DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2016.09.019
连续空间中机器人的情绪交互模型
解仑,刘欣,贺苗,王志良
(北京科技大学 计算机与通信工程学院,北京,100083)
摘要:根据交互过程中的场力理论,在有源场情绪状态空间中建立起服务机器人的连续可控的情感调节过程。首先,在费希纳-韦伯定律的基础上,定量分析Gross策略中情绪的自发性认知重评与指导性认知重评过程;其次,根据情感强度第三定律提出一种与情绪效价相关联的情绪强度衰减模型;再次,依据动力心理学理论,建立起基于有源场的情绪能量空间,用于模拟外界刺激情绪与机器人自身情绪的相互作用过程;并建立起基于情绪唤醒度的机器人行为表达抑制模型。在此研究基础上,提出基于HMM的情绪状态刺激转移算法;并将以上模型算法用于13自由度的服务机器人平台中,实现非典型表情交互环境中机器人不确定性情绪过程的动态、可控调节。通过在连续情绪状态空间中的不确定性计算将离散的情绪状态拓展到连续空间中,并产生多种中间状态以及发挥机器人情绪调节的拟人特征。研究结果表明:具有认知能力及情绪控制力的机器人可以在交互过程中使参与者的满意程度得到一定提升。
关键词:机器人;人机交互;认知重评;情绪调节;有源场情绪空间
中图分类号:TP242.6 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2016)09-3050-08
Robot emotional interaction model in continuous space
XIE Lun, LIU Xin, HE Miao, WANG Zhiliang
(School of Computer and Communication Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing,
Beijing 100083, China)
Abstract: A service robot’s continuous and controlled emotional regulation in active field state space was proposed based on field force theory in human-robot interaction. First, on the basis of Fechner-Weber law, emotional spontaneous and guidable cognitive reappraisal in Gross strategies were analyzed quantitatively. Second, emotional attenuation model associated with valence was set up by the emotion intensity third law, and energy space in active field was proposed for simulating the interaction between external stimulus and robot’s emotion. Finally, the stimulating emotional transfer algorithm based on Hidden Markov Model (HMM) was come up with to realize real-time dynamic control on 13 DOF service robot for uncertainty emotional regulation in interaction with atypical facial expressions. The anthropomorphic emotional regulation which