DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2020-35761
热矫正次数对7N01铝合金应力腐蚀开裂的影响
李 帅1,董红刚2,王星星1,刘中英1,赵俊杰1
(1. 华北水利水电大学 机械学院,郑州 450045;
2. 大连理工大学 材料科学与工程学院,大连 116024)
摘 要:采用慢应变速率拉伸试验(SSRT)和透射电镜(TEM)测试分析方法研究了热矫正次数对7N01-T5铝合金应力腐蚀敏感性的影响。结果表明:随着热矫正次数的增加,7N01-T5铝合金应力腐蚀敏感性增加。原因主要在于晶界析出相的转变以及溶质元素Zn和Mg从基体向晶界的不断扩散。基于非平衡偏聚理论可知,三次热矫正的等效恒温时间小于临界时间tc。因此,随着热矫正次数的增加,晶界处Zn和Mg元素含量逐渐增加,增大了晶界与基体间的腐蚀电位差,使7N01-T5铝合金应力腐蚀敏感性增加。
关键词:慢应变速率拉伸试验;热矫正;应力腐蚀开裂;非平衡偏聚;铝合金
文章编号:1004-0609(2020)-05-1010-09 中图分类号:TG404 文献标志码:A
铝合金具有屈服强度较低和线性热膨胀系数较高的特点,因此容易产生焊接变形。焊接变形的控制是焊接过程中的一大难题。焊接变形不但会影响结构件的装配精度,同时还会导致结构件的力学性能(抗拉强度、疲劳强度和屈服强度等)大幅度降低,进而引发结构件失效或施工期延长等问题,严重影响结构件的安全性,为企业带来巨大的经济损失[1-2]。由于影响焊接变形因素较多,焊接变形又不可避免。因此,焊接后常采用热矫正的方式降低焊接变形。Al-Zn-Mg系合金常用的热矫正温度为350 ℃[3],这一过程会导致Al-Zn-Mg系合金的析出相发生转变,进而影响其力学性能和腐蚀性能。
郭丹[4]采用火焰加热的方式,研究了矫正温度和矫正次数对Al-4.5Zn-1.5Mg(质量分数,%)合金力学性能和腐蚀性能的影响,结果表明热矫正会导致合金耐蚀性能降低。姜澜[5]也使用火焰加热方式对7020铝合金焊接变形进行矫正,结果表明当矫正温度为125 ℃时,焊接接头的力学性能无变化;高于225 ℃后,随着矫正温度升高,接头的抗拉强度逐渐升高。因此,建议7020铝合金矫正温度要低于325 ℃。温度场测试表明,火焰矫正时产生的是瞬时温度场,无法获得稳定温度场,且易受操作因素的影响[6]。AVENT等[7-8]指出,热矫正更像一门艺术,而不是科学研究。可以看出,采用直接火焰加热的方式无法精确分析合金性能变化的原因。为更好地探讨热矫正参变量对7N01铝合金组织和性能的影响,熊志亮[6]借助Gleeble热模拟试验机,研究了热矫正温度对高速列车铝合金接头组织与力学性能的影响;结果表明焊缝区硬度对热矫正温度不敏感,当温度低于300 ℃时,7N01铝合金母材和热影响区硬度下降,而在300~350 ℃内硬度上升。
对于Al-Zn-Mg系合金的腐蚀行为,已有相关腐蚀机理研究报道[9-12],但研究主要集中于Al-Zn-Mg系合金时效工艺规范的优化和合金元素对其组织及性能的影响,属于合金制备范畴。而对于热矫正后Al-Zn-Mg系合金应力腐蚀敏感性的研究相对较少。为此,本文作者以7N01铝合金为实验材料,采用热处理模拟热矫正过程的方式研究热矫正次数对7N01铝合金应力腐蚀敏感性的影响,为深入理解Al-Zn-Mg系合金服役过程中失效行为和失效机制提供理论支撑。
1 实验
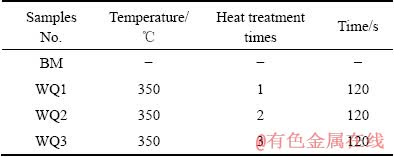
