surface and produces a hydrophobic surface. The xanthate oxidation process is accompanied by the concurrent reduction of oxygen [13], while the oxygen chemisorption energetically favors the oxidation of xanthate anions to produce an adsorbed hydrophobic species. This reaction can be expressed by the following equations:
O2+e=(O2-)ads (1)
ROCS2-=(ROCS2)ads+e (2)
Oxygen is a critical factor affecting the natural floatability of sulfide minerals. ROSSO et al [14] studied the interaction of gaseous O2, H2O and their mixtures with clean (100) surfaces of pyrite. Ab initio cluster calculations of adsorption energies and the interaction of O2 and water species with the surface indicate that H2O dissociatively sorbs when O2 is present on the surface. The study of ROSSO et al [14] suggests that O2 can be influential on H2O adsorption on the sulfide surfaces. In addition, pyrite exhibits surface chemistry that can profoundly affect the very environment in which it is present. One of the most striking examples of how the reactivity of pyrite can affect an environment is associated with anthropogenic activities. The oxidative decomposition of pyrite at coal and metal mining sites leads to the devastating environmental problem known as acid mine drainage [15,16]. Therefore, the role of O2 in the floatation of sulfides becomes one of the most important issues in the study of floatation of sulfides.
In this work, the interaction of O2 with pyrite, marcasite and pyrrhotite surfaces was studied using density functional theory (DFT) method, including adsorption model, adsorption energy, surface charge distribution and charge transfer, and density of states (DOS). This study can provide important insight into the mechanism of O2 adsorption and the subsequent flotation behavior of sulfides.
2 Computational methods and models
2.1 Computational methods
The calculations were performed using the Cambridge Serial Total Energy Package (CASTEP) developed by PAYNE et al [17]. DFT calculations within the generalized gradient approximation (GGA) using the Perdew, Burke and Ernzerhof (PBE) functional were carried out to study O2 adsorption on the surfaces of pyrite, marcasite and pyrrhotite [18]. The interactions between valence electrons and ionic core were represented by ultrasoft pseudoptentials [19,20]. The valence electron configurations included Fe 3d64s2, S 3s23p4 states. Based on the test results, a plane wave cut-off energy of 270 eV was used for all calculations. The convergence tolerances for structure optimization and energy calculation were set to the maximum displacement of 0.002  , the maximum force of 0.08 eV/
, the maximum force of 0.08 eV/  , the maximum energy change of 2.0×10-5 eV/atom and the maximum stress of 0.1 GPa, and the self-consistent field (SCF) convergence tolerance was set to 2.0×10-6 eV/atom.
, the maximum energy change of 2.0×10-5 eV/atom and the maximum stress of 0.1 GPa, and the self-consistent field (SCF) convergence tolerance was set to 2.0×10-6 eV/atom.
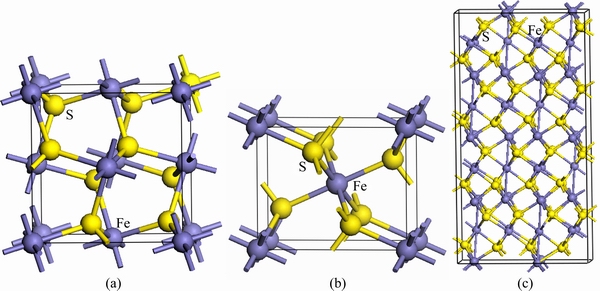
Fig. 1 Bulk FeS2 unit cell of pyrite (a), marcasite (b) and pyrrhotite (c)
2.2 Computational models
Common pyrite (FeS2) possesses a cubic crystal structure, and has a space group of Pa3, which has good symmetry. The conventional unit cell is presented in Fig. 1(a). Each cell contains four FeS2 units, with Fe atoms located at each of the corners and the centers of all the cube faces. Each Fe atom coordinates with adjacent six S atoms, each S atom is tetrahedrally coordinated by three Fe atoms and one S atom with the S2 dimer formed. The mineral marcasite, sometimes called white iron pyrite, is iron sulfide (FeS2) with orthorhombic crystal structure. It is a mineral with the same composition as pyrite, but differing in crystal structure. Both structures do have in common that they contain the disulfide S22- ion having a short bonding distance between the sulfur atoms. The structures differ in how these dianions are arranged around the Fe2+ cations. The model of marcasite is shown in Fig. 1(b). Pyrrhotite is a nonstoichiometric compound, general formula of Fe1-xS, based on Fe(II) and S2- ions. The values for x vary from 0 (FeS) to 0.125 (Fe7S8). Each metal atom is in a distorted octahedral coordination with six sulphur atoms but the six iron neighbours of a sulphur atom are displaced at the corners of a trigonal prism. Common pyrrhotite possesses a monoclinic crystal structure, as shown in Fig. 1(c). Monoclinic pyrrhotite (Fe7S8) has a crystal structure based on the NiAs structure (hence with a slightly distorted hexagonal close-packed array of anions) arising from the ordering of Fe vacancies.