operates in a continuous 3D emotional space enables a wide range of intermediary emotional states to be obtained. The results show that the robot with cognition and emotional control ability could serve more participants’ emotional needs in the human-robot interaction (HRI).
Key words: robot; human-robot interaction; cognitive reappraisal; emotional regulation; active field emotional space
由于人类之间的沟通与交流是自然而富有情感的,因此,在人机交互的过程中,人们也很自然地期望计算机具有认知情感能力。如何使计算机能够识别和产生人类的情绪,已经越来越多地受到计算机科学、心理学等学科的关注,逐渐诞生了认知情感计算这一交叉领域[1-2]。认知情感计算(cognitive affective computing)就是要赋予计算机类似于人一样的观察、理解和生成各种情绪状态的能力,最终使计算机像人一样能进行自然、亲切和生动地交互[3-5]。近年来,机器人研究领域涌现出众多有价值的情绪模型。LAZARUS[6]指出认知调节与期望价值理论(动机心理学中最有影响价值的理论之一)在情绪与行为相关社科领域的发展将进一步促进有限情绪状态分类方法的研究。基于面部表情研究,EKMAN[7]提出了6种基本的情绪状态,包括:快乐、恐惧、悲伤、愤怒、惊讶和厌恶,该分类方法得到诸多表情与情绪研究领域学者的认可。AMERO[8]将情绪划分为愤怒、厌倦、恐惧、快乐、有趣和悲伤,并将其应用到社交机器人的情绪建模研究中。GADANHO[9]将4种基本情绪状态(快乐、恐惧、悲伤和愤怒)与特定事件相联系来开展情绪建模研究。VEL SQUEZ[10]提出了一种基于有限情绪状的自主机器人控制方法,此方法将6种基本情绪状态(愤怒、恐惧、懊悔、快乐、厌恶和惊讶)应用于机器人的先天个性形成与后天学习能力培养的研究中。MURPHY等[11]将任务链中获取的4种基本情绪状态(快乐、自信、关心和挫败)应用到多Agent系统建模中。随着认知情感研究的不断深入,越来越多的学者将离散的情绪集扩展到连续的情绪状态空间中。MEHRABIAN等[12]提出了PAD(pleasure-arousal-dominance)三维情感模型,PAD 情绪模型用愉悦度、激活度和优势度这 3个相互独立的维度来描述和测量情绪状态。其中,愉悦度表示个体情绪状态的正负情感特性,也就是情绪的效价;激活度表示个体的神经生理激活水平和心理警觉状态;优势度表示个体对环境和他人的控制状态,即处于优势状态还是处于顺从状态[13-14]。在此基础上,SCHERER等[15-16]改进了PAD三维情绪空间并将其应用于社交机器人的情绪决策系统中。ZECCA等[17]将建立的APC (arousal-pleasant-certain)三维心理向量空间应用于机器学习、动态情绪调节及机器的个性化研究领域。此外,BREAZEAL[18]在对表情机器人Kismet的研究过程中提出了AVS(arousal-valence-stance)情绪空间模型。针对目前人机交互过程中的认知缺失问题,本文作者提出了一种基于Gross认知重评的连续状态情绪调节方法。首先,在情绪的动态调节过程中,建立基于Gross认知策略的指导性及自发性认知重评模型,以完成个性化的认知过程,增强机器人的动态认知性能。其次,在有源场情绪空间中,定义情绪衰减因子,以此描述情绪随时间迁移的变化过程,并空间中的能量分布得到机器人的情绪状态转移概率。最终,结合隐马尔科夫双重随机过程来描述机器人的情绪调节与表达,并以13自由度的机器人实验平台为情绪表达的基础,来实现人与机器人的动态认知情绪互动。