实验材料为7N01-T5铝合金,具体成分如表1所示。实验样品尺寸为5 mm×40 mm×140 mm。7N01铝合金的热矫正温度为350 ℃,加热时间控制在2 min内[3]。采用KSL-1200X型加热炉(合肥科晶材料技术有限公司)和GP20型(日本横河公司)高精度温控仪记录热处理过程中的热循环曲线,如图1所示。为了讨论方便,自定义了试样的编号,如表2所示。
表1 7N01铝合金的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of 7N01 aluminum alloy (mass fraction, %)
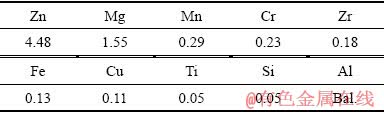
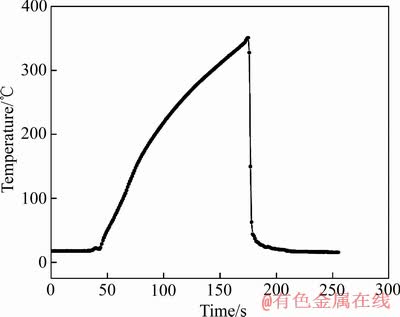
图1 热矫正模拟热循环曲线
Fig. 1 Thermal cycle curve to simulate heat straightening
表2 7N01-T5铝合金热矫正工艺参数
Table 2 Heat straightening parameter of 7N01-T5 alloy samples
慢应变速率拉伸试验(Slow strain rate test, SSRT)参照HB 7235—95标准进行[13]。利用西安力创WDML-5型SSRT试验机进行试验,试样尺寸如图2所示。试验介质分别为空气和3.5% NaCl+10 mL/L H2O2,实验温度为室温。SSRT试样安装完成后,加载一定的载荷以便消除夹具间隙,应变速率为6×10-6 s-1。由标准HB 7235—95可知,利用ISSRT指数比单项力学性能指数能够更好地评价应力腐蚀敏感性[13]。ISSRT指数的计算公式如下:
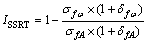 (1)
(1)
式中: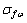 和
和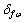 分别为试样在3.5% NaCl+10 mL/L H2O2溶液中的拉伸强度(MPa)和伸长率(%);
分别为试样在3.5% NaCl+10 mL/L H2O2溶液中的拉伸强度(MPa)和伸长率(%);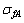 和
和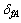 分别为试样在空气中的拉伸强度(MPa)和伸长率(%)。
分别为试样在空气中的拉伸强度(MPa)和伸长率(%)。
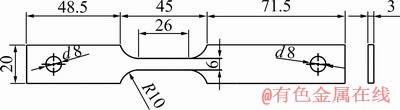
图2 慢应变速率拉伸实验试样尺寸
Fig. 2 Dimensions of slow strain rate test (SSRT) samples (Unit: mm)
透射电镜(TEM)主要用于分析7N01铝合金析出相在晶粒内、晶界附近的分布状况,并借助能谱仪(EDS)对晶界析出相、晶内析出相及无沉淀析出带的化学成分进行分析,探针直径为3 nm左右。TEM样品经机械减薄至30 mm左右后,制备成直径为3 mm的圆盘状样品,经离子减薄后进行观察。在Tecnai G2 20 S-Twin型透射电镜上进行样品观察,加载电压为200 kV。
2 结果与分析
2.1 微观组织
经过不同热矫正次数后,7N01铝合金析出相分布情况如图3所示。从图3(a)~(d)可知,随着热矫正次数的增加,η′相和η相逐渐回溶到基体中,晶界析出相经历回溶再析出的过程。由于析出相回溶,试样会形成过饱和固溶体,并在随后自然时效过程中会有GP区形成,如图3(e)~(f)所示。