Based on the test results, the pyrite (100), marcasite (101) and pyrrhotite (001) faces were chosen for calculations because of being the most stable. All surfaces were obtained from the bulk sulfides with the optimum unit cell volume. The pyrite (100), marcasite (101) and pyrrhotite (001) faces were modeled using (2×2×1), (2×2×1) and (1×2×1) supercell geometries, respectively, where the central cell, periodic in 3D, contains a slab that has two surfaces and a vacuum gap above and below the surfaces separating the adjacent mirror images of slab. The surface energies of a range of surfaces with varying slab thicknesses were calculated to determine the slab size. Figures 2(a)-(c) are the most stable surface models resulted from DFT calculations. During all geometry optimization calculations, the central atomic layer of slab was kept fixed to prevent the slab from drifting vertically along the supercell.
2.3 Calculation of adsorption energy
The adsorption energies of O2 on sulfide surfaces can be expressed by following equation:
 (3)
(3)
where 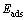 is the adsorption energy,
is the adsorption energy, 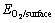 is the total energy of the pyrite, marcasite, or pyrrhotite slab with adsorbed O2,
is the total energy of the pyrite, marcasite, or pyrrhotite slab with adsorbed O2, 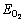 is the energy of O2 molecules calculated in a cubic cell,
is the energy of O2 molecules calculated in a cubic cell, 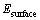 is the energy of pyrite, marcasite, or pyrrhotite slab. According to this definition, a negative value represents an exothermic process. The greater the value, the stronger the adsorption interaction between O2 and sulfide surface.
is the energy of pyrite, marcasite, or pyrrhotite slab. According to this definition, a negative value represents an exothermic process. The greater the value, the stronger the adsorption interaction between O2 and sulfide surface.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Adsorption models of O2 on pyrite, marcasite and pyrrhotite surfaces
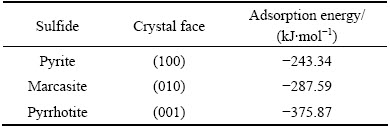
The adsorption of O2 on the pyrite (100), marcasite (010) and pyrrhotite (001) surfaces was investigated on different adsorption sites, including its molecular axis perpendicular or parallel to the surface as well as located in atop, bridge and hollow sites. These adsorption sites were used as initial configurations for calculating the most favourable adsorption geometry, with oxygen pointing either towards or away from the surface. The most stable adsorption configurations of all species through optimization test of various adsorption sites are shown in Fig. 3. The calculated adsorption energies of O2 molecules on pyrite, marcasite and pyrrhotite surfaces are displayed in Table 1. The data reveal that the adsorption energy of O2 on the pyrrhotite surface is the largest, -375.87 kJ/mol, followed by that on the marcasite surface, -287.59 kJ/mol, and pyrite surface, -243.34 kJ/mol (negative sign represents exothermic reaction).
After O2 adsorption, one oxygen atom is bonded to one sulfur atom, the other is bonded to one iron atom on pyrite surface (Fig. 3(a)). One oxygen is bonded to one sulfur atom and one iron atom, the other is bonded to another sulfide atom and another iron atom on marcasite surface (Fig. 3(b)). In the case of pyrrhotite surface, one oxygen is only attached to one sulfur atom, while the other is attached to three iron atoms (Fig. 3(c)). These different configurations lead to different adsorption energies for O2 molecule on pyrite, marcasite and pyrrhotite surfaces.