SQUEZ[10]提出了一种基于有限情绪状的自主机器人控制方法,此方法将6种基本情绪状态(愤怒、恐惧、懊悔、快乐、厌恶和惊讶)应用于机器人的先天个性形成与后天学习能力培养的研究中。MURPHY等[11]将任务链中获取的4种基本情绪状态(快乐、自信、关心和挫败)应用到多Agent系统建模中。随着认知情感研究的不断深入,越来越多的学者将离散的情绪集扩展到连续的情绪状态空间中。MEHRABIAN等[12]提出了PAD(pleasure-arousal-dominance)三维情感模型,PAD 情绪模型用愉悦度、激活度和优势度这 3个相互独立的维度来描述和测量情绪状态。其中,愉悦度表示个体情绪状态的正负情感特性,也就是情绪的效价;激活度表示个体的神经生理激活水平和心理警觉状态;优势度表示个体对环境和他人的控制状态,即处于优势状态还是处于顺从状态[13-14]。在此基础上,SCHERER等[15-16]改进了PAD三维情绪空间并将其应用于社交机器人的情绪决策系统中。ZECCA等[17]将建立的APC (arousal-pleasant-certain)三维心理向量空间应用于机器学习、动态情绪调节及机器的个性化研究领域。此外,BREAZEAL[18]在对表情机器人Kismet的研究过程中提出了AVS(arousal-valence-stance)情绪空间模型。针对目前人机交互过程中的认知缺失问题,本文作者提出了一种基于Gross认知重评的连续状态情绪调节方法。首先,在情绪的动态调节过程中,建立基于Gross认知策略的指导性及自发性认知重评模型,以完成个性化的认知过程,增强机器人的动态认知性能。其次,在有源场情绪空间中,定义情绪衰减因子,以此描述情绪随时间迁移的变化过程,并空间中的能量分布得到机器人的情绪状态转移概率。最终,结合隐马尔科夫双重随机过程来描述机器人的情绪调节与表达,并以13自由度的机器人实验平台为情绪表达的基础,来实现人与机器人的动态认知情绪互动。
1 机器人的认知情绪处理
1.1 认知重评策略
GROSS[19-20]认为情绪调节(emotion regulation)是个体对产生何种情绪、情绪何时发生、如何进行情绪体验与表达抑制影响的过程。简单地说,情绪调节是指个体对情绪发生、体验与表达施加影响的过程[16]。情绪调节涉及对情绪的潜伏期、发生时间、持续时间、行为表达、心理体验、生理反应等的改变,是一个动态过程。Gross提出了5种情绪调节策略[21]:情境选择、情境修正、注意分配、认知重评与表达抑制。认知重评是发生在情绪调节过程早期的先行聚焦策略,认知重评策略包括自发性认知重评和指导性认知重评2部分。自发性认知重评主要依赖于情绪体验中内部意志和个性因素的影响,自导性认知重评则与指导情绪的强度和当前情绪状态的开放程度。当个体处于困境或心理期待与现实存在差距时,将会催生诸如悲伤、焦虑、愤怒、痛苦等负向情绪。一般而言,认知重评过程可以有效降低负向情绪强度,改善个体的情绪体验。此外,在情绪调节的过程中,表达抑制策略也可以促进负向情绪体验程度的降低。然而,心理学家研究证明,相比于其他4种情绪调节策略,认知重评策略对于抑制负向情绪的体验最为有效。
人的心理由内在需求与外在环境的相互作用决定,当人的需求未得到满足时,会产生内部张力,而环境(可具体到目标或对象)起着诱导作用。因此,人的行为B是个体P与环境E的函数:
 (1)
(1)
可以将情绪空间想象为一个整体,该整体被划分为多个不同的区域。其中,每一区域代表着一类情绪状态,或至少一种行为的可能。通过行为的交互,目标的情绪对主体自身情绪发出吸引或排斥的作用力,即场力理论。
由此可见,人的心理行为由内在行为与外在环境共同决定。在本文涉及的人与机器人的交互过程中,环境因素重点考虑到交互者的情绪状态的类型以及外在指导性情绪的强度;个性因素主要通过机器人模拟人类的自发性认知重评来实现。
1.2 指导性认知重评建模