对于Al-Zn-Mg系合金,热矫正过程会引起析出相变化,进而影响其性能。7N01-T5铝合金主要析出相为GP区、η′相和η相,其析出温度范围分别为20~120 ℃、120~250 ℃和150~300 ℃[14-16]。经过不同次数的热矫正后,影响7N01-T5铝合金性能的析出相会发生部分回溶,转变过程主要与经受的热循环过程和析出相的初始状态(析出相类型和尺寸)有关。对于试样WQ1、WQ2和WQ3,经受的热循环过程分别是:1) 一次热矫正(包括升温过程和淬火过程)+自然时效;2) 两次热矫正+自然时效;3) 三次热矫正+自然时效。相应的主要析出相分别为η′+GP区、少量η′+GP区、GP区,如图3所示。
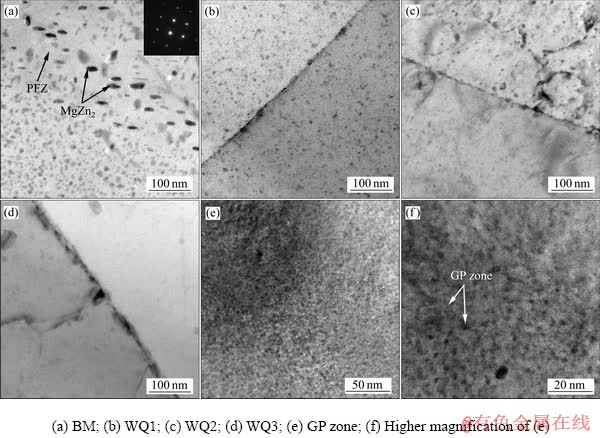
图3 不同热矫正次数下7N01-T5铝合金晶界析出相形貌
Fig. 3 Morphologies of grain boundary precipitations of 7N01-T5 aluminum alloy with different heat straightening numbers
NICOLAS等[14]研究表明,在非等温热处理过程中,析出相溶解临界半径可由式(2)求出:
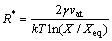 (2)
(2)
式中:γ为界面能;vat为析出相的原子体积;T为热力学温度;X 为溶质分数;Xeq是平衡溶质分数。
当温度恒定时,由于析出相溶解,溶质元素回溶到基体中,导致回溶析出相的临界半径降低。因此,原来不稳定的析出相由于临界半径降低而变得稳定[14]。当溶质元素含量恒定时,析出相回溶临界半径随着温度的升高而增加[14]。然而,由于热矫正过程中,升温速率很快,临界半径往往远远大于析出相的平均半径。因此,随着热矫正次数的增加,η′相的密度不断降低,并在随后的自然时效过程中形成GP区,如图3(e)和(f)所示。
2.2 应力腐蚀敏感性
不同热矫正次数试样的慢应变速率拉伸曲线如图4所示,具体的拉伸数据及应力腐蚀敏感系数ISSRT详见表3。由表3可知,经历不同热矫正次数后,7N01-T5铝合金在空气中的抗拉强度较母材有所增加。随着热矫正次数的增加,7N01-T5铝合金应力腐蚀敏感性逐渐增加,腐蚀敏感性系数ISSRT分别为0.039、0.050和0.074。
依据阳极溶解理论,Al-Zn-Mg系合金应力腐蚀敏感性的变化主要与晶界析出相的微观结构和微电化学性能有关[17-20]。大量研究表明,降低晶界析出相和基体之间的腐蚀电位差以及降低沿晶界的腐蚀扩展速率可以提高Al-Zn-Mg(Cu)系铝合金的抗腐蚀性能。一般来讲,增加晶界析出相中Cu含量或者降低Zn含量的方法能够降低晶界析出相的电化学活性。此外,通过优化工艺参数,调控晶界析出相的分布情况能够降低沿晶腐蚀开裂的速率,例如回归再时效(RRA),高温预析出等热处理工艺。
在本文中,多次热矫正后析出相会发生转变,进而导致7N01-T5铝合金应力腐蚀敏感性发生变化。从慢应变速率拉伸实验结果可知,随着热矫正次数的增加,7N01-T5铝合金的应力腐蚀敏感性增加。对于经受热循环的试样,微观组织的转变主要包括:已有析出相的回溶,溶质元素从基体向晶界处的扩散和自然时效过程中形成GP区。在这些因素的综合作用下,7N01-T5铝合金的应力腐蚀敏感性发生变化。此外,η'相和GP区中x(Zn)/x(Mg)分别为1.2~1.3和1[21-22]。因此,经过热矫正后,基体中Zn含量增加,如表4所示。
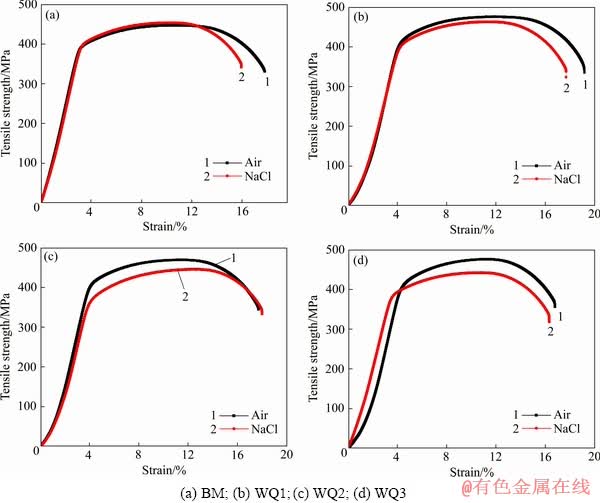
图4 不同热矫正次数下7N01-T5铝合金试样在3.5%+10 mL/L H2O2溶液中的SSRT曲线
