铜离子对镍在玻碳电极上电结晶行为的影响
刘宇,谭澄宇,贾志强,胡炜
(中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,有色金属材料科学与工程教育部重点实验室,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘 要:利用循环伏安法和恒电位阶跃技术,研究浓度为0.01 mol/L 铜离子对镍在玻碳电极上电结晶行为的影响。研究结果表明:在含0.01 mol/L 铜离子的Watts镀液中,电位在-0.3 V左右出现铜的还原反应峰,当电位负移到-0.75 V时,镍开始结晶沉积;与纯Watts镀液(电位约-0.85 V)相比,铜离子的引入促进了镍的电结晶形核和生长,这是因为铜离子的存在降低了镍电结晶形核过电位;在含0.01 mol/L铜离子的Watts镀液中,电结晶过程仍基本遵循Scharifker-Hill模型,铜离子的引入并没有改变镍电结晶行为;高负电位下,金属离子的结晶成核方式遵循瞬时成核机制,低负电位下则趋向遵循连续成核机制。
关键词:电结晶;形核;循环伏安;计时安培
中图分类号:TG174.44 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2010)01-0144-06
Effect of copper ions on behavior of nickel electro-crystallization on glassy carbon electrode
LIU Yu, TAN Cheng-yu, JIA Zhi-qiang, HU Wei
(Key Laboratory for Nonferrous Materials Science and Engineering, Ministry of Education,
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Effect of 0.01 mol/L copper ions on the nickel electro-crystallization behavior on glassy carbon electrode (GCE) was investigated by means of chronoamperometry method in conjunction with the cyclic voltammetry (CV) method. The CV curves show that when 0.01 mol/L copper ions are brought into Watts solution, the peak of copper deoxidizing reaction is at potential -0.3 V (vs. SCE) or so and nickel begins to deposit at -0.75 V. Compared with Watts solution (the potential is about -0.85 V), the entering of copper ions promotes nickel electro-crystallization nucleation/growth because the existence of copper ions debases over-potential of nickel nucleation. Electro- crystallization of Watts solution with 0.01 mol/L copper ions follows Scharifker-Hill model, and the entering of copper ions doesn’t change nickel electro-crystallization behavior. In the case of higher negative potential, the nucleation process of metal ion follows the instantaneous nucleation mechanism. In the case of lower negative potential, it is close to the progressive nucleation mechanism.