在人机交互的过程中,参与者可以通过语言、行为或面部表情的表达方式给予机器人鼓励和安慰,以此达到指导性认知重评的目的,本文将以参与者的表情作为指导性认知重评的依据。在有源场状态空间中,指导性认知重评的发生将会改变外界刺激情绪的位置,经调查问卷的统计分析可知经重评后的认知情绪状态出现在外界刺激情绪状态与指导情绪状态间的概率分布服从高斯分布,如图1所示。
在认知的过程中,指导情绪的强度 对状态分布的分散性产生影响,机器人当前情绪状态的开放度s对分布的中心位置起到决定性作用,因此,得到此高斯分布的数学期望
对状态分布的分散性产生影响,机器人当前情绪状态的开放度s对分布的中心位置起到决定性作用,因此,得到此高斯分布的数学期望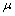 和方差
和方差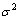 分别为:
分别为:
 (2)
(2)
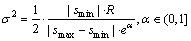 (3)
(3)
其中:R为外界刺激情绪状态与指导情绪的距离;e为欧拉数。
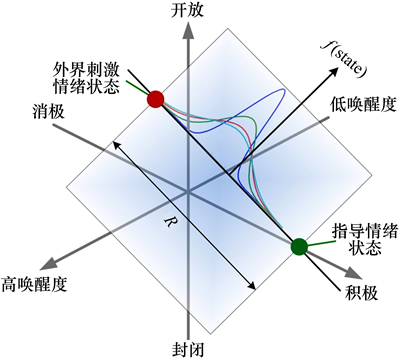
图1 指导性认知重评策略
Fig. 1 Instructive cognition and reappraisal
1.3 自发性认知重评建模
费希纳-韦伯定律指出内在感受强度与外界刺激强度的对数成正比,即
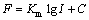 (4)
(4)
其中:F为感受强度;I为刺激强度;Km和C为常数。显然,这是一个普适的规律,但由于心理耐受力等个性因素的影响,经自发性认知重评后的感受强度规律并不如此统一。因此,本文引入个性重评因子 ,从而式(4)可表示为
,从而式(4)可表示为
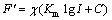 (5)
(5)
根据AVS三维情感模型,可以设计出简化版的情感量表,每个维度(A,V,S)分别用4个项目进行测量,唤醒度通过平静-兴奋、支配-顺从、痛苦-高兴、感兴趣-放松4项进行测量;效价通过愤怒-困倦、受控-主控、友好-轻蔑、平静-兴奋4项进行测量;开放度通过谦卑-高傲、兴奋-激怒、拘谨-惊讶、有影响力-被影响4项进行测量。根据九点语义差异量表的设计方法,每个项目可由1对在其他2个维度上基本无差异,在其所属维度上对立的情绪状态形容词组成,并将词间的间隔分为9段。针对简化版的情感量表,设计了对应7种典型外界刺激情绪状态的7个实验场景,并随机选择500名不同年龄段的志愿者(11~20岁,21~30岁,31~40岁,41~50岁,51~60岁各100人),通过实验获得各种外界刺激状态下的AVS数据。经自发性认知后的情绪状态分布如图2所示。经统计发现:认知后正向情景对应的500个AVS数据无明显的变化,负向情景对应的500个AVS数据近似服从高斯分布。从而,可以用一组满足高斯分布的随机数据模拟自发性认知的参数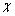 ,使机器人具有不确定性的、多元化的自发认知方式。
,使机器人具有不确定性的、多元化的自发认知方式。
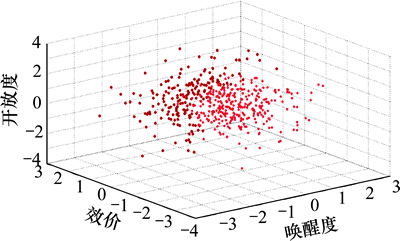
图2 经自发性认知后的情绪状态分布
Fig. 2 Emotional state distribution after spontaneous cognition
2 机器人的动态情绪调节过程
2.1 情绪状态的空间描述
与传统有限情绪状态不同的是,本文将情绪调节过程定义在连续时间连续状态空间中,以使机器人的情绪过程更加细腻、拟人。机器人的自身情绪状态空间S涵盖了其内心所有情绪体验,在外界刺激作用下,机器人的情绪状态可以在该空间中自由的转换。情绪状态St可以看作t时刻在有源场状态空间中的位置。在有源场状态空间中,每个情绪状态的强度都可以通过其情绪势能来量度。在Ekman 6种基本情绪理论的基础上,将平静引入到外界刺激情绪集中,以此构成具有7种基本情绪状态的外界刺激基本空间:
W={愤怒,厌恶,恐惧,高兴,悲伤,惊讶,平静}
2.2 连续空间中的情绪建模
动力心理学表明,人类的情绪调节过程与其他物理系统一样,需要能量的驱动,在心理学中称之为心理能量。因此,本文将场的概念引入到Kismet机器人的唤醒度-效价-开放度(AVS)三维情绪状态间中,用于描述情绪的时空特性,并可以定量地衡量情绪调节过程中能量的动态转移过程。在此有源场状态空间中,机器人感受到的外界刺激情绪与其当前自身情绪状态的相互作用如图3所示,其中,场的强度与分布由情绪状态的激活类型与强度决定。
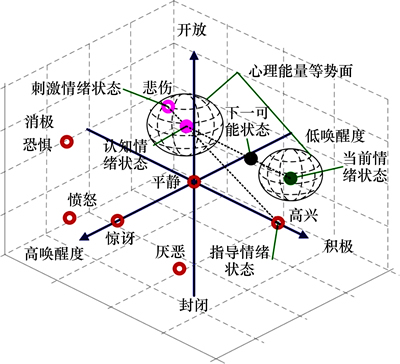
图3 有源场情绪空间模型
Fig. 3 Emotion space model in active field
在此情绪状态空间中,情绪势能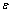 将心理学物理学相结合描述出情绪空间内的各情绪状态的激活情况。在机器人当前情绪状态
将心理学物理学相结合描述出情绪空间内的各情绪状态的激活情况。在机器人当前情绪状态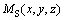 与经认知分析后的外界刺激状态
与经认知分析后的外界刺激状态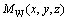 的共同作用下,机器人产生下一种情绪状态
的共同作用下,机器人产生下一种情绪状态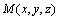 ,其位置介于当前状态与刺激状态之间,情绪势能为
,其位置介于当前状态与刺激状态之间,情绪势能为
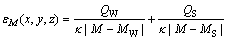 (6)
(6)
其中:QW为经认知分析后外界刺激情绪状态的强度;QS为当前情绪状态的强度;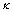 为常量。
为常量。
2.3 情绪强度的衰减
在AVS三维情绪状态空间中,坐标轴效价(valence)用于表达情绪的特性,与情绪强度的衰减尺度紧密相关。换而言之,情绪强度的衰减受到效价轴坐标v的影响。从而得到情绪的衰减系数 为
为
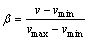 (7)
(7)
情绪强度除了受到情绪自身特性的影响外,还会随着时间的迁移逐渐衰减。根据情感强度第三定律(情感强度时间衰减定律)可知:情绪强度与持续时间T成负指数关系。从而可以得到情绪强度的衰减规律(如图4所示)。
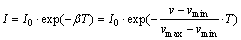 (8)
(8)
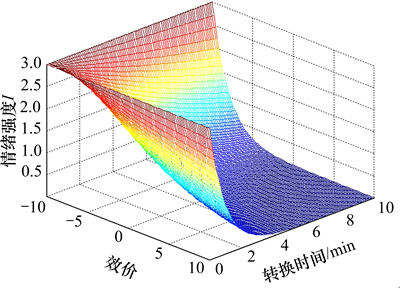
图4 情绪强度的衰减
Fig. 4 Attenuation of emotional intensity
当然,从绝对意义上来说,任何情感的强度都不会无限接近于0,因为,任何情感的强度一方面在“情感强度第三定律”的作用下不断趋于0,另一方面又在众多随机变量的扰动下不断偏离0,从而形成情绪不断调节的波动过程。
2.4 基于HMM的动态情绪调节
人与机器人的情绪交互可以划分为2部分:基于认知的个性化情绪调节和机器人的情绪行为表达。此交互过程可以看作一个双重随机过程,因此,本文采用隐马尔可夫模型对其进行模拟如图5所示。理论上,机器人的情绪状态由心理能量的驱使产生,具有情绪状态的能量越大,其被激活的可能性也随之上升。但在实际心理过程中,情绪状态的能量并不能趋近于无穷大(过激)或无穷小(过敏),而是在一定阈值内被激活与感知,因此,需要定义情绪的可感知阈值[L, H]。当情绪状态的能量在L与H之间时,此情绪状态存在被激活的可能性。从而得到在有源场状态空间中,机器人的下一情绪状态概率为
 (9)
(9)
式中: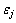 为情绪状态j的情绪势能。