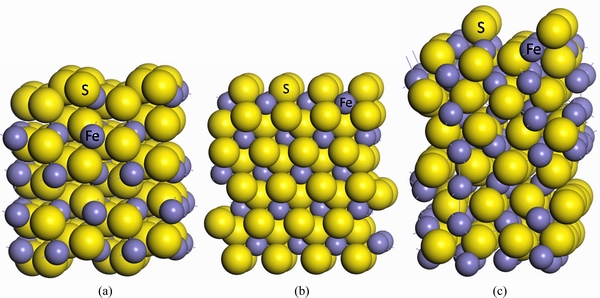
Fig. 2 Surface models of (2×2) pyrite (100) (a), (2×2) marcasite (101) (b) and (1×2) pyrrhotite (001) (c)
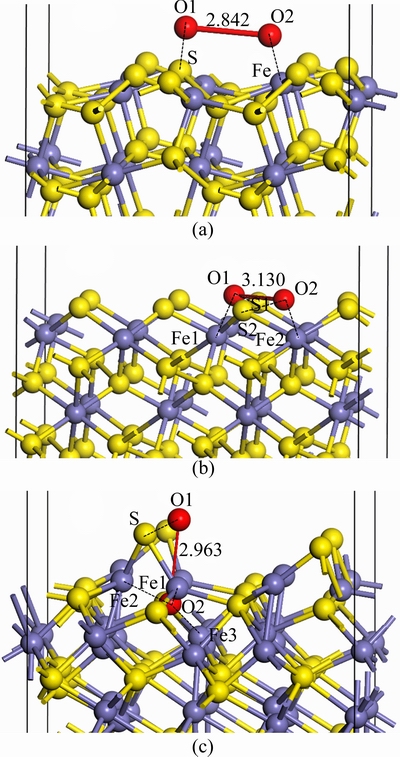
Fig. 3 Optimized configurations of O2 on pyrite (100) (a), marcasite (010) (b) and pyrrhotite (001) (c) surfaces
Table 1 Adsorption energies of O2 molecules on sulfides surfaces (Negative sign represents exothermic reaction)
3.2 Interaction between oxygen and surface atoms of sulfides
The distances between two oxygen atoms after O2 absorbed on pyrite, marcasite and pyrrhotite surfaces are 2.842, 3.130 and 2.963  , respectively, which are marked in Fig. 3. The sulfur and iron atoms of pyrite, marcasite and pyrrhotite surfaces are very active. There is significant reconstruction for the O atom of O2 molecules and the surface atoms of sulfides upon O2 adsorption. The O—O bond in O2 molecule is broken in order to form the O—S bonds and O—Fe bonds. Figure 4 shows the electron density of oxygen atoms and surface atoms of pyrite, marcasite and pyrrhotite after O2 adsorption, in which the bondings of O atoms and surface atoms of sulfides are reconstructed. It is clear that O2 molecules in three sulfide surfaces are all dissociated. Instead, oxygen atoms are attached to the sulfur and iron atoms of sulfide surfaces. It is found from Fig. 4 that the electron densities in O1—S and O2—Fe regions of pyrite surface are very great (Fig. 4(a)), indicating the strong covalent bonds between O1 and S, and between O2 and Fe. The electron density of O1—S1 region for marcasite surface is greater than that of O2—S2, while the electron density of O1—Fe1 region is smaller than that of O2—Fe2 region (Fig. 4(b)), showing that O1—S1 bond is stronger than O2—S2, while O1—Fe1 bond is weaker than O2—Fe2. On the pyrrhotite surface, the electron density of O1—S is very great, those of O2—Fe1, O2—Fe2 and O2—Fe3 regions are close. However, the electron density of O2—Fe1 is the slightly largest, followed by those of O2—Fe2 and O3—Fe3. In other words, the covalent bond of O2—Fe1 is the strongest, while that of O3—Fe3 is the weakest. These results suggest that O2 molecules interact strongly with pyrite, marcasite and pyrrhotite surfaces.
, respectively, which are marked in Fig. 3. The sulfur and iron atoms of pyrite, marcasite and pyrrhotite surfaces are very active. There is significant reconstruction for the O atom of O2 molecules and the surface atoms of sulfides upon O2 adsorption. The O—O bond in O2 molecule is broken in order to form the O—S bonds and O—Fe bonds. Figure 4 shows the electron density of oxygen atoms and surface atoms of pyrite, marcasite and pyrrhotite after O2 adsorption, in which the bondings of O atoms and surface atoms of sulfides are reconstructed. It is clear that O2 molecules in three sulfide surfaces are all dissociated. Instead, oxygen atoms are attached to the sulfur and iron atoms of sulfide surfaces. It is found from Fig. 4 that the electron densities in O1—S and O2—Fe regions of pyrite surface are very great (Fig. 4(a)), indicating the strong covalent bonds between O1 and S, and between O2 and Fe. The electron density of O1—S1 region for marcasite surface is greater than that of O2—S2, while the electron density of O1—Fe1 region is smaller than that of O2—Fe2 region (Fig. 4(b)), showing that O1—S1 bond is stronger than O2—S2, while O1—Fe1 bond is weaker than O2—Fe2. On the pyrrhotite surface, the electron density of O1—S is very great, those of O2—Fe1, O2—Fe2 and O2—Fe3 regions are close. However, the electron density of O2—Fe1 is the slightly largest, followed by those of O2—Fe2 and O3—Fe3. In other words, the covalent bond of O2—Fe1 is the strongest, while that of O3—Fe3 is the weakest. These results suggest that O2 molecules interact strongly with pyrite, marcasite and pyrrhotite surfaces.