Fig. 4 SSRT curves of 7N01-T5 alloy in 3.5%+10 mL/L H2O2 solution with different heat straightening number
表3 不同热矫正次数下7N01-T5铝合金应力腐蚀开裂敏感指数
Table 3 Effect of heat straightening number on stress corrosion cracking of 7N01-T5 aluminum alloy
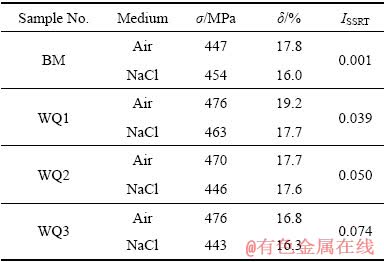
在铝合金腐蚀过程中,晶界往往是阳极,因此优先腐蚀[23]。由于基体析出相的转变,基体的腐蚀电位降低。然而,试样应力腐蚀敏感性随着热矫正次数的增加,逐渐增加。因此,晶界析出相的电化学性能需要重点考虑。在热矫正过程中,试样在120~350 ℃范围内的停驻时间为120 s左右。因此,在此过程中大量溶质元素会从基体向晶界处扩散,使溶质元素在晶界处偏聚。在这些溶质元素中,Zn、Mg和Cu含量的变化会引起晶界处电位的变化,其中Zn含量的增加会导致晶界处电位降低,而Cu元素有相反的作用[17, 24-25]。应该注意到7N01-T5铝合金中Cu元素为微量元素,同时Cu元素在铝合金中的扩散速率比Zn的低,而且只有温度高于150 ℃时,扩散现象才会明显[26]。基于以上原因,可知Cu含量变化很小,如表4所示。因此,Cu含量变化对晶界电位的影响可以忽略不计,电位变化主要受Zn和Mg元素的扩散影响。
表4 不同热矫正次数下试样溶质元素含量的变化
Table 4 Variation of solute elements of samples after different heat treatments
随着热矫正次数的增加,基体中粗大析出相逐渐回溶到基体中,同时Zn和Mg元素在晶界处的偏聚越来越严重,导致晶界处电化学活性增强。在腐蚀过程中,晶界析出相和晶界处的富Zn区最先腐蚀,如图5所示。热矫正过程中析出相演变原理如图6所示。随着热矫正次数的增加,母材中小于临界半径的析出相逐渐回溶到基体中(见图6(a)),Zn和Mg元素逐渐向晶界处偏聚,如图6(b)~(d)所示。晶界处的Zn和Mg元素以两种形式存在,即固溶体和GP区[27]。由于GP区中x(Zn)/x(Mg)约为1[21-22],GP区尺寸较小,GP区的电化学活性同溶质元素中的Zn元素相似[24],晶界处Zn元素的偏聚导致形成连续的腐蚀通道,进而使试样的应力腐蚀敏感性不断增加。基于以上讨论可知,晶界处Zn和Mg元素偏聚造成的不利因素超过了基体析出相回溶导致的有利因素,使晶界和基体间的腐蚀电位差增加,进而导致试样的应力腐蚀敏感性不断增加。SVENNINGSEN等[28]研究了AlMgSi系铝合金腐蚀性能随时效时间的演变规律,也发现晶界处富Cu膜的存在状态对合金的腐蚀性能有很大影响,这与本文中Zn元素在晶界处分布状况的演变相似。
2.3 溶质元素偏聚机理
溶质元素的偏聚可分为平衡偏聚和非平衡偏聚。非平衡偏聚的主要特征是偏聚往往发生于冷却过程中。极速冷却是一个理想状态,因此大多数情况下,冷却过程中都伴随着非平衡偏聚。非平衡偏聚现象是由溶质原子与空位组成复合体进行扩散引起的,而平衡偏聚往往是单一溶质原子向晶界扩散的结果。理论计算和实验都证实复合体的扩散速率比单一溶质原子的扩散速率高2~3个数量级[29]。因此,冷却过程中溶质元素的偏聚以非平衡偏聚为主。
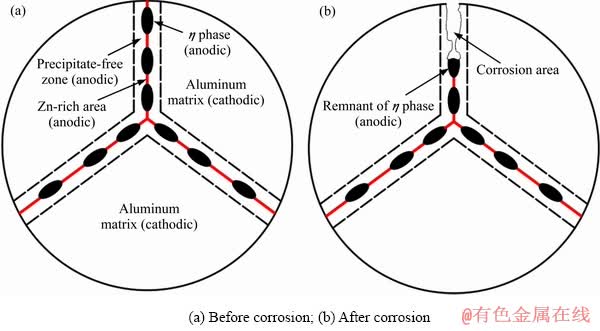
图5 腐蚀机理示意图