Key words: electro-crystallization; nucleation; cyclic voltammetry; chronoamperometry
多层膜是指一种金属或合金沉积在另一种金属或合金上形成的组分或结构呈周期性变化的多层膜材料。由于存在界面电子相互作用,2种不同材料在近原子尺度上的堆垛将导致材料性质发生根本变化,其显著性能可能包括超模量及超导性、磁性、电性、光学和力学性能[1]。在过去20年中,多层膜的研究成为物理学和材料科学领域的热门研究课题。电沉积法制备多层膜由于可以避免制备过程中薄膜层间的热扩散,且设备简单、沉积速度快、生产成本低而受到重视[2-4]。单槽法电沉积可以避免双槽法镀液交叉污染的缺点,同时,通过严格控制电源和溶液传质等参数可以精确控制膜层结构,因此,其应用较广泛[2]。采用电化学方法制备的金属多层膜样品有:Cu-Ni,Ni-Mo,Co-Ni,Ni-Fe,Cu-Zn,Cu-Co,Fe-Cu,Ni-Zn和Co-NiP等。单槽法是将2种或几种活性不同的金属离子以合适的配比加入同一电解液中,控制沉积电位或电流,使其在一定范围内周期性变化,得到成分和结构呈周期变化的金属膜[4-5]。关于单金属沉积电结晶行为如铜或镍在玻碳电极上形核-生长的模式,辜敏等[6-9]对其进行了研究,若采用单槽法制备多层膜,必然需要采用混合溶液进行电镀,但是,目前人们对各类金属离子在混合镀液中的电结晶模式与动力学行为的研究较少。采用电沉积制备Cu-Ni多层膜时,镍和铜的结晶行为直接影响镀层的质量,因此,探索电化学沉积机制非常必要。在此,本文作者采用在Watts镀液中添加少量硫酸铜(浓度为0.01 mol/L)的混合镀液体系,研究0.01 mol/L 铜离子对金属镍离子在玻碳电极上电结晶模式与动力学行为的影响,并与纯Watts镀液中镍电结晶行为进行比较,并就单槽法制备Cu-Ni多层膜结晶过程中,铜离子对镍沉积行为的影响进行分析。
1 实验方法
采用经典的三电极体系,即以直径为3 mm的玻璃碳电极为工作电极,232型饱和甘汞电极为参比电极,辅助电极采用宽度×长度为1 cm×4 cm的光亮铂片。电解液组成为:Watts镀液+0.01 mol/L CuSO4?5H2O,以下简称Ni-Cu镀液。溶液均采用分析纯化学试剂,利用二次蒸馏水配制,pH值为3.8~4.0。
电化学测试在上海辰华仪器公司CHI660C电化学工作站上进行。实验前,电解液通15 min氮气,除氧。将试样放置在电解液中稳定约5 min后再进行测试,实验温度为室温(25±1) ℃。在不同扫描速度下测循环伏安曲线。根据循环伏安曲线,在-0.70~-0.92 V范围内利用电位阶跃技术测定电流-时间(I-t)曲线,并根据测得的I-t曲线绘制无因次曲线(I/Im)2-t/tm(其中,Im为峰值电流,tm为峰值时间),利用Scharifker-Hill模型对实验曲线进行拟合。为了方便讨论,还对Watts镀液进行相应测试,并将试验结果进行对比和分析。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 电结晶理论基础
金属电沉积发生在电极/溶液界面,该过程包括一系列成相现象,其中,结晶直接与成核和晶体的生长相关,并在很大程度上决定了镀层的物理化学性质。因此,需要对金属的电结晶形成机理以及电沉积初期行为即核生成和核生长机理的动力学进行研究[10]。
电结晶过程主要涉及成核和核的生长。成核模型一般有二维圆盘、三维半球模型、三维圆锥形晶核 等[11-12]。其中,已得到普遍认可的是Scharifker等建立的三维半球模型和Bewick等建立的三维圆锥模型[12]。
Scharifker和Hill基于假定(即对于电极上随机分布的半球形晶核在扩散控制下长大,而且每个晶核周围逐渐扩展的扩展区内不能形成新晶核),并考虑扩展区的重叠,推导出恒电位暂态曲线的方程[12]:

式中:I为暂态电流; ;
;
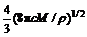 ;F为法拉第常数,C/mol;z为电荷数;M为摩尔质量,g/mol;ρ为密度,g/cm3;c为浓度,mol/cm3;N0为最大晶核数密度或表面活性位点数,cm-2;D为扩散系数,cm/s;t为时间,s;A为成核速率常数,s-1。
;F为法拉第常数,C/mol;z为电荷数;M为摩尔质量,g/mol;ρ为密度,g/cm3;c为浓度,mol/cm3;N0为最大晶核数密度或表面活性位点数,cm-2;D为扩散系数,cm/s;t为时间,s;A为成核速率常数,s-1。