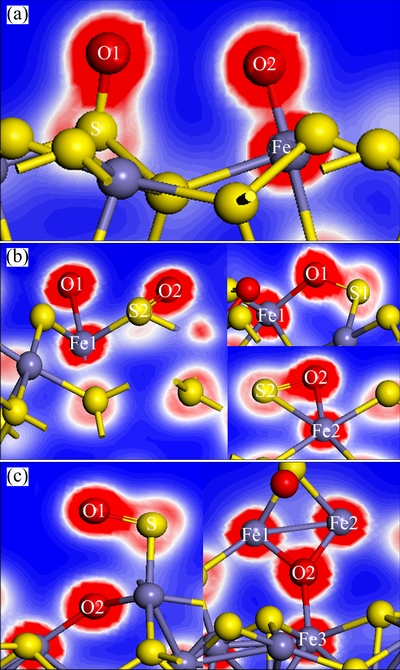
Fig. 4 Electron density of O2 adsorption on pyrite (a), marcasite (b) and pyrrhotite (c) surfaces
Table 2 Mulliken bond populations of oxygen atoms and surfaces atoms of sulfides after O2 adsorption
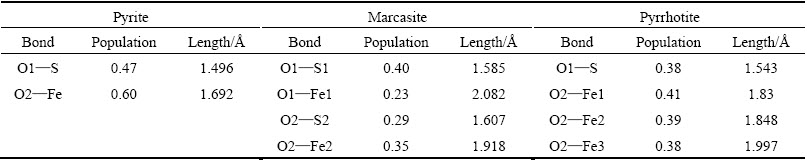
Table 2 shows the Mulliken bond populations of O atoms of O2 molecules and surface atoms of pyrite, marcasite and pyrrhotite surfaces after O2 adsorption. The greater the value, the stronger the adsorption interaction between O2 and sulfide surface. The greater the value of the bond population, the stronger the covalent interaction. It is clearly shown that the populations of O1—S and O2—Fe for pyrite surface are larger than those of O—S and O—Fe for marcasite and pyrrhotite surfaces. However, the adsorption energy of O2 on pyrite surface is the smallest. That may be because relatively few atoms of pyrite surface interact with O2 molecule compared with those of marcasite and pyrrhotite. Only two atoms (one sulfur atom and one iron atom) on pyrite surface interact with oxygen molecule, while four atoms (two sulfur atoms and two iron atoms for marcasite, one sulfur atom and three iron atoms for pyrrhotite) interact with oxygen on marcasite and pyrrhotite surfaces. Overall, the bond populations of O—S (O1—S) and O—Fe (O2—Fe1, O2—Fe2, O2—Fe3) for pyrrhotite surface are larger than those of marcasite surface (O1—S1, O1—Fe1, O2—S2, O2—Fe2), which could result in larger adsorption energy of oxygen molecule on pyrrhotite surface compared with those on marcasite surface. In addition, the population values of O1—S bond and O2—Fe bond are large for pyrite surface. The population of O1—S1 bond is larger than that of O2—S2 bond for marcasite surface, while the population of O1—Fe1 bond is smaller than that of O2—Fe2 bond. As for pyrrhotite surface, the population of O1—S bond is large. Among O2—Fe1, O2—Fe2 and O2—Fe3, the population of O2—Fe1 bond is the slightly largest, followed by those of O2—Fe2 and O2—Fe3. These results are in good agreement with the electron density of O2 adsorption on sulfide surfaces (Fig. 4).
3.3 Electronic shift between O atoms of O2 molecules and surface atoms of sulfides
Tables 3-5 show the Mulliken charge populations of O atoms and pyrite, marcasite and pyrrhotite surfaces atoms before and after O2 adsorption, respectively. It is found that oxygen is electron acceptor, while iron and sulfur atoms of pyrite, marcasite and pyrrhotite surfaces are electron donors when oxygen molecules are adsorbed on the sulfide surfaces. The total charge of oxygen atoms (O1 and O2) on pyrite surface is the smallest, -1.20 e. The charges of oxygen atoms on marcasite and pyrrhotite surfaces are very close (-1.38 e on marcasite surface; -1.32 e on pyrrhotite surface). This means that it is not easy to lose electrons for pyrite surface atoms compared with marcasite and pyrrhotite surface atoms, while the donor power for marcasite and pyrrhotie surface is nearly identical.