Fig. 5 Schematic diagram of corrosion mechanism
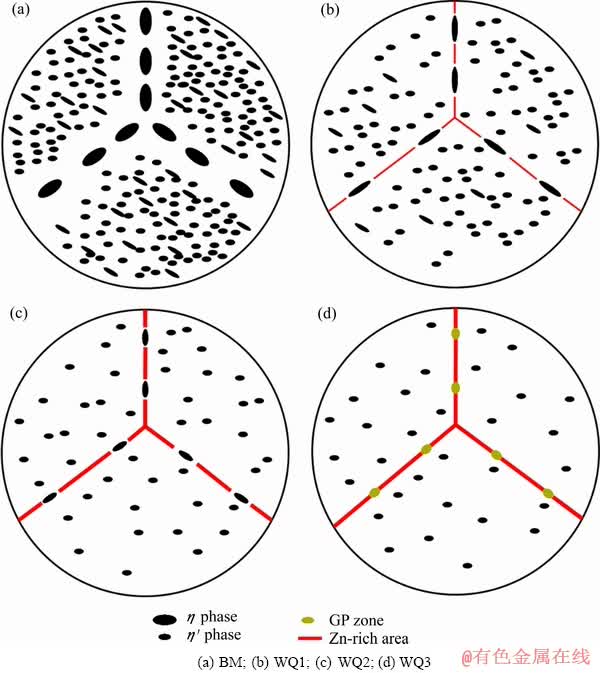
图6 不同热矫正次数下试样析出相演变示意图
Fig. 6 Schematic diagram of precipitation evolution for samples under different heat straightening number
JIANG等[30-31]利用非平衡偏聚理论模型预测了热处理过程对7150铝合金无沉淀析出带宽度、晶界析出相以及晶界析出相间距的影响。多次热矫正过程包含冷却过程,满足形成非平衡偏聚的条件,同时表4所示晶界处Zn和Mg元素含量变化也证实了非平衡偏聚的存在。XU等[29, 32]指出任意连续冷却过程都可用图7所示的曲线来表示,而曲线又可以用图7中虚线所示的阶梯型折线代替。折线的台阶分别由平行于温度坐标和时间坐标的线段组成。那么冷却过程中每个台阶在某一温度T的等效时间可以用式(3)表示:
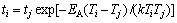 (3)
(3)
式中:EA为扩散激活能;ti是tj在温度Ti的等效时间;k为玻尔兹曼常数。将所有台阶在此温度的等效时间相加得到:
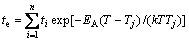 (4)
(4)
式(4)表示按照图7所示的折线冷却,溶质元素扩散的效果等于试样在温度T恒温te时间的扩散效果。若折线充分细小,可以近似代替连续冷却曲线。此时可以根据式(4)获得连续冷却过程在温度T时的等效时间。也就是说,连续冷却时引起的溶质扩散效果等于扩散体系在温度T恒温式(4)中te时间的扩散效果。因此,可以利用上述等效时间方法,计算连续热矫正过程中发生的溶质元素非平衡晶界偏聚量。
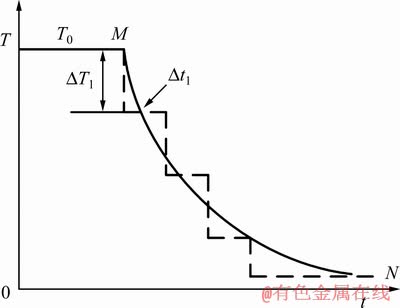
图7 实际冷却曲线及近似阶梯曲线示意图[29, 32]
Fig. 7 Schematic diagram of actual cooling curve and approximate step curve[29, 32]
由表4可知,随着热矫正次数的增加,晶界处Zn和Mg含量不断增加。产生这种现象的原因跟非平衡偏聚另外一个重要的参变量临界时间tc有关:
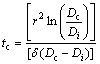 (5)
(5)
式中:r为晶粒尺寸;Di和Dc分别为溶质原子和复合体在基体中的扩散系数;δ为常数。依据式(5)能够获得溶质元素与恒温时间的关系,如图8所示。当非平衡偏聚等效时间t<tc时,随着恒温时效时间的增加,晶界溶质浓度逐渐增加;当等效时间t>tc时,晶界溶质浓度逐渐降低。由表4可见,晶界处Zn和Mg含量随着热矫正次数的增加而增加,表明本文中三次热矫正的等效恒温时间小于临界时间tc。因此,随着热矫正次数的增加,7N01-T5铝合金的应力腐蚀敏感性逐渐增加。
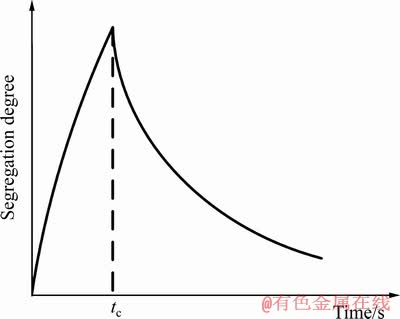
图8 某一温度下溶质元素偏聚量与恒温时间关系示意图[29, 32]
Fig. 8 Schematic diagram of segregation as function of isothermal holding time at a certain temperature[29, 32]
3 结论
1) 随着热矫正次数的增加,7N01-T5铝合金应力腐蚀敏感性增加。应力腐蚀敏感性的变化主要和晶界析出相的转变以及溶质元素Zn和Mg元素从基体向晶界的不断扩散有关。