为情绪状态j的情绪势能。
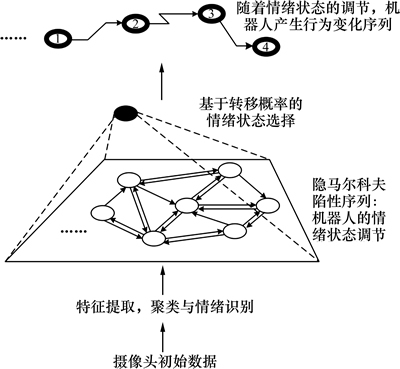
图5 基于HMM的动态情绪调节过程
Fig. 5 Regulation process of dynamic emotion based on HMM
3 机器人的行为交互及实现
3.1 机器人的机械结构
机器人的机械结构依据成人身体及四肢比例设计,如图6所示,机器人共有13个自由度(如表1所示),可以实现百余种表情交互。手臂及颈部采用多关节联合驱动方式,提高了机器人对各运动关节的协同驱动能力并解决了延时影响交互效果的问题,通过PWM双向控制技术,实现机器人任意方向精度的姿态控制。此外,机器人采用三轮式全向移动底盘设计,如图7所示,双前轮驱动方式有效提高了机器人的驱动能力和负载能力,通过增量式PID控制整个调节的过程,实现机器人任意方向精确的直线及弧线运动实现自动避让障碍和路径规划。
3.2 机器人的情绪表达模型
在人机交互过程中,机器人不断唤起与体验自身情绪,并通过面部表情这一情绪反应核心部分表现出其当前情绪状态。在Gross认知情绪理论中,表达抑制作为反应关注情绪调节在情绪反应趋势之后进行,可以通过自我控制的方式降低主观的过激情绪行为,也就是说,表达抑制与情绪的可控性密切相关。在心理学研究中,情绪的激活程度与可控性相互对立,当具备较高激活程度的情绪时,其表达抑制的影响会相对减弱。在AVS情绪状态空间中,情绪状态在唤醒度坐标的位置可以表现出该情绪所具备的激活程度,因此,唤醒度的坐标a影响着机器人的表达抑制能力。通过预处理,可得到表情机器人的情绪抑制因子:
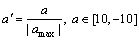 (10)
(10)

图6 机器人的机械结构设计
Fig. 6 Mechanical structure design of robot
表1 机器人的自由度分配
Table 1 Freedom degree distribution of robot
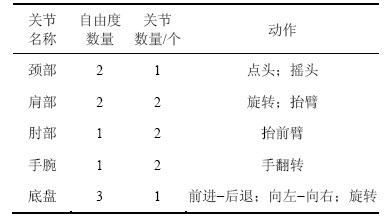
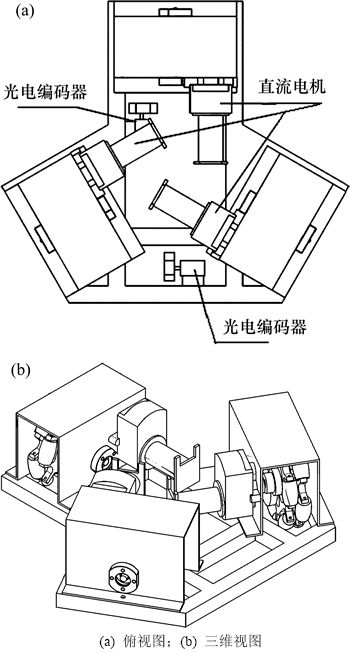
图7 三轮式全向移动底盘设计
Fig. 7 Three-wheeled omnidirectional mobile chassis design
假设机器人的标准动作幅度为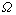 ,则在表达抑制作用后实际动作幅度(如图8所示)为
,则在表达抑制作用后实际动作幅度(如图8所示)为
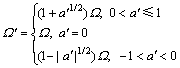 (11)
(11)
3.3 行为交互的实现
本文所提出的情绪交互模型被应用于实时交互的情景中进行有效性验证,机器人采用基于Gabor小波的表情识别方法捕捉参与者的情绪状态,捕捉结果如图9所示。
在有源场情绪空间中,可以通过机器人的认知情绪状态与当前情绪状态得到其在空间中的情绪状态转移概率分布。在某时刻,指导情绪状态坐标为(0, 5, 0),由表情分析得到的外界刺激状态为悲伤,其坐标位于(-6, -4, 0)。从而得到其认知情绪状态遵循数学期望为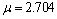 ,标准差为
,标准差为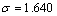 的高斯分布,如图10所示。从图10可以得到点(-4.5, -1.75, 0)处的概率为函数的最大值。在处于相同认知情绪状态,而机器人的当前情绪状态不同时,其下一情绪状态的转移概率不同。图11所示为认知情绪状态位于(-4.5, -1.75, 0)时,不同情绪状态周围的心理势能分布。