Table 3 Mulliken charge populations of O atoms and pyrite surface atoms
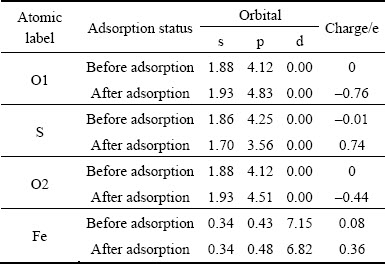
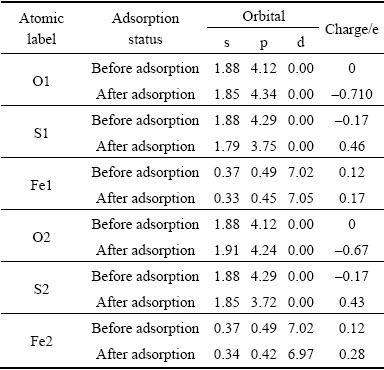
Table 4 Mulliken charge populations of O atoms and marcasite surface atoms
It is known from Table 3 that the charges mainly transfer from S 3p orbital and S 3s orbital of pyrite surface to O1 2p orbital for O1—S, while O 2s orbital gains a small number of electrons. In Mulliken charge population of Fe atom, there exists the p orbital of Fe, which is due to the hybridization of Fe atom. The charges mainly transfer from d-p hybridization orbitals of Fe to 3s and 3p orbitals of O2 for O2—Fe.
Table 5 Mulliken charge populations of O atoms and pyrrhotite surface atoms
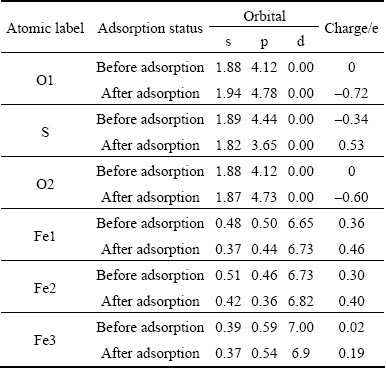
After O2 adsorption on marcasite surface, O1 atom gains electrons (charges from 0 to -0.71 e), S1 and Fe1 atoms coordinated with O1 lose electrons (S1: charges from -0.17 e to 0.46 e; Fe1: charges from 0.12 to 0.28 e), as shown in Table 4. So O1—S1 bond and O1—Fe1 bond form. The p orbitals of Fe atoms occur here in the Mulliken charge populations, it can be speculated that there exists the hybridization of s-p-d orbitals. The charges mainly transfer from O1 2p orbital to the p orbital of S1 and s-p-d hybrid orbitals of Fe1, while O1 2s orbital loses a small number of electrons. Similarly, O2 atom gains electrons (charges from 0 to -0.67 e), S2 and Fe2 atoms coordinated with O2 lose electrons (S2: charges from -0.17 e to 0.43 e; Fe2: charges from 0.12 e to 0.28 e), which forms O2—S2 bond and O2—Fe2 bond. The charges mainly transfer from O2 2p orbital to 3p orbital of S2 and s-p-d hybrid orbitals of Fe2. The contributions of O 2s and S 3s orbitals are relatively small. Unlike O1 2s orbital, O2 2s orbital gains a small number of electrons.
Different from pyrite and marcasite, one oxygen atom (O1) is only bonded to one sulfur atom (S), while the other oxygen atom (O2) is attached to three iron atoms (Fe1, Fe2 and Fe3) when O2 is adsorbed on pyrrhotite surface. According to Table 5, it is mainly 2p orbital of O1 atom gains electrons from 3p orbital of S atom, and forms O1—S bond (O1: charges from 0 to -0.72 e; S: charges from -0.34 e to 0.53 e), the contributions of O 2s and S 3s orbitals are relatively small. The 2p orbital of O2 atom gains electrons from s-p-d hybrid orbitals of Fe1, Fe2 and Fe3 atoms, which form O2—Fe1, O2—Fe2 and O2—Fe3 bonds.