式(1)和(2)分别描述了瞬时成核和连续成核的暂态电流。每一种状态都是电流先达到最大值,然后接近平面电极的极限扩散电流。分别求一阶导数,并令一阶导数为0求极值,可得到电流密度的无因次表达式。因此,在分析电结晶机理时,应将I-tn 曲线与无因次曲线进行综合分析以确定成核模型。
2.2 循环伏安曲线分析
Ni-Cu镀液的循环伏安曲线如图1所示。由图1(a)可以看到:在Ni-Cu镀液中,随着电位向负方向扫描,在-0.35 V附近出现1个小的还原电流峰,从位置以及混合镀液的组成来看,该峰对应着铜的沉积还原反应;当电位继续负移,扫描到-0.75 V左右时,电流开始增大,这实际上对应着镍沉积的起始电位,反映了玻碳电极上镍开始形核、生长的过程。此外,随着电位扫描速度(0.01~0.07 V/s)的增加,镍沉积的起峰电位显著负移。当电位向正方向扫描时存在2个阳极反应氧化峰,估计是金属铜与镍的溶解峰。图1(b)所示为-0.15~-0.60 V电位下的局部放大图,可见:在-0.2 V附近铜开始沉积,且随着扫描速度的增加,峰电流增大;从图1(b)中的局部放大图(扫描速度为0.01 V/s)可以看出:除了在-0.3 V出现铜的还原峰外,在-0.2 V左右,逆向扫描时电流大于阴极方向扫描电流,即在该电位处出现了明显的“感抗性电流环”,这表明镀液中铜的沉积是通过成核/生长机理进行的。
(a) 扫描速度为0.01~0.07 V/s;(b) 局部放大
图1 Ni-Cu镀液的循环伏安曲线
Fig.1 Cyclic voltammetry curves in Ni-Cu solution
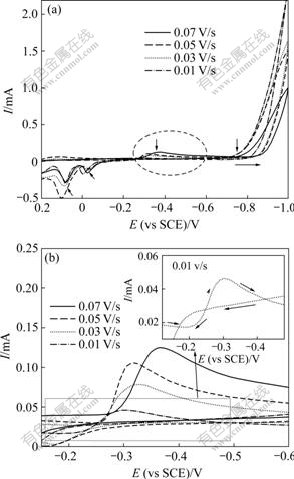
当扫描速度为0.1 V/s时,Watts镀液和Ni-Cu镀液的循环伏安曲线如图2所示。由图2可以看到:2种镀液的循环伏安曲线比较相似;与Watts镀液的镍起峰电位约-0.85 V相比较,Ni-Cu镀液的镍起峰电位(-0.75 V)明显提前。沉积电位正移,即铜离子的存在降低了镍电结晶的过电位,这与陈永言等[13]得到的结果一致。经分析认为,在Watts镀液中,镍是在玻碳基底上直接结晶沉积,由于镍和玻碳电极材料晶格不匹配,沉积所需能量较高,导致镍沉积电位较负。当镀液中含有铜离子时,由于铜的沉积电位较正,铜离子较镍先结晶沉积,随后,镍结晶将在覆盖有铜薄层的玻碳电极上沉积。由于铜和镍都是属于fcc晶体结构,且晶格参数又十分相近,因而,镍离子在铜薄膜上沉积形核所需的能量较低,致使沉积电位明显正移。
1—Ni-Cu镀液;2—Watts镀液
图2 Watts镀液和Ni-Cu镀液的循环伏安曲线
Fig.2 Cyclic voltammetry curves in Watts and Ni-Cu solutions
2.3 计时安培分析
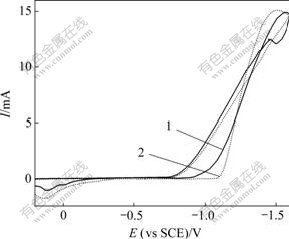
不同阶跃电位下,玻碳电极上Ni-Cu镀液中的恒电位I-t曲线如图3所示。由图3可以看出:当阶跃电位为-0.74 V时,由于电结晶形核/生长所引起的电流明显上升;当阶跃电位为-0.74~-0.92 V时,I-t曲线均呈现随时间电流逐渐上升,达到最大值后出现衰减,并基本趋于稳定,此时,整个电极表面反应表现为扩散控制;随着阶跃电位的负移,即过电位增加,峰电流Im增大,其对应的tm(出现峰电流的时间)呈规律性缩短,说明过电位升高导致成核速率提高,成核诱导时间减小。
(a) -0.7~-0.8 V;(b) -0.84~-0.92 V
图3 Ni-Cu镀液中的恒电位I-t曲线
Fig.3 Potentiostatic I-t curves for electro-crystallization in Ni-Cu solution
图4(a)所示为不同阶跃电位下Watts镀液中电沉积的I-t曲线。可以看出:电位在比-0.82 V更负时才能够观察到镍电沉积引起的电流上升。图4(b)所示为不同阶跃电位下Ni-Cu和Watts镀液电沉积的I-t曲线比较结果,可见:Watts镀液与Ni-Cu镀液电沉积的I-t曲线形式相近,且Ni-Cu镀液的形核弛豫时间tm较短,这说明铜离子的存在会降低形核过电位,促进镍电结晶形核,这与循环伏安曲线所得到的结论相一致。
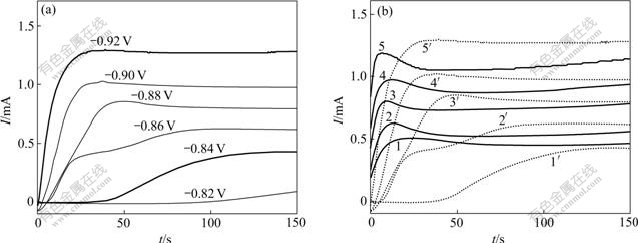