2) 基于非平衡偏聚理论,定性分析了不同热矫正次数下7N01-T5铝合金应力腐蚀敏感性演变机理。指出三次热矫正的等效恒温时间小于临界时间tc,因此随着热矫正次数的增加。晶界处Zn和Mg含量逐渐增加,增大了晶界及附近区域与基体间的腐蚀电位差,进而使7N01-T5铝合金应力腐蚀敏感性增加。
REFERANCES
[1] LI S, GUO D, DONG H G. Effect of flame rectification on corrosion property of Al-Zn-Mg alloy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2017, 27(2): 250-257.
[2] DENG D. FEM prediction of welding residual stress and distortion in carbon steel considering phase transformation effects[J]. Materials & Design,2009, 30(2): 359-366.
[3] 魏书波. 铝合金车体结构焊接变形的调修方法研究[J]. 装备制造技术, 2012(10): 61-62.
WEI Shu-bo. Research on the adjusting mehtod of weld deformation of aluminum alloy cardody[J]. Equipment Manufacturing Technology, 2012(10): 61-62.
[4] 郭 丹. 火焰调修对Al-Zn-Mg合金微观组织及性能的影响规律[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2015: 16-25.
GUO Dan. Influence of flame correction on microstructure and properties of Al-Zn-Mg alloy[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2015: 16-25.
[5] 姜 澜. 高速列车用铝合金的焊接接头性能与矫形温度研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2003: 20-26.
JIANG Lan. Study on performance and straightening temperature of welded joints of aluminum alloys used for the high-speed trains[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2003: 20-26.
[6] 熊志亮. 热矫形温度对高速列车铝合金接头组织与性能的影响机制[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2014: 66-67.
XIONG Zhi-liang. Effect mechanism of heat-straightening temperature on microstructure and properties of aluminum alloy joint in high-speed trains[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2014: 66-67.