According to the analyses above, the charges all transfer from surface atoms (S and Fe) of pyrite, marcasite and pyrrhotite to O atoms of O2 molecules. As a result, there are rich electrons in the vicinity of O atoms of O2 molecules, while lack of electrons around S atoms and Fe atoms coordinated with oxygen on pyrite, marcasite and pyrrhotite surfaces, as shown in Figs. 5(a)-(c). In Fig. 5, the blue contours correspond to electron density depletion, and the red contours represent increased electron density. Note that the regions near Fe and S atoms of sulfide surfaces are blue, implying a decrease of electron density, while the regions near the O atom are red, indicating an increase of density.
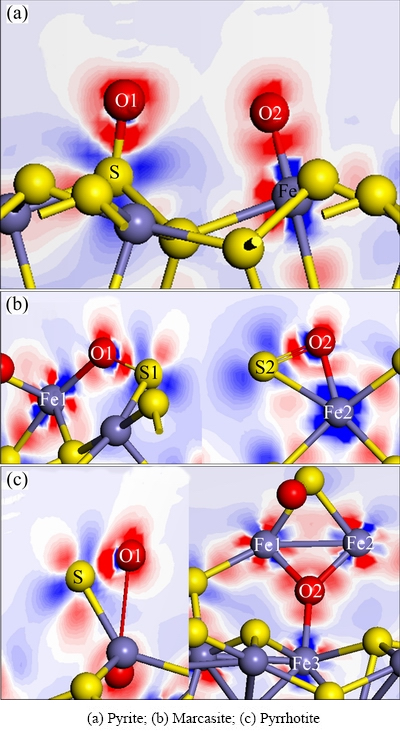
Fig. 5 Electron density difference map of sulfides with O2 adsorption
3.4 Density of state of sulfide surfaces with O2 adsorption
Figure 6 shows the DOS results of interactions between oxygen atoms of O2 molecules and surface atoms of sulfides. The EF value, the position of Fermi level, is 0 eV. Figure 6(a) plots the interactions between O1 and S, and between O2 and Fe in pyrite. The DOS curve of O1 atom interaction with S shifts down to lower energies compared with that of O2 atom interaction with Fe. This can be because of more electrons obtained from sulfur atom for O1 (Table 3), indicating a strong covalent interaction between O1 and S. In the DOS curve of O2—Fe, the s, p and d orbitals of Fe atom are involved in the interaction, the hybridization of d-s-p orbitals leads to stronger interaction between O2 and Fe.
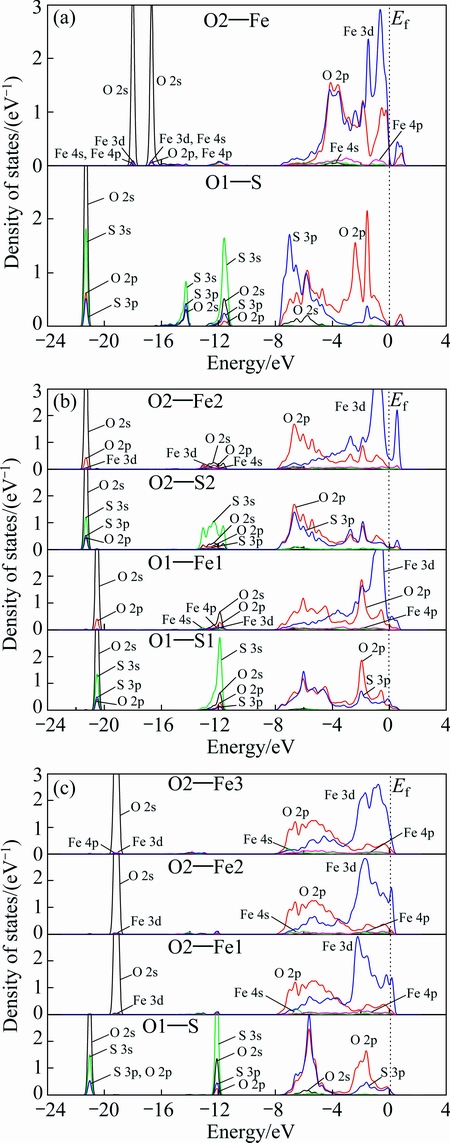
Fig. 6 DOS results of O atoms and surface atoms of pyrite (a), marcasite (b) and pyrrhotite (c) after O2 adsorption
Figure 6(b) shows the interactions between O and S (O1 and S1, O2 and S2), and between O and Fe (O1 and Fe1, O2 and Fe2) on marcasite surface. It is clear that the peaks of DOS curves of O2—S2 and O2—Fe2 located at about -21.5 eV move towards low energy compared with those of O1—S1 and O1—Fe1 (about -20.5 eV). It is related to the gain or loss of electrons for oxygen atom. O1 2s orbital orbital loses the electrons, while O2 2s obtains the electrons (Table 4). Besides the peak mentioned above (bonding), there exist anti- bonding peaks for O1—S1 and O2—S2 at about -12 eV. The anti-bonding peak of O2—S2 is wider than that of O1—S1, and its non-locality is strong, indicating stronger anti-bonding effect for O2—S2. In the range of -8 eV to 1 eV for O1—S1 and O2—S2, there exist some hybridization of O 2p and S 3p orbitals in bonding and anti-bonding. However, the anti-bonding of O2—S2 is far stronger than that of O1—S1. As a result, the interaction between O1 and S1 is stronger than that between O2 and S2. The peak located at about -12 eV for O2—Fe2 has a stronger non-locality compared with that for O1—Fe1, showing the stronger interaction between O2 and Fe2, which is mainly due to that O2 interacts with hybrid s-p-d orbitals of Fe1 and Fe2 (Table 4). In addition, there exist two hybrid peaks in the range of 0 to -4 eV in the DOS curve of O2—Fe2, while there is only one hybrid peak at about -2 eV in the DOS curve of O1—Fe1, which results in stronger interaction between O2 and Fe2. These results are in good agreement with the results of Mulliken charge population (Table 4).