的高斯分布,如图10所示。从图10可以得到点(-4.5, -1.75, 0)处的概率为函数的最大值。在处于相同认知情绪状态,而机器人的当前情绪状态不同时,其下一情绪状态的转移概率不同。图11所示为认知情绪状态位于(-4.5, -1.75, 0)时,不同情绪状态周围的心理势能分布。
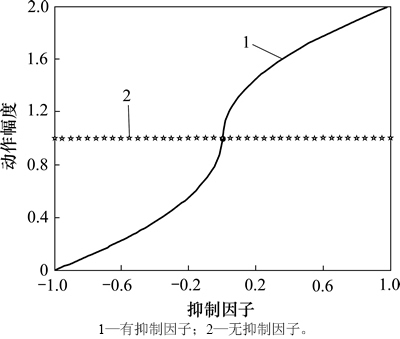
图8 情绪抑制因子对行为动作幅度的影响
Fig. 8 Effect of emotional inhibition factor on action range
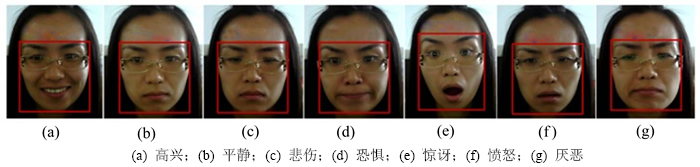
图9 实时的情绪捕捉结果
Fig. 9 Results of real-time emotion
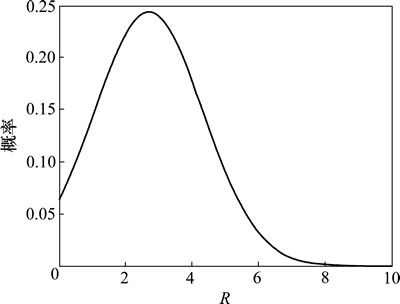
图10 认知情绪状态的概率分布
Fig. 10 Probability distribution of cognitive emotional state
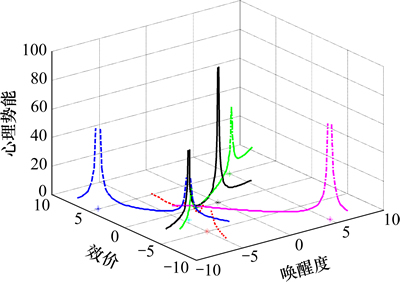
图11 相同认知情绪下机器人的心理能量分布
Fig. 11 Mental energy distribution of robot with same cognitive emotion
4 实验及结果分析
表2所示为以悲伤为外界刺激,高兴为指导认知情绪时,机器人的情绪调节过程。在外界刺激发生前,机器人处于平静状态。当悲伤的外界刺激发生时,若无认知重评与表达抑制模型,机器人的情绪表现为极度悲伤并大哭。然而,在积极的情绪指导与表达抑制的共同作用下,机器人的实际反应并不激烈,只是变现出淡淡的悲伤,这将在交互过程中起到适当的互动与情绪指引作用,并不会使交互陷入以参与者为主导的偏激循环中。随着时间的迁移,机器人的情绪状态将在强度衰减作用下慢慢恢复平静。
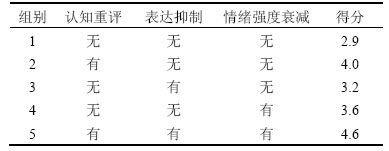
在交互过程中,设置5组交互模式对比实验,如表3所示,以分别评估认知重评、表达抑制以及情绪衰减强度对交互效果的影响。在10 min情绪交互实验后,30名参与者分别对每种交互模式进行打分(满分为5分),最终取30名参与者的平均分作为最终得分。从评估结果可知,无任何情绪模型的组1得分最低,而综合融入认知重评、表达抑制、情绪强度衰减的组5最贴近用户的需求。此外,从分数差可以看出:认知重评对改善参与者的体验最为有效,表达抑制次之,情绪强度衰减贡献最小。
表2 机器人的情绪调节过程
Table 2 Emotion regulation process of robot
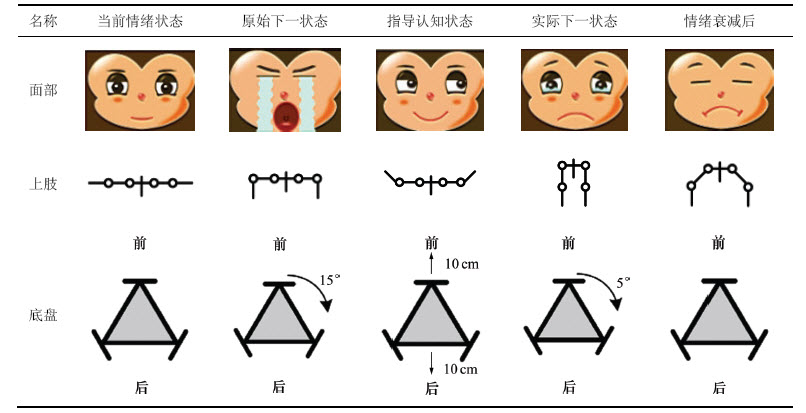
表3 参与者的评估结果
Table 3 Evaluation results of participants
5 结论
1) 以13自由度的机器人实验平台为基础,将Gross认知重评策略引入到基于隐马尔科夫的情绪交互模型中,建立起连续空间中的机器人情绪交互模型。在此情绪状态空间中,首先,可以通过指导情绪的强度、自发性心理调节机制与当前机器人对外界情绪的开放度计算得到认知情绪的概率分布;其次,可以依据情绪自身属性(情绪的效价)计算得到机器人的情绪随时间的衰减规律;最后,可以通过与情绪的唤醒度息息相关的表达抑制作用来得到机器人外在情绪表现的动作幅度。从而,由心理能量驱动的机器人的情绪调节过程可以通过空间的三维坐标值得以量化。
2) 将认知重评、情绪强度衰减、表达抑制与HMM的不确定性情绪调节模型相结合,得到连续空间中个性化的机器人情绪交互模型,以此模仿人类的情绪交流过程。实验证明,具备认知及情绪控制能力的机器人可以在交互过程中得到参与者更多的认可。
参考文献:
[1] VINCIARELLI A, MOHAMMADI G. A survey of personality computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2014, 5(3): 273-291.