[7] AVENT R R, MUKAI D J, HEYMSFIELD E. Repair of localized damage in steel by heat straightening[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2001, 127(10): 1121-1128.
[8] AVENT R R, MUKAI D J. What you should know about heat straightening repair of damaged steel[J]. Engineering Journal, 2001, 38(1): 27-49.
[9] 彭 景, 陈志国, 任杰克, 马文静. 新型热机械处理对7050铝合金微观组织与性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2018, 28(11): 2182-2190.
PENG Jing, CHEN Zhi-guo, REN Jie-ke, MA Wen-jing. Effect of novel thermo-mechanical treatment on microstructure and properties of 7050 aluminum alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2018, 28(11): 2182-2190.
[10] 万 里, 邓运来, 范世通. 时效处理对7050铝合金厚板材料组织、性能及残余应力的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2018, 28(7): 1277-1283.
WAN Li, DENG Yun-lai, FAN Shi-tong. Effects of aging on microstructures, properties and residual stress of 7050 aluminum alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2018, 28(7): 1277-1283.
[11] LI Hui-zhong, YAO San-cheng, LIANG Xiao-peng, CHEN Yong-hui, LIU Chao, HUANG Lan. Grain boundary pre-precipitation and its contribution to enhancement of corrosion resistance of Al-Zn-Mg alloy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26(10): 2523-2531.
[12] 钱鹏伟, 邓运来, 张 臻, 赵 龙, 唐鸿运, 叶凌英. 自然时效对Al-Zn-Mg合金型材抗应力腐蚀性能的影响[J].中国有色金属学报, 2017, 27(8): 1542-1550.
QIAN Peng-wei, DENG Yun-lai, ZHANG Zhen, ZHAO Long, TANG Hong-yun, YE Ling-ying. Effect of natural aging time on stress corrosion cracking of aluminum alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2017, 27(8): 1542-1550.
[13] HB 7235—1995. 慢应变速率应力腐蚀试验方法[S].
HB 7235—1995. Method for slow strain rate testing[S].
[14] NICOLAS M, DESCHAMPS A. Characterisation and modelling of precipitate evolution in an Al-Zn-Mg alloy during non-isothermal heat treatments[J]. Acta Materialia, 2003, 51(20): 6077-6094.
[15] MAYA JOHNSON S, SANTA J F, MEJIA O L, ARISTIZABAL S, OSPINA S, CORTES P A, GIRALDO J E. Effect of the number of welding repairs with GTAW on the mechanical behavior of AA7020 aluminum alloy welded joints[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2015, 46(5): 2332-2339.
[16] MA T, DEN OUDEN G. Softening behaviour of Al-Zn-Mg alloys due to welding[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1999, 266(1/2): 198-204.
[17] SONG F, ZHANG X, LIU S, TAN Q, LI D. The effect of quench rate and overageing temper on the corrosion behaviour of AA7050[J]. Corrosion Science, 2014, 78: 276-286.
[18] SONG F X, Zhang X M, LIU S D, TAN Q, LI D F. The effect of quench transfer time on microstructure and localized corrosion behavior of 7050-T6 Al alloy[J]. Materials and Corrosion, 2014, 65(10): 1007-1016.
[19] XIAO YP, PAN Q L, LI W B, LIU X Y, HE YB. Influence of retrogression and re-aging treatment on corrosion behaviour of an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy[J]. Materials & Design, 2011, 32(4): 2149-2156.
[20] SUN X Y, ZHANG B, LIN H Q, ZHOU Y, SUN L, Wang J Q, HAN E H, KE W. Correlations between stress corrosion cracking susceptibility and grain boundary microstructures for an Al-Zn-Mg alloy[J]. Corrosion Science, 2013, 77: 103-112.
[21] SHA G, CEREZO A. Early-stage precipitation in Al-Zn-Mg- Cu alloy (7050)[J]. Acta Materialia, 2004, 52(15): 4503-4516.
[22] SHA G, CEREZO A. Kinetic Monte Carlo simulation of clustering in an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy (7050)[J]. Acta Materialia, 2005, 53(4): 907-917.