Figure 6(c) plots the interactions between O1 and S, between O2 and Fe (Fe1, Fe2, Fe3) in pyrrhotite. It is clearly shown that the peaks of O1—S located at about -21 eV move towards low energy compared with those of O2—Fe1, O2—Fe2 and O2—Fe3 (about -19 eV). This is because of the gain (O1) or loss (O2) of electrons for O 2s. There are bonding and anti-bonding orbitals for O1—S at -21 eV and -12 eV, respectively. In addition, there exist hybridizations of O 2p and S 3p orbitals at about -5.8 eV, -1.7 eV and -0.2 eV, which leads to strong interaction between O1 and S. The DOS curves of O2—Fe1, O2—Fe2 and O2—Fe3 are similar. It is mainly due to that O2 2p orbital interacts strongly with hybrid s-p-d orbitals of Fe1, Fe2 and Fe3 (Table 5).
4 Conclusions
1) The adsorption energy of O2 on pyrrhotite surface is the largest, -375.87 kJ/mol, followed by that on marcasite surface, -287.59 kJ/mol, and pyrite surface, –243.34 kJ/mol.
2) The oxygen atoms of O2 molecule and surface atoms of pyrite, marcasite and pyrrhotite have different bonding structures. Two oxygen atoms adsorbed on pyrite surface are bonded to one sulfur atom and one iron atom, respectively. One oxygen atom adsorbed on marcasite surface is bonded to one sulfur atom and one iron atom, the other is bonded to another sulfide atom and another iron atom. One oxygen adsorbed on pyrrhotite surface is only bonded to one sulfur atom, while the other is bonded to three iron atoms.
3) Due to more atoms of pyrrhotite and marcasite interaction with oxygen atom, the adsorption energies of O2 on pyrrhotite and marcasite surfaces are larger than that of O2 on marcasite surface.
4) The bond populations of O—S and O—Fe for pyrrhotite surface are larger than those for marcasite surface, which results in larger adsorption energy of oxygen molecule on pyrrhotite surface compared with that on marcasite surface.
References
[1] SUN R, CHAN M K Y, CEDER G. First-principles electronic structure and relative stability of pyrite and marcasite: Implications for photovoltaic performance [J]. Physical Review B, 2011, 83(23): 235311.
[2]  M, BUSECK P R. Structural relationship between pyrite and marcasite [J]. American Mineralogist, 1996, 81: 119-125.
M, BUSECK P R. Structural relationship between pyrite and marcasite [J]. American Mineralogist, 1996, 81: 119-125.
[3] BROSTIGEN G, KJEKSHUS A. On the relationships between the structure types pyrite, marcasite, and arsenopyrite [J]. Acta Chemica Scandinavica, 1970, 24: 2983-2992.
[4] WARD J C. The structure and properties of some iron sulphides [J]. Reviews in Pure and Applied Chemistry, 1970, 20: 175-206.
[5] THOMAS J E, SKINNER W M, SMART R St C. A mechanism to explain sudden changes in rates and products for pyrrhotite dissolution in acide solution [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2001, 65(1): 1-12.