(a) Watts镀液;(b) Ni-Cu镀液和Watts镀液的曲线比较
Ni-Cu镀液:1— -0.84 V;2—-0.86 V;3—-0.88 V;4—-0.90 V;5—-0.92 V
Watts镀液:1′—-0.84 V;2′—-0.86 V;3′—-0.88 V;4′—-0.90 V;5′—-0.92 V
图4 金属离子电结晶的I-t曲线
Fig.4 Potentiostatic I-t curves for the electro-crystallization of metal ions
图5所示为电沉积过程的无因次(I/Im)2-t/tm曲线。由图5(a)可以看出:镍的电结晶过程基本遵循Scharifker- Hill模型,近于三维半球形成核模式;在低过电位下,电结晶初期形核过程接近于连续成核曲线,表明低过电位遵循电化学控制的三维连续成核机制;在高过电位下,镍的电结晶遵循扩散控制的三维瞬时成核机理。这是因为过电位增加,电极表面的活性成核点数目增多,所以,成核较快。赵旭山等[14]在铜电极上得到类似结果。Gomez等[15]采用恒电位阶跃技术及循环伏安法对氯化镍体系中不同阴极沉积电位下镍的电结晶初期行为进行了研究,认为在过电位较低的条件下,镍电结晶按连续成核的三维生长机制进行,在过电位较高时,则按瞬时成核的三维生长方式进行。这与本实验结果相吻合。
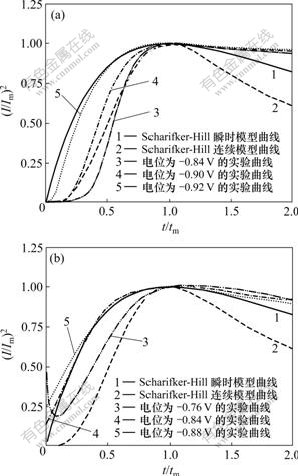
(a) Watts镀液;(b) Ni-Cu镀液
图5 电沉积过程的无因次(I/Im)2-t/tm曲线
Fig.5 Non-dimensional (I/Im)2 vs. t/tm plots for the electro-deposition
图5(b)所示为Ni-Cu镀液在不同阶跃电位下无因次(I/Im)2-t/tm曲线。可见:在低过电位下,电结晶初期形核过程介于Scharifker-Hill模型连续成核和瞬时成核理论曲线之间,并接近连续成核曲线;在高过电位下,电结晶形核则遵循扩散控制的瞬时成核机制。比较图5(a)和图5(b)可以发现:铜离子的引入并不改变镍的电结晶机理。陈永言等[12]的研究也表明,铜的存在加速镍的电结晶过程,但不改变镍电结晶的机理。
事实上,任何理论模型都是对应某种理想状态在多个限制条件下描述发生的过程。对于三维成核过程,瞬时成核和连续成核过程就是2种理想情况,而实际发生的过程往往较复杂,有时候是某种成核占优势,另外一种处于弱势,如图5所示的低电位实验曲线,介于Scharifker-Hill模型连续成核理论曲线和瞬时成核理论曲线之间,充分地证明了这一点。
表1所示为不同阶跃电位下Watts镀液和Ni-Cu镀液在玻碳电极上电结晶的实验结果。可以发现:随着过电位增加,2种镀液电结晶形核的弛豫时间tm均逐渐减少,最大电流Im均呈规律性地逐渐增大。对比2组镀液的tm发现:在相同电位下,Ni-Cu镀液的形核弛豫时间较短,说明铜离子的引入将促进镍离子结晶形核;由表1还可看到,2组Im2tm随过电位的提高而增大,反映了Watts镀液和Ni-Cu镀液中电结晶成核数增多的事实。
表1 Watts镀液和Ni-Cu镀液在玻碳电极上电结晶的实验结果
Table 1 Experimental result for the electro-crystallization in Watts and Ni-Cu solutions on GCE

3 结论
(1) 含0.01 mol/L 铜离子的Ni-Cu镀液中,电位在-0.3 V左右出现铜的还原峰,电位负移到-0.75 V,镍开始沉积。与Watts镀液(电位约-0.85 V)相比,镀液中引入0.01 mol/L 铜离子将促进镍的电结晶形核和生长过程,即铜离子的存在降低了镍电结晶的过电位。
(2) 含0.01 mol/L铜离子的Ni-Cu镀液电结晶过程基本遵循Scharifker-Hill模型,铜离子的引入并没有改变镍的电结晶机理。在低过电位下,电结晶初期形核趋向于Scharifker-Hill模型连续成核,在高过电位下遵循扩散控制的瞬时成核机制。
(3) 随着过电位增加,含0.01 mol/L 铜离子的Ni-Cu镀液的形核弛豫时间tm均逐渐减少,峰电流Im逐渐增大。在相同电位下,Ni-Cu镀液形核弛豫时间比Watts镀液的弛豫时间短,进一步表明铜离子的引入在不同电位下均促进镍离子结晶形核。
参考文献:
[1] 卡恩 R W. 金属与合金工艺[M]. 雷廷权, 译. 北京: 科学出版社, 1999.