[23] SONG F X, ZHANG X M, LIU S D, TAN Q, LI D F. Exfoliation corrosion behavior of 7050-T6 aluminum alloy treated with various quench transfer time[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(7): 2258-2265.
[24] MARLAUD T, MALKI B, HENON C, DESCHAMPS A, BAROUX B. Relationship between alloy composition, microstructure and exfoliation corrosion in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys[J]. Corrosion Science, 2011, 53(10): 3139-3149.
[25] LIU S D, CHEN B, LIC B, DAI Y, DENG Y L, ZHANG X M. Mechanism of low exfoliation corrosion resistance due to slow quenching in high strength aluminium alloy[J]. Corrosion Science, 2015, 91: 203-212.
[26] XU D K, BIRBILIS N, ROMETSCH P A. The effect of pre-ageing temperature and retrogression heating rate on the strength and corrosion behaviour of AA7150[J]. Corrosion Science, 2012, 54: 17-25.
[27] SONG R G, TSENG M K, ZHANG B J, LIU J, JIN Z H, SHIN K S. Grain boundary segregation and hydrogen- induced fracture in 7050 aluminium alloy[J]. Acta Materialia, 1996, 44(8): 3241-3248.
[28] SVENNINGSEN G, LARSEN M H, WALMSLEY J C, NORDLIEN J H, NISANCIOGLU K. Effect of artificial aging on intergranular corrosion of extruded AlMgSi alloy with small Cu content[J]. Corrosion Science, 2006, 48(6): 1528-1543.
[29] XU T, ZHENG L, WANG K, MISRA R D K. Unified mechanism of intergranular embrittlement based on non-equilibrium grain boundary segregation[J]. International Materials Reviews, 2013, 58(5): 263-295.
[30] JIANG H, FAULKNER R G. Modelling of grain boundary segregation, precipitation and precipitate-free zones of high strength aluminium alloys-II. Application of the models[J]. Acta Materialia, 1996, 44(5): 1865-1871.
[31] JIANG H, FAULKNER R G. Modelling of grain boundary segregation, precipitation and precipitate-free zones of high strength aluminium alloys-I. The model[J]. Acta Materialia, 1996, 44(5): 1857-1864.
[32] XU T D, CHENG B Y. Kinetics of non-equilibrium grain-boundary segregation[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2004, 49(2): 9-208.
Effect of times in heat straightening on stress corrosion cracking of 7N01 aluminum alloy
LI Shuai1, DONG Hong-gang2, WANG Xing-xing1, LIU Zhong-ying1, ZHAO Jun-jie1
(1. School of Mechanical Engineering, North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power, Zhengzhou 450045, China;
2. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, China)
Abstract: Stress corrosion cracking behavior of 7N01-T5 aluminum alloy was investigated using slow strain rate test (SSRT) and transmission electron microscope (TEM). The results show that the stress corrosion cracking susceptibility increases with increasing the times in heat straightening. The main reason lies in the transformation of intergranular precipitation and the diffusion of solute elements Zn and Mg from matrix to grain boundary. The effective time of non-equilibrium segregation of solute elements Zn and Mg during three times of heat straightening is less than the critical time, tc, according to the theory of non-equilibrium segregation. Consequently, the contents of solute elements Zn and Mg at grain boundaries gradually increase with increasing the times in heat straightening, which leads to an increase in corrosion potential difference between the grain boundary and its surrounding substrate, thus results in the increase of stress corrosion cracking susceptibility of 7N01-T5 aluminum alloy.
Key words: slow strain rate test; heat straightening; stress corrosion cracking; non-equilibrium segregation; aluminum alloy
Foundation item: Project(51705151) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(201811034) supported by the Research Foundation for High-level Talent Scholars in North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power; Projects(2018XB129, 2018XB130) supported by the Program of the University Students Innovation and Pioneering in North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power
Received date: 2019-04-16; Accepted date: 2019-11-25
Corresponding author: LI Shuai; Tel: +86-371-69127295; E-mail: lyctlishuai@163.com
(编辑 何学锋)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51705151);华北水利水电大学高层次人才科研启动项目(201811034);华北水利水电大学创新创业训练计划资助项目(2018XB129,2018XB130)
收稿日期:2019-04-16;修订日期:2019-11-25
通信作者:李 帅,讲师,博士;电话:0371-69127295;E-mail:lyctlishuai@163.com