[6] JANZEN M P, NICHOLSON R V, SCHARER J M. Pyrrhotite reaction kinetics: Reaction rates for oxidation by oxygen, ferric iron, and for nonoxidative dissolution [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64(9): 1511-1522.
[7] ZHAO C H, WU B Z, CHEN J H, LI Y Q, CHEN Y. Electronic structure and properties of FeS2 with the space groups of Pa3 and P1 [J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2013, 20(7): 671-677.
[8] CHEN J H, ZHONG J L, LI Y Q, CHEN Y, GUO J. Electronicstructuresand floatability of pyrite, marcasite and pyrrhotite [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(7): 1719-1727. (in Chinese)
[9] ZHAO C H, WU B Z, CHEN J H. Electronic structure and flotation behavior of monoclinic and hexagonal pyrrhotite [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2015, 22(2): 466-471.
[10] LI Y Q, CHEN J H, CHEN Y, GUO J. Density functional theory study of influence impurity on electronic properties and reactivity of pyrite [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(8): 1887-1895.
[11] MATTILA S, LEIRO J A, HEINONEN M. XPS study of the oxidized pyrite surface [J]. Surface Science, 2004, 566-568: 1097-1101.
[12] USHER C R, PAUL K W, NARAYANSAMY J, KUBICKI J D, SPARKS D L, SCHOONEN M A A, STRONGIN D R. Mechanistic aspects of pyrite oxidation in an oxidizing gaseous environment: An in situ HATR-IR isotope study [J] Environmental Science and Technology, 2005, 39: 7576-7584.
[13] RICHARDSON P E, O’DELL C S. Semiconducting characteristics of galena electrodes relationship to mineral flotation [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1985, 132: 1350-1356.
[14] ROSSO K M, BECKER U, HOCHELLA M F. The interaction of pyrite {100} surfaces with O2 and H2O: Fundamental oxidation mechanisms [J]. American Mineralogist, 1999, 84: 1549-1561.
[15] WOODS R. Electrochemical potential controlling flotation [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2003, 72: 151-162.
[16] WOODS R. Recent advances in electrochemistry of sulfide mineral flotation [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2000, 10 (S1): s26-s29.
[17] PAYNE M C, TETER M P, ALLAN D C, ARIAS T A, JOANNOPOULOS J D. Iterative minimization techniques for ab initio total energy calculation: Molecular dynamics and conjugate gradients [J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 1992, 64: 1045–1097.
[18] PERDEW J, BURKE K, ERNZERHOF M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple [J]. Physical Review Letters, 1996, 77: 3865-3868.
[19] PERDEW J P, WANG Y. Accurate and simple analytic representation of the electron-gas correlation energy [J]. Physical Review B, 1992, 45: 13244–13249.
[20] VANDERBILT D. Soft self-consistent pseudopotentials in a generalized eigenvalue formalism [J]. Physical Review B, 1990, 41: 7892-7895.
赵翠华1,陈建华2,李玉琼2,陈 晔2,李伟洲1
1. 广西大学 材料科学与工程学院,南宁 530004;
2. 广西大学 广西高校矿物工程重点实验室,南宁 530004
摘 要:为了获得黄铁矿、白铁矿和磁黄铁矿的氧化机制,采用第一性原理方法研究氧分子与这三种矿物表面的作用。计算结果表明:氧分子在磁黄铁矿表面的吸附能最大,在白铁矿表面的吸附能次之,在黄铁矿表面的吸附能最小。氧分子在黄铁矿、白铁矿和磁黄铁矿表面都发生了解离。氧原子与黄铁矿、白铁矿和磁黄铁矿的表面原子具有不同的键合结构。由于白铁矿和磁黄铁矿表面与氧作用的原子数较多,因此,氧分子在白铁矿和磁黄铁矿表面的吸附能比在黄铁矿表面的吸附能大。磁黄铁矿表面相对较大的O—Fe键布局值导致氧分子在磁黄铁矿表面的吸附能比在白铁矿表面的吸附能大。
关键词:硫化矿;氧吸附;表面氧化;第一性原理
(Edited by Mu-lan QIN)
Foundation item: Project supported by the High Level Innovation Team and Outstanding Scholar Program in Guangxi Colleges (the second batch), China; Projects (51304054, 51364002) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project supported by the Open Foundation of Guangxi Colleges and University Key Laboratory of Minerals Engineering in Guangxi University, China
Corresponding author: Jian-hua CHEN; Tel: +86-771-3232200; E-mail: jhchen@gxu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(16)64141-9