Kan R W. Technics of metals and alloy[M]. LEI Ting-quan, trans. Beijing: Science Press, 1999.
[2] 杨会静, 孙立萍, 刘长虹. 纳米多层膜的制备方法及比较[J]. 唐山师范学院学报, 2006, 28(5): 61-63.
YANG Hui-jing, SUN Li-ping, LIU Chang-hong. The preparing process of nano multilayers and some comparsions[J]. Tangshan Teachers College, 2006, 28(5): 61-63.
[3] Gupta D, Nayak A C, Mazhe R J, et al. In-situ atomic force microscopic study of reverse pulse plated Cu/Co-Ni-Cu films[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2004, 39(5): 1615-1620.
[4] 喻敬贤, 陈永言, 黄清安. 纳米金属多层膜的电化学制备与性能研究的现状[J]. 材料保护, 1997, 30(7): 1-4.
YU Jing-xian, CHEN Yong-yan, HUANG Qing-an. Electrochemical preparation and properties measurement of nanolaminar metallic multilayers[J]. Materials Protection, 1997, 30(7): 1-4.
[5] 桂枫, 姚素薇. 电镀纳米金属多层膜研究现状[J]. 电镀与环保, 2000, 20(1): 3-5.
GUI Feng, YAO Su-wei. The status of the study of nano metal multi-layer plating[J]. Electroplating & Pollution Control, 2000, 20(1): 3-5.
[6] 辜敏, 李强, 鲜晓红, 等. PEG-Cl-添加剂存在下的铜电结晶过程研究[J]. 化学学报, 2007, 65(10): 881-886.
GU Min, LI Qiang, XIAN Xiao-hong, et al. Electrocrystallization of copper in the presence of PEG-Cl- additive[J]. Acta Chemica Sinica, 2007, 65(10): 881-886.
[7] Grujicic D, Pesic B. Electrodeposition of copper: the nucleation mechanisms[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2002, 47(18): 2901-2912.
[8] 黄令, 董俊修, 许书楷, 等. 钕离子作用下的镍电沉积初期行为研究[J]. 材料保护, 1999, 32(2): 1-3.
HUANG Ling, DONG Jun-xiu, XU Shu-kai, et al. Effects of Nd3+ on initial stage of nickel electrodeposition[J]. Materials Protection, 1999, 32(2): 1-3.
[9] 胡光辉, 吴辉煌, 杨防祖, 等. 硫脲对镍电沉积的作用[J]. 电化学, 2004, 10(1): 94-97.
HU Guang-hui, WU Hui-huang, YANG Fang-zu, et al. Effect of thiourea on nickel deposition[J]. Electrochemistry, 2004, 10(1): 94-97.
[10] Budevski E, Staikov G, Lorenz W J. Electrocrystallization nucleation and growth phenomena[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2000, 45(12): 2559-2574.
[11] 查全性. 电极过程动力学导论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004: 306-311.
CHA Quan-xing. Introduction to the kinetics of electrode processes[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2004: 306-311.
[12] Scharifker B, Hills G. Theoretical and experimental studies of multiple nucleation[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1983, 28(7): 879-889.
[13] 陈永言, 喻敬贤, 黄清安. 铜离子对镍电沉积行为的影响[C]//郦振声, 高万振. 第二界表面工程国际会议论文集. 武汉: 材料保护, 2000: 137-139.
CHEN Yong-yan, YU Jing-xian, HUANG Qing-an. Effect of Cu2+ on the electrodepositon behavior of nickel[C]//LI Zhen-sheng, GAO Wan-zhen. Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Surface Engineering. Wuhan: Journal of Materials Protection Publishing House, 2000: 137-139.
[14] 赵旭山, 谭澄宇, 陈文敬, 等. Ni-SiC复合镀层电结晶初期动力学分析[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2008, 18(5): 823-828.
ZHAO Xu-shan, TAN Cheng-yu, CHEN Wen-jing, et al. Nucleation kinetics analysis of Ni-SiC composite film during early electrocrystallization processes[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 18(5): 823-828.
[15] Gomez E, Muller C, Proud W G, et al. Electrodeposition of nickel on vitreous carbon: influence of potential on deposit morphology[J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 1999, 22(9): 872-876.
收稿日期:2009-05-12;修回日期:2009-08-10
基金项目:国家民口配套项目(MKPT-98-106)
通信作者:谭澄宇(1963-),男,湖南长沙人,博士,教授,从事金属材料表面研究;电话:0731-88830270;E-mail: tanchengyu@yahoo.com.cn
(编辑 陈灿华)