[2] WHITEHILL J, SERPELL Z, LIN Y C, et al. the faces of engagement: automatic recognition of student engagement from facial expressions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2014, 5(1): 86-98.
[3] WEN Wanhui, LIU Guangyuan, CHENG Nanpu, et al. Emotion recognition based on multi-variant correlation of physiological signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2014, 5(2): 126-140.
[4] MEULEMAN B, SCHERER K R. Nonlinear appraisal modeling: an application of machine learning to the study of emotion production[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2013, 4(4): 398-411.
[5] BROEKENS J, BOSSE T, MARSELLA S C. Challenges in computational modeling of affective processes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2013, 4(3): 242-245.
[6] LAZARUS R S. Relational meaning and discrete emotions. Appraisal processes in emotion: theory, methods, research[M]. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2001: 37-67.
[7] EKMAN P. Lie catching and microexpressions[M]. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2009: 118-133.
[8] AMERO D. Modeling motivations and emotions as a basis for intelligent behavior[C]// 1st International Symposium Autonomous Agents, New York: ACM, 1997: 148-155.
[9] GADANHO S. Reinforcement learning in autonomous robots: an empirical investigation of the role of emotions[D]. Edinburgh: University of Edinburgh, 1999: 35-47.
[10] VEL SQUEZ J. An emotion-based approach to robotics[C]// IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. NJ: IEEE, 1999: 235-240.
SQUEZ J. An emotion-based approach to robotics[C]// IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. NJ: IEEE, 1999: 235-240.
[11] MURPHY R, LISETTI C, TARDIF R, et al. Emotion based control of cooperating heterogeneous mobile robots[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 2002, 18(5): 744-757.
[12] MEHRABIAN A. Pleasure arousal dominance: a general framework for describing and measuring individual differences in temperament[J]. Current Psychology: Developmental, Learning, Personality, Social, 1996, 14(4): 2612-2621.
[13] WU Qi, SHEN Xunbing, FU Xiaolan. The machine knows what you are hiding: an automatic micro-expression recognition system[C]// Proceedings 4th International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction. Berlin: Springer-verlag, 2011: 152-162.
[14] LIU T, CHEN W, LIU C H, et al. Benefits and costs of uniqueness in multiple object tracking: the role of object complexity[J]. Vision Research, 2012, 66: 31-38.
[15] SCHERER K, EKAM P. Approaches to emotions[M]. Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1984: 158-169.
[16] ORTONY A, CLORE G L, COLLINS A. The cognitive structure of emotions[M]. London: Cambridge University Press, 1988: 23-29.
[17] ZECCA M, ROCCELLA S, MIWA H. On the development of the emotion expression humanoid robot WE-4RII with RCH-1[C]// Proceedings of the 4th IEEE/RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots. Tokyo, Japan, 2005: 235-252.
[18] BREAZEAL C. Function meets style: insights from emotion theory applied to HRI[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C: Applications and Reviews, 2004, 34(2): 187-194.
[19] GROSS J J. Emotion regulation: affective, cognitive, and social consequences[J]. Psychophysiology, 2002, 39(3): 281-291.
[20] GROSS J J. Emotion regulation in adulthood: timing is everything[J]. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 2001, 10(6): 214-219.
[21] LIU Xin, XIE Lun, YANG Wenxiang, et al. Dynamic regulation process of facial expression robot[J]. Journal of Control Theory and Applications, 2011, 28(7): 936-946.
[22] GROSS J J. The emerging field of emotion regulation: an integrative review[J]. Review of General Psychology, 1998, 2(3): 271-299.
(编辑 赵俊)
收稿日期:2015-05-26;修回日期:2015-09-24
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(61672093,61432004);国家科技支撑计划项目(2014BAF08B04);北京市自然科学基金资助项目(4164091);中国博士后科学基金资助项目(2015M580048);中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金资助项目(FRF-TP-15-034A1) (Projects(61672093, 61432004) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2014BAF08B04) supported by the National Science and Technologies Pillar Program of China; Project(4164091) supported by Beijing Natural Science Foundation; Project(2015M580048) supported by National Science Foundation for Postdoctoral Scientists of China; Project(FRF-TP-15-034A1) supported by Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities)
通信作者:解仑,博士,教授,博士生导师,从事机器人、人工智能、认知情感计算研究;E-mail: xielun@ustb.edu.